ERTFM: An Effective Model to Fuse Chinese GF-1 and MODIS Reflectance Data for Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux Estimation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
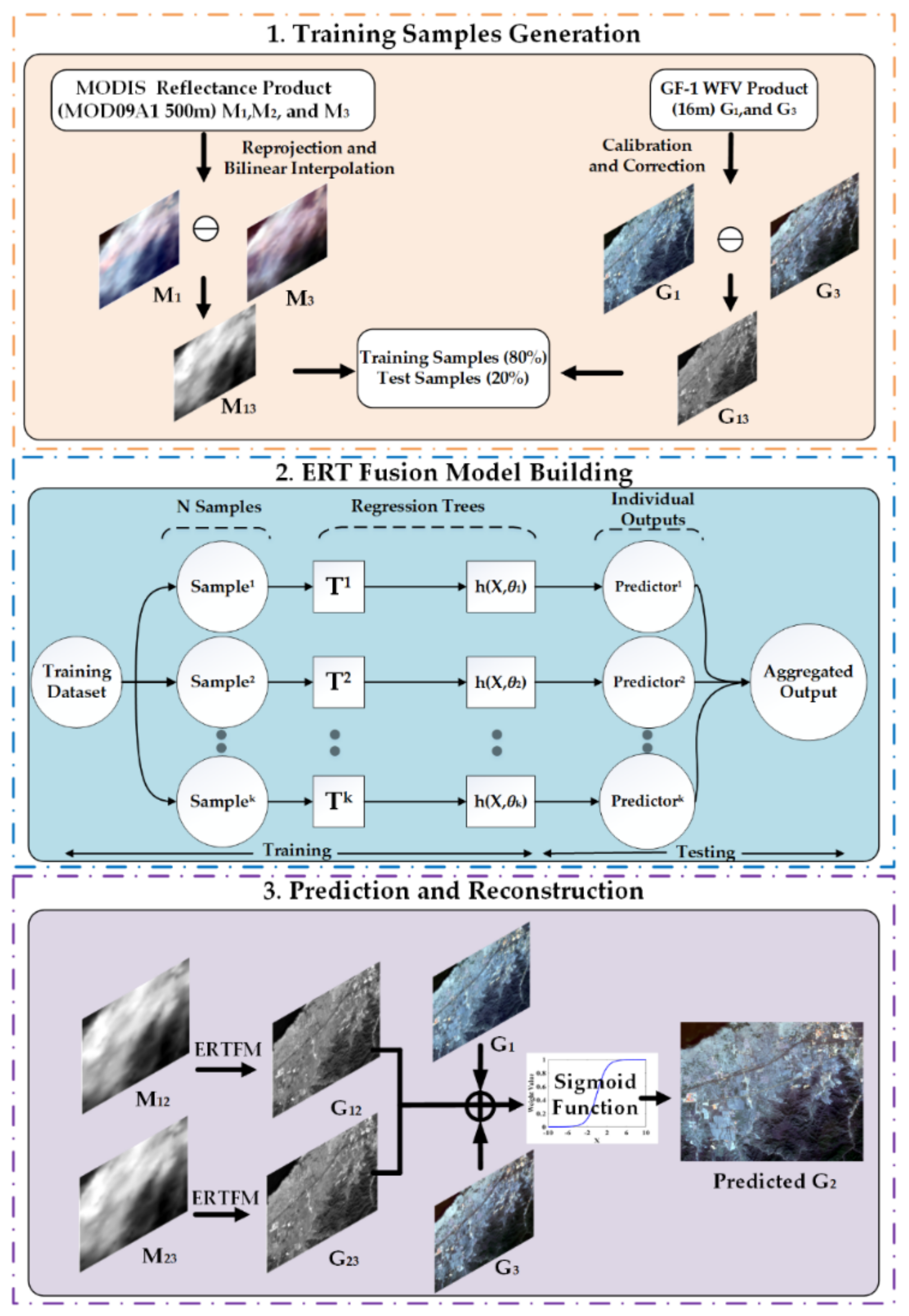
2.1. The ERTFM Logic
2.2. Comparison to Other Fusion Methods
2.2.1. STARFM
2.2.2. ESTARFM
2.2.3. FSDAF
2.2.4. Fit-FC
2.3. LE Computation
2.4. Assessment Metrics
2.5. Experimental Data and Preprocessing
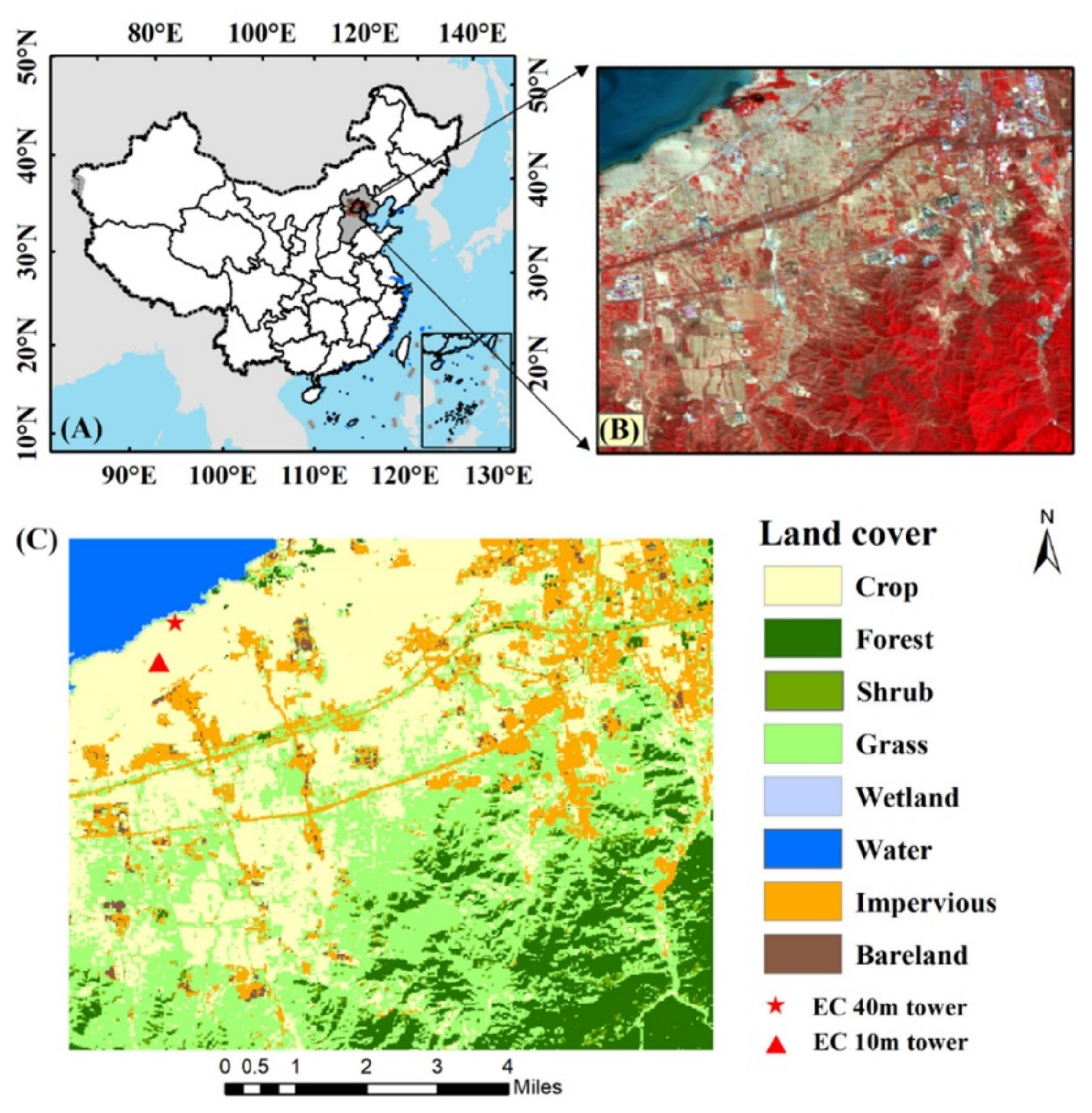
2.5.1. Study Area
2.5.2. Remotely-Sensed Data
2.5.3. Auxiliary Data
3. Results
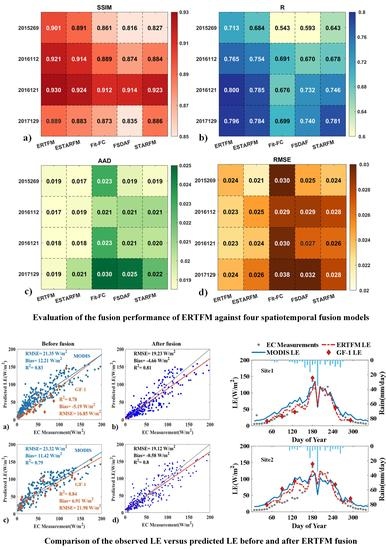
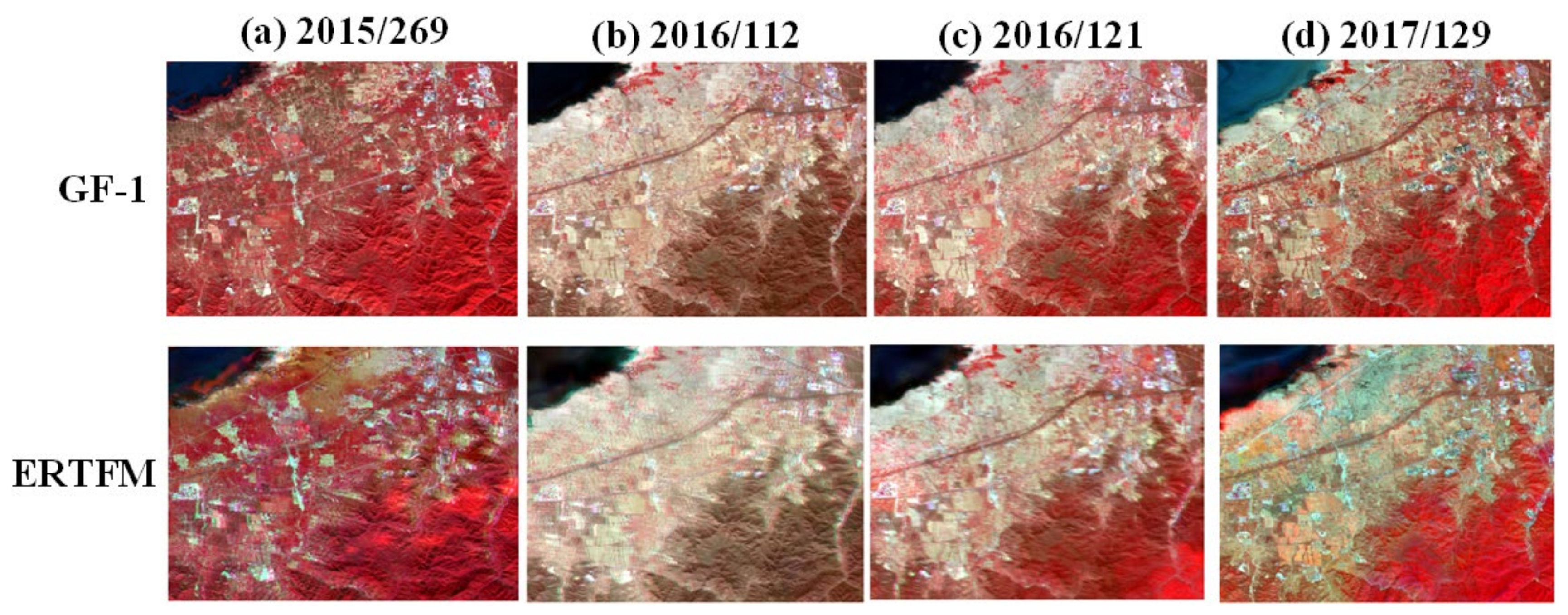
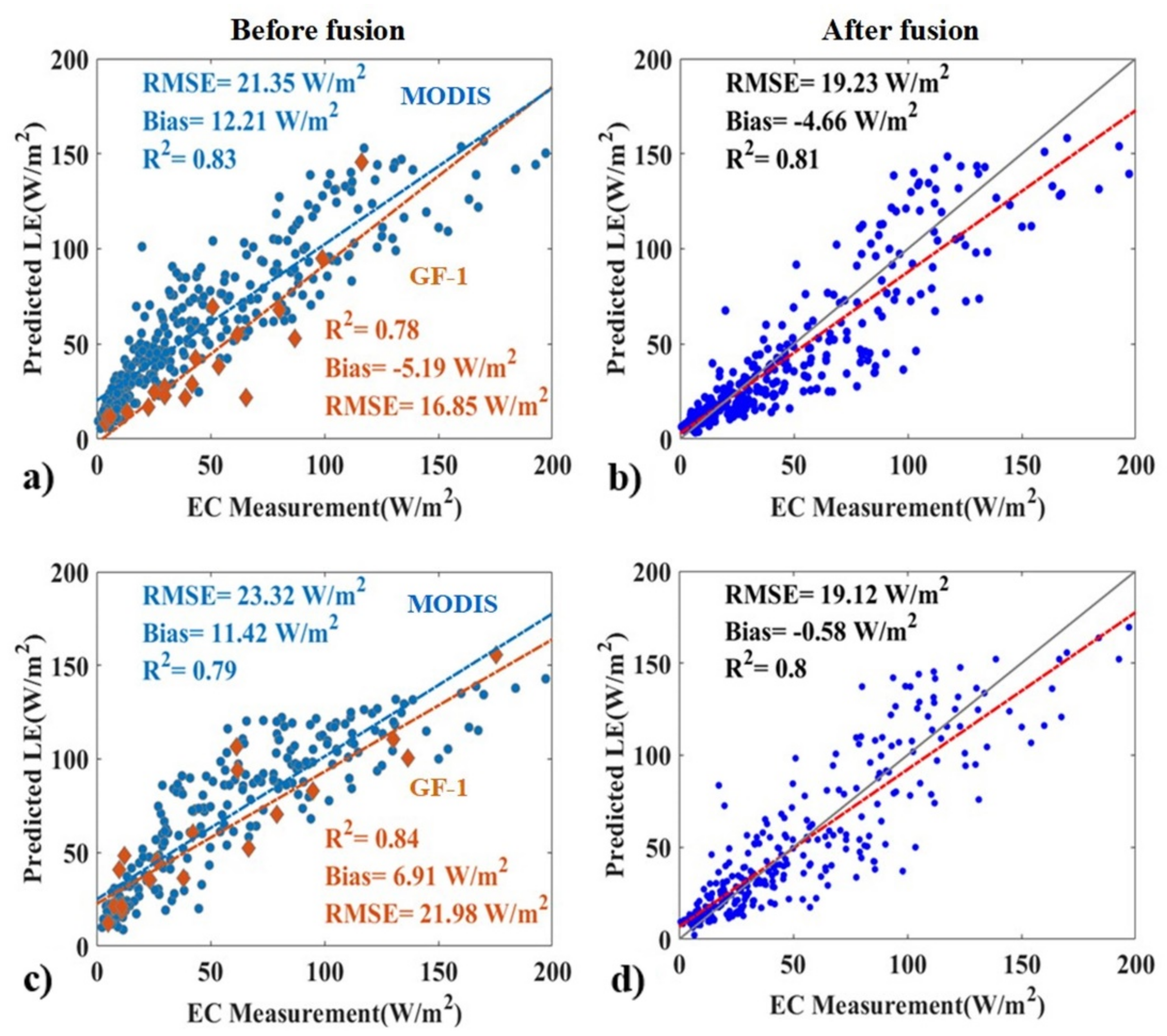
3.1. Evaluation of the ERTFM
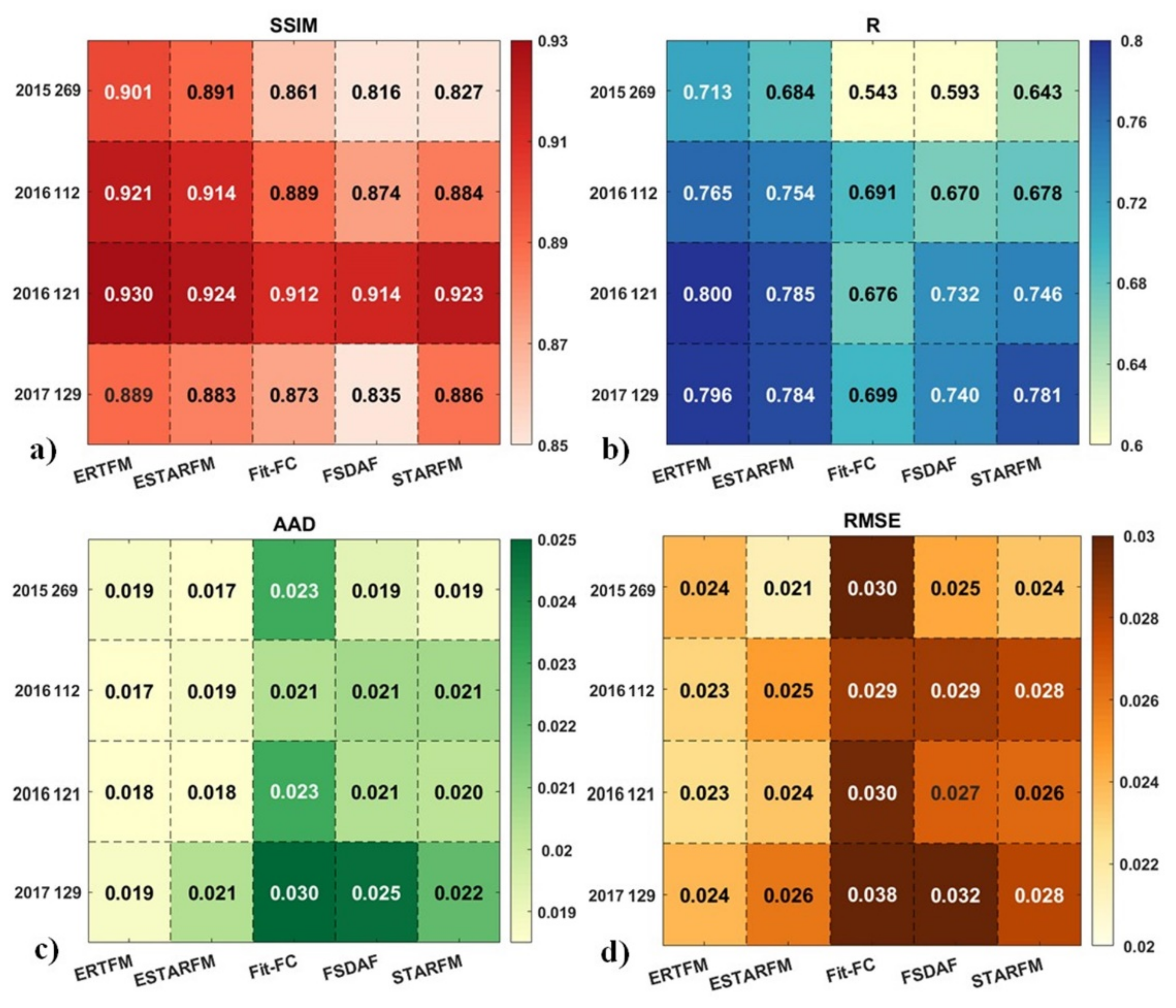
3.2. Comparison with Other Fusion Methods
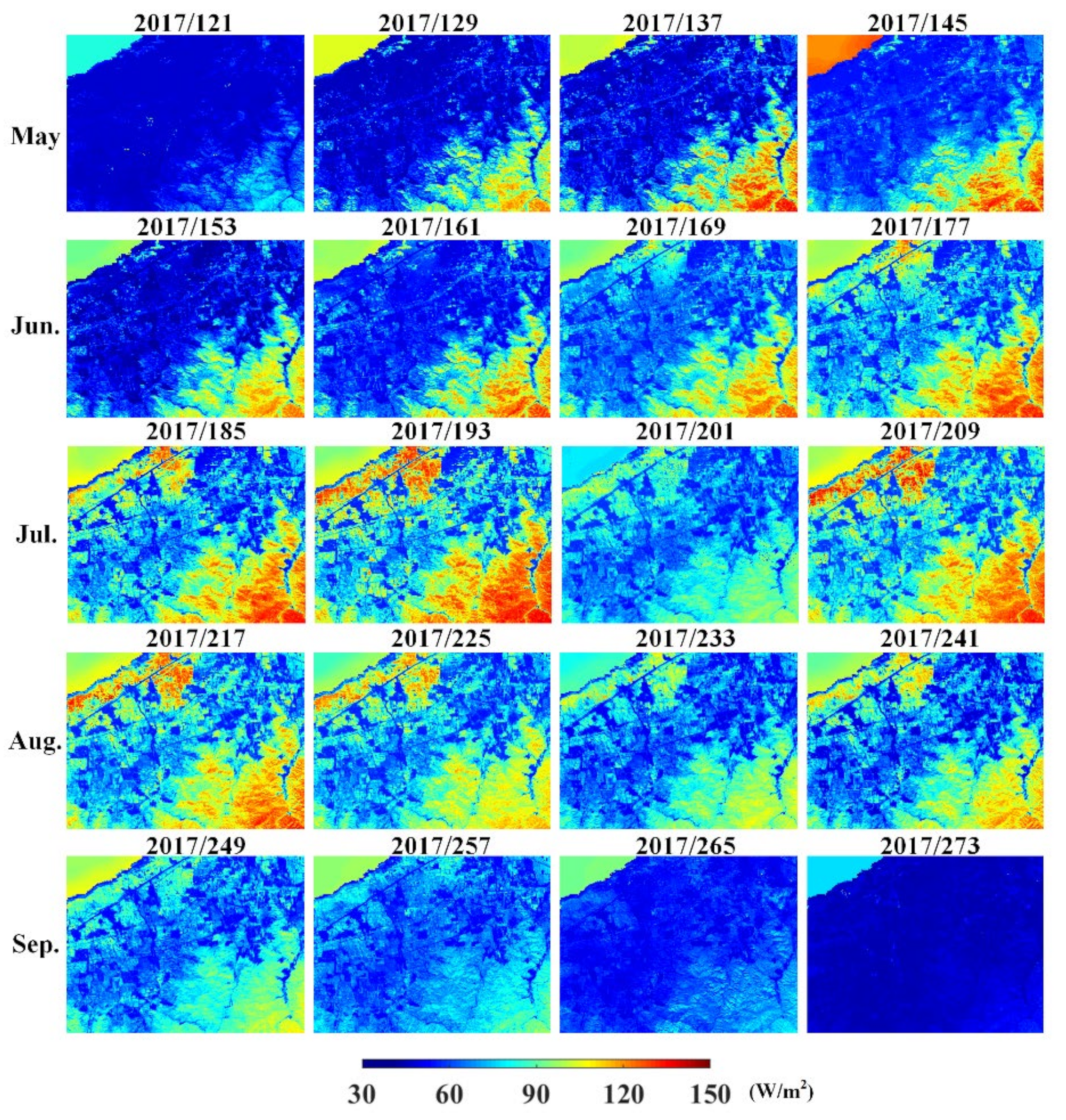
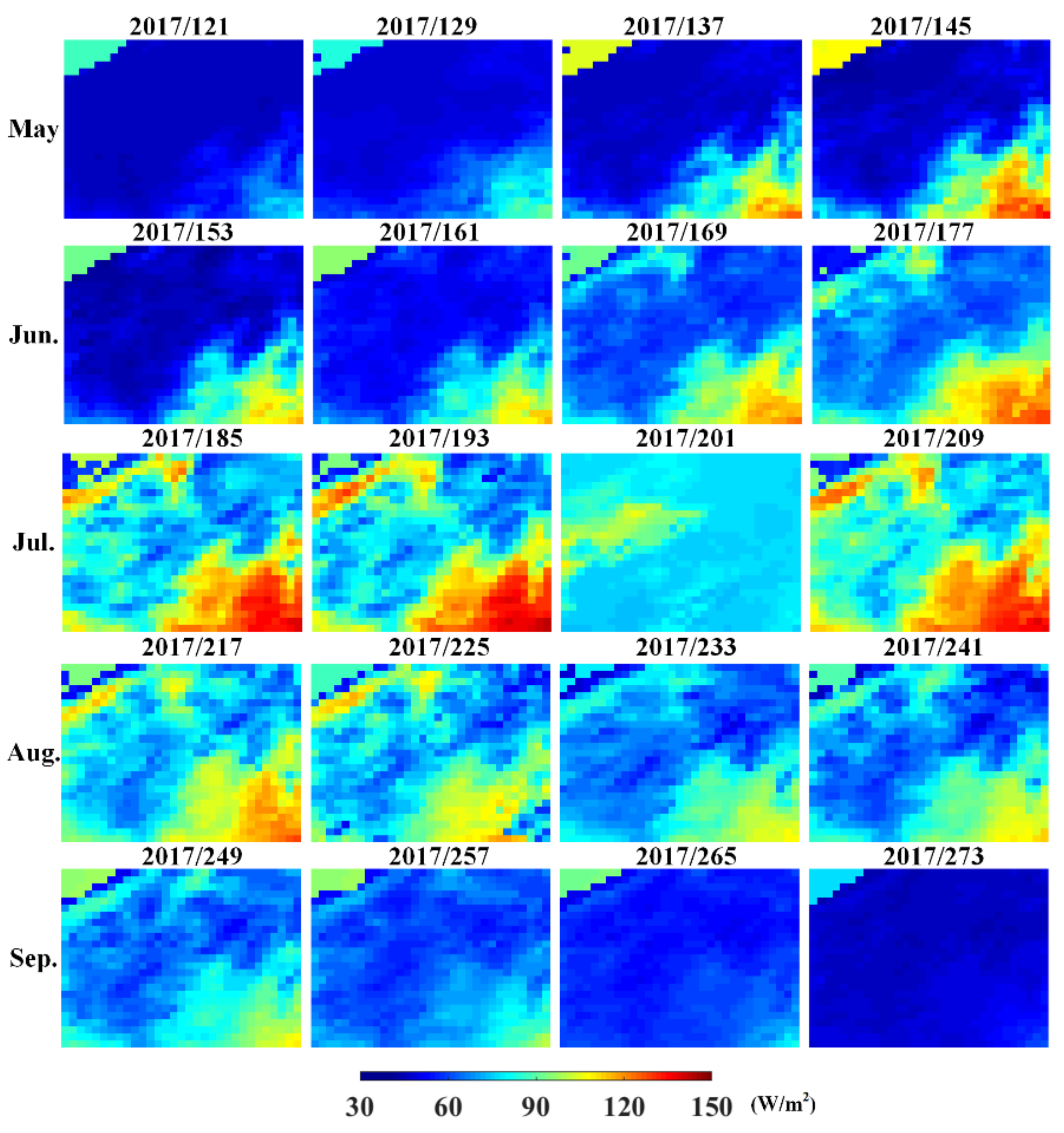
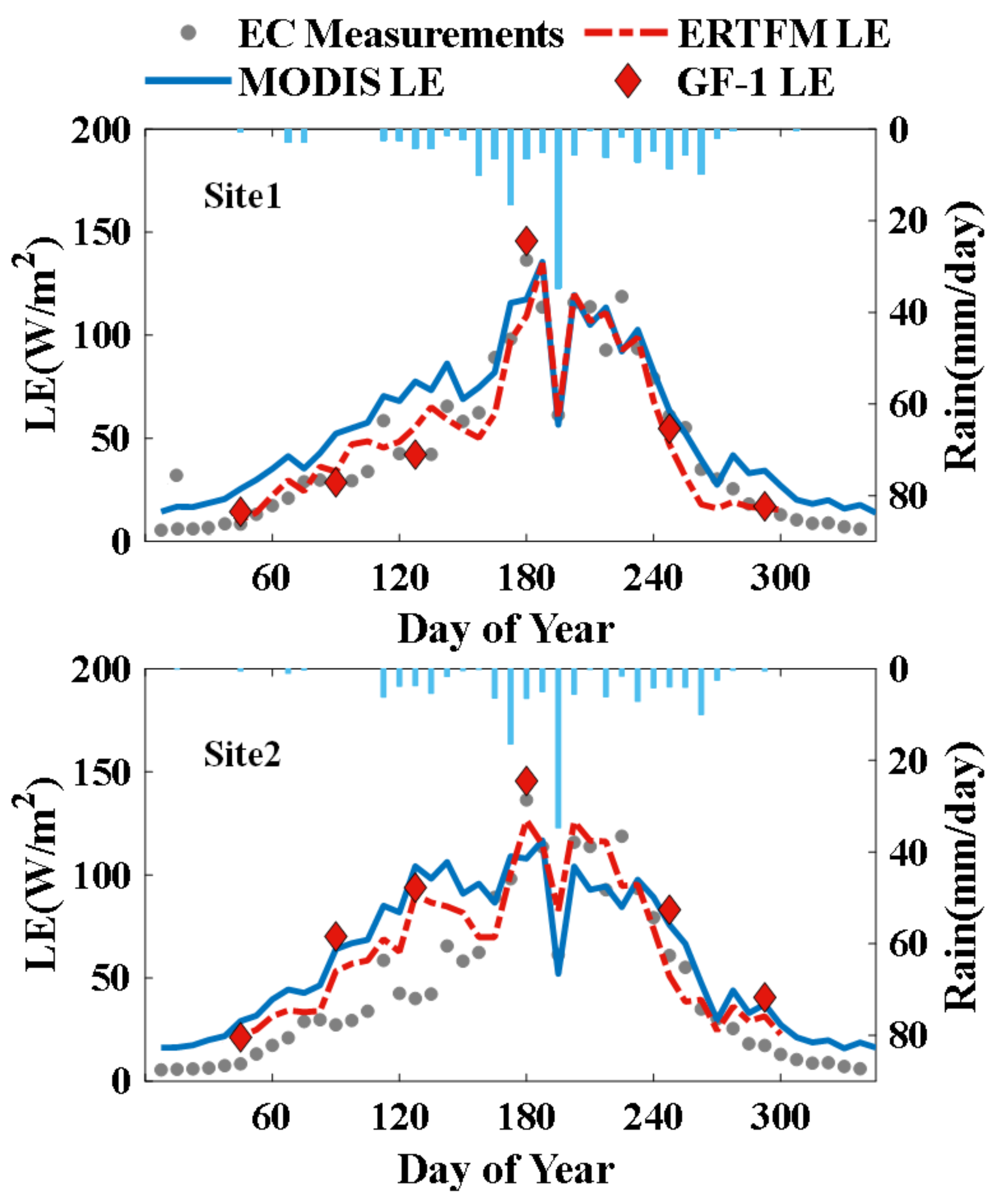
3.3. The Application of the ERTFM on LE Estimation
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance of the ERTFM
4.2. Comparison with Other Fusion Models
4.3. The Application of ERTFM
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, C.; Guan, K.; Pan, M.; Ryu, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, S. BESS-STAIR: A framework to estimate daily, 30-meter, and allweather crop evapotranspiration using multi-source satellite data for the U.S. Corn Belt. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalma, J.D.; McVicar, T.R.; McCabe, M.F. Estimating Land Surface Evaporation: A Review of Methods Using Remotely Sensed Surface Temperature Data. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 421–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Lin, Y.; Fisher, J.B.; McVicar, T.R.; Cheng, J.; Jia, K.; et al. A simple temperature domain two-source model for estimating agricultural field surface energy fluxes from Landsat images. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5211–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, S.; Song, L.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhu, Z. Estimation of daily evapotranspiration and irrigation water efficiency at a Landsat-like scale for an arid irrigation area using multi-source remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Fu, P.; Gao, F. Generating daily land surface temperature at Landsat resolution by fusing Landsat and MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Hilker, T.; Zhu, X.; Anderson, M.; Masek, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, Y. Fusing Landsat and MODIS Data for Vegetation Monitoring. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wild, M. Review on Estimation of Land Surface Radiation and Energy Budgets From Ground Measurement, Remote Sensing and Model Simulations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Jia, K.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, B.; Fisher, J.B.; Mu, Q.; et al. A satellite-based hybrid algorithm to determine the Priestley–Taylor parameter for global terrestrial latent heat flux estimation across multiple biomes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Development of a global evapotranspiration algorithm based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-Based Energy Balance for Mapping Evapotranspiration With Internalized Calibration (METRIC)—Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammalleri, C.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P. Upscaling of evapotranspiration fluxes from instantaneous to daytime scales for thermal remote sensing applications. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Gu, X.; Baret, F.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Fractional vegetation cover estimation algorithm for Chinese GF-1 wide field view data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Y.; Liu, S.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Shang, K.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Estimation of Daily Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux with High Spatial Resolution from MODIS and Chinese GF-1 Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, C.M.; García-Haro, F.J. A comparison of STARFM and an unmixing-based algorithm for Landsat and MODIS data fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, W.; Gowda, P.H.; Howell, T.A. A review of downscaling methods for remote sensing-based irrigation management: Part I. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 831–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z. Regression-then-Fusion or Fusion-then-Regression? A Theoretical Analysis for Generating High Spatiotemporal Resolution Land Surface Temperatures. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Cai, F.; Tian, J.; Williams, T.K.A. Spatiotemporal Fusion of Multisource Remote Sensing Data: Literature Survey, Taxonomy, Principles, Applications, and Future Directions. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Linke, J.; McDermid, G.; Masek, J.G.; Gao, F.; White, J.C. A new data fusion model for high spatial- and temporal-resolution mapping of forest disturbance based on Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.; Lewis, P.; Schaaf, C.; Gao, F.; Hansen, M.; Lindquist, E. Multi-temporal MODIS Landsat data fusion for relative radiometric normalization, gap filling, and prediction of Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3112–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, B. A Rigorously-Weighted Spatiotemporal Fusion Model with Uncertainty Analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhukov, B.; Oertel, D.; Lanzl, F.; Reinhackel, G. Unmixing-based multisensor multiresolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita-Milla, R.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Schaepman, M.E. Unmixing-based landsat TM and MERIS FR data fusion. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. IEEE 2008, 5, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maselli, F.; Rembold, F. Integration of LAC and GAC NDVI data to improve vegetation monitoring in semi-arid environments. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2475–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Huang, W.; Niu, Z.; Wang, C. Generating Daily Synthetic Landsat Imagery by Combining Landsat and MODIS Data. Sensors 2015, 15, 24002–24025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Bo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, P.; Bi, J.; He, Y. Blending multi-resolution satellite sea surface temperature (SST) products using Bayesian maximum entropy method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Leung, Y.; Fung, T. An Unmixing-Based Bayesian Model for Spatio-Temporal Satellite Image Fusion in Heterogeneous Landscapes. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.; Song, H. Spatiotemporal Reflectance Fusion via Sparse Representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3707–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Deng, C.; Wang, S.; Huang, G.; Zhao, B.; Lauren, P. Fast and Accurate Spatiotemporal Fusion Based Upon Extreme Learning Machine. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 2039–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Atkinson, P.M. Spatio-temporal fusion for daily Sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Liu, S.; Fisher, J.B.