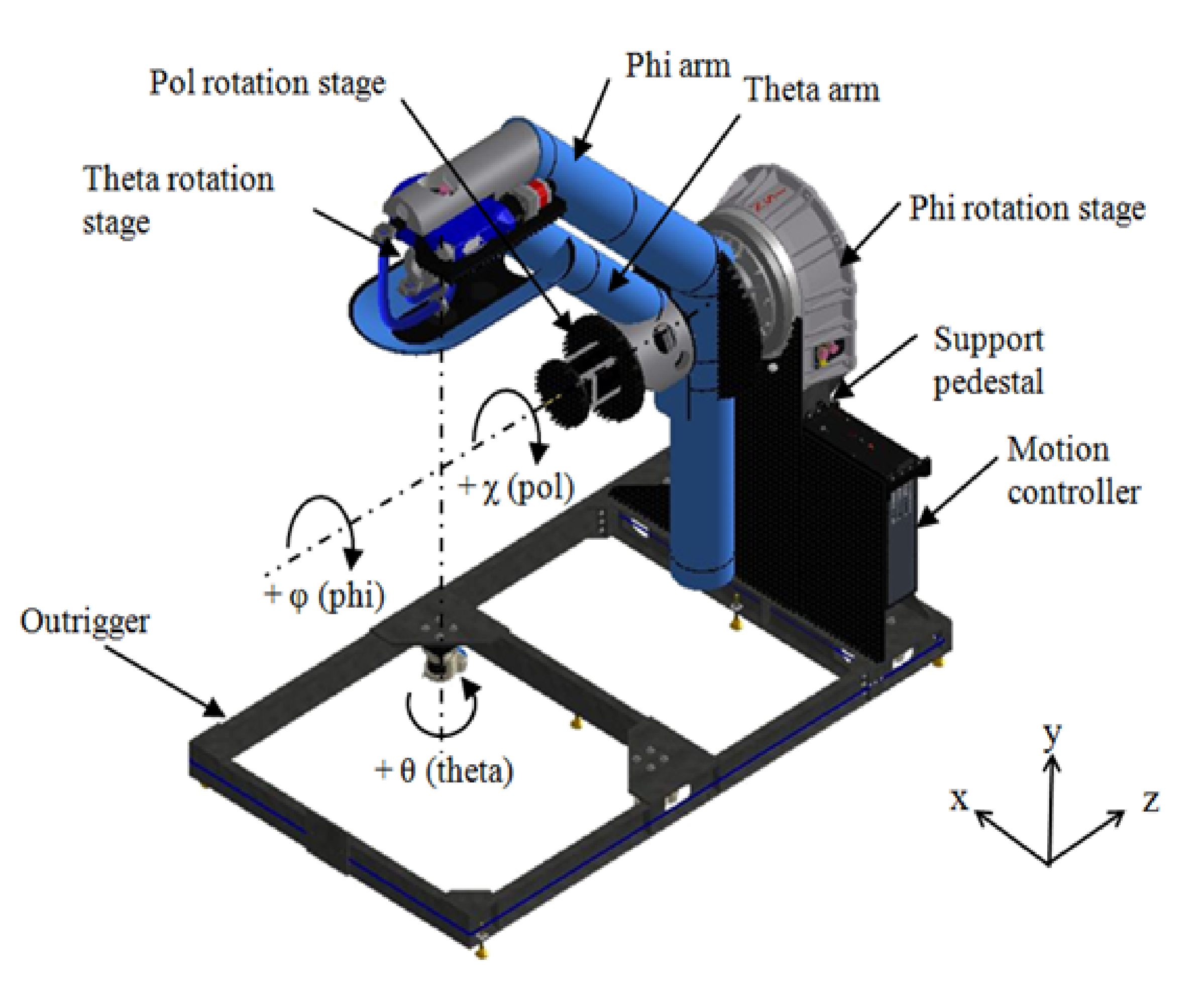
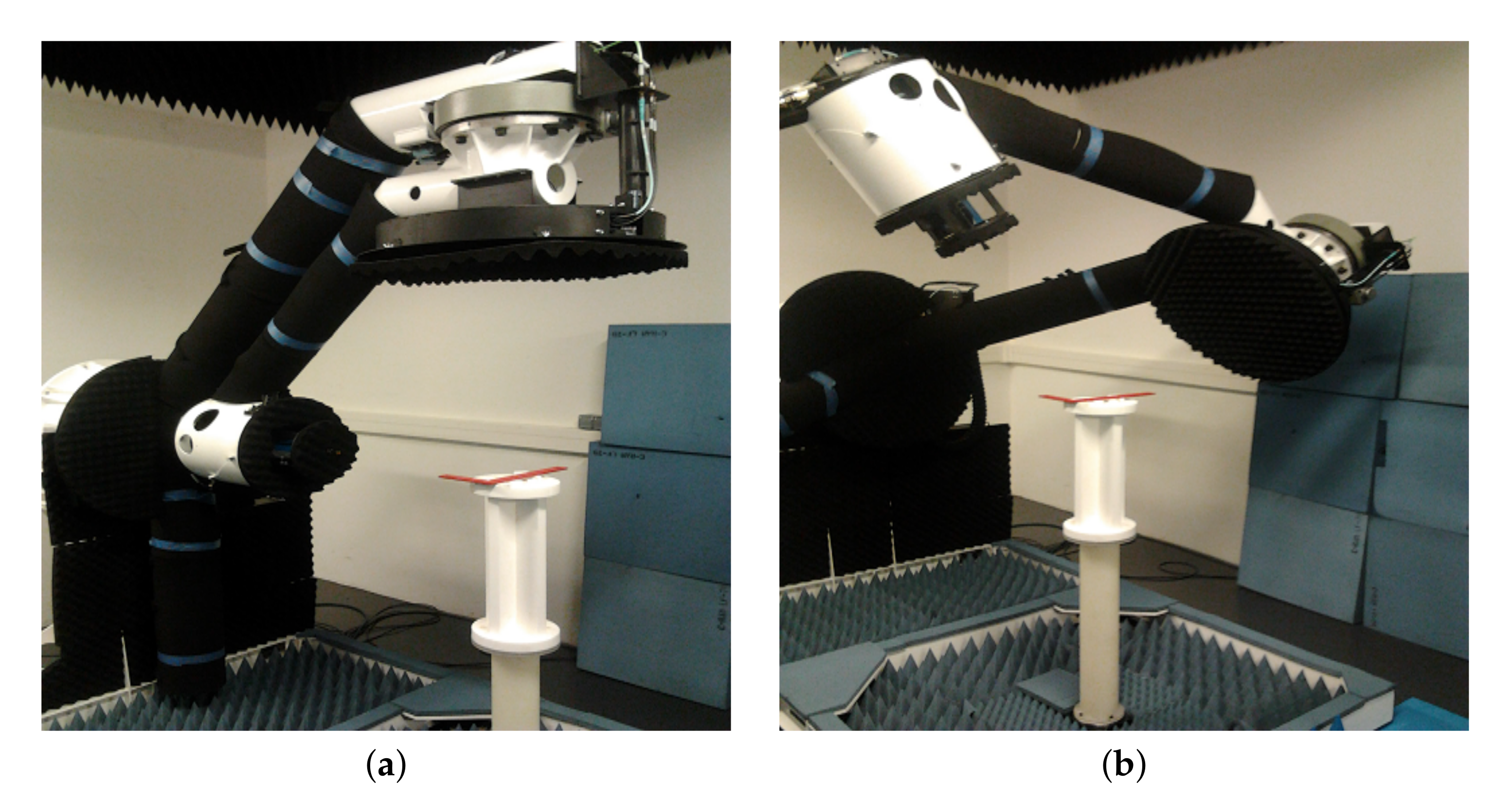
Figure 1.
Radar data acquisition setup.
Figure 1.
Radar data acquisition setup.
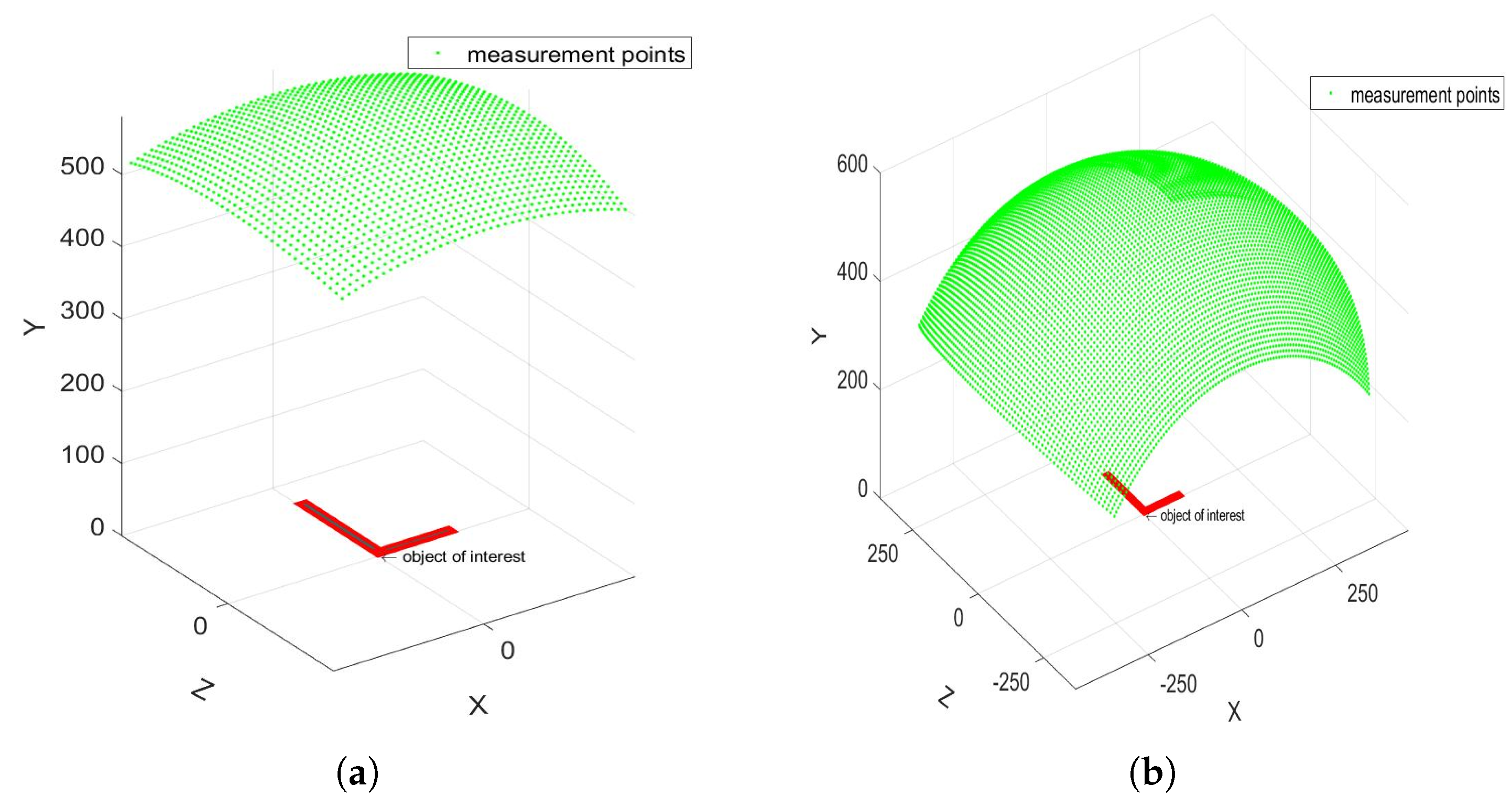
Figure 2.
Schematics of the acquisition principles: (a) small angle, (b) large angle.
Figure 2.
Schematics of the acquisition principles: (a) small angle, (b) large angle.
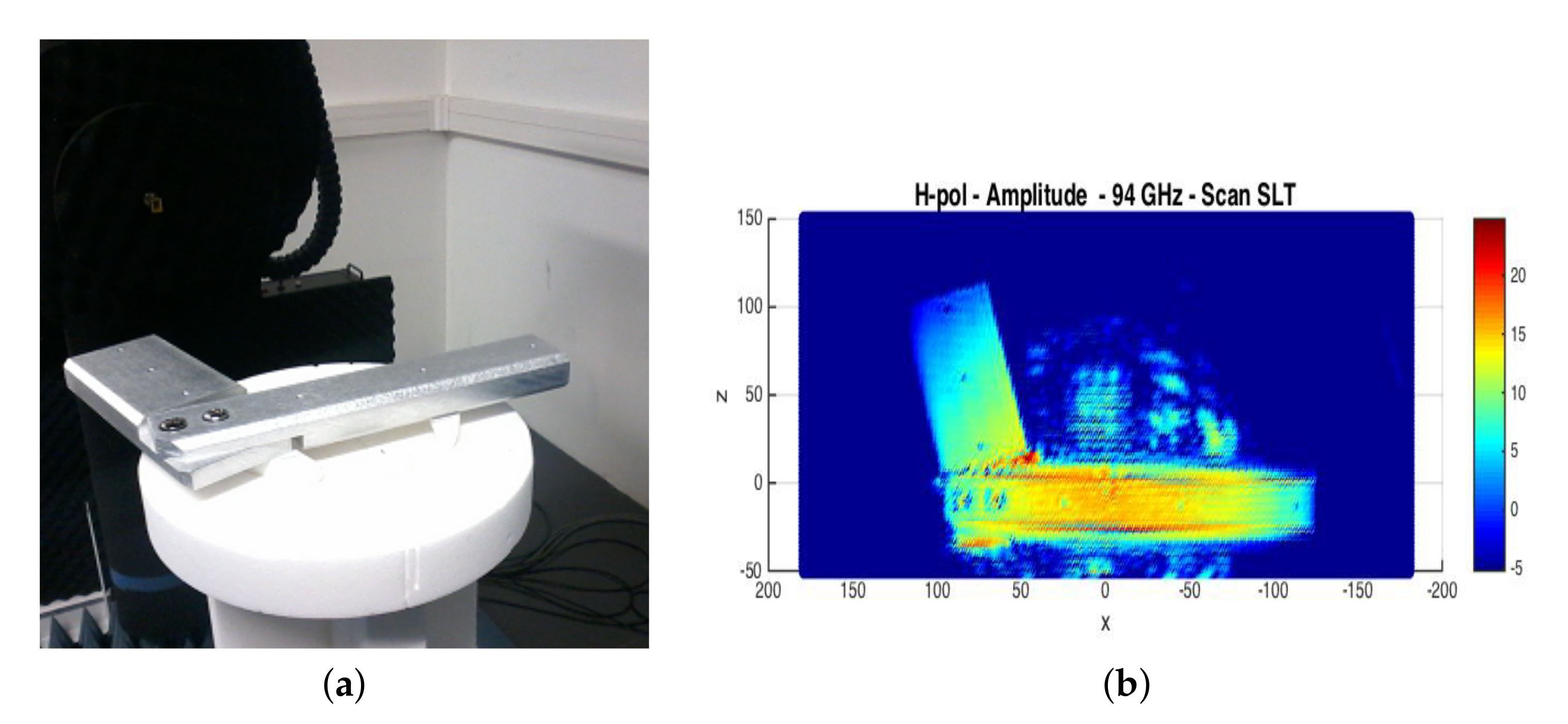
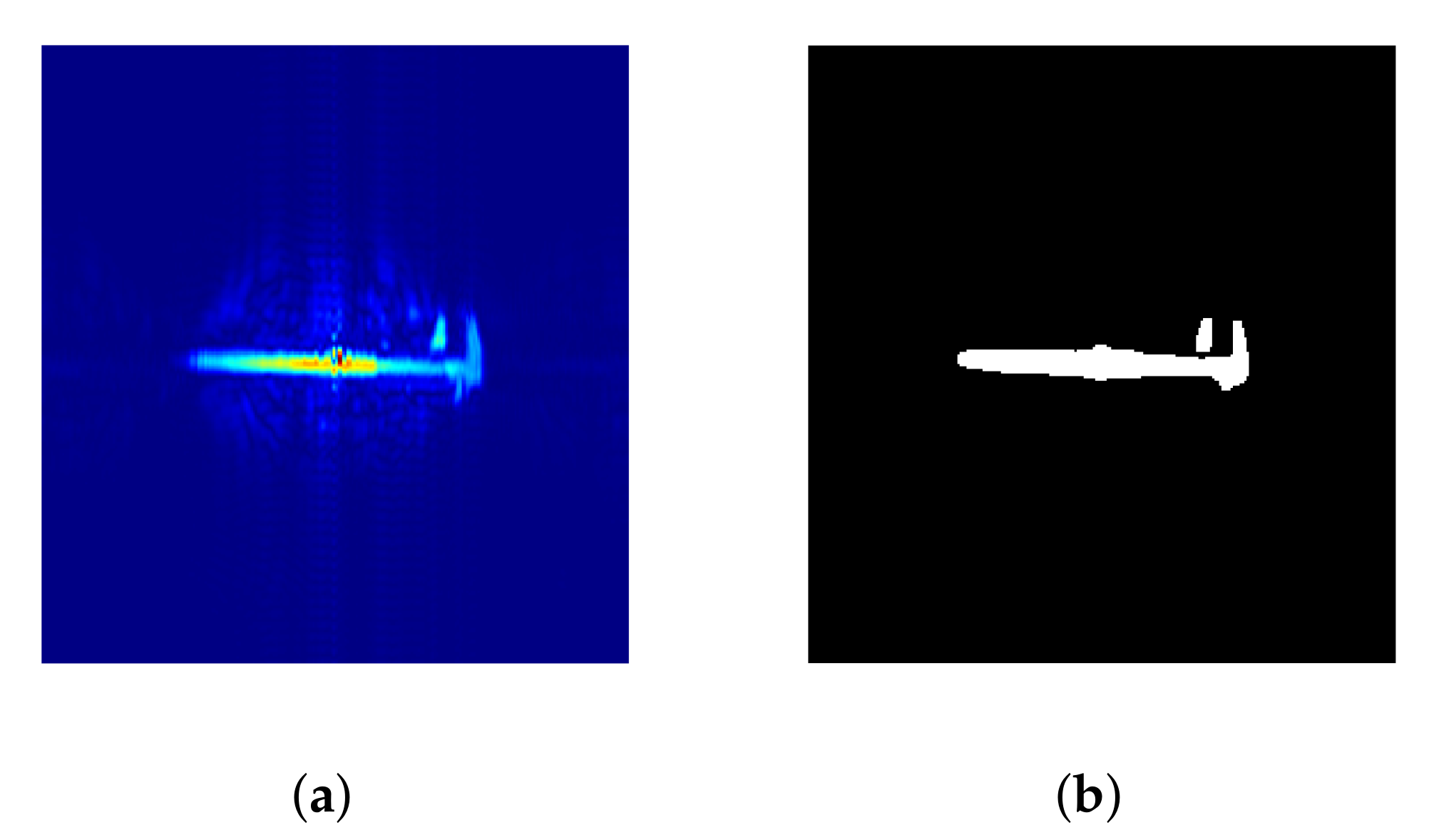
Figure 3.
