Unknown SAR Target Identification Method Based on Feature Extraction Network and KLD–RPA Joint Discrimination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose an end to end feature extraction network model (FEN), which is capable of implementing feature mapping of SAR targets and building a stable and efficient target feature mapping space.
- (2)
- The KLD similarity measurement method is introduced to realize fast and rough identification of unknown SAR targets.
- (3)
- Aiming at the problem of multitarget spatial collinear aliasing that easily appears in the process of absolute angle measurement, this paper proposes a target feature measurement method based on relative position angles (RPA). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to use RPA measurement for the analysis and calculation of SAR image data. In addition, we believe that this RPA measurement method can also be applied to the other types of data.
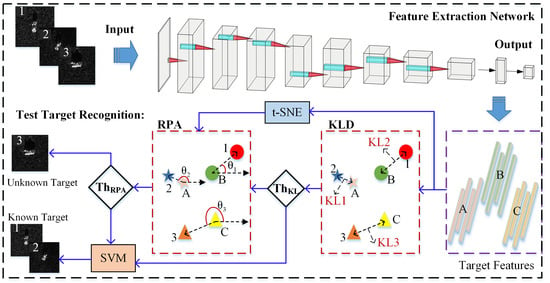
2. Fea-DA Overall Framework
3. Feature Extraction Network
3.1. Multiscale Features
3.2. SVM Classifier
4. KLD-RPA Joint Discrimination
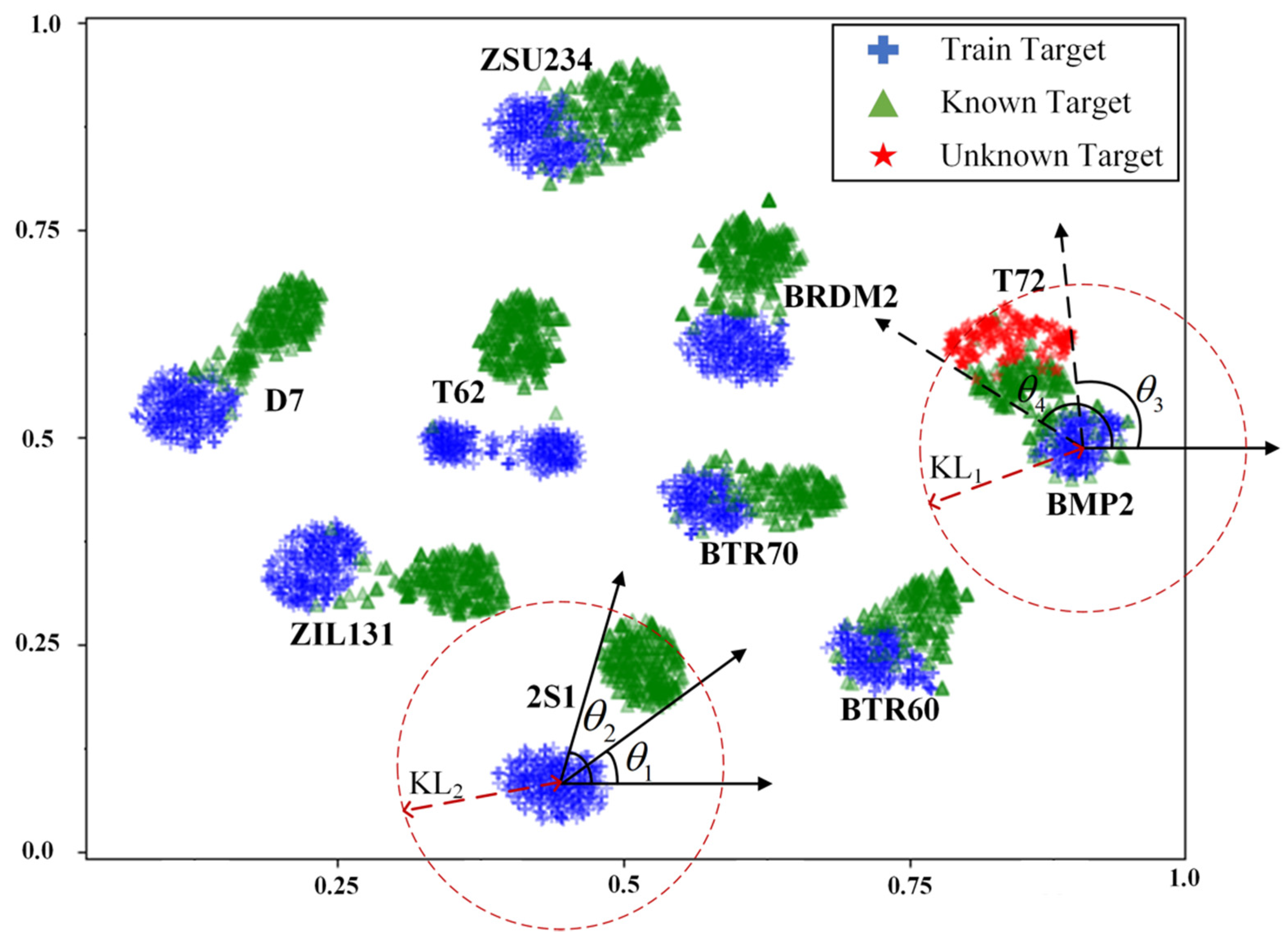
4.1. KL Divergence Discrimination
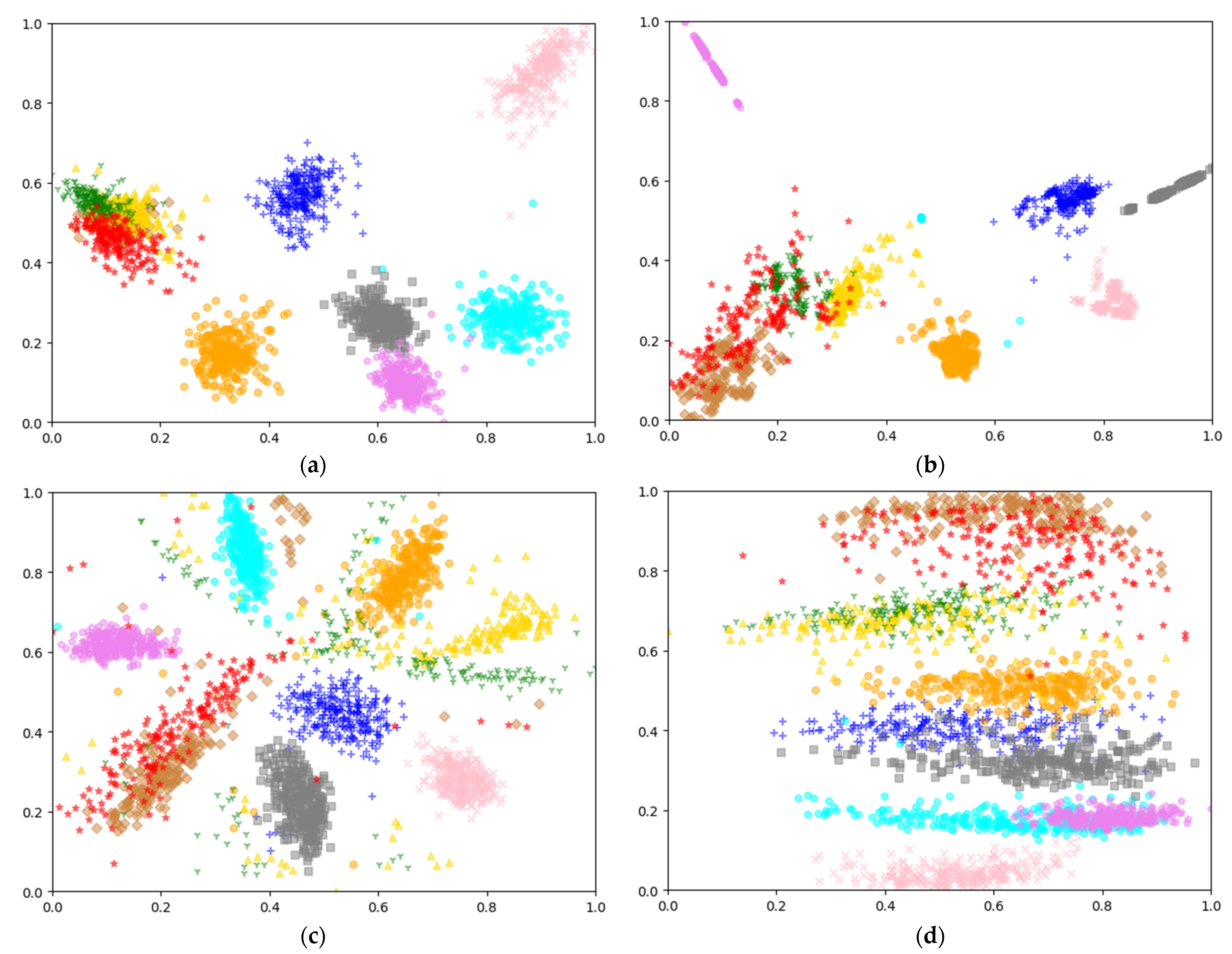
4.2. t-SNE Dimensionality Reduction and Visualization Technology
4.3. Reletive Position Angle Identification
4.4. Threshold Setting
4.4.1. KLD Threshold
4.4.2. RPA Threshold
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
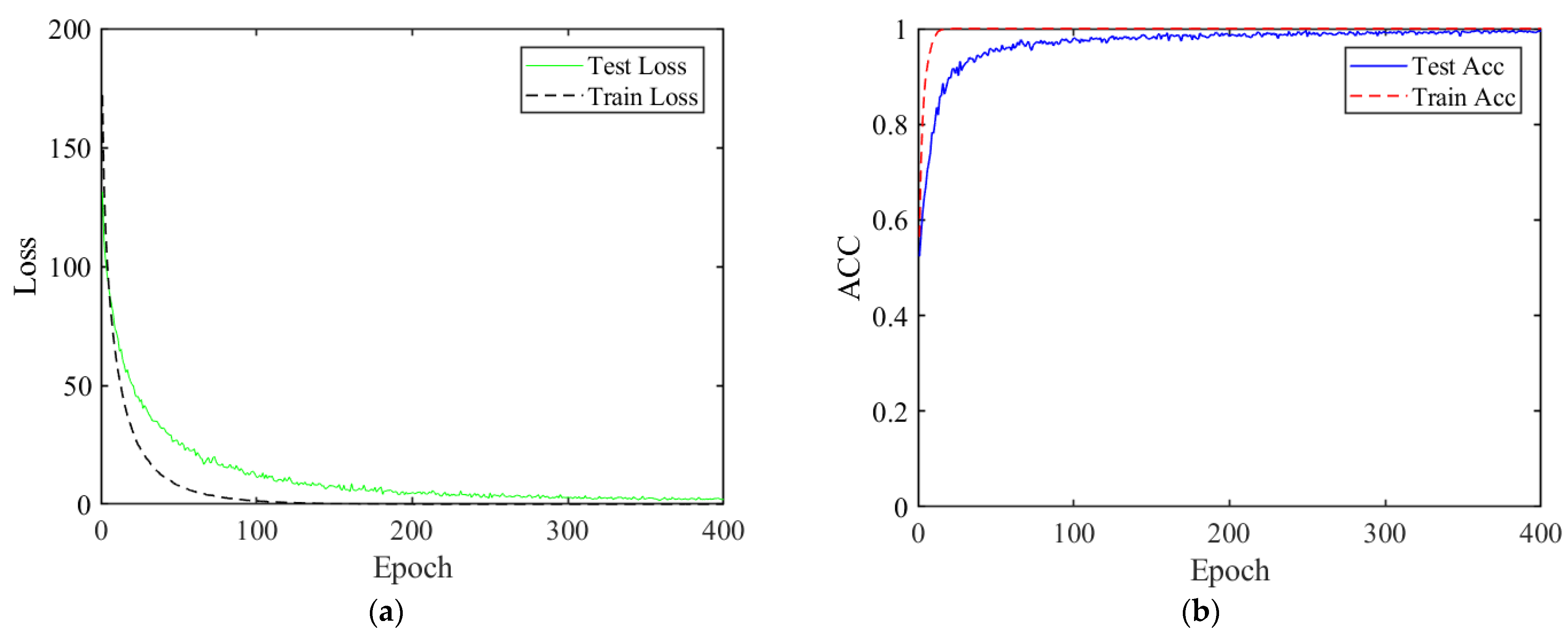
5.1. The Learning Ability of FEN
5.1.1. Test Error
5.1.2. Test Accuracy
5.2. Unknown SAR Target Identification
5.2.1. The 1-Type Unknown Target Test
5.2.2. The 3-Type Unknown Target Test
6. Discussion
6.1. Feature Subspace Mapping
6.2. The t-SNE Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction
6.3. Ablation Experiments
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Fu, X.; Xia, K. Target Classification for Single-Channel SAR Images Based on Transfer Learning with Subaperture Decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bai, X.; Zhou, F. SAR ATR of Ground Vehicles Based on ESENet. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, S. Combination of convolutional feature extraction and support vector machines for radar ATR. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Salamanca, Spain, 7–10 July 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Belloni, C.; Balleri, A.; Aouf, N.; Le Caillec, J.M.; Merlet, T. Explainability of Deep SAR ATR Through Feature Analysis. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 57, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Housseini, A.; Toumi, A.; Khenchaf, A. Deep Learning for target recognition from SAR images. In Proceedings of the 2017 Seminar on Detection Systems Architectures and Technologies (DAT), Algiers, Algeria, 20–22 February 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Pei, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, J. When Deep Learning Meets Multi-Task Learning in SAR ATR: Simultaneous Target Recognition and Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Application of deep-learning algorithms to MSTAR data. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 3743–3745. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Pei, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. A Deformable Convolution Neural Network for SAR ATR. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 2639–2642. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2016, 54, 4806–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, C.; Pallotta, L.; Gaglione, D.; Maio, A.D.; Soraghan, J.J. Automatic Target Recognition of Military Vehicles with Krawtchouk Moments. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, K.; Zou, H.; Zhen, X. Multi-Stream Convolutional Neural Network for SAR Automatic Target Recognition. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, L.; Bai, X.; Hui, Y. SAR ATR of ground vehicles based on LM-BN-CNN. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 7282–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, Q. Semi-supervised deep transfer learning-based on adversarial feature learning for label limited SAR target recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 152412–152420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Ni, J.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, W. SAR target small sample recognition based on CNN cascaded features and AdaBoost rotation forest. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Dang, S.; Cao, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, N. SAR Target Recognition in Large Scene Images via Region-Based Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Bai, X.; Gong, C.; Zhou, F. Hybrid Inference Network for Few-Shot SAR Automatic Target Recognition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X. Few-Shot SAR Target Classification via Metalearning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Wang, J.; Jiao, L.; Stolkin, R.; Hou, B.; Li, Y. SAR targets classification based on deep memory convolution neural networks and transfer parameters. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2834–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. SAR Image Representation Learning with Adversarial Autoencoder Networks. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 9498–9501. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, J. SAR Target Recognition with Limited Training Data Based on Angular Rotation Generative Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatucci, M.M.; Pomerleau, D.A.; Hinton, G.E.; Mitchell, T. Zero-shot learning with semantic output codes. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–10 December 2009; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1410–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, C.H.; Nickisch, H.; Harmeling, S. Attribute-based classification for zero-shot visual object categorization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Sato, H.; Oyama, S.; Kurihara, M. Transfer learning based on the observation probability of each attribute. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 October 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 3627–3631. [Google Scholar]
- Socher, R.; Ganjoo, M.; Sridhar, H.; Bastani, O.; Manning, C.D.; Ng, A.Y. Zero-shot learning through cross-modal transfer. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information, Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 935–943. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xiang, T.; Gong, S. Learning a deep embedding model for zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2021–2030. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, B.; Al-Najjar, H.A.H.; Sameen, M.I.; Tsang, I.; Alamri, A.M. Unseen Land Cover Classification from High-Resolution Orthophotos Using Integration of Zero-Shot Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.R.; He, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.A. Learn to Recognize Unknown SAR Targets from Reflection Similarity. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changpinyo, S.; Chao, W.-L.; Gong, B.; Sha, F. Synthesized classifiers for zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 5327–5336. [Google Scholar]
