Abstract
The Chinese Fengyun–4A geostationary meteorological satellite was successfully launched on 11 December 2016, carrying an Advanced Geostationary Radiation Imager (AGRI) to provide the observations of visible, near infrared, and infrared bands with improved spectral, spatial, and temporal resolution. The AGRI infrared observations can be assimilated into numerical weather prediction (NWP) data assimilation systems to improve the atmospheric analysis and weather forecasting capabilities. To achieve data assimilation, the first and crucial step is to characterize and evaluate the biases of the AGRI brightness temperatures in infrared channels 8–14. This study conducts the assessment of clear–sky AGRI full–disk infrared observation biases by coupling the RTTOV model and ERA Interim analysis. The AGRI observations are generally in good agreement with the model simulations. It is found that the biases over the ocean and land are less than 1.4 and 1.6 K, respectively. For bias difference between land and ocean, channels 11–13 are more obvious than water vapor channels 9–10. The fitting coefficient of linear regression tests between AGRI biases and sensor zenith angles manifests no obvious scan angle–dependent biases over ocean. All infrared channels observations are scene temperature–dependent over the ocean and land.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the new generation of geostationary meteorological satellites has developed quickly, and geostationary meteorological data are playing an increasingly important role in monitoring severe weather, lighting, air pollution development, and surface solar irradiance, and assimilating data by numerical weather prediction (NWP) models [1,2,3,4,5]. The three–axis stabilized FY–4A is the first in a series of Chinese new generation geostationary meteorological satellites and will be operational for seven years. It was launched on 11 December 2016, and was positioned at 104.7°E above the equator at an altitude of 35,786 km. The primary payloads of the FY–4A are as follows: the Advanced Geostationary Radiation Imager (AGRI) [6,7,8], Geostationary Interferometric Infrared Sounder (GIIRS) [9,10], and Lightning Mapping Imager (LMI) [11]. The AGRI is an instrument similar to the Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) on board the Japanese satellite Himawari–8 [12], the Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) on board the U.S. Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES)–R [13], and the Flexible Combined Imager (FCI) which will be on board the European Meteosat Third Generation Imaging (MTG–I) satellite [14]. As the successor to the VISSR on broad FY–2 series, AGRI will introduce many new products such as cloud liquid water, aerosol optical depth, land surface temperature, convective initiation, and others, to provide enhanced applications and services.
The geostationary imager observations were applied to identify and track the rapidly changing weather phenomena and deduce quantitative products which are critical for weather services and now–casting applications. The visible, shortwave infrared, and thermal infrared measurements from geostationary imagers are useful for retrieving cloud information, such as optical thickness, effective particle radius, and cloud–top properties [15]. The cloud property products are widely applied to monitor cloud processes [16], rainfall rate retrieval [17], and severe weather forewarning [18]. Besides conventional applications, by using machine learning methods, the geostationary infrared observations can be directly applied to study the meteorological conditions, such as total precipitable water, tropical thunderstorms, quantitative precipitation estimates, dynamical tropopause pressure retrieval, and so on [18,19,20,21]. Even more remarkable, is the research on radiance assimilation of the geostationary infrared observations is gradually deepened and expanded from clear sky observations to all-sky observations. Otkin assimilated the water vapor sensitive infrared brightness temperature observations from the Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) into the WRF–DART (Data Assimilation Research Testbed) ensemble data assimilation system during a high impact weather event across the central U.S., and found improvements in not only the 3D moisture distribution, but also the temperature, cloud, and wind fields [22]. Yang and Liu first assimilated GOES imager radiance data using a rapid refresh assimilation system with a hybrid 3D EnVar scheme and obtained some significant positive impacts on convection-permitting forecasts over Mexico [23]. Other studies also demonstrated that the geostationary infrared radiance assimilation can positively impact the precipitation forecasting skills [24,25,26]. In the last decade, many achievements have been made in the study of the all–sky geostationary infrared radiance assimilation, and obtained significant improvements in fast-evolving weather systems (such as typhoon, precipitation, and flood) forecasts [27,28].
For the atmospheric parameter retrievals and numerical weather prediction (NWP), geostationary imager observations calibration and validation are the key prerequisites. Furthermore, before the geostationary imager radiances can be assimilated into the data assimilation systems, it is critical to properly quantify the biases and errors since the deviation between satellite observation information and background field data will decrease the accuracy of numerical weather forecasts [29,30]. One common way to assess the differences between satellite observations and model simulations is by using the NWP analysis and radiation transmission model to generate model-simulated brightness temperature [31,32,33,34]. However, despite the study of the AGRI infrared data biases assessment in a selected region based on the Weather Research and Forecasting model data assimilation (WRFDA) and the radiative transfer for TIROS Operational Vertical Sounder (RTTOV) [35], there are still no publications concerning the assessment of full disk AGRI infrared data bias characteristics based on the FY–4A observation and cloud mask (CLM) data. In this study, the full disk ocean area and selected land area clear sky AGRI data biases are assessed by the difference between observations and simulations which are obtained by directly using RTTOV and ERA Interim analysis, thus providing preparation for the assimilation application of FY–4A AGRI data to the NWP model.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the AGRI instrument characteristics, the AGRI observations and the fast radiative transfer models for AGRI simulations. Section 3 details the biases and standard deviations estimated for AGRI infrared channels 8–14, as well as the scene temperature and scan angle dependences of AGRI biases. Discussion and conclusions are provided in Section 4 and Section 5, respectively.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AGRI Instrument
The AGRI on board FY–4A provided significant advancements over those of the FY–2 series in terms of the number of bands, spatial resolution, and temporal frequency. It finishes one sector scan every 1 min and completes full-disk coverage every 15 min. The AGRI has a total of 216 sensors for 14 spectral bands, three for visible (VIS), three for near-infrared (NIR), two for mid-wave IR, two for water-vapor IR, and four for long-wave IR. The spectral bands cover a range of wavelengths from 0.45 to 13.8 μm. It is sampled at 1 km at nadir in the VIS, 2 km in the NIR, and 4 km in the IR.