(a) Fake gun; (b) radar acquisition.
Figure 3.
(a) Fake gun; (b) radar acquisition.
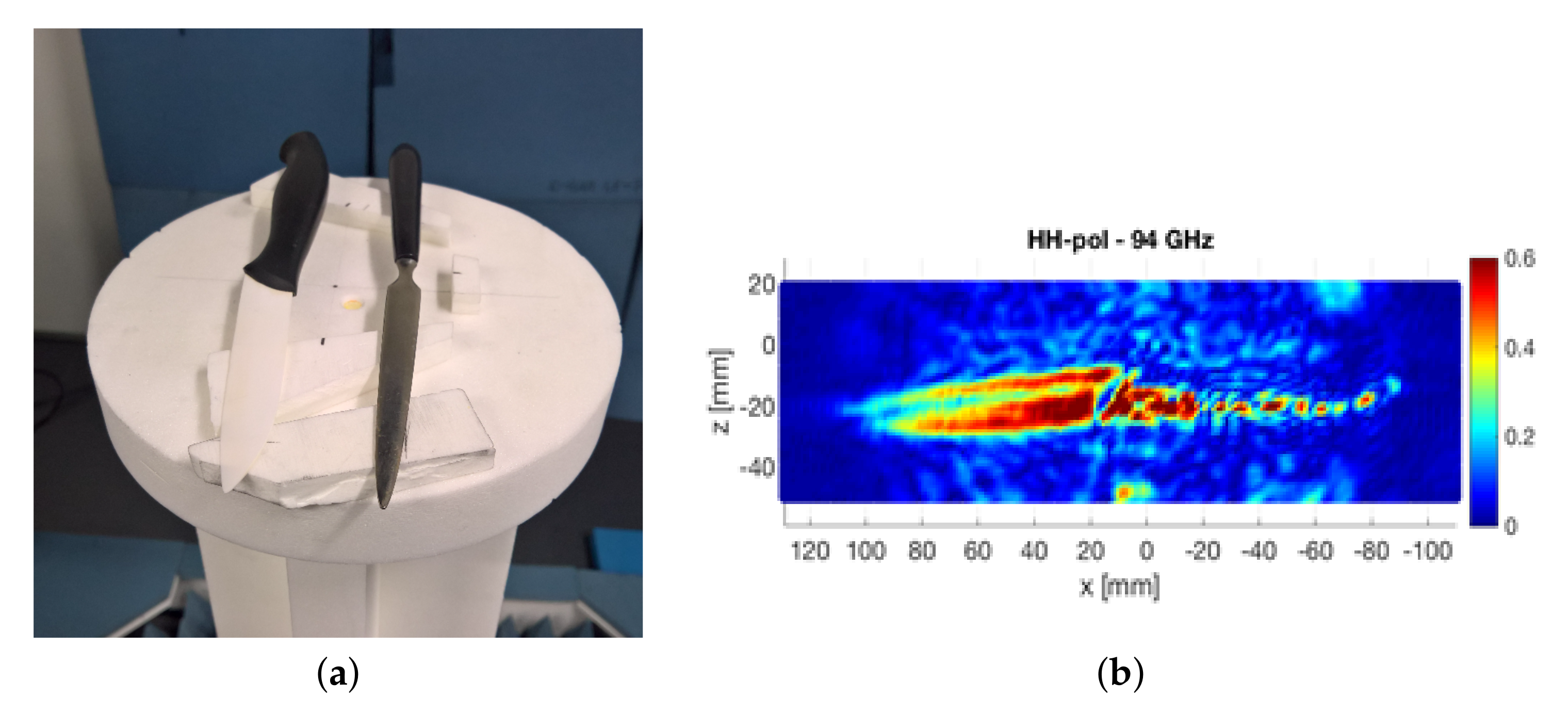
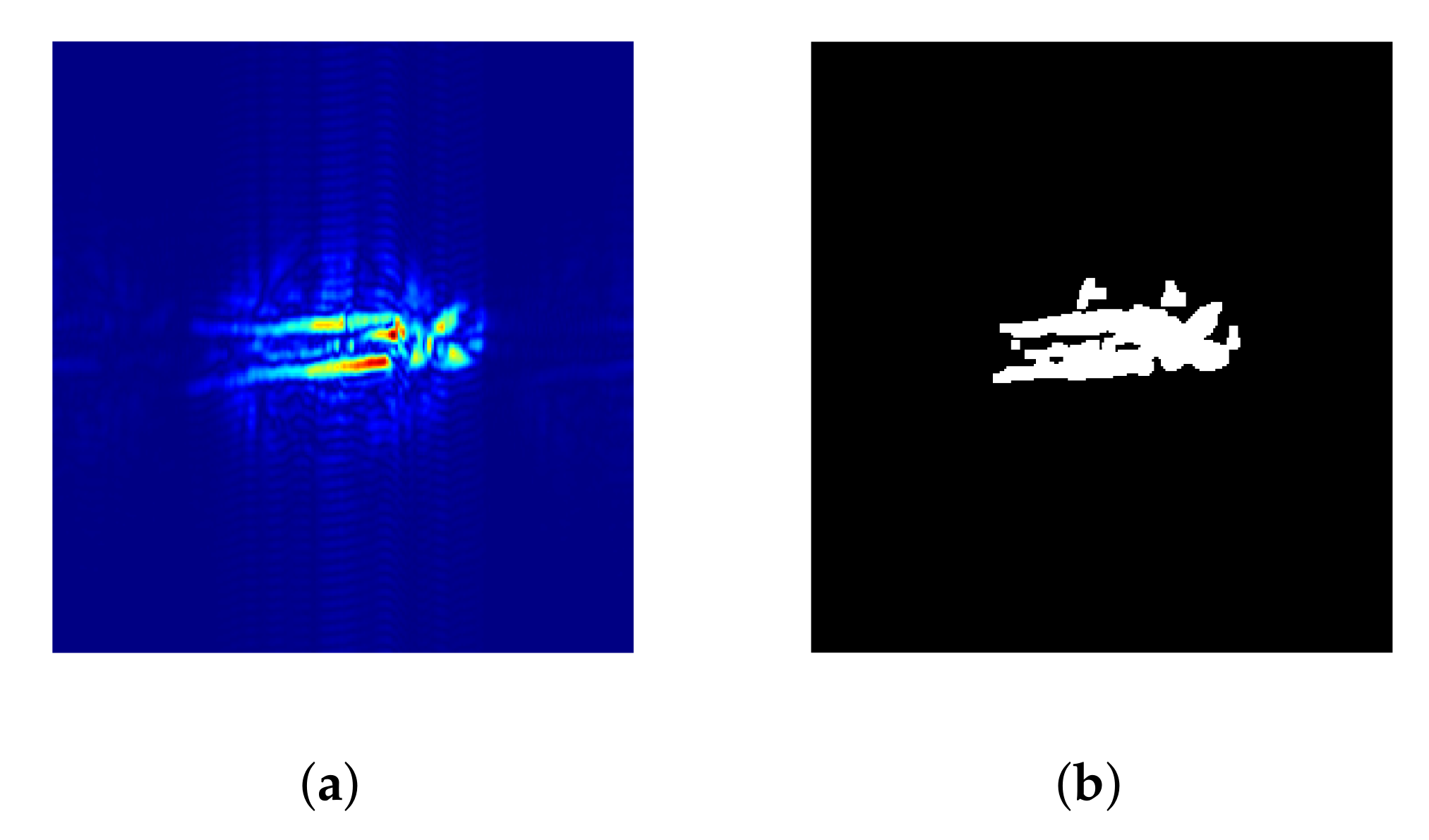
Figure 4.
(a) Knives; (b) radar acquisition.
Figure 4.
(a) Knives; (b) radar acquisition.
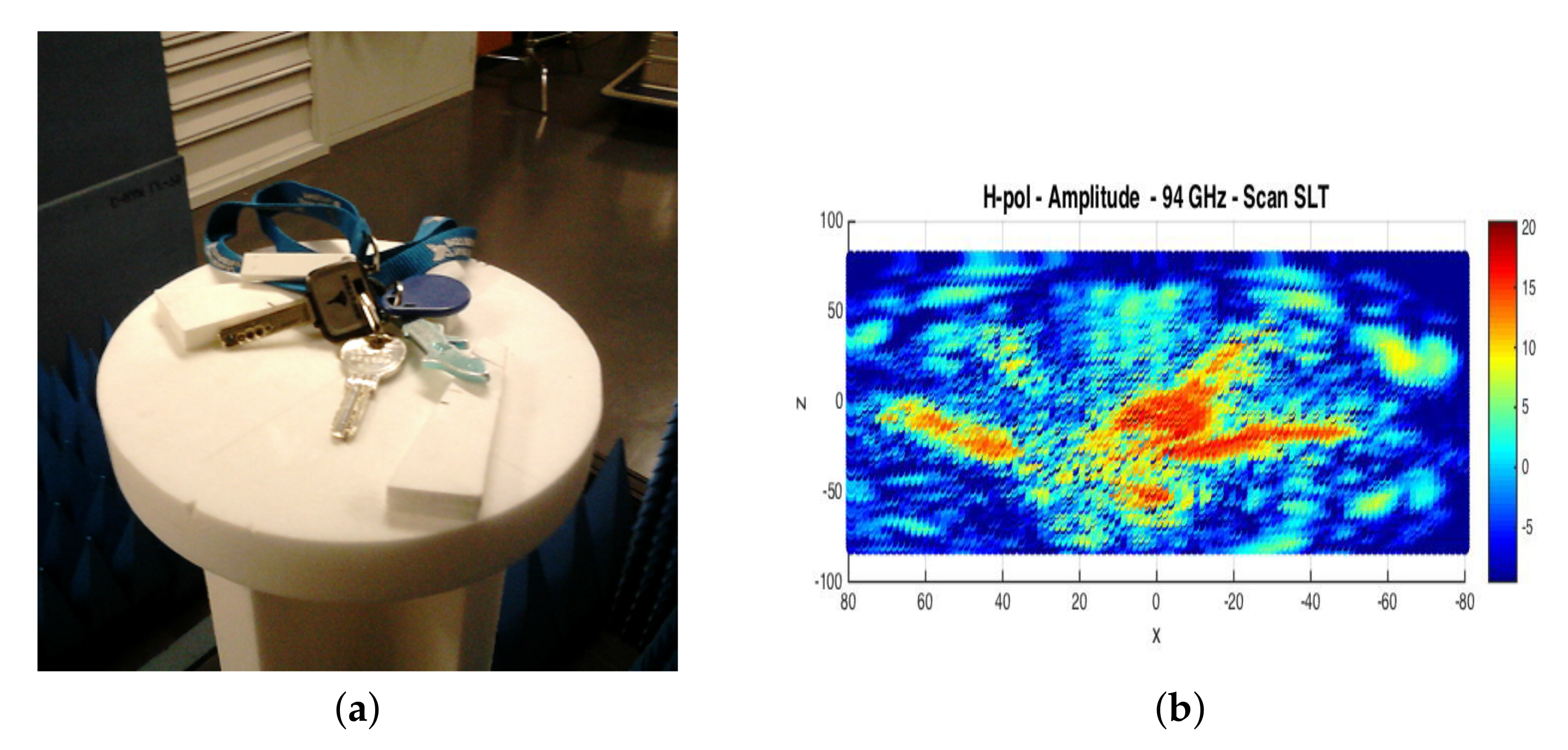
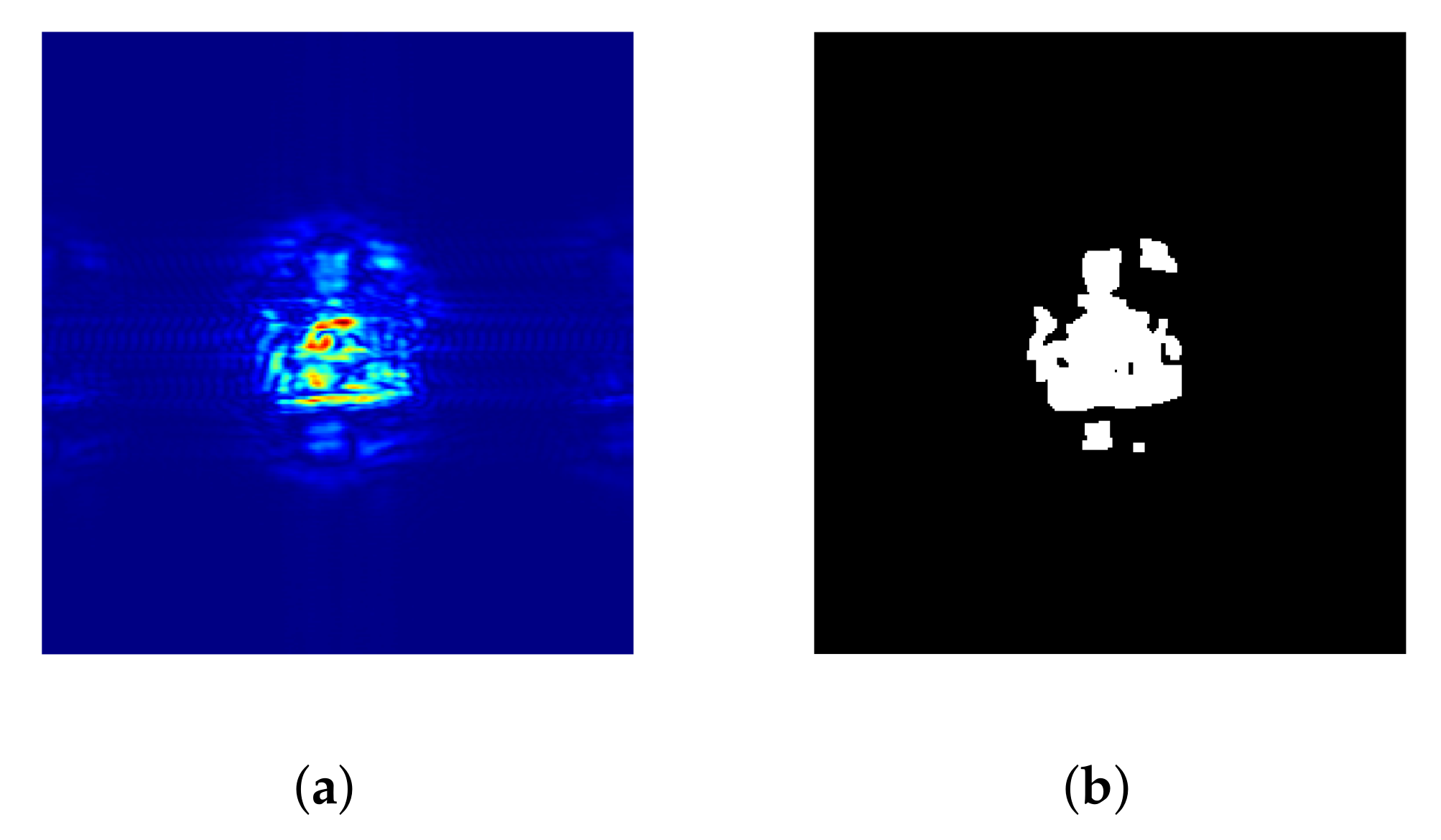
Figure 5.
