Abstract
The development of a snow depth product over North America is investigated by applying two-dimensional optimal interpolation to passive microwave satellite-derived and in-situ measured snow depth. At each snow-covered satellite footprint, the technique computes a snow depth increment as the weighted average of data increments, and updates the satellite-derived snow depth accordingly. Data increments are computed as the difference between the in-situ-measured and satellite snow depth at station locations surrounding the satellite footprint. Calculation of optimal weights is based on spatial lag autocorrelation of snow depth increments, modelled as functions of horizontal distance and elevation difference between pairs of observations. The technique is applied to Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer 2 (AMSR2) snow depth and in-situ snow depth obtained from the Global Historical Climatology Network. The results over North America during January–February 2017 indicate that the technique greatly enhances the performance of the satellite estimates, especially over mountain terrain, albeit with an accuracy inferior to that over low elevation areas. Moreover, the technique generates more accurate output compared to that from NOAA’s Global Forecast System, with implications for improving the utilization of satellite data in snow assessments and numerical weather prediction.
1. Introduction
Snow depth distribution is utilized for regional snow assessments over a range of time scales. Figure 1, obtained from the WMO Global Cryosphere Watch (GCW) website (https://globalcryospherewatch.org/assessments/snow/2019/) displays a map of the percent difference in mean snow depth over the Northern Hemisphere in January 2019 compared to the 20-year average as derived from Canadian Meteorological Center (CMC)’s operational snow depth analysis.
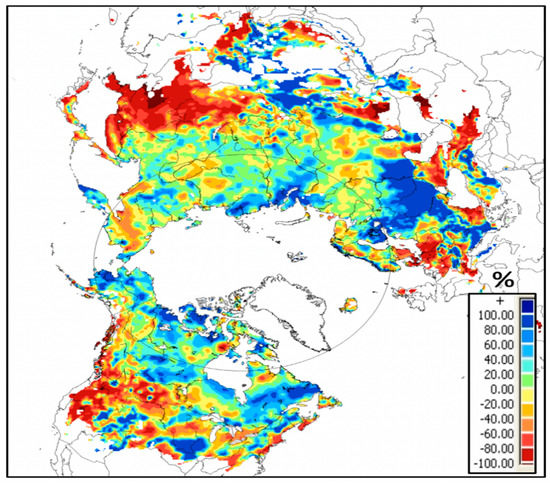
Figure 1.
Percent change of snow depth from Canadian Meteorological Center (CMC) snow depth analysis in January 2019 compared to the 20-year average (1998–2017).
Such information can provide important clues to water management planners and policy makers, which relies heavily on the ability of the snow analysis to accurately characterize the snow depth distribution. Another important use of snow-depth-based analyses is for numerical weather prediction (NWP) models, to update snow states within embedded land surface schemes and improve predictions of the meteorological atmospheric variables. Moreover, snow depth is highly correlated to snow water equivalent (SWE) [1], the most hydrologically important snow property and is used as predictor in simple equations to estimate SWE distribution with reasonable accuracy.
In-situ snow depth measurements are made routinely in many locations worldwide. They are considered the gold standard for the high local accuracy and as such are relied upon in global snow analyses. A disadvantage of analyses relying on station data is that their distribution is spatially uneven, less dense or completely lacking in high-mountain or remote areas. In contrast, satellite remote sensing offers excellent spatial coverage and temporal frequency ideal for large area monitoring but snow depth estimated from satellite data has an absolute accuracy inferior to in-situ measurements. Passive microwave measurements provide the most mature snow retrieval products of all available satellite systems, e.g., from Special Sensor Microwave/Imager (SSM/I), Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR-E), Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit (AMSU) and more recently Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer 2 (AMSR2) instruments [2,3,4,5,6]. Methods based on active microwave measurements have shown potential for improved results but only in theoretical, experimental or small-scale studies (e.g., [7]). Light detection and ranging (LIDAR) is a recent and promising airborne remote sensing technology that measures snow depth directly with high accuracy and spatial resolution (e.g., [8]) but large-area applications are currently not feasible.
