Developing an Atlas of Harmful Algal Blooms in the Red Sea: Linkages to Local Aquaculture
Abstract
1. Introduction
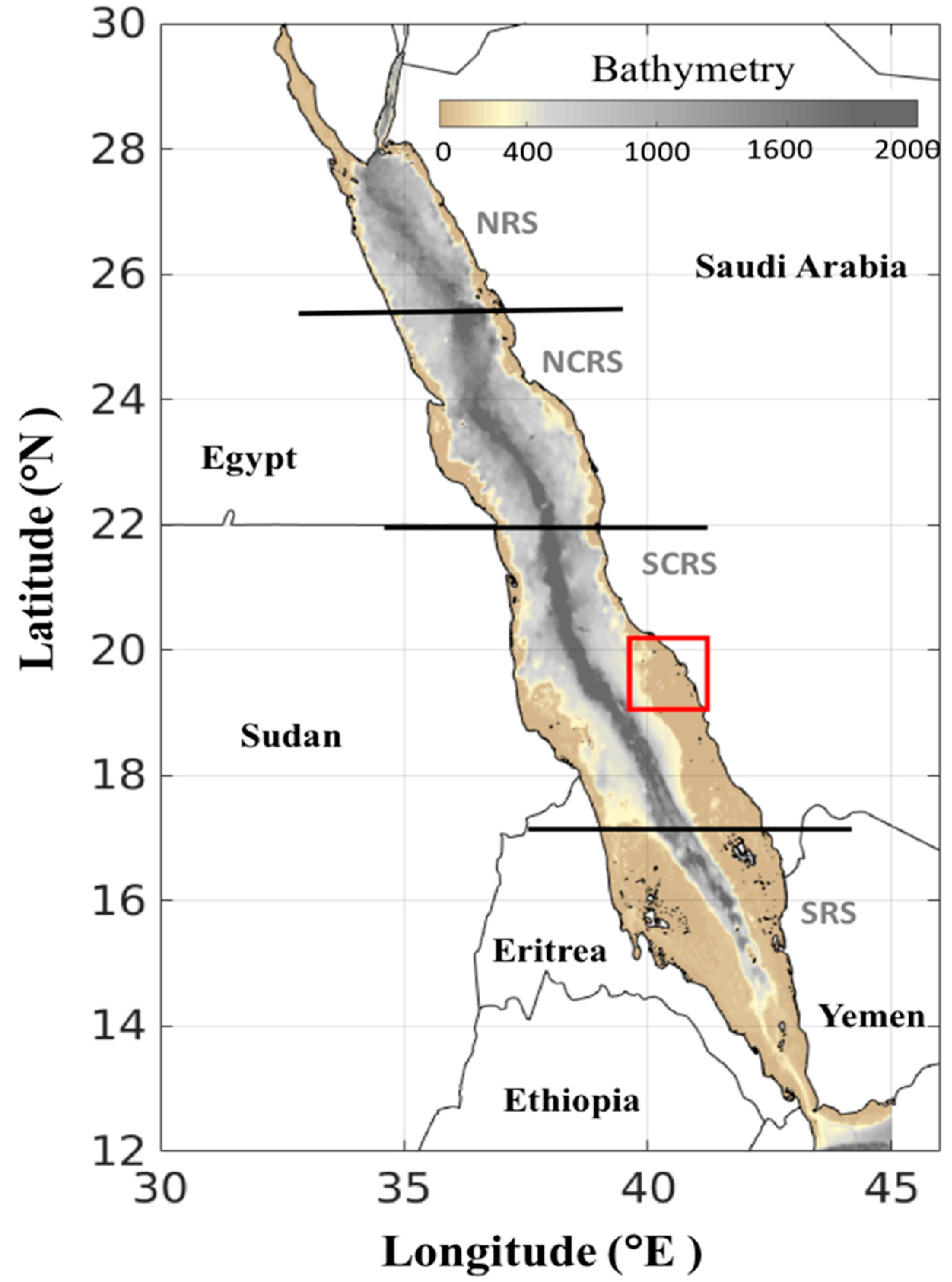
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Satellite Datasets
2.2. Aquaculture Production Dataset
2.3. Approach
3. Results
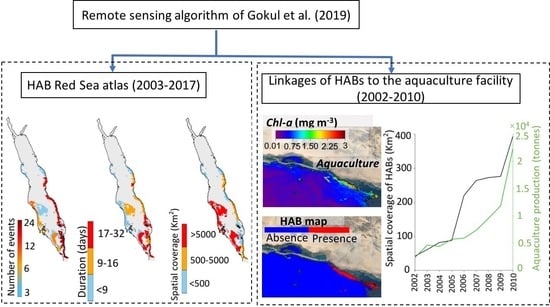
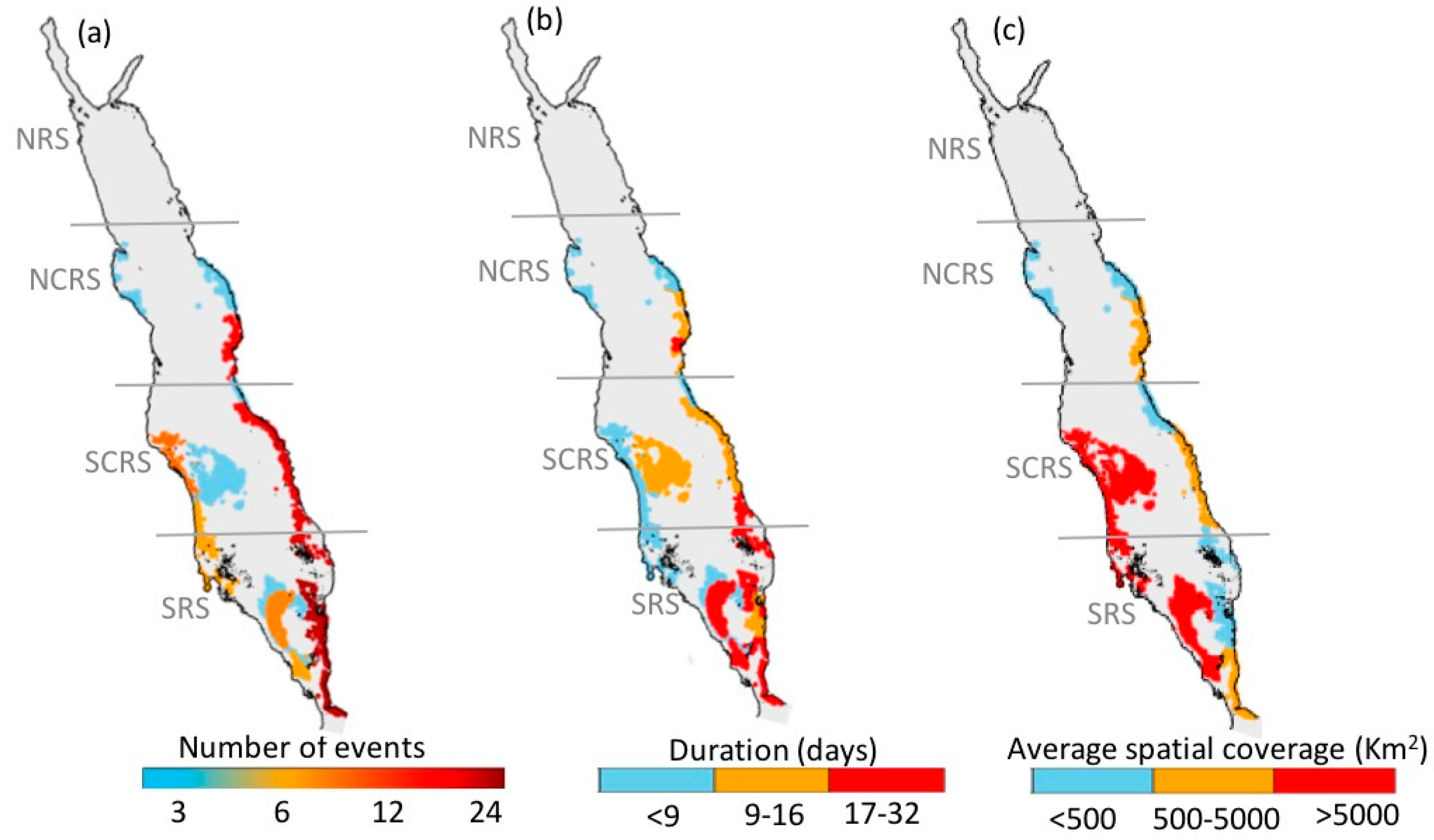
3.1. Atlas of HABs in the Red Sea
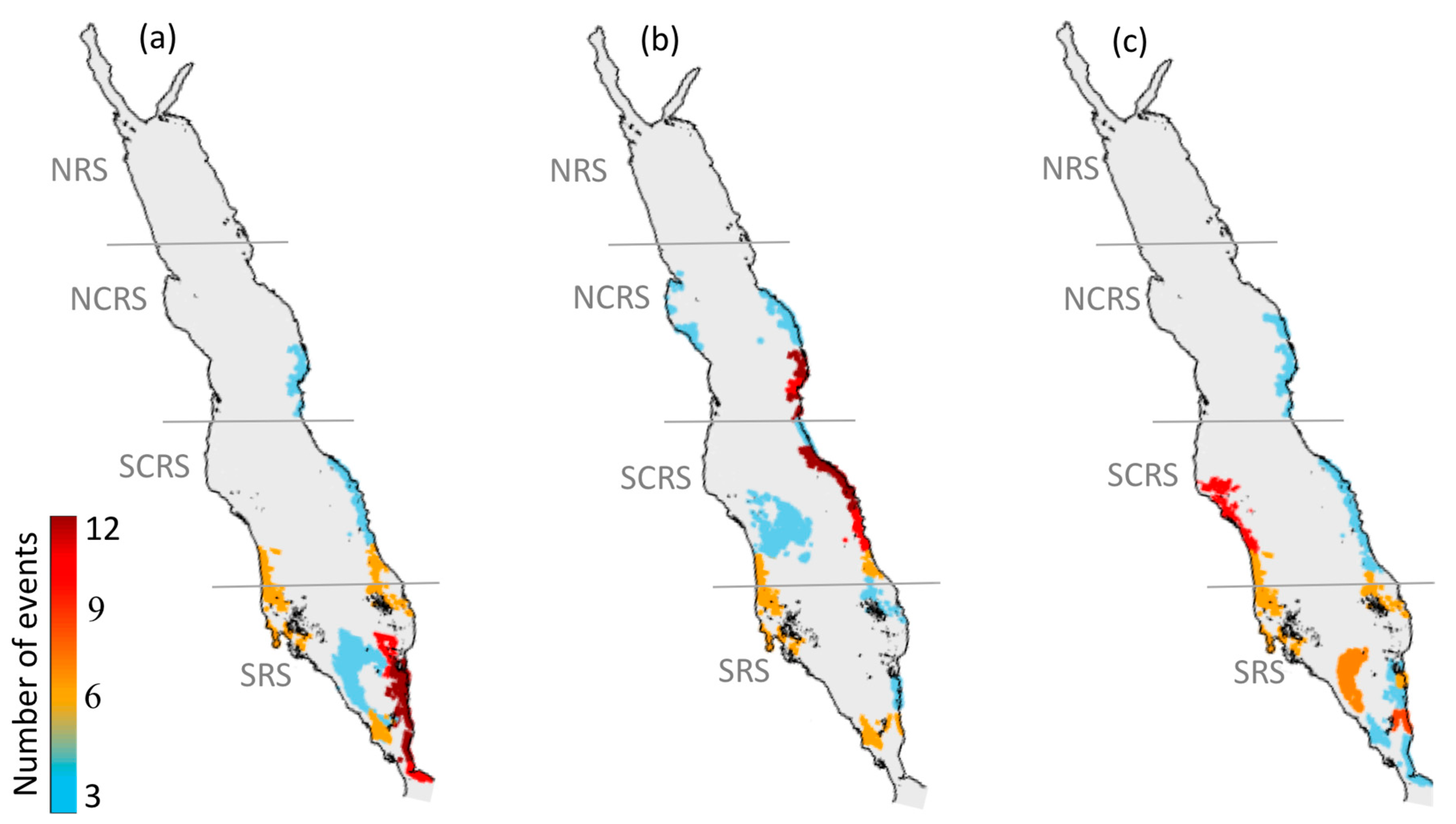
3.1.1. North-Central Red Sea
3.1.2. South-Central Red Sea
3.1.3. Southern Red Sea
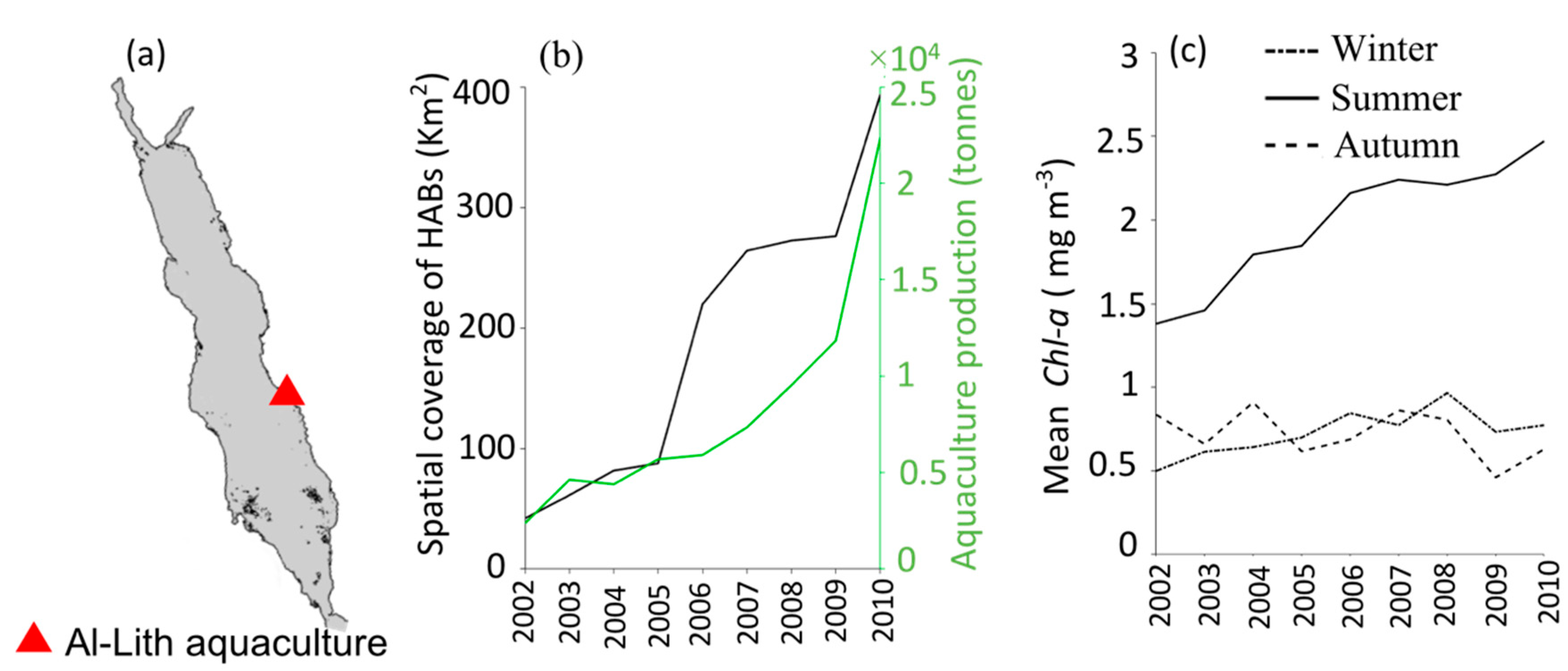
3.2. Interactions of HABs with Aquaculture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 562–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M. Approaches to monitoring, control and management of harmful algal blooms (HABs). Ocean Coast Manag. 2009, 52, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokul, E.A.; Shanmugam, P. An optical system for detecting and describing major algal blooms in coastal and oceanic waters around India. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 4097–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, B.; Edwards, M.; Reid, P.C. Climate change and harmful algal blooms. Ecol. Harmful Algae 2006, 367–378. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, S.K.; Trainer, V.L.; Mantua, N.J.; Parker, M.S.; Laws, E.A.; Backer, L.C.; Fleming, L.E. Impacts of climate variability and future climate change on harmful algal blooms and human health. Environ. Health 2008, 7, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glibert, P.M.; Allen, J.I.; Bouwman, A.F.; Brown, C.W.; Flynn, K.J.; Lewitus, A.J.; Madden, C.J. Modeling of HABs and eutrophication: Status, advances, challenges. J. Marine Syst. 2010, 83, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Mesaad, I. First report on Noctiluca scintillans blooms in the Red Sea off the coasts of Saudi Arabia: Consequences of eutrophication. Oceanologia 2007, 49, 337–351. [Google Scholar]
