Multi-Scene Building Height Estimation Method Based on Shadow in High Resolution Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
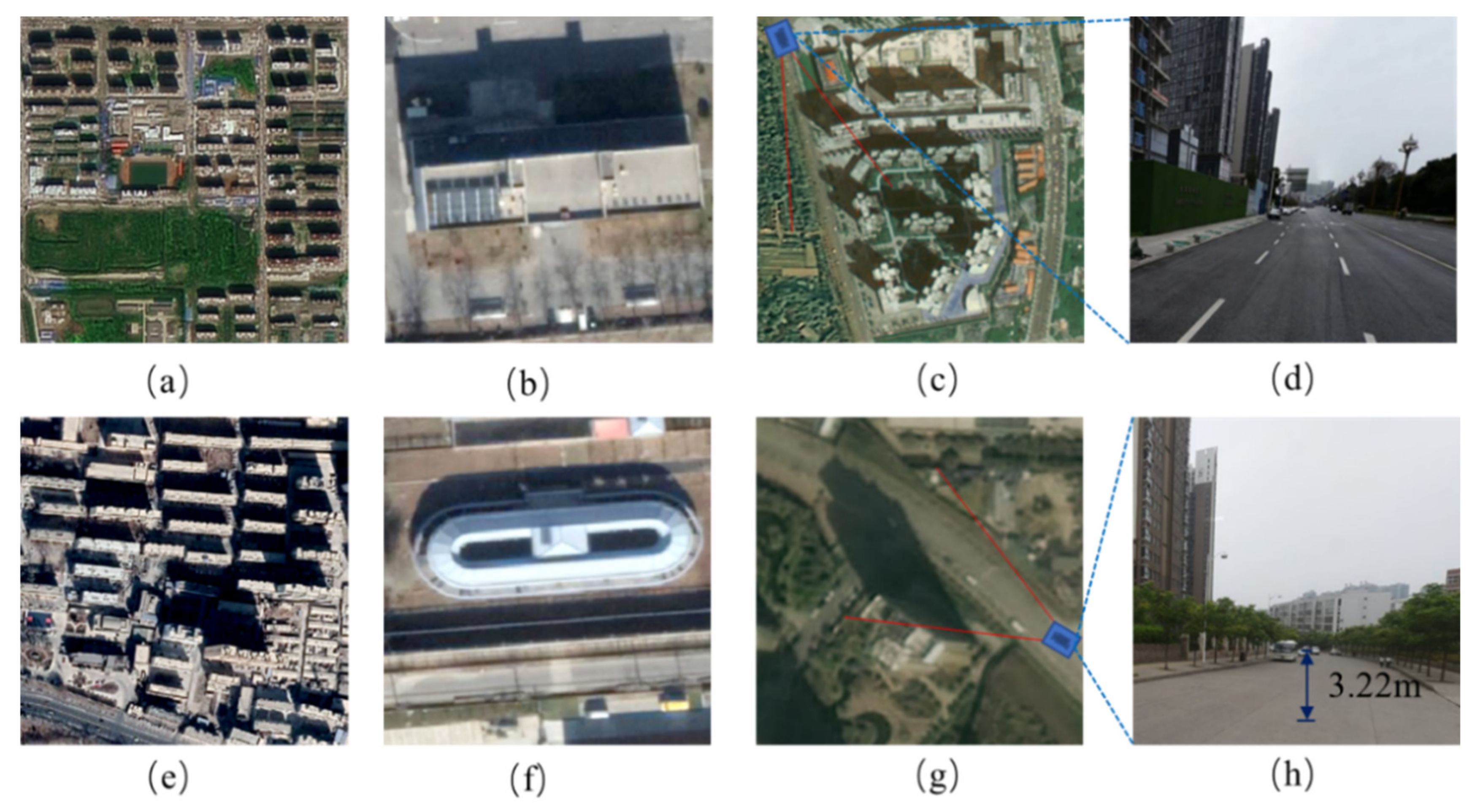
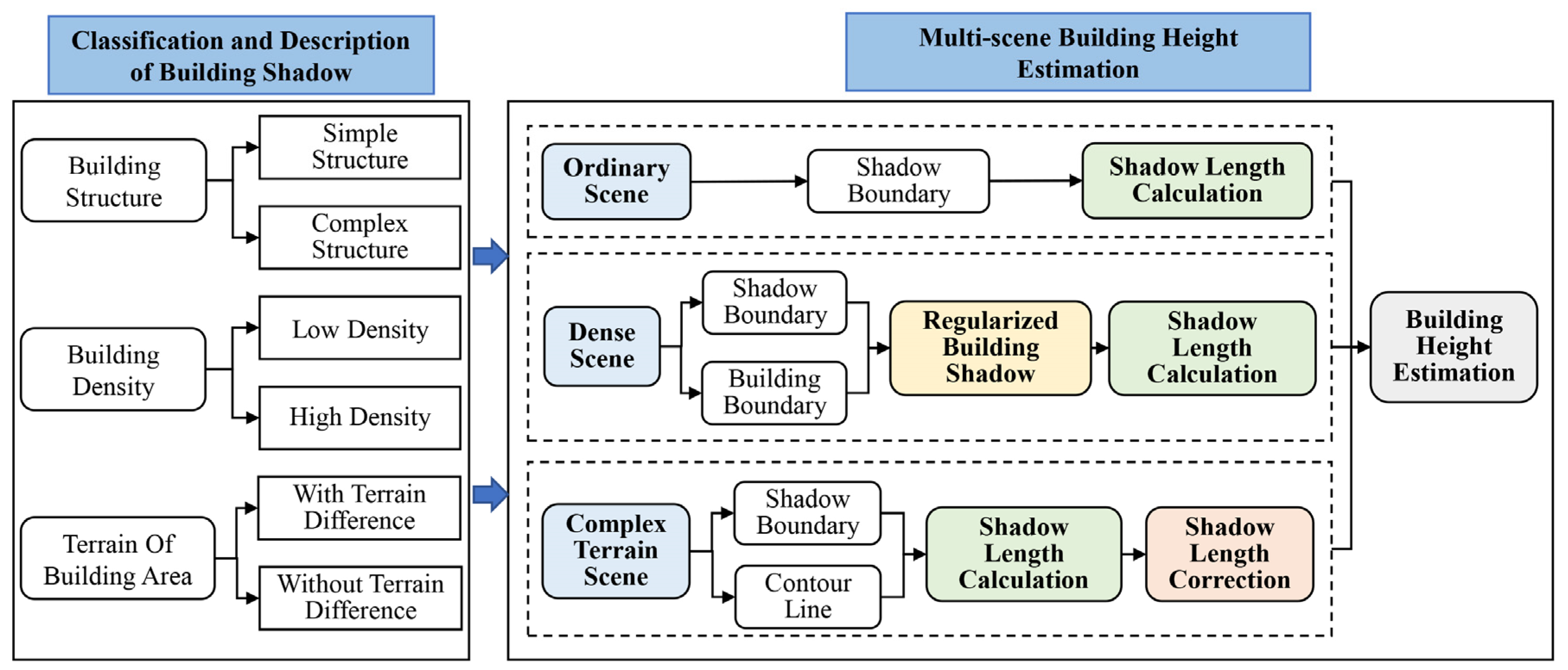
2.1. Classification and Description of Building Shadow
2.2. Multi-Scene Building Height Estimation
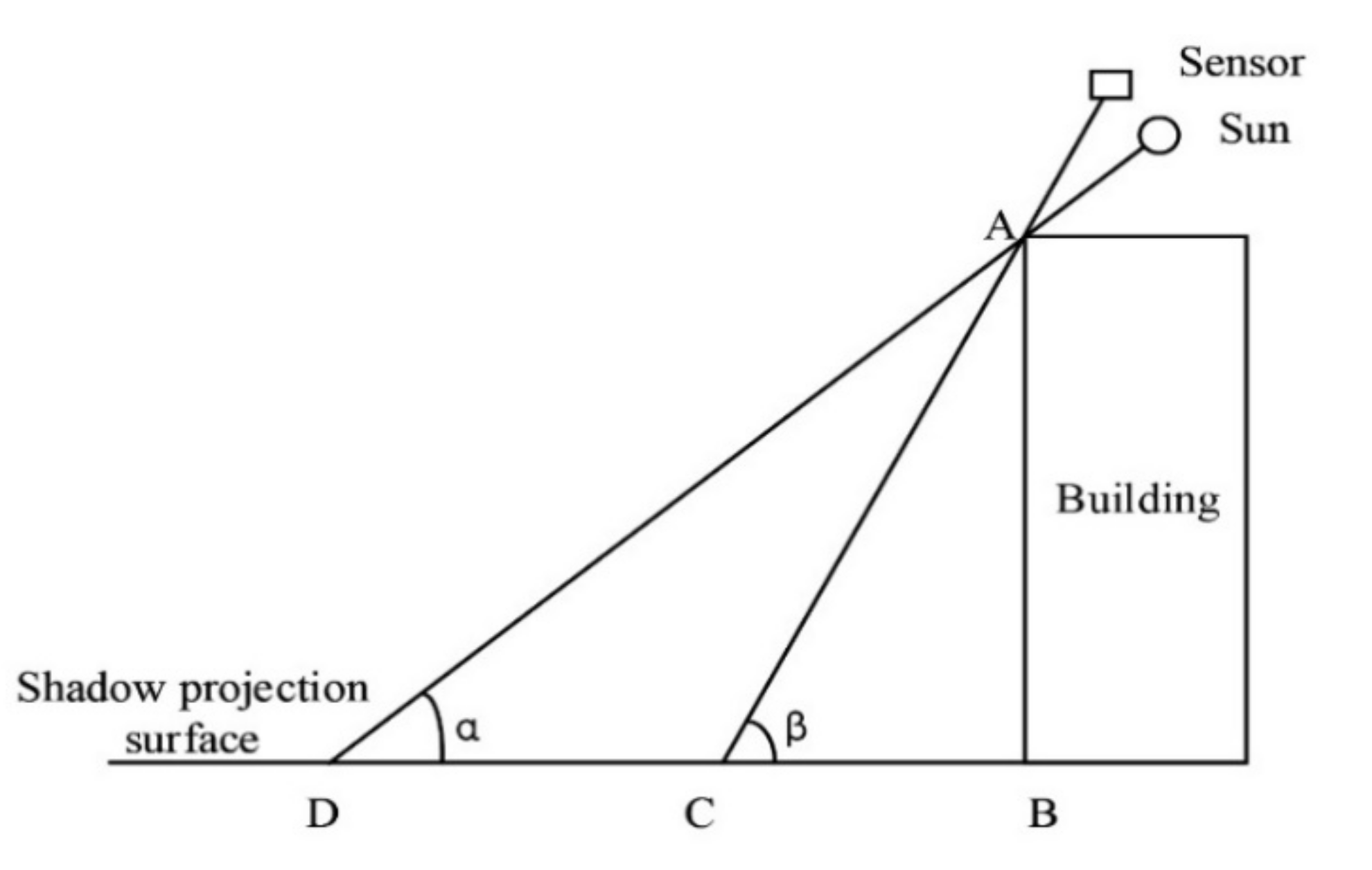
2.2.1. Building Height Estimation Model Based on Shadow
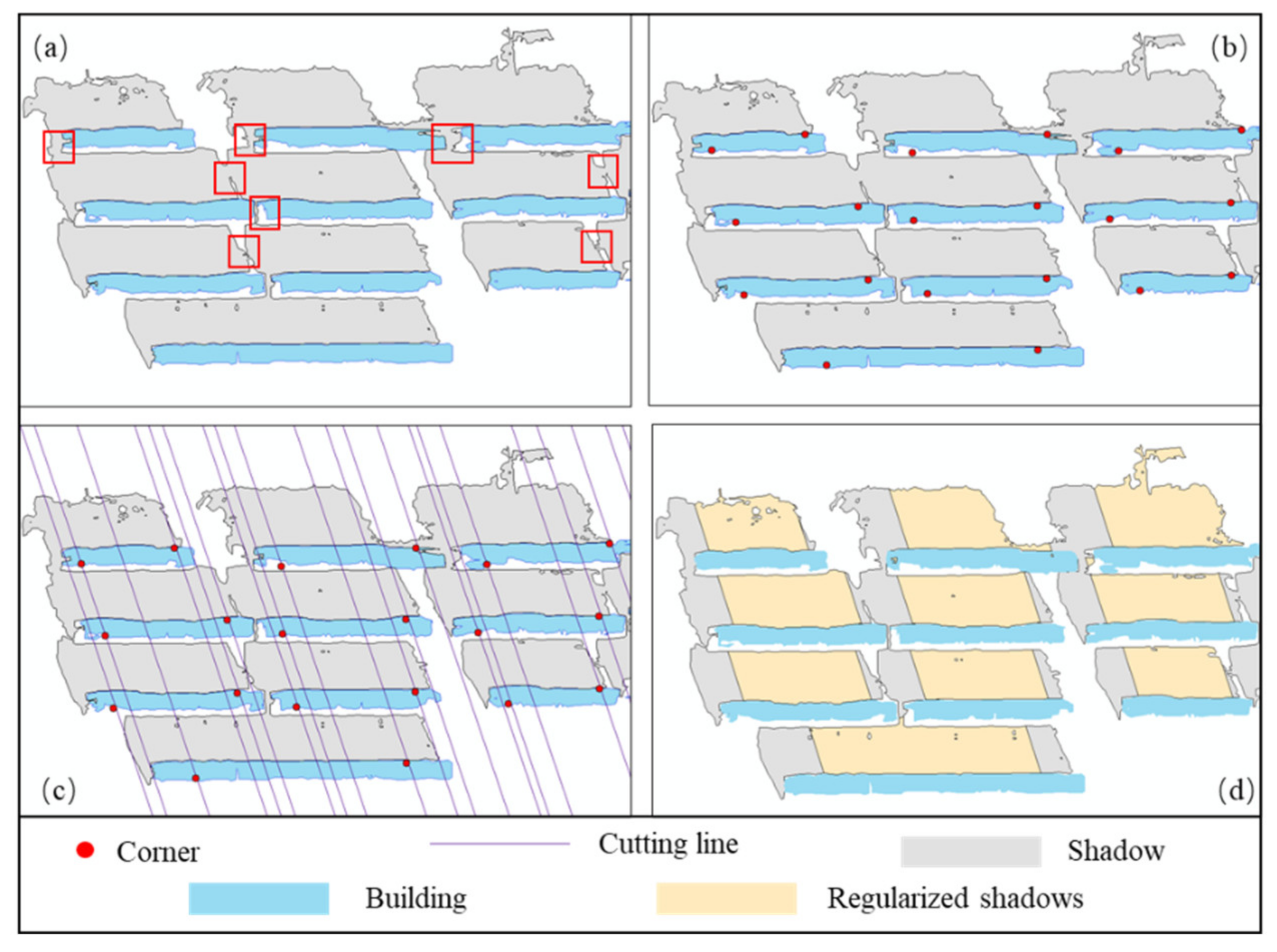
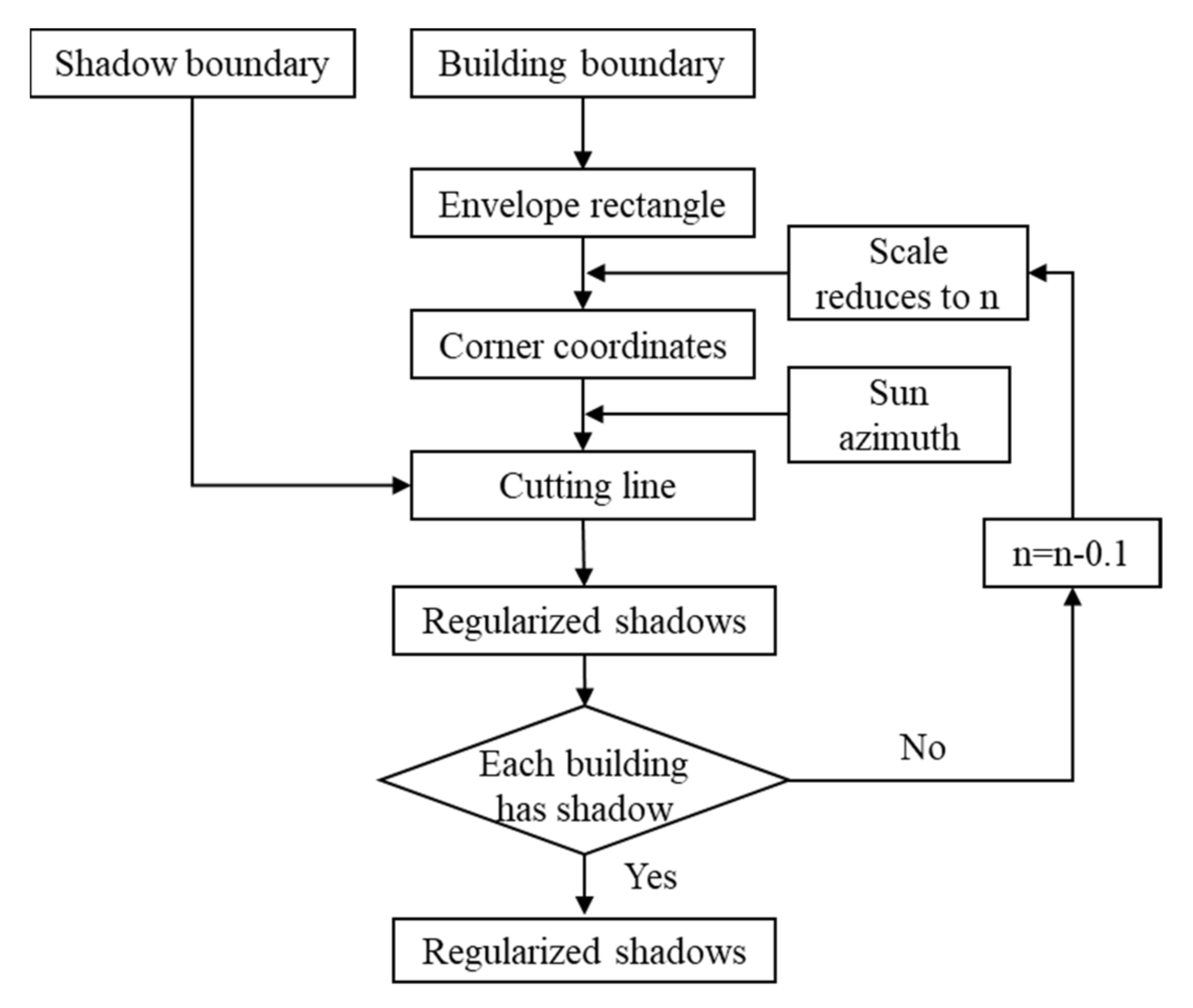
2.2.2. Regularized Extraction of Building Shadow in Dense Areas
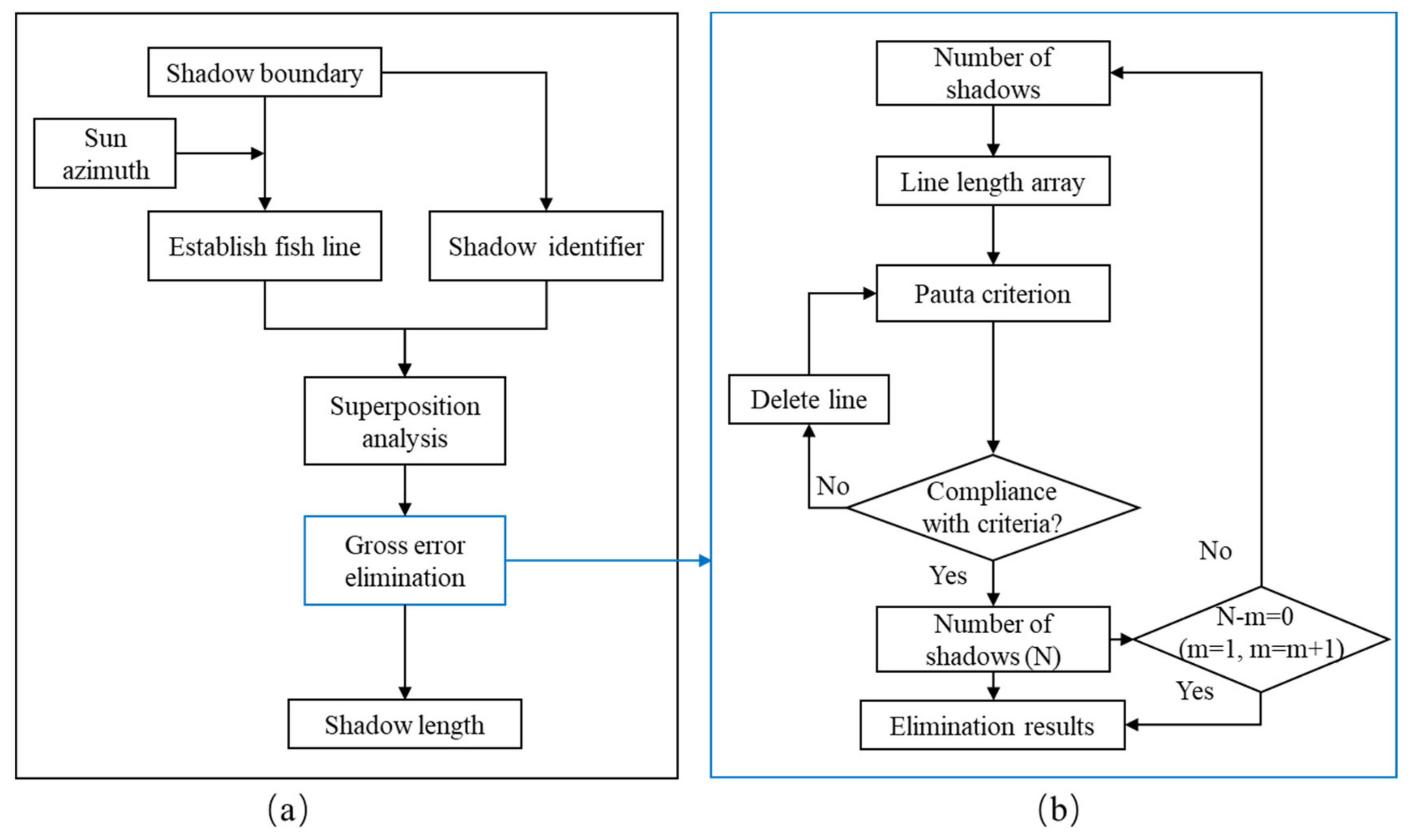
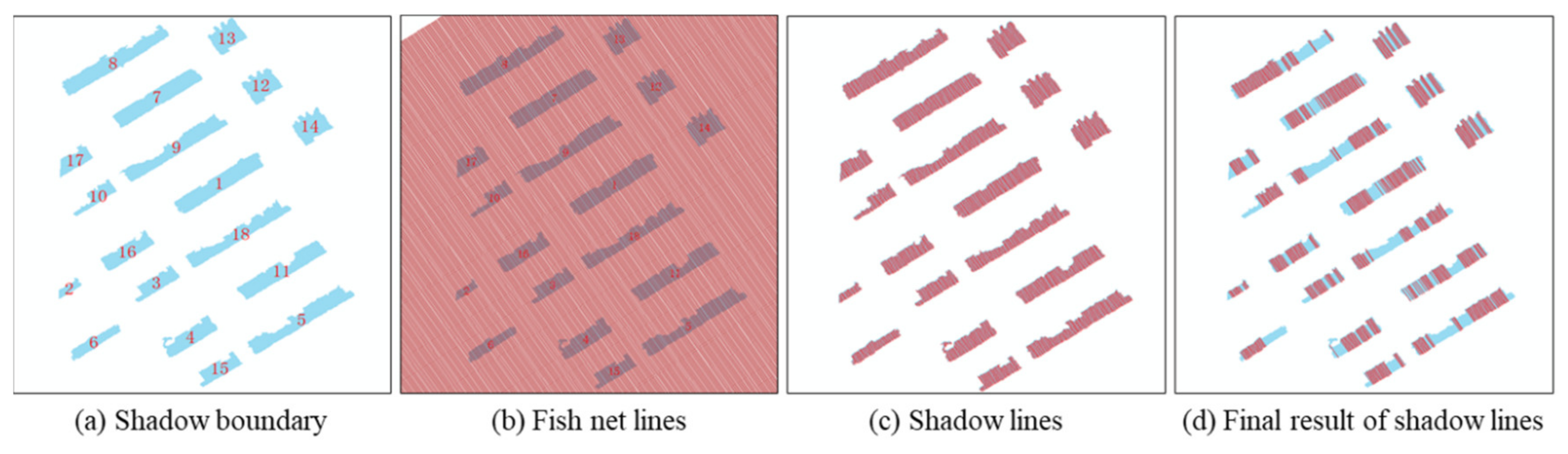
2.2.3. Shadow Length Calculation Combine Fish Net and Pauta Criterion
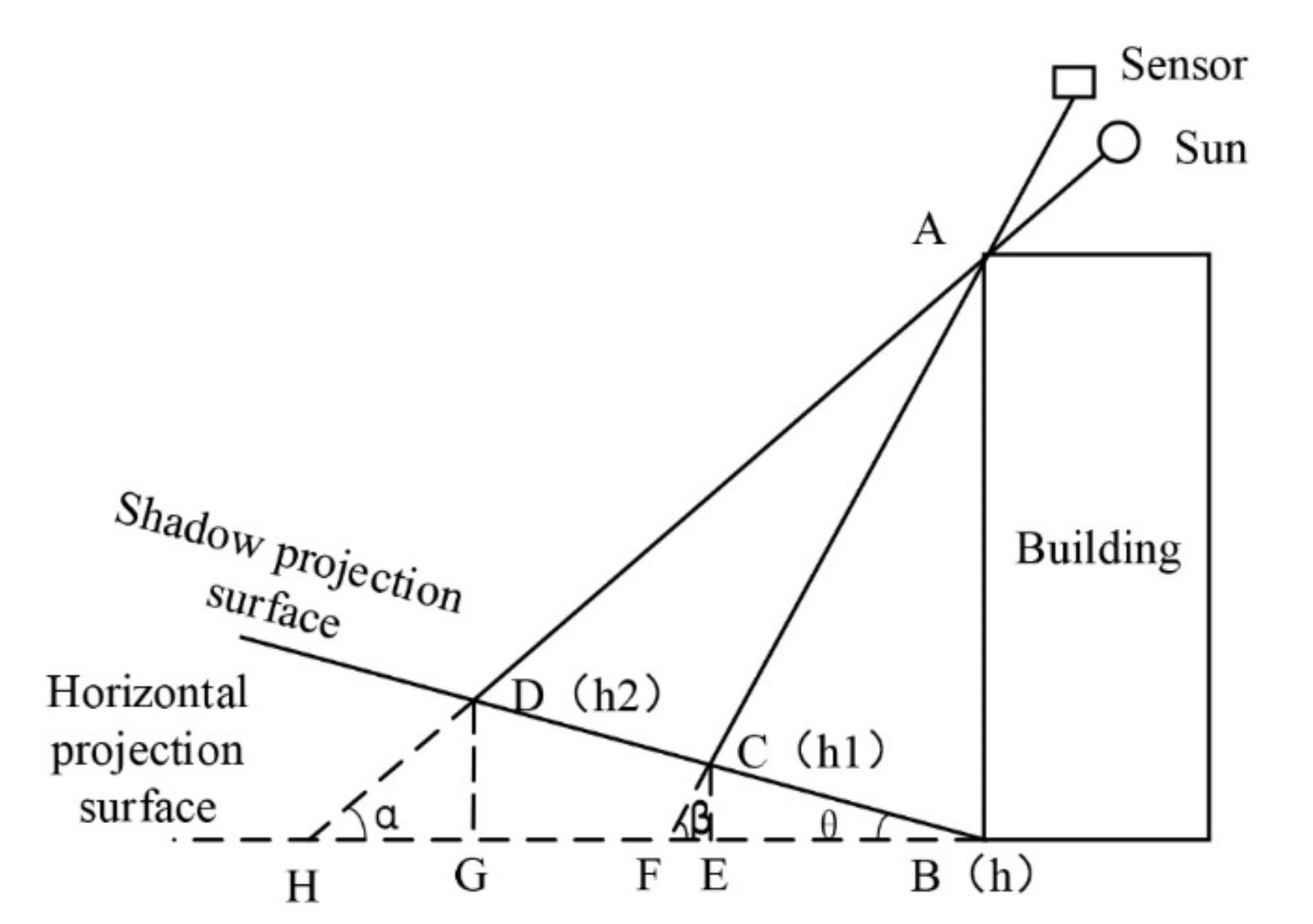
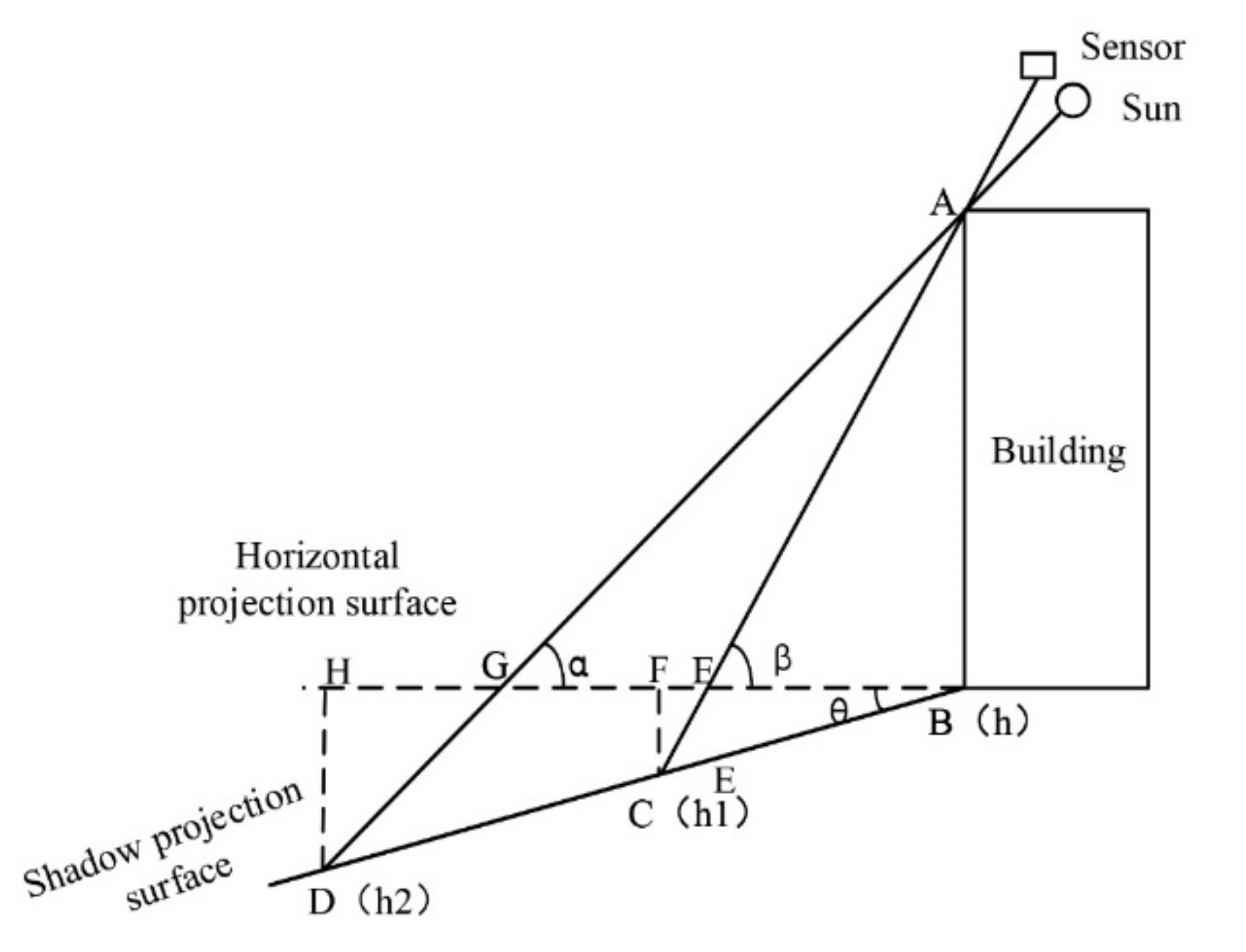
2.2.4. Shadow Length Correction under Complex Terrain
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Building Height Estimation of Ordinary Scene
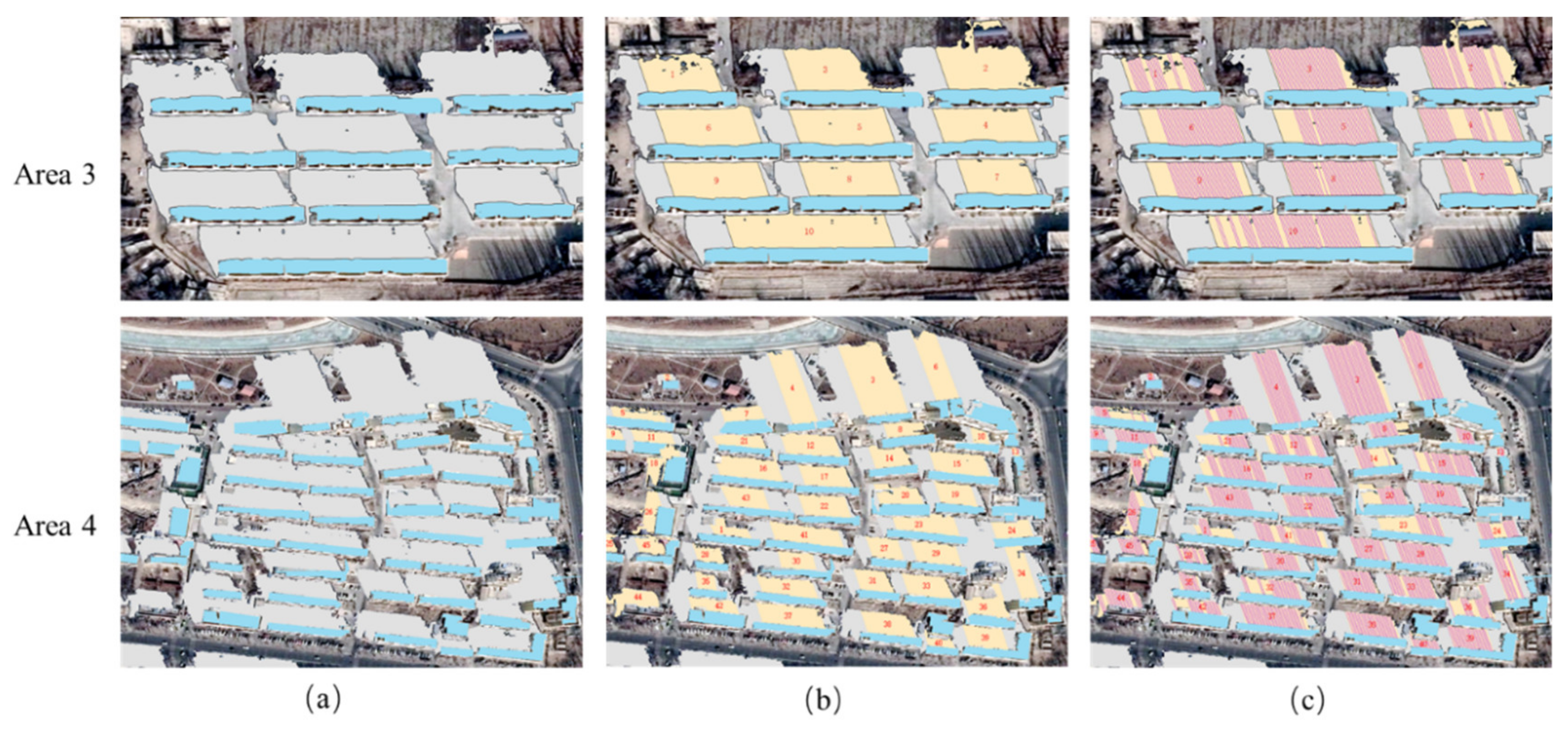
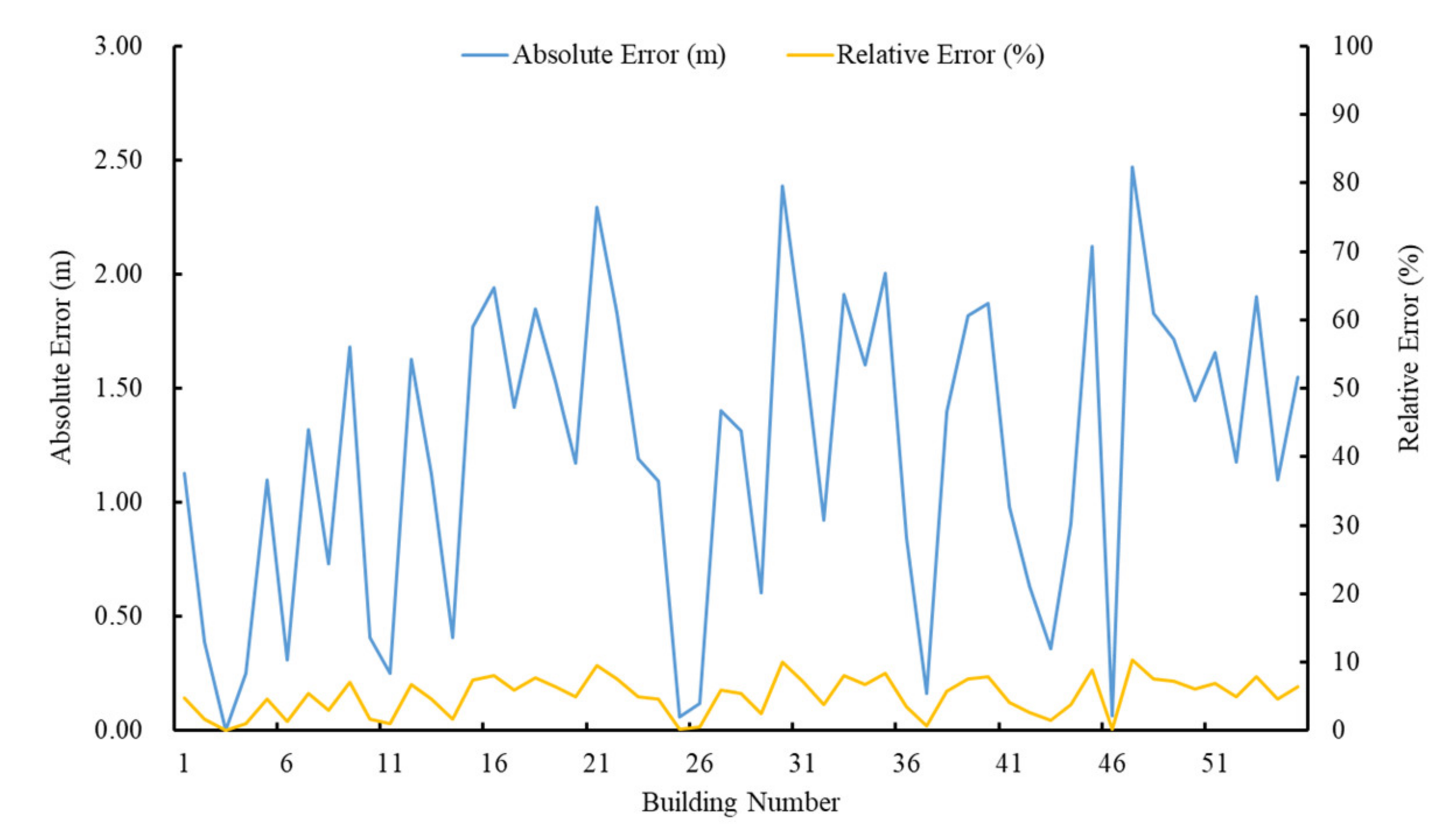
3.2. Building Height Estimation in Dense Scene
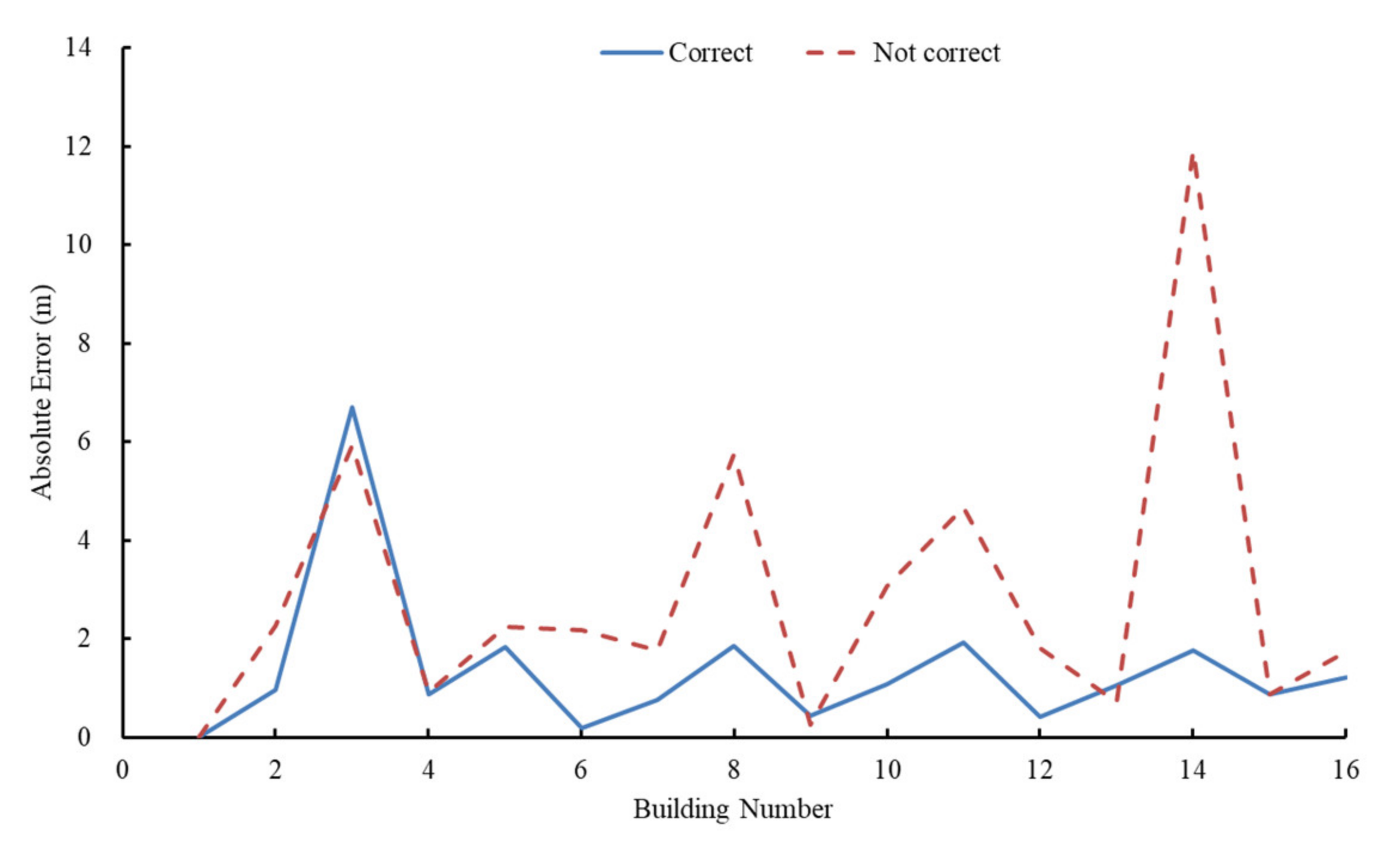
3.3. Building Height Estimation for Complex Terrain Scene
3.4. Comparison with Different Methods
3.5. Speed Analysis of the Proposed Algorithm
4. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Li, P.; Wang, X. A new segmentation method for very high resolution imagery using spectral and morphological information. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Yue, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhang, C.H. Fusion of remote sensing and internet data to calculate urban floor area ratio. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J. A survey on object detection in optical remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 117, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-J.; Krylov, V.; Kane, P.; Kavanagh, G.; Dahyot, R. IM2ELEVATION: Building height estimation from single-view aerial imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, D.; Schug, F.; Okujeni, A.; Navacchi, C.; Wagner, W.; van der Linden, S.; Hostert, P. National-scale mapping of building height using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 time series. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, K.; Roschlaub, R. Bavarian 3d building model and update concept based on lidar, image matching and cadastre information. In Innovations in 3D Geo-Information Sciences; Isikdag, U., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 143–157. [Google Scholar]
- Gamba, P.; Houshmand, B. Digital surface models and building extraction: A comparison of IFSAR and LIDAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Im, J.; Rhee, J.; Hodgson, M. Building type classification using spatial and landscape attributes derived from LiDAR remote sensing data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 130, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, C.; Thiele, A.; Hinz, S. Building detection and building parameter retrieval in InSAR phase images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, A.; Cadario, E.; Schulz, K.; Thoennessen, U.; Soergel, U. Building recognition from multi-aspect high-resolution insar data in urban areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 45, 3583–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, S.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A.; Pottier, E. Multi-aspect POLInSAR 3D urban scene reconstruction at L-band. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2–5 June 2008; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Stal, C.; Tack, F.; De Maeyer, P.; De Wulf, A.; Goossens, R. Airborne photogrammetry and lidar for DSM extraction and 3D change detection over an urban area—A comparative study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 1087–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takaku, J.; Tadono, T.; Tsutsui, K.; Ichikawa, M. Validation of "AW3D" global DSM generated from ALOS prism. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, III-4, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unger, J.; Reich, M.; Heipke, C. UAV-based photogrammetry: Monitoring of a building zone. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, XL-5, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Ling, F. Building heights estimation using ZY3 data-A case study of Shanghai, China. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 1749–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.P. Building extraction from high resolution imagery based on multi-scale object oriented classification and probabilistic hough transform. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Korea, 25–29 July 2005; pp. 2250–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, P.; Cheng, F. Delimiting the building heights in a city from the shadow on a panchromatic SPOT-image: Part 2: Test of a complete city. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2829–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Thiel, K.-H. Delimiting the building heights in a city from the shadow in a panchromatic SPOT-image—Part 1. Test of forty-two buildings. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liasis, G.; Stavrou, S. Satellite images analysis for shadow detection and building height estimation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soergel, U.; Thoennessen, U.; Gross, H.; Stilla, U. Segmentation of interferometric SAR data for building detection. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sportouche, H.; Tupin, F.; Denise, L. Building detection by fusion of optical and SAR features in metric resolution data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July 28–2 August 2019; pp. 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, J.D.; Ziehn, J.R.; Soergel, U. Combining high-resolution optical and InSAR features for height estimation of buildings with flat roofs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 5840–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, D.; Lemoine, G.; Bruzzone, L.; Greidanus, H. Building height retrieval from vhr sar imagery based on an iterative simulation and matching technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 1487–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.T.; Yamazaki, F.; Matsuoka, M. Multi-scale solution for building extraction from LiDAR and image data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinformation 2009, 11, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Zhu, F.; Hao, Y. Interactive 3D city modeling using Google Earth and ground images. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Image and Graphics, Chengdu, China, 22–24 August 2007; pp. 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.J.; XU, G.Y.; Shi, Y.C. Automated 3D building modeling based on urban aerial stereopair. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2002, 1, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalabi, D.-C.H.A.; Massalabi, A.; He, D.-C.; Bénié, G.; Beaudry, E. Detecting information under and from shadow in panchromatic IKONOS images of the city of Sherbrooke. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; Volume 3, pp. 2000–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Javzandulam, T.; Lee, T.-Y. Semiautomatic reconstruction of building height and footprints from single satellite images. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 4737–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Wang, Y. A new calculation method for shape coefficient of residential building using Google Earth. Energy Build. 2014, 76, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Kim, T. Automatic building height extraction by volumetric shadow analysis of monoscopic imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5834–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comber, A.J.; Umezaki, M.; Zhou, R.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, H.; Jiang, H.; Tewkesbury, A. Using shadows in high-resolution imagery to determine building height. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 3, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irvin, R.B.; McKeown, D.M. Methods for exploiting the relationship between buildings and their shadows in aerial imagery. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1989, 19, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izadi, M.; Saeedi, P. Three-dimensional polygonal building model estimation from single satellite images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2254–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Wang, X.H. Information extraction of building height and density based on quick bird image in Kunming, China. In Proceedings of the 2009 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Shanghai, China, 20–22 May 2009; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Zhai, J.Z.; Dang, G. Building height estimation using Google Earth. Energy Build. 