Assessment of Soil Structural Stability of Coal Mine Roof Using Multidimensional Elliptical Copula and Data Augmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
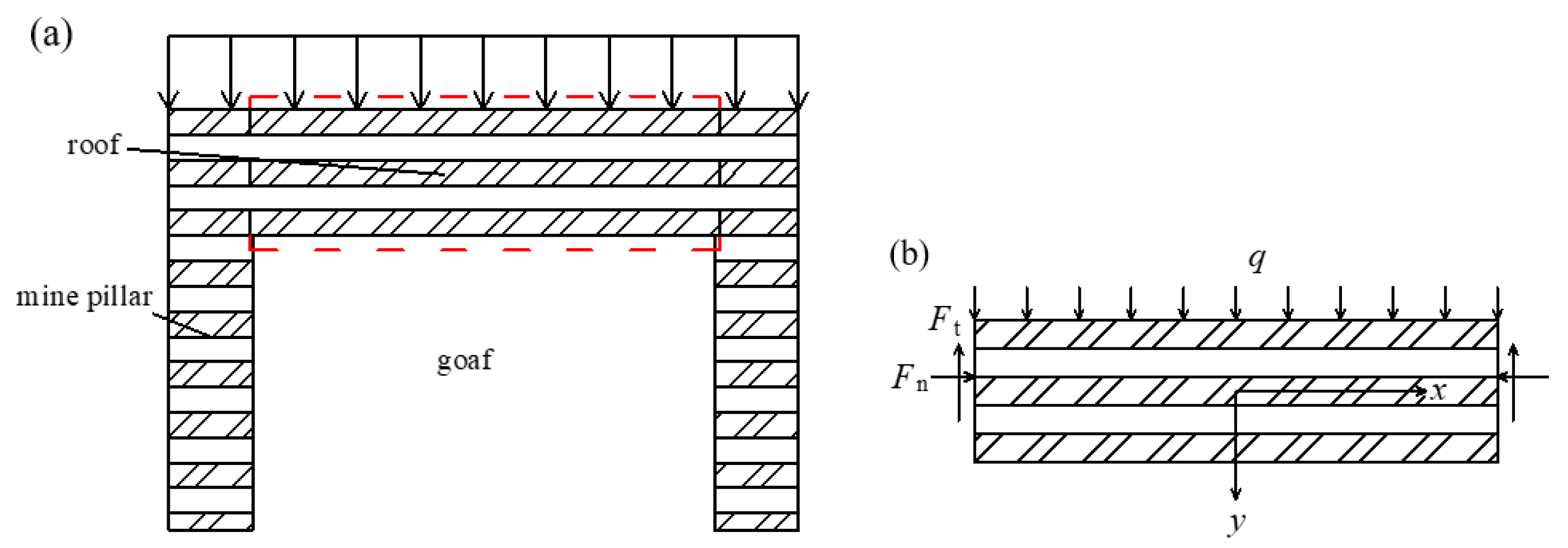
2. Stability Analysis Model for Coal Mine Roof Soil Structures
2.1. Reliability Function of Coal Mine Roof
2.2. Multidimensional Elliptical Copula Model
2.2.1. Multidimensional Gaussian Copula
2.2.2. Multidimensional t Copula
2.3. Hybrid Adaptive Multi-Method Data Augmentation (HAMDA) Method
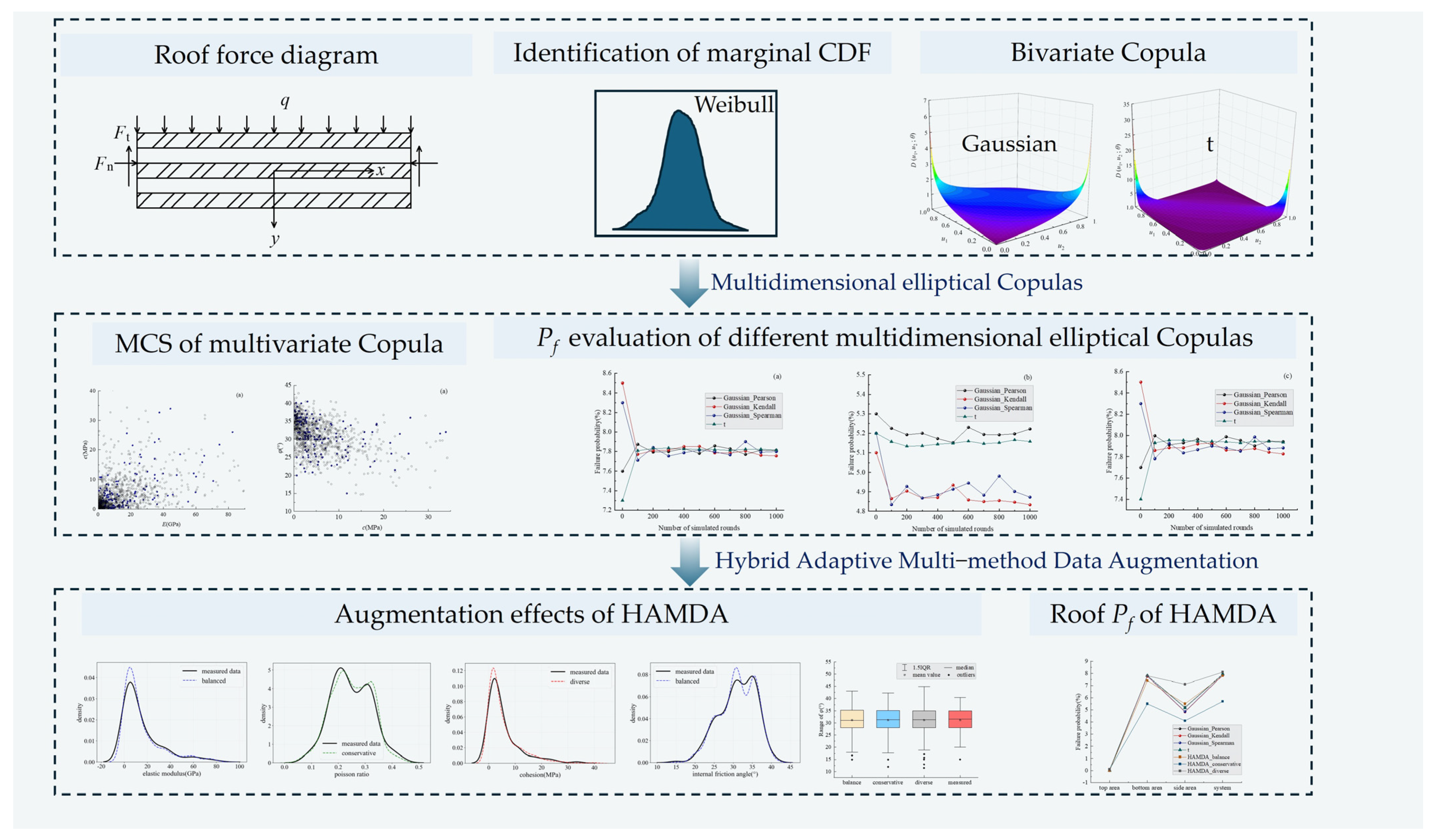
3. Illustrative Example
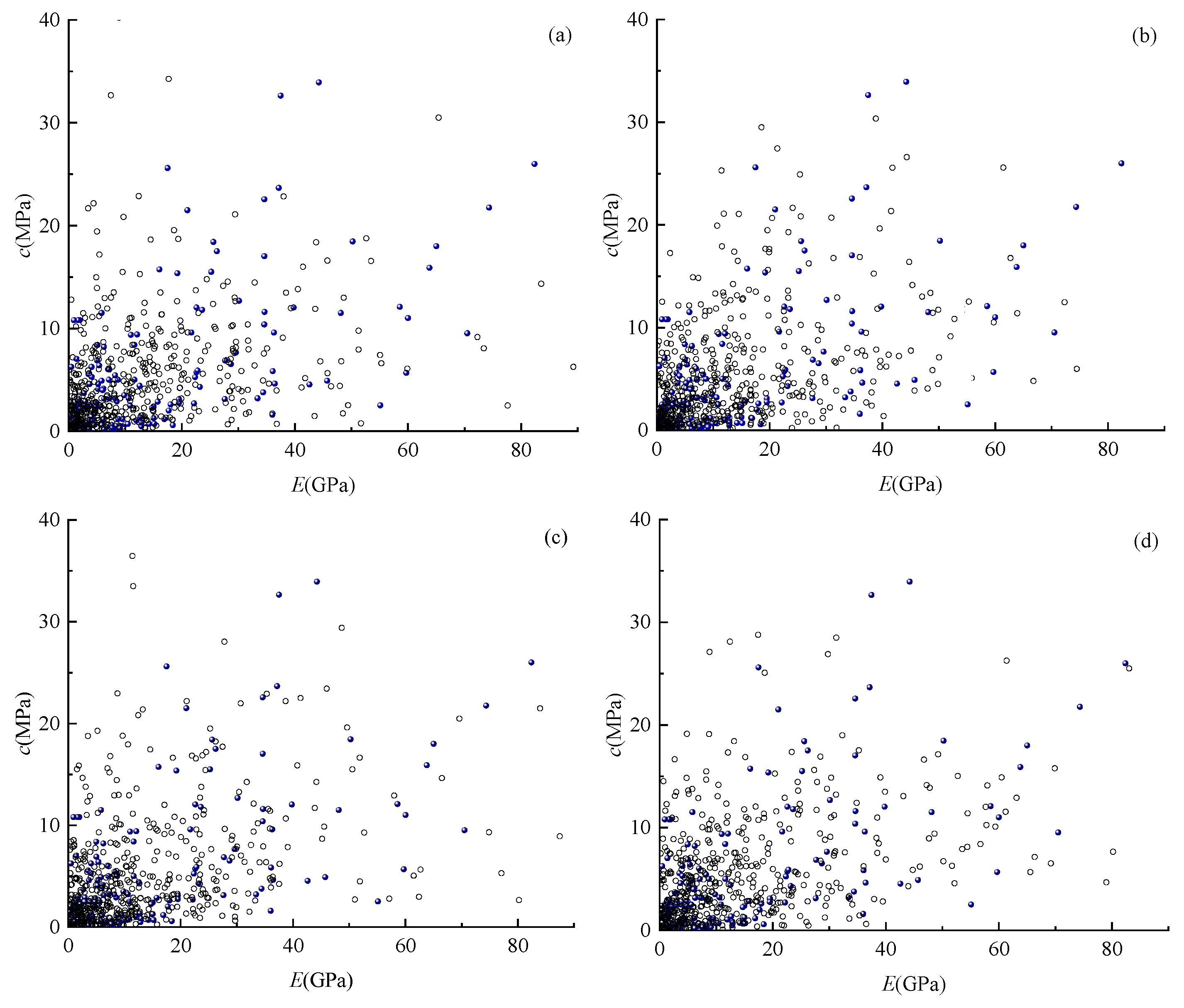
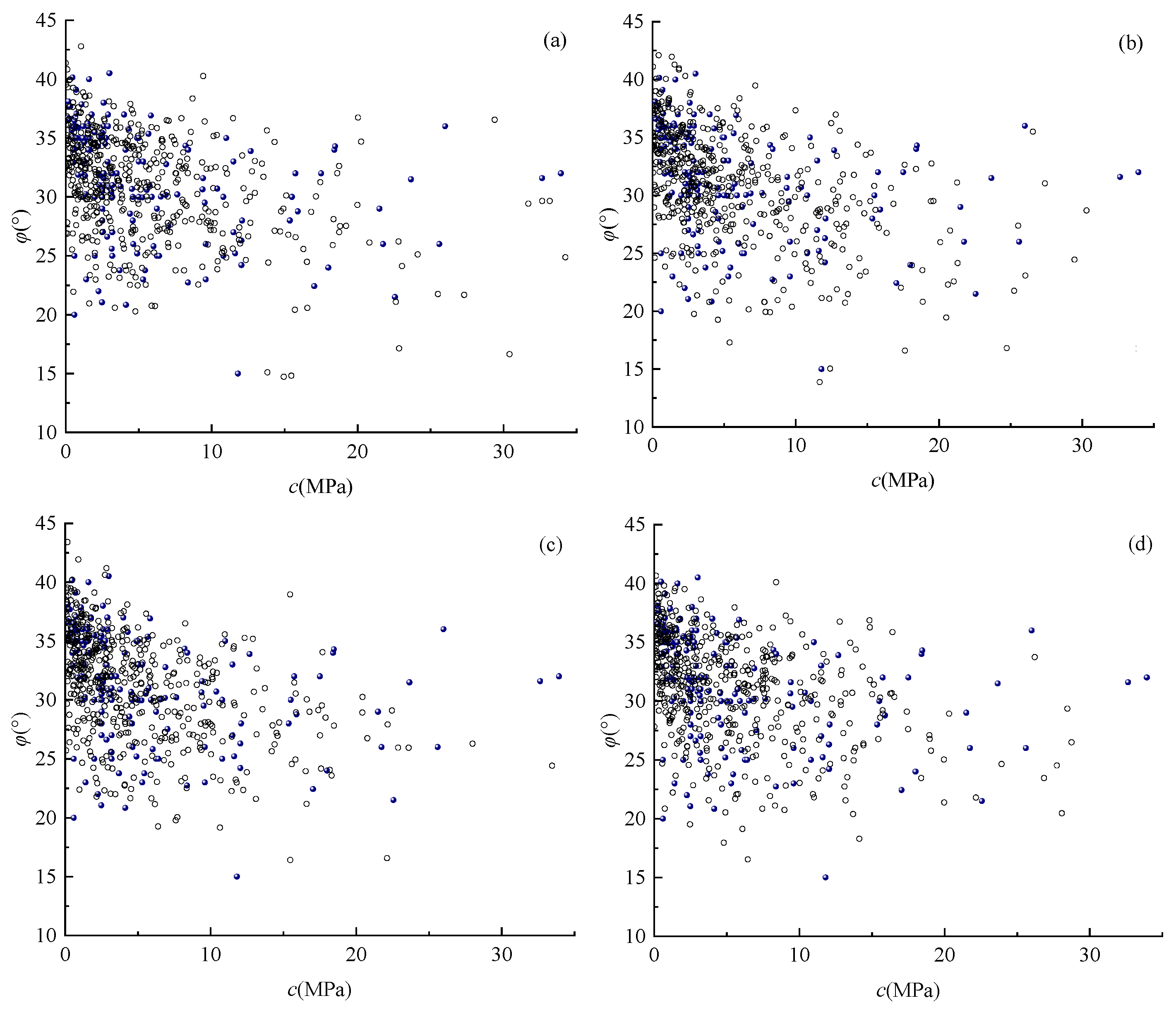
3.1. Construction of Multidimensional Elliptical Copula Models
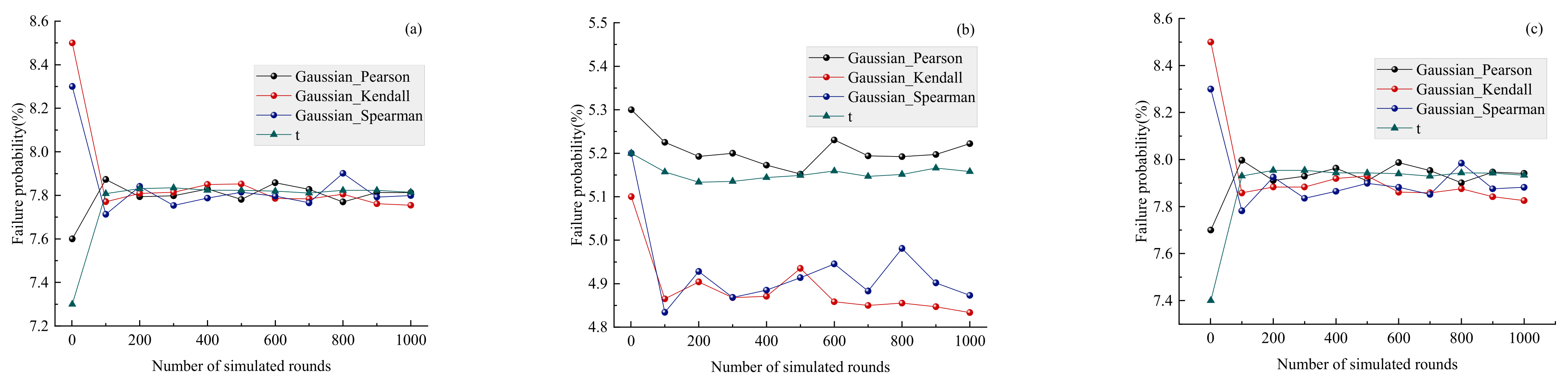
3.2. Stability Analysis of Coal Mine Roof Based on Multidimensional Elliptical Copula Models