- Alkershi, A.; Menon, N. Phytoplankton in polluted waters of the Red Sea coast of Yemen. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. India 2011, 53, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Al-Shehri, A.M. Occurrence and germination of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments from the Red Sea off the coasts of Saudi Arabia. Oceanologia 2011, 53, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Al-Shehri, A.M. The link between shrimp farm runoff and blooms of toxic Heterosigma akashiwo in Red Sea coastal waters. Oceanologia 2012, 54, 287–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkawri, A. Seasonal variation in composition and abundance of harmful dinoflagellates in Yemeni waters, southern Red Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkawri, A.; Al-Areeki, M.; Alsharaby, K. The first recorded bloom of Protoperidinium quinquecorne and its link to a massive fish kill in Yemeni coastal waters, Southern Red Sea. Plankton Benthos Res. 2016, 11, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkawri, A.; Abker, M.; Qutaei, E.; Alhag, M.; Qutaei, N.; Mahdy, S. The first recorded bloom of Pyrodinium bahamense var bahamense plate in Yemeni coastal waters off Red Sea, near Al Hodeida City. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 16, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banguera-Hinestroza, E.; Eikrem, W.; Mansour, H.; Solberg, I.; Curdia, J.; Holtermann, K.; Edvardsen, B.; Kaartvedt, S. Seasonality and toxin production of Pyrodinium bahamense in a Red Sea lagoon. Harmful Algzae 2016, 55, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catania, D.; Richlen, M.L.; Mak, Y.L.; Morton, S.L.; Laban, E.H.; Xu, Y.; Anderson, D.M.; Chan, L.L.; Berumen, M.L. The prevalence of benthic dinoflagellates associated with ciguatera fish poisoning in the central Red Sea. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokul, E.A.; Raitsos, D.E.; Gittings, J.A.; Alkawri, A.; Hoteit, I. Remotely sensing harmful algal blooms in the Red Sea. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A. Potentially harmful microalgae and algal blooms in the Red Sea: Current knowledge and research needs. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 140, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, J.R.W.; Morán, X.A.J.; Raitsos, D.E.; Gittings, J.A.; Calleja, M.L.; Viegas, M.; Ansari, M.I.; Al-Otaibi, N.; Huete-Stauffer, T.M.; Hoteit, I. Factors regulating the relationship between total and size-fractionated chlorophyll-a in coastal waters of the