Vertical Structure of Air Pollutant Transport Flux as Determined by Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observations in Fen-Wei Plain, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Measurements and Methodology
2.1. Overview of the Measurement Station
2.2. MAX-DOAS Measurements
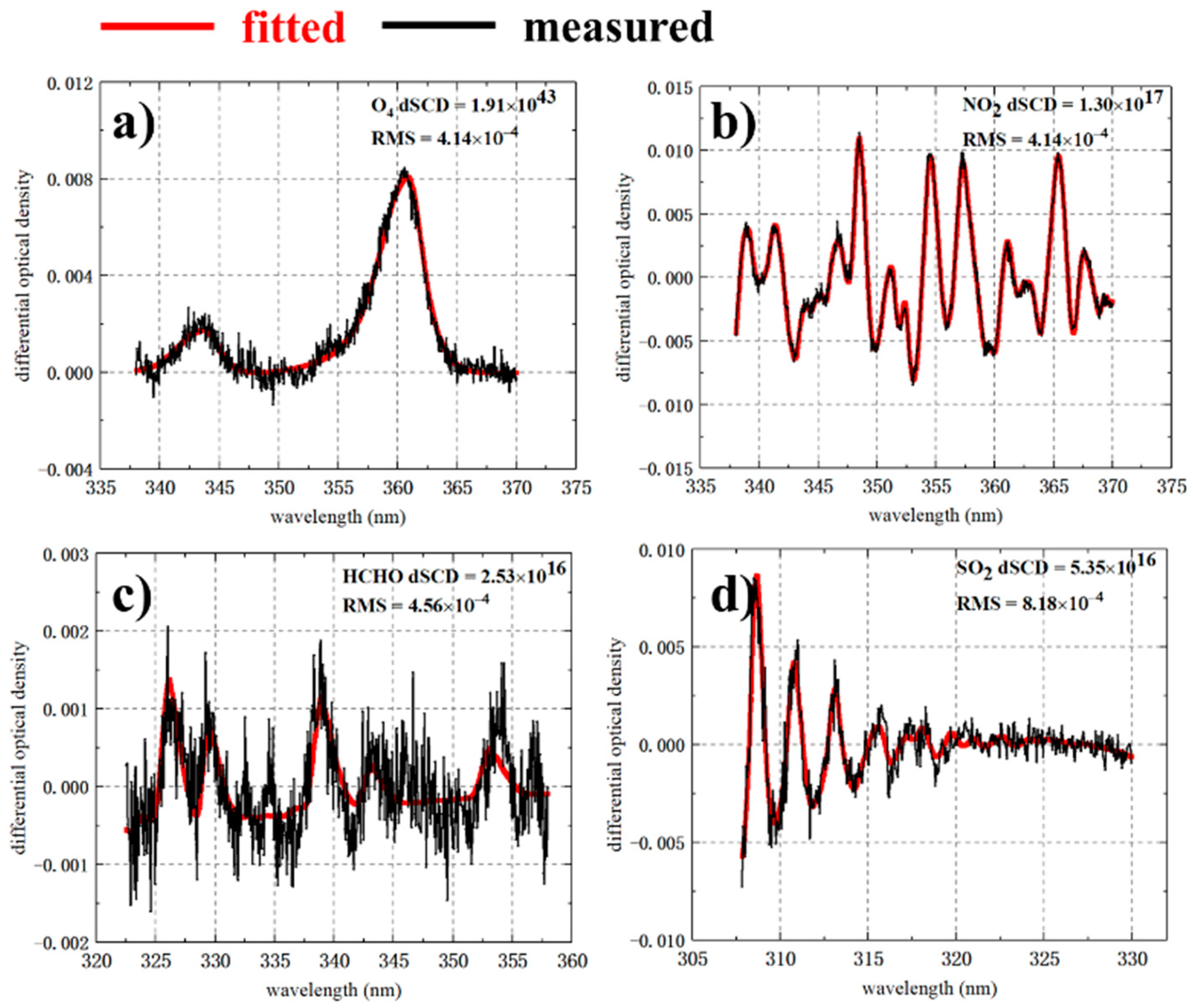
2.2.1. DOAS Analysis of O4, NO2, HCHO and SO2 Differential Slant Column Densities (dSCDs)
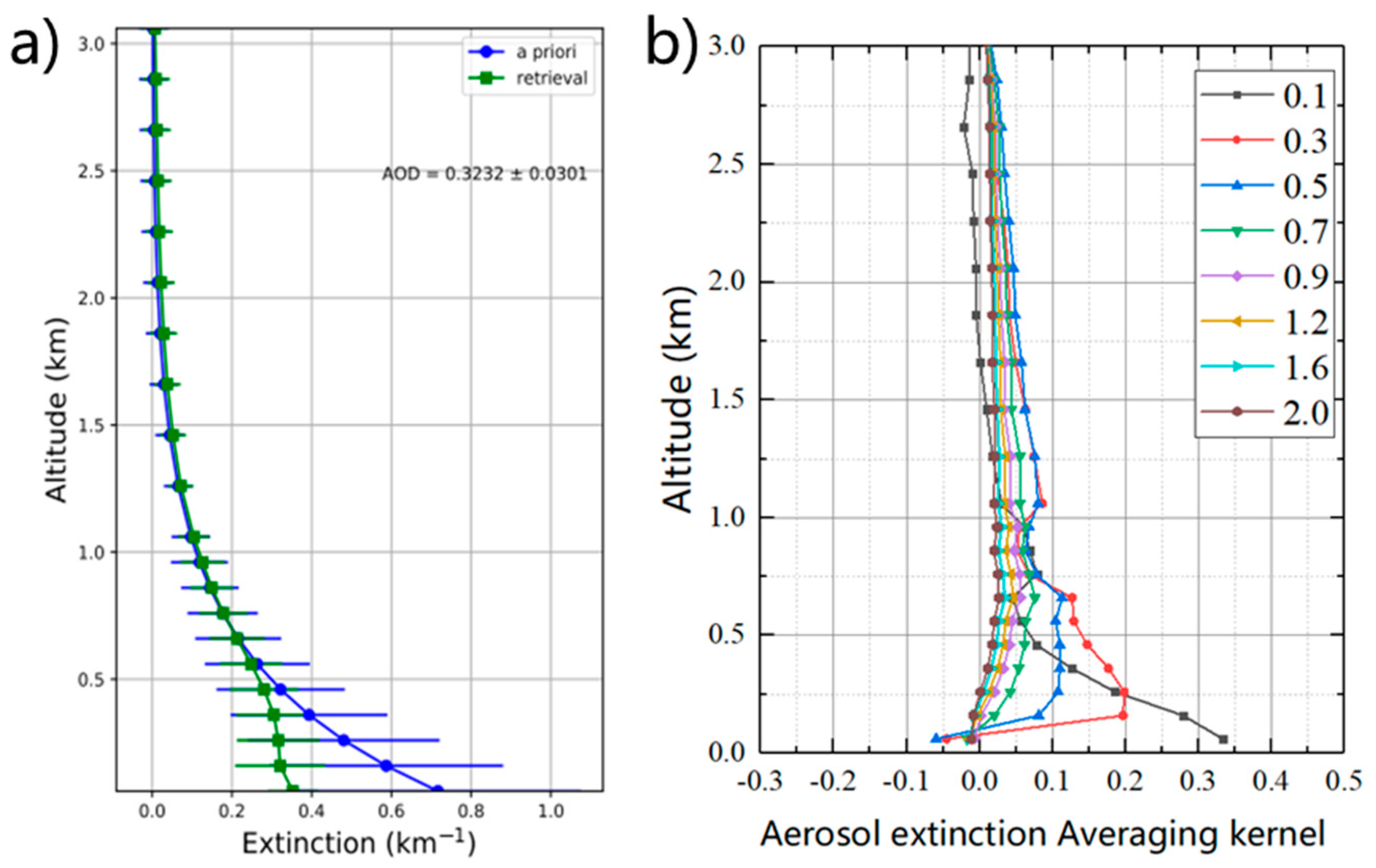
2.2.2. Vertical Profile Retrieval
2.3. Doppler Wind Lidar Measurements
2.4. Flux Calculation
2.5. Date from China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC)
3. Results
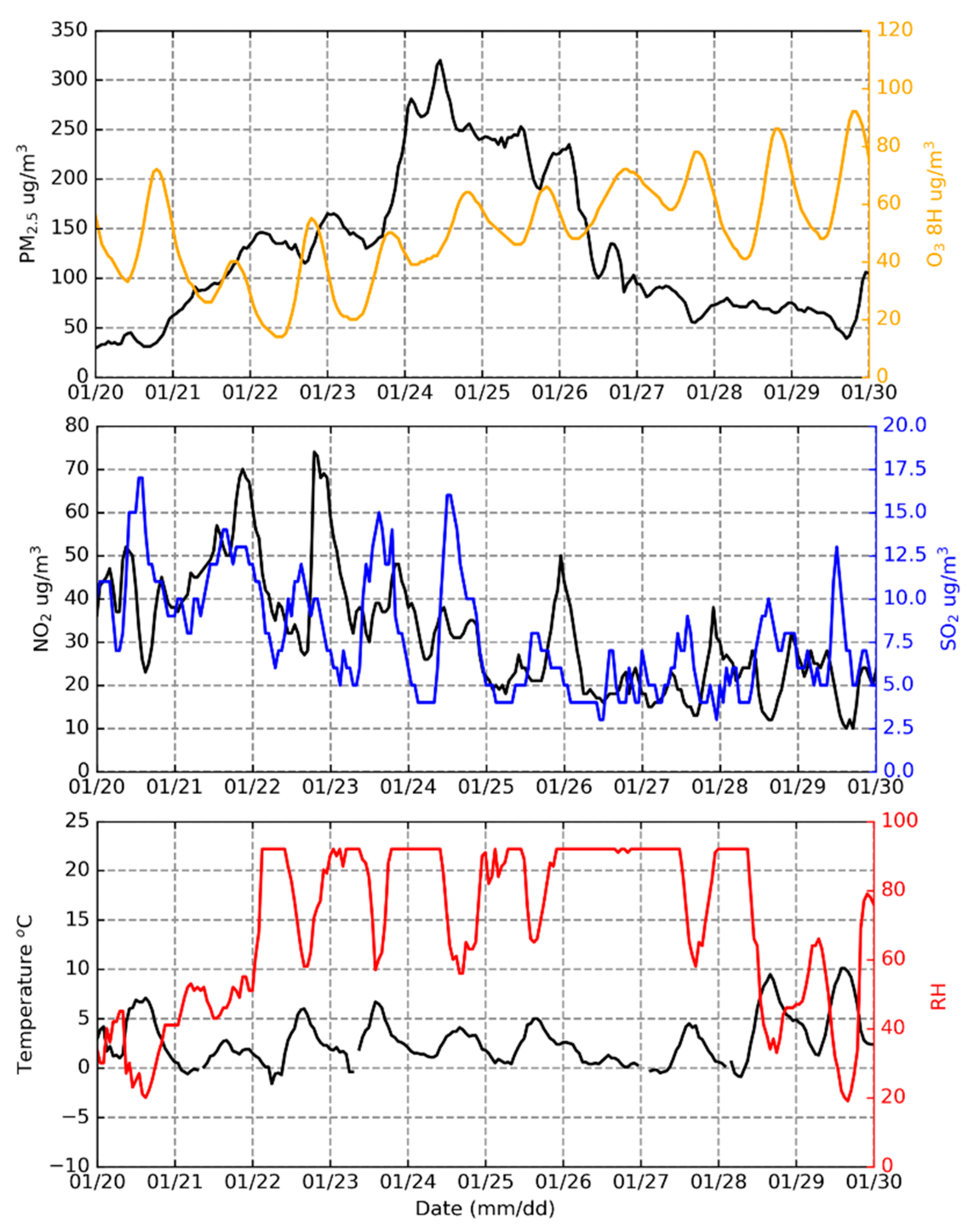
3.1. Temporal Variations of Pollutants in Boundary Layer
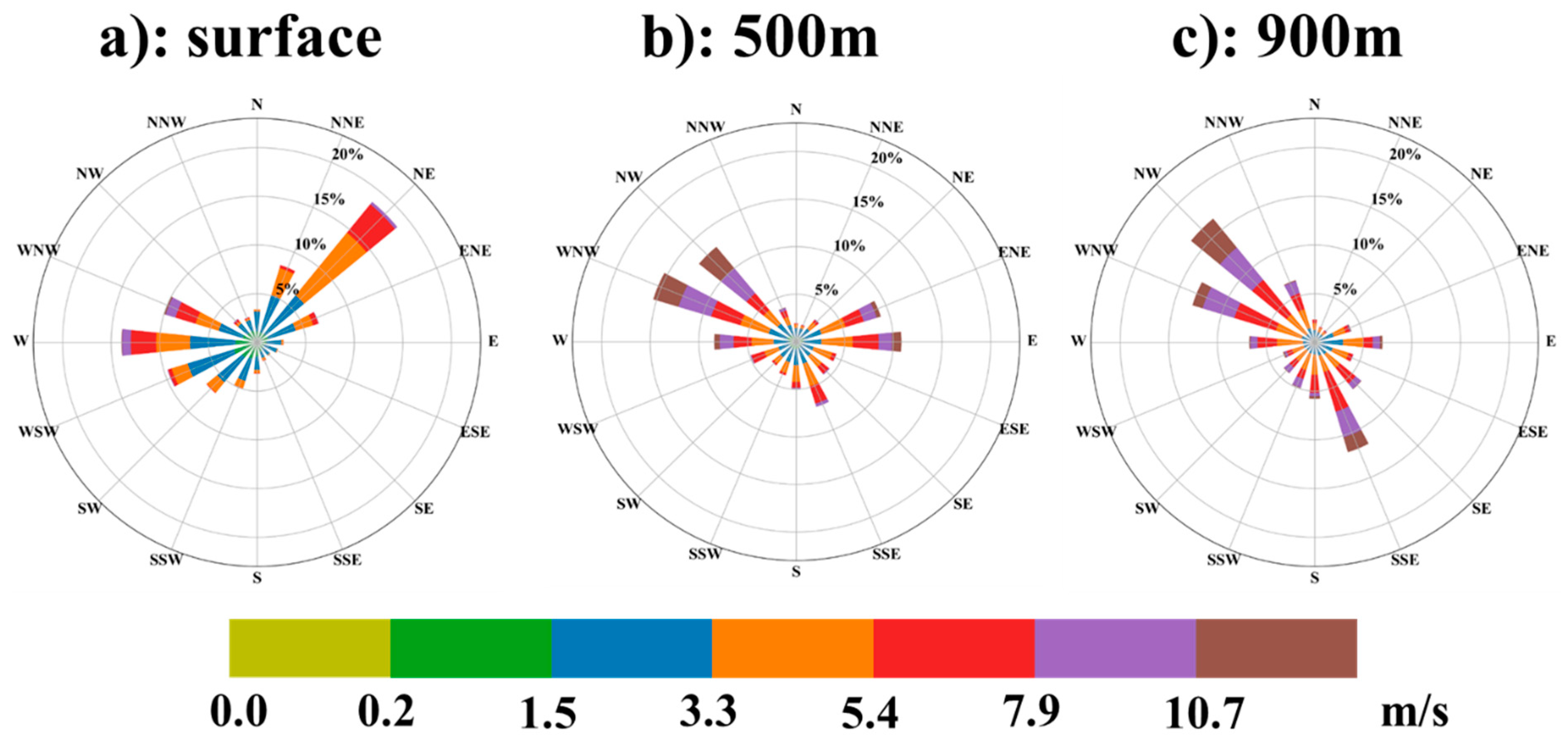
3.2. Statistics of Wind and Pollutant Transport Characterization
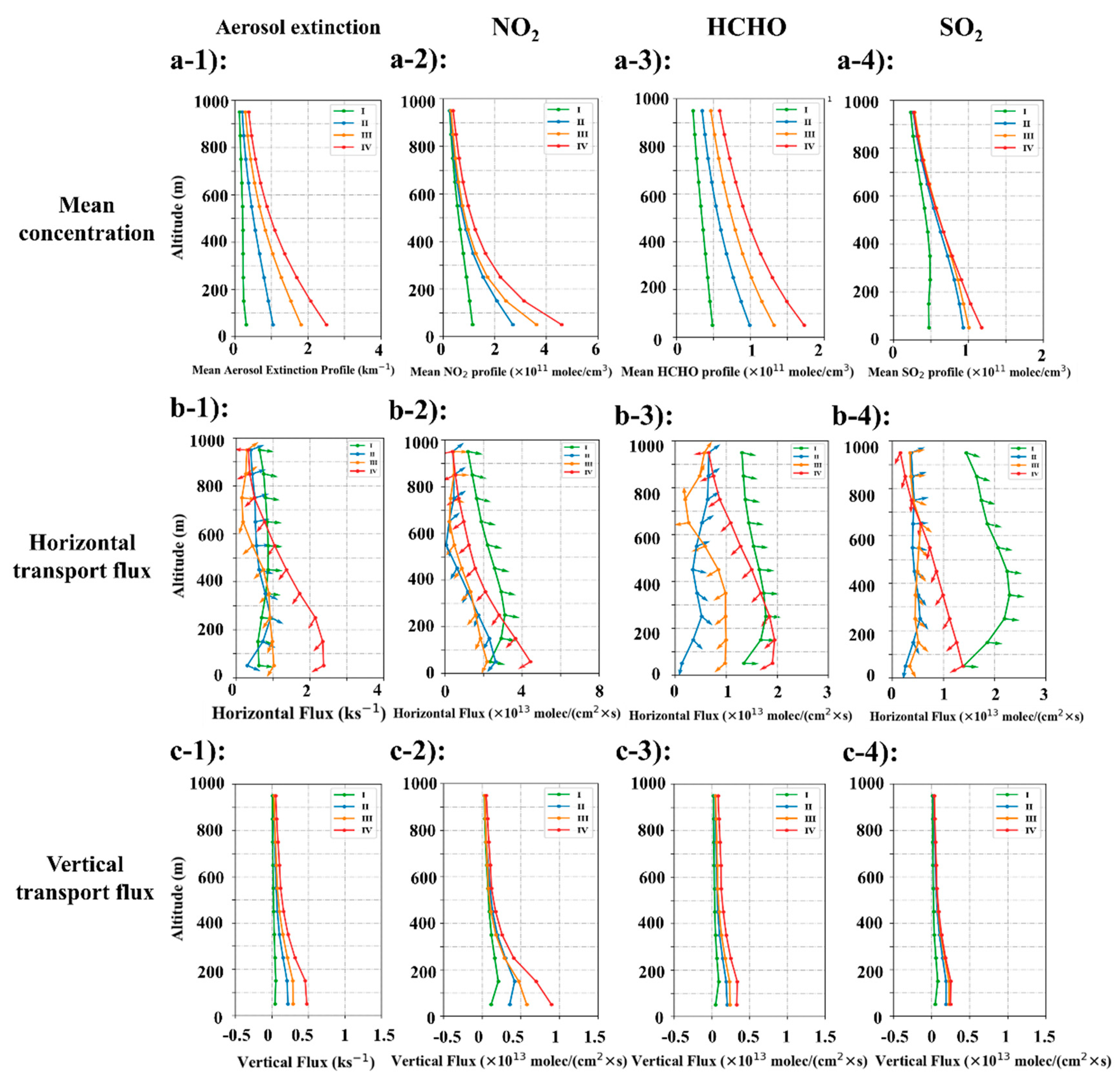
3.3. Vertical Structure of Transport Flux from Privileged Wind Directions
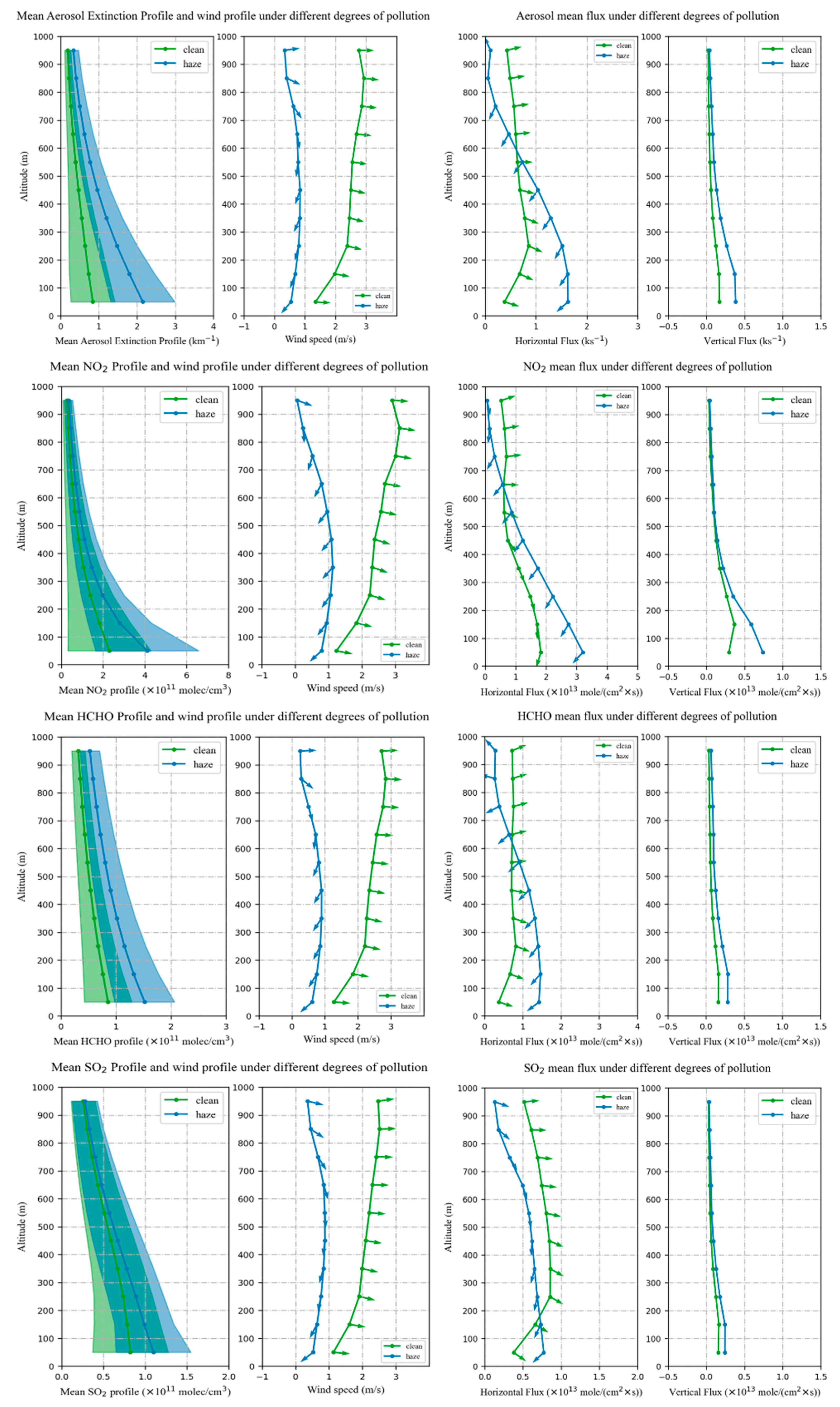
3.4. Structure of the Transport Flux under Different Pollution Degrees
4. Discussion
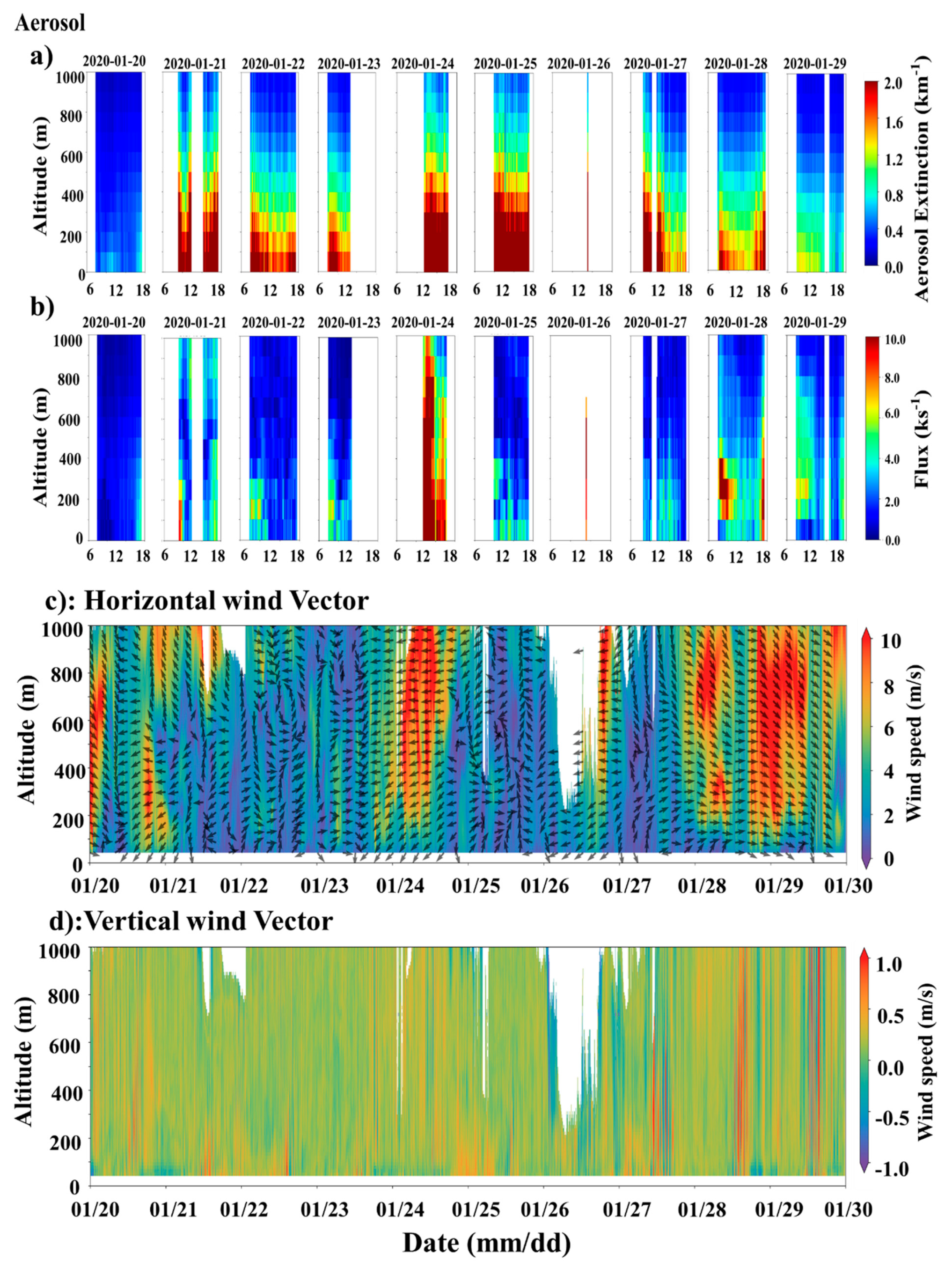
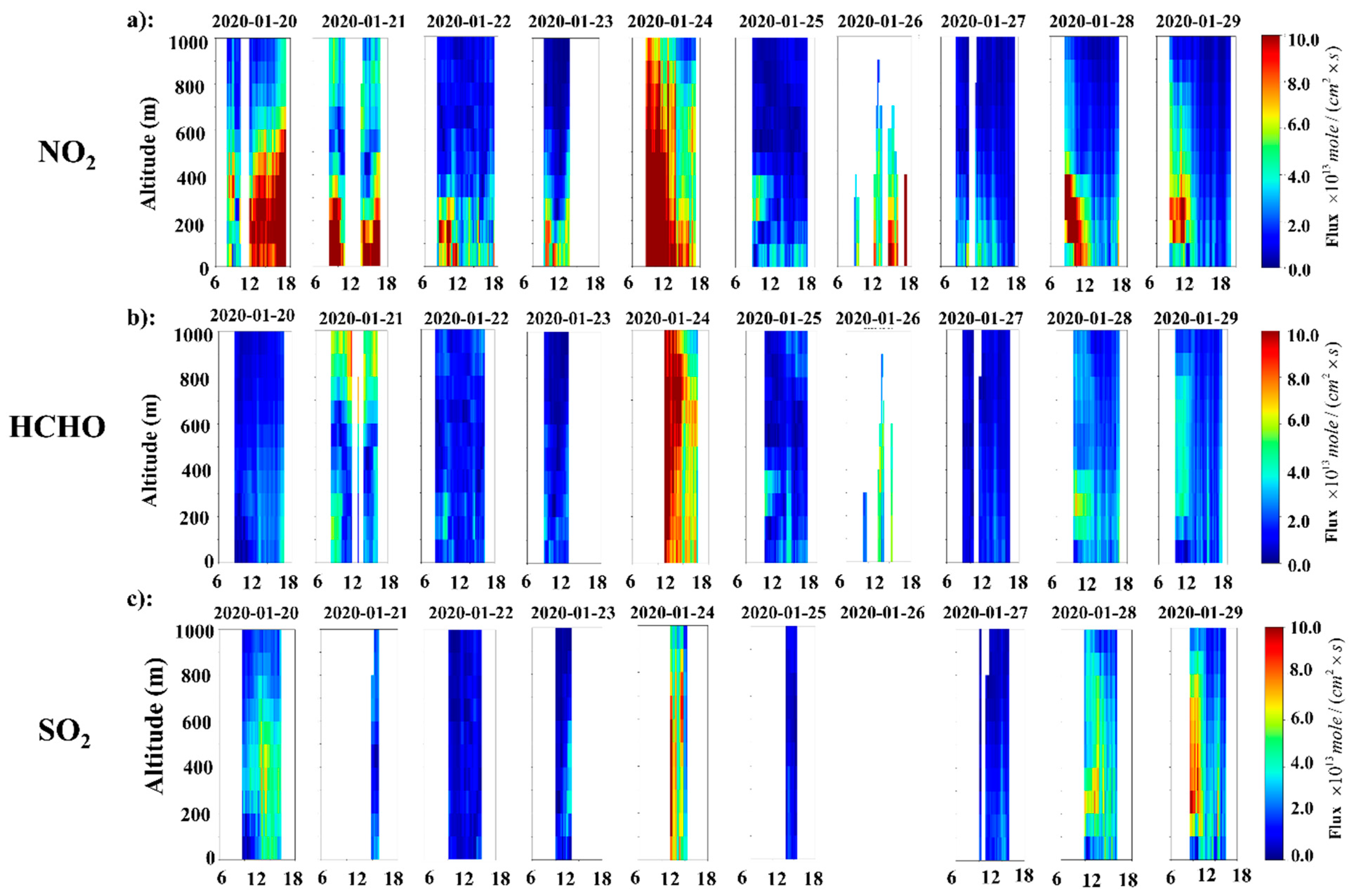
4.1. Transport Flux Variations during Severe-Haze Days
4.2. Transport Flux during the Low-Emission COVID-19 Period
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Validations of MAX-DOAS Results
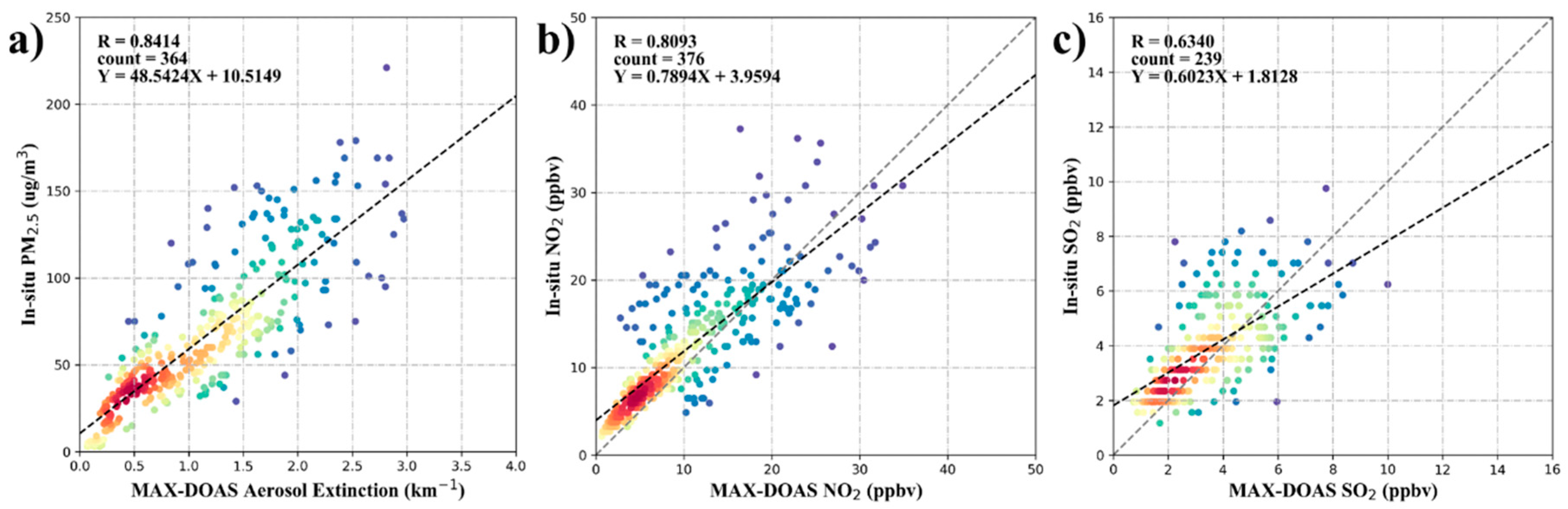
| Aerosol Extinction | NO2 | HCHO | SO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| surface | 84.92% | 79.72% | 88.48% | 53.96% |
| elevated | 15.08% | 20.28% | 11.52% | 46.04% |
Appendix A.2. Description of Z-Score Method
- (1)
- The absolute Zi is greater than 4 (|Zi| > 4).
- (2)
- The variation of Zi compared with its previous Zi−1 is greater than 9 (|Zi − Zi−1| > 9).
- (3)
- The ratio of three times Zi compared with its centered sum (Zi−1 + Zi + Zi+1) is greater than 2 (3 × Zi/(Zi−1 + Zi + Zi+1) > 2).
Appendix A.3. Discussion about the Classification Criteria of Polluted Days
References
- Shen, F.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Tang, M.; Gai, X.; Chen, M.; Ge, X. Temporal variations of six ambient criteria air pollutants from 2015 to 2018, their spatial distributions, health risks and relationships with socioeconomic factors during 2018 in China. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, G.; Hong, C.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; Tong, D.; Wu, R.; Zheng, B. Decadal changes in anthropogenic source contribution of PM 2.5 pollution and related health impacts in China, 1990–2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7783–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Yao, T.; Fung, J.C.; Lau, A.K. Assessment of health burden caused by particulate matter in southern China using high-resolution satellite observation. Environ. Int. 2017, 98, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Characterizing multi-pollutant air