2016, 118, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettigara, V.K.; Sumerling, G.M. Height determination of extended objects using shadows in SPOT images. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1998, 64, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türker, M.; Sümer, E. Building-based damage detection due to earthquake using the watershed segmentation of the post-event aerial images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3073–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Semiautomatic extraction of building information and variation detection from high resolution remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the Remotely Sensed Data and Information, Wuhan, China, 28 October 2006; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Taff, G.N.; Walsh, S.J. Shadow detection and building-height estimation using IKONOS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 6929–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; LeDoux, H.; Stoter, J. Generating 3D city models without elevation data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 64, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H. Research on Buildings Shadow Detection Method and Height Inversion with Hight Resolution Sensed Image. Master’s Thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China, May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Zheng, J.; Gao, F. A building extraction method using shadow in high resolution multispectral images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 1862–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Feng, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M. Building shadow detection with integrated characteristic components for high resolution remote sensing images. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2018, 10, 16–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cao, Y.; Feng, D.; Hu, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, L. Refined extraction of building outlines from high-resolution remote sensing imagery based on a multifeature convolutional neural network and morphological filtering. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 1842–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Du, S. Mining parameter information for building extraction and change detection with very high-resolution imagery and GIS data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 38–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, X. Reliability assessment for multi-source data of mechanical parts of civil aircraft based on the model. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 3205–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Building Heigh Information Extraction from Shadow Derived from High Resolution Satellife Image Based on Scene Classification. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xian, China, July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Building Number | Average (m) | Median (m) | Pauta Criterion (m) | Building Number | Average (m) | Median (m) | Pauta Criterion (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.26 | 2.84 | 0.57 | 10 | 12.13 | 13.34 | 1.68 |
| 2 | 0.87 | 1.12 | 0.43 | 11 | 3.63 | 2.00 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 9.19 | 1.33 | 0.59 | 12 | 15.81 | 4.32 | 1.19 |
| 4 | 6.90 | 2.42 | 0.12 | 13 | 17.92 | 5.81 | 0.47 |
| 5 | 4.07 | 1.09 | 0.35 | 14 | 19.40 | 5.11 | 1.45 |
| 6 | 3.86 | 3.22 | 1.81 | 15 | 7.35 | 4.24 | 0.53 |
| 7 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 16 | 4.89 | 0.74 | 0.79 |
| 8 | 4.05 | 0.84 | 0.24 | 17 | 0.76 | 0.21 | 0.16 |