(a) Set of keys; (b) radar acquisition.
Figure 5.
(a) Set of keys; (b) radar acquisition.
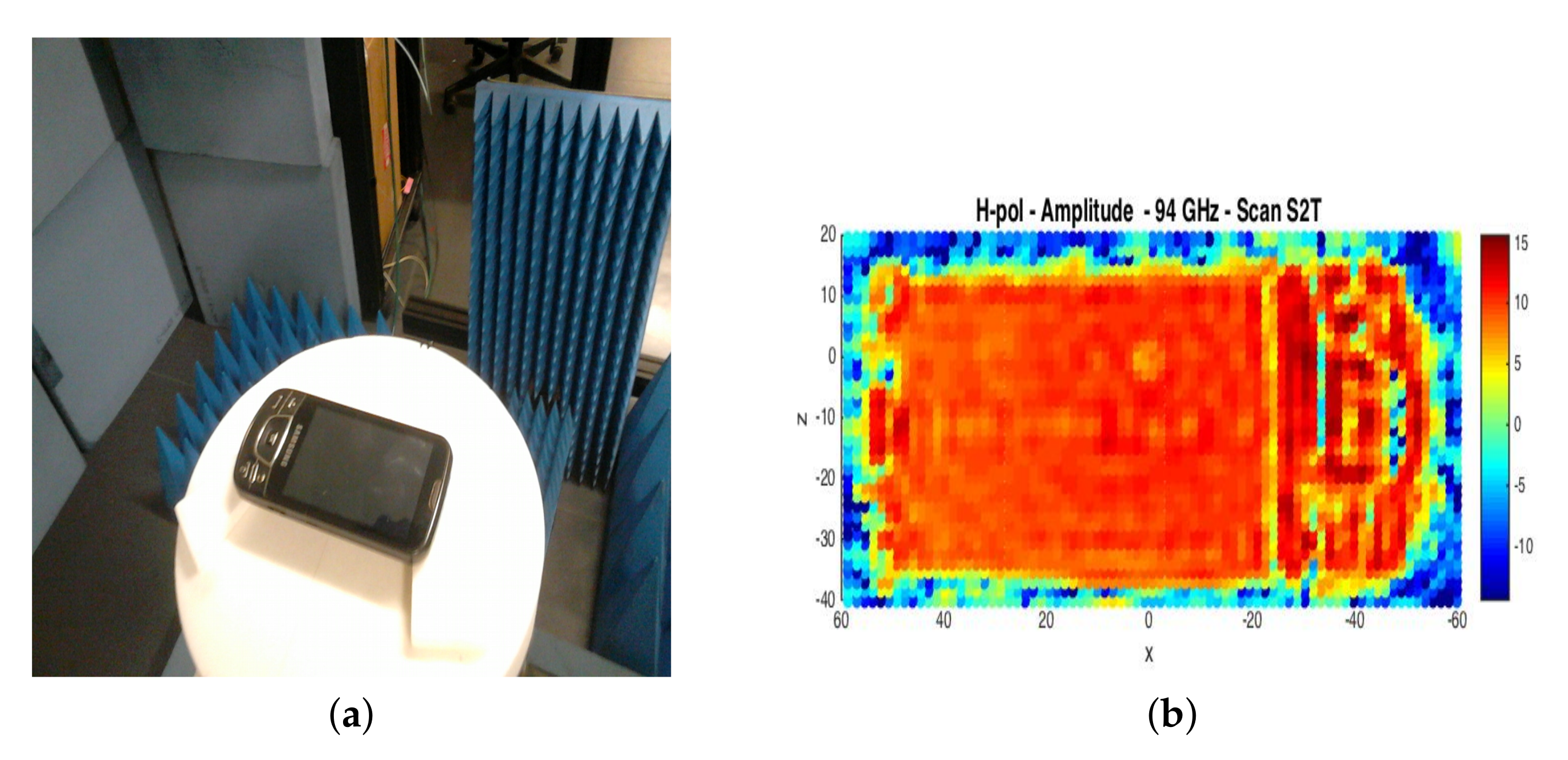
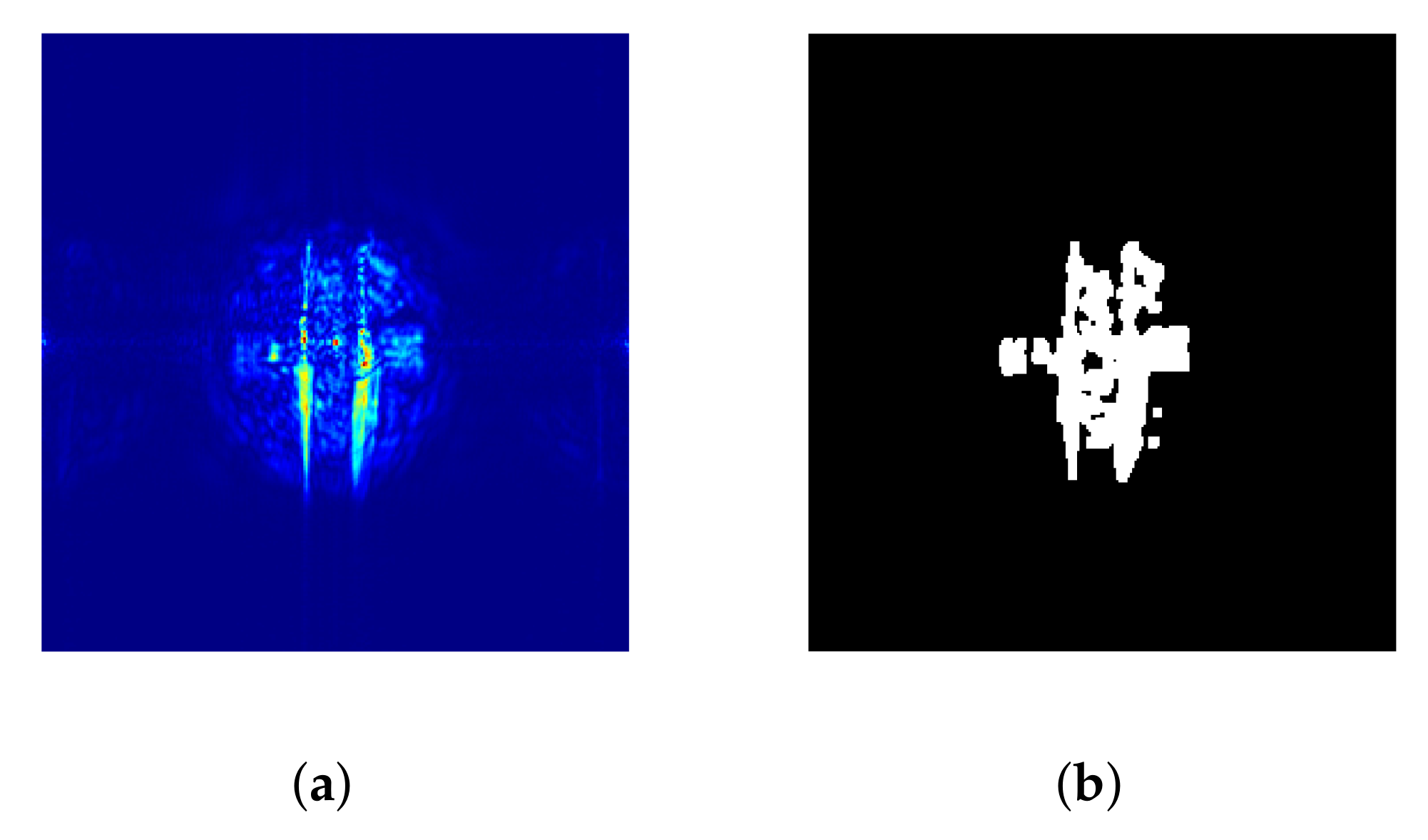
Figure 6.
(a) smartphone; (b) radar acquisition.
Figure 6.
(a) smartphone; (b) radar acquisition.
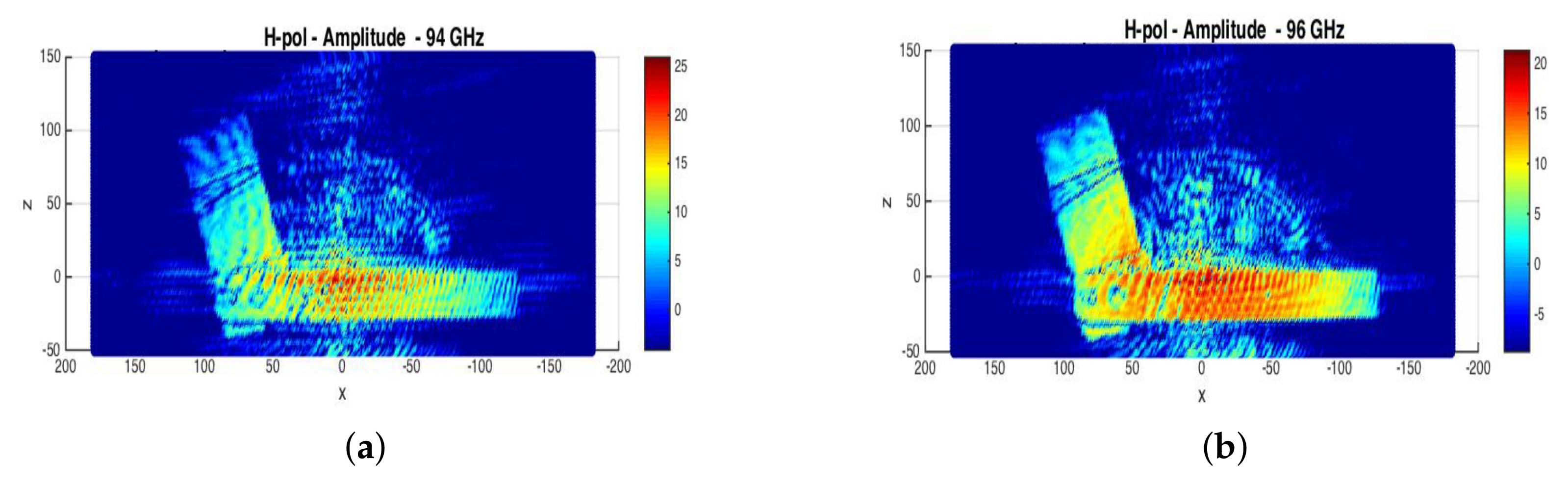
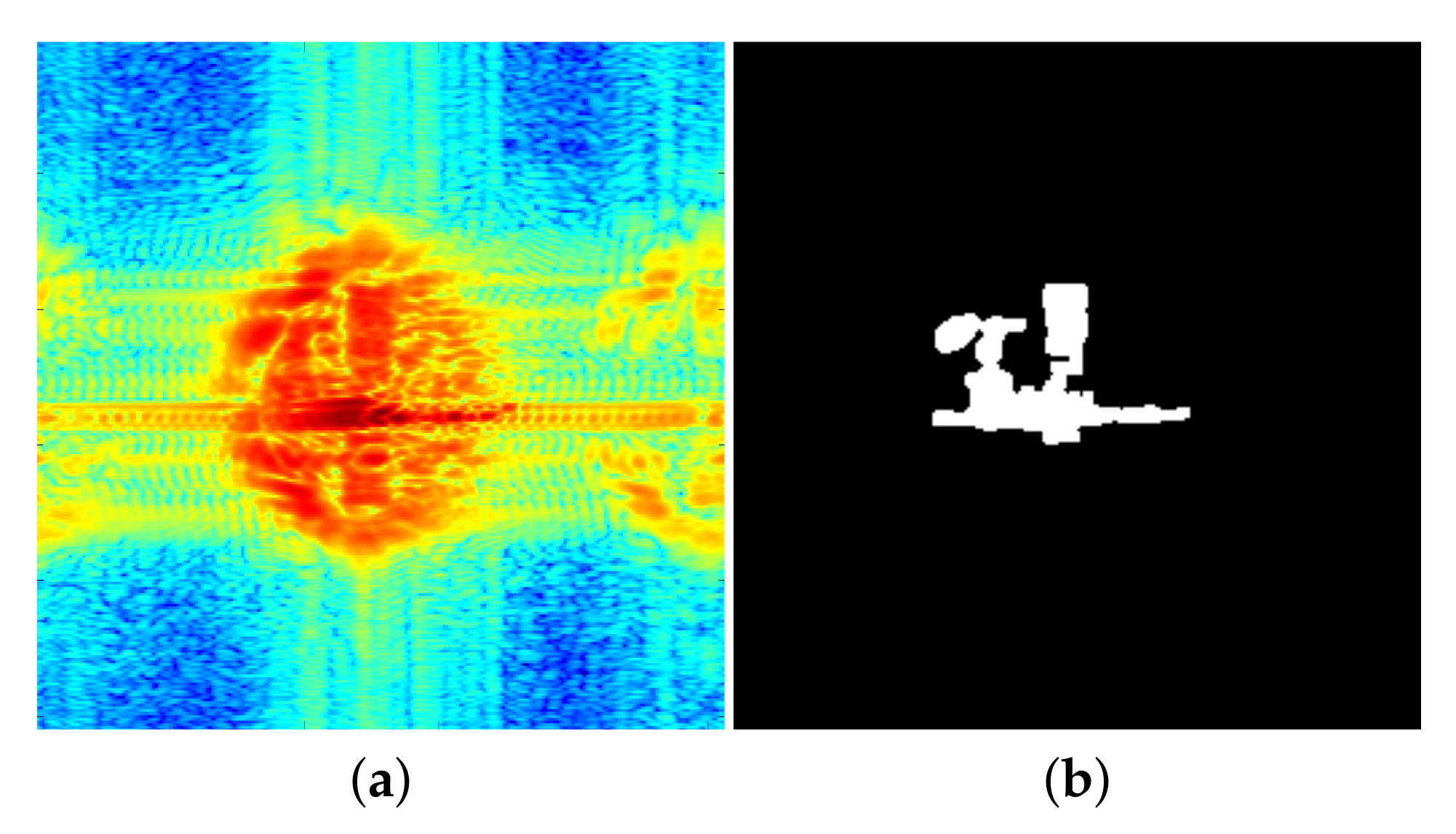
Figure 7.
Scan amplitudes of a concealed gun, ‘’ polarization: (a) 94 GHz; (b) 96 GHz.
Figure 7.
Scan amplitudes of a concealed gun, ‘’ polarization: (a) 94 GHz; (b) 96 GHz.
