Mapping Paddy Rice Fields by Combining Multi-Temporal Vegetation Index and Synthetic Aperture Radar Remote Sensing Data Using Google Earth Engine Machine Learning Platform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
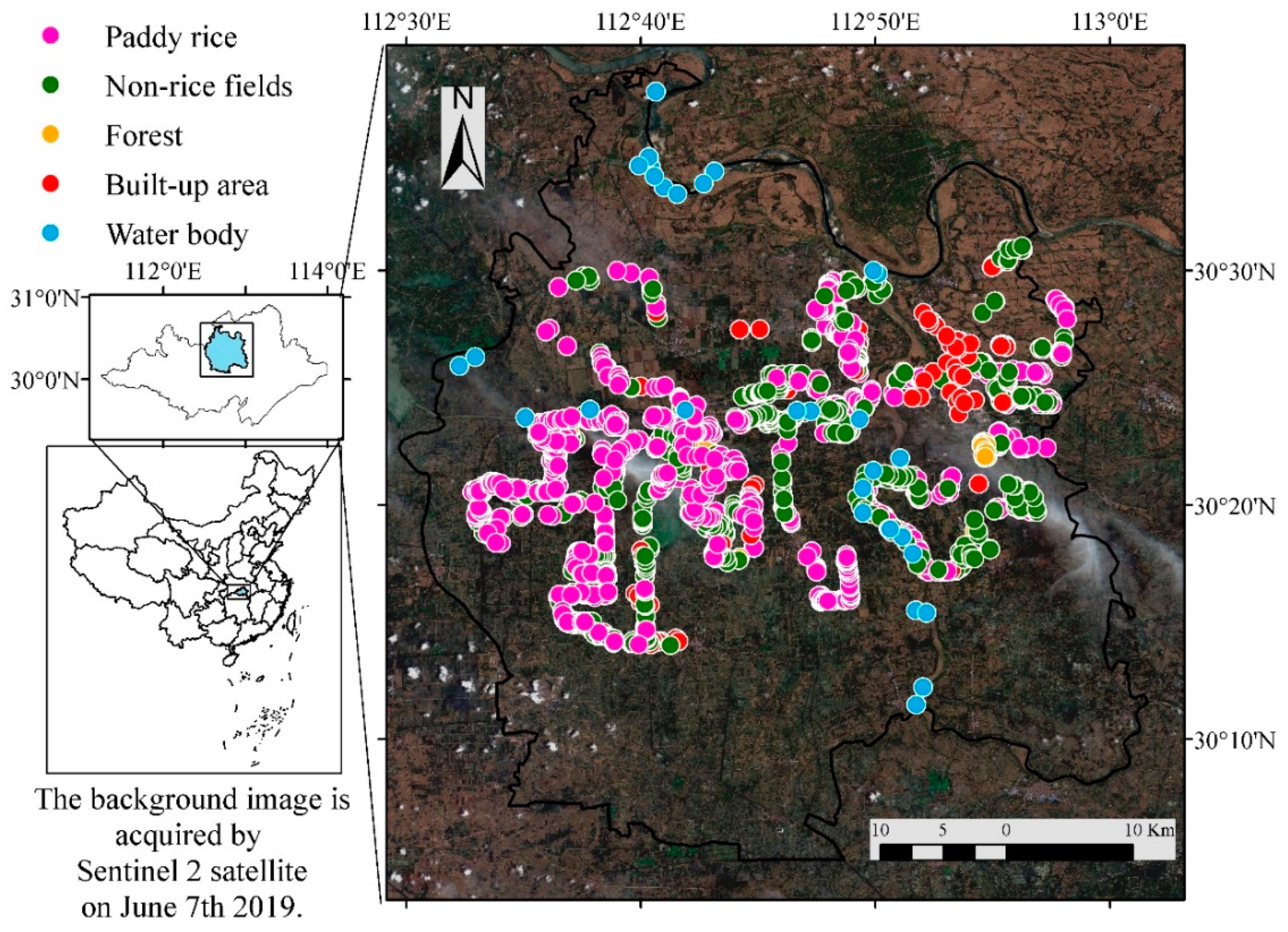
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets and Pre-Processing
2.2.1. Sentinel Data
2.2.2. Field Samples
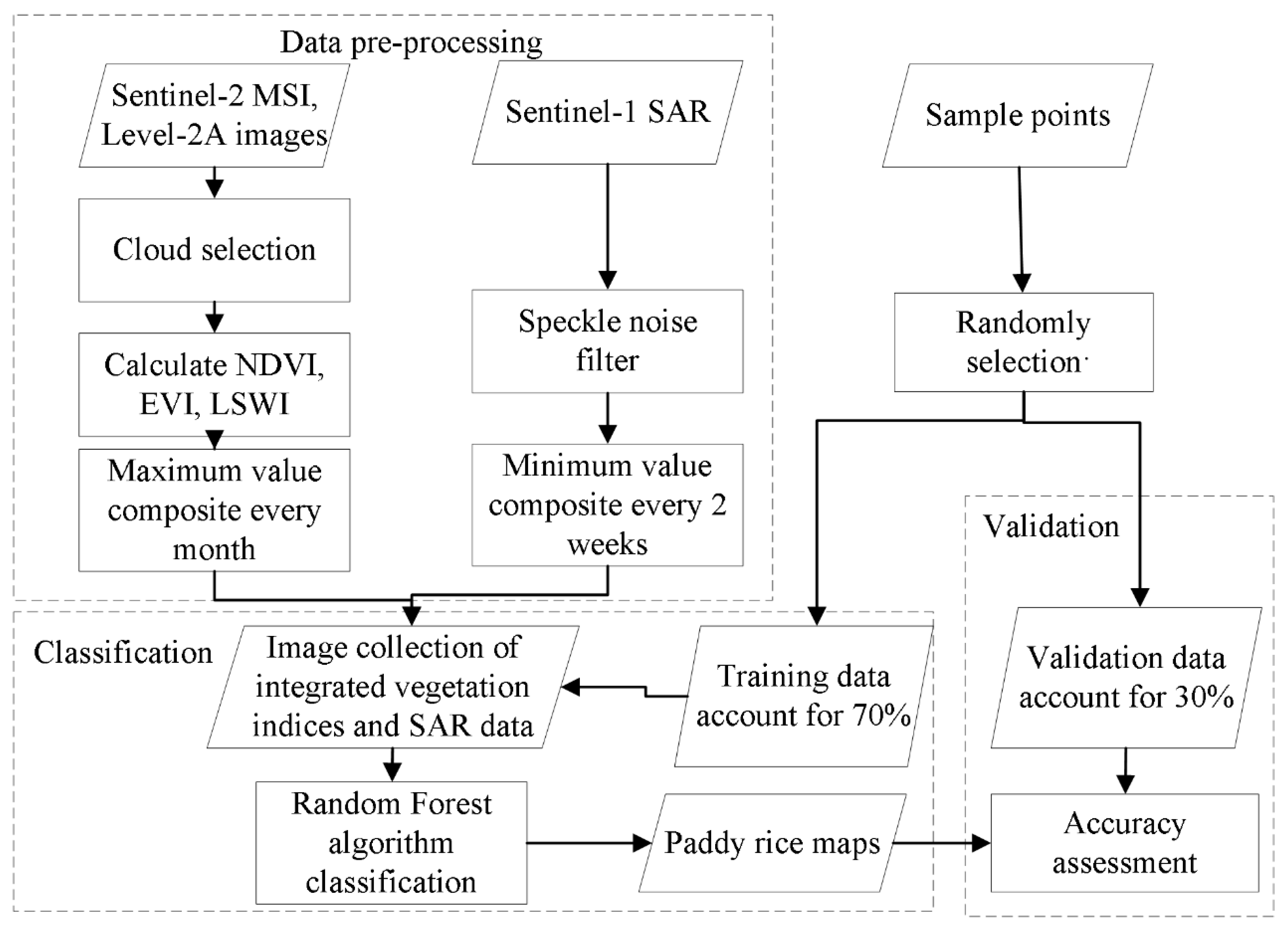
2.2.3. Methodology