Red Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kürten, B.; Khomayis, H.S.; Devassy, R.; Audritz, S.; Sommer, U.; Struck, U.; El-Sherbiny, M.M.; Al-Aidaroos, A.M. Ecohydrographic constraints on biodiversity and distribution of phytoplankton and zooplankton in coral reefs of the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Ecol. 2015, 36, 1195–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozumi, A.; Hong, P.Y.; Kaartvedt, S.; Røstad, A.; Jones, B.H. Water quality, seasonality, and trajectory of an aquaculture-wastewater plume in the Red Sea. Aquac. Environ. Interacact. 2018, 10, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittings, J.A.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Raitsos, D.E.; Kheireddine, M.; Ouhssain, M.; Jones, B.; Hoteit, I. Remotely sensing phytoplankton size structure in the Red Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, R.J.; Raitsos, D.E.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Zarokanellos, N.; Jackson, T.; Racault, M.F.; Boss, E.S.; Sathyendranath, S.; Jones, B.H.; Hoteit, I. Regional ocean- color Chl-a algorithms for the Red Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 64–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racault, M.F.; Raitsos, D.E.; Berumen, M.L.; Brewin, R.J.; Platt, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Hoteit, I. Phytoplankton phenology indices in coral reef ecosystems: Application to ocean-color observations in the Red Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreano, D.; Raitsos, D.E.; Gittings, J.; Krokos, G.; Hoteit, I. The Gulf of Aden intermediate water intrusion regulates the southern Red Sea summer phytoplankton blooms. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittings, J.A.; Raitsos, D.E.; Kheireddine, M.; Racault, M.F.; Claustre, H.; Hoteit, I. Evaluating tropical phytoplankton phenology metrics using contemporary tools. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D. The Sea Around Us Project: Documenting and communicating global fisheries impacts on marine ecosystems. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2007, 36, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibaldi, L. The FAO global capture production database: A six-decade effort to catch the trend. Mar. Policy 2012, 36, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.; Pauly, D. Mariculture: A global analysis of production trends since 1950. Mar. Policy 2013, 39, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitsos, D.E.; Pradhan, Y.; Brewin, R.J.; Stenchikov, G.; Hoteit, I. Remote sensing the phytoplankton seasonal succession of the Red Sea. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzert, W.C. Wind-induced reversal in Red Sea circulation. Deep Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1974, 21, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.P.; Johns, W. Direct observations of seasonal exchange through the Bab el Mandab Strait. Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1998, 3, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofianos, S.S.; Johns, W.E. An oceanic general circulation model (OGCM) investigation of the Red Sea circulation, 1. Exchange between the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2002, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiki, H.; Takahashi, K.; Yamagata, T. The Red Sea outflow regulated by the Indian monsoon. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 1448–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, J.H.; Bower, A.S.; McCorkle, D.C.; Abualnaja, Y. The transport of nutrient-rich Indian Ocean water through the Red Sea and into coastal reef systems. J. Mar. Res. 2014, 72, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Hoteit, I.; Pratt, L.J.; Bower, A.S.; Zhai, P.; Köhl, A.; Gopalakrishnan, G. Seasonal overturning circulation in the Red Sea: 1. Model validation and summer circulation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 2238–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittings, J.A.; Raitsos, D.E.; Racault, M.F.; Brewin, R.J.; Pradhan, Y.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T. Seasonal phytoplankton blooms in the Gulf of Aden revealed by remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 189, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitsos, D.E.; Brewin, R.J.; Zhan, P.; Dreano, D.; Pradhan, Y.; Nanninga, G.B.; Hoteit, I. Sensing coral reef connectivity pathways from space. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Raitsos, D.E.; Krokos, G.; Gittings, J.A.; Zhan, P.; Hoteit, I. Physical connectivity simulations reveal dynamic linkages between coral reefs in the southern Red Sea and the Indian Ocean. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, W.E.; Sofianos, S.S. Atmospherically-forced exchange through the Bab el Mandeb. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Hoteit, I.; Pratt, L.J.; Bower, A.S.; Köhl, A.; Gopalakrishnan, G.; Rivas, D. Seasonal overturning circulation in the Red Sea: 2. Winter circulation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 2263–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, G.; Yao, F.; Petihakis, G.; Tsiaras, K.P.; Raitsos, D.E.; Hoteit, I. Exploring the Red Sea seasonal ecosystem functioning using a three-dimensional biophysical model. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 1791–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.F.; Dedej, Z.; Gottlieb, R.; Li, H.; Thomas, D.N.; El-Absawi, M.; El-Naggar, A.; El-Gharabawi, M.; Sommer, U. Spatial and temporal distribution of Trichodesmium spp. in the stratified Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 239, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, F.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Aamer, M. Phytoplankton population along certain Egyptian coastal regions of the Red Sea. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2010, 14, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nassar, M.Z.; El-Din, N.G.; Gharib, S.M. Phytoplankton variability in relation to some environmental factors in the eastern coast of Suez Gulf, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 648, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touliabah, H.E.; Abu El-Kheir, W.S.; Kuchari, M.G. Phytoplankton composition at Jeddah coast-Red Sea, Saudi Arabia in relation to some ecological factors. J. King Abdulaziz Univ. Sci. 2010, 148, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, A.G.; Nasr, D.H. Studies in planktonic populations in Port Sudan coastal area. Sudan J. Sci. 1989, 4, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.H.M. Ecological Study on the Phytoplankton in the Sudanese Red Sea Coast (Port Sudan Area). Master’s Thesis, University of Khartoum, Khartoum, Sudan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, J.; Staalstrøm, A.; Wathne, B.M.; Omer, R.K.; Ahmed, S.E. Marine