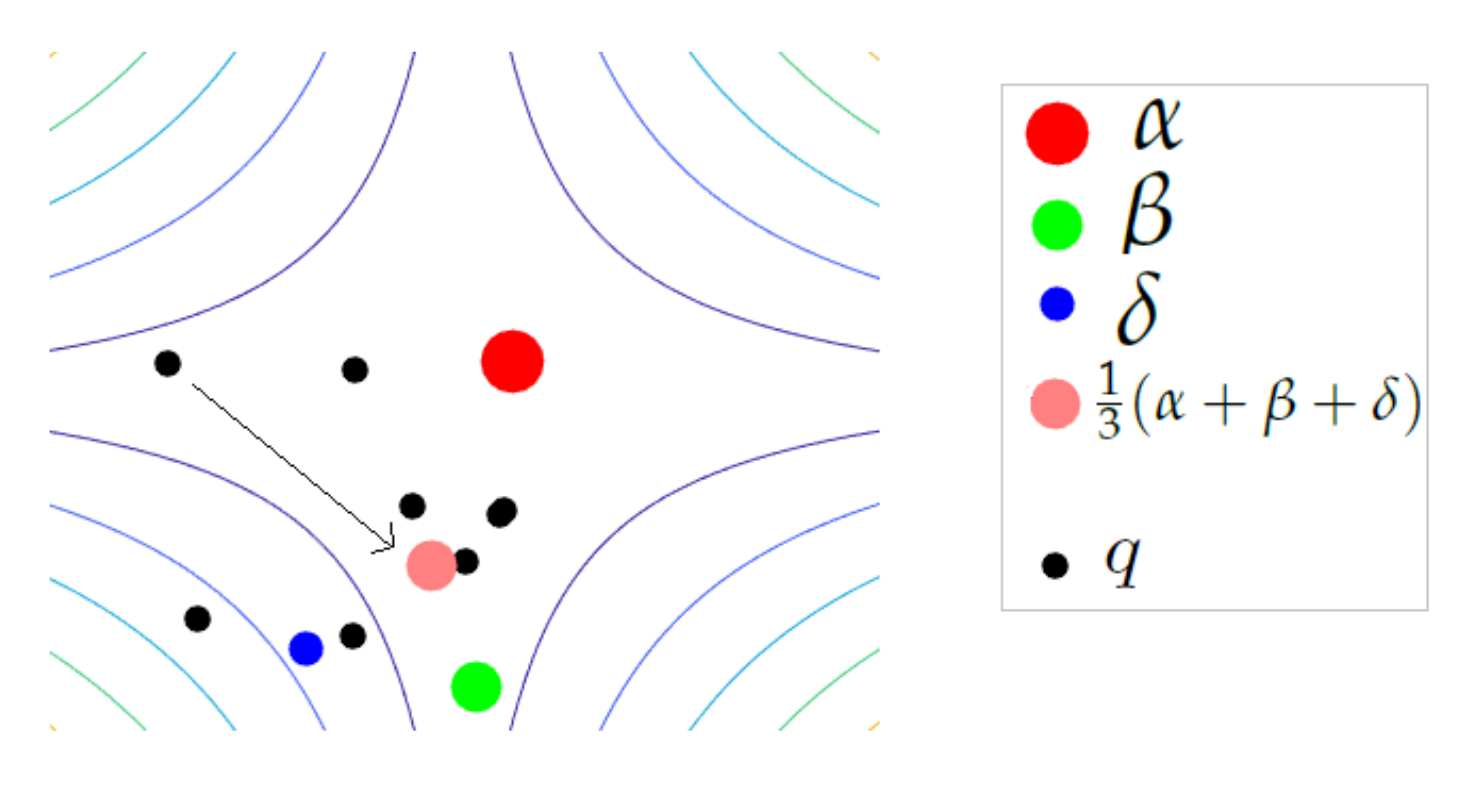
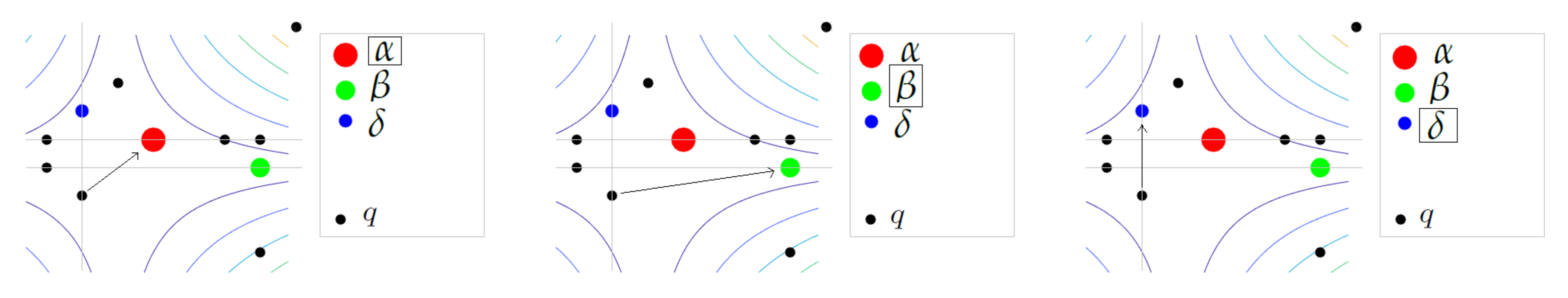
Figure 8.
Continuous GWO: displacement of an agent q towards the center of mass of the leaders.
Figure 8.
Continuous GWO: displacement of an agent q towards the center of mass of the leaders.
Figure 9.
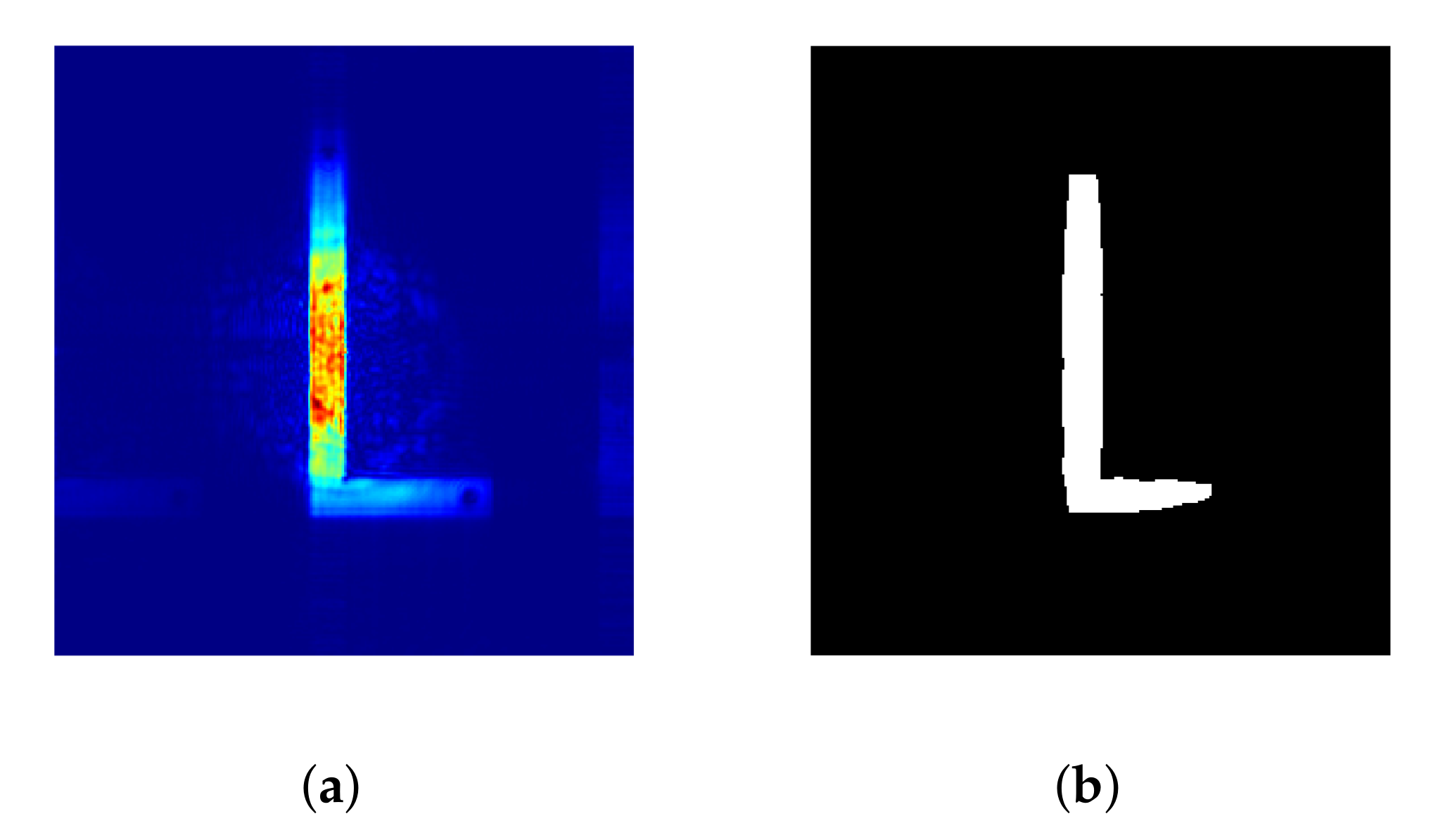
Discrete GWO: displacement of an agent q towards a leader, either , , or , selected at random.
Figure 9.
Discrete GWO: displacement of an agent q towards a leader, either , , or , selected at random.
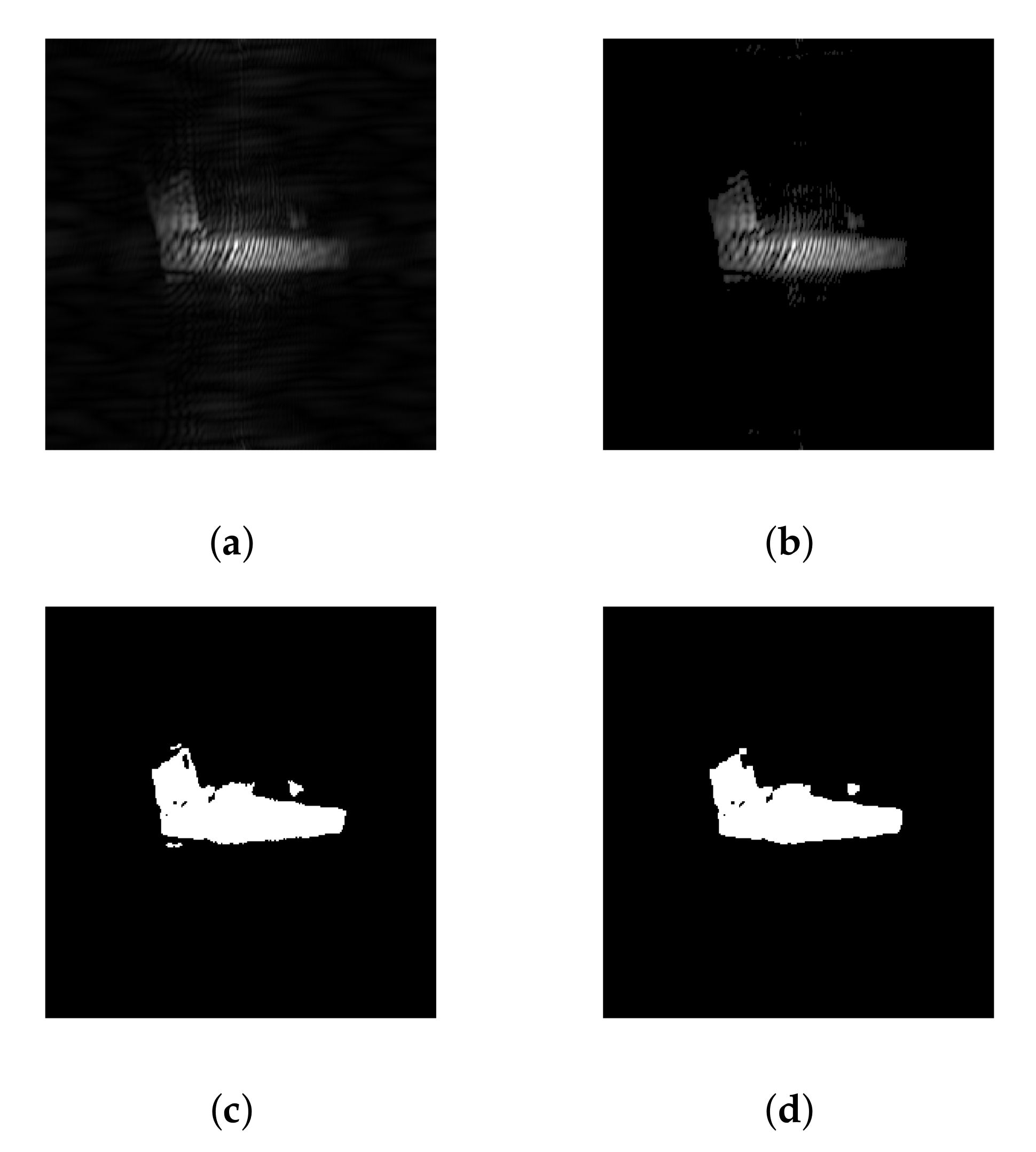
Figure 10.
Illustration of the image processing chain on a concealed gun, ‘’ polarization, 94 GHz: (a) grey level, (b) enhanced, (c) binarized, (d) mathematical morphology.
Figure 10.
Illustration of the image processing chain on a concealed gun, ‘’ polarization, 94 GHz: (a) grey level, (b) enhanced, (c) binarized, (d) mathematical morphology.
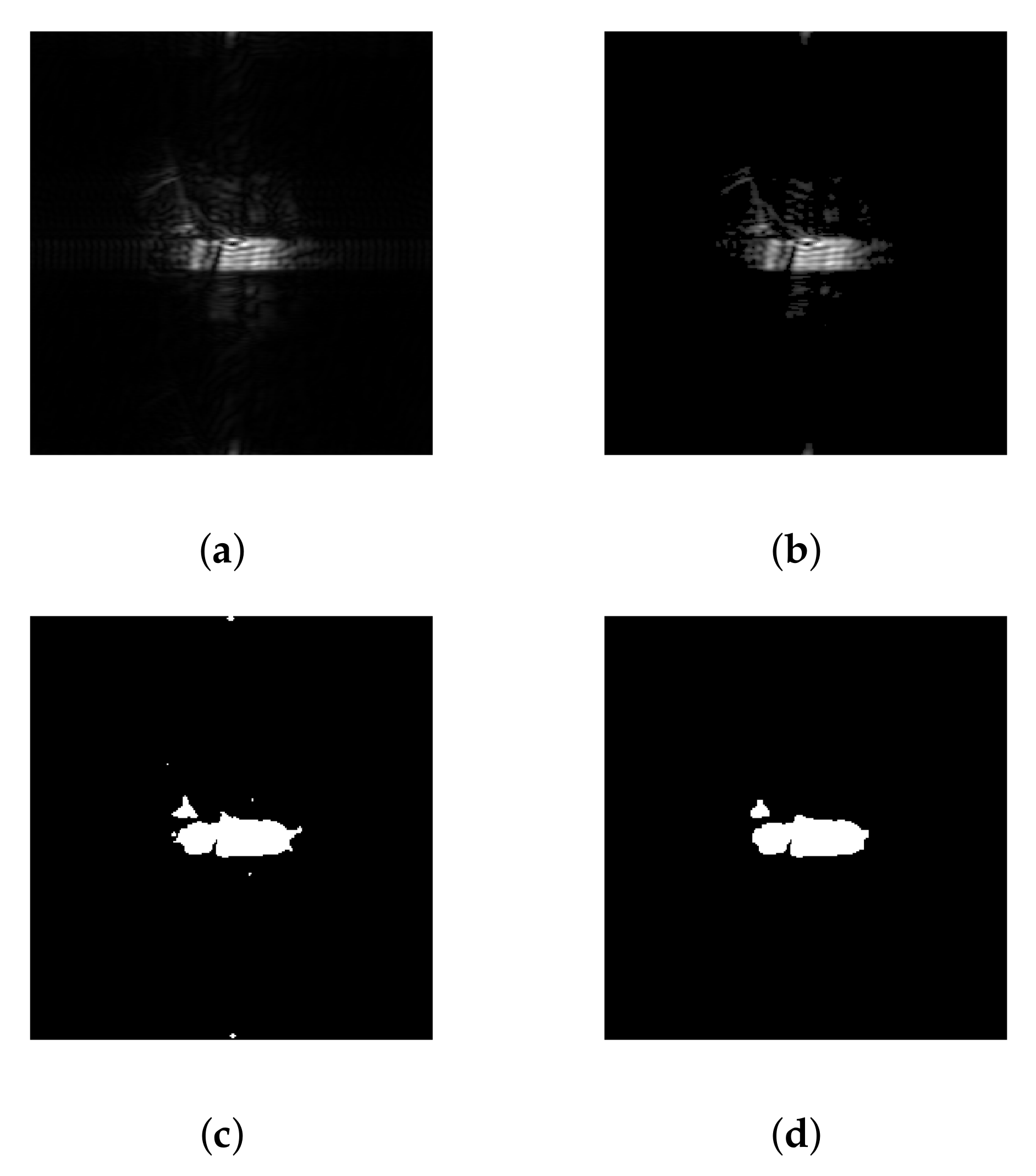
Figure 11.
