Quantitatively Estimating of InSAR Decorrelation Based on Landsat-Derived NDVI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Landsat5 Data
2.3. ALOS-1/PALSAR-1 Data
3. Methodology
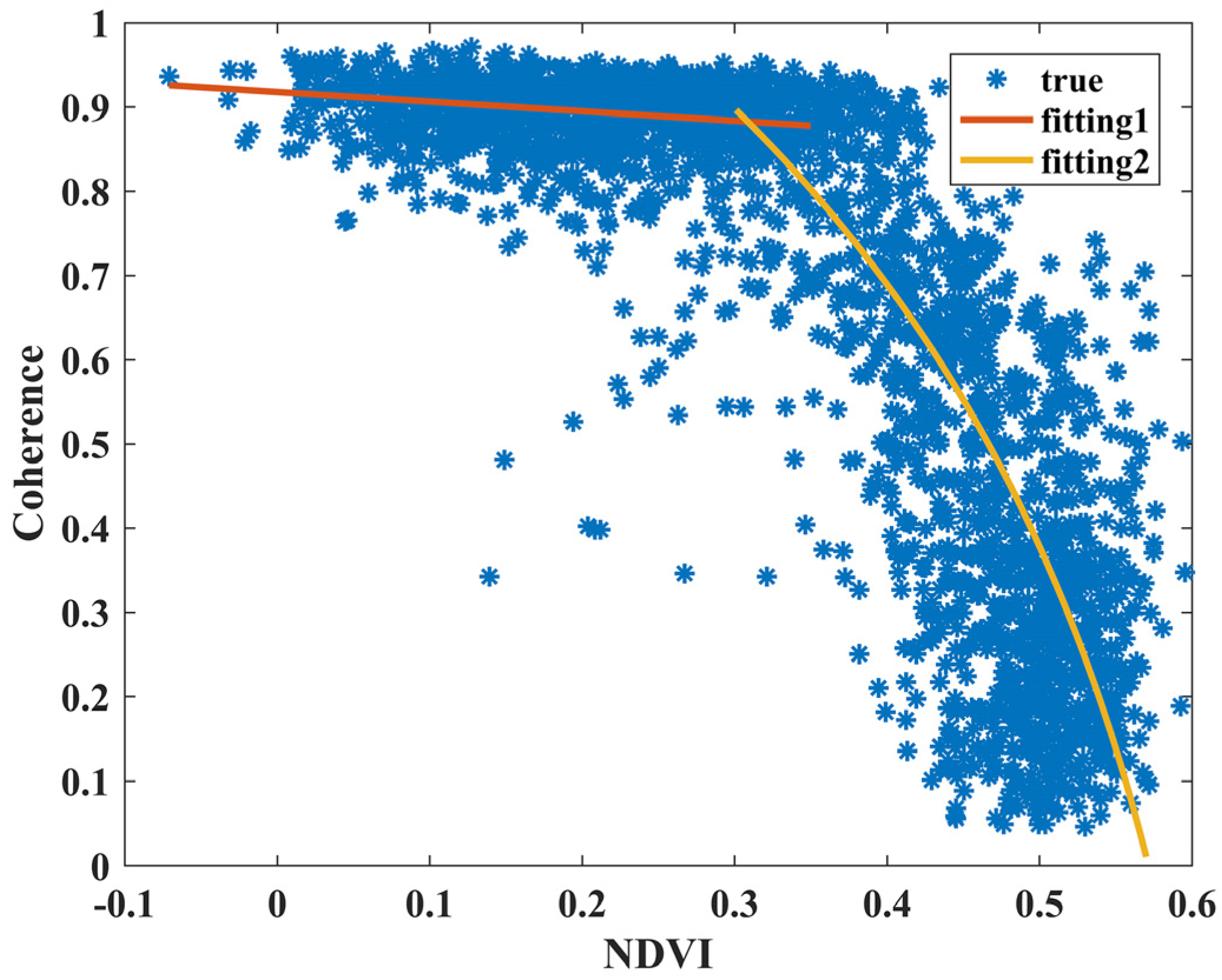
3.1. Sampling Based on Correlation Estimation Model
3.2. Effect of Perpendicular-Temporal Baseline Variation
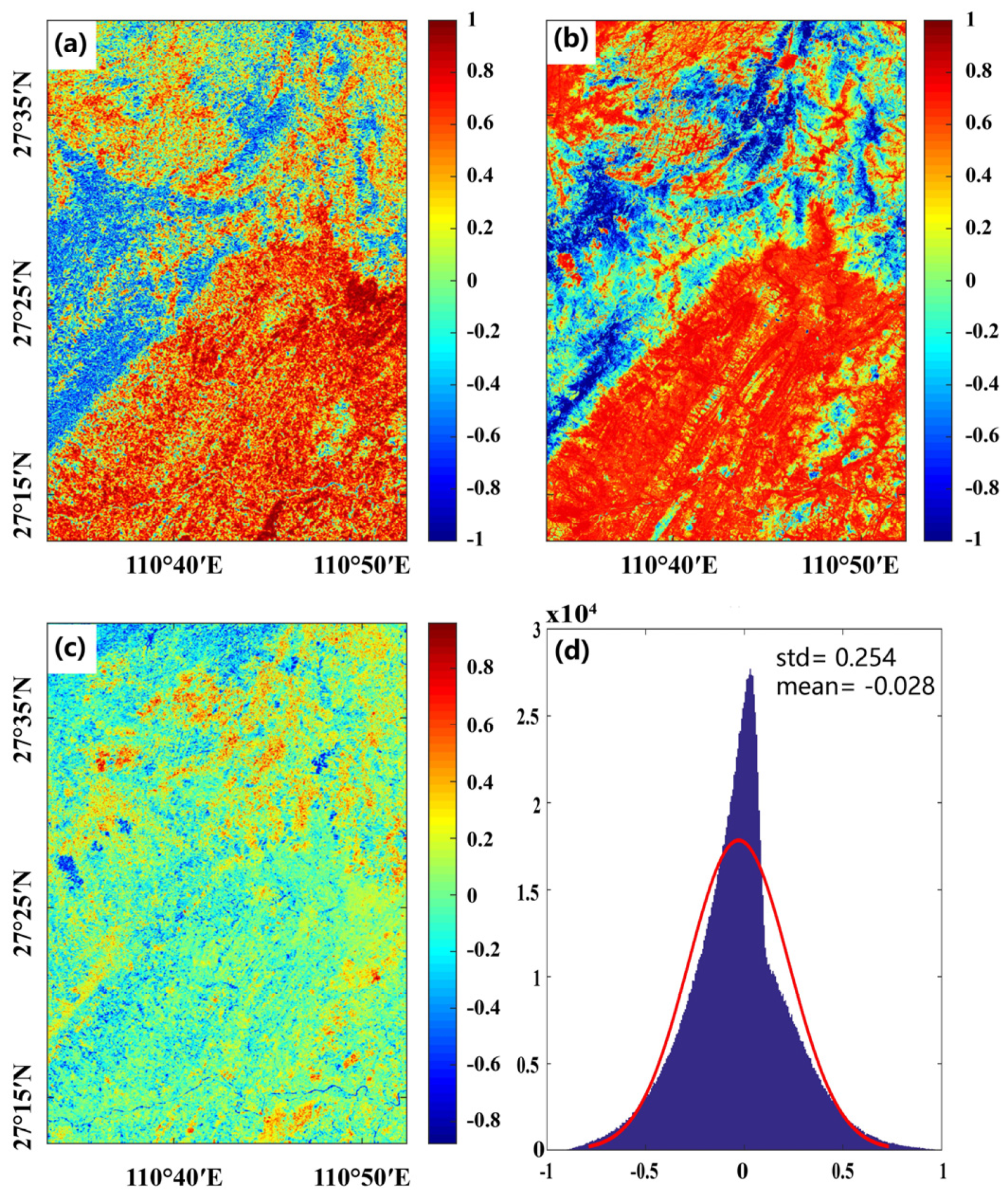
3.3. Establishment of Decorrelation Noise Model
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. Resolving three-dimensional surface displacements from InSAR measurements: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 133, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Hu, J.; Liang, H. Investigation of Slow-Moving Landslides from ALOS/PALSAR Images with TCPInSAR: A Case Study of Oso, USA. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Bawden, G.W.; Kim, J.-W.; Zhao, C.; Qu, W. Mapping ground deformation over Houston–Galveston, Texas using multi-temporal InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Zhang, B.; Lu, Z.; Kim, J.W.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Hao, M.; Zhu, W.; Qu, F. Source Parameter Estimation of the 2009 Ms6.0 Yao’an Earthquake, Southern China, Using InSAR Observations. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; Siqueira, P.; Treuhaft, R. A physical scattering model of repeat-pass InSAR correlation for vegetation. Waves Random Complex Medium 2017, 27, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Sandwell, D.T. Decorrelation of L-Band and C-Band Interferometry Over Vegetated Areas in California. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2942–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoonyol, L.; Jian Guo, L. Analysis of topographic decorrelation in SAR interferometry using ratio coherence imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liao, M.; Perissin, D. InSAR Coherence-Decomposition Analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liao, M.S. Accurate extraction of InSAR temporal decorrelation component. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2016, 35, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatton, K.C.; Crawford, M.M.; Evans, B.L. Fusing interferometric radar and laser altimeter data to estimate surface topography and vegetation heights. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2470–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshqi Molan, Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Lu, Z.; Agram, P. L-Band Temporal Coherence Assessment and Modeling Using Amplitude and Snow Depth over Interior Alaska. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, N.; Baumann, M.; Ehammer, A.; Fensholt, R.; Grogan, K.; Hostert, P.; Jepsen, M.R.; Kuemmerle, T.; Meyfroidt, P.; Mitchard, E.T.A.; et al. A Review of the Application of Optical and Radar Remote Sensing Data Fusion to Land Use Mapping and Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamkuan, N.; Nagai, M. Fusion of Multi-Temporal Interferometric Coherence and Optical Image Data for the 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake Damage Assessment. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Tian, B.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, J. A method for monitoring hydrological conditions beneath herbaceous wetlands using multi-temporal ALOS PALSAR coherence data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadimanesh, F.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Brisco, B.; Motagh, M. Multi-temporal, multi-frequency, and multi-polarization coherence and SAR backscatter analysis of wetlands. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 142, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.; Wegmuller, U.; Askne, J.I.H. Signatures of ERS–Envisat Interferometric SAR Coherence and Phase of Short Vegetation: An Analysis in the Case of Maize Fields. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1702–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedze, M.; Heggy, E.; Bretar, F.; Berveiller, D.; Jacquemoud, S. L-band InSAR Decorrelation Analysis in Volcanic Terrains using Airborne LiDAR Data and in Situ Measurements: The Case of the Piton de la Fournaise Volcano, France. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 3907–3910. [Google Scholar]
- Arab-Sedze, M.; Heggy, E.; Bretar, F.; Berveiller, D.; Jacquemoud, S. Quantification of L-band InSAR coherence over volcanic areas using LiDAR and in situ measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notti, D.; Meisina, C.; Zucca, F.; Colombo, A. Models to predict Persistent Scatterers data distribution and their capacity to register movement along the slope. In Proceedings of the Fringe 2011 Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 19–23 September 2011; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Voormansik, K.; Zalite, K.; Sünter, I.; Tamm, T.; Koppel, K.; Verro, T.; Brauns, A.; Jakovels, D.; Praks, J. Separability of Mowing and Ploughing Events on Short Temporal Baseline Sentinel-1 Coherence Time Series. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, F.; Qin, Y.; Shirazi, Z. Shifting trends and probability distribution of vegetation conditions over China. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Fang, S.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, G.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J. Could Vegetation Index be Derive from Synthetic Aperture Radar?–The Linear Relationship between Interferometric Coherence and NDVI. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pulella, A.; Aragão Santos, R.; Sica, F.; Posovszky, P.; Rizzoli, P. Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 Backscatter and Coherence for Rainforest Mapping. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, T.-H.; Simard, M.; Denbina, M.; Lamb, M.P. Monitoring Water Level Change and Seasonal Vegetation Change in the Coastal Wetlands of Louisiana Using L-Band Time-Series. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamler, R.; Hartl, P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Inverse Prob. 1998, 14, R1–R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Huete, A. A feedback based modification of the NDVI to minimize canopy background and atmospheric noise. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei-Chao, X. A review on correlation coefficients. J. Guangdong Univ. Technol. 2012, 29, 12–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, S.P. Instability of least squares, least absolute deviation and least median of squares linear regression, with a comment by Stephen Portnoy and Ivan Mizera and a rejoinder by the author. Stat. Sci. 1998, 13, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Fang, P.; Xiong, D.; Wang, W.; Liao, M. A Point Pattern Chamfer Registration of Optical and SAR Images Based on Mesh Grids. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallick, J.; AlMesfer, M.K.; Singh, V.P.; Falqi, I.I.; Singh, C.K.; Alsubih, M.; Kahla, N.B. Evaluating the NDVI–Rainfall Relationship in Bisha Watershed, Saudi Arabia Using Non-Stationary Modeling Technique. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Shi, H. Effects of Precipitation Intensity and Temperature on NDVI-Based Grass Change over Northern China during the Period from 1982 to 2011. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10164–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karkauskaite, P.; Tagesson, T.; Fensholt, R. Evaluation of the Plant Phenology Index (PPI), NDVI and EVI for Start-of-Season Trend Analysis of the Northern Hemisphere Boreal Zone. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treuhaft, R.N.; Siqueira, P.R. Vertical structure of vegetated land surfaces from interferometric and polarimetric radar. Radio Sci. 2000, 35, 141–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Location | Data | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Meitanba | 21 May 2008 | 30 m |
| Longhui | 21 May 2008 |
| Location | Master Date | Slave Date | Bt | B⊥ | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meitanba | 11 January 2008 | 26 February 2008 | 46 day | 437 m | 30 m |
| Longhui | 16 January 2008 | 17 April 2008 | 92 day | 752 m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Sun, Q.; Hu, J. Quantitatively Estimating of InSAR Decorrelation Based on Landsat-Derived NDVI. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132440
Chen Y, Sun Q, Hu J. Quantitatively Estimating of InSAR Decorrelation Based on Landsat-Derived NDVI. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(13):2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132440
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yaogang, Qian Sun, and Jun Hu. 2021. "Quantitatively Estimating of InSAR Decorrelation Based on Landsat-Derived NDVI" Remote Sensing 13, no. 13: 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132440
APA StyleChen, Y., Sun, Q., & Hu, J. (2021). Quantitatively Estimating of InSAR Decorrelation Based on Landsat-Derived NDVI. Remote Sensing, 13(13), 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132440