Table 1 summarizes the specifications of the FY–4A/AGRI bands: wavelength ranges, spatial resolutions, measurement precisions, and primary applications. Channels 1–6 are visible and near-infrared bands observing the energy coming from the sun and detecting the solar energy reflected (or scattered) by the earth’s surface or atmosphere during the day. Channels 7–8 are the mid-wave infrared bands that detect the information from the sun, land surface, and clouds. Channels 9–10 are infrared absorption bands with low atmospheric transmittance and are strongly affected by water vapor in the middle and upper troposphere. Channel 14 is affected by carbon dioxide in the lower troposphere. Channels 11–13 are infrared window bands with high atmospheric transmittance, so they are also called surface channels. These features enable AGRI to play an essential role in the tropical storm activity continuous monitoring, severe weather warning, environmental observations and even data assimilation.

Table 1.
Advanced Geostationary Radiation Imager (AGRI) channel characteristics of wavelength range, spatial resolution, SNR at 100% albedo for VIS and NIR channels, and noise-equivalent differential temperature (NEdT) for IR channels.
Figure 1 shows the weighting functions and transmittance of the AGRI infrared channels 8–14 calculated using RTTOV with the American Standard atmosphere profile as input. The weighting function represents the contribution of each layer of atmosphere to the radiation detected by the sensors. The weighting function peaks of channels 8 and 11–13 are located near the land surface and the atmospheric transmittance above the near-surface layer is high, so the surface and cloud information can be detected by these channels. Channels 9 and 10, with their peak weighting functions located at 397 and 521 hPa, respectively, can be used to detect water vapor information in the middle and upper troposphere where the atmospheric transmittance decrease to near zero. Channel 14 is a carbon dioxide absorption band with weighting function peak located at 750 hPa, and its atmospheric transmittance decreases with height, thus this carbon dioxide channel is in fact a low tropospheric temperature–sounding channel. Hereafter, upper-level channels represent channels 9–10 and 14, and surface channels represent channels 8 and 11–13.
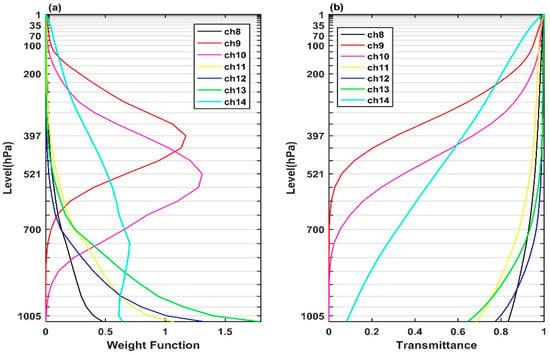
Figure 1.
FY-4A AGRI infrared channels 8-14 (a) weighting function and (b) transmittance, calculated using RTTOV with the U.S. standard atmospheric profile as the input. Channel number is displayed in the legend.
2.2. AGRI Data
The AGRI observation and CLM data can be obtained from the National Meteorological Information Center. The China Meteorological Data Service Center developed a unified and operational cloud mask algorithm that produces a four–level (clear, probably clear, probably cloudy, and cloudy) cloud mask product with 4 km spatial resolution at 15 min intervals. The consistent spatial resolution and geometry parameters for CLM and all AGRI infrared channels are conducive to the accuracy of the selection of clear sky pixels. The cloud-masking is more accurate in determining the cloudy scenes than the clear scenes, and more accurate over water than over land [36]. Figure 2 presents the AGRI observations and cloud mask of Typhoon Maria at 0000 UTC on 11 July 2018. Figure 2a is a VIS cloud image of Typhoon Maria, the typhoon spiral clouds with high albedo are in good spatial consistency with the low bright temperature pixel of channel 9 (Figure 2b). The lowest brightness temperature at channel 9 (Figure 2b) is in the region with ice and the second lowest brightness temperature in the region with overlapping clouds and cirrus, which are distributed around the ice clouds while the highest brightness temperature occurs when there are clear pixels (Figure 2c). Water clouds and cirrus are more difficult to see in a single channel than ice or overlapping clouds, referring to the AGRI VIS channel 2 (Figure 2a) and AGRI cloud types (Figure 2c), mainly because the convective clouds have a very cold cloud top temperature while the cirrus cloud is optically thin to the point that the imager can hardly feature cloud signatures from instrument noise in the infrared band without the assistance of visible light channels. The infrared band radiation is mainly composed of surface radiation and atmospheric radiation, while the surface radiation in the cloud region cannot reach the satellite, so the cloudy regions in Figure 2d are spatially well correlated with the low brightness temperature of channel 9 (Figure 2b). The probably cloudy pixels and probably clear pixels are located at the edges of cloudy regions and clear regions, respectively (Figure 2d).
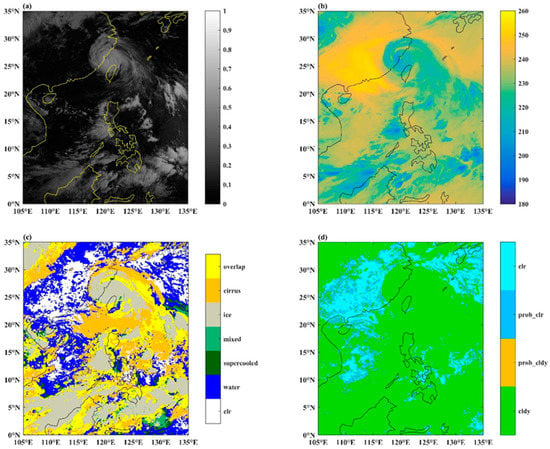
Figure 2.
(a) Albedo of Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) visible channel 2; (b) brightness temperature of AHI channel 9; (c) AGRI cloud types, including clear (clr), water cloud (water), supercooled water (supercooled, green), mixed cloud (mixed), ice cloud (ice), cirrus (cirrus), overlapping (overlap); (d) distribution of AGRI cloud mask (clear (clr), probably clear (prob_clr), probably cloudy (prob_cldy), and cloudy (cldy)) at 0000 UTC 11 July 2018.