3. Result
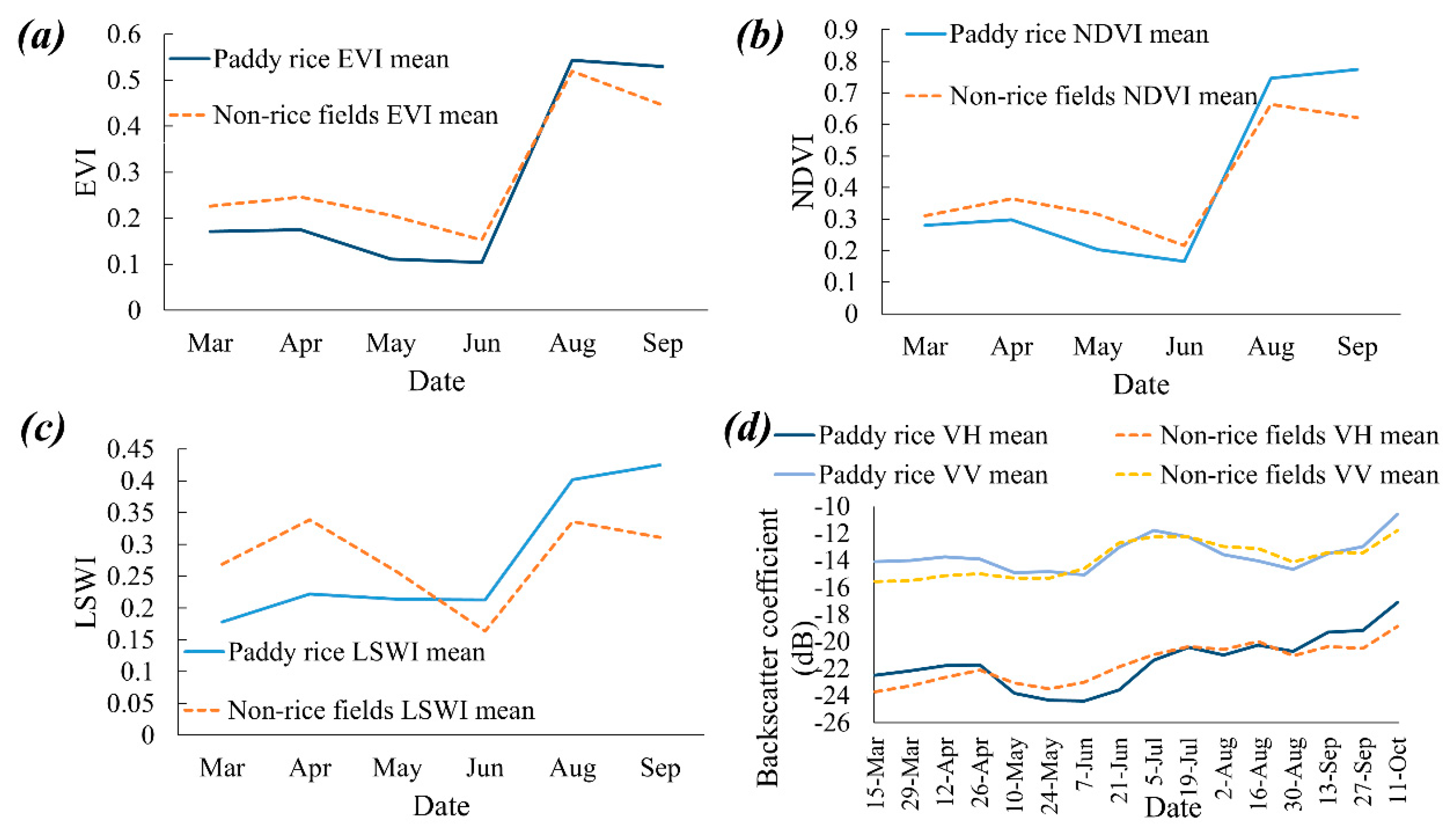
3.1. NDVI, LSWI, and EVI Results
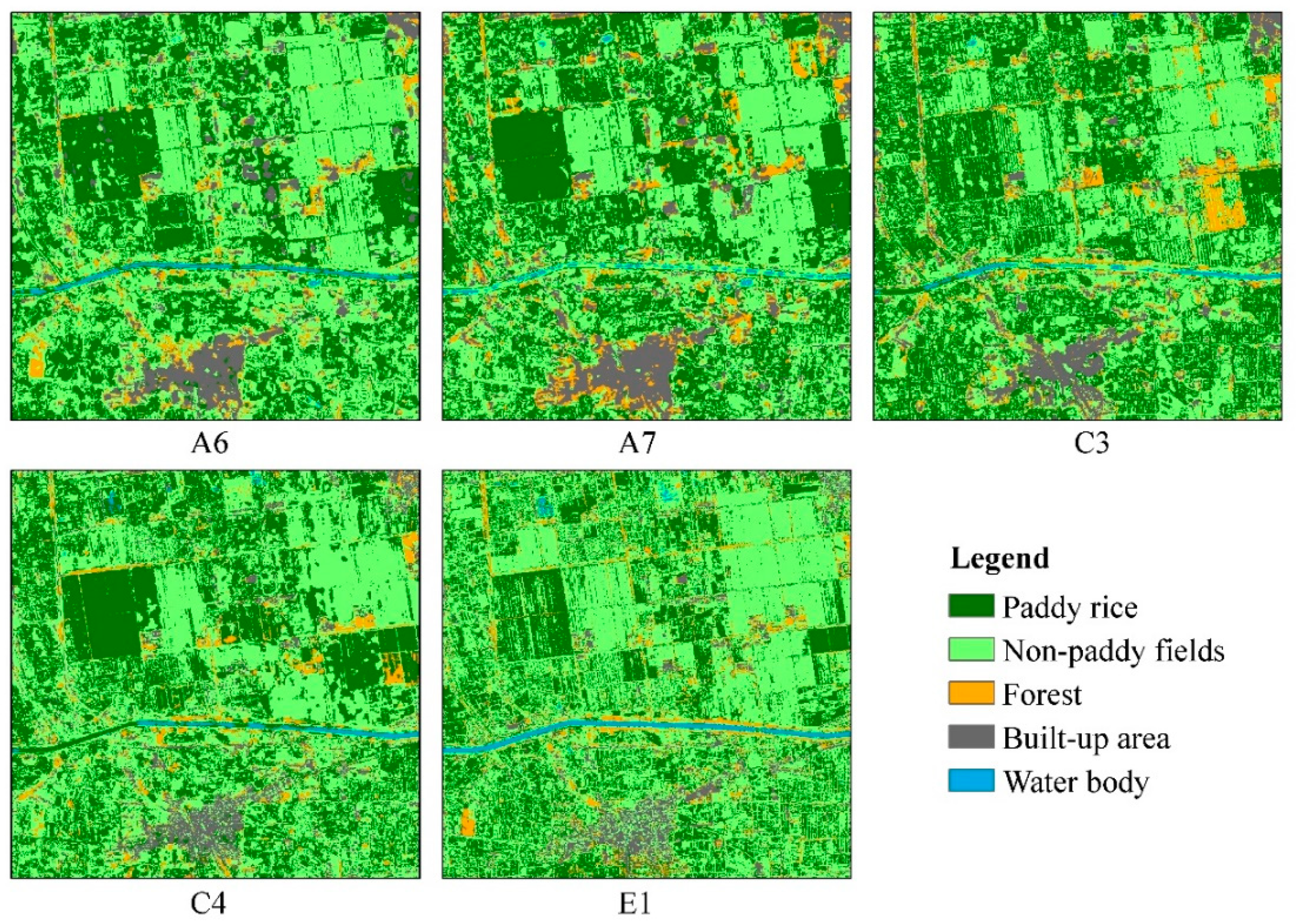
3.2. Paddy Rice Mapping Results
3.3. Variable Importance Results
4. Discussions
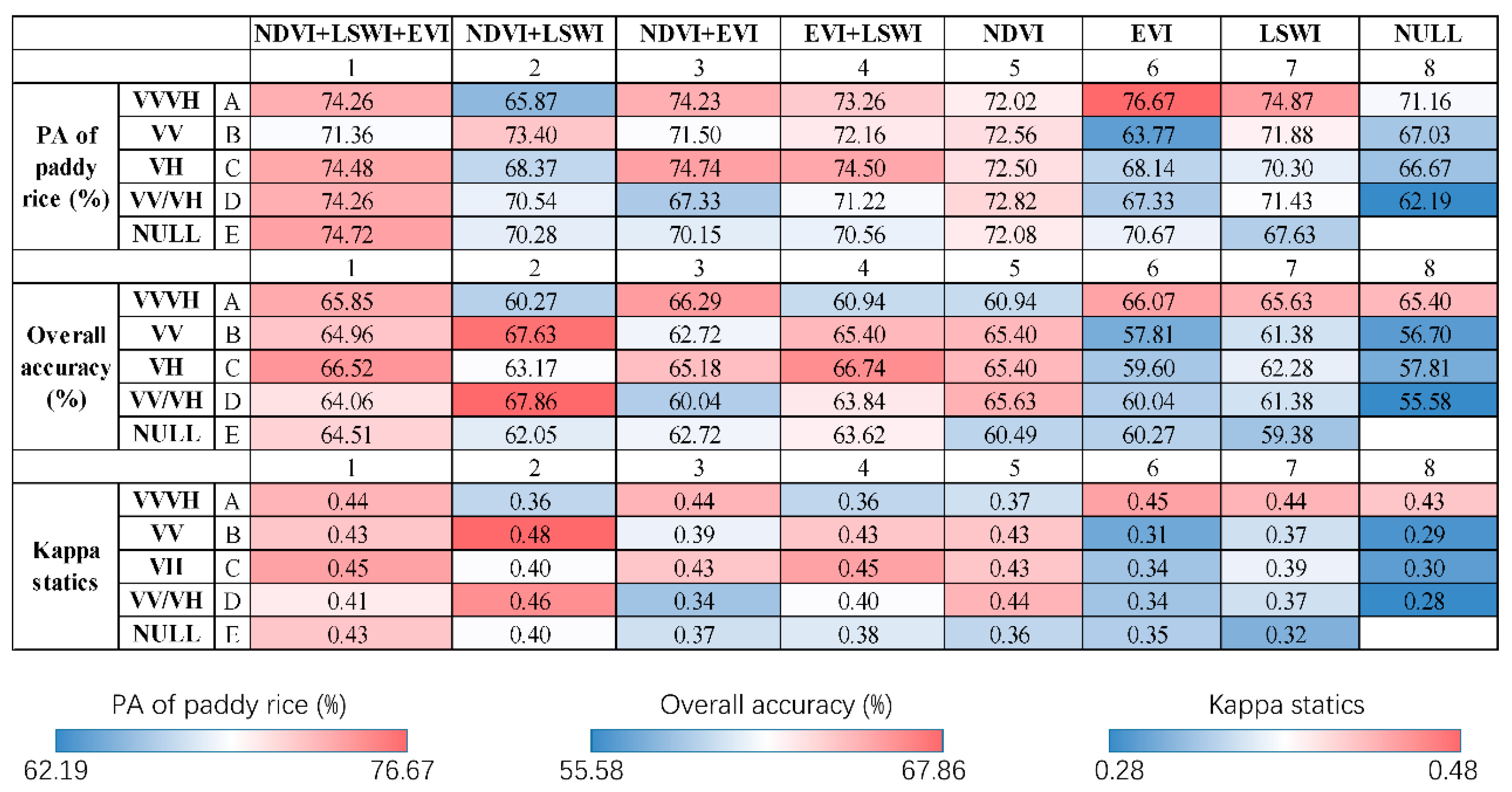
4.1. Classification Improvement by Integrating SAR Data
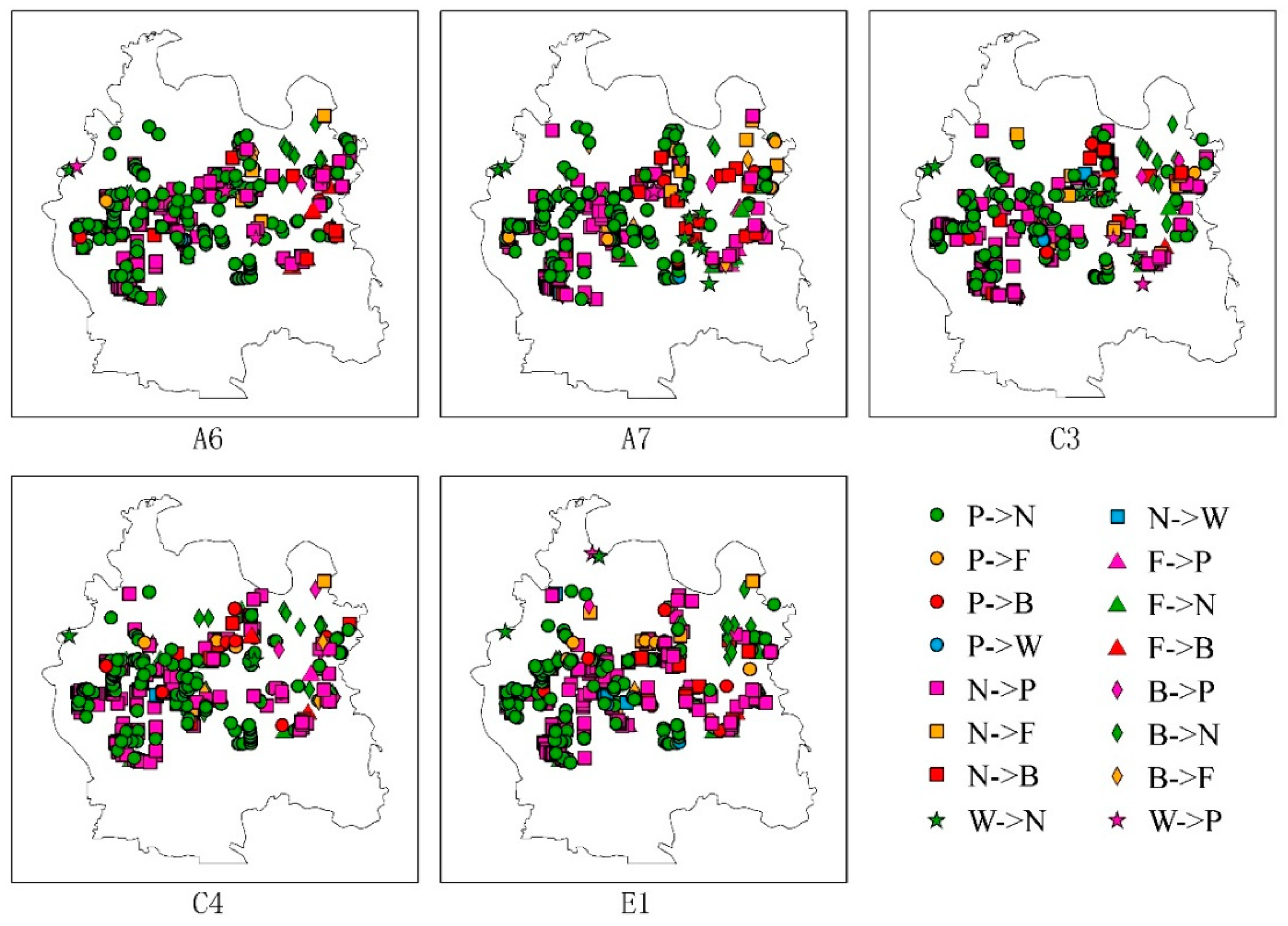
4.2. Error Analysis for Different Data Combinations
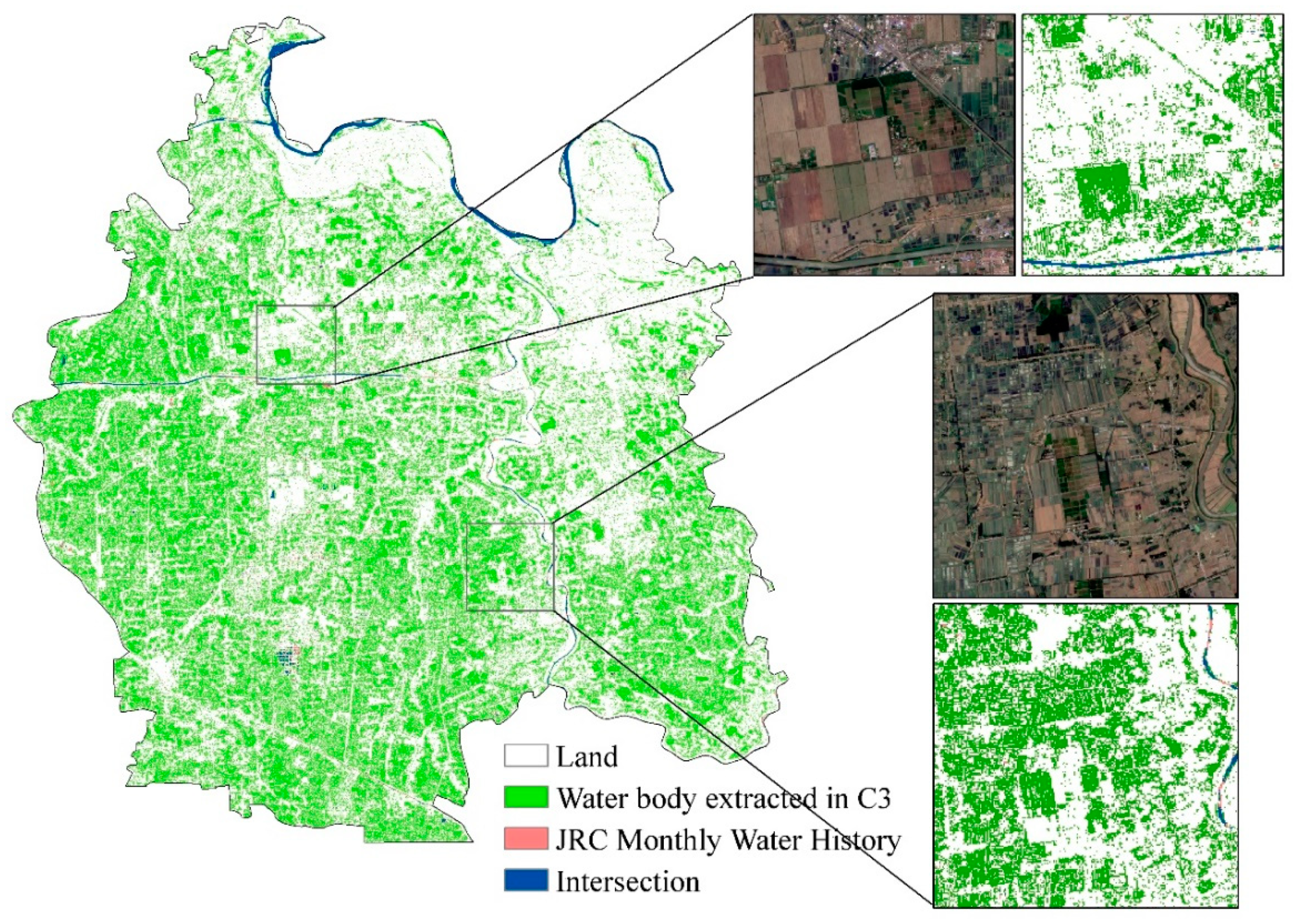