Illustration of the image processing chain on a concealed gun, ‘’ polarization, 96 GHz: (a) grey level, (b) enhanced, (c) binarized, (d) mathematical morphology.
Figure 11.
Illustration of the image processing chain on a concealed gun, ‘’ polarization, 96 GHz: (a) grey level, (b) enhanced, (c) binarized, (d) mathematical morphology.
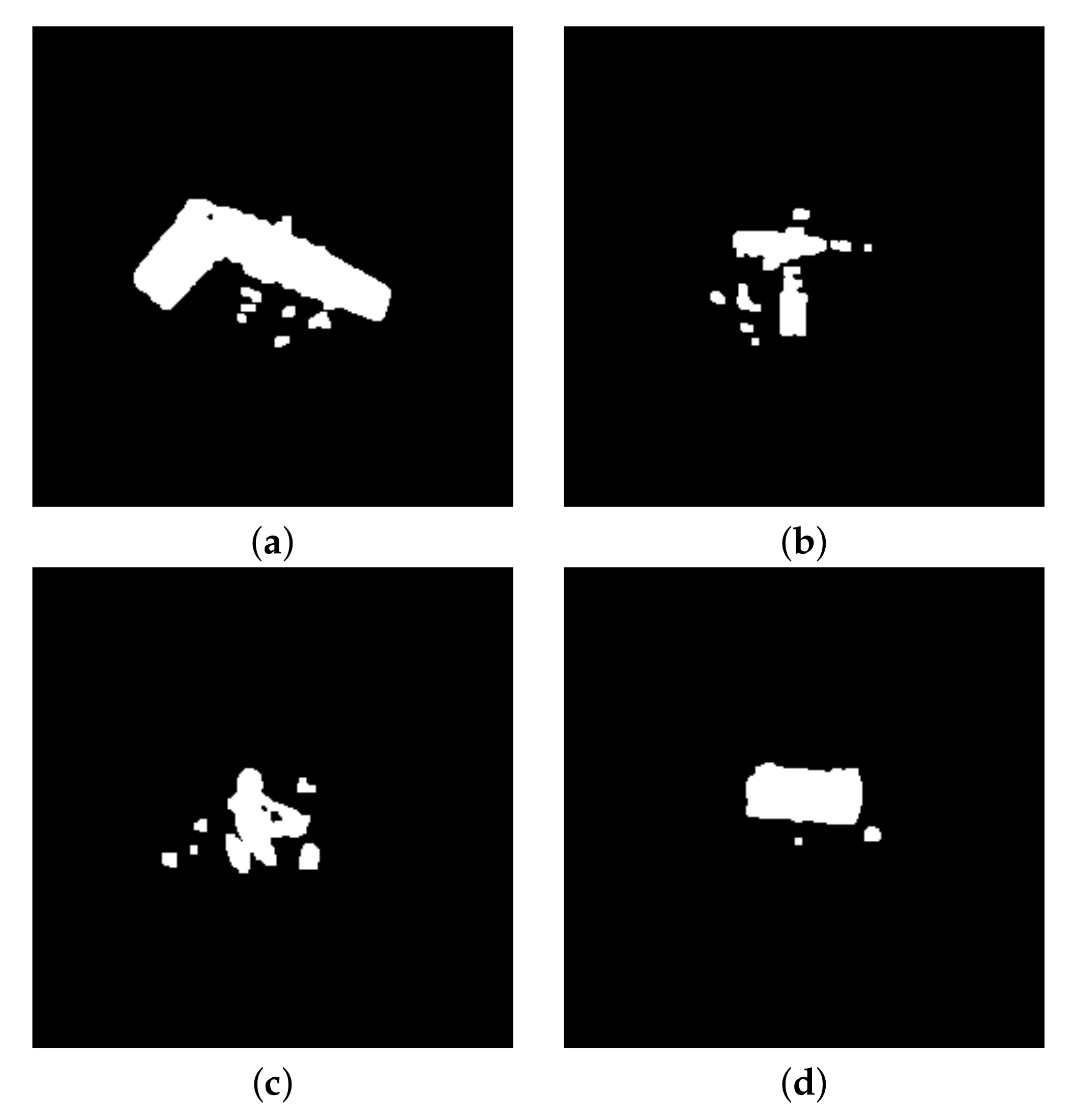
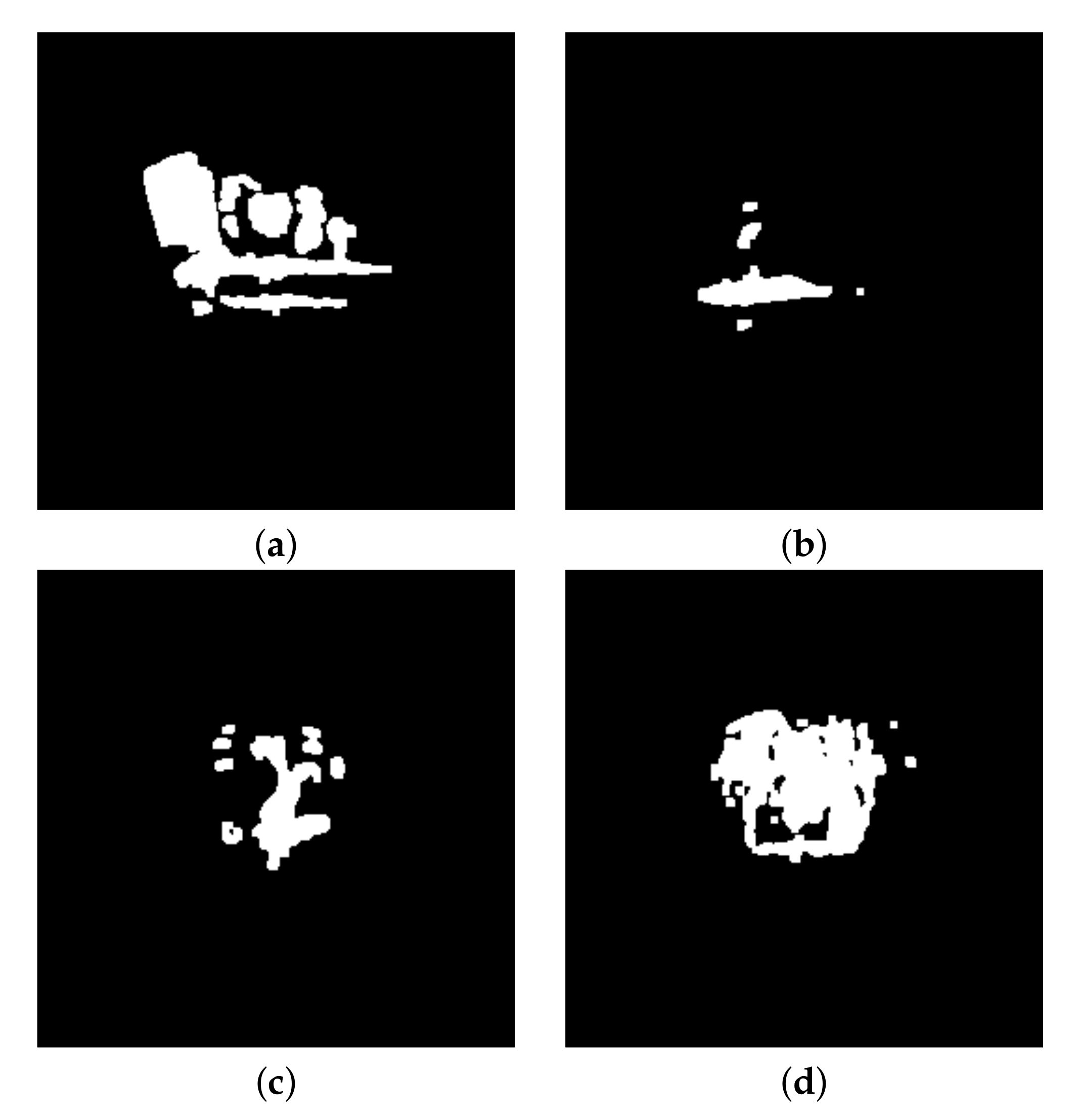
Figure 12.
Segmentation of ‘’ images, at frequency 94 GHz: (a) concealed gun, (b) knife, (c) keys, (d) smartphone.
Figure 12.
Segmentation of ‘’ images, at frequency 94 GHz: (a) concealed gun, (b) knife, (c) keys, (d) smartphone.
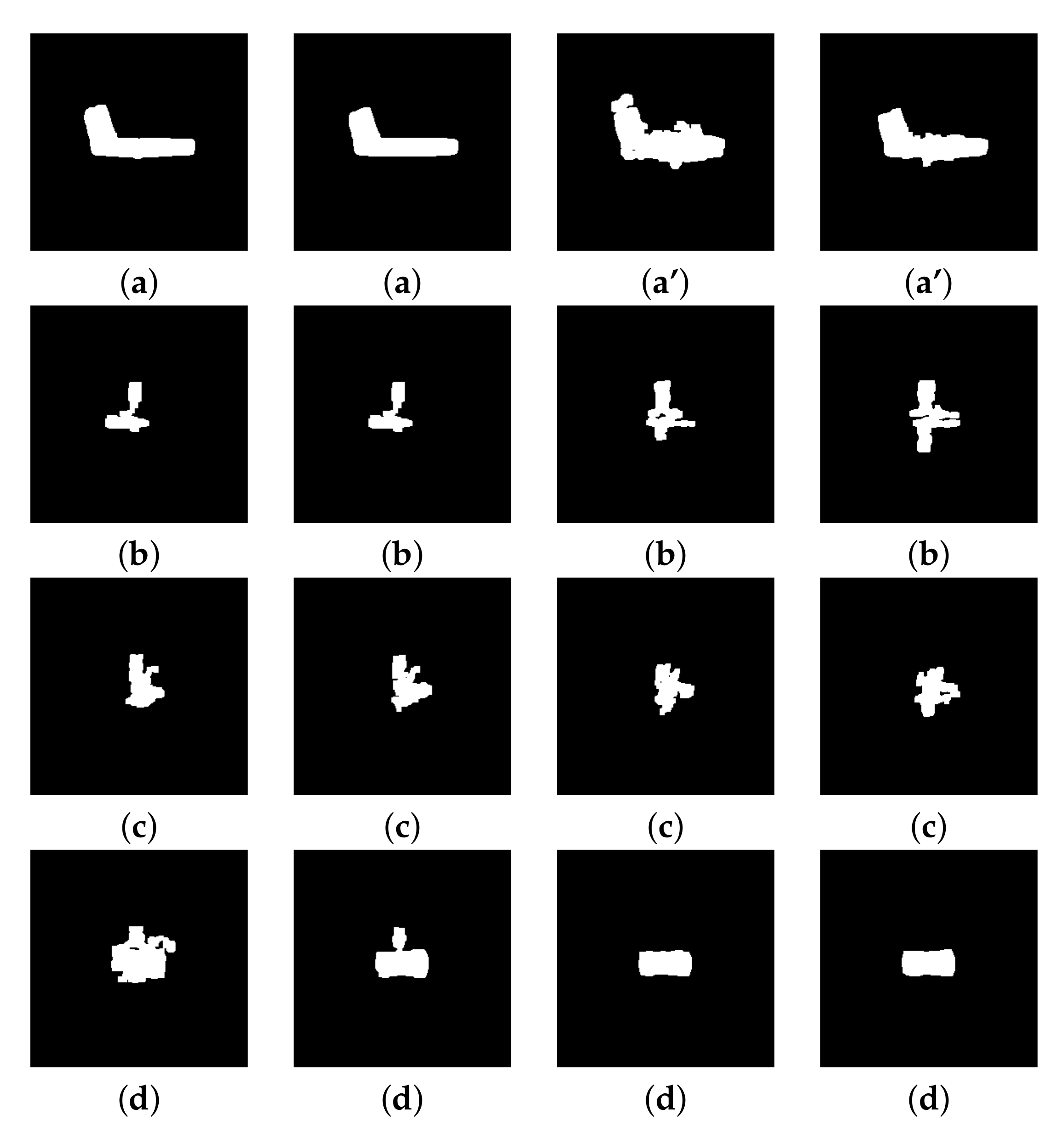
Figure 13.
Segmentation of ‘’ images, at frequency 94 GHz, with threshold parameter 0.87 and size 4 for the structuring element: (a) gun, (a’) concealed gun, (b) knife, (c) keys, (d) smartphone.
Figure 13.
Segmentation of ‘’ images, at frequency 94 GHz, with threshold parameter 0.87 and size 4 for the structuring element: (a) gun, (a’) concealed gun, (b) knife, (c) keys, (d) smartphone.
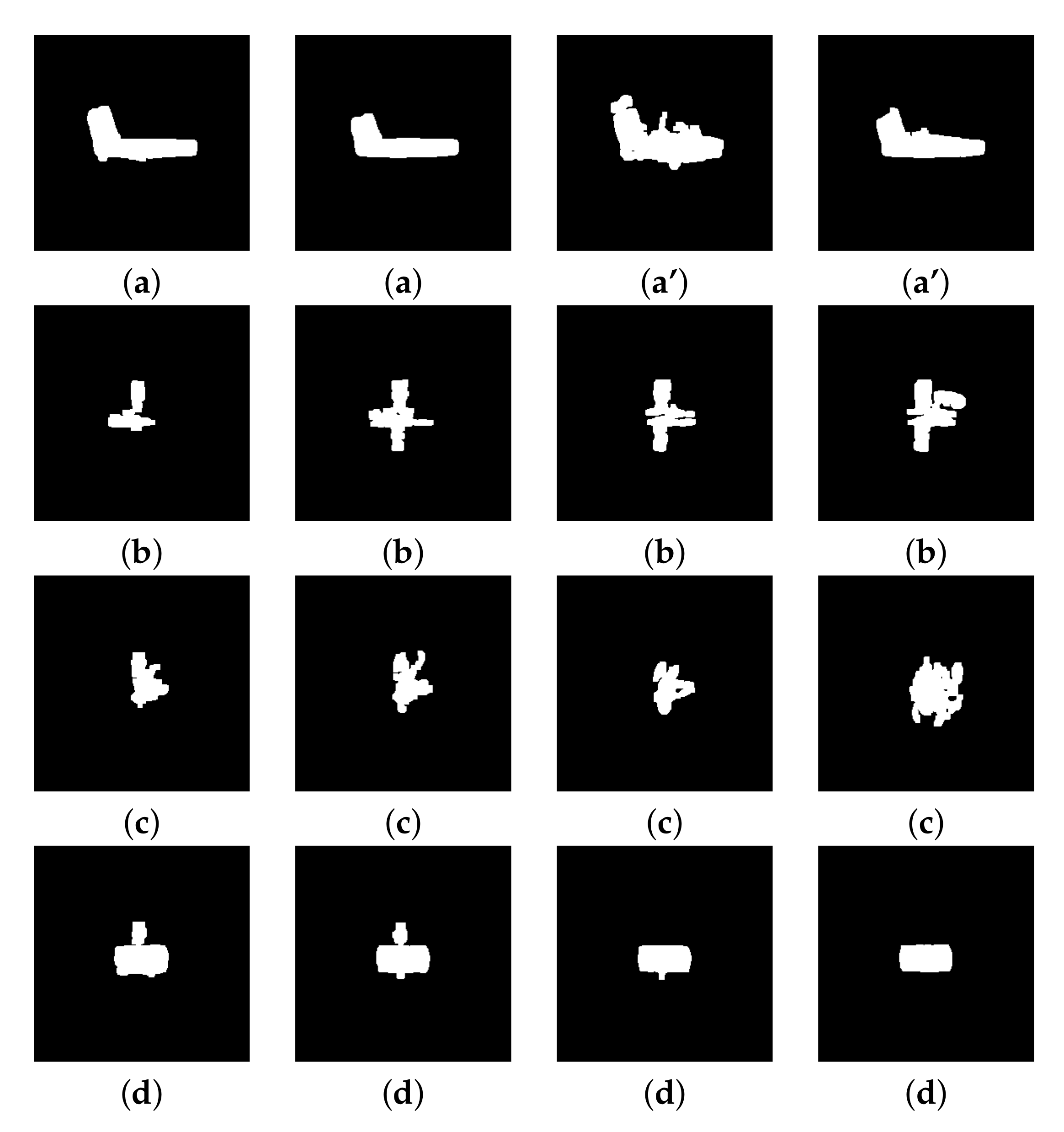
Figure 14.
