A Novel Method for Refocusing Moving Ships in SAR Images via ISAR Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
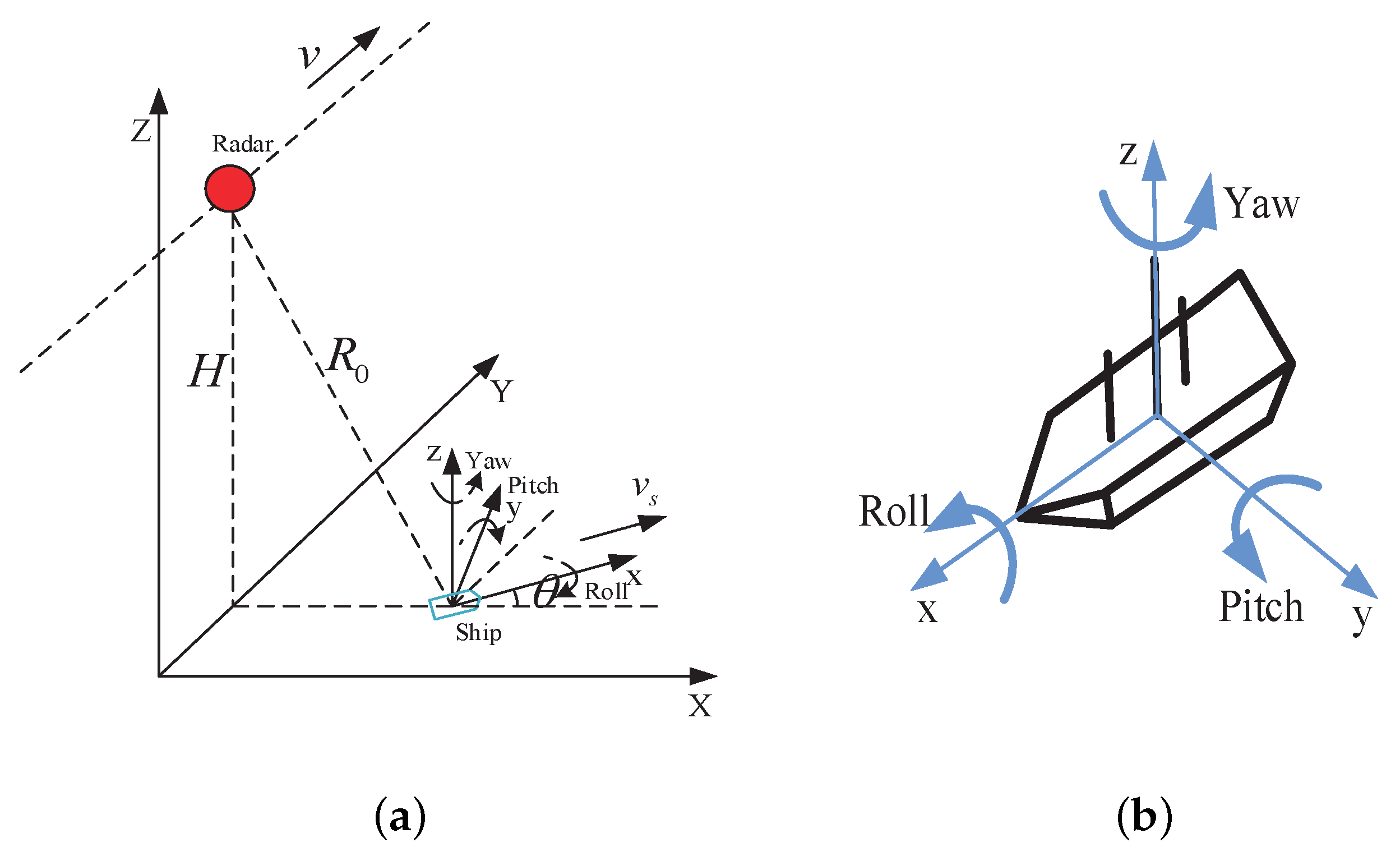
2. Geometry and Signal Model
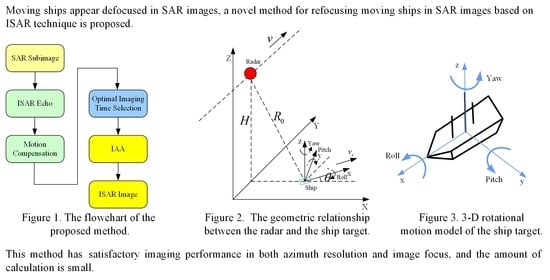
3. Method
3.1. Motion Compensation
- 1.