A strategy for improving the accuracy of passive microwave satellite-based snow depth is to combine it with in-situ measured snow depth. One blending approach is the variational data assimilation of passive microwave brightness temperatures at specific frequencies, modelled as a function of snow properties using a semiempirical snow emission model. In this method, in-situ snow depth measurements are used initially as input to estimate (via the snow emission model applied to satellite brightness temperatures) an effective snow grain size at station locations, which in turn is interpolated spatially and subsequently used to retrieve snow depth via snow emission model inversion. This is the approach applied to produce the European Space Agency (ESA)’s GlobSnow snow water equivalent (SWE) product (https://nsidc.org/data/NSIDC-0595), described in [9,10]. Evaluation results have shown that GlobSnow is superior to products based purely on passive microwave measurements such as the AMSR-E SWE [6], although errors increase (but to a lesser degree) for deeper snow [11]. However, microwave emission modelling is a work in progress, and forward modelling of brightness temperatures in the 20–150 GHz frequency range is plagued by large uncertainties [12].
Another blending approach is optimal statistical interpolation applied to satellite snow depth and in-situ snow depth measurements from surrounding stations, taking into account data errors (satellite and in-situ snow depth increments) and terrain dependent error correlations of snow depth increments, modelled as functions of horizontal distance and elevation difference between pairs of observations. This technique, also called “two-dimensional optimal interpolation”, was introduced in operational snow analysis for numerical weather prediction by [13]. However, operational snow depth analyses do not currently assimilate satellite snow depth, probably due to the perceived unreliability of satellite estimates. An application of the technique to satellite and in-situ snow depth over selected regions of western US and Alaska is described in [14,15]. Here, the satellite estimate is used as first guess and updated by blending it with in-situ snow depth from surrounding stations.
In this paper, we use a similar blending approach to demonstrate the large-scale operational applicability of the technique for improving the mapping of AMSR2-based snow depth. To this end, the blending optimal interpolation technique is applied to global satellite and in-situ data and its output is evaluated over North America during one typical winter season. Additionally, to demonstrate the potential benefit of the technique for NWP model applications, snow depth output obtained from a global forecast model is intercompared with the satellite and the blended analysis outputs. The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 provides a description of the satellite, in-situ, forecast and ancillary data. Section 3 describes the two-dimensional optimal interpolation method, followed by description of the global blended analysis scheme and its evaluation methodology. Section 4 presents and discusses the evaluation results. Section 5 provides a summary of the paper and its main conclusions.
2. Data
Input and testing data were assembled for January–February 2017 period. Inspection of the snow cover distribution through in-situ data and maps of snow cover extent indicated an active winter season over North America, with large snow accumulations in the western US, episodes of snowfall and melting in low-lying areas of midwestern and eastern US and stable snow cover in northern Canada and Alaska. Details of each dataset are described below. Details of snow conditions over North America for the period of evaluation are provided in Section 3.3 ”Evaluation Methodology”.
2.1. Satellite Snow Data
Satellite snow data were obtained from NOAA’s suite of passive microwave snow products—snow cover, snow depth and SWE—which utilizes brightness temperatures at specific window frequencies from AMSR2 onboard the GCOM-W1 (Global Change Observation Mission—Water) satellite (https://www.ospo.noaa.gov/Products/atmosphere/gpds/about_amsr2.html). AMSR2 is a successor to AMSR on Japanese ADEOS-II and AMSR-E on Aqua, a NASA satellite. AMSR2 level 1B swath brightness temperature data are used to retrieve snow depth and snow cover extent, whereas SWE is estimated frrom the retrieved snow depth and snow density, the latter obtained from climatology using a look-up table. The snow cover algorithm is based on the passive microwave classification method described in detail in [16,17]. The snow depth retrieval algorithm is adopted from the official NASA SWE algorithm technique described in [6]. This is a dynamical statistical algorithm that estimates snow depth from analytical equations fitted to snow depth in-situ data. The dynamical nature of the algorithm stems from the varying equation coefficients that are estimated from brightness temperatures. A detailed description of the NOAA’s snow cover and snow depth algorithms is found in [18].