- Toizumi, T.; Sagi, K.; Senda, Y. Automatic association between sar and optical images based on zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Xu, F. Zero-shot learning of SAR target feature space with deep generative neural networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2245–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Chen, H.; Xu, F.; Cui, T.J. EM Simulation-Aided Zero-Shot Learning for SAR Automatic Target Recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafino, F.; Lugni, C.; Nieto Borge, J.C.; Soldovieri, F. A Simple Strategy to Mitigate the Aliasing Effect in X-band Marine Radar Data: Numerical Results for a 2D Case. Sensors 2011, 11, 1009–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, K.W.; Wilson, C.R.; Chen, J.; Waliser, D.E. GRACE’s spatial aliasing error. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 172, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayinde, B.; Inanc, T.; Zurada, J. Regularizing Deep Neural Networks by Enhancing Diversity in Feature Extraction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 2650–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Wei, L.; Yang, M.-H.; Wu, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Ling, H.; Wang, J. Deepsaliency: Multi-task deep neural network model for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 3919–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Hu, H. Scale-aware hierarchical loss: A multipath RPN for multi-scale pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 10–13 December 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wu, M. Pedestrian detection based on multi-scale fusion features. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Network Infrastructure and Digital Content (IC-NIDC), Guiyang, China, 22–28 August 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger, J.; Gordon, S.; Greenspan, H. An Efficient Image Similarity Measure Based on Approximations of KL-Divergence Between Two Gaussian Mixtures. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Nice, France, 13–16 October 2003; Volume 3, pp. 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.S.; Weng, C.Y.; Wu, M.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.M.; Tsai, C.S. A KL Divergence Function for Randomized Secret Shares. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing (IIH-MSP), Adelaide, SA, Australia, 23–25 September 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 231–234. [Google Scholar]