- Initialize the compensation phase , ;
- 2.
- According to the Equation (16), The echo after range alignment can be used to obtain ISAR image ;
- 3.
- Calculate the entropy of ISAR image, and set the termination condition (e.g., if the entropy difference between this iteration and the previous iteration is small, then, break; otherwise, go to next step);
- 4.
- Calculate the value of in this iteration process;
- 5.
- Update the compensation phase , , go to step 2.
3.2. Image Contrast Based Optimal Imaging Time Selection
3.3. IAA
| Algorithm 1. The specific implementation of IAA. |
| Initialization: ; |
| Repeat: |
| ; |
| ; |
| for |
| ; |
| end for |
| Until a certain number of iterations is reached. |
4. Experimental Results
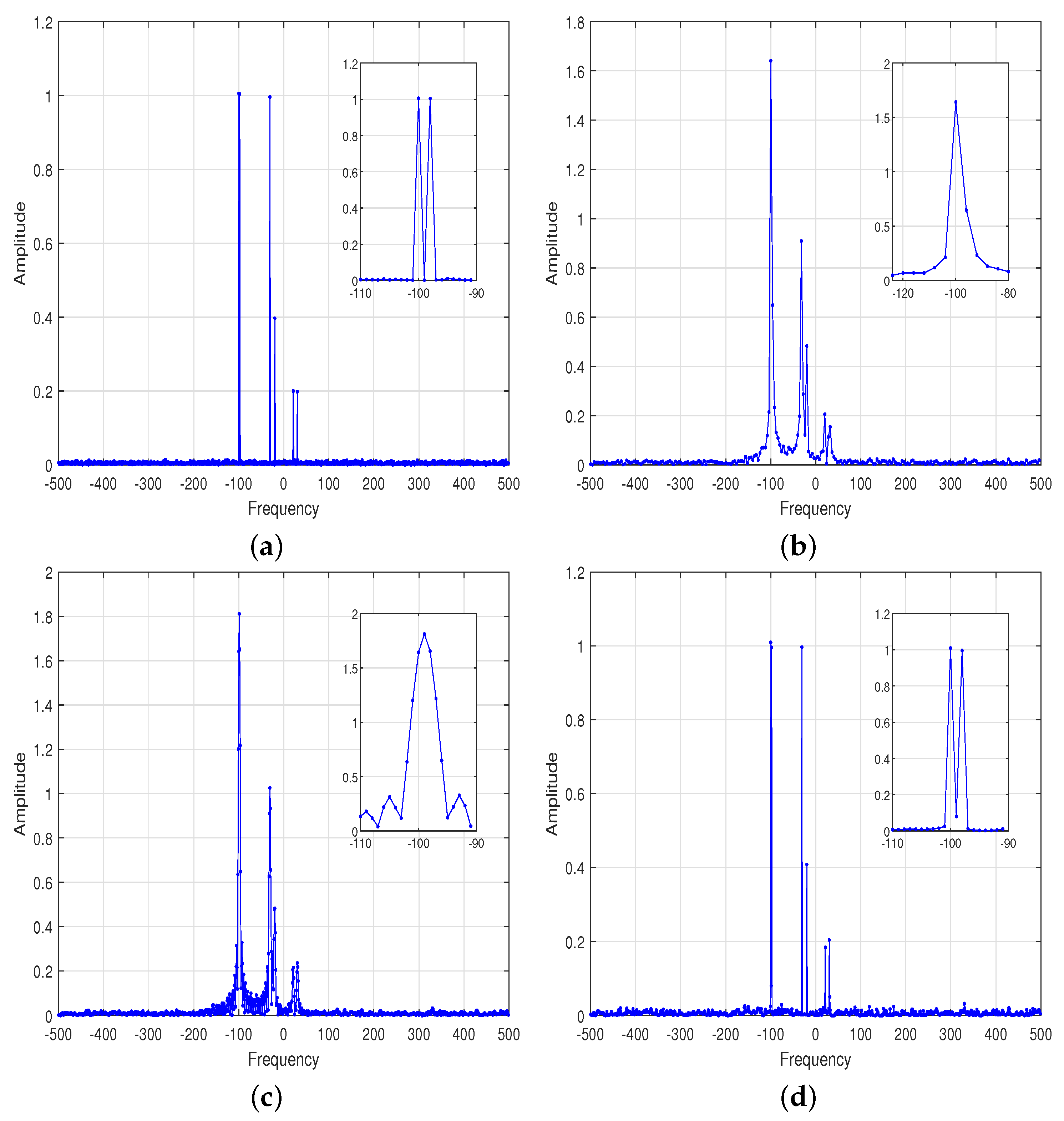
4.1. IAA Super-Resolution Experiment
4.2. Moving Ship Simulation Experiment
4.3. Real Data of Gaofen-3
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raney, R. Synthetic Aperture Imaging Radar and Moving Targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1971, AES-7, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelich, R.; Longépé, N.; Mercier, G.; Hajduch, G.; Garello, R. Vessel Refocusing and Velocity Estimation on SAR Imagery Using the Fractional Fourier Transform. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1670–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Lei, P.; Li, G.; Hong, W. High-Resolution SAR-Based Ground Moving Target Imaging With Defocused ROI Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J. Refocusing of Moving Targets in SAR Images via Parametric Sparse