To reduce the system deviations introduced in the calculation, the following 2–step quality control method was adopted: (1) due to the uncertainty arising either from the inadequate simulation of the radiance transfer model (RTM) in the cloud region or the inaccurate location of the hydrometeors, only clear sky observations were retained using the CLM product in this study. (2) The deformation of the observation pixels beside the satellite nadir point increases with the satellite’s zenith angle due to the large variation in the air mass. When reaching above 60°, the deformation rate is 3 times that of the satellite nadir point, so the observation pixels with a zenith angle greater than 60° are eliminated [37,38].
In this paper, we focus on the brightness temperature bias estimation of AGRI clear sky pixels over the full disk. It is well known that global cloud cover is approximately 70% and some cloudy weather systems stay in the same area for one to two days or longer. Therefore, for the purpose of filling the full disk with as many clear pixels as possible, data in different seasons are selected as follows: 1–3 September and 1–3 December 2017, as well as 1–2 March and 1–2 June 2018. Eight matching times were selected for each season to match the ERA-Interim analysis time at 00, 06, 12, 18 UTC each day, and the missing AGRI data at 18 UTC on 1–2 September and 1–2 December 2017 was supplemented by the subsequent time at 00, 06 UTC on 3 December and 3 December 2017. Figure 3a illustrates a composite map of areas with at least one clear sky pixel (cyan) or no clear pixel (white). The total clear–sky pixel counts over ocean and selected land area (20°N~40°N, 85°E~125°E) within the 2-degree grid of the 10 days are shown in Figure 3b and Figure 3c, respectively.
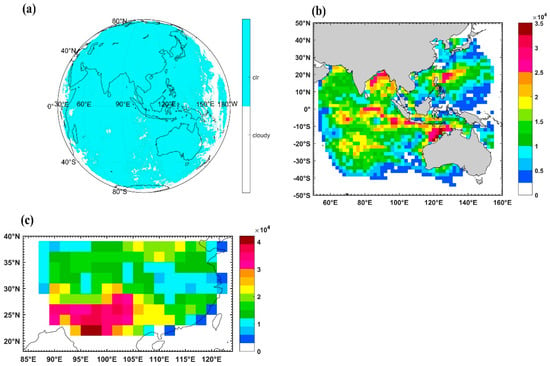
Figure 3.
(a) Composite map of areas with at least one clear sky pixel (cyan) or no clear pixel (white), (b) total clear–sky pixels counts over ocean and (c) selected land area (20°N~40°N, 85°E~125°E) within the 2–degree grid of the 10 days: 1–3 September and 1–3 December 2017, as well as 1–2 March and 1–2 June 2018.
2.3. Methodology
With the atmospheric conditions generated by an NWP system or observation, the radiance observed by a satellite sensor can be simulated by solving the radiance transfer equation (1). The top of the atmosphere upwelling clear-sky radiance, , can be written as:
Where is viewing angle, is the surface to space transmittance, is the surface emissivity and is the Planck function for a frequency and temperature T.
More and more RTMs have been specifically designed for the DA purpose, and the RTTOV was originally developed at ECMWF in the early 1990s [39]. The model has since undergone several developments [40,41] through the European Organization for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) NWP Satellite Application Facility (SAF), and its latest version RTTOV v12 was utilized in this study. The RTTOV model can be used to simulate clear-sky radiances for given vertical atmospheric profiles, surface properties at radiometer zenith angles, as well as solar and satellite geometry parameters. Table 2 summarizes the detailed description of the input variables for RTTOV. The atmosphere profiles and surface variables were obtained from ERA–Interim global reanalysis data with 60 vertical levels, and 0.25° × 0.25° resolution at 6-h intervals. Because the temporal and spatial resolution of the AGRI observations and ERA–Interim analyses are different, only the data on the ERA-Interim analyses time and grid points are used.

Table 2.
Input variables and parameters for clear-sky simulations with RTTOV 12.2.
The basic flowchart for simulation of the satellite infrared brightness temperature based on the coupling of the RTTOV model and ECMWF ERA–Interim analysis is illustrated in Figure 4. The ECMWF analysis provides the atmospheric profiles of the temperatures, pressure and specific humidity, together with winds, temperatures, pressure and humidity at the surface level. The geometry variables such as latitude, longitude, satellite and solar angles, and surface parameters are extracted from AGRI data. The atmospheric conditions and geometry variables mentioned above are transformed to the simulated brightness temperatures by the RTTOV model. By comparing the difference between the simulated and observed brightness temperatures, the bias characteristics can be assessed. The study domain is the entire ocean surface of the AGRI full disk observation area which is located at 104.7°E above the equator, together with a selected land surface domain over east China covering from 20°N to 40°N and 85°E to 125°E. Statistics were performed for each 2-degree grid, and simulated brightness temperatures corresponding to the observed pixels in each grid were obtained by RTTOV simulation after matching the grid from the ERA–Interim analysis to the observation pixel based on the adjacent interpolation. The pixels in each grid can be composed of observations coming from different times at different seasons mentioned in sub–Section 2.2, and the number of pixels in each grid in most areas can reach thousands or tens of thousands. Because of the high precision of the radiative transfer model in the clear sky simulation, statistical analysis based on this sample pixels is expected to obtain representative results, which is an expedient measure to deal with the large calculation cost of statistics for the entire year.
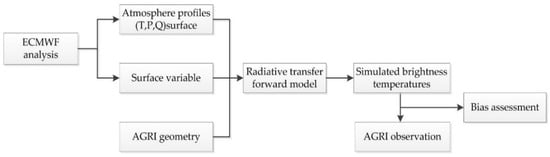
Figure 4.
Flowchart for the coupling of the numerical weather prediction (NWP) output and the radiative transfer models used to simulate the Chinese FY–4A/AGRI infrared observations for bias assessment.