2.2. In-Situ Snow Data
In-situ station data for snow depth and elevation were extracted from the Global Historical Climatology Network (GHCN-Daily) available at NOAA’s National Center for Environmental Information (NCEI, https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov). This is a large dataset that includes synoptic and other snow recording stations. For example, over the continental US and Alaska, snow data include synoptic (from the Global Telecommunication System or GTS) and cooperative (COOP) stations, the latter available only over the US. Station records flagged as “snow on the ground” were selected along with measured snow depth and elevation information.
2.3. Forecast Data
Additional snow depth data were obtained from the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) Global Forecast System (GFS; [19]). GFS includes a land surface modelling scheme called the Noah land surface model (LSM; [20]). The Noah LSM is a moderately complex community model, is widely used in weather and regional climate models and is the operational land surface scheme for NCEP National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). It is also used in land data assimilation systems such as the North America Land Data Assimilation System, the Land Information System and High Resolution Data Assimilation System (HRLDAS). The GFS surface flux files containing snow depth fields were obtained from NOAA’s National Operational Model Archive and Distribution System (NOMADS). The downloaded model data have various resolutions. The GFS surface data used in this study were available at approximately 12 km resolution on a Gaussian grid.
2.4. Ancillary Data
Elevation information is critical to the technique and is needed at every grid cell over the analysis domain. Static gridded elevation data at the analysis resolution of 12 km were constructed from the global 1-km raster data product called GTOPO30 (US Geological Survey; https://www.usgs.gov).
3. Methods
3.1. Two-Dimensional Optimal Interpolation
Snow depth at an analysis grid point k is estimated as the sum of a background field (first guess) and an analysis snow depth increment ΔSDk, the latter computed as weighted average of data increments at surrounding locations.
where ∆SDi is the data increment, expressed as the difference between the observed snow depth and the first guess (satellite-derived) snow depth at each observation point I [i = 1, N] and wi is the spatial weight of observation point i. The vector of optimum weights at analysis point k is computed by solving the set of N linear equations expressed as:
where is the matrix of spatial correlation coefficients between pairs of data points, is the covariance matrix of observation errors relative to those of the background and is the vector of correlation coefficients between pairs of data and analysis point. To compute correlation coefficients needed in Equation (2) [13] introduced a two-dimensional spatial correlation function of snow depth increments as a function of horizontal distance and altitude applied in a global analysis of snow depth for numerical weather prediction. The correlation functions were taken from [21] and have the form:
where μ is the correlation coefficient of snow depth increments between two locations with horizontal separation distance r and elevation difference z. Also, α(r) is the correlation function of horizontal distance and β(z) is the correlation function for the elevation difference:
where c and h are fixed scale parameters: c = 0.018 km−1 (corresponding to an e-folding distance of about 120 km) and h = 800 m. The e-folding scales are defined as the separation distance (horizontal or vertical) at which SD correlation coefficient drops to e−1. Equations (4) and (5) and the scale parameters have been widely adopted in operational snow analyses for numerical weather prediction models, e.g., at EMC, European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecast (ECMWF) and Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) [13,22,23,24] and in studies involving analysis over smaller areas, e.g., [14,15].
3.2. Blended Snow Depth Scheme and its Application
The overall blending snow depth algorithm is presented in Figure 2.
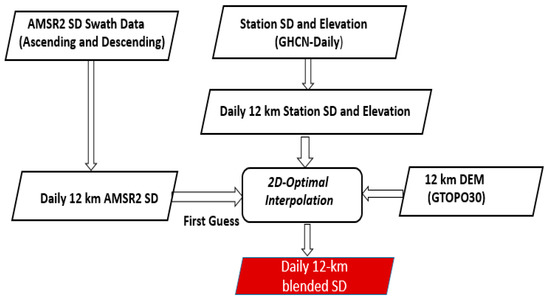
Figure 2.
Flow diagram of the snow depth (SD) analysis application using two-dimensional (2D) optimal interpolation.