Segmentation of ‘’ images, at frequency 94 GHz, with threshold parameter 0.59 and size 2 for the structuring element: (a) concealed gun, (b) knife, (c) keys, (d) smartphone.
Figure 14.
Segmentation of ‘’ images, at frequency 94 GHz, with threshold parameter 0.59 and size 2 for the structuring element: (a) concealed gun, (b) knife, (c) keys, (d) smartphone.
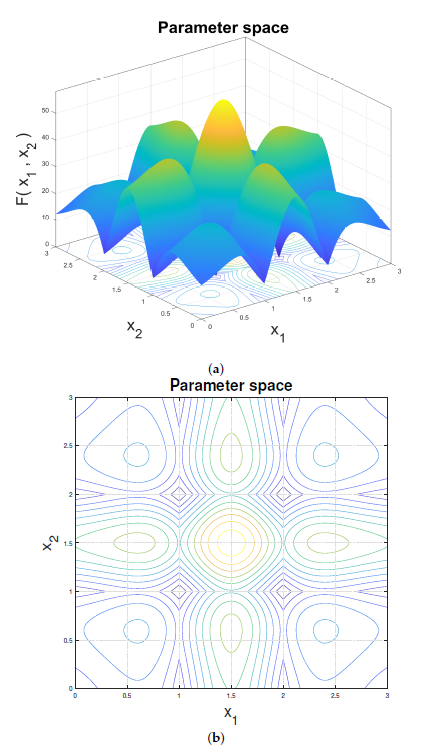
Figure 15.
Objective function: (a) 3D plot; (b) 2D plot.
Figure 15.
Objective function: (a) 3D plot; (b) 2D plot.
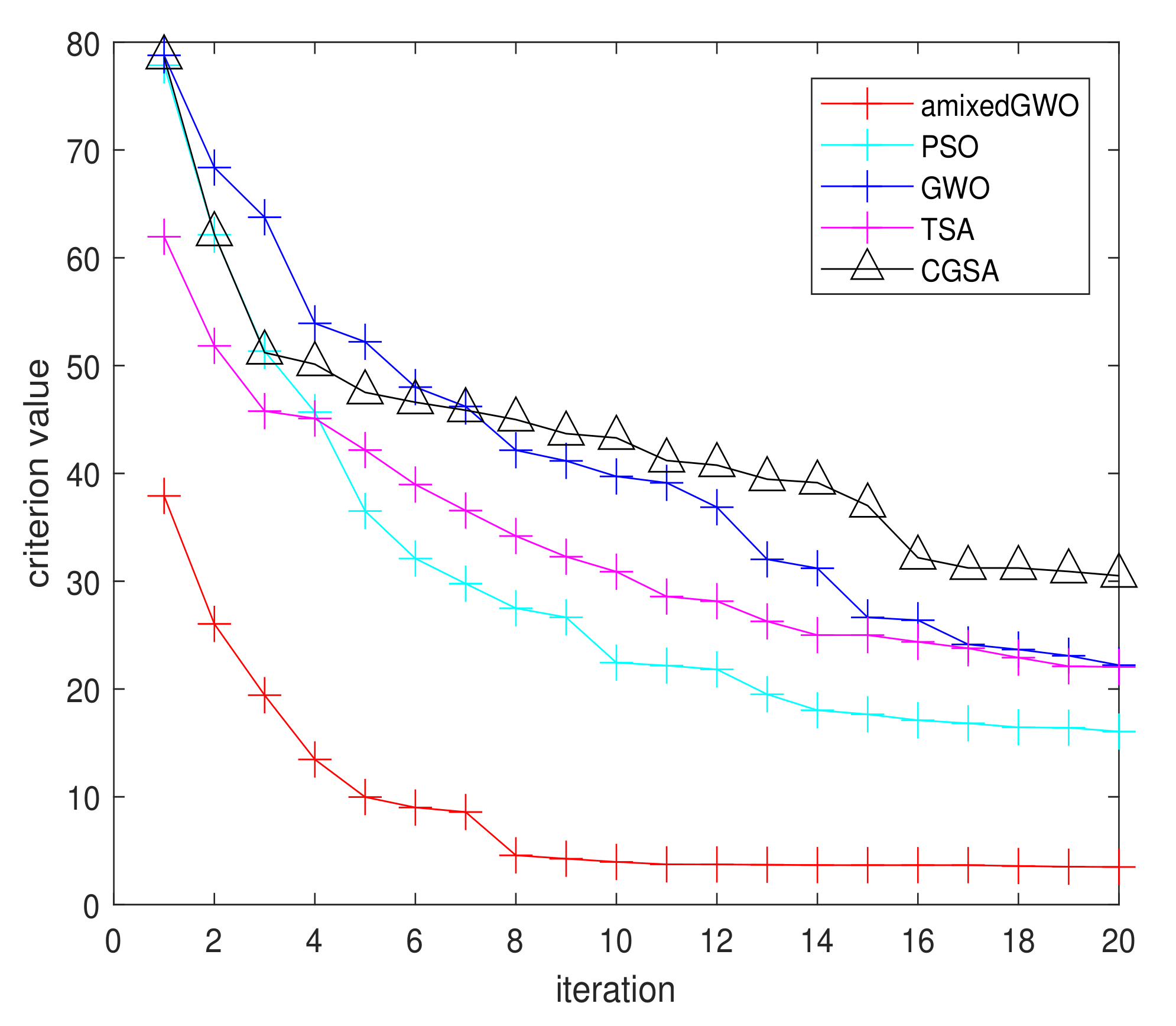
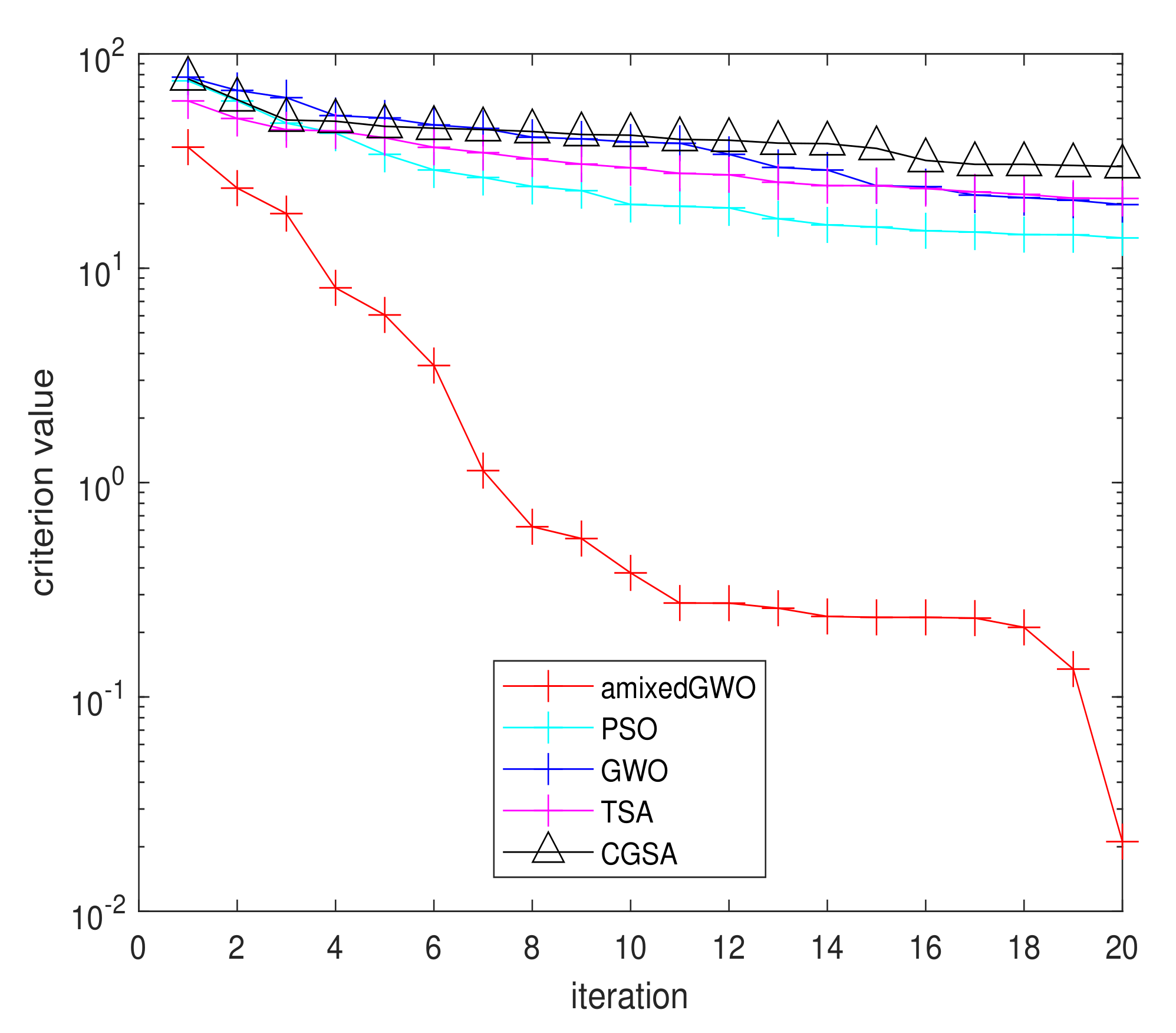
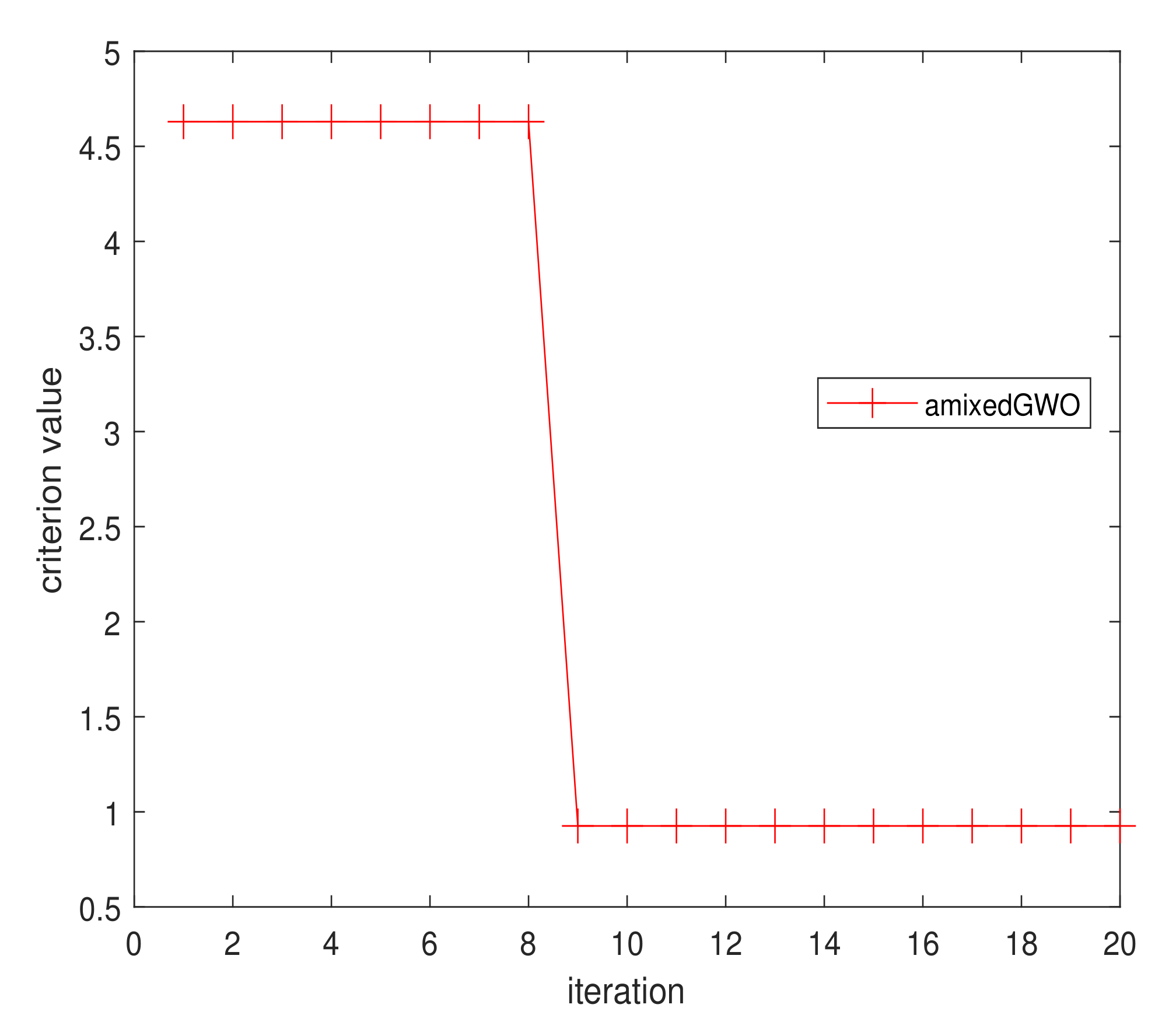
Figure 16.
Arithmetic mean of the convergence curves for amixedGWO, PSO, GWO, TSA, CGSA.
Figure 16.
Arithmetic mean of the convergence curves for amixedGWO, PSO, GWO, TSA, CGSA.
Figure 17.
Geometric mean (semi-log scale) of the convergence curves for amixedGWO, PSO, GWO, TSA, CGSA.
Figure 17.
Geometric mean (semi-log scale) of the convergence curves for amixedGWO, PSO, GWO, TSA, CGSA.