pollution in China: Comparison of three air quality indices. Environ. Int. 2015, 84, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Song, T.; Münkel, C.; Hu, B.; Schäfer, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Mixing layer height and its implications for air pollution over Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Tang, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Miao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. The interaction between urbanization and aerosols during a typical winter haze event in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 9855–9870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Xing, C.; Tan, W.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Geng, T.; et al. Evolution of the vertical structure of air pollutants during winter heavy pollution episodes: The role of regional transport and potential sources. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Lang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, X. Estimating the contribution of regional transport to PM2.5 air pollution in a rural area on the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tang, G.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.; Xin, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Münkel, C.; Wang, Y. Regional pollution and its formation mechanism over North China Plain: A case study with ceilometer observations and model simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 14574–14588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ye, C.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tan, Z.; Lin, W.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, T. Observation of regional air pollutant transport between the megacity Beijing and the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14265–14283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, J.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Che, H. Feedback effects of boundary-layer meteorological factors on cumulative explosive growth of PM2.5 during winter heavy pollution episodes in Beijing from 2013 to 2016. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, C.; Liao, H.; Zhang, L.; Yue, X.; Dang, R.; Yang, Y. Persistent ozone pollution episodes in North China exacerbated by regional transport. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Wang, Z.; Ding, K.; Gao, J.; Chai, F.; Fu, C. Amplified transboundary transport of haze by aerosol–boundary layer interaction in China. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koracin, D.; Vellore, R.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Watson, J.G.; Koracin, J.; McCord, T.; DuBois, D.W.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Kumar, N.; Knipping, E.M.; et al. Regional source identification using Lagrangian stochastic particle dispersion and HYSPLIT backward-trajectory models. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.; Cohen, M.