3. Results
In the three–dimensional variation (3DVar) assimilation approach, the conjugate gradient method is used to minimize the cost function when analyzing the control variables, and estimate the atmospheric state.
where x is the control variables, is the priori background vector from NWP forecast model, y is the vector of observations (radiances for satellite channels), and H(x) is the observation operator such as RTTOV. B and R represent NWP background state and observation covariance matrices, respectively. Observation errors mainly come from the observation data and observation operator. The errors of each channel are generally considered to be independent, so the diagonal elements of the observation error covariance matrix R are the errors of each channel, and by evaluating the difference between the observed and simulated brightness temperatures, the uniform systematic bias and R can be estimated. Otherwise, in assimilation systems, the background and observation errors are assumed to be unbiased Gaussian distributions, and the relative biases between them should be removed to satisfy this requirement. Thus, the crucial step towards assimilation is to evaluate of the biases and standard deviations of the AGRI infrared channels. The characteristics of these departures and their dependence on geophysical and instrument variables will be examined in following sub-sections.
3.1. AGRI Data Biases Distribution over Ocean and Land
The spatial biases distributions of the full disk ocean surface area and the selected land surface are presented using shaded figures (Figure 5 and Figure 6) with the warm tones of red and yellow representing a positive value for observation minus simulation, while the cool tones of blue and green represent a negative value, and the darker the color, the greater the bias. Figure 5 presents the spatial distributions of brightness temperature biases of AGRI infrared channels 8–14 over the ocean. The biases, observation minus background (simulated with RTTOV by using ERA–Interim profiles as input), are calculated within 2° × 2° grid boxes. There are some large positive biases greater than 3 K at the edge of the observations along longitude of AGRI channel 8 at low latitudes from −20°S to 20°N while most of the positive and negative biases in other areas are within 1 K. The AGRI water vapor channel 9 has positive biases almost everywhere within 2 K and channel 10 has a relatively uniform positive and negative biases distribution within 1 K, implying that the model water vapor for channel 9 in the upper troposphere is probably systematically too wet and the model water vapor for channel 10 in the middle troposphere is close to reality [37]. The surface channels 11–13 have negative biases, mostly within 2 K, in the full disk ocean area. The possible reasons for the negative biases include the systematically underestimated model surface emissivity or the residence of near-surface low clouds caused by the difficulty in detecting near surface clouds due to the similar temperature and emissivity of the cloud top and the sea surface [42]. The biases of channel 14 are characterized by positive ratings within 2 K.
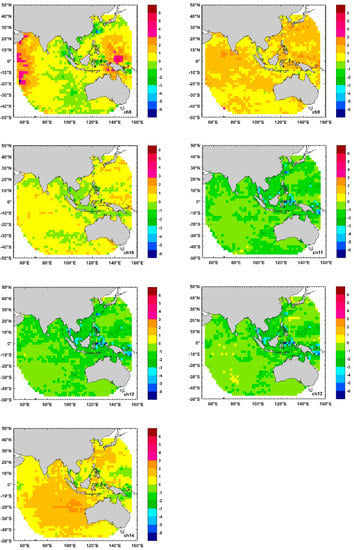
Figure 5.
Spatial distributions of biases (OMB, observation minus background) of AGRI channels 8–14 over ocean within grid boxes.
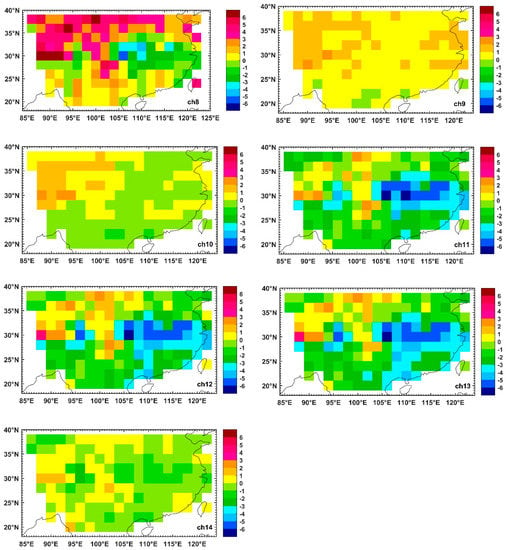
Figure 6.
Spatial distributions of biases (OMB, observation minus background) of AGRI channels 8–14 over selected land area (20°N~40°N, 85°E~125°E) within 2° × 2° grid boxes.
Figure 6 shows the spatial distribution of brightness temperature biases of AGRI infrared channels 8–14 over a selected land area. The positive and negative biases of channel 8 are scattered and the proportion of positive biases with a value greater than 1 K on the land is higher than that on the ocean. The biases of channel 9 and 10 over land are consistent with those on the ocean surface, and the biases of channel 9 are mostly positive and within 2K, while the positive bias proportion of channel 10 is greater than the negative bias, but most are within 1K. The water vapor channels 9–10 have small biases difference in the distribution of land and ocean, indicating that the channels are not sensitive to the surface information. The biases of near-surface channels 11–13 on the land surface are mainly negative, which are consistent with the bias characteristics over the ocean, but negative values are larger than those on the ocean. The bias of channel 14 on the land is different from that over the ocean, with a higher proportion of negative values than positive values, but most of them are within −1 K to 1 K.
Figure 7 presents the spatially averaged biases and standard deviations over the ocean (a) and land (b) in channel 8–14 with satellite zenith angles less than 60°. As shown in Figure 7 top panel, the positive and negative bias trends of each channel are consistent across the ocean and land, that is, the biases of the near-surface channels 11–13 are negative while the biases of the remaining channels are positive. The largest bias over the ocean and land is 1.4 K in channel 14 and 1.6 K in channel 8, respectively. As shown in Figure 7 bottom panel, the standard deviation of each channel over land is greater than that over the ocean. Channel 8 has the highest standard deviation on the land and its standard deviation over the ocean is also significantly greater than the remaining channels. It indicates that the bias distribution of channel 8 is the most dispersed. Moreover, the standard deviations of surface sensitive channels 11–13 over land can be as large as several degrees, significantly higher than those of water vapor channels 9–10, while this feature does not exist over ocean. The biases and standard deviations for water vapor channels 9–10 have the smallest difference between land and ocean––the difference of bias and standard deviation between land and ocean is less than 0.1 K and 1 K, respectively. The biases and the standard deviations of water vapor channels 9–10 are distinctly smaller than those of other channels over the land, mainly due to the tropospheric water vapor and temperature profiles which affect the water vapor channels, having relatively small differences in the middle and upper troposphere across ocean and land.