Representation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noviello, C.; Fornaro, G.; Martorella, M. Focused SAR Image Formation of Moving Targets Based on Doppler Parameter Estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ji, K.; Leng, X.; Dong, G.; Xing, X. Refocusing Moving Ship Targets in SAR Images Based on Fast Minimum Entropy Phase Compensation. Sensors 2019, 19, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, V.; Lipps, R. ISAR Imaging of Small Craft with Roll, Pitch and Yaw Analysis. In Proceedings of the Record of the IEEE 2000 International Radar Conference [Cat. No. 00CH37037], Alexandria, VA, USA, 12 May 2000; pp. 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Jin, Y.Q. A Study of Ship Rotation Effects on SAR Image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3132–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Qi, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Effect of 6-DOF Oscillation of Ship Target on SAR Imaging. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Cui, C.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, M. A Novel Ship Imaging Method with Multiple Sinusoidal Functions to Match Rotation Effects in Geosynchronous SAR. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorella, M.; Berizzi, F. Time Windowing for Highly Focused ISAR Image Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2005, 41, 992–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorella, M.; Berizzi, F.; Haywood, B. Contrast Maximisation Based Technique for 2-D ISAR Autofocusing. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2005, 152, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martorella, M.; Giusti, E.; Berizzi, F.; Bacci, A.; Dalle Mese, E. ISAR Based Technique for Refocusing Non-Cooperative Targets in SAR Images. