A Systematic Review on the Intersection of the Cold Chain and Digital Transformation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ1. How is DT impacting the cold chain industry?
- RQ2. How can digital twins enhance cold chain operations, and what are the key implementation considerations?
- RQ3. How does DT affect cold chain sustainability?
- RQ4. What are the key benefits and challenges of integrating digital technologies in cold chain operations?
- RQ5. What are the future trends and opportunities for digitalization in the cold chain?
2. Materials and Methods
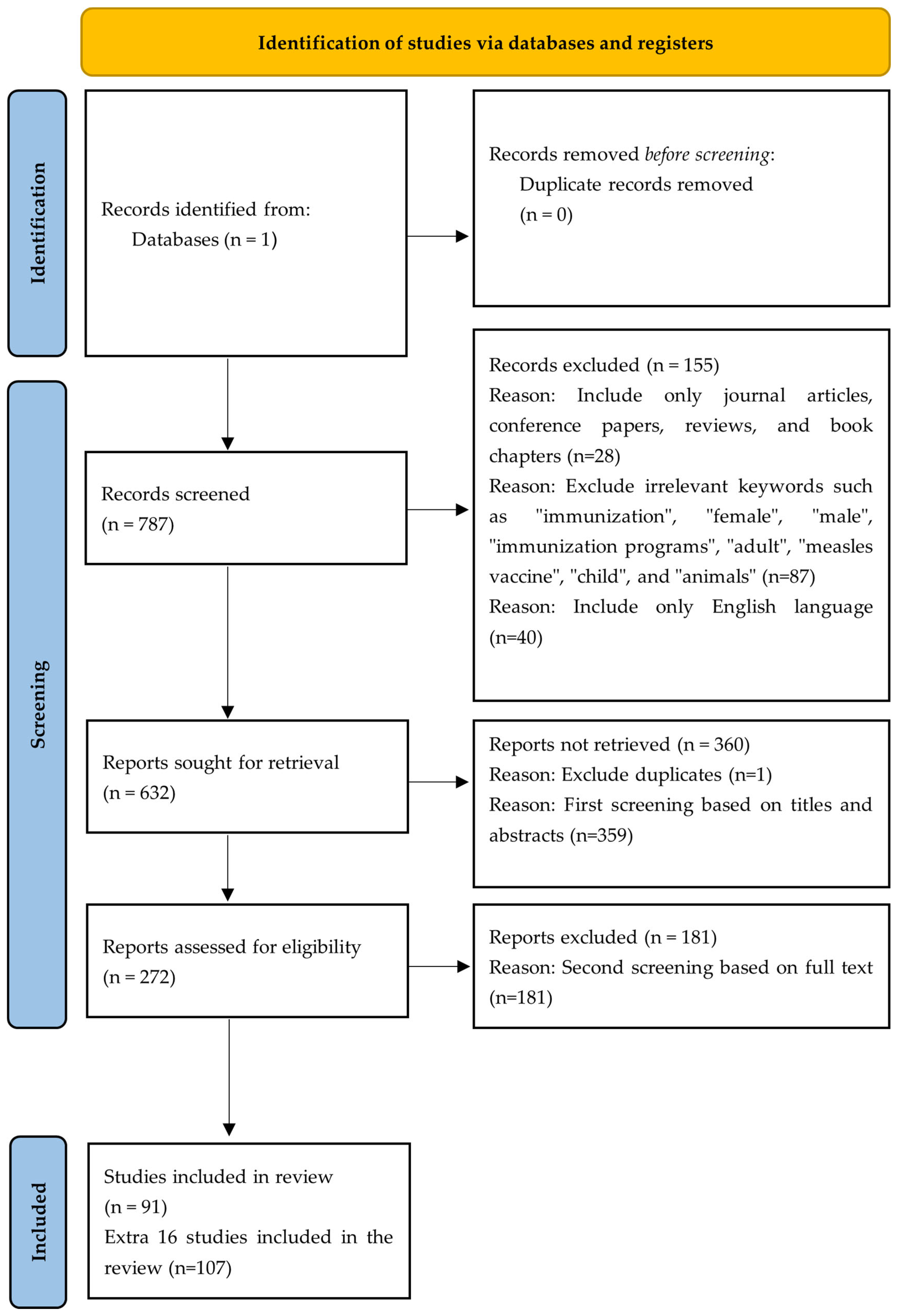
2.1. PRISMA Framework
2.2. Detailed Document Search Process
2.3. Chronological Growth of Publications
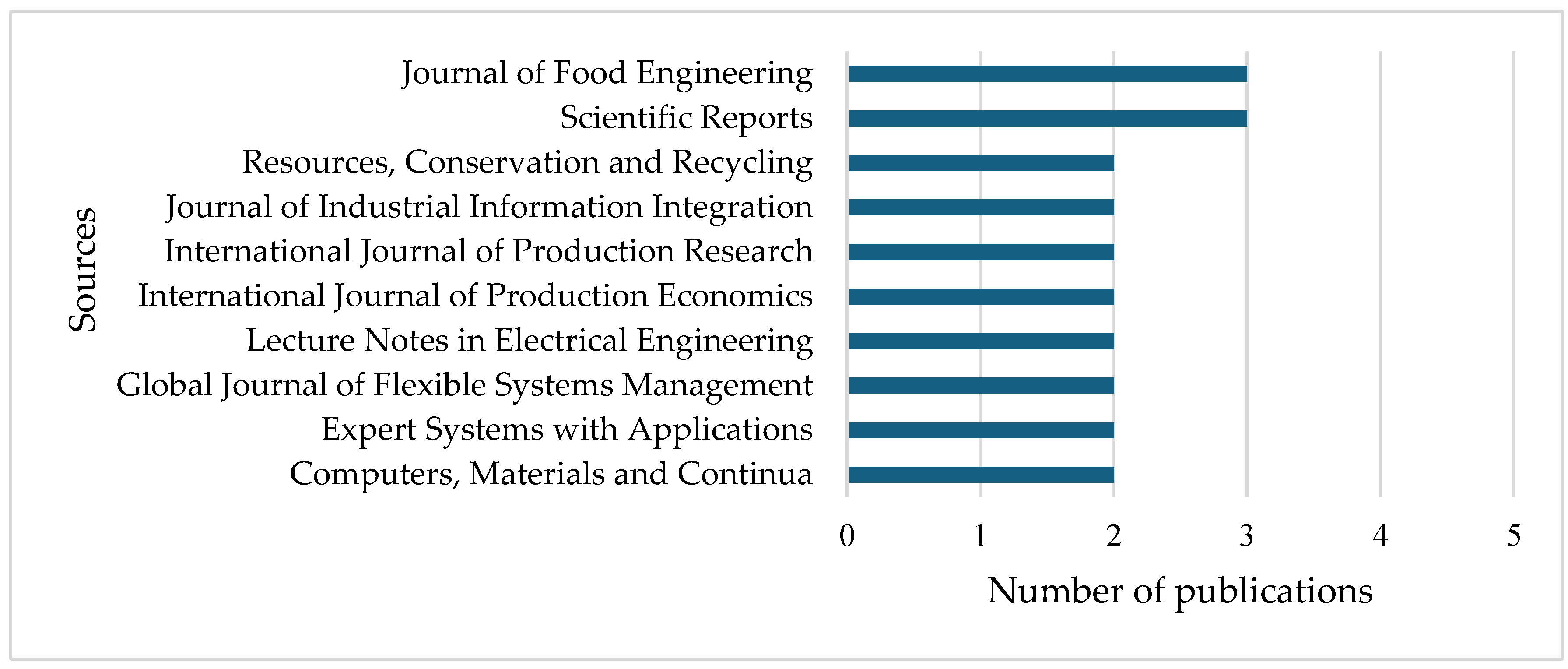
2.4. Top Sources of Publication
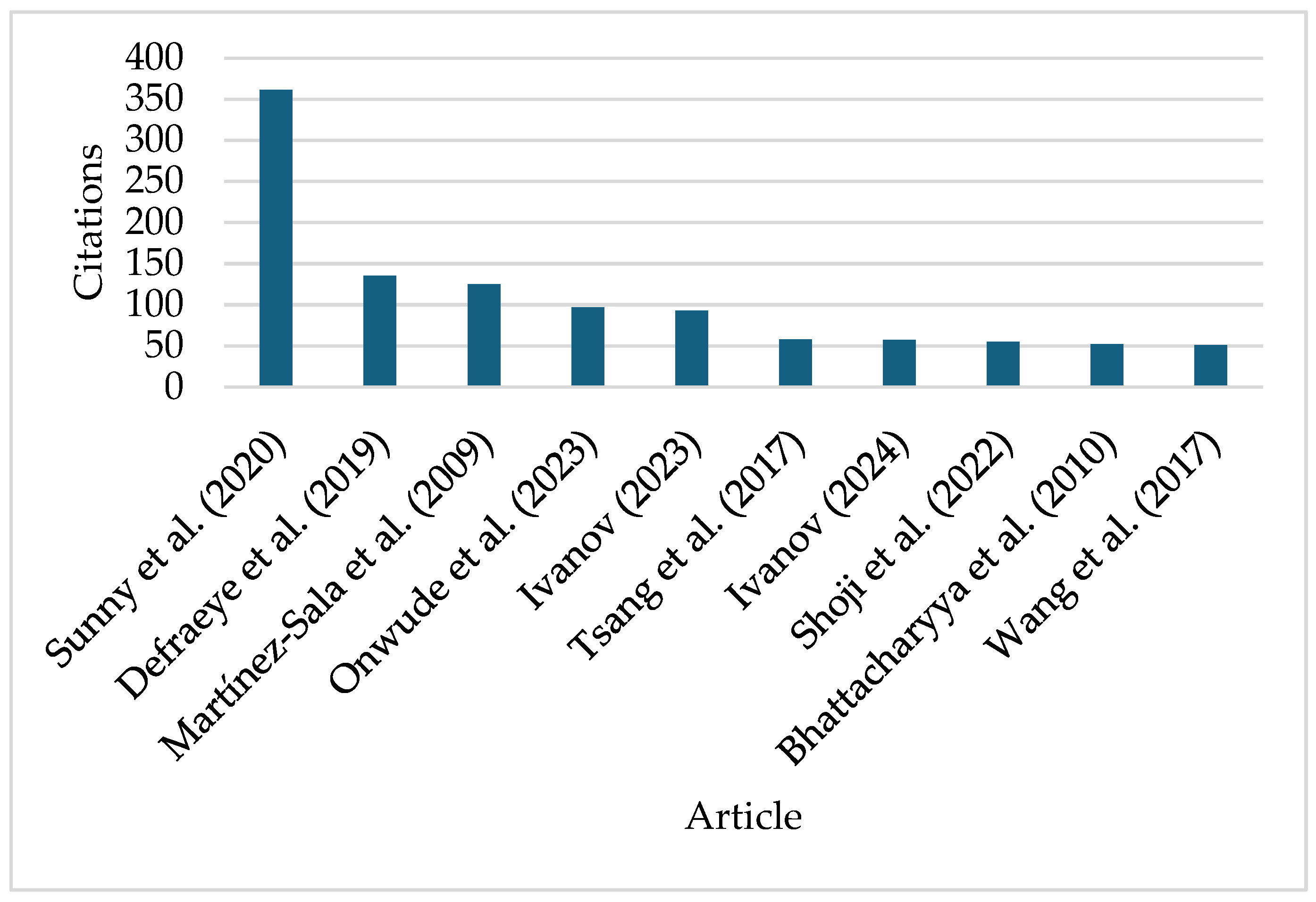
2.5. Citation Impact of the Reviewed Articles
3. Discussion of Key Findings
3.1. Overview of Cold Chain Issues and Technological Solution
| Cold Chain Issue/Problem | Cold Chain Stage | Consequences | Technological Solution | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality, safety, and temperature control and monitoring | Storage, Warehousing, Transportation, Last-Mile Delivery, Outbound Logistics, Entire Cold Chain. | Spoilage, quality degradation, vaccine inefficacy, food loss, economic and operational losses, emissions, public health and safety risks, illness outbreaks, product recalls, contamination, reduced efficiency, and environmental impact. | 3G, 5G, Acoustic Impulse Sensors, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Neural Network, Anticipatory Shipping, Advanced Telematics Systems, Barcode, Battery-free Sensing, Big Data Analytics, Bluetooth Low Energy, Blockchain, Controlled Atmosphere Systems, Cloud Computing, Data Collection Systems, Data Loggers, Database Systems, Data Mining, Digital Twins, Distributed Ledger Technology, Electronic Data Interchange, Electronic Nose, General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), Grid Computing, Imaging Systems, Intelligent Packaging, Internet of Everything (IoE), Machine Learning (ML), Mobile Apps, Multi-Gas Sensors, Multi-Sensors, Near Field Communication Sensors, Optimization Algorithms, Printed Sensors, Real-Time Systems, Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID), Stacked Auto-Encoder,, Smart Reefers, Solar Harvesting, Time Temperature Integrators, Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN), ZigBee. | [29,30,32,39,46,47,48,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90] |
| Efficiency and Operational | Post-harvest, Storage, Transportation, Entire Cold Chain. | Product quality deterioration and spoilage, inventory obsolescence and waste, high energy use and associated environmental impact, increased operational costs and reduced profitability, customer dissatisfaction and reduced food security, safety incidents, and worker hazards, and data integrity, information-sharing, and cybersecurity and blockchain vulnerabilities. | IoT, RFID, WSN, Neural Networks, GPS, Temperature Sensors, Phase Change Materials (PCMs), Predictive Algorithms, Internet of Vehicles, Sensors, Big Data Analytics, Genetic Algorithm, Digital Twins, AI, ML, Real-time Sensors, Edge Computing, Cloud, Blockchain,, IoE, BLE, Real-time Detection, T&H Monitoring, Mobile Apps, Motion Detection, Positioning. | [34,45,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98] |
| Energy consumption and Environmental Impact | Storage, Transportation, Entire Cold Chain. | High and inefficient energy use leading to higher costs and financial losses, increased emissions and pollution with associated quality damage, food loss and waste operational disruptions and unmet demand, data and cybersecurity risks, safety and worker hazards, and reduced investment, implementation difficulties, and loss of stakeholder trust. | AI, IoT, Improved Fireworks–Artificial Bee Colony, Blockchain, Photovoltaic Panels, Kinetic Energy Recovery System, PCMs, Sensors, Ant Colony Algorithm, Cloud, Big Data Analytics, Digital Twin Service (DTS), IoE. | [43,44,49,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106] |