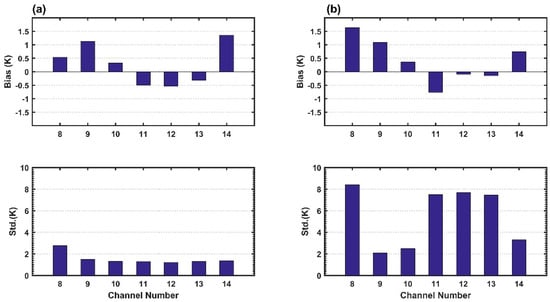
Figure 7.
Biases (top panel) and standard deviations (bottom panel) statistics for all data over the ocean (a) and land (b) with satellite zenith angles less than 60°.
3.2. Bias of Scan Angle Dependence over Ocean and Land
It is well known that scan dependent bias can be found in satellite radiance observations due to the different scan angles within a scan line caused by scanning mode [43]. Therefore, it is necessary to further investigate whether these scan dependent biases exist in AGRI observations. As the sensor zenith angle can be easily converted to the scan angle, the scan dependent bias can be converted to the relationship between the sensor zenith angle and the bias [41]. Figure 8 illustrates the variations in the biases and standard deviations of the OMB with respect to the satellite zenith angle as well as the data counts at 2° interval over the ocean. The observation counts at 2° intervals are shaded in gray in Figure 8b, the number of observations with zenith angles below 10° is relatively small compared with other angles, and the observations are mainly concentrated between 15 ° and 60°. As shown in Figure 8a, the biases of channels 8, 10, and 14 change from negative to positive with increases in the satellite zenith angle, but the bias values are within 1, 0.6 and 1.8 K, respectively. Channel 9 maintains a positive bias range of less than 1.4 K. Channels 11–13 have negative biases at any satellite zenith angle, and the biases gradually decrease with the increase of satellite zenith angles in the range of 0 to 20 degrees, but remain about −0.5 K in the range of 20 to 60 degrees. Thus, the biases of the AGRI channels are weak or negligible dependent on the satellite zenith angles. As presented in Figure 8b, apart from channel 8, the standard deviations of the AGRI channels have no significant dependence on the zenith angle of the satellite. The standard deviation of channel 8 changes significantly with the satellite zenith angle and increases significantly when the satellite zenith angle is greater than 30°. The main reason is that channel 8 is located in the mid-wave infrared band and can be more easily affected by the scattered or reflected solar short-wave radiation during the daytime when the satellite zenith angle is larger [37]. The standard deviations of channels 9–14 are concentrated in the range of 1 to 1.5 K, and the variation amplitudes with the satellite zenith angles are very small, except for small fluctuations that may be caused by relatively large nonhomogeneous biases in the 20–30 degree. The reason for the large standard deviation of the satellite zenith angle (less than 10 degrees) is probably the small amount of data, which is obviously less than the amount of data with a zenith angle greater than 10 degrees, as shown by grey shading in the Figure 8b.
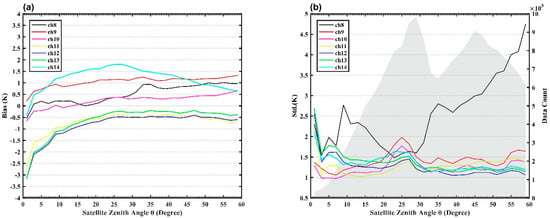
Figure 8.
The dependence of (a) biases (OMB, unit: K) over the ocean and (b) standard deviations on satellite zenith angle (unit: degree) at 2° intervals for AGRI channels 8–14 over the ocean. Observation counts at 2° intervals are shaded gray in (b).
Figure 9 presents the dependence of biases and standard deviations on satellite zenith angles at 2° intervals for AGRI channels 8–14 over the land. As shown in Figure 9a, channel 8 has the largest bias which is between 1 K and 5 K, while other channels have the biases of less than 2k, and all channels show positive biases at the satellite zenith angle from 36 to 44 degrees. As shown in Figure 9b, the standard deviations of water vapor channels 9–10 are significantly smaller than those of surface channels 11–13 with a value of several degrees, and all channels have their peak standard deviations in the range of 35° to 40°. By comparing Figure 8 and Figure 9, it can be found that the variations of biases over the ocean are obviously smaller than over the land, and the differences of the standard deviation between the water vapor channels and the surface channels over land are larger than those of the ocean. Over land, the RTTOV surface emissivity model uses surface emissivity lookup tables that generate emissivity as a function of wavenumber, latitude, longitude, and month to simulate brightness temperature [44]. Therefore, the complex land surface type and albedo that are not adequately considered in the surface emissivity model may cause the radiation received by the surface–sensitive channels to be affected by the observation angle, while the water vapor channels 9--10 and carbon dioxide channel 14 are less affected as they mainly receive radiation from the middle and upper troposphere.
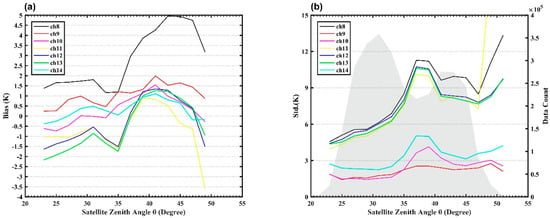
Figure 9.
The dependence of (a) biases (OMB, unit: K) over the land and (b) standard deviations on satellite zenith angle (unit: degree) at 2° intervals for AGRI channels 8–14 over land. Observation counts at 2° intervals are shaded gray in (b).