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2012, 6, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, P.; Dai, Y. Application of an Existing Approach to Refocusing Maritime Moving Targets on Radarsat-2 SLC Images. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Singapore, 1–4 September 2015; pp. 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H. An Optimal Imaging Time Interval Selection Technique for Marine Targets ISAR Imaging Based on Sea Dynamic Prior Information. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 4940–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffar, M.; Nel, W.; Inggs, M. Selecting Suitable Coherent Processing Time Window Lengths for Ground-Based ISAR Imaging of Cooperative Sea Vessels. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.; Tang, Z.; Yuan, B. Research on High-Resolution Ship Targets Radar Imaging at Sea. In Proceedings of the 2007 1st Asian and Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Huangshan, China, 5–9 November 2007; pp. 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.S.; Ryu, B.H.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, K.T. Improved Frame-Selection Scheme for ISAR Imaging of Targets in Complex 3-D Motion. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Bayesian Bistatic ISAR Imaging for Targets With Complex Motion Under Low SNR Condition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2447–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihaczek, A.W.; Hershkowitz, S.J. Choosing imaging intervals for small ships. In Radar Processing, Technology, and Applications IV; Miceli, W.J., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1999; Volume 3810, pp. 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastina, D.; Spina, C. Slope-Based Frame Selection and Scaling Technique for Ship ISAR Imaging. IET Signal Process. 2008, 2, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, L.; Zhu, D. Optimal ISAR Imaging Time Selection of Ship Targets Using Real Data. In Proceedings of the IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 14–16 April 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Wang, L.; Cao, Z.; Zhu, D. Doppler-Estimation Based Methods for Airborne ISAR Imaging of Non-Cooperative Ship Targets: Demonstration and Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 18th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Prague, Czech Republic, 28–30 June 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Dong, X.; Zeng, T.; Ke, M. A Ship ISAR Imaging Algorithm Based on Generalized Radon-Fourier Transform With Low SNR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6385–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, D.; Tan, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Liao, G. ISAR Imaging for Maneuvering Targets with Complex Motion Based on Generalized Radon-Fourier Transform and Gradient-Based Descent under Low SNR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.; Qian, S. Joint Time-Frequency Transform for Radar Range-Doppler Imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1998, 34, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Su, F.; Gao, J.; Jin, X. High-Squint