| Lack of end-to-end visibility and traceability | Storage, Transportation, Last-Mile Delivery, Entire Cold Chain. | Energy inefficiency, resource waste, and inadequate infrastructure increase costs and cause economic losses, maintenance, capacity, and coordination problems create bottlenecks, and poor forecasting, limited traceability, weak data integration, and handling errors lead to spoilage, safety risks, and reduced transparency across the cold chain. | ZigBee Technology, Sensor Technology, Integrated Development, ML, Real-Time Data, Intelligent Technology, Stochastic Process, WSN, AI, IoT, Big Data, RFID, GPRS, Kalman Filter, Cloud Computing, Digital Twins, Blockchain, Temperature Devices, Technological Infrastructure, Deep Neural Networks, Logistic Regression, IoE, Adaptive Data Smoothing and Compression, Smart Contracts, 5G, GIS, GPS, Stackelberg Models, Sensors. | [13,30,40,41,45,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125] |
3.2. Digital Twins in Cold Chain
| Digital Twin Application | References | Cold Chain Stage | Applicability of Digital Twin in Real-World (Future Application) | Benefits of Applying Digital Twin | Challenges of Applying Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Control and Traceability | [30,32,46,64,76,88,89,90,98,117] | Storage, transportation, and the entire cold chain | Real-time monitored, quality-controlled logistics with food-quality prediction; optimized energy use; greater resilience and efficiency; less food waste; and improved cybersecurity and sustainability via IoT, AI, and blockchain integration. | Digital twin applications enable simulation of operational impacts, real-time monitoring of environmental parameters, and integration of live data for informed decision-making. They help predict quality degradation, optimize refrigeration and logistics, enhance cybersecurity, and improve overall efficiency while reducing food and energy losses. | Model accuracy, verification and validation processes, ethical considerations, integration challenges, data utilization, interoperability, standardization, cost and resource constraints, lack of technical expertise, simplification of models, generalizability of results, need for further research on rollout. Simplification of models, low generalizability, need for further research on rollout. Cost and resource constraints, interoperability, standardization, lack of technical expertise. |
| Real-time Monitoring and Optimization | [12,30,32,33,45,46,53,64,72,76,88,89,98,117,118] | Postharvest, storage, transportation, and retail. | Improvement in operational efficiency, resilience, and sustainability in food supply chains. Improvement of product quality and economic profitability. | Real-time monitoring and optimization of cold chain operations strengthen supply chain resilience, enable automatic control of refrigeration systems, and enhance product quality and economic performance. | |
| Decision Support | [12,30,33,35,46,53,64,76,88,89,118] | Postharvest, logistics, storage, transportation, and retail. | Enhancement in decision-making and performance across sectors, enhancement of growing practices, postharvest logistics, retail marketing, and cold chain strategies. | Digital twins provide real-time insights and predictive analytics that enhance visibility, transparency, collaboration, and traceability, supporting informed decision-making and optimizing overall supply chain operations. | |
| Risk Assessment and Mitigation | [46,76,88,127] | Storage and transportation | Improvement in risk prediction and management, automation of processes, enhanced resilience, assessment of supplier risks, monitoring of compliance, development of contingency plans. | Enhanced resilience through automation and real-time data acquisition, enabling faster decision-making, simplified process control, and early risk detection during disruptions. | |
| Predictive Maintenance | [32,45,46,89] | Packaging, pre-cooling, transportation, storage, postharvest. | Anticipation of maintenance needs, optimization of processes, improved efficiency. | Real-time monitoring and data-driven insights enhance decision-making, improve efficiency, and enable continuous operational improvement. | |
| Real-time Occupational Safety Monitoring | [54] | Storage | Heightening of occupational safety monitoring, real-time safety tracking, incident handling improvement. | Real-time monitoring with dynamic tracking maps integrates worker status and environmental conditions, enabling rapid response to anomalies. | |