| 9 | 3.85 | 3.21 | 0.99 | 18 | 2.35 | 3.38 | 0.98 |
| Methods | Mean Absolute Error (m) | Mean Relative Error (%) | Aggregate Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liasis et al. [19] | 4.89 | 17.28 | 5.14 |
| Chen [47] | 2.37 | 9.54 | 2.37 |
| Our method | 1.13 | 3.49 | 0.54 |
| Methods | Mean Absolute Error (m) | Mean Relative Error (%) | Aggregate Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chen [47] | 2.38 | 4.15 | 10.78 |
| Our method | 1.36 | 2.97 | 1.24 |
| Area | Device1 (min) | Device2 (min) | Device3 (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area1 | 2.1 | 3.6 | 5.1 |
| Area2 | 3.3 | 4.9 | 6.8 |
| Area3 | 7.2 | 8.6 | 10.9 |
| Area4 | 9.3 | 12.7 | 15.2 |
| Area5 | 3.6 | 5.4 | 7.6 |
| Average time | 5.1 | 7.0 | 9.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Feng, D.; Xiong, S.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y. Multi-Scene Building Height Estimation Method Based on Shadow in High Resolution Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152862
Xie Y, Feng D, Xiong S, Zhu J, Liu Y. Multi-Scene Building Height Estimation Method Based on Shadow in High Resolution Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(15):2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152862
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yakun, Dejun Feng, Sifan Xiong, Jun Zhu, and Yangge Liu. 2021. "Multi-Scene Building Height Estimation Method Based on Shadow in High Resolution Imagery" Remote Sensing 13, no. 15: 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152862
APA StyleXie, Y., Feng, D., Xiong, S., Zhu, J., & Liu, Y. (2021). Multi-Scene Building Height Estimation Method Based on Shadow in High Resolution Imagery. Remote Sensing, 13(15), 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152862