SAR Imaging of Maritime Ship Targets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y. ISAR Imaging of a Ship Target Using Product High-Order Matched-Phase Transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gui, X.; Liu, H.; Su, J.; Xiong, H. An ISAR Imaging Algorithm for Maneuvering Targets with Low SNR Based on Parameter Estimation of Multicomponent Quadratic FM Signals and Nonuniform FFT. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 5688–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Fan, H.; Zhang, Z. Nonuniformly-Rotating Ship Refocusing in SAR Imagery Based on the Bilinear Extended Fractional Fourier Transform. Sensors 2020, 20, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Lu, X. Ship Target Imaging in Airborne SAR System Based on Automatic Image Segmentation and ISAR Technique. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1985–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Zheng, M.; Yu, W.; Li, N.; Hou, L. Super-Resolution Doppler Beam Sharpening Imaging Based on an Iterative Adaptive Approach. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Bi, G.; Liu, H.; Bi, H. Novel ISAR Range Alignment via Minimizing the Entropy of the Sum Range Profile. In Proceedings of the 2020 21st International Radar Symposium (IRS), Warsaw, Poland, 5–8 October 2020; IEEE: Warsaw, Pakistan, 2020; pp. 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.; Tao, Q.; Zhu, Z. Robust ISAR Range Alignment via Minimizing the Entropy of the Average Range Profile. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Qiu, X.; She, Z. ISAR motion compensation using modified Doppler centroid tracking method. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1996 National Aerospace and Electronics Conference NAECON 1996, Dayton, OH, USA, 20–22 May 1996; Volume 1, pp. 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.; Eichel, P.; Ghiglia, D.; Jakowatz, C. Phase gradient autofocus-a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z. Minimum-Entropy Phase Adjustment for ISAR. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2004, 151, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berizzi, F.; Corsini, G. Autofocusing of Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Images Using Contrast Optimization. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1996, 32, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardibi, T.; Li, J.; Stoica, P.; Xue, M.; Baggeroer, A.B. Source Localization and Sensing: A Nonparametric Iterative Adaptive Approach Based on Weighted Least Squares. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.; Stoica, P.; Li, J.; Yardibi, T.; Sadjadi, F.A. Iterative Adaptive Approaches to MIMO Radar Imaging. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2010, 4, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Ding, C.; Zhong, L.; Liu, J.; Qiu, X.; Hu, Y.; Lei, B. The GF-3 SAR Data Processor. Sensors 2018, 18, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

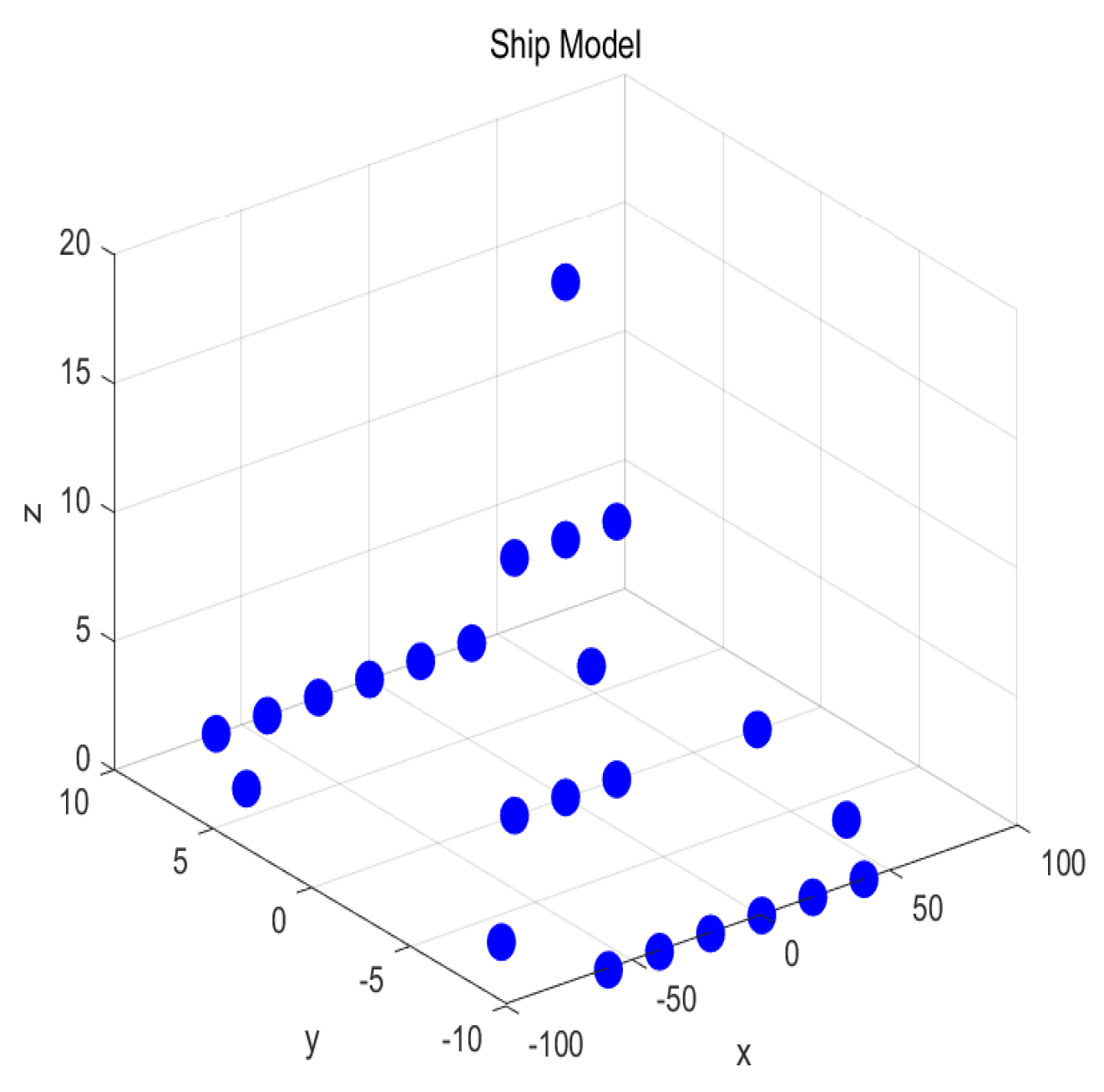
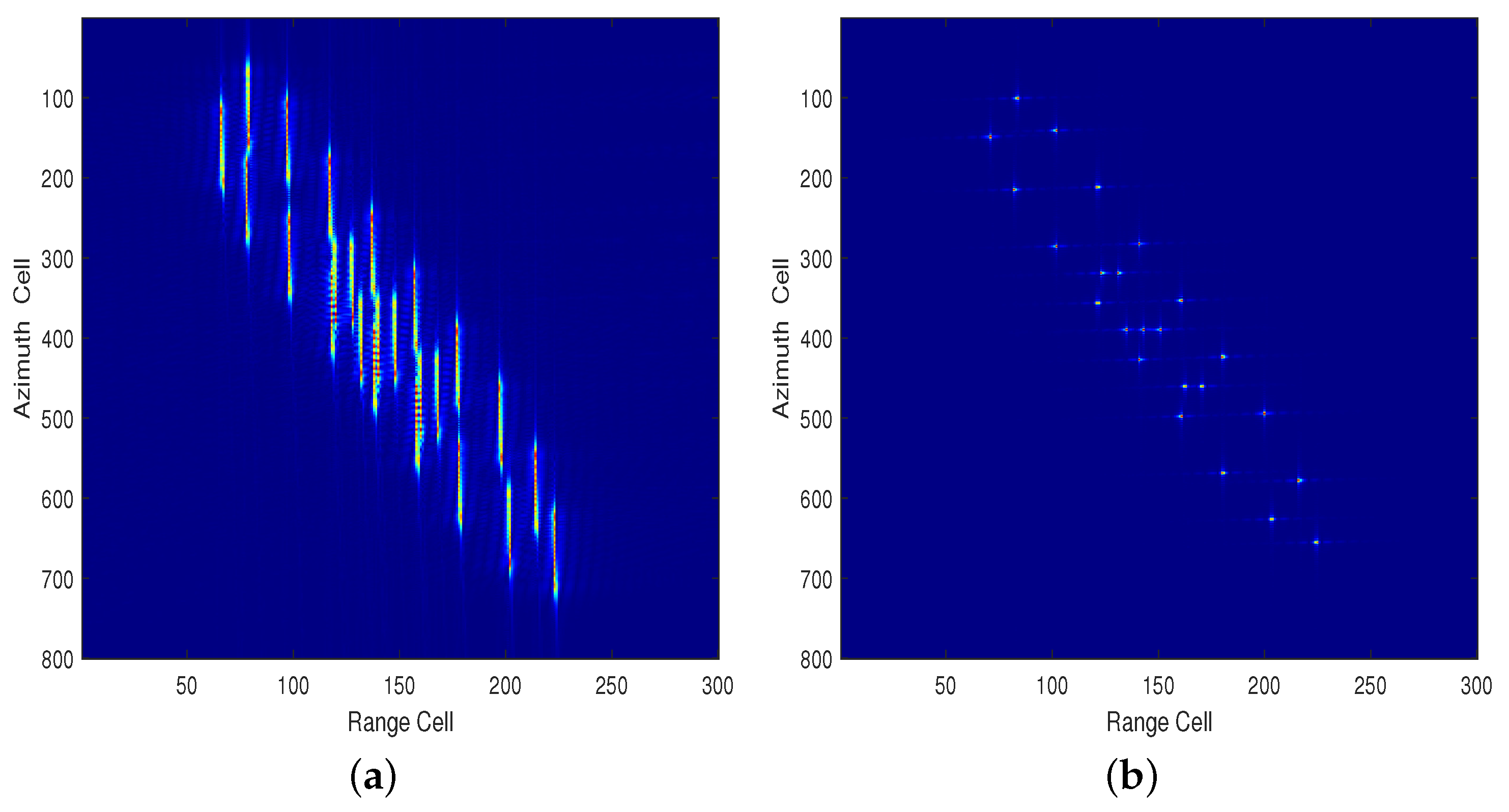
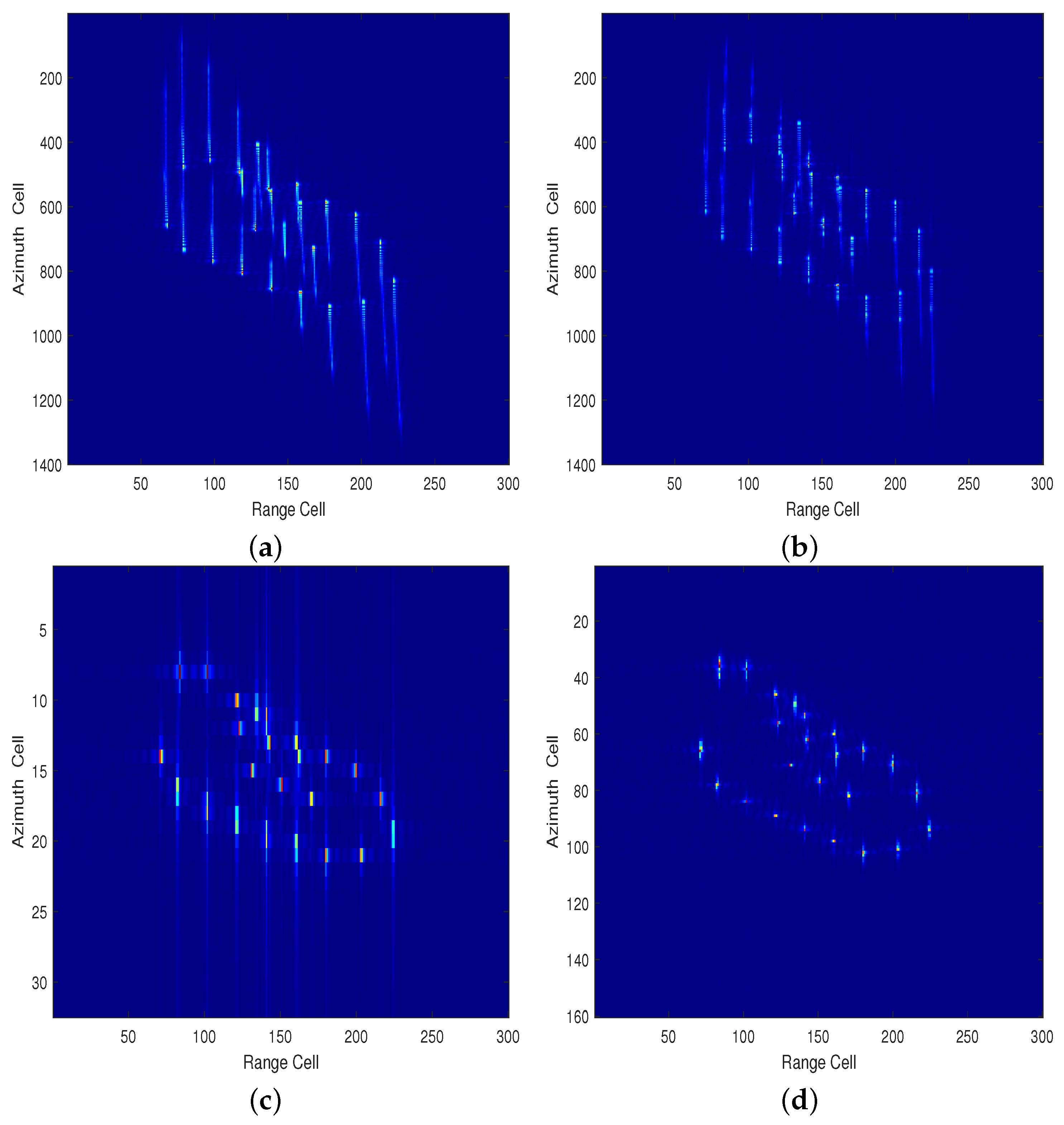


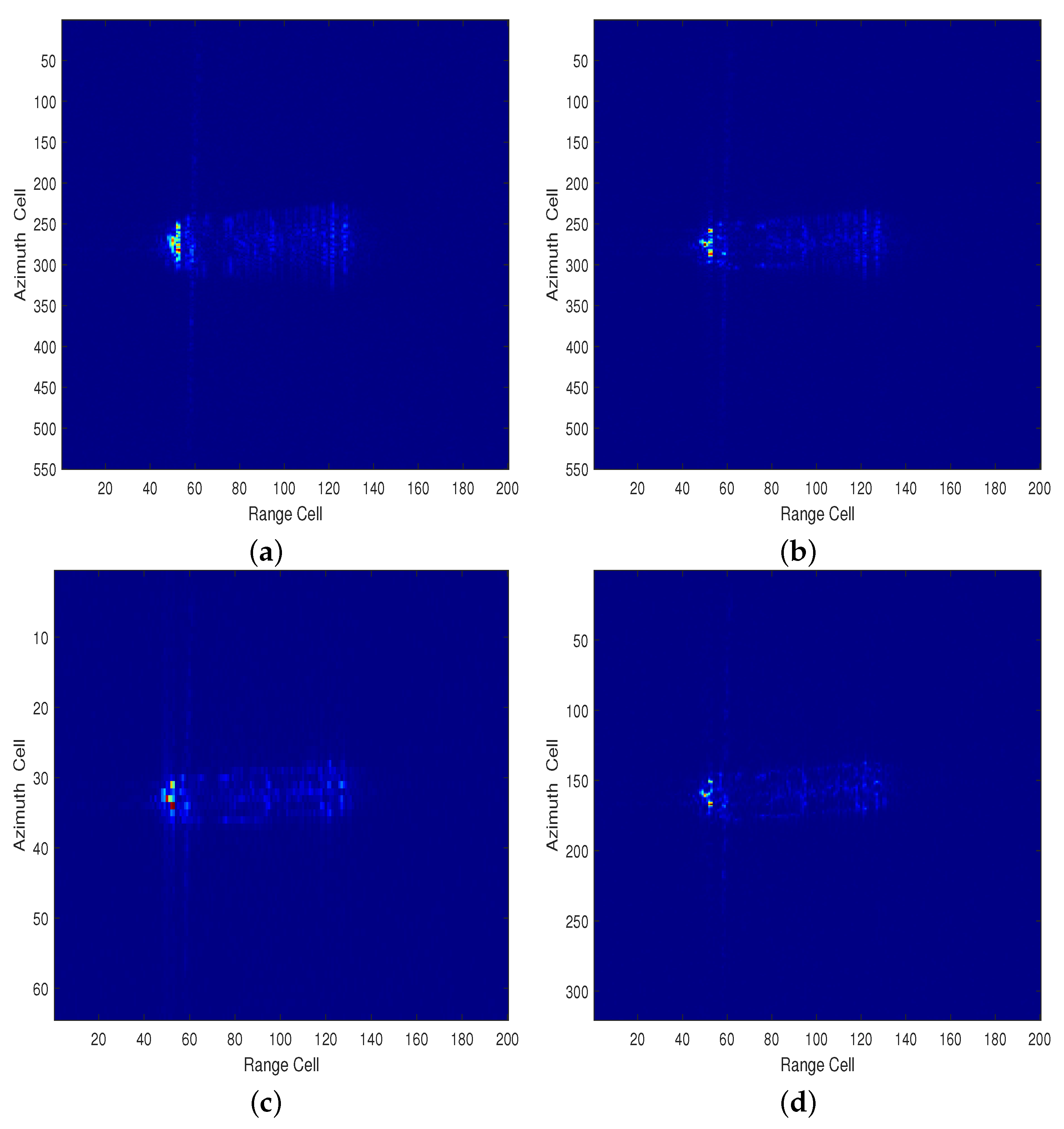
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency (GHz) | 5.4 |
| Platform velocity (m/s) | 150 |