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, B.; Cai, S.; Hao, J. Assessment of inter-city transport of particulate matter in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4843–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.G.; Gustafson, W., Jr.; Easter, R.C.; Barnard, J.C.; Ghan, S.J.; Pekour, M.S.; Fast, J.D. Coupling aerosol-cloud-radiative processes in the WRF-Chem model: Investigating the radiative impact of elevated point sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 945–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giez, A.; Ehret, G.; Schwiesow, R.L.; Davis, K.J.; Lenschow, D.H. Water vapor flux measurements from ground-based vertically pointed water vapor differential absorption and Doppler lidars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, R.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Žeromskis, E.; Althausen, D.; Wehner, B. Lidar observations of the vertical aerosol flux in the planetary boundary layer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, G.; Zhou, L.; Hu, B.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Mixing layer transport flux of particulate matter in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 9531–9540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Liu, C.; Xing, C.; Hu, Q.; Hong, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Tan, W.; Ji, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Validation of Water Vapor Vertical Distributions Retrieved from MAX-DOAS over Beijing, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Beirle, S.; Brauers, T.; Deutschmann, T.; Frieß, U.; Hak, C.; Halla, J.; Heue, K.; Junkermann, W.; Li, X. Inversion of tropospheric profiles of aerosol extinction and HCHO and NO2 mixing ratios from MAX-DOAS observations in Milano during the summer of 2003 and comparison with independent data sets. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Chan, K.L.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Y.; Fan, G. Observations of the vertical distributions of summertime atmospheric pollutants and the corresponding ozone production in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 14275–14289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Barthelmie, R.; Clifton, A.; Pryor, S. Wind measurements from arc scans with Doppler wind lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 2024–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildmann, N.; Päschke, E.; Roiger, A.; Mallaun, C. Towards improved turbulence estimation with Doppler wind lidar velocity-azimuth display (VAD) scans. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4141–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ning, M.; Lei, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Defending blue sky in China: Effectiveness of the “Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan” on air quality improvements from 2013 to 2017. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 252, 109603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Jacob, D.J.; Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, K.; Zhao, T.; Liao, H. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) trends in China, 2013–2018: Separating contributions from anthropogenic emissions and meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11031–11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z. Characteristics of winter haze pollution in the Fenwei plain and the possible influence of EU during 1984–2017. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Differential absorption spectroscopy. In Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 135–174. [Google Scholar]
- Perner, D.; Platt, U. Absorption of light in the atmosphere by collision pairs of oxygen (O2) 2. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1980, 7, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Dix, B.; Von Friedeburg, C.; Frieß, U.; Sanghavi, S.; Sinreich, R.; Platt, U. MAX-DOAS O4 Measurements: A New Technique to Derive Information on Atmospheric Aerosols—Principles and Information Content. Available online: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/2004JD004904 (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Vandaele, A.C.; Hermans, C.; Simon, P.C.; Carleer, M.; Colin, R.; Fally, S.; Merienne, M.-F.; Jenouvrier, A.; Coquart, B. Measurements of the NO2 absorption cross-section from 42,000 cm−1 to 10,000 cm−1 (238–1000 nm) at 220 K and 294 K. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1998, 59, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandaele, A.C.; Simon, P.C.; Guilmot, J.M.; Carleer, M.; Colin, R. SO2 absorption cross section measurement in the UV using a Fourier transform spectrometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 25599–25605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, R.; Moortgat, G.K. Temperature dependence of the absorption cross sections of formaldehyde between 223 and 323 K in the wavelength range 225–375 nm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 7089–7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdyuchenko, A.; Gorshelev, V.; Weber, M.; Chehade, W.; Burrows, J. High spectral resolution ozone absorption cross-sections–Part 2: Temperature dependence. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thalman, R.; Volkamer, R. Temperature dependent absorption cross-sections of O2—O2 collision pairs between 340 and 630 nm and at atmospherically relevant pressure. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 15371–15381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, O.C.; Hartmann, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Orphal, J. New ultraviolet absorption cross-sections of BrO at atmospheric temperatures measured by time-windowing Fourier transform spectroscopy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2004, 168, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, K.V.; Spurr, R.J. Ring effect studies: Rayleigh scattering, including molecular parameters for rotational Raman scattering, and the Fraunhofer spectrum. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 5224–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chance, K.; Kurucz, R.L. An improved high-resolution solar reference spectrum for earth’s atmosphere measurements in the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliwell, S.; Van Roozendael, M.; Johnston, P.; Richter, A.; Wagner, T.; Arlander, D.; Burrows, J.; Fish, D.; Jones, R.; Tørnkvist, K.; et al. Analysis for BrO in zenith—Sky spectra: An intercomparison exercise for analysis improvement. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, ACH-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Wiegner, M.; Wenig, M.; Pöhler, D. Observations of tropospheric aerosols and NO2 in Hong Kong over 5 years using ground based MAX-DOAS. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.L.; Wiegner, M.; van Geffen, J.; De Smedt, I.; Alberti, C.; Cheng, Z.; Ye, S.; Wenig, M. MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric NO2 and HCHO in Munich and the comparison to OMI and TROPOMI satellite observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4499–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Wang, Z.; Ding, A.; Heue, K.-P.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Hao, N.; Wenig, M. MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric NO2 and HCHO in Nanjing and a comparison to ozone monitoring instrument observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10051–10071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodgers, C.D. Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding: Theory And Practice; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, B.; Kylling, A. The libRadtran software package for radiative transfer calculations—Description and examples of use. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1855–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, W.; Anderson, J.; Blumenthal, D.; Husar, R.; Gillani, N.; Husar, J.; Wilson, W.J.S. Formation and transport of secondary air pollutants: Ozone and aerosols in the St. Louis urban plume. Science 1976, 194, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Dai, G.; Song, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, L. Observations of water vapor mixing ratio profile and flux in the Tibetan Plateau based on the lidar technique. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Y.; Fan, G.; Xiang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, N.; Chu, B.; et al. Observations of particle extinction, PM2.5 mass concentration profile and flux in north China based on mobile lidar technique. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 164, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, P.; Li, A.; Xu, J.; Ren, H.; Ren, B.