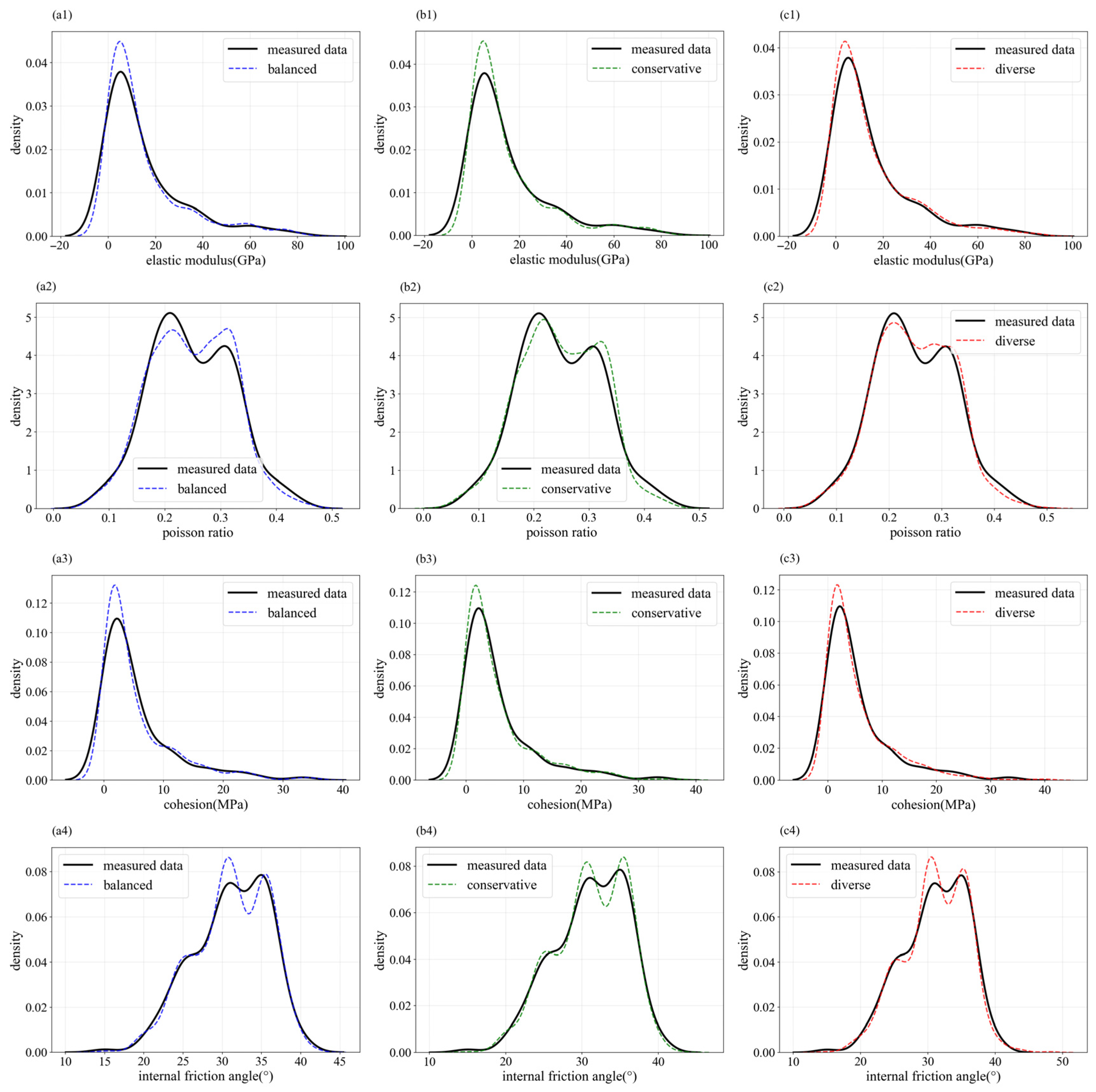
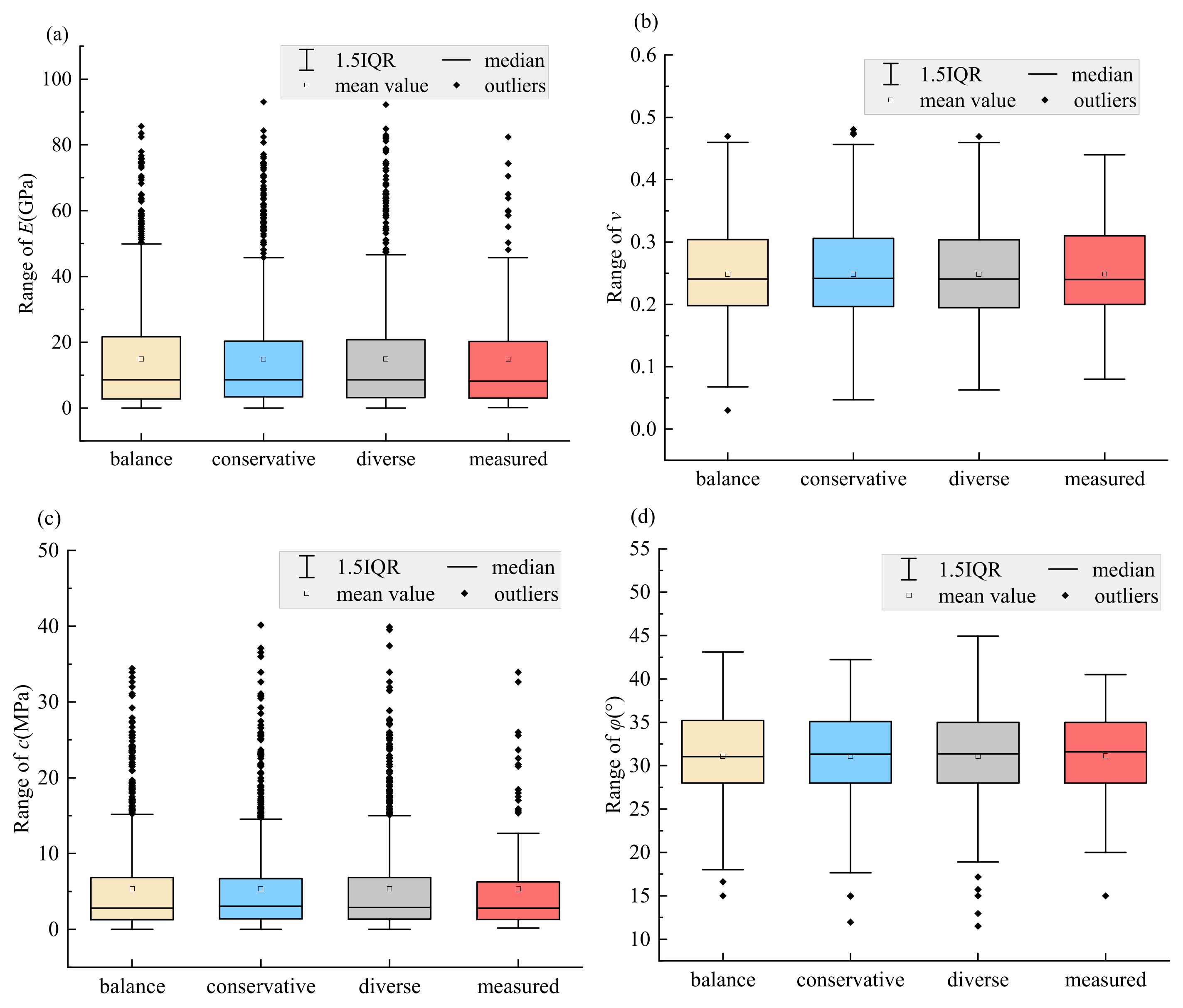
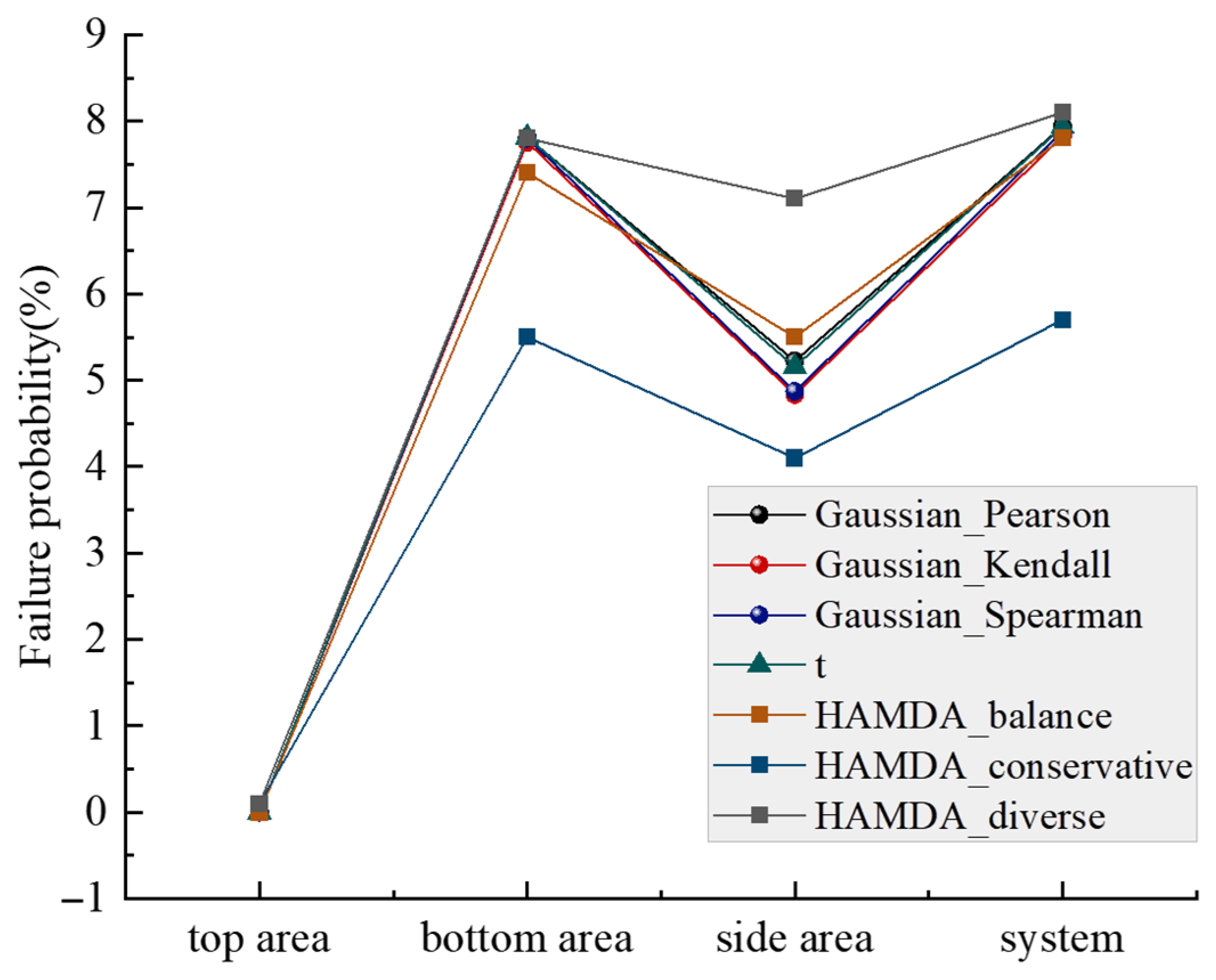
3.3. Stability of Coal Mine Roof Based on HAMDA
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
- (1)
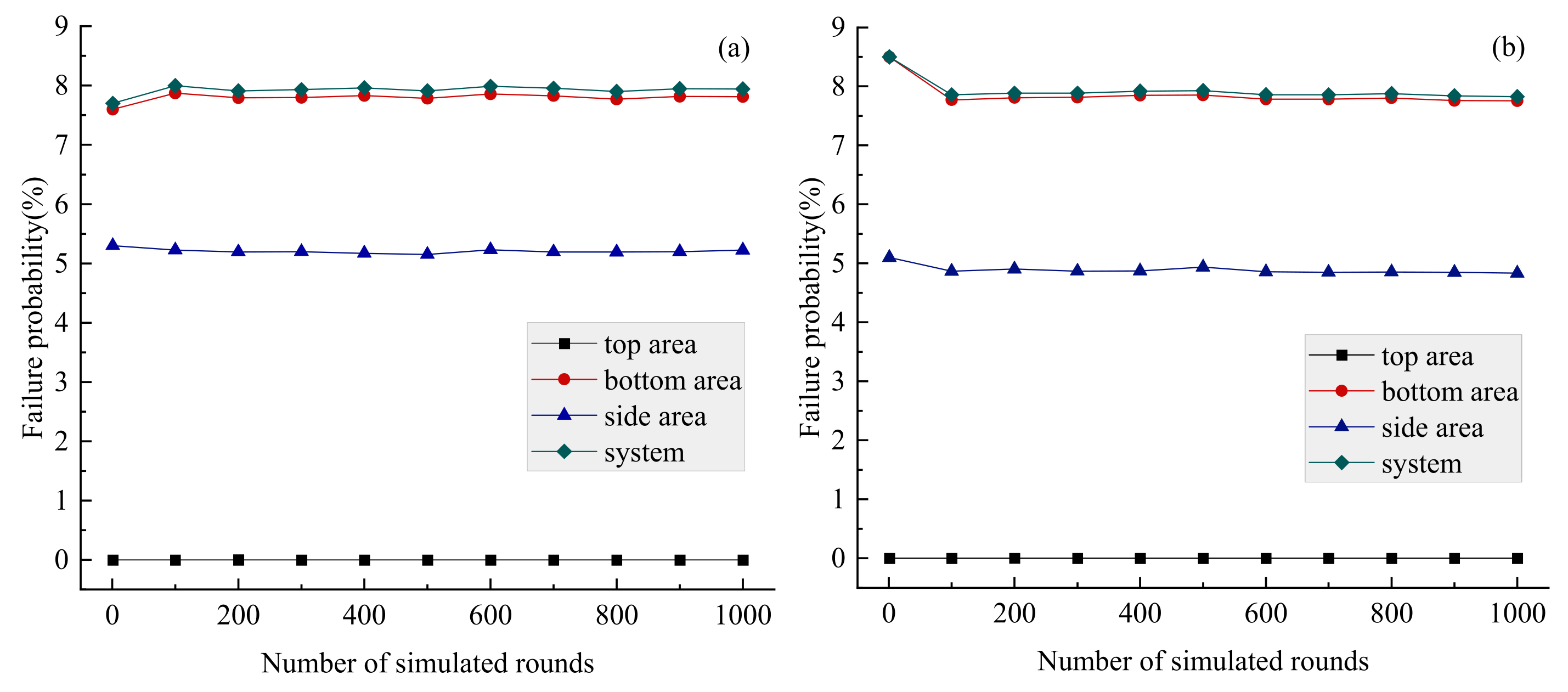
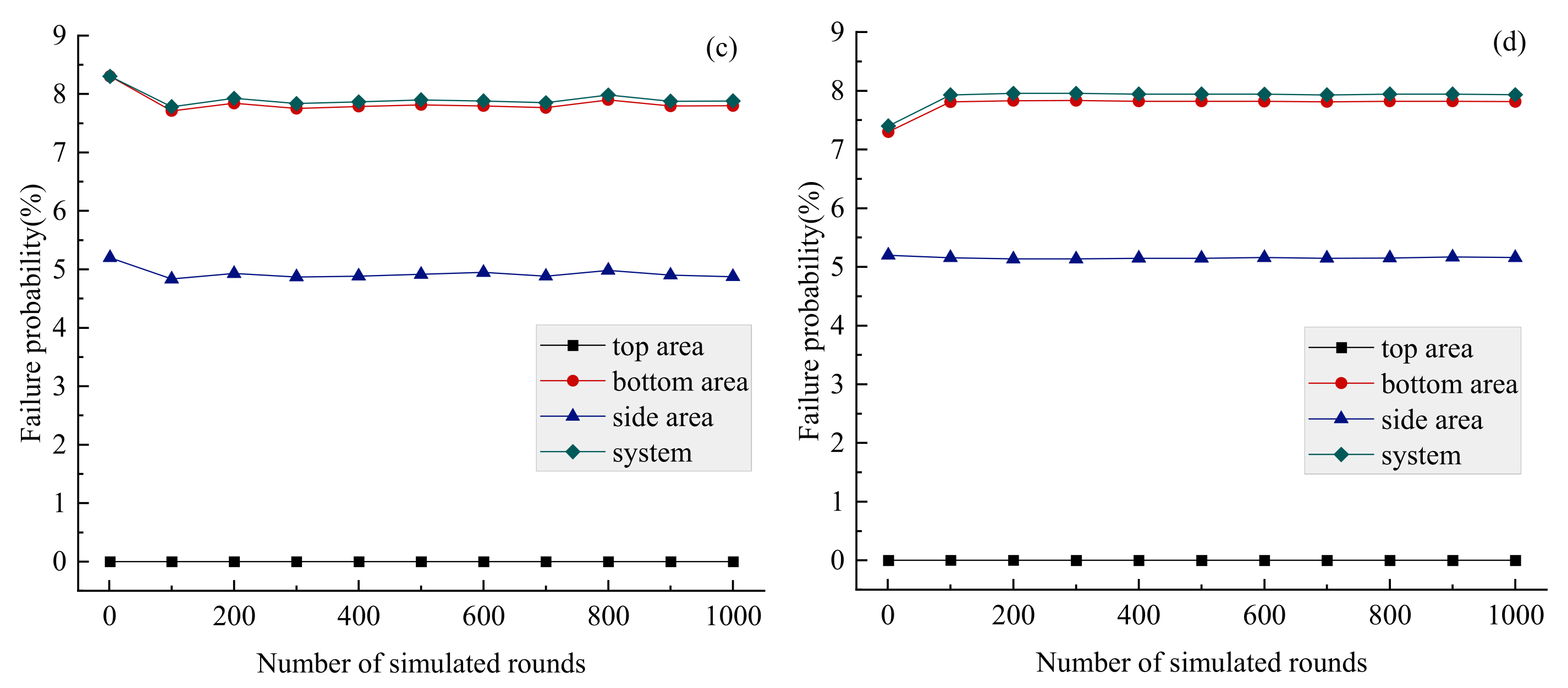
- Multidimensional elliptical Copulas can effectively simulate the correlation structure of multidimensional coal mine roof mechanical parameters with high variability, offering the advantages of convenience and efficiency. Their simulation results accurately reflect the variation patterns of failure probability across different locations within the coal mine roof soil structure, providing valuable guidance for engineering practice.
- (2)