4.3. Comparison with a Current Water Body Product
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maclean, J.L.; Dawe, D.C.; Hardy, B.; Hettel, G.P. Rice Almanac: Source Book for the Most Important Economic Activity on Earth; Int. Rice Res. Inst.: Los Baños, Philippines, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bouman, B. How much water does rice use? Rice Today 2009, 8, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Ren, J.; Tang, H.; Shi, Y.; Liu, J. Progress and perspectives on agricultural remote sensing research and applications in China. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 748–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumma, M.K.; Nelson, A.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Singh, A.N. Mapping rice areas of South Asia using MODIS multitemporal data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2011, 5, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Li, W.; Tang, Z.; Chen, C.; Qi, W. Mapping paddy rice areas based on vegetation phenology and surface moisture conditions. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 56, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; McIver, D.K.; Hodges, J.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Muchoney, D.; Strahler, A.H.; Woodcock, C.E.; Gopal, S.; Schneider, A.; Cooper, A.; et al. Global land cover mapping from MODIS: Algorithms and early results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicheron, P.; Defourny, P.; Brockmann, C.; Schouten, L.; Vancutsem, C.; Huc, M.; Bontemps, S.; Leroy, M.; Achard, F.; Herold, M.; et al. GLOBCOVER: Products Description and Validation Report. 2008. Available online: http://due.esrin.esa.int/page_globcover.php (accessed on 29 July 2020).