Ecological Baselines and Environmental Impact Assessment Studies in the Sudanese Coastal Zone. A Review; Norsk Institutt for Vannforskning: Oslo, Norway, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, E.B.; Churchill, J.H.; Barthel, K.; Skjelvan, I.; Omar, A.M.; de Lange, T.E.; Eltaib, E.B. Seasonal variations of hydrographic parameters off the Sudanese coast of the Red Sea, 2009–2015. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, R. Coral reefs and communities of the central and southern Red Sea (Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, and Yemen). In the Red Sea; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 409–451. [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz, F.; Deschamps, P.Y.; Ramon, D. Atmospheric correction in presence of sun glint: Application to MERIS. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9783–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitsos, D.E.; Yi, X.; Platt, T.; Racault, M.F.; Brewin, R.J.; Pradhan, Y.; Papadopoulos, V.P.; Sathyendranath, S.; Hoteit, I. Monsoon oscillations regulate fertility of the Red Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, W.G. Shrimp culture: A global overview. SEAFDEC Asian Aquac. 1999, 21, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Grindle, A.K.; Siddiqi, A.; Anadon, L.D. Food security amidst water scarcity: Insights on sustainable food production from Saudi Arabia. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2015, 2, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.; Hughen, K.; Mincer, T.J.; Ossolinski, J.; Weber, L.; Apprill, A. Impact of prawn farming effluent on coral reef water nutrients and microorganisms. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2017, 9, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alday-Sanz, V.; Brock, J.; Flegel, T.W.; McIntosh, R.; Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Salazar, M.; Subasinghe, R. Facts, truths and myths about SPF shrimp in Aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVantier, L.; Turak, E.; Al-Shaikh, K.; De ath, G. Coral communities of the central-northern Saudi Arabian Red Sea. Fauna Arabia. 2000, 18, 23–66. [Google Scholar]