| ESG Evaluation | [98] | Storage and transportation | Enhancement of ESG-driven transformation in energy enterprises by supporting long-term digital twin deployment through coordinated government incentives and private equity investments. | Predictive analytics and real-time monitoring enhance decision-making, strengthen traceability in sustainable logistics, and improve data management and security. | |
| Others | [33,35] | Entire cold chain | Enhancement of decision-making, visualization, analysis, simulation, and optimization of supply chains. | Enhanced management capabilities, real-time data-driven decision-making, descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, recognition of physical supply chain structure. |
3.3. Sustainability Initiatives Through Digital Transformation in Cold Chain
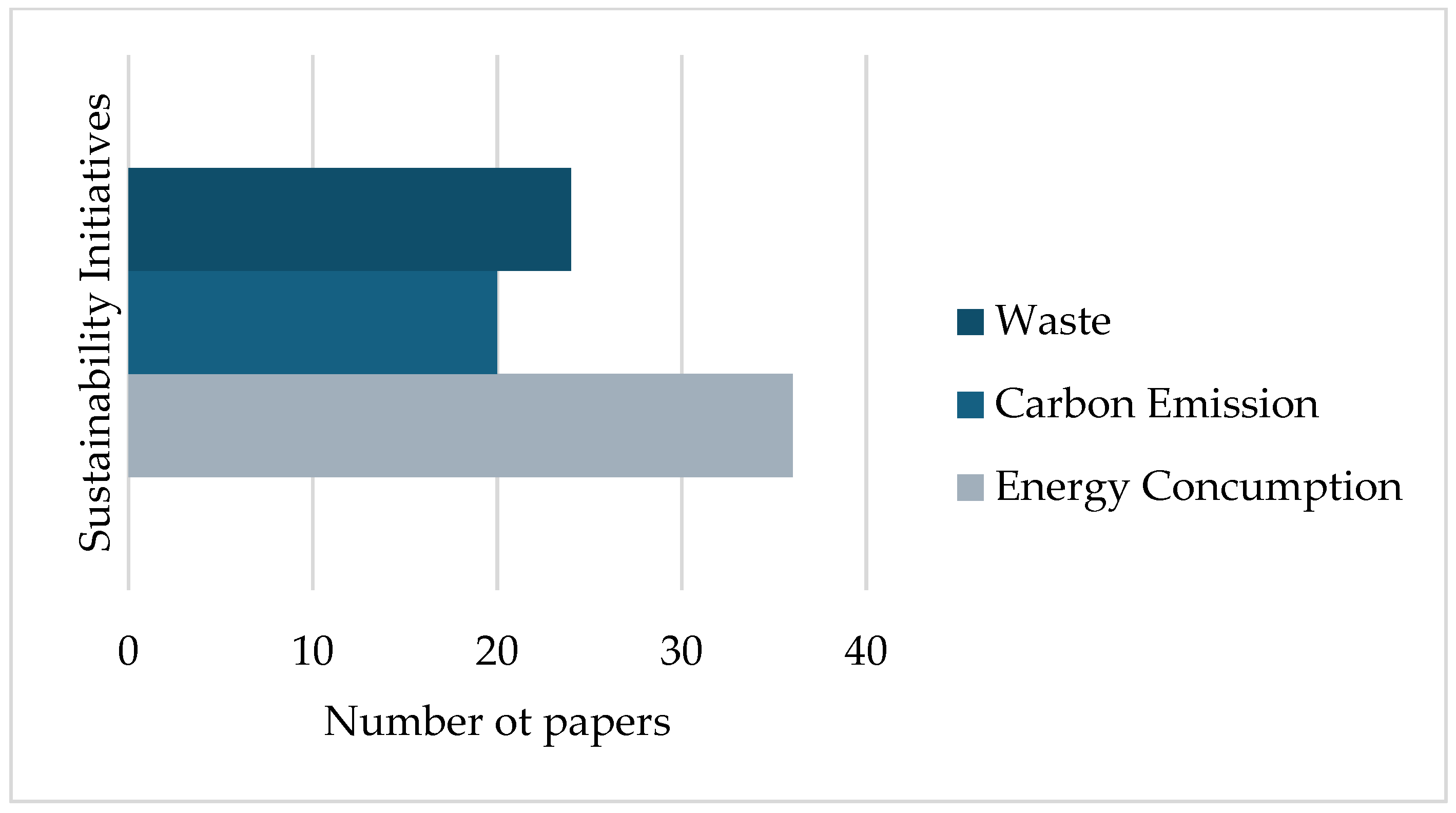
3.4. Applications and Benefits of Digital Transformation in Cold Supply Chains
| Benefits of Digital Transformation in Cold Chain | Reference | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Efficiency and Productivity | [34] | Improves operational effectiveness and enhanced customer satisfaction, with the obsolescence rate for handling environmentally sensitive products decreasing from 13% to 8%. |
| [49] | Reduces the total delivery cost by 3.30% and 4.93% compared to other algorithms. | |
| [67] | Results in a 35% increase in deliveries and a 3.23% reduction in forklift travel distances, leading to lower operational costs and enhanced logistics efficiency. | |
| [68] | Improves transparency, traceability, and efficiency in logistics operations, enhances service quality, and strengthens data security and management. | |
| [99] | Achieves a minimum comprehensive loss value of 3.374, demonstrating superior sustainability compared with constant low-temperature storage. | |
| [105] | Reduces discarded reefer containers by 42.1% and associated GHG emissions by 21.8%, demonstrating the technology’s effectiveness in improving food safety and lowering costs. | |
| [108] | Results in 34.76% reduction in costs and a 15.6% reduction in resource wastage, which improves overall resource utilization and minimizes unnecessary expenses. | |
| [111] | Cuts vehicle requirements from 12 to 6, revealing higher logistics efficiency. | |
| [77,85,94,96] | Improves efficiency through smart logistics platforms that provide real-time visualization, automated alerts, and intelligent decision support. | |
| [74,76,93,103,129] | Optimizes cold chain logistics operations through improved scheduling, distribution, and warehouse management. | |
| Enhanced Visibility and Traceability | [29] | Provides blockchain-based traceability solutions tackle the shortcomings of centralized traceability solutions. |
| [40] | Enhances data processing and supervision, supports evidence-based decisions, improves logistics flow, and safeguards food safety. | |
| [13,53] | Strengthens traceability and quality control, improves efficiency, reduces medication risks, and enhances transparency, trust, and secure data management. | |
| [41,59] | Improves transparency, traceability, and accountability, strengthens quality assurance, and increases efficiency across the food supply chain. | |
| [84] | Improves the efficiency of food-cold chain logistics traceability through Bar code technology and RFID. | |
| Enhanced Sustainability | [73] | Reduces average energy consumption by 87.04% compared to battery powered systems and decreases costs by 15.3% when compared to traditional battery powered wireless sensing systems. |
| [100] | Enables prolonged operation without direct sunlight through PCMs. | |
| [99] | Reduces emissions and costs while optimizing energy use and logistics efficiency. | |
| [101] | Improves efficiency and traceability using blockchain and sensors to monitor environmental conditions in fresh food distribution. | |
| Cost Optimization | [55] | Improves recognition accuracy, achieving 97.4% with three feature values and 98.6% with six feature values, while maintaining low-cost increases for temperature management in cold chain logistics |