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Study of aerosol characteristics and sources using MAX-DOAS measurement during haze at an urban site in the Fenwei Plain. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 107, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Kuang, X.; Xu, X.; Kan, H. Particulate air pollution and mortality in a cohort of Chinese men. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Saide, P.E.; Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pagowski, M.; Guttikunda, S.K.; Carmichael, G.R. Estimates of health impacts and radiative forcing in winter haze in eastern China through constraints of surface PM2.5 predictions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Hendrick, F.; Wang, P.; Tang, G.; Clémer, K.; Yu, H.; Fayt, C.; Hermans, C.; Gielen, C.; Müller, J.-F.; et al. Evaluation of tropospheric SO2 retrieved from MAX-DOAS measurements in Xianghe, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11149–11164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otmani, A.; Benchrif, A.; Tahri, M.; Bounakhla, M.; El Bouch, M.; Krombi, M. Impact of Covid-19 lockdown on PM10, SO2 and NO2 concentrations in Salé City (Morocco). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, S.K.; Lewis, A.C.; Carslaw, D.C. Source apportionment advances using polar plots of bivariate correlation and regression statistics. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 145, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Qin, X.; Huang, K.; Wang, D.; Fu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, B. Aerosol vertical profile retrieved from ground-based MAX-DOAS observation and characteristic distribution during wintertime in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 192, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Q.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Xing, C.; Tan, W.; Liu, T.; Liu, J. Vertical distributions of tropospheric SO2 based on MAX-DOAS observations: Investigating the impacts of regional transport at different heights in the boundary layer. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 103, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, K.; Ho, S.S.H.; Louie, P.K.; Chan, C.; Lee, S.; Hu, D.; Chan, P.; Lee, J.C.W.; Ho, K. Seasonal behavior of carbonyls and source characterization of formaldehyde (HCHO) in ambient air. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Jacob, D.J.; Mickley, L.J.; Marais, E.A.; Cohan, D.S.; Yoshida, Y.; Duncan, B.N.; Abad, G.G.; Chance, K.V. Anthropogenic emissions of highly reactive volatile organic compounds in eastern Texas inferred from oversampling of satellite (OMI) measurements of HCHO columns. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 114004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, T.; Xie, M.; Zhao, H. Numerical modeling of a continuous photochemical pollution episode in Hong Kong using WRF–chem. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8717–8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Gao, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, D.; Qi, X.; Tang, R.; Wang, J.; Ren, C.; Nie, W. Enhanced Secondary Pollution Offset Reduction of Primary Emissions During COVID-19 Lockdown in China. Available online: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2004JD004904 (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Le, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Yung, Y.L.; Li, G.; Seinfeld, J.H. Unexpected air pollution with marked emission reductions during the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Science 2020, 369, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Page, A.; Strode, S.A.; Yoshida, Y.; Choi, S.; Zheng, B.; Lamsal, L.N.; Li, C.; Krotkov, N.A.; Eskes, H. Abrupt decline in tropospheric nitrogen dioxide over China after the outbreak of COVID-19. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Brasseur, G.P. The Response in Air Quality to the Reduction of Chinese Economic Activities during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z.; Hu, Q.; Andreae, M.O.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Elevated dust layers inhibit dissipation of heavy anthropogenic surface air pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 14917–14932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Apituley, A.; Bais, A.; Beirle, S.; Benavent, N.; Borovski, A.; Bruchkouski, I.; Chan, K.L.; Donner, S.; Drosoglou, T.; et al. Inter-comparison of MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric HONO slant column densities and vertical profiles during the CINDI-2 campaign. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 5087–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirpitz, J.-L.; Frieß, U.; Hendrick, F.; Alberti, C.; Allaart, M.; Apituley, A.; Bais, A.; Beirle, S.; Berkhout, S.; Bognar, K.; et al. Intercomparison of MAX-DOAS vertical profile retrieval algorithms: Studies on field data from the CINDI-2 campaign. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreher, K.; Roozendael, M.V.; Hendrick, F.; Apituley, A.; Dimitropoulou, E.; Frieß, U.; Richter, A.; Wagner, T.; Lampel, J.; Abuhassan, N. Intercomparison of NO2, O4, O3 and HCHO slant column measurements by MAX-DOAS and zenith-sky UV–visible spectrometers during CINDI-2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2169–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, M.; Orza, J.; Cabello, M.; Cantón, L. Categorisation of air quality monitoring stations by evaluation of PM10 variability. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.; Jin, T.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.; et al. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Hong, J.; Zhang, L.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Severe surface ozone pollution in China: A global perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Cross Section | Species | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O4 | NO2 | HCHO | SO2 | ||