The input and ancillary data are averaged on a daily basis over a common regular grid at 12-km spatial resolution. For AMSR2, this spatial resolution is a reasonable approximation to the native resolution of brightness temperatures used to estimate snow depth. Both the descending and ascending satellite estimates are used in obtaining the daily average. Given the relative coarse spatial distribution of in-situ data, averaging yields only one value per grid cell for the majority of the grid cells considered.
Satellite snow depth from AMSR2 is used as a first guess and as a snow mask to constrain the analysis, i.e., analysis is performed only over satellite snow cover grid cells. Only station-averaged snow depth (at 12 km) within a fixed range centered at each grid cell were considered. Equations (4) and (5) were used to compute correlations. The scale parameters were fixed at 0.018 km−1 (for Equation (4)) and 800 m (for Equation (5)). As in [13], errors in neighboring observations are assumed to be uncorrelated, in which case reduces to the identity matrix multiplied by σ2/b2, the ratio of the observation error variance to the background error variance. The variances were chosen arbitrarily to be 10 cm2 for the satellite background and 10 cm2 for the observations (1:1). Additionally, the maximum number of in-situ data considered for blending closest to an analysis grid point was fixed at 50, as in the snow depth analysis used at ECMWF [22]. Implementation of the analysis over North America during the evaluation period indicated that a radius of influence of 600 km centered at each (satellite snow cover) grid cell would be adequate to have at least two in-situ observations available for blending with the first guess satellite estimate. Therefore, a 600-km maximum distance from each analysis grid point was set to screen in-situ data for consideration (in addition to the maximum number of observations). Note that in well-monitored areas, the actual range (the most distant snow depth observation considered) is on average much smaller. For example, over the continental US, the median range during the period of investigation was about 260 km. In contrast, over Canada and Alaska, the median range was about 580 km, and the median number of observations considered was only 21. This means that a radius of influence much smaller than 600 km would negatively impact the analysis over poorly monitored areas.
3.3. Evaluation Methodology
The blended analysis scheme was evaluated during the January–February 2017 snow season over North America using the bias and root-mean-square error (RMSE) as metrics. Figure 3 and Figure 4 display maps of snow cover extent on specific days of the selected period obtained from NOAA’s snow analysis, called the Interactive Multi-sensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS; [25]).
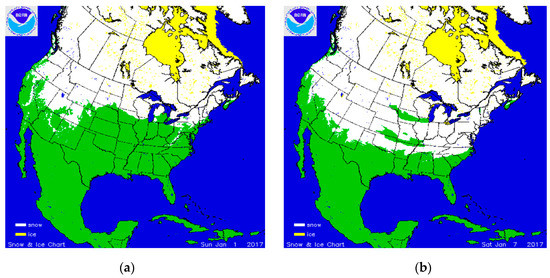
Figure 3.
Interactive multi-sensor and snow mapping system (IMS) snow maps over US and parts of North America on (a) 1 January 2017 and (b) 7 January 2017.
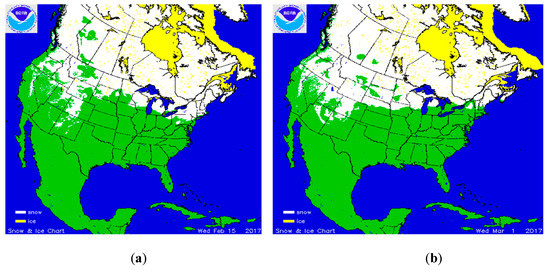
Figure 4.
IMS snow maps over the US and parts of North America on (a) 15 February 2017 and (b) 1 March 2017.
New snowfall occurred during early January over the continental US, increasing snow extent substantially over northeastern US from 1 January to 7 January (Figure 3). Snow coverage shrank back due to warming and subsequent melting that occurred after 7 January. The large-scale snow cover distribution appears more stable during the month of February, as shown in snow maps of 15 February and 1 March (Figure 4).
Evaluation was conducted using gridded in-situ snow depth as “ground truth”. Gridded in-situ snow depth coinciding with an analysis grid cell was removed from the analysis and used only as ground truth. GFS forecast snow depth was intercompared with the satellite (first guess) and the analysis estimate and evaluated against ground truth. It is important to note that GHCN-Daily data include only snow depth reporting stations and thus the daily station count changes depending on the snow coverage. Figure 5 shows maps of the distribution of in-situ snow depth on 1 January 2017 and 7 January 2017.