- Frolking, S.; Qiu, J.; Boles, S.; Xiao, X.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, C.; Qin, X. Combining remote sensing and ground census data to develop new maps of the distribution of rice agriculture in China. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 38-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfreda, C.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Farming the planet: 2. Geographic distribution of crop areas, yields, physiological types, and net primary production in the year 2000. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloy, K.R.; Smith, F.R.; Robinson, M.R. Monitoring rice areas using LANDSAT MSS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1987, 8, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.P.N.; Rao, V.R. Rice crop identification and area estimation using remotely-sensed data from Indian cropping patterns. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1987, 8, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H. Rice crop area estimation of an administrative division in China using remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 3411–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguro, Y.; Suga, Y.; Takeuchi, S.; Ogawa, M.; Konishi, T.; Tsuchiya, K. Comparison of SAR and optical sensor data for monitoring of rice plant around Hiroshima. Adv. Space Res. 2001, 28, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.-Z.; Uchida, S.; Liang, Y.; Hirano, A.; Sun, B. Discriminating different landuse types by using multitemporal NDXI in a rice planting area. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; De Bie, C.A.J.M.; Ali, A.; Smaling, E.M.A.; Chu, T.H. Mapping the irrigated rice cropping patterns of the Mekong delta, Vietnam, through hyper-temporal SPOT NDVI image analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Salas, W.; Moore, B.; Li, C.; He, L.; Zhao, R. Observation of flooding and rice transplanting of paddy rice fields at the site to landscape scales in China using VEGETATION sensor data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3009–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; van Phung, C.; Kotera, A.; Nguyen, K.D.; Yokozawa, M. Analysis of rapid expansion of inland aquaculture and triple rice-cropping areas in a coastal area of the Vietnamese Mekong Delta using MODIS time-series imagery. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-S.; Huang, J.-F.; Huete, A.R.; Peng, D.-L.; Zhang, F. Mapping paddy rice with multi-date moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) data in China. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 2009, 10, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbick, N.; Salas, W.A.; Hagen, S.; Xiao, X. Monitoring Rice Agriculture in the Sacramento Valley, USA with Multitemporal PALSAR and MODIS Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X. Evolution of regional to global paddy rice mapping methods: A review. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridhikitti, A.; Overcamp, T.J. Estimation of Southeast Asian rice paddy areas with different ecosystems from moderate-resolution satellite imagery. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Shen, S.; Li, B.; Toan, T.L.; He, W. Rice Mapping and Monitoring Using ENVISAT ASAR Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, A.; le Toan, T. Use of ENVISAT/ASAR wide-swath data for timely rice fields mapping in the Mekong River Delta. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Brisco, B.; Yun, S.; Touzi, R. Polarimetric decomposition with RADARSAT-2 for rice mapping and monitoring. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 38, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.; Setiyono, T.; Rala, A.B.; Quicho, E.D.; Ninh, N.H. Towards an Operational SAR-Based Rice Monitoring System in Asia: Examples from 13 Demonstration Sites across Asia in the RIICE Project. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, M.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, X. High resolution paddy rice maps in cloud-prone Bangladesh and Northeast India using Sentinel-1 data. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onojeghuo, A.O.; Blackburn, G.A.; Wang, Q.; Atkinson, P.M.; Kindred, D.; Miao, Y. Mapping paddy rice fields by applying machine learning algorithms to multi-temporal sentinel-1Aand landsat data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 1042–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, P.; Serre, M.L. A novel geostatistical approach combining Euclidean and gradual-flow covariance models to estimate fecal coliform along the Haw and Deep rivers in North Carolina. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess 2018, 32, 2537–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhai, H.; Shen, Y.; Lou, B.; Jiang, C.; Li, T.; Hussain, S.B.; Shen, G. Large-Scale Crop Mapping From Multisource Remote Sensing Images in Google Earth Engine. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, G.; Pi, J.; Chen, G.; Li, C. On the river–lake relationship of the middle Yangtze reaches. Geomorphology 2007, 85, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Hao, Z.; Yuan, F.; Ju, Q.; Hao, J. Regional Frequency Analysis of Precipitation Extremes and Its Spatio-Temporal Patterns in the Hanjiang River Basin, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-C.Y.; Zhu, A.; Gong, Z.-H. The Present Situation and Development Trend of Rice Production in Qianjiang City. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Clevers, J.; Gitelson, A.A. Remote estimation of crop and grass chlorophyll and nitrogen content using red-edge bands on Sentinel-2 and-3. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amazirh, A.; Merlin, O.; Er-Raki, S.; Gao, Q.; Rivalland, V.; Malbeteau, Y.; Khabba, S.; Escorihuela, M.J. Retrieving surface soil moisture at high spatio-temporal resolution from a synergy between Sentinel-1 radar and Landsat thermal data: A study case over bare soil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Vuolo, F.; Atzberger, C. First Experience with Sentinel-2 Data for Crop and Tree Species Classifications in Central Europe. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussul, N.; Lavreniuk, M.; Skakun, S.; Shelestov, A. Deep Learning Classification of Land Cover and Crop Types Using Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Fan, X.; Liu, H.; Xiao, J.; Ross, S.; Brisco, B.; Brown, R.; Staples, G. Rice monitoring and production estimation using multitemporal RADARSAT. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdogan, M.; Gutman, G. A new methodology to map irrigated areas using multi-temporal MODIS and ancillary data: An application example in the continental US. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3520–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Lunetta, R.S. Comparison of support vector machine, neural network, and CART algorithms for the land-cover classification using limited training data points. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2012, 70, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Du, X.; Wen, N.; Tao, Q. County-level rice area estimation in southern China using remote sensing data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random Forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, K.; Yamashiki, Y.; Torres, M.A.C.; Taipe, C.L.R. Crop classification of upland fields using Random forest of time-series Landsat 7 ETM+ data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 115, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, L.; Liu, D.; Gong, P. Mapping global land cover in 2001 and 2010 with spatial-temporal consistency at 250m resolution. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.B.; Gruber, A.; Wagner, W. Mapping rice extent and cropping scheme in the Mekong Delta using Sentinel-1A data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Kou, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Jin, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Biradar, C.; et al. Tracking the dynamics of paddy rice planting area in 1986–2010 through time series Landsat images and phenology-based algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Datasets | Optical Datasets | Microwave SAR Datasets |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Sentinel-2 MSI, Level-2A images | Sentinel-1 SAR GRD |
| Time span | March to September 2019 | March to September 2019 |
| Spatial resolution | 10–20 m | 10 m |
| Pre-processing | Cloud coverage < 20% | Speckle filter |
| Composition | Maximum Value Composite during one month | The minimum value of each pixel in a period of two weeks |
| Border Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Paddy rice | Early rice (double cropping rice or ratoon rice), middle rice (single-season rice or middle-late rice, mainly single-season rice), crayfish paddy rice, ratoon rice |
| 2 | Non-rice fields | Rape, cotton, wormwood, lotus, grass, wetland vegetation, corn, other vegetables |
| 3 | Forest | Orchard, evergreen broad-leaf forest, broadleaved deciduous forest, coniferous forest, shrub |
| 4 | Built-up area | Greenhouse |
| 5 | Water body | Lake, river, and pond |
| Vegetation Indices Combination | Polarization Band Combination | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CODE | Combination | CODE | Combination |
| 1 | NDVI + LSWI + EVI | A | VVVH |
| 2 | NDVI + LSWI | B | VV |
| 3 | NDVI + EVI | C | VH |
| 4 | EVI + LSWI | D | VV/VH |
| 5 | NDVI | E | null |
| 6 | EVI | ||
| 7 | LSWI | ||
| 8 | null | ||
| Estimated Classification | Paddy Rice | Non-Rice Fields | Forest | Built-Up Area | Water Body | User’s Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed Classification | |||||||
| Paddy rice | 138 | 73 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 63% | |
| Non-rice fields | 40 | 121 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 70% | |
| Forest | 0 | 5 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 57% | |
| Built-up area | 1 | 10 | 1 | 22 | 0 | 65% | |
| Water body | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 88% | |
| Producer’s accuracy (PA) | 77% | 58% | 67% | 65% | 54% | ||
| Estimated Classification | Paddy Rice | Non-Rice Fields | Forest | Built-Up Area | Water Body | User’s Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed Classification | |||||||
| Paddy rice | 144 | 65 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 66% | |
| Non-rice fields | 64 | 90 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 52% | |
| Forest | 0 | 5 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 57% | |
| Built-up area | 1 | 6 | 10 | 17 | 0 | 50% | |
| Water body | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 63% | |
| Producer’s accuracy (PA) | 68% | 54% | 29% | 65% | 31% | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, N.; Yu, L.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Zeng, L.; Hu, Q.; Niyogi, D. Mapping Paddy Rice Fields by Combining Multi-Temporal Vegetation Index and Synthetic Aperture Radar Remote Sensing Data Using Google Earth Engine Machine Learning Platform. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182992
Chen N, Yu L, Zhang X, Shen Y, Zeng L, Hu Q, Niyogi D. Mapping Paddy Rice Fields by Combining Multi-Temporal Vegetation Index and Synthetic Aperture Radar Remote Sensing Data Using Google Earth Engine Machine Learning Platform. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(18):2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182992
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Nengcheng, Lixiaona Yu, Xiang Zhang, Yonglin Shen, Linglin Zeng, Qiong Hu, and Dev Niyogi. 2020. "Mapping Paddy Rice Fields by Combining Multi-Temporal Vegetation Index and Synthetic Aperture Radar Remote Sensing Data Using Google Earth Engine Machine Learning Platform" Remote Sensing 12, no. 18: 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182992
APA StyleChen, N., Yu, L., Zhang, X., Shen, Y., Zeng, L., Hu, Q., & Niyogi, D. (2020). Mapping Paddy Rice Fields by Combining Multi-Temporal Vegetation Index and Synthetic Aperture Radar Remote Sensing Data Using Google Earth Engine Machine Learning Platform. Remote Sensing, 12(18), 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182992