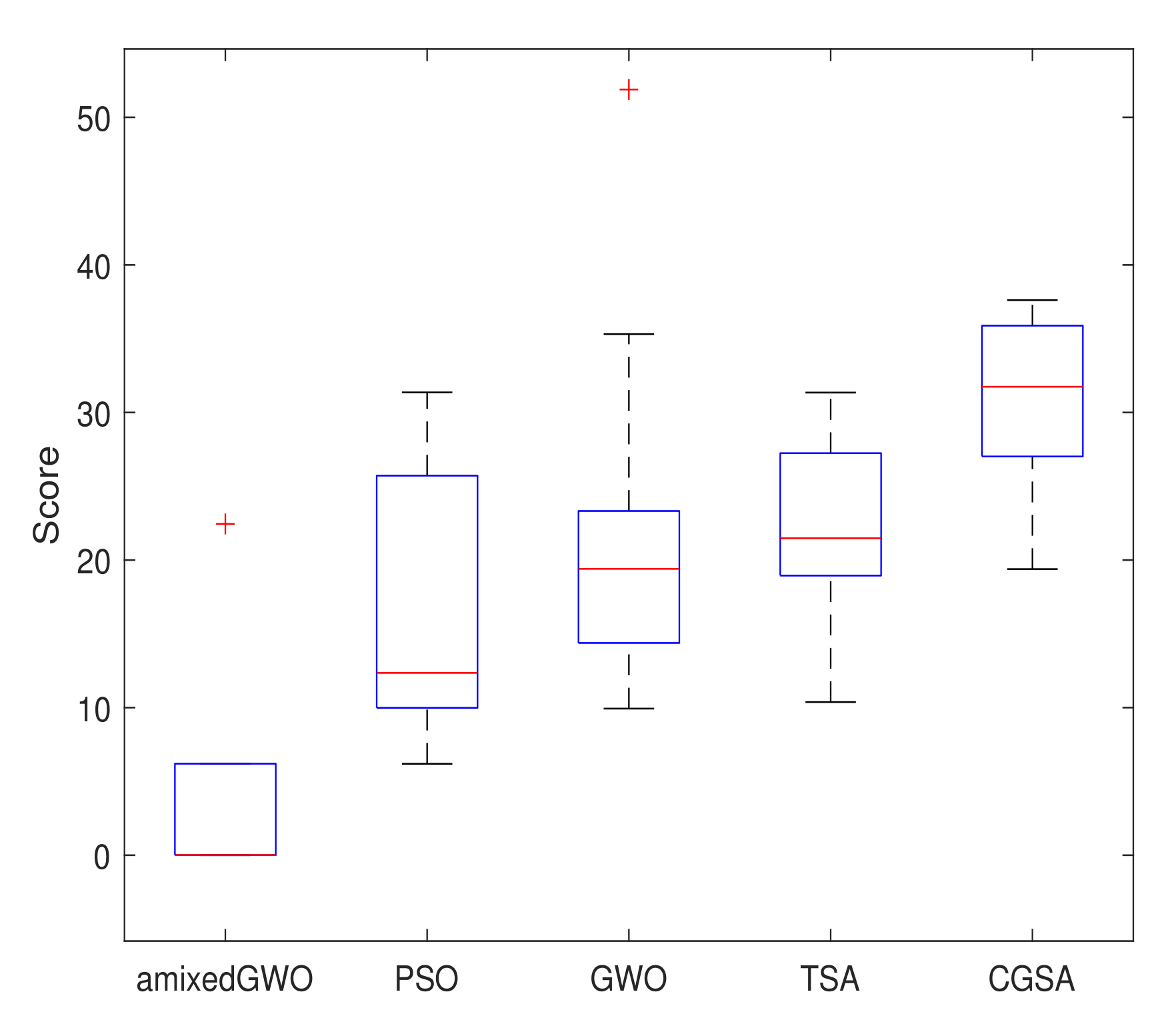
Figure 18.
Box plot of the performances for all methods.
Figure 18.
Box plot of the performances for all methods.
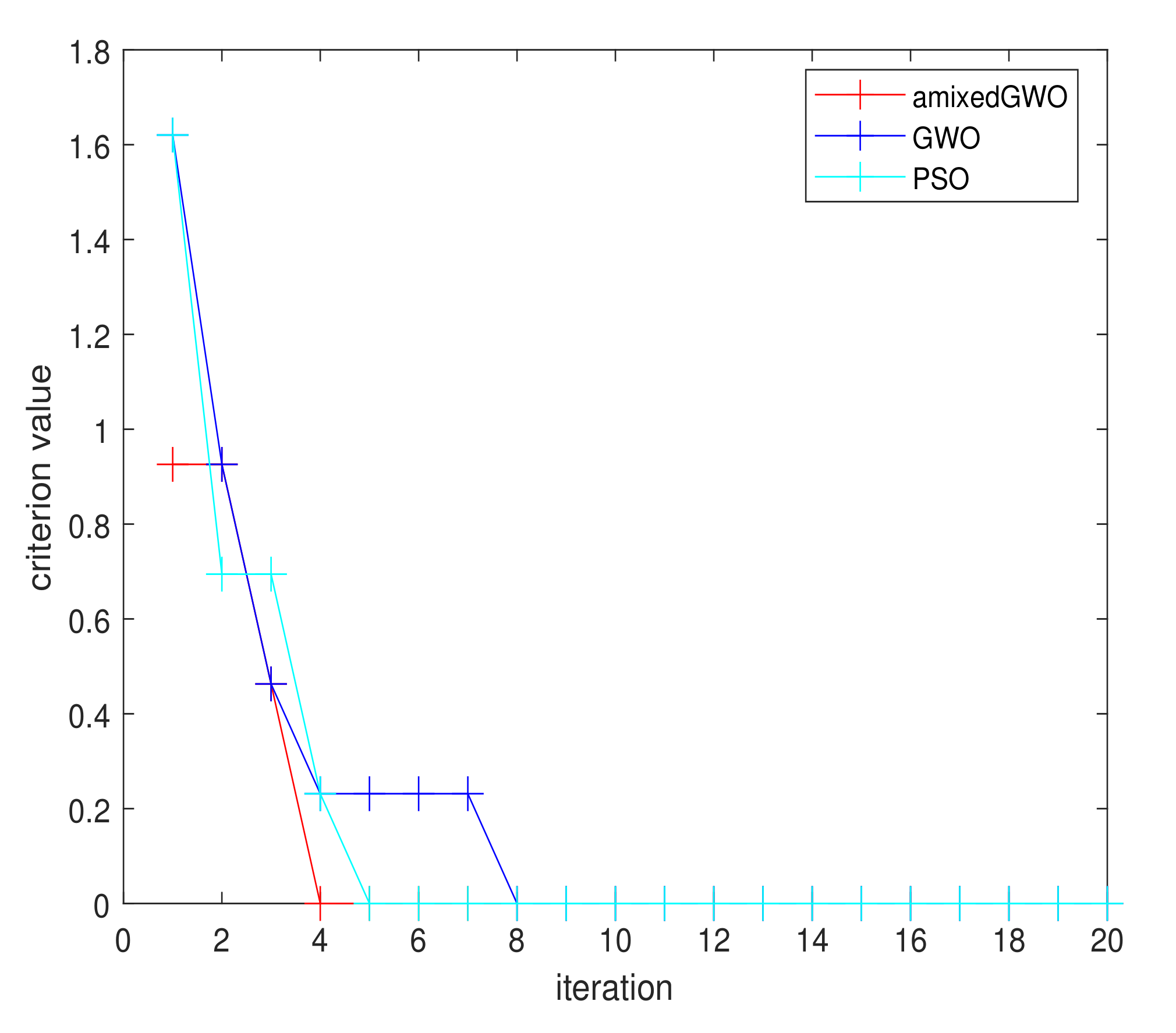
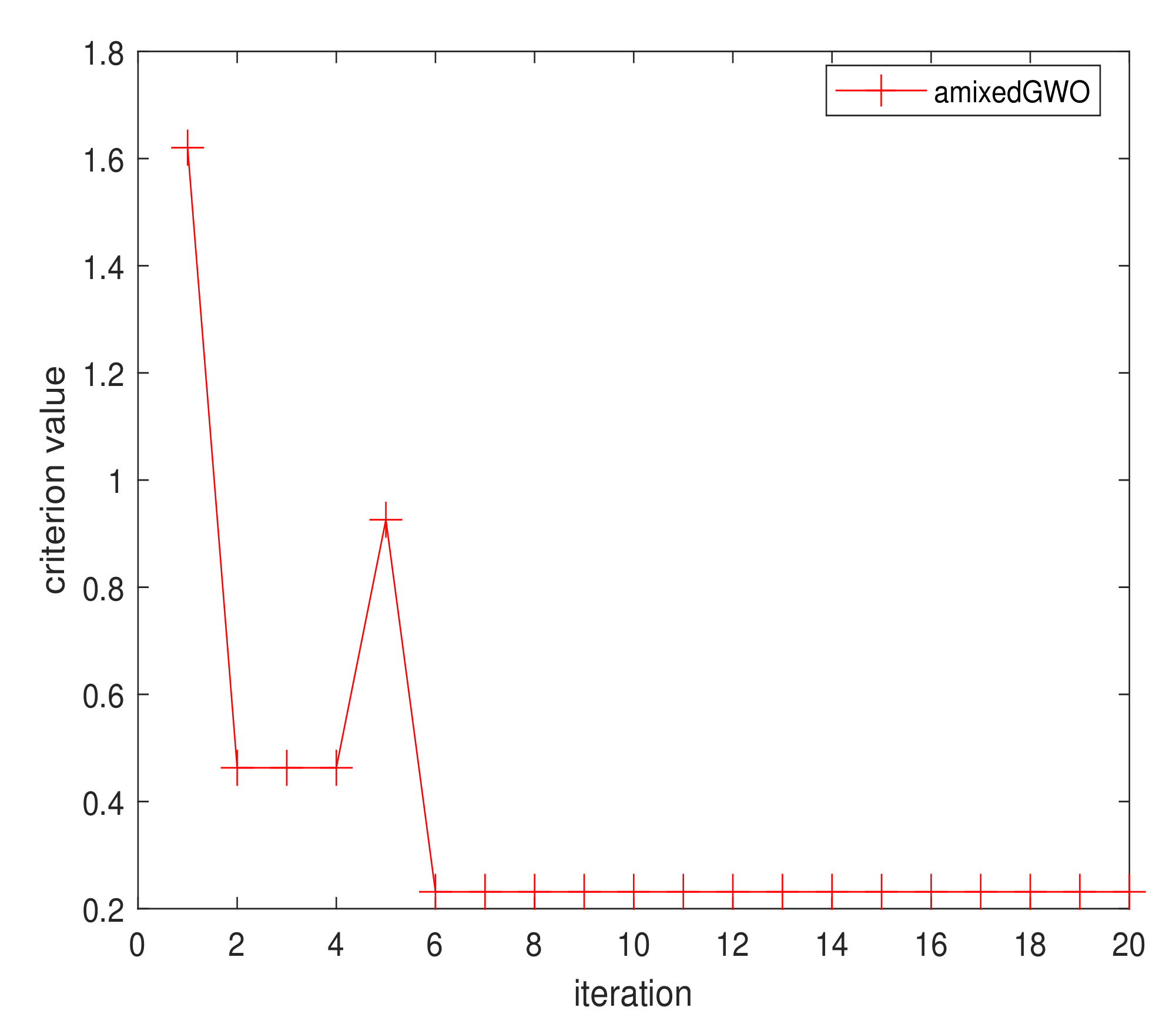
Figure 19.
Convergence curve for amixedGWO, PSO and GWO: 16 original acquisitions, 144 images in total.
Figure 19.
Convergence curve for amixedGWO, PSO and GWO: 16 original acquisitions, 144 images in total.
Figure 20.
Photographs of the acquisition principles: (a) small angle, (b) large angle.
Figure 20.
Photographs of the acquisition principles: (a) small angle, (b) large angle.
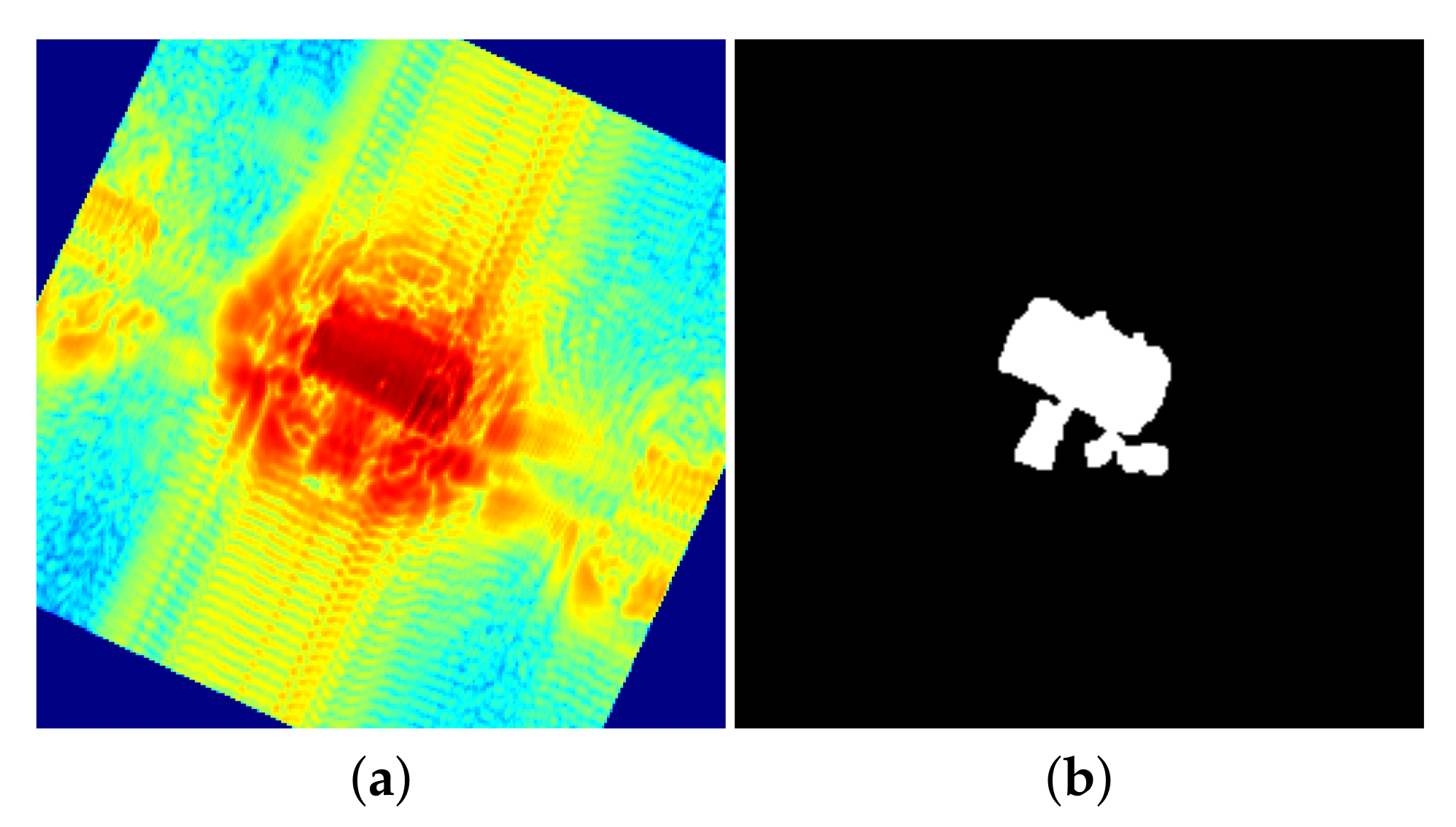
Figure 21.
Segmented acquisitions, large angle: (a) gun, (b) knife, (c) keys, (d) smartphone.
Figure 21.
Segmented acquisitions, large angle: (a) gun, (b) knife, (c) keys, (d) smartphone.
Figure 22.
Convergence curve for amixedGWO, 36 acquisitions.
Figure 22.
Convergence curve for amixedGWO, 36 acquisitions.