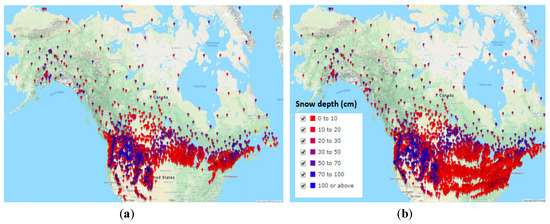
Figure 5.
Distribution of Global Historical Climatology Network (GHCN)-Daily snow depth stations over North America on (a) 1 January 2017 and (b) 7 January 2017.
Notice the striking similarity between station spatial coverage shown in Figure 5 and snow cover distribution shown in Figure 3. Notice also the contrast between the high density of in-situ data over continental US with the sparsity of in-situ stations over northern Canada and Alaska. The distribution of stations between 15 February and 1 March (not shown) was not markedly different since snow cover distribution patterns between 15 February and 1 March were similar (Figure 4).
4. Results and Discussion
Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 display time series plots of daily bias and root-mean-square error (RMSE) of snow depth over North America from AMSR2, from the optimal interpolation (OI) technique and from GFS, where bias and RMSE are based on the differences between each of these datasets and the gridded in-situ snow depth that was removed from the analysis. The evaluation was done for two elevation bands of satellite grid cells: low (less than or equal to 800 m elevation) and high (greater than 800 m elevation).
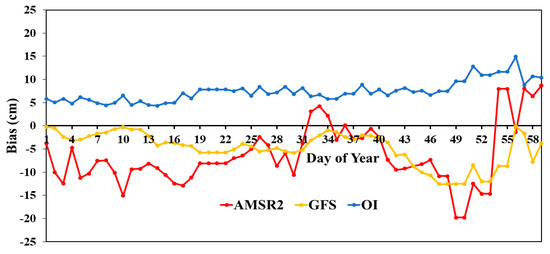
Figure 6.
Time series of daily bias during January–February 2017 for low elevation grid points (elevation less than/equal to 800 m).
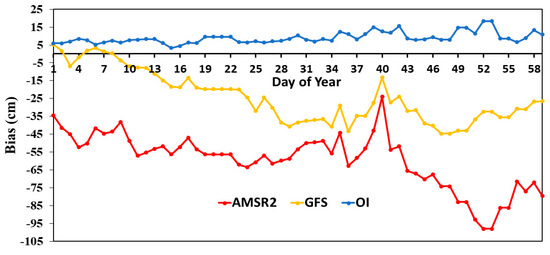
Figure 7.
Time series of daily bias during January–February 2017 for high elevation grid points. (elevation greater than 800 m).
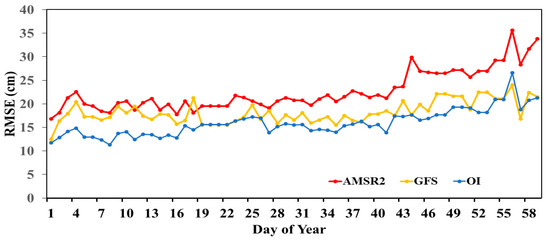
Figure 8.
Time series of daily root-mean-square error (RMSE) during January–February 2017 for low elevation grid points (elevation less than/equal to 800 m).
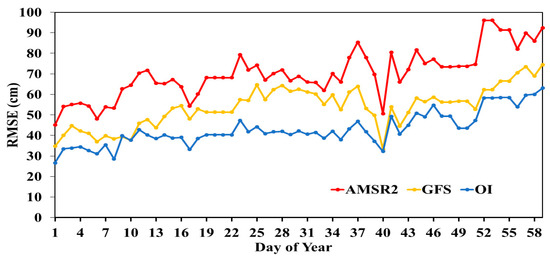
Figure 9.
Time series of daily RMSE during January–February 2017 for high elevation grid points (elevation greater than 800 m).