| Slant range of scene center (Km) | 10 |
| A/D sampling rate (MHz) | 240 |
| Squint angle () | 0 |
| Bandwidth (MHz) | 200 |
| Pulse width (s) | 1 |
| Pulse repetition frequency (Hz) | 750 |
| Rotational Mode | Amplitude (°) | Period (s) | Central Time Phase (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roll | 5 | 12.2 | 0 |
| Pitch | 1.7 | 6.7 | 0 |
| Yaw | 1.9 | 14.2 | 0 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency (GHz) | 5.4 |
| Platform velocity (m/s) | 7571 |
| Slant range of scene center (Km) | 856.33 |
| A/D sampling rate (MHz) | 266.67 |
| Bandwidth (MHz) | 240 |
| Pulse width (s) | 45 |
| Pulse repetition frequency (Hz) | 3591 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, X.; Song, H.; He, W. A Novel Method for Refocusing Moving Ships in SAR Images via ISAR Technique. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2738. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142738
Jia X, Song H, He W. A Novel Method for Refocusing Moving Ships in SAR Images via ISAR Technique. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(14):2738. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142738
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Xinlin, Hongjun Song, and Wenjing He. 2021. "A Novel Method for Refocusing Moving Ships in SAR Images via ISAR Technique" Remote Sensing 13, no. 14: 2738. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142738
APA StyleJia, X., Song, H., & He, W. (2021). A Novel Method for Refocusing Moving Ships in SAR Images via ISAR Technique. Remote Sensing, 13(14), 2738. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142738