In order to quantify the correlation of all channels, linear regression fitting was performed between the bias and satellite zenith angles. Table 3 provides detailed information on the fitting coefficient. Except for channels 8 and 14, the fitting coefficients of the remaining channels are less than 0.01K/degree, indicating that all channels are almost independent of the satellite zenith angle over the ocean. The fitting coefficient over land is larger than the ocean, and channel 8 has the largest fitting coefficient value. On the whole, the biases do not depend on the satellite zenith angle over the ocean, so it is not necessary to correct the scan dependent bias for AGRI bias correction, but the observations over land should be eliminated due to the uncertainties of the surface emissivity model in RTTOV.

Table 3.
Fitting coefficient between biases and satellite zenith angles for all channels over the ocean and land.
3.3. Bias of Scene Temperature Dependence over Ocean and Land
The AGRI, like other infrared imagers, is self–calibrated on board with a black body inside the instrument as the heat source and the space as the cold source. The nonlinear problem is an important factor affecting the calibration accuracy of infrared imager, which will lead to the bias in the detection of cold and warm targets [45]. However, the imager is assumed to be linear in response to incident radiation, ignoring tiny nonlinearities that actually exist. Therefore, it is necessary to further study whether these biases and errors show a dependence on scene temperature [32,46]. The bias (a, c), standard deviation (b) and data count (d) dependence on scene temperature at 1K interval over the ocean and land are demonstrated in Figure 10 and Figure 11, respectively. All infrared channels seem to have scene temperature dependent biases. The water vapor channels 9–10 over ocean share positive biases and slightly decrease as the scene temperature increases. All surface channels 11–13 over ocean in Figure 10c share negative biases, and when the scene temperature is higher than 295 K most of the negative bias increases negatively as the scene temperature increases. As shown in Figure 11, all surface channels 8 and 11–13 over land show greater biases (c) and standard deviations (b) than that over ocean (Figure 10), and the variability in the amplitudes of surface channels biases with scene temperature is more significant than that of upper-level channels. It also can be found in Figure 10 and Figure 11 that the biases are relatively small in the scene temperature range with large data counts. Channel 8 shows extremely strong scene temperature dependent biases both over ocean and land, caused primarily by the instrumental nonlinearity [45]. In general, all infrared channels are scene-dependent and the variation of bias for the surface channels 8 and 11–13 is larger in the high scene temperature range than in the remaining range, indicating a scene temperature-dependent setting of R (observation covariance matrix, in function (2)) may be more appropriate when assimilating AGRI observations [42].
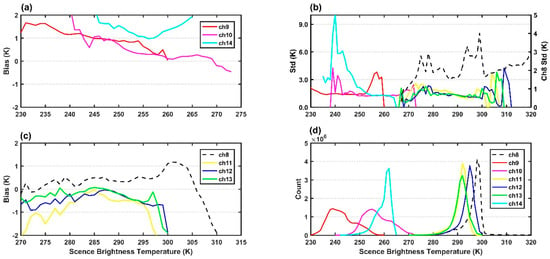
Figure 10.
The dependence of (a,c) biases, (b) standard deviation and (d) count on scene brightness temperature (units: K) at 1 K intervals for AGRI data for channels 8–14 over ocean.
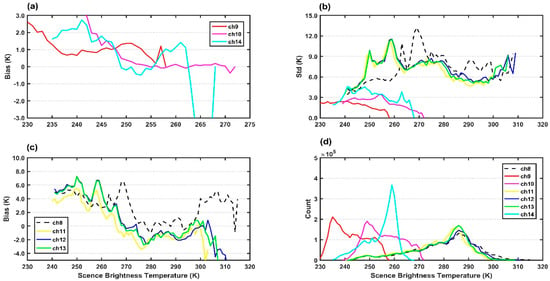
Figure 11.
The dependence of (a,c) biases, (b) standard deviation and (d) count on scene brightness temperature (units: K) at 1 K intervals for AGRI data for channels 8–14 over ocean.
4. Discussion
The FY4A/AGRI infrared observational bias characteristics were assessed preliminarily in this study, and we acknowledge that there are many uncertainties that exist in the diagnostic methodology for comparing the OMB differences, which may be systematic, geographically local, or random. Systematic differences are large global biases and random differences may arise from satellite instrument noise. The mechanisms underlying these differences can be the sensor calibration errors, NWP model prediction errors, or radiative transfer errors; therefore, there remain gaps in quantitative assessment capacity. According to the study results [34], inter-model differences are not critical for this study because the OMB bias statistics are very similar for different NWP fields. Otherwise, the accuracy of the NWP field will improve as the data assimilation and observation processing systems at NWP centers undergo regular upgrades. We suppose that the radiative transfer model (RTTOV) itself is robust, but there are uncertainties in the estimates for surface–sensitive window channels. The uncertainty is mainly due to the surface emission patterns in the RTTOV model, although advances have been made recently [47]. In addition, uncertainties can also result from the scale mismatch between satellite footprint and the NWP model grid. Furthermore, the short study period that the analysis is based on can lead to uncertainties, and if sufficient computational resources are available, a longer time period such as one year should be calculated to achieve climatological statistics.
Based on the aforementioned uncertainties discussion, the mean OMB bias within the mesh grid is evaluated to avoid the footprint grid mismatch errors, the bias values over the ocean and land surface are evaluated, respectively, and the bias dependence on satellite scan angle and scene temperature are considered. Future studies are needed to study the quality control and deviation correction scheme of the data to anticipate the positive effects of future data assimilation and to improve the initial field and numerical prediction effects of the NWP. Furthermore, the infrared imaging instruments that will be on board the subsequent satellites in the operational FY–4 series have optics and calibration designs similar to those of the AGRI. The AGRI data bias characterization studies will be helpful for future applications of the follow-up infrared imager on board the FY–4 series.
5. Conclusions
AGRI is one of the foremost instruments on board the FY–4A, representing an improved and new capability of Chinese geostationary weather satellite system. With its high temporal, spatial, and spectral resolution data sources, AGRI will provide great benefits for improving NWP through retrieval products and data assimilation. An investigation of bias characteristics of the AGRI infrared channel measurements was performed in this study.