Visual inspection of the plots indicates a positive low to moderate bias (between 5 and 15 cm) for the OI-based snow depth throughout the evaluation period, whereas the bias for AMSR2 and GFS is predominantly negative, with a much larger magnitude for the high elevation band. The bias for AMSR2 for the high elevation band deteriorates significantly as the snow season progresses whereas the bias for OI increases only slightly, exhibiting remarkable stability relative to AMSR2 and GFS. The positive bias of the OI-based analysis could be attributed to the lack of zero snow depth data and/or the snow cover omissions of the AMSR2-based snow cover extent product. As noted earlier, in-situ stations considered in the analysis report only positive snow depth which could have contributed to the analysis positive bias. Additionally, AMSR2-based snow mask employed here suffers from omission errors (e.g., [18]), a common problem to passive microwave algorithms, leading to the removal of legitimate shallow snow cover grid cells from the analysis and further skewing of the analysis results. A potential remedy to this situation would be to include in the analysis grid cells without snow cover as virtual zero snow depth stations and/or zero snow depth reports.
Unlike the bias, RMSE of OI-based snow depth is smaller over low elevation (between 10 and 20 cm) compared to that over high elevation (between 30 and 50 cm) grid cells. However, RMSE of the OI-based snow depth is smaller compared to AMSR2 and GFS, especially over high elevation grid cells (between 50 and 90 cm for AMSR2 and between 40 and 70 cm for GFS). These results indicate that the analysis could be particularly beneficial over high elevation areas where the satellite and forecast snow depth products display major weaknesses.
Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12 display maps of snow depth distribution over North America on 7 January and 15 February for AMSR2, for OI-based and GFS snow depth, respectively. The three snow depth distributions share a common AMSR2 snow mask. Visual comparison of these maps with the IMS snow cover on 7 January (Figure 3b) indicate that the small scale features of snow cover distribution over midwestern US on 7 January are not well captured by AMSR2 snow cover extent product, although the predominance of shallow snow (snow depth less than 10 cm) from the new snowfall accumulations as depicted on each map in Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12 suggests that each of the snow depth products, AMSR2, OI and GFS, were able to capture these new snow accumulations reasonably well. On 15 February, snow cover over same areas had disappeared due to snowmelt, which is well captured. In terms of the snow depth distribution, AMSR2 displays less snow accumulation than the OI-based and GFS products over western US/Canada and Alaska. Furthermore, over these areas, AMSR2 shows no obvious large-scale increase in snow depth from 7 January to 15 February. In contrast, OI-based analysis shows an increase in snow depth over Alaska and the western US that would be consistent with increased snow accumulations over northern climates from early to mid-winter periods.

Figure 10.
Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer 2 (AMSR2)-based snow depth (cm) over North America on (a) 7 January 2017 and (b) 15 February 2017.
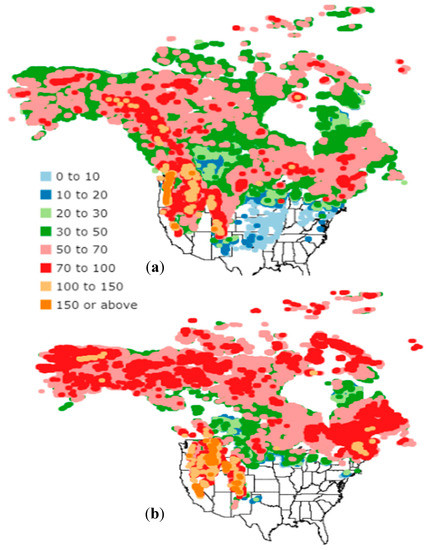
Figure 11.
Optimal interpolation (OI)-based snow depth (cm) over North America on (a) 7 January 2017 and (b)15 February 2017.

Figure 12.
Global Forecast System (GFS) forecast snow depth (cm) over North America on (a) 7 January 2017 and (b) 15 February 2017.
Table 1 and Table 2 give summary statistics (mean snow depth and standard deviation for in-situ ground truth, bias and RMSE for AMSR2, GFS and OI-based snow depth) on 7 January and 15 February for the low and high elevation bands.