- Laurens, V.D.M.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.; Jiang, J.; Kong, Q.; Shi, J.; Sheng, Q.; Zhou, T. Radar HRRP target recognition based on t-SNE segmentation and discriminant deep belief network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1609–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavacs, H.; Hummel, K. Cooperative Positioning when Using Local Position Information: Theoretical Framework and Error Analysis. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2013, 12, 2091–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Cai, B.; Rizos, C.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y. A New Train Integrity Resolution Method Based on Online Carrier Phase Relative Positioning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 10519–10530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, Y.; Katkar, V.; Sarode, S. Early alert system using relative positioning in Vehicular Ad-hoc Network. In Proceedings of the 2014 Annual International Conference on Emerging Research Areas: Magnetics, Machines and Drives (AICERA/iCMMD), Kerala, India, 24–26 July 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Shi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wei, S.; Zhang, X. Semisupervised Learning-Based SAR ATR via Self-Consistent Augmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Kuang, G. Target Recognition in SAR Images via Classification on Riemannian Manifolds. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, K. Modified polar mapping classifier for SAR automatic target recognition. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 1092–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagias-Stamatis, O.; Aouf, N. Fusing Deep Learning and Sparse Coding for SAR ATR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

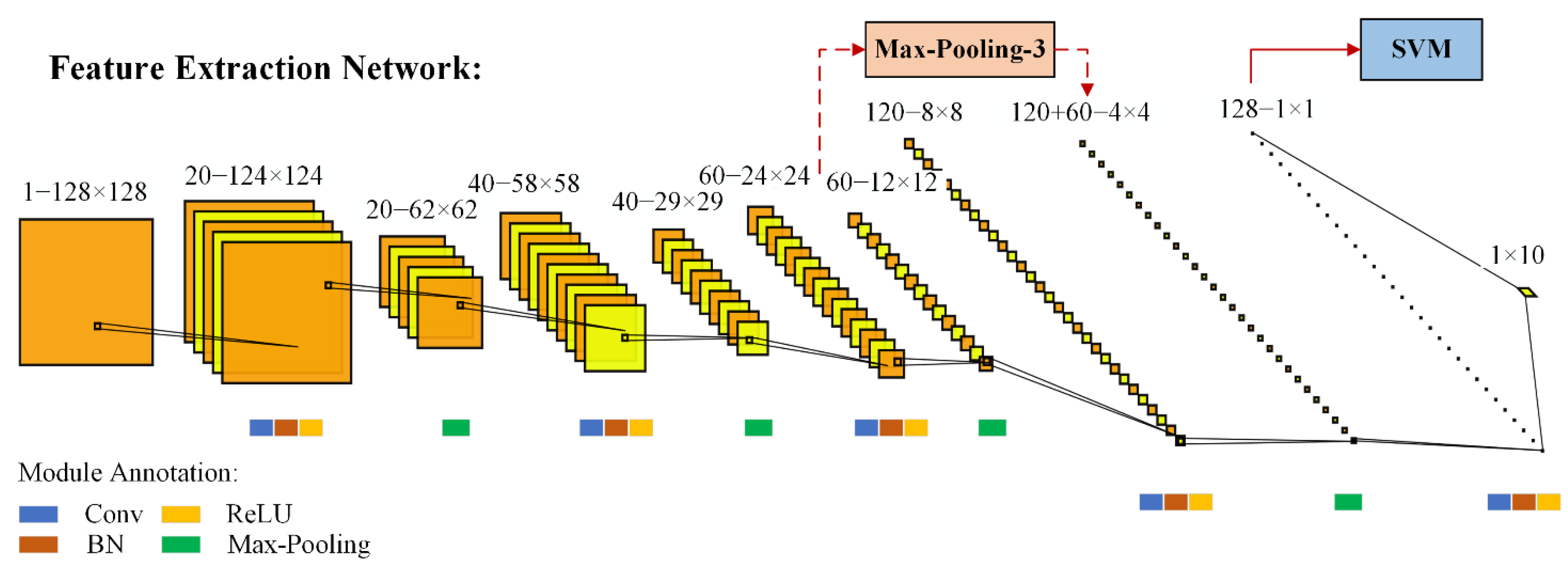




| Pathway | Layer Composition | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Input Layer | - | 1 − 128 × 128 |
| Conv Layer1 | Conv-20-5 × 5 BN ReLU Max-Pooling-2 | 20 − 62 × 62 |
| Conv Layer2 | Conv-40-5 × 5 BN ReLU Max-Pooling-2 | 40 − 29 × 29 |