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. Merging the MODIS and Landsat Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux Products Using the Multiresolution Tree Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 2811–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Cai, J.; Fu, P.; Hu, L.; Liu, T. Deep learning-based fusion of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 images for a harmonized surface reflectance product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Helmer, E.H.; Gao, F.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Lefsky, M.A. A flexible spatiotemporal method for fusing satellite images with different resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 172, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ling, F.; Foody, G.M.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y. Generating a series of fine spatial and temporal resolution land cover maps by fusing coarse spatial resolution remotely sensed images and fine spatial resolution land cover maps. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 196, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmens, K.A.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Gao, F.; Alfieri, J.G.; McKee, L.; Prueger, J.H.; Hain, C.R.; Cammalleri, C.; Yang, Y.; et al. Monitoring daily evapotranspiration over two California vineyards using Landsat 8 in a multi-sensor data fusion approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, Y.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Gong, H. Spatiotemporal downscaling approaches for monitoring 8-day 30 m actual evapotranspiration. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 126, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uddin, M.T.; Uddiny, M.A. Human activity recognition from wearable sensors using extremely randomized trees. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information Communication Technology (ICEEICT), Savar, Bangladesh, 21–23 May 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Geurts, P.; Louppe, G. Learning to rank with extremely randomized trees. In Proceedings of the Learning to Rank Challenge, PMLR, Haifa, Israel, 25 June 2010; pp. 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Feng, C.; Yang, S.; Jia, K.; Yao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, B. A New Long-Term Downward Surface Solar Radiation Dataset over China from 1958 to 2015. Sensors 2020, 20, 6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, K.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Bei, X.; Guo, X. Fusion of Five Satellite-Derived Products Using Extremely Randomized Trees to Estimate Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux over Europe. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.; Fisher, J.B.; Zhang, X.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X.; Qing, Q.; Zhao, B.; et al. MODIS-driven estimation of terrestrial latent heat flux in China based on a modified Priestley-Taylor algorithm. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, C.H.B.; Taylor, R.J. On the Assessment of Surface Heat Flux and Evaporation Using Large-Scale Parameters. Mon. Weather Rev. 1972, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.B.; Tu, K.P.; Baldocchi, D.D. Global estimates of the land-atmosphere water flux based on monthly AVHRR and ISLSCP-II data, validated at 16 FLUXNET sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, X. Satellite-Derived Spatiotemporal Variations in Evapotranspiration over Northeast China during 1982–2010. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Twine, T.E.; Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Cook, D.R.; Houser, P.R.; Meyers, T.P.; Prueger, J.H.; Starks, P.J.; Wesely, M.L.; Argonne National Lab. Correcting eddy-covariance flux underestimates over a grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 103, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, T.; Sarangi, C.; Krishnan, M.; Tripathi, S.N.; Morrison, R.; Evans, J. Biases in model-simulated surface energy fluxes during the Indian monsoon onset period. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2019, 170, 323–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingwersen, J.; Imukova, K.; Högy, P.; Streck, T. On the use of the post-closure methods uncertainty band to evaluate the performance of land surface models against eddy covariance flux data. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 2311–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Cai, K.; Ge, Q. Retrieval and Validation of Aerosol Optical Depth by using the GF-1 Remote Sensing Data. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 68, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Yao, Y.; Tan, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Shang, K.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Bei, X. Integrating Latent Heat Flux Products from MODIS and Landsat Data Using Multi-Resolution Kalman Filter Method in the Midstream of Heihe River Basin of Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Yuan, W.; Cheng, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Tang, H.; et al. A long-term Global LAnd Surface Satellite (GLASS) data-set for environmental studies. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X.; Wei, X.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X. Generating High Spatio-Temporal Resolution Fractional Vegetation Cover by Fusing GF-1 WFV and MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, B.; Song, H. A robust adaptive spatial and temporal image fusion model for complex land surface changes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.J.; de Beurs, K.M.; Wynne, R.H.; Gao, F. Evaluation of Landsat and MODIS data fusion products for analysis of dryland forest phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Shang, K.; Yang, J.; Bei, X.; Guo, X. ANN-Based Estimation of Low-Latitude Monthly Ocean Latent Heat Flux by Ensemble Satellite and Reanalysis Products. Sensors 2020, 20, 4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Ke, Y.; Yin, Q.; Chen, X.; Im, J. Comparison of Five Spatio-Temporal Satellite Image Fusion Models over Landscapes with Various Spatial Heterogeneity and Temporal Variation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, J.; Ryu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Dechant, B.; Houborg, R.; Guan, K.; Zhu, X. Evaluation of four image fusion NDVI products against in-situ spectral-measurements over a heterogeneous rice paddy landscape. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 297, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Martínez, Á.; Izquierdo-Verdiguier, E.; Maneta, M.P.; Camps-Valls, G.; Robinson, N.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; Sedano, F.; Clinton, N.; Running, S.W. Multispectral high resolution sensor fusion for smoothing and gap-filling in the cloud. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanova, I.V.; McVicar, T.R.; Van Niel, T.G.; Li, L.T.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M. Assessing the accuracy of blending Landsat MODIS surface reflectances in two landscapes with contrasting spatial and temporal dynamics: A framework for algorithm selection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, H. Crop Phenology Detection Using High Spatio-Temporal Resolution Data Fused from SPOT5 and MODIS Products. Sensors 2016, 16, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Anderson, M.C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Alfieri, J.G.; Kustas, W.P.; Mueller, R.; Johnson, D.M.; Prueger, J.H. Toward mapping crop progress at field scales through fusion of Landsat and MODIS imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Li, M. An Evaluation of Eight Machine Learning Regression Algorithms for Forest Aboveground Biomass Estimation from Multiple Satellite Data Products. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galelli, S.; Castelletti, A. Assessing the predictive capability of randomized tree-based ensembles in streamflow modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2669–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eslami, E.; Salman, A.K.; Choi, Y.; Sayeed, A.; Lops, Y. A data ensemble approach for real-time air quality forecasting using extremely randomized trees and deep neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 32, 7563–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
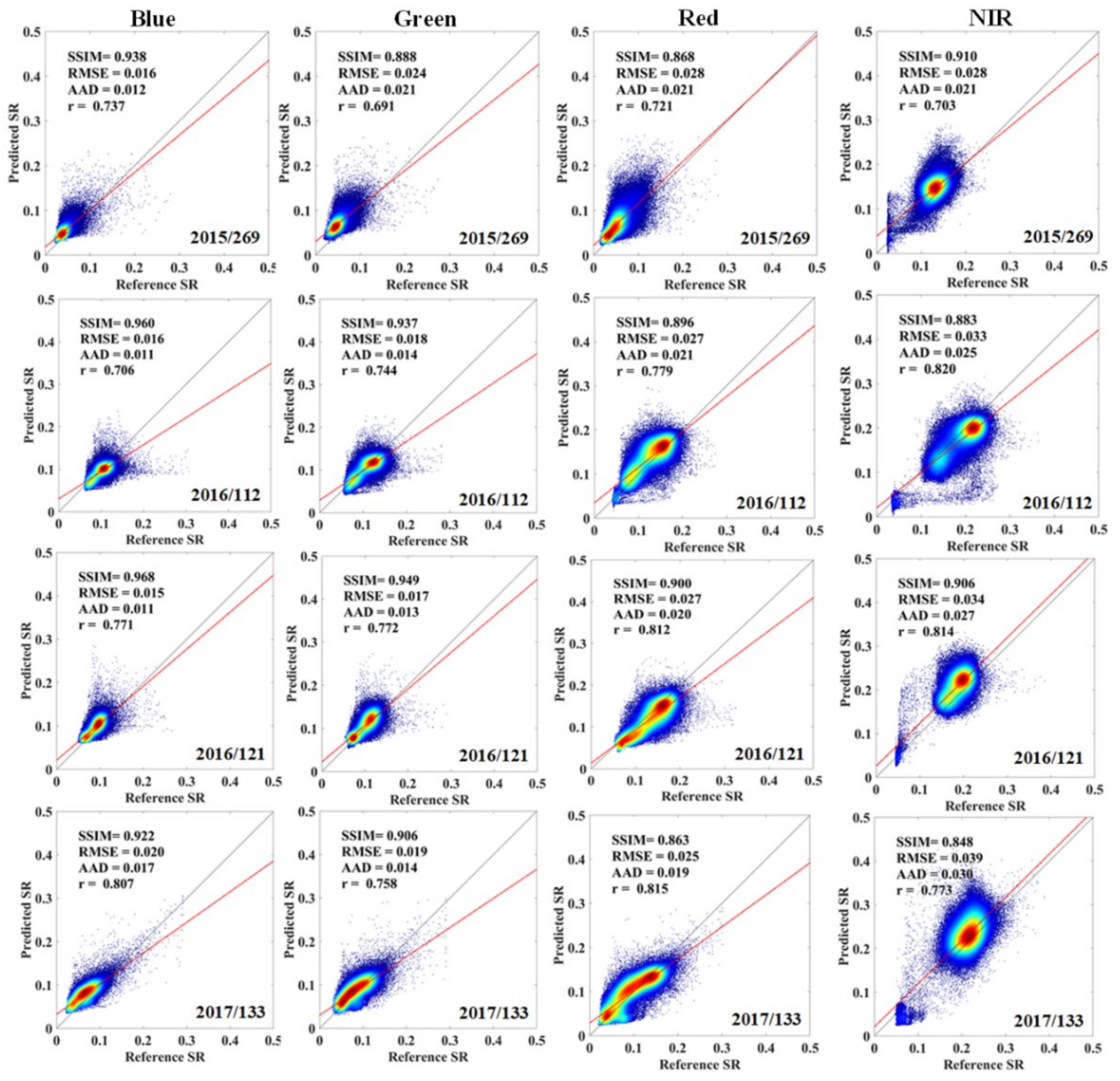
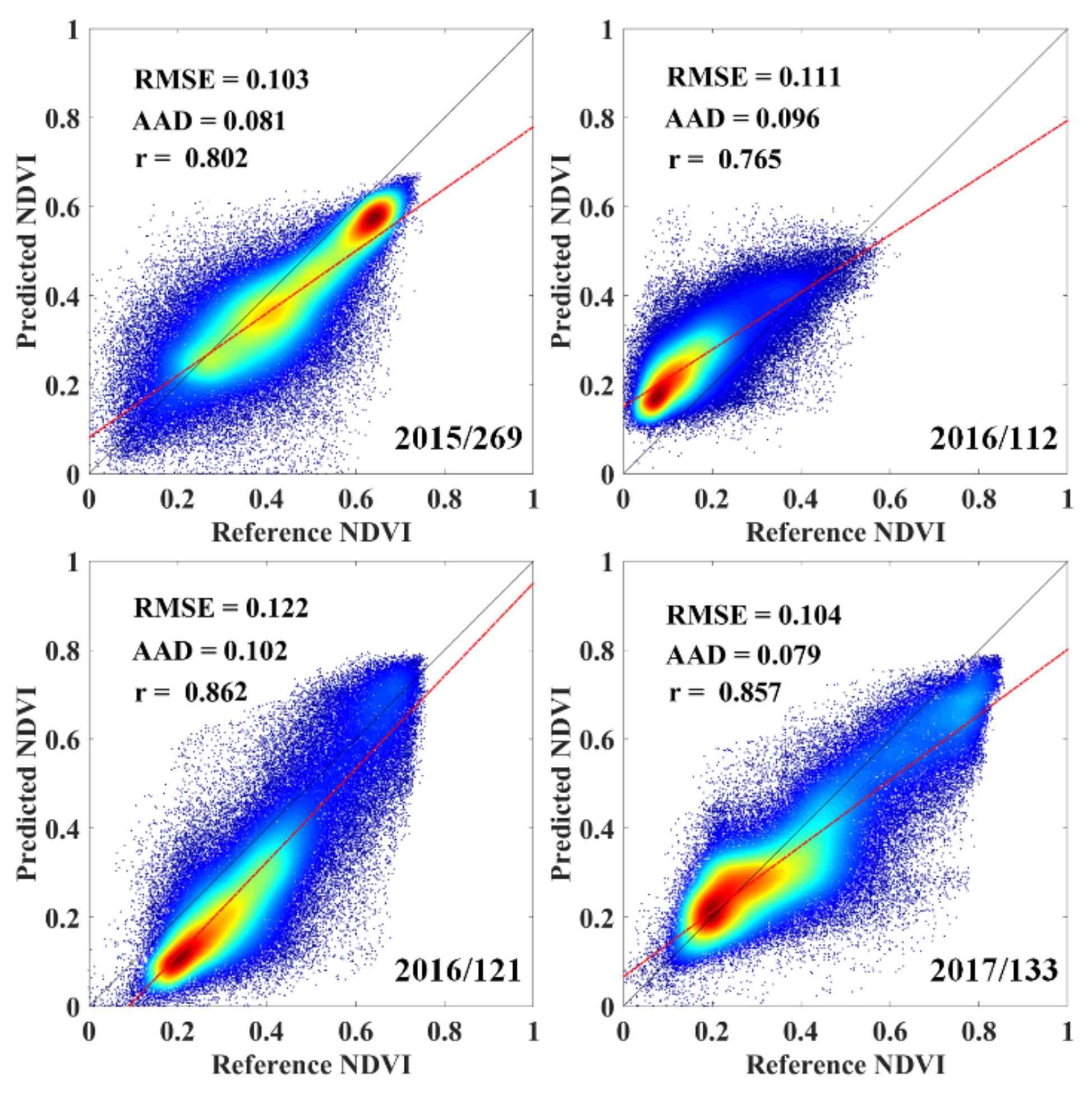
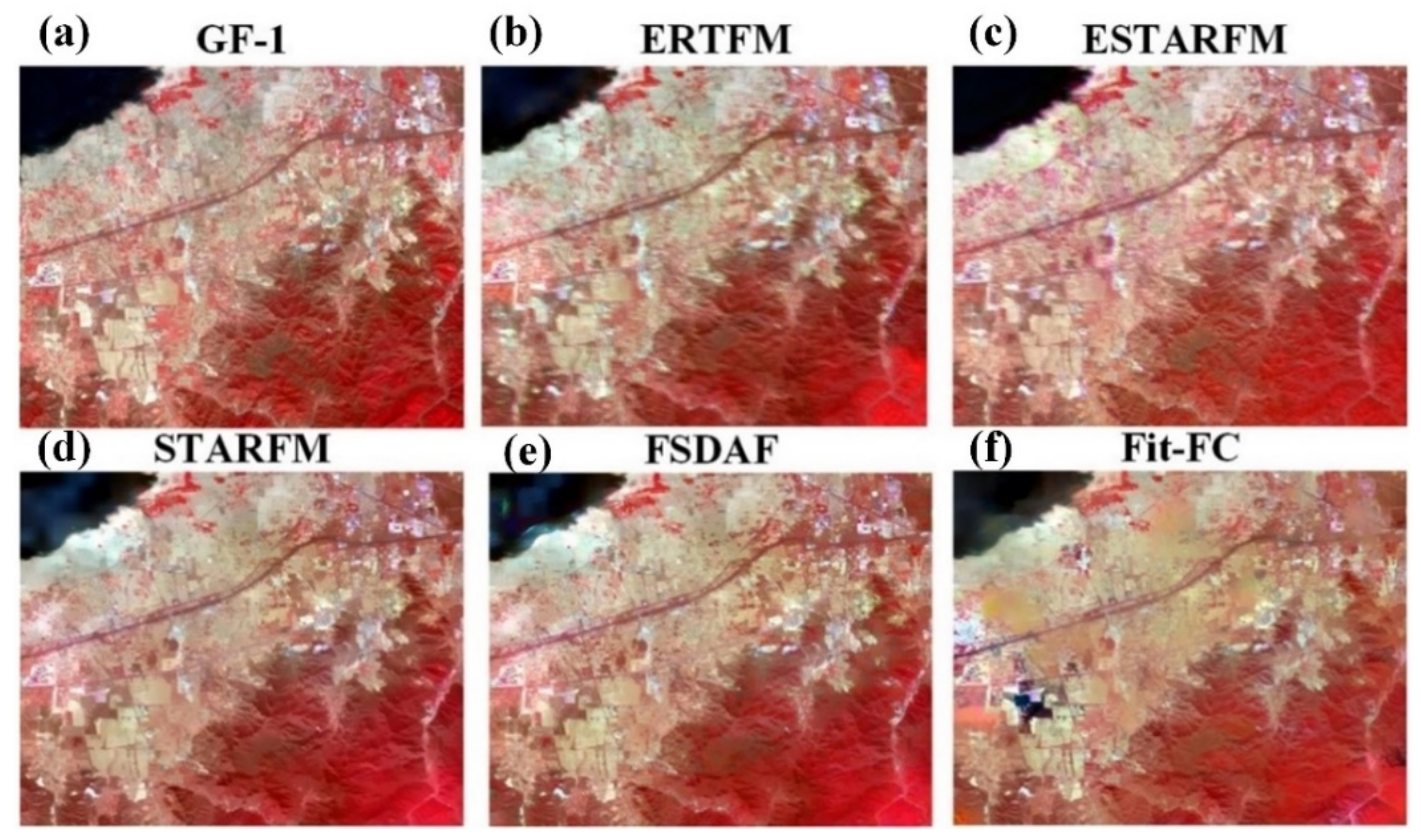
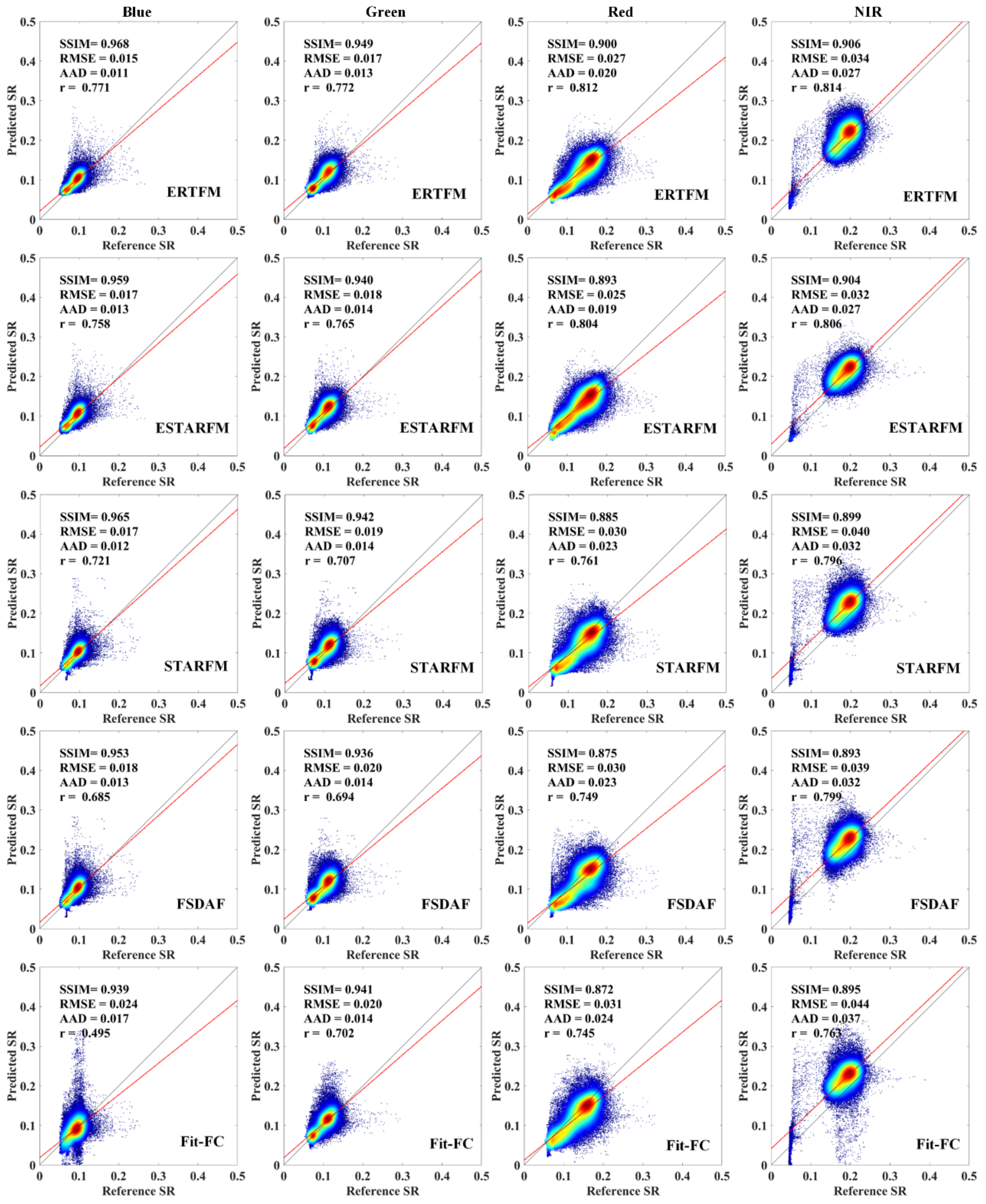
| Category | Description | Method | References | Experimental Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight function-based | Introduced adjacent similarity pixel information to predict the target pixels and combine spectral similarity, spatial distance, as well as temporal differences | STARFM | Gao et al. [19] | MODIS, Landsat |
| ESTARFM | Zhu et al. [20] | MODIS, Landsat | ||
| STAARCH | Hilker et al. [21] | MODIS, Landsat | ||
| Semi-Physical Fusion Approach | Roy et al. [22] | MODIS, Landsat | ||
| SADFAT | Weng et al. [5] | MODIS, Landsat | ||
| RWSTFM | Wang et al. [23] | MODIS, Landsat | ||
| Unmixing-based | Definition of endmembers, unmixing of coarse pixels, and assignment of pixels to fine classes | MMT | Zhukov et al. [24] | Landsat, MERIS |
| Constrained unmixing | Zurita-Milla et al. [25] | Landsat, MERIS | ||
| LAC-GAS | Maselli et al. [26] | AVHRR LAC, GAC NDVI | ||
| STDFA | Wu et al. [27] | MODIS, Landsat | ||
| Bayesian-based | Based on the Bayesian theory, developed the maximum posterior probability model to estimate the fine pixel value | BME | Li et al. [28] | MODIS, AMSR-E |
| Spatio-Temporal-Spectral fusion | Xue et al. [29] | MODIS, Landsat | ||
| Learning-based | Adopted machine learning to establish correspondences between fine and coarse datasets | SPSTFM | Huang et al. [30] | MODIS, Landsat |
| ELM learning | Liu et al. [31] | MODIS, Landsat | ||
| Fit-FC | Wang et al. [32] | Sentinel-2, Sentinel-3 | ||
| MRT | Xu et al. [33] | MODIS, Landsat | ||