Table 1.
Summary statistics for 6 January 2017 and 15 February 2017, low-elevation grid points.

Table 2.
Summary statistics for 7 January 2017 and 15 February 2017, high-elevation grid points.
These summaries show statistics for only a sample of snow depth distribution over the entire domain (at station locations). Over low elevation, the statistics indicate a negative bias for AMSR2 and GFS and a positive bias for the OI-based snow depth. On the other hand, the OI snow depth has the smallest RMSE. Interestingly, consistent with ground truth, the OI and AMSR2 mean snow depth increased from 7 January to 16 February, indicating that the overall large-scale accumulation was well represented, albeit with a lower accuracy by AMSR2. In contrast, GFS mean snow depth decreased slightly. Over high elevation, the statistics indicate large negative bias for AMSR2 and GFS and a small positive bias for the OI-based analysis. RMSE is also the smallest for the OI snow depth. The increase in observed mean snow depth by about 26 cm indicates large accumulations over high elevation areas, well represented by the OI snow depth (about 28.5 cm). In contrast, mean snow depth for AMSR2 and GFS decreased substantially from 7 January to 16 February.
These results indicate that for the period of evaluation both AMSR2 and GFS-based snow depth are not reliable products for regional snow assessments over high elevation areas. Conversely, the optimal interpolation technique improves the accuracy of the satellite product to the extent that it can be relied upon for large-scale snow assessments over high elevation regions where the density of in-situ stations is typically less than over low-lying areas. The proposed technique demonstrates that the utility of satellite snow depth can be substantially improved. A major problem of the technique as it is applied here is that it relies on the AMSR2 snow mask. The large gaps in satellite snow coverage over parts of Canada on 15 February 2017 should be noted. These omission errors are common to passive satellite microwave measurements during warmer winter weather or wet snow conditions. Application of the technique using a more accurate snow mask is being explored and will be reported in a separate investigation
5. Conclusions
The main thrust of the study is to test the large-scale applicability of the two-dimensional optimal interpolation in improving satellite snow depth by combining it with routine in-situ station data. The method uses a satellite estimate of snow depth as first guess and updates it by blending it with in-situ snow depth from surrounding stations. This blending approach is applied to snow depth retrieved from AMSR2 onboard the GCOM-W1 satellite and in-situ snow depth obtained from NOAA’s Global Historical Climatology Network. Next, the utility of the AMSR2 satellite snow depth and the blended output are evaluated over North America during the winter months of January and February 2017. To investigate the potential benefit of the technique for numerical weather prediction (NWP) model applications, snow depth obtained from NOAA’s Global Forecast System is also intercompared with the satellite and blended outputs. The main finding of the study was that the blending technique greatly enhances the performance of the satellite product, especially over mountain terrain, making it suitable for reliable large-scale snow assessments over these regions. Moreover, the technique generates more accurate blended output compared to forecast snow depth from NOAA’s Global Forecast System, demonstrating the benefit of the technique for NWP model applications. A deficiency of the technique is that it is applied over snow-covered areas as identified by AMSR2, resulting in omission errors common to passive satellite microwave measurements during warmer winter weather or wet snow conditions. It was hypothesized that these omission errors may have also contributed to the small but consistent positive bias of blended snow depth. Application of the technique using a more accurate snow mask is needed to remedy these deficiencies.
Author Contributions
C.K. wrote the paper with contributions from all the co-authors. T.M.S. and J.K. contributed to conceptualization, analysis and review of the paper.