| Conv Layer3 | Conv-60-6 × 6 BN ReLU Max-Pooling-2 | 60 − 12 × 12 |
| Conv Layer4 | Conv-120-5 × 5 BN ReLU Max-Pooling-2 | 120 − 4 × 4 |
| Conv Layer5 | Conv-128-4 × 4 BN ReLU | 128 − 1 × 1 |
| FC Layer | - | 10 × 1 |
| Categories | Training Set (Depression Angle: 17°) | Testing Set (Depression Angle: 15°) |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2S1 | 299 | 274 |
| 2-BMP2 | 233 | 195 |
| 3-BRDM2 | 298 | 274 |
| 4-BTR60 | 256 | 195 |
| 5-BTR70 | 233 | 196 |
| 6-D7 | 299 | 274 |
| 7-T62 | 299 | 273 |
| 8-T72 | 232 | 196 |
| 9-ZIL131 | 299 | 274 |
| 10-ZSU234 | 299 | 274 |
| Total | 2747 | 2425 |
| Datasets | Known Categories | Unknown Categories | Training Set | Testing Set |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-type | 2, 5, 8 | - | 698 | 587 |
| 10-type | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 | - | 2747 | 2425 |
| 1-type unknown | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10 | 8 | 2515 | 2229 |
| 3-type unknown | 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9 | 5, 8, 10 | 1983 | 1759 |
| Datasets | Models | ACC |
|---|---|---|
| 3-type | FEN | 100% |
| A-ConvNets | 99.49% | |
| TL-SD | 99.66% | |
| L1-2-CCNN | 99.33% | |
| M-PMC | 98.83% | |
| KLSF | 89.1% | |
| 10-type | FEN | 99.63% |
| A-ConvNets | 99.13% | |
| TL-SD | 99.64% | |
| L1-2-CCNN | 99.86% | |
| M-PMC | 98.81% | |
| KLSF | 96.1% |
| Models | Known Target Accuracy | Unknown Target Accuracy | Overall Target Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fea-DA | 97.58% | 84.69% | 96.53% |
| EM simulation-ZSL | 91.93% | 79.08% | 88.01% |
| VGG+PCA-ZSL | 84.07% | 71.42% | 83.05% |
| VGG-ZSL | 67.83% | 57.14% | 66.97% |
| Category | 2S1 | BMP2 | BRDM2 | BTR60 | BTR70 | D7 | T62 | ZIL131 | ZSU234 | T72 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2S1 | 270 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| BMP2 | 0 | 154 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41 |
| BRDM2 | 0 | 0 | 274 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BTR60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 195 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BTR70 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 186 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| D7 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 272 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| T62 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 271 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| ZIL131 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 273 | 1 | 0 |