- Under the roof soil stability model developed in this study, roof system instability typically occurs with failure at the bottom of the roof. Concurrently, there is a 60% probability of instability in the side area, while the top area of roof remains in a relatively safe position. This requires attention in stability structural design.
- (3)
- Using the integration of multiple data augmentation methods effectively combines the advantages of each approach. The three proposed HAMDA programs can effectively enhance data limitations arising from small sample conditions in coal mine roof soil structures. The density distributions fitted by the expanded mechanical parameter samples and the box plot statistical results are both very close to the measured samples.
- (4)
- The failure probability of roof soil structure calculated by the HAMDA_conservative program is significantly lower than results from other programs, indicating potential risks in roof stability design. Conversely, in the side area of roof, the failure probability calculated by the HAMDA_diverse program is markedly higher than that from the multidimensional elliptical copula model, leading to overly conservative stability designs for these side regions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, G.; Lai, X.; Shan, P.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, H. Stability analysis of the false roof made of cemented tailings backfill in deep mine: A case study. ASE Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e04046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xie, P.; Hu, B.; Lang, D.; Wang, H. Stability analysis of ‘roof-coal pillar’ structure in longwall multi-section mining of steeply dipping coal seam. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2024, 15, 2359998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, F.; Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Disaster-Causing Mechanism of Spalling Rock Burst Based on Folding Catastrophe Model in Coal Mine. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2025, 58, 7591–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Xue, Y.; Du, F.; Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhai, M.; et al. Diffusion Evolution Rules of Grouting Slurry in Mining-induced Cracks in Overlying Strata. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2025, 58, 6493–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huan, H.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Du, F.; Cao, Z.; Fan, X.; Ren, H. Determination method of rational position for working face entries in coordinated mining of section coal pillars and lower sub-layer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 