- Genevier, L.G.; Jamil, T.; Raitsos, D.E.; Krokos, G.; Hoteit, I. Marine heatwaves reveal coral reef zones susceptible to bleaching in the Red Sea. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 2338–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozumi, A.; Kaartvedt, S.; Røstad, A.; Berumen, M.L.; Cochran, J.E.; Jones, B.H. Acoustic backscatter at a Red Sea whale shark aggregation site. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 20, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, J.E.; Braun, C.D.; Cagua, E.F.; Campbell, M.F., Jr.; Hardenstine, R.S.; Kattan, A.; Priest, M.A.; Sinclair-Taylor, T.H.; Skomal, G.B.; Sultan, S.; et al. Multi-method assessment of whale shark (Rhincodon typus) residency, distribution, and dispersal behavior at an aggregation site in the Red Sea. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acker, J.; Leptoukh, G.; Shen, S.; Zhu, T.; Kempler, S. Remotely-sensed chlorophyll a observations of the northern Red Sea indicate seasonal variability and influence of coastal reefs. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 69, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkawri, A.; Gamoyo, M. Remote sensing of phytoplankton distribution in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 33, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gokul, E.A.; Raitsos, D.E.; Gittings, J.A.; Hoteit, I. Developing an Atlas of Harmful Algal Blooms in the Red Sea: Linkages to Local Aquaculture. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223695
Gokul EA, Raitsos DE, Gittings JA, Hoteit I. Developing an Atlas of Harmful Algal Blooms in the Red Sea: Linkages to Local Aquaculture. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(22):3695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223695
Chicago/Turabian StyleGokul, Elamurugu Alias, Dionysios E. Raitsos, John A. Gittings, and Ibrahim Hoteit. 2020. "Developing an Atlas of Harmful Algal Blooms in the Red Sea: Linkages to Local Aquaculture" Remote Sensing 12, no. 22: 3695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223695
APA StyleGokul, E. A., Raitsos, D. E., Gittings, J. A., & Hoteit, I. (2020). Developing an Atlas of Harmful Algal Blooms in the Red Sea: Linkages to Local Aquaculture. Remote Sensing, 12(22), 3695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223695