| ZSU234 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 272 | 2 |
| T72 | 0 | 23 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 166 |
| Model | Unknown Category | Known Target Accuracy | Unknown Target Accuracy | Overall Target Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fea-DA | 5 | 95.62% | 86.73% | 94.73% |
| 8 | 95.05% | 88.78% | 94.42% | |
| 10 | 97.56% | 97.44% | 97.54% | |
| 5, 8, 10 | 91.43% | 86.33% | 90.72% |
| Models | Known Target Accuracy | Unknown Target Accuracy | Overall Target Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fea-DA | 97.58% | 84.69% | 96.53% |
| KLD-ACA | 82.05% | 81.63% | 82.02% |
| KLD | 80.04% | 81.12% | 80.12% |
| Model | Unknown Category | Known Target Accuracy | Unknown Target Accuracy | Overall Target Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KLD-ACA | 5 | 90.79% | 83.67% | 90.08% |
| 8 | 75.50% | 73.47% | 75.29% | |
| 10 | 94.26% | 93.80% | 94.20% | |
| 5, 8, 10 | 86.36% | 82.00% | 85.72% | |
| KLD | 5 | 92.44% | 82.14% | 91.41% |
| 8 | 75.67% | 73.98% | 75.50% | |
| 10 | 93.63% | 94.89% | 93.80% | |
| 5, 8, 10 | 85.96% | 81.67% | 85.33% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Z.; Sun, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, H. Unknown SAR Target Identification Method Based on Feature Extraction Network and KLD–RPA Joint Discrimination. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152901
Zeng Z, Sun J, Xu C, Wang H. Unknown SAR Target Identification Method Based on Feature Extraction Network and KLD–RPA Joint Discrimination. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(15):2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152901
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Zhiqiang, Jinping Sun, Congan Xu, and Haiyang Wang. 2021. "Unknown SAR Target Identification Method Based on Feature Extraction Network and KLD–RPA Joint Discrimination" Remote Sensing 13, no. 15: 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152901
APA StyleZeng, Z., Sun, J., Xu, C., & Wang, H. (2021). Unknown SAR Target Identification Method Based on Feature Extraction Network and KLD–RPA Joint Discrimination. Remote Sensing, 13(15), 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152901