| [67] | Delivers a 35% rise in deliveries, a 3.23% reduction in forklift travel, and 10–15% lower labor and resource costs, yielding annual savings of EUR 26,880–40,320. | |
| [68] | Shows an increase of 32% in total income and improves environmental criteria in a real-world case study on the poultry supply chain. Additionally, a 4% reduction in total profit can lead to a 12% increase in total greenness and human health. | |
| [92,116] | Optimizes costs through greater efficiency, better resource use, streamlined warehouse operations, and cost-effective system design. | |
| [108] | Achieves a 34.76% reduction in costs and a 15.6% reduction in resource wastage, which improves overall resource utilization and minimizes unnecessary expenses. | |
| [110] | Improves monitoring accuracy, achieving prediction errors as low as 0.98 °F surpassing manufacturer-reported temperature precision. | |
| [41,63,97,123] | Strengthens quality management and data integrity, enhances trust and transparency, improves tracking and tracing efficiency, and reinforces quality and safety assurance in frozen and chilled product distribution. | |
| Improved Quality and Safety | [47] | Enables continuous temperature monitoring, identification of critical breach points, and data-driven temperature control, ensuring stronger vaccine preservation. |
| [65] | Enables real-time collection of temperature and humidity data, improving quality control and reducing food waste. | |
| [33,114,123,127] | Enhances quality management and data integrity, strengthens transparency and trust, supports informed decision-making and demand forecasting, optimizes transportation, reduces food waste, and improves visibility, risk assessment, and scenario simulation for proactive management. | |
| Enhanced Decision-Making | [45] | Reduces food wastage about 30% globally each year due to poor supply chain management. |
| [89] | Provides detailed insight into fruit quality degradation during transport, showing that fruits lose 43–85% of their quality before reaching retail outlets. | |
| [112] | Reduces spoilage rates of 25–30% in fruits, preventing nearly 12 million tons of annual losses. | |
| [39,111,113,118] | Improves visibility, traceability, and efficiency, optimizes resource use, reduces product loss, boosts sustainability and customer satisfaction through reliable data and logistics tracking. | |
| Improved Customer Satisfaction | [67] | Results in a 35% increase in deliveries and a 3.23% reduction in forklift travel, lowering operational costs and enhancing logistics efficiency during peak demand periods. |
| [121] | Achieves 96.35% accuracy, 97% precision, and 94.89% recall in predicting commodity purchase volume, showing the effectiveness of technology in enhancing supply chain management. |
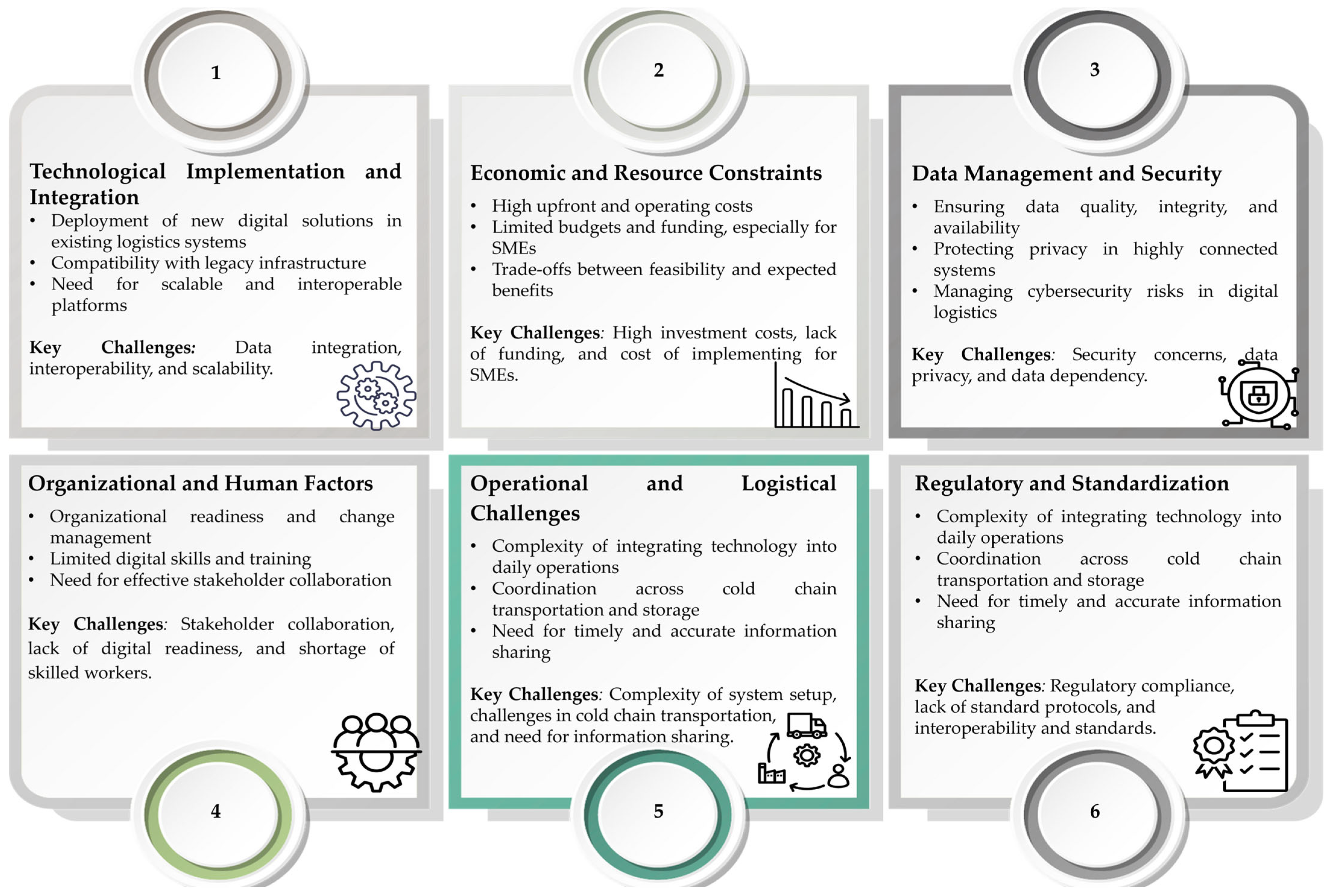
3.5. Challenges of Digital Transformation in Cold Supply Chains
4. Research Gaps and Further Research Recommendations
4.1. Limitations and Future Research Recommendations
4.2. Managerial and Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar Kanike, U. Factors Disrupting Supply Chain Management in Manufacturing Industries. J. Supply Chain Manag. Sci. 2023, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piprani, A.Z.; Jaafar, N.I.; Ali, S.M.; Mubarik, M.S.; Shahbaz, M. Multi-Dimensional Supply Chain Flexibility and Supply Chain Resilience: The Role of Supply Chain Risks Exposure. Oper. Manag. Res. 2022, 15, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siagian, H.; Tarigan, Z.J.H.; Jie, F. Supply Chain Integration Enables Resilience, Flexibility, and Innovation to Improve Business Performance in COVID-19 Era. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.J.; Paulraj, A. Understanding Supply Chain Management: Critical Research and a Theoretical Framework. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2004, 42, 131–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryciuk, U.; Zabrocka, A. Investigating Challenges and Responses in Supply Chain Management amid Unforeseen Events. Eng. Manag. Prod. Serv. 2024, 16, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, S. The Role of Supply Chain Flexibility in Adapting Marketing Strategies to Changing Consumer Preferences. Preprints 2024. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202406.1759 (accessed on 10 December 2025).