Funding
This research was funded by NOAA, grant number NA18NWS4680053.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions. The views, opinions, and findings contained in this report are those of the authors and should not be construed as an official National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration or U.S. Government position, policy, or decision.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sturm, M.; Taras, B.; Liston, G.E.; Dirksen, C.; Jonas, T.; Leas, J. Estimating Snow Water Equivalent Using Snow Depth Data and Climate Classes. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 1380–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Foster, J.; Hall, D. Nimbus-7 SMMR derived global snow cover parameters. Ann. Glaciol. 1987, 9, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodison, B.E. Determination of areal snow water equivalent on the Canadian prairies using passive microwave satellite data. In Proceedings of the 12th Canadian Symposium on Remote Sensing Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–14 July 1989; Volume 3, pp. 1243–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, R.E.; Chang, A.T.; Tsang, L.; Foster, J.L. A prototype AMSR-E global snow area snow depth algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongoli, C.; Grody, N.C.; Ferraro, R.R. Interpretation of AMSU measurements for the retrievals of snow water equivalent and snow depth. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D24111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.E. The AMSR-E Snow Depth Algorithm Description and Initial Results. J. Remote Sens. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 29, 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Brogioni, M.; Macelloni, G.; Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P.; Pettinato, S.; Santi, E.; Xiong, C.; Crepaz, A. Sensitivity analysis of microwave backscattering and emission to snow water equivalent: Synergy of dual sensor observations. In Proceedings of the XXXth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–20 August 2011; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Deems, J.S.; Painther, T.H.; Finnegan, D.C. LIDAR measurement of snow depth—A review. J. Glaciol. 2013, 59, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulliainen, J.; Grandell, J.; Hallikainen, M.T. HUT snow emission model and its applicability to snow water equivalent retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 1378–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulliainen, J. Mapping of snow water equivalent and snow depth in boreal and sub-arctic zones by assimilating space-borne microwave radiometer data and ground-based observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takala, M.; Luojus, K.; Pulliainen, J.; Derksen, C.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Kärnä, J.-P.; Koskinen, J.; Bojkov, B. Estimating northern hemisphere snow water equivalent for climate research through assimilation of spaceborne radiometer data and ground-based measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3517–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grody, N. Relationship between snow parameters and microwave satellite measurements: Theory compared withAdvanced Microwave Sounding Unit observations from 23 to 150 GHz. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D22108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasnett, B. A global analysis of snow depth for numerical weather prediction. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1999, 38, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Kumar, S.; Foster, J.L.; Shaw, M.; Tian, Y.; Fall, G.M. Assimilating satellite-based snow depth and snow cover products for improving snow predictions in Alaska. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 54, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Kumar, S.V.; Arsenault, K.R.; Mocko, D.M. Blending satellite-based snow depth products with in situ observations for streamflow predictions in the upper Colorado River Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 1182–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grody, N.C. Classification of snow cover and precipitation using the Special Sensor Microwave Imager. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 7423–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grody, N.C.; Basist, A.N. Global identification of snowcover using SSM/I measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Kongoli, C.; Key, J. An in-depth evaluation of NOAA’s snow heritage algorithms for snow cover and snow depth using AMSR-E and AMSR2 measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 2319–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMC. The GFS Atmospheric Model; NOAA/NWS/NCEP, NCEP Office Note 442; 2003; p. 14. Available online: http://www.lib.ncep.noaa.gov/ncepofficenotes/files/on442.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2019).
- Ek, M.B.; Mitchell, K.E.; Lin, Y.; Rogers, E.; Grunmann, P.; Koren, V.; Gayno, G.; Tarpley, J.D. Implementation of Noah land surface model advances in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction operational mesoscale Eta model. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, R. Atmospheric Data Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991; p. 457. [Google Scholar]
- de Rosnay, P.; Balsamo, G.; Albergel, C.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Isaksen, L. Initialisation of Land Surface Variables for Numerical Weather Prediction. Surv. Geophys. 2012, 35, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusabiraki, H. Offline validation of a multi-layer snow scheme for a new land surface model in the operational regional NWP model at JMA. In Proceedings of the 13th EMS Annual Meeting and 11th European Conference on Applications of Meteorology, Reading, UK, 13 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kusabiraki, H. Improvement of Snow Analysis Using an Offline Land-Surface Model. JSC/CAS Working Group on Numerical Experimentation (WGNE). Research Activities in Oceanic and Atmospheric Modelling; Blue Book; World Meteorological Organization (WMO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich, S.R.; McNamara, D.; Ramsay, B.H.; Baldwin, T.; Kasheta, T. Enhancements to and Forthcoming Developments to the Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS). Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 1576–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).