To characterize the bias between observations and model simulations for the seven AGRI infrared channels 8–14, we coupled the RTTOV and ECMWF ERA Interim 60 model–level analyses to simulate the clear-sky brightness temperature for the full disk ocean area and the selected land area. The positive biases exist in channels 8–10 and 14, while negative biases exist in channels 11–13 (Figure 5 and Figure 6). The difference in biases distribution of surface channels 11–13 over the ocean and land is large, and the distribution of biases over land is complex. The AGRI biases of the seven infrared channels over ocean and land are less than 1.4 K and 1.6 K, respectively (Figure 7). In addition, the differences of the biases and standard deviations of water vapor channels 9–10 are relatively small, less than 0.1 K and 1 K over the ocean and land, respectively. AGRI biases over ocean are independent of satellite zenith angles as they are all less than 0.0073 in amplitudes except for channels 8 and 14, for which fitting coefficients are 0.0194 and −0.226, respectively. In contrast, the biases over land vary with satellite zenith angles, and as shown in Table 3 the biases and fitting coefficient amplitudes are larger than that over ocean. The standard deviations of the surface channels are also larger than those of the upper-level channels by several degrees in Figure 9b. Therefore, it is not necessary to correct the scan dependent bias for AGRI bias over the ocean because the biases vary little with the satellite scan angles and fitting coefficient amplitudes are extremely close to zero, but rather eliminate the observations in surface channels 8 and 11–13 over the land as the uncertainties exist in emissivity model in RTTOV. All infrared channels seem to have scene temperature dependent biases. The dependence of channels 8 and 11–13 on scene temperature over the ocean is more evident than that of water vapor channels 9–10 and 14 when the scene temperatures are high. In terms of the biases over land, the water vapor channels 9–10 and 14 appear to be less scene-dependent than the surface channels 8 and 11–13. Furthermore, the biases and standard deviations in surface channels show a much more scene-dependent on land than ocean, and the upper-level channels 9–10 and 14 do not show this feature.
Overall, the AGRI observations are in good agreement with the RTM model simulations. The scan dependent biases are not necessary for AGRI water vapor channels 9–10 bias characterization after the following quality control processes: 1. eliminate observations with zenith angles greater than 60°; 2. exclude the observations with brightness temperatures less than 230 K and higher than 320 K, respectively. All infrared channels observations should be evaluated for scene temperature dependence. The observational bias assessment is of great importance for NWP applications and the bias and error variance can be directly incorporated into the data assimilation system as a first step in assimilating AGRI observations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z. and J.S.; methodology, J.Z. and J.S.; software, J.Z.; validation, J.Z.; formal analysis, J.Z and J.S.; data curation, J.Z. and W.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.S. and J.Z.; visualization, J.Z.; project administration, J.S.; funding acquisition, J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the research program from science and technology committee of Shanghai, grant number 19dz1200101.
Acknowledgments
The computation was supported by the ECNU Multifunctional Platform for Innovation (001). AGRI data and cloud mask product are obtained from the National Meteorological Information Center (http://data.cma.cn/), ERA-Interim data are obtained from European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (https://apps.ecmwf.int/datasets/), RTTOV model are download from NWP SAF (https://nwp-saf.eumetsat.int/site/software/rttov/). The authors thank the two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and for the constructive suggestions that significantly improved the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yumimoto, K.; Nagao, T.M.; Kikuchi, M.; Sekiyama, T.T.; Murakami, H.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Ogi, A.; Irie, H.; Khatri, P.; Okumura, H.; et al. Aerosol data assimilation using data from Himawari-8, a next-generation geostationary meteorological satellite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 5886–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gao, X.; Li, Z.; Jia, D.; Jiang, J. Nowcasting of Surface Solar Irradiance Using FengYun-4 Satellite Observations over China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, W.; Huang, F.; Liu, R. Characteristics of lightning signals over the Tibetan Plateau and the capability of FY-4A LMI lightning detection in the Plateau. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 4605–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y.; Di, D.; Wang, P.; Li, J. Evaluation of Environmental Moisture from NWP Models with Measurements from Advanced Geostationary Satellite Imager—A Case Study. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Han, W.; He, J.; Chen, M. Case Study of a Retrieval Method of 3D Proxy Reflectivity from FY-4A Lightning Data and Its Impact on the Assimilation and Forecasting for Severe Rainfall Storms. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, C.; Lu, F.; Guo, Q. Introducing the New Generation of Chinese Geostationary Weather Satellites, Fengyun-4. B. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1637–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, D.; Han, W.; Yin, J. Typhoon Cloud System Identification and Forecasting Using the Feng-Yun 4A/Advanced Geosynchronous Radiation Imager Based on an Improved Fuzzy Clustering and Optical Flow Method. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, K.; Han, W.; Wang, D.; Qiu, X. Typhoon Maria Precipitation Retrieval and Evolution Based on the Infrared Brightness Temperature of the Feng-Yun 4A/Advanced Geosynchronous Radiation Imager. Adv. Meteorol. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Jiong, S. Channel selection of atmosphere vertical sounder (GIIRS) onboard the FY-4A geostationary satellite. J. Infrared Millim. 2018, 37, 545–552. [Google Scholar]
- Di, D.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Bai, W.; Wu, C.; Menzel, W.P. Enhancing the Fast Radiative Transfer Model for FengYun-4 GIIRS by Using Local Training Profiles. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 12–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-X.; Liu, J.; Pessi, A.; Hui, W.; Cheng, W. Preliminary Study on the Influence of FY-4 Lightning Data Assimilation on Precipitation Predicitions. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2019, 25, 528–541. [Google Scholar]