29440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, Z.; Cao, Z.; Ren, H. Study on coal drawing parameters of deeply buried hard coal seams based on PFC. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Shi, C.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Du, F.; Cao, Z.; Lu, P.; Liu, L. Overburden failure characteristics and fracture evolution rule under repeated mining with multiple key strata control. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 28029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, D. Assessment of spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity of seasonally frozen ground in Northeast China. Eng. Geol. 2020, 274, 105741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cao, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhou, G. Characterizing anisotropic spatial variations of uncertain mechanical parameters for clay layer using incomplete probability data. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2024, 76, 103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Lyu, M. Capturing the random mechanical behavior of granular materials: A comprehensive stochastic discrete element method study. Géotechnique 2025, 75, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, A.; Shen, S. Stability of unsaturated soil slope considering stratigraphic uncertainty and rotated anisotropy of soil properties. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2023, 48, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Wu, Z. Seismic risk analysis based on imprecise distribution and failure probability function under multidimensional limit state. Structures 2023, 50, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Xiao, C.; Han, H.; Ding, L.; Cui, X.; Dan, H. Effect of Moisture Content on the Evaluation of Subgrade Compaction Quality using Intelligent Compaction Measurement Values. Transp. Geotech. 2025, 55, 101699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, D.; Rong, G.; Phoon, K.; Zhou, C. Impact of copula selection on geotechnical reliability under incomplete probability information. Comput. Geotech. 2013, 49, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, T.; Zhou, G.; Feng, X.; Zhu, C. Parameter estimation of grouting pressure and surface subsidence on the reliability of shield tunnel excavation under incomplete probability information. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 173, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Jia, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