| ESRCNN | Shao et al. [34] | Landsat, Sentinel-2 | ||
| Hybrid methods | Combined the advantages of two or more of the above four methods to improve fusion performance | FSDAF | Zhu et al. [35] | MODIS, Landsat |
| STRUM | Gevaert et al. [35] | MODIS, Landsat | ||
| STIMFM | Li et al. [36] | MODIS, Landsat |
| Date | Band | SSIM | RMSE | AAD | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015/269 | Band1 | 0.938 | 0.016 | 0.012 | 0.74 |
| Band2 | 0.888 | 0.024 | 0.021 | 0.69 | |
| Band3 | 0.868 | 0.028 | 0.021 | 0.72 | |
| Band4 | 0.91 | 0.028 | 0.021 | 0.7 | |
| 2016/112 | Band1 | 0.96 | 0.016 | 0.012 | 0.71 |
| Band2 | 0.937 | 0.018 | 0.021 | 0.74 | |
| Band3 | 0.896 | 0.027 | 0.021 | 0.78 | |
| Band4 | 0.89 | 0.031 | 0.021 | 0.83 | |
| 2016/121 | Band1 | 0.968 | 0.015 | 0.012 | 0.71 |
| Band2 | 0.949 | 0.017 | 0.021 | 0.74 | |
| Band3 | 0.9 | 0.027 | 0.021 | 0.78 | |
| Band4 | 0.904 | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.83 | |
| 2017/129 | Band1 | 0.922 | 0.02 | 0.017 | 0.81 |
| Band2 | 0.906 | 0.019 | 0.014 | 0.76 | |
| Band3 | 0.863 | 0.025 | 0.019 | 0.82 | |
| Band4 | 0.866 | 0.032 | 0.025 | 0.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Yao, Y.; Bei, X.; Li, Y.; Shang, K.; Yang, J.; Guo, X.; Yu, R.; Xie, Z. ERTFM: An Effective Model to Fuse Chinese GF-1 and MODIS Reflectance Data for Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux Estimation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183703
Zhang L, Yao Y, Bei X, Li Y, Shang K, Yang J, Guo X, Yu R, Xie Z. ERTFM: An Effective Model to Fuse Chinese GF-1 and MODIS Reflectance Data for Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux Estimation. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(18):3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183703
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lilin, Yunjun Yao, Xiangyi Bei, Yufu Li, Ke Shang, Junming Yang, Xiaozheng Guo, Ruiyang Yu, and Zijing Xie. 2021. "ERTFM: An Effective Model to Fuse Chinese GF-1 and MODIS Reflectance Data for Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux Estimation" Remote Sensing 13, no. 18: 3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183703
APA StyleZhang, L., Yao, Y., Bei, X., Li, Y., Shang, K., Yang, J., Guo, X., Yu, R., & Xie, Z. (2021). ERTFM: An Effective Model to Fuse Chinese GF-1 and MODIS Reflectance Data for Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux Estimation. Remote Sensing, 13(18), 3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183703