| Fitting interval (nm) | 338–370 | 338–370 | 322.5–358 | 307.5–330 | |
| NO2 | Vandaele et al. [32] 220 K, 294 K, I0-correction (SCD of 1017 molecules/cm2) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓(only 294 K) | ✓(only 294 K) |
| SO2 | Vandaele et al. [33], 298 K | ✓ | |||
| HCHO | Meller and Moortgat [34], 297 K | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| O3 | Serdyuchenko et al. [35], 223 K, 243 K, I0-correction (SCD of 1020 molecules/cm2) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| O4 | Thalman and Volkamer [36], 293 K | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| BrO | Fleischmann et al. [37], 223 K | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Ring | Ring spectra calculated with QDOAS according to Chance and Spurr [38] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Polynomial degree | Order 5 | Order 5 | Order 5 | Order 5 | |
| Intensity offset | Constant | Constant | Order 1 | Order 1 | |
| Wavelength calibration | Based on a high resolution solar reference spectrum (SAO2010 solar spectra) [39] | ||||
| Technical Index | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Wavelength | 1.5 um |
| Temporal resolution | 1 min |
| Spatial resolution | 14 m (vertical) |
| Wind speed Measurement range | 0–75 m/s |
| Detection height | 30~3000 m |
| Wind speed accuracy | Less than 0.1 m/s |
| Wind direction accuracy | Less than 3° |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, X.; Hu, Q.; Hu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Xing, C.; Lin, H.; Lin, J. Vertical Structure of Air Pollutant Transport Flux as Determined by Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observations in Fen-Wei Plain, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3664. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183664
Ji X, Hu Q, Hu B, Wang S, Liu H, Xing C, Lin H, Lin J. Vertical Structure of Air Pollutant Transport Flux as Determined by Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observations in Fen-Wei Plain, China. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(18):3664. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183664
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Xiangguang, Qihou Hu, Bo Hu, Shuntian Wang, Hanyang Liu, Chengzhi Xing, Hua Lin, and Jinan Lin. 2021. "Vertical Structure of Air Pollutant Transport Flux as Determined by Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observations in Fen-Wei Plain, China" Remote Sensing 13, no. 18: 3664. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183664
APA StyleJi, X., Hu, Q., Hu, B., Wang, S., Liu, H., Xing, C., Lin, H., & Lin, J. (2021). Vertical Structure of Air Pollutant Transport Flux as Determined by Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observations in Fen-Wei Plain, China. Remote Sensing, 13(18), 3664. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183664