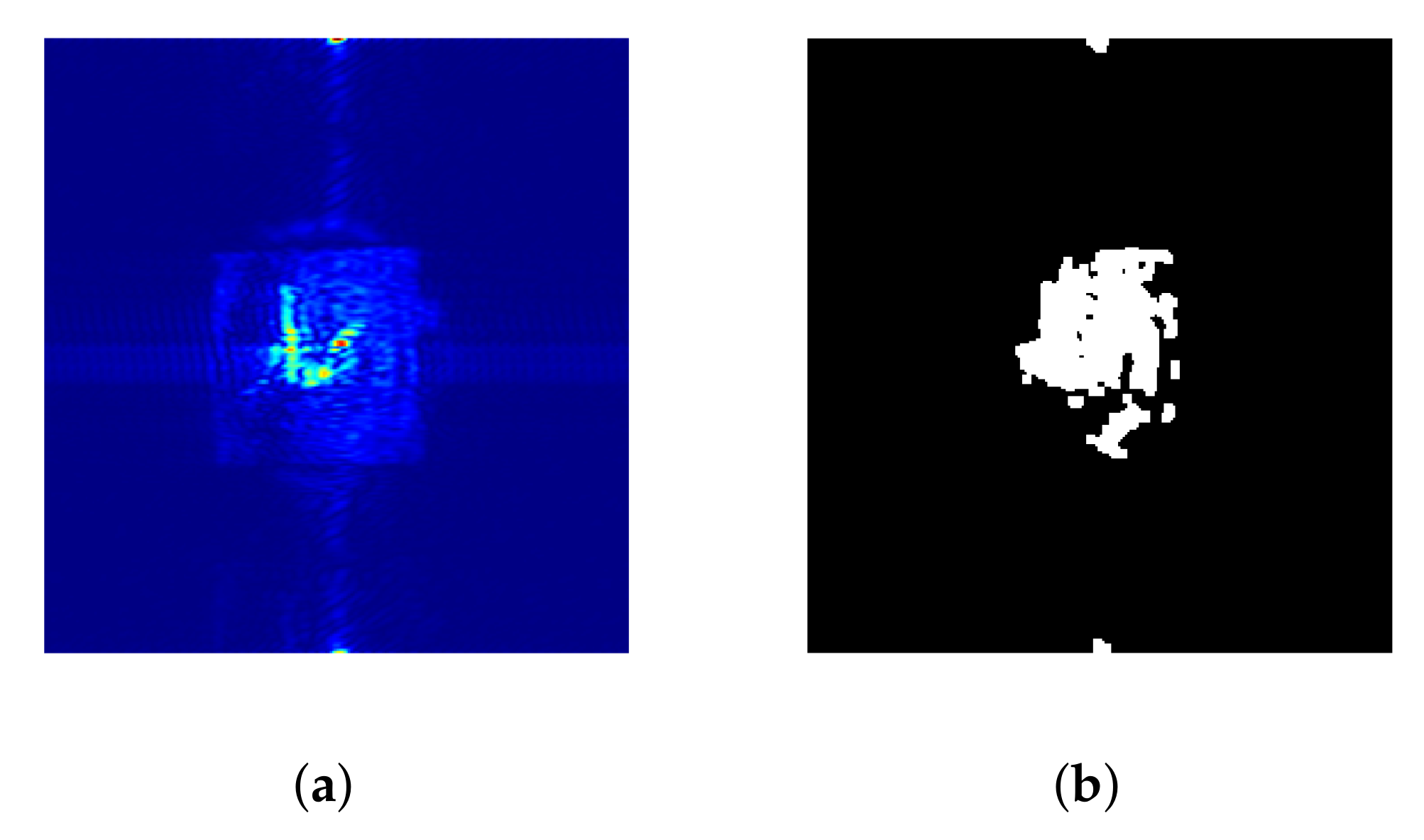
Figure 23.
Misclassified image of a set of keys: (a) RGB mmW scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 23.
Misclassified image of a set of keys: (a) RGB mmW scan; (b) Segmented image.
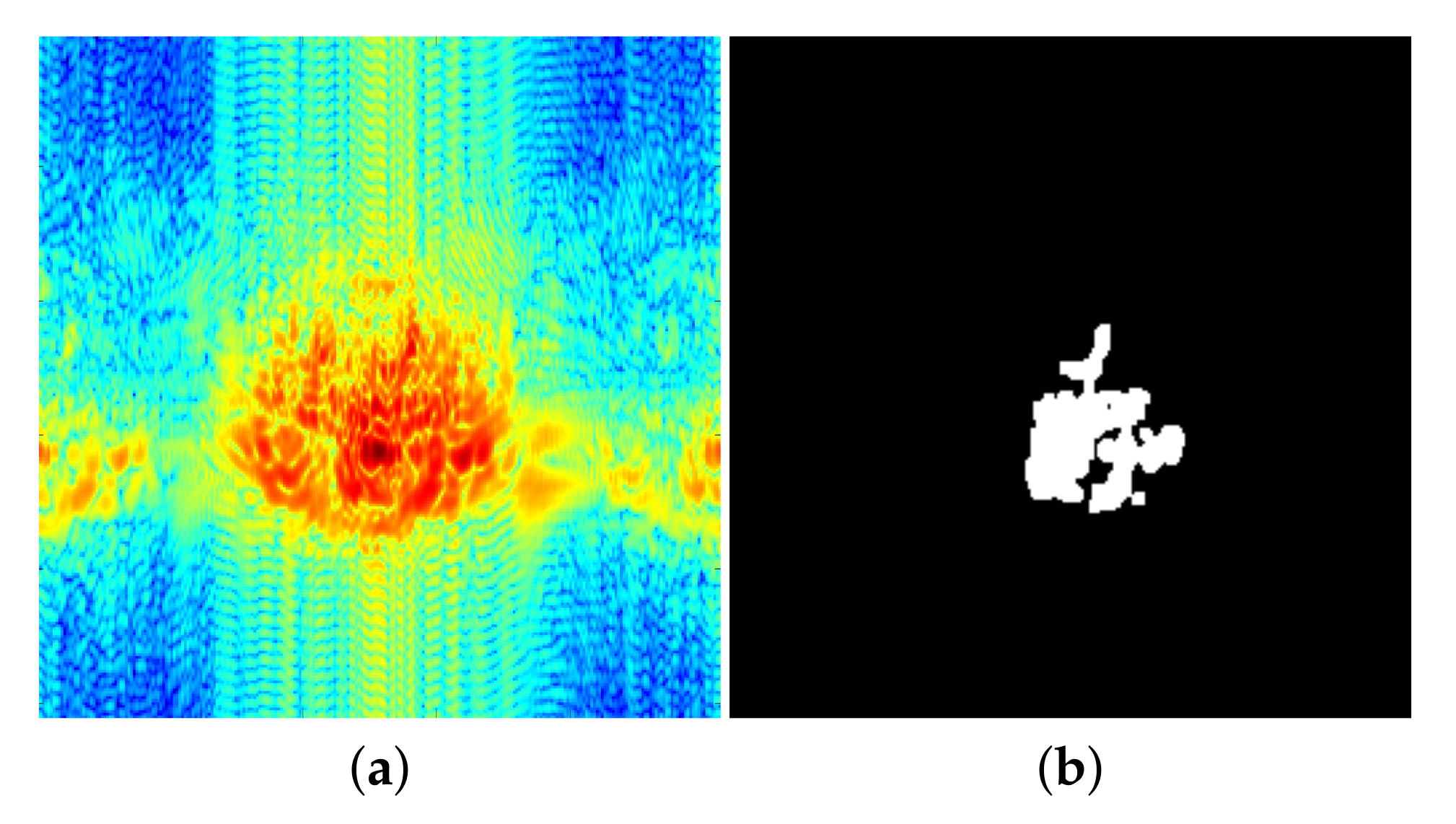
Figure 24.
Example of image of knife: (a) RGB mmW scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 24.
Example of image of knife: (a) RGB mmW scan; (b) Segmented image.
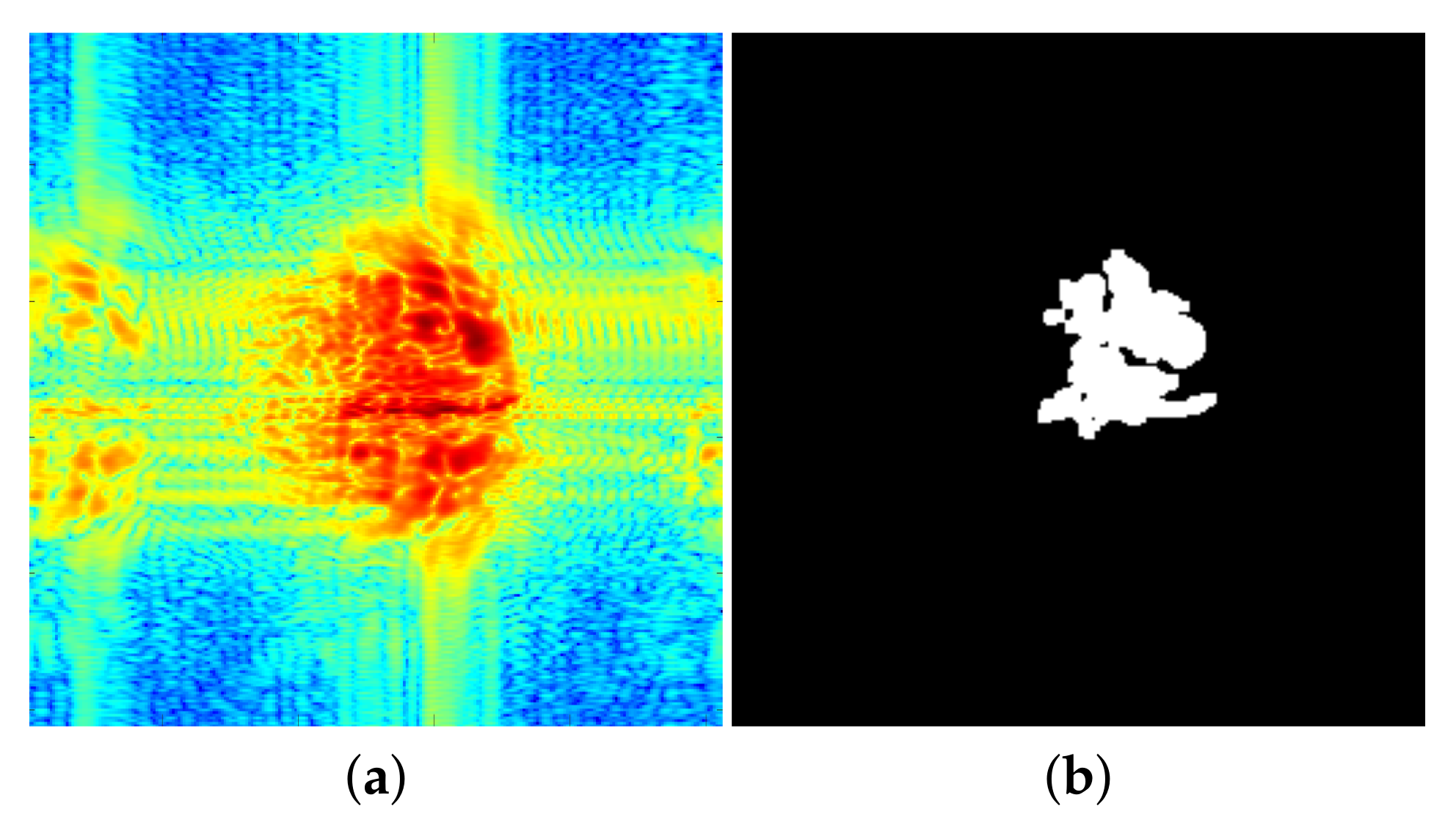
Figure 25.
Misclassified image of knife: (a) RGB mmW scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 25.
Misclassified image of knife: (a) RGB mmW scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 26.
Example of image of a smartphone: (a) RGB mmW scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 26.
Example of image of a smartphone: (a) RGB mmW scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 27.
Convergence curve for amixedGWO, with fixed frequency 92 GHz.
Figure 27.
Convergence curve for amixedGWO, with fixed frequency 92 GHz.
Figure 28.
New set of keys: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 28.
New set of keys: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 29.
Billfold: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 29.
Billfold: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 30.
Two knives: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 30.
Two knives: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 31.
Caliper: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 31.
Caliper: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 32.
Pliers: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 32.
Pliers: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 33.
Bracket: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Figure 33.
Bracket: (a) Scan; (b) Segmented image.
Table 1.
Codeword generated by the ECOC classifier for each class.
Table 1.
Codeword generated by the ECOC classifier for each class.
| Class | Codeword |
|---|
| class 1: guns | |
| class 2: kives | |
| class 3: licit | |
Table 2.
Number of missclassified images for various conditions for the acquisition and the procecessing of the radar images.
Table 2.
Number of missclassified images for various conditions for the acquisition and the procecessing of the radar images.
| | (Polarization, Frequency) | (H+V, 94) | (H, 94) | (V, 94) | (H+V, 96) | (H, 96) | (V, 96) |
|---|
| (Threshold Factor, Scale) | |
|---|
| (0.1, 1000) | 167 | 195 | 267 | 125 | 125 | 191 |
| (0.2, 100) | 37 | 43 | 53 | 67 | 53 | 76 |
| (0.4, 10) | 6 | 7 | 5 | 32 | 17 | 23 |
| (0.6, 1) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 10 | 4 |
| (0.8, 10) | 5 | 5 | 6 | 11 | 14 | 9 |
Table 3.
Search spaces for adaptive mixed GWO optimizer: parameter index vs. search space properties.
Table 3.
Search spaces for adaptive mixed GWO optimizer: parameter index vs. search space properties.
| i | | |
|---|
| 1 | 3 | |
| 2 | 2 | |
| 3 | | |
| 4 | 4 | |
| 5 | 3 | |
| 6 | 3 | |
| 7 | 4 | |
| 8 | 4 | |
Table 4.
Relevant figures computed over all experiments for all comparative methods on the obtained final scores: arithmetic mean, geometric mean, minimum value.
Table 4.
Relevant figures computed over all experiments for all comparative methods on the obtained final scores: arithmetic mean, geometric mean, minimum value.
| | Methods | amixedGWO | PSO | GWO | TSA | CGSA |
|---|
| Figures | |
|---|
| arithmetic mean | 3.49 | 16.05 | 22.21 | 22.04 | 30.50 |
| geometric mean | 2.11 × 10−2 | 13.84 | 19.80 | 21.15 | 29.79 |
| minimum value | 1.00 × 10−5 | 6.19 | 9.93 | 10.37 | 19.38 |
Table 5.
Confusion matrix of licit/non licit object classification.
Table 5.
Confusion matrix of licit/non licit object classification.
| Objects | Guns | Knives | Licit |
|---|
| Guns | 144 | 0 | 0 |
| Knives | 0 | 144 | 0 |
| Licit | 0 | 0 | 144 |
Table 6.
Number of misclassified images in various conditions, for a set of 432 images in total.
Table 6.
Number of misclassified images in various conditions, for a set of 432 images in total.
| | Polarization | ‘H + V’ | ‘H’ | ‘V’ |
|---|
| Kernel | |
|---|
| linear | 9 | 1 | 2 |
| rbf | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| polynomial | 2 | 3 | 0 |
Table 7.
Number of misclassified images in various conditions, for a set of 432 images in total.
Table 7.
Number of misclassified images in various conditions, for a set of 432 images in total.
| | Polarization | ‘H + V’ | ‘H’ | ‘V’ |
|---|
| (Threshold, Factor) | |
|---|
| (0.4, sd) | 32 | 25 | 18 |
| (0.6, Z) | 3 | 0 | 8 |
| (0.8, comb) | 3 | 1 | 3 |
Table 8.
Number of missclassified images out of 54 images for various system configurations and testing conditions.
Table 8.
Number of missclassified images out of 54 images for various system configurations and testing conditions.
| | Learning Conditions | Amixed GWO
Equation (10) | PSO
Equation (11) | GWO
Equation (12) |
|---|
| Experiment | |
|---|
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
Table 9.
Confusion matrix of lethal/licit object classification.
Table 9.
Confusion matrix of lethal/licit object classification.
| Objects | Guns | Knives | Licit |
|---|
| Guns | 36 | 0 | 0 |
| Knives | 0 | 36 | 0 |
| Licit | 0 | 1 | 35 |
Table 10.
Statistical study: number of misclassifications vs. counts, for 1000 counts in total.
Table 10.
Statistical study: number of misclassifications vs. counts, for 1000 counts in total.
| Number of Misclassified Images | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Counts | 0 | 392 | 0 | 385 | 96 | 79 | 27 | 18 | 0 | 3 |
Table 11.
Confusion matrix of licit/non licit object classification, for the best parameters at frequency 92 GHz.
Table 11.
Confusion matrix of licit/non licit object classification, for the best parameters at frequency 92 GHz.
| Objects | Guns | Knives | Licit |
|---|
| Guns | 144 | 0 | 0 |
| Knives | 0 | 143 | 1 |
| Licit | 0 | 0 | 144 |
Table 12.
Confusion matrix for additional objects; test phase only; 9 images among which 8 obtained by bootstrap.
Table 12.
Confusion matrix for additional objects; test phase only; 9 images among which 8 obtained by bootstrap.
| | Predicted Class | Gun | Knife | Licit |
|---|
| Tested Objects | |
|---|
| new set of keys | 0 | 4 | 5 |
| billfold | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| two knives | 0 | 3 | 6 |
| caliper | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| pliers | 1 | 8 | 0 |
| bracket | 7 | 2 | 0 |
Table 13.
Confusion matrix for additional objects; cross-validation and test phase; 9 images among which 8 obtained by bootstrap.
Table 13.
Confusion matrix for additional objects; cross-validation and test phase; 9 images among which 8 obtained by bootstrap.
| | Predicted Class | Gun | Knife | Licit |
|---|
| Tested Objects | |
|---|
| new set of keys | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| billfold | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| two knives | 0 | 7 | 2 |
| caliper | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| pliers | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| bracket | 4 | 0 | 5 |