- Lee, J. Leveraging Digital Tools and Analytics for Temperature Management in Cold Chain Systems for Gene Therapies. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Eveloy, V.; Ayou, D.S. Sustainable District Cooling Systems: Status, Challenges, and Future Opportunities, with Emphasis on Cooling-Dominated Regions. Energies 2019, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatorachian, H.; Pawar, K. Waste Efficiency in Cold Supply Chains through Industry 4.0-Enabled Digitalisation. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2025, 18, 2461564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ononiwu, M.I.; Onwuzulike, O.C.; Shitu, K. The Role of Digital Business Transformation in Enhancing Organizational Agility. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 23, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.; da Costa, T.P.; Cama-Moncunill, X.; Cadden, T.; Condell, J.; Cowderoy, T.; Ramsey, E.; Murphy, F.; Kull, M.; Gallagher, R.; et al. Real-Time Anomaly Detection in Cold Chain Transportation Using IoT Technology. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, I.; Namdar, J.; Saénz, M.J.; Elmquist, R.A., III; Dávila Novoa, L.R. Revolutionize Cold Chain: An AI/ML Driven Approach to Overcome Capacity Shortages. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2025, 63, 2190–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Wang, Y.; Liang, K.; Li, J.; Niu, X. Advancing Emergency Supplies Management: A Blockchain-Based Traceability System for Cold-Chain Medicine Logistics. Adv. Theory Simul. 2024, 7, 2300704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, K.; Schudel, S.; Shrivastava, C.; Onwude, D.; Defraeye, T. Optimizing the Postharvest Supply Chain of Imported Fresh Produce with Physics-Based Digital Twins. J. Food Eng. 2022, 329, 111077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Smart, P. Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review. Br. J. Manag. 2003, 14, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Mohammad, J. Sustainability of Perishable Food Cold Chain Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review. Sage Open 2024, 14, 21582440241280455. [Google Scholar]
- Rolf, B.; Beier, A.; Jackson, I.; Müller, M.; Reggelin, T.; Stuckenschmidt, H.; Lang, S. A Review on Unsupervised Learning Algorithms and Applications in Supply Chain Management. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 63, 1933–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Assaf, K.; Bahroun, Z.; Ahmed, V. Transforming Service Quality in Healthcare: A Comprehensive Review of Healthcare 4.0 and Its Impact on Healthcare Service Quality. Informatics 2024, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yao, L.; Wang, W.; Tang, S. Developing an Effective and Sustainable National Immunisation Programme in China: Issues and Challenges. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e1064–e1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, W.; Folorunso, O.; McCord, J.; Roche, G.; Tien, M.; Hatch, B.; Spisak, C.; Genovese, E.; Pare, B.; Donatien, K.; et al. Redesigning Immunization Supply Chains: Results from Three Country Analyses. Vaccine 2021, 39, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavia, A.; Fred, B.; Eleanor, T. Gaps in Vaccine Management Practices during Vaccination Outreach Sessions in Rural Settings in Southwestern Uganda. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.D. An Optimization Model for the Vehicle Routing Problem in Multi-Product Frozen Food Delivery. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2014, 12, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, X. Toward an Intelligent Solution for Perishable Food Cold Chain Management. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS), Beijing, China, 26–28 August 2016; IEEE: New York City, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 852–856. [Google Scholar]
- Babagolzadeh, M.; Shrestha, A.; Abbasi, B.; Zhang, Y.; Woodhead, A.; Zhang, A. Sustainable Cold Supply Chain Management under Demand Uncertainty and Carbon Tax Regulation. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2020, 80, 102245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, R.; Ghazanfari, M.; Rasouli, M.R. A Decision Support System for Resilient Vehicle Route Planning Using Mathematical Modeling and Artificial Neural Networks: A Case Study. Kybernetes, 2024; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-Y.; Tseng, M.-L.; Wang, C.-H.; Xiao, C.; Fei, T. Low-Carbon CSold Chain Logistics Using Ribonucleic Acid-Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Vehicle Routing Problem for Cold-Chain Drug Distribution with Epidemic Spread Situation. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2025, 262, 125186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, E. Citation Analysis as a Tool in Journal Evaluation. Science 1972, 178, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunny, J.; Undralla, N.; Madhusudanan Pillai, V. Supply Chain Transparency through Blockchain-Based Traceability: An Overview with Demonstration. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 150, 106895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defraeye, T.; Tagliavini, G.; Wu, W.; Prawiranto, K.; Schudel, S.; Assefa Kerisima, M.; Verboven, P.; Bühlmann, A. Digital Twins Probe into Food Cooling and Biochemical Quality Changes for Reducing Losses in Refrigerated Supply Chains. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 149, 778–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sala, A.S.; Egea-López, E.; García-Sánchez, F.; García-Haro, J. Tracking of Returnable Packaging and Transport Units with Active RFID in the Grocery Supply Chain. Comput. Ind. 2009, 60, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwude, D.I.; Chen, G.; Eke-emezie, N.; Kabutey, A.; Khaled, A.Y.; Sturm, B. Recent Advances in Reducing Food Losses in the Supply Chain of Fresh Agricultural Produce. Processes 2020, 8, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D. Intelligent Digital Twin (IDT) for Supply Chain Stress-Testing, Resilience, and Viability. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 263, 108938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, Y.; Choy, K.; Wu, C.; Ho, G.; Lam, H.; Koo, P. An IoT-Based Cargo Monitoring System for Enhancing Operational Effectiveness under a Cold Chain Environment. Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag. 2017, 9, 1847979017749063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D. Conceptualisation of a 7-Element Digital Twin Framework in Supply Chain and Operations Management. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 2220–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Floerkemeier, C.; Sarma, S. RFID Tag Antenna Based Temperature Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on RFID (IEEE RFID 2010), Orlando, FL, USA, 14–16 April 2010; IEEE: New York City, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; He, Q.; Matetic, M.; Jemric, T.; Zhang, X. Development and Evaluation on a Wireless Multi-Gas-Sensors System for Improving Traceability and Transparency of Table Grape Cold Chain. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 135, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbano, O.; Perles, A.; Pedraza, C.; Rubio-Arraez, S.; Castelló, M.L.; Ortola, M.D.; Mercado, R. Cost-Effective Implementation of a Temperature Traceability System Based on Smart RFID Tags and IoT Services. Sensors 2020, 20, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.M.; Chau, K.Y.; Kuo, W.T.; Liu, X.X. IoT-Based Information System on Cold-Chain Logistics Service Quality (ICCLSQ) Management in Logistics 4.0. Inf. Syst. Front. 2024, 26, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Research on Cold Chain Food Logistics Traceability Method Based on Big Data Technology; Association for Computing Machinery (ACM): New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Chen, E. Development and Assessment of Blockchain-IoT-Based Traceability System for Frozen Aquatic Product. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Qin, Q. Understanding Food Cold Chain: Balance and a Sustainable Future. J. Int. Econ. Glob. Gov. 2024, 1, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandana; Sangwa, N.R.; Ertz, M.; Shashi. Sustainable and Resilient Cold Chains: Enhancing Adaptability, Consistency, and Digital Transformation for Success in a Turbulent Market. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2024, 33, 6689–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Mu, X. Decentralized Solution for Cold Chain Logistics Combining IoT and Blockchain Technology. Taiwan Ubiquitous Inf. 2023, 8, 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Vedashree, R.; Ashok, P.; Pillai, S. Transforming Cold Chain Management: The Role of Digital Twins in Post-Harvest Logistics. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd World Conference on Communication and Computing, WCONF 2024, Raipur, India, 12–14 July 2024; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, M.F.M.S.; Navaranjan, N.; Demirovic, A. Food Cold Chain Logistics and Management: A Review of Current Development and Emerging Trends. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, H.K.; Sharma, D.; Dhir, S.; Sushil, S.; Ghosh, R.S.; Bagchi, S.N.; Singh, S.; Pooja, P.; Kothari, K.; Monfardini, E.; et al. Ensuring Vaccine Temperature Integrity: Monitoring from Storage to Last-Mile Delivery. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2024, 25, 559–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Wang, X.; Rahbari, A.; Hangi, M. Optimisation of a Portable Phase-Change Material (PCM) Storage System for Emerging Cold-Chain Delivery Applications. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 104855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M. Optimization of Distribution Paths in Cold Chain Logistics Management Based on IFW-ABC Algorithm. Intell. Decis. Technol. 2024, 18, 1711–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akindotei, O.; Emmanuel, I.; Awotiwon, B.O.; Otakwu, A. Blockchain Integration in Critical Systems Enhancing Transparency, Efficiency, and Real-Time Data Security in Agile Project Management, Decentralized Finance (DeFi), and Cold Chain Management. Int. J. Sci. Res. Mod. Technol. IJSRMT 2024, 3, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, G.; Sharma, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Ahmad, I.; Qureshi, S.; Ishfaq, M. Blockchain Technology: Benefits, Challenges, Applications, and Integration of Blockchain Technology with Cloud Computing. Future Internet 2022, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, S. RFID Technology Application on the Supervision of Cold-Chain Logistics Warehousing. In Advanced Graphic Communications, Packaging Technology and Materials; Ouyang, Y., Xu, M., Yang, L., Ouyang, Y., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 619–626. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Tao, X.; Zhang, Y. Construction of Digital Twin System for Cold Chain Logistics Stereo Warehouse. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 73850–73862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Wu, W.; Shen, L.; Liao, W.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, J. Industrial Internet of Things and Unsupervised Deep Learning Enabled Real-Time Occupational Safety Monitoring in Cold Storage Warehouse. Saf. Sci. 2022, 152, 105766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xie, R.; Liao, J.; Shen, X.; Yang, S. A Cost-Effective over-Temperature Alarm System for Cold Chain Delivery. J. Food Eng. 2024, 368, 111914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tan, C.; Ip, W.H.; Wu, C.H. Dynamic Blockchain Adoption for Freshness-Keeping in the Fresh Agricultural Product Supply Chain. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 217, 119494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Morales, K.; Liu, G.; Manzardo, A. An Improved Artificial Neural Network Using Multi-Source Data to Estimate Food Temperature during Multi-Temperature Delivery. J. Food Eng. 2023, 351, 111518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergine, V.; Sergi, I.; Montanaro, T.; Shumba, A.T.; Luca Benvenuto, F.; Patrono, L. Leveraging Internet of Things and Distributed Ledger Technology for Cold Chain Management in Freight Transportation. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech), Split/Bol, Croatia, 20–23 June 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Spitalleri, A.; Kavasidis, I.; Cartelli, V.; Mineo, R.; Rundo, F.; Palazzo, S.; Spampinato, C.; Giordano, D. BioTrak: A Blockchain-Based Platform for Food Chain Logistics Traceability. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Communication, Networking and Services (ICCNS), Valencia, Spain, 19–22 June 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lim, M.K.; Tseng, M.-L.; Tan, C.; Li, Y. An Intelligent Green Scheduling System for Sustainable Cold Chain Logistics. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ye, J.; Li, S. The Road Cold Chain Transportation Information Traceability Platform Based on “IOT+ Blockchain” Allows Cold Chain Transportation Management More Credible. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Engineering (ICITE 2021), Beijing, China, 29–31 October 2021; Zhang, Z., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1015–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, H. Construction of Third-Party Cold Chain Logistics Platform Based On Radio Frequency Identification Technology. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 452, 042186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoglou, M.; Touli, A.; Platakou, E.; Tsironi, T.; Taoukis, P.S. Predictive Modeling and Selection of TTI Smart Labels for Monitoring the Quality and Shelf-Life of Frozen Seafood. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 26, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukasse, L.J.S.; Schouten, R.E.; Castelein, R.B.; Lawton, R.; Paillart, M.J.M.; Guo, X.; Woltering, E.J.; Tromp, S.; Snels, J.C.M.A.; Defraeye, T. Perspectives on the Evolution of Reefer Containers for Transporting Fresh Produce. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 140, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, J.; Duan, Y.; Eze, E.; Ramanathan, R.; Ajmal, T. Machine Learning-Based Optimal Temperature Management Model for Safety and Quality Control of Perishable Food Supply Chain. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, T.; Baser, M.; Tyagi, A.; Ng, E.Y.K. CRYOMOVE: Cold Chain Real-Time Management of Vaccine Delivery Using PCM and Deep Learning. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 255, 123962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenc, A. Cross-Docking Layout Optimization in FlexSim Software Based on Cold Chain 4PL Company. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshdadi, A.; Kamel, S.; Alsolami, E.; Lytras, M.D.; Boubaker, S. An IoT Smart System for Cold Supply Chain Storage and Transportation Μanagement. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2024, 14, 13167–13172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Mohit, T.; Sachdeva, A. Model Development and Assessment for Temperature Processing Technologies Used in Cold Chain Industries. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 10, 2021–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabsheybani, A.; Alireza, A.K.; Pishvaee, M.S. Sustainable Cold Supply Chain Design for Livestock and Perishable Products Using Data-Driven Robust Optimization. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2024, 19, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Jin, P.; Li, G. Investment Decision of Blockchain Technology in Fresh Food Supply Chains Considering Misreporting Behavior. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma Pargaien, A.; Pargaien, S.; Adhikari, M.; Maan, M.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, H. The Role of IOT for Monitoring the Wastage of Vaccines Due to Poor Cold Chain Management. In Proceedings of the 2021 Fifth International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC), Palladam, India, 11–13 November 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X. Sustainable Solar Powered Battery-Free Wireless Sensing for Food Cold Chain Management. Sens. Int. 2022, 3, 100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, S.; Ryu, K. Prediction of Refrigerated Vehicle Environment for Optimization of Cold-Chain Logistics. ICIC Express Lett. Part B Appl. 2023, 14, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, B.S.; Vanitha, A.; Palav, M.R.; Tilak Babu, S.B.G.; Nair, A.M.; Bogiri, N. IoT Applications in Cold Chain Management for Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring Product Integrity and Safety. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Recent Trends in Computer Science and Technology (ICRTCST), Jamshedpur, India, 15–16 April 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Shen, L.; Zhao, Z.; Harish, A.R.; Zhong, R.Y.; Huang, G.Q. Internet of Everything and Digital Twin Enabled Service Platform for Cold Chain Logistics. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2023, 33, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C. Application of 5G Private Network and Internet of Things in Smart Cold Chain Logistics Park. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Conference on Telecommunications, Optics and Computer Science (TOCS), Virtually, 11–12 December 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan, U.; Ramanathan, R.; Adefisan, A.; Da Costa, T.; Cama-Moncunill, X.; Samriya, G. Adapting Digital Technologies to Reduce Food Waste and Improve Operational Efficiency of a Frozen Food Company—The Case of Yumchop Foods in the UK. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, C.; Zhang, H.; Chang, M.L. Improving End-to-End Traceability and Pharma Supply Chain Resilience with Blockchain. Blockchain Healthc. Today 2022, 5, 10-30953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masudin, I.; Ramadhani, A.; Restuputri, D.P.; Amallynda, I. The Effect of Traceability System and Managerial Initiative on Indonesian Food Cold Chain Performance: A COVID-19 Pandemic Perspective. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2021, 22, 331–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Zhou, L. Construction of Logistics Network System Based on Internet+. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1176, 022027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-C.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Adhikari, B. Recent Developments in Smart Freezing Technology Applied to Fresh Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2835–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabiha, S.; Ezzeddine, T. Simulation of Cold Chain Traceability Based on RFID and WSN. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd World Symposium on Web Applications and Networking (WSWAN), Sousse, Tunisia, 21–23 March 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X. A Research about the Tracing Technology and System Designing of Food-Cold Chain. In Proceedings of the 2011 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Management Science and Electronic Commerce (AIMSEC), Zhengzhou, China, 8–10 August 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 2729–2732. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Xu, W.; Wang, M. The Grid-Computing Based Instrumented Monitoring Platform for Cold Chain Logistics. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Logistics Engineering and Intelligent Transportation Systems, Wuhan, China, 26–28 November 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Rollo, A.; Gnoni, M.G. Performance Analysis of Rfid Applications in Cold Chain Management. In Business Performance Measurement and Management: New Contexts, Themes and Challenges; Taticchi, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 61–71. ISBN 978-3-642-04800-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sreevathsan, S.; Bhavana, B.K.; Debnath, S.; Mudliar, S.N. Advanced Computational Tools for Enhanced Food Quality and Safety. In Engineering Aspects of Food Quality and Safety; Hebbar, H.U., Sharma, R., Chaurasiya, R.S., Ranjan, S., Raghavarao, K.S.M.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 207–247. ISBN 978-3-031-30683-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, H.Y.; Tang, V.; Ho, G.T.S. A Digital Twins Model for Analyzing and Simulating Cold Chain Risks. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Bali, Indonesia, 20–23 February 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, C.; Schudel, S.; Shoji, K.; Onwude, D.; da Silva, F.P.; Turan, D.; Paillart, M.; Defraeye, T. Digital Twins for Selecting the Optimal Ventilated Strawberry Packaging Based on the Unique Hygrothermal Conditions of a Shipment from Farm to Retailer. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 199, 112283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwude, D.; Cronje, P.; North, J.; Defraeye, T. Digital Replica to Unveil the Impact of Growing Conditions on Orange Postharvest Quality. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-T.; Chou, C.-T.; Wen, C.-H.; Chen, M.-C. Optimized Vehicle Exploitation Period Decision in Cold-Chain Logistics Companies. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2024, 57, 101235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emenike, C.C.; Eyk, N.P.V.; Hoffman, A.J. Improving Cold Chain Logistics through RFID Temperature Sensing and Predictive Modelling. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–4 November 2016; pp. 2331–2338. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, J. Cold Chain Logistics and Joint Distribution: A Review of Fresh Logistics Modes. Systems 2024, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, A.A.; Jaffer, Z.; Wasmi Zaydan, N.R.; Hussam, R.; Salman, H.D.; Shnain, A.H. Smart Logistics Based on Internet of Vehicles for Sustainable Supply Chain Management. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Smart Systems for Electrical, Electronics, Communication and Computer Engineering (ICSSEECC), Coimbatore, India, 28–29 June 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 757–762. [Google Scholar]
- Moyo, E.H.; Carstens, S.; Walters, J. Simulation Model for a Sustainable Food Supply Chain in a Developing Country: A Case Study of the Banana Supply Chain in Malawi. Logistics 2024, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Peng, Y.; Xiong, K. Intelligent Cold Chain Monitoring Platform Based on Internet of Things and Edge Computing. In Advances in Artificial Systems for Logistics Engineering IV; Hu, Z., Zhang, Q., He, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.K.; Shweta; Kumar, D. Blockchain Technology and Vaccine Supply Chain: Exploration and Analysis of the Adoption Barriers in the Indian Context. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 255, 108716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, P.P.; Huang, G.Q. ESG transformation through private equity and digital twin in energy supply chain: An evolutionary game analysis. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2025; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Qian, J.; Li, H.; Lin, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z. Dynamic Multi-Objective Time-Temperature Management for Climacteric Fruit Cold Storage Considering Ripeness Windows and Energy Consumption. J. Food Eng. 2025, 387, 112350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilenti, C.; Petruzziello, F.; Grilletto, A.; Aprea, C.; Maiorino, A. Utilizing Phase Change Materials for Sun-Powered Refrigerators: Experimental Validation in Outdoor Environments. Ann. Chim. Sci. Des. Mater. 2024, 48, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lim, M.K.; Xiong, W.; Huang, X.; Shi, Y.; Wang, S. An Electric Vehicle Routing Model with Charging Stations Consideration for Sustainable Logistics. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2024, 124, 1076–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ma, X.; Wang, K. The Electric Vehicle Promotion in the Cold-Chain Logistics under Two-Sided Support Policy: An Evolutionary Game Perspective. Transp. Policy 2022, 121, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F. Application of a Cold-Chain Logistics Distribution System Based on Cloud Computing and Web Delivery Date Management. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Supply Chain Manag. 2023, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; He, Y.; He, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; You, W.; Zhu, J. A Review of the Energy-Saving Potential of Phase Change Material-Based Cascaded Refrigeration Systems in Chinese Food Cold Chain Industry. Energies 2024, 17, 4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Yi, S.; Lee, E. Including the Reefer Chain into Genuine Beef Cold Chain Architecture Based on Blockchain Technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Shang, W.-L.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Yang, Z.-L.; Zhao, Z. Precooling Energy and Carbon Emission Reduction Technology Investment Model in a Fresh Food Cold Chain Based on a Differential Game. Appl. Energy 2022, 326, 119945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M. Research on Cold Storage Environment Monitoring System Based on ZigBee. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Security (ICSPCS 2024), Chengdu, China, 24–26 May 2024; Mahalle, P.N., Karras, D.A., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J. Optimization of Frozen Goods Distribution Logistics Network Based on K-Means Algorithm and Priority Classification. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Guo, H.; Xiang, M.; Sang, J. Optimization of “Vehicle-UAV” Joint Distribution Routing for Cold Chain Logistics Considering Risk of Epidemic Spreading and Green Cost. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanoglu, M.B.; Uysal, I. ML Approach to Improve the Costs and Reliability of a Wireless Sensor Network. Sensors 2023, 23, 4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Li, G.; Zhou, H. Cold Chain Logistics Transportation Management Strategy Based on ABC-ACO Algorithm and Intelligent Digital. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Data Science and Network Security (ICDSNS), Tiptur, India, 28–29 July 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Huihui, L.; Na, L.; Qingqing, K. Research on Green Cold Chain Logistics Information System under Computer Big Data. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Computers, Information Processing and Advanced Education (CIPAE), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 26–28 August 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wei, W. IoT Network for International Trade Cold Chain Logistics Tracking Based on Kalman Algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1608167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Vidal, A.; Gomez-Bernal, P.; Mendoza-Bernal, J.; Skarmeta, A.F. BIGcoldTRUCKS: A BIG Data Dashboard for the Management of COLD Chain Logistics in Refrigerated TRUCKS. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–18 December 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 2894–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H. Intelligent Coordination Distribution of the Whole Supply Chain Based on the Internet of Things. Complexity 2021, 2021, 5555264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Zhao, M. Research on Cold Chain Logistics Joint Distribution Model Based on Cloud Logistics. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC), Xi’an, China, 3–5 October 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 802–806. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Chen, Y. From Farm to Market: Research Progress and Application Prospects of Artificial Intelligence in the Frozen Fruits and Vegetables Supply Chain. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 153, 104730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanifar, G.; Mohammadi, M.; Golabian, M.; Sherafat, A.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Fusco, G.; Colombaroni, C. Integrated Location and Routing for Cold Chain Logistics Networks with Heterogeneous Customer Demand. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2024, 38, 100573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Jia, S.; Guo, H. Internet of Things (IoT)-Enabled Framework for a Sustainable Vaccine Cold Chain Management System. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavalala, M.M.; Bag, S.; Pretorius, J.H.C.; Rahman, M.S. A Multi-Method Study on the Barriers of the Blockchain Technology Application in the Cold Supply Chains. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2024, 37, 745–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W. E-Commerce Logistics and Supply Chain Network Optimization for Cross-Border. J. Grid Comput. 2024, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Ahmad, V.; Kumar, R.; Yamsani, N.; Amir, M.; Arora, J. Blockchain and Internet-of-Things: A Technological Solution for Issues in Cold Chain. In Proceedings of the 2024 3rd International Conference on Sentiment Analysis and Deep Learning (ICSADL), Bhimdatta, Nepal, 13–14 March 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 632–636. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Lan, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wu, W.; Huang, G.Q. Edge-Cloud Blockchain and IoE-Enabled Quality Management Platform for Perishable Supply Chain Logistics. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, G. Impacts of Blockchain-Based Digital Transition on Cold Supply Chains with a Third-Party Logistics Service Provider. Transp. Res. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2023, 170, 103014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Xin, X. Stackelberg Game-Based Resource Allocation with Blockchain for Cold-Chain Logistics System. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 75, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Suman, R. Digital Twin Applications toward Industry 4.0: A Review. Cogn. Robot. 2023, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Ivanov, D.; Sgarbossa, F. A Digital Twin–Based Approach to Reinforce Supply Chain Resilience: Simulation of Semiconductor Shortages. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Advances in Production Management Systems, Trondheim, Norway, 17–21 September 2023; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 563–576. [Google Scholar]
- Ugochukwu, N.A.; Goyal, S.B.; Arumugam, S. Blockchain-Based IoT-Enabled System for Secure and Efficient Logistics Management in the Era of IR 4.0. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 7295395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J. Simulation of Logistics Real Time Data Processing and Prediction Model Based on Decision Tree Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2024 Asia-Pacific Conference on Software Engineering, Social Network Analysis and Intelligent Computing (SSAIC), New Delhi, India, 10–12 January 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 954–959. [Google Scholar]
- Ogundele, R. Nuvern Applied Science Reviews Resilience and Vulnerabilities in Global Supply Chain Infrastructure: A Cybersecurity Risk Assessment. Nuvern Appl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.F.A.; Ngah, A.H.; Tio, M.B.Y. Third-Party Logistics Intention to Provide Cold Transportation Services. The Mediating Effect of Top Management Support and Organizational Readiness in TOE Framework. OPSEARCH 2023, 60, 1603–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajić, V.; Andrejić, M.; Chatterjee, P. Enhancing Cold Chain Logistics: A Framework for Advanced Temperature Monitoring in Transportation and Storage. Mechatron. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 3, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, O.A.; Adibe, M. Quality Assessment of Cold Chain Storage Facilities for Regulatory and Quality Management Compliance in a Developing Country Context. Int. J. Health Plan. Manag. 2022, 37, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruin, S.; De Bruin, T.; Rosemann, P.M.; Freeze, R.; Kulkarni, P.U.; Carey, W.P. Understanding the Main Phases of Developing a Maturity Assessment Model. In Proceedings of the 6th Australasian Conference on Information Systems, Sydney, Australia, 29 November–2 December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, M.; Vaccari, L.; Posada, M.; Gattwinkel, D. An Application Programming Interface(API) Framework for Digital Government; European Commission, Joint Research Centre: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Falkenberg, R.; Masoudinejad, M.; Buschhoff, M.; Venkatapathy, A.K.R.; Friesel, D.; Ten Hompel, M.; Spinczyk, O.; Wietfeld, C. PhyNetLab: An IoT-Based Warehouse Testbed. In Proceedings of the 2017 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems, FedCSIS 2017, Prague, Czech Republic, 3–6 September 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1051–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Aljohani, A. Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning for Real-Time Supply Chain Risk Mitigation and Agility. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemanek, J.E., Jr.; Kros, J.F. Risk-Mitigation Strategies for Autonomous Delivery Vehicles in the Last Mile: A Comprehensive Overview of the Current State and Future Potential of Autonomous Delivery Technologies in the Supply Chain. J. Compr. Bus. Adm. Res. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.M. Insights from the COVID-19 Pandemic on Building Resilience Capabilities in Vaccine Supply Chains Supporting Mass Vaccination. J. Humanit. Logist. Supply Chain. Manag. 2025, 15, 309–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, H.W.; Akhtar, S.; Ahmad, A.; Anwar, I.; Sulaiman, M.A.B.A. Developing a Conceptual Framework Model for Effective Perishable Food Cold-Supply-Chain Management Based on Structured Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
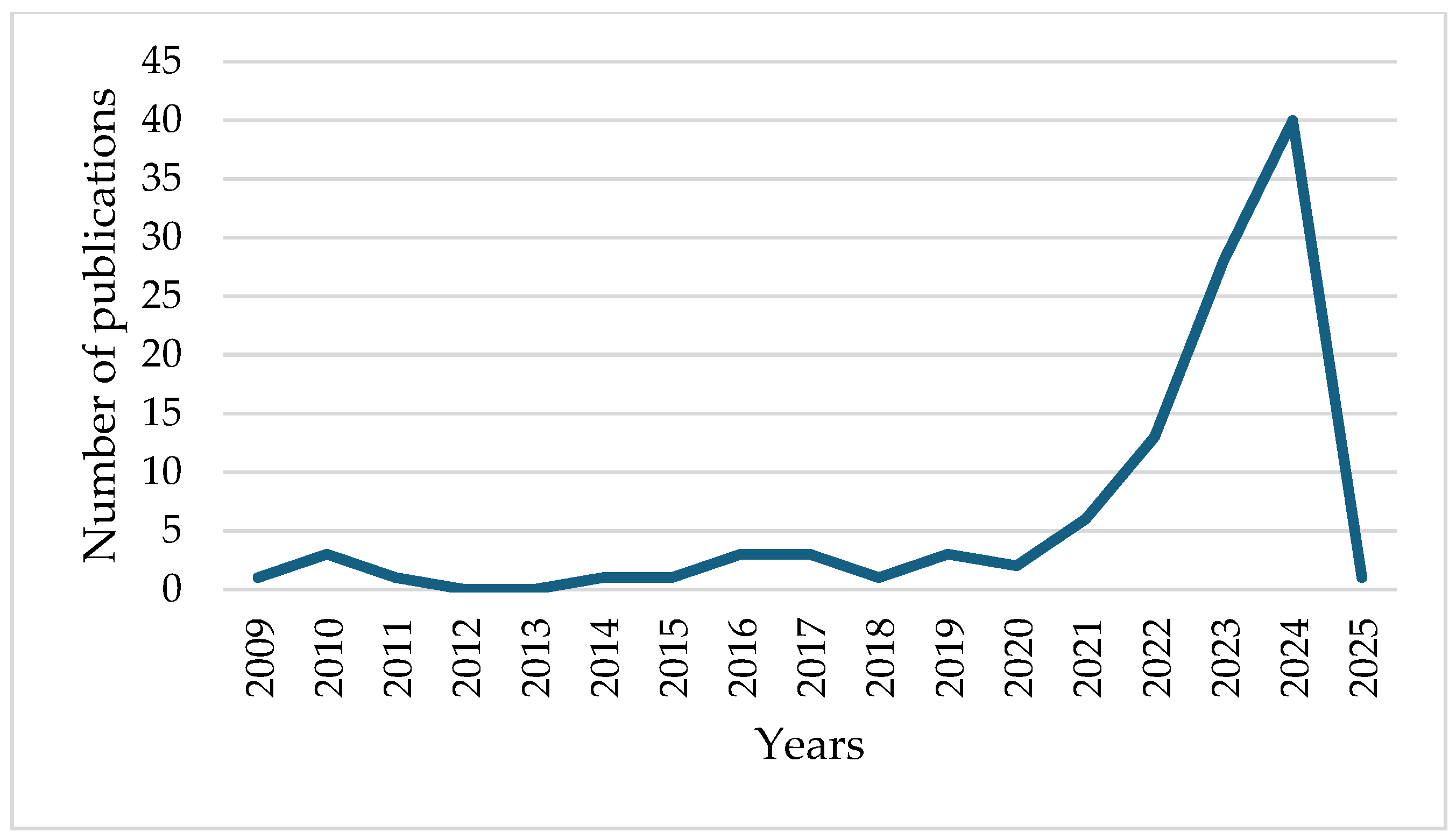
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alherimi, N.; Ben-Daya, M. A Systematic Review on the Intersection of the Cold Chain and Digital Transformation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 11202. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411202
Alherimi N, Ben-Daya M. A Systematic Review on the Intersection of the Cold Chain and Digital Transformation. Sustainability. 2025; 17(24):11202. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411202
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlherimi, Nadin, and Mohamed Ben-Daya. 2025. "A Systematic Review on the Intersection of the Cold Chain and Digital Transformation" Sustainability 17, no. 24: 11202. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411202
APA StyleAlherimi, N., & Ben-Daya, M. (2025). A Systematic Review on the Intersection of the Cold Chain and Digital Transformation. Sustainability, 17(24), 11202. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411202