- Bessho, K.; Date, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Imai, T.; Inoue, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Murata, H.; Ohno, T.; et al. An Introduction to Himawari-8/9 Japan’s New-Generation Geostationary Meteorological Satellites. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 94, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmit, T.J.; Lindstrom, S.S.; Gerth, J.J.; Gunshor, M.M. Applications of the 16 spectral bands on the Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI). J. Oper. Meteorol. 2018, 06, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, H.; Ruddick, K. The potential use of geostationary MTG/FCI to retrieve chlorophyll-a concentration at high temporal resolution for the open oceans. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2399–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecikalski, J.R.; Bedka, K.M.; Paech, S.J.; Litten, L.A. A Statistical Evaluation of GOES Cloud-Top Properties for Nowcasting Convective Initiation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 4899–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Nagao, T.M.; Nakajima, T.Y.; Riedi, J.; Ishimoto, H.; Baran, A.J.; Shang, H.; Sekiguchi, M.; Kikuchi, M. Ice Cloud Properties From Himawari-8/AHI Next-Generation Geostationary Satellite: Capability of the AHI to Monitor the DC Cloud Generation Process. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2019, 57, 3229–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnlein, M.; Appelhans, T.; Thies, B.; Nauss, T. Improving the accuracy of rainfall rates from optical satellite sensors with machine learning—A random forests-based approach applied to MSG SEVIRI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Han, D.; Ahn, M.; Im, J.; Lee, S.J. Retrieval of Total Precipitable Water from Himawari-8 AHI Data: A Comparison of Random Forest, Extreme Gradient Boosting, and Deep Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Bai, C.; Guo, J.; Sun, F.; Liu, C.; Wang, F.; Xu, H.; Tang, S.; Li, B.; Di, D.; et al. Estimating Summertime Precipitation from Himawari-8 and Global Forecast System Based on Machine Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2019, 57, 2557–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Lee, J.; Im, J.; Sim, S.; Lee, S.; Han, H. A Novel Framework of Detecting Convective Initiation Combining Automated Sampling, Machine Learning, and Repeated Model Tuning from Geostationary Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Lu, F.; Shou, S. High-Resolution Fengyun-4 Satellite Measurements of Dynamical Tropopause Structure and Variability. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otkin, J.A. Assimilation of water vapor sensitive infrared brightness temperature observations during a high impact weather event. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D19203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Gao, F.; Childs, P.P.; Min, J. Impact of assimilating GOES imager clear-sky radiance with a rapid refresh assimilation system for convection-permitting forecast over Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 5472–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Qin, Z.; Zheng, Y. Improved Tropical Storm Forecasts with GOES-13/15 Imager Radiance Assimilation and Asymmetric Vortex Initialization in HWRF. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 2485–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.A.; Wang, X.; Skinner, P.; Johnson, A.; Wang, Y. Assimilation of GOES-13 Imager Clear-Sky Water Vapor (6.5 μm) Radiances into a Warn-on-Forecast System. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 1077–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, S.; Min, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T. Added Value of Assimilating Himawari-8 AHI Water Vapor Radiances on Analyses and Forecasts for “7.19” Severe Storm Over North China. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 3374–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamide, M.; Zhang, F. Assimilation of All-Sky Infrared Radiances from Himawari-8 and Impacts of Moisture and Hydrometer Initialization on Convection-Permitting Tropical Cyclone Prediction. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 3241–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Kotsuki, S.; Lien, G.Y.; Maejima, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Miyoshi, T. Assimilation of Himawari-8 All-Sky Radiances Every 10 Minutes: Impact on Precipitation and Flood Risk Prediction. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P. Bias and data assimilation. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2005, 131, 3323–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auligné, T.; McNally, A.P.; Dee, D.P. Adaptive bias correction for satellite data in a numerical weather prediction system. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2007, 133, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ignatov, A.; Kihai, Y. Implementation of the Community Radiative Transfer Model in Advanced Clear-Sky Processor for Oceans and validation against nighttime AVHRR radiances. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zou, X.; Weng, F.; You, R. An Assessment of the FY-3A Microwave Temperature Sounder Using the NCEP Numerical Weather Prediction Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2012, 50, 4860–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Boukabara, S. Community Radiative Transfer Model (CRTM) applications in supporting the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (SNPP) mission validation and verification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, S.; Carminati, F.; Lawrence, H.; Bormann, N.; Salonen, K.; Bell, W. Assessment of New Satellite Missions within the Framework of Numerical Weather Prediction. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Min, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D. Analysis of FY-4A AGRI bias characteristics and correction experiment. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 44, 679–694. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Min, M.; Wang, F.; Guo, J.; Li, B.; Tang, S. Intercomparisons of Cloud Mask Products Among Fengyun-4A, Himawari-8, and MODIS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. 2019, 57, 8827–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhuge, X.; Weng, F. Characterization of Bias of Advanced Himawari Imager Infrared Observations from NWP Background Simulations Using CRTM and RTTOV. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2016, 33, 2553–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L. A case study of GOES-15 imager bias characterization with a numerical weather prediction model. Front. Earth Sci. 2016, 10, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, J. A fast radiative transfer model for satellite sounding systems. ECMWF Tech. Memo. 1991, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.; Matricardi, M.; Brunel, P. An improved fast radiative transfer model for assimilation of satellite radiance observations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 1407–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matricardi, M.; Chevallier, F.; Kelly, G.; Thépaut, J. An improved general fast radiative transfer model for the assimilation of radiance observations. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2004, 130, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, C. Preliminary assessment of the Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) measurement onboard Himawari-8 geostationary satellite. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zou, X.; Zeng, M. An Alternative Bias Correction Scheme for CrIS Data Assimilation in a Regional Model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2019, 147, 809–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.L.; Liu, Q.; Han, Y.; Weng, F. Evaluating a satellite-derived global infrared land surface emissivity data set for use in radiative transfer modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.W.; Blackmore, T.A.; Candy, B.; Francis, P.N.; Hewison, T.J. Monitoring Satellite Radiance Biases Using NWP Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2013, 51, 1124–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Bell, W.; Bauer, P.; Bormann, N.; Peubey, C. Characterizing the FY-3A Microwave Temperature Sounder Using the ECMWF Model. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2011, 28, 1373–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.; Hocking, J.; Turner, E.; Rayer, P.; Rundle, D.; Brunel, P.; Vidot, J.; Roquet, P.; Matricardi, M.; Geer, A.; et al. An update on the RTTOV fast radiative transfer model (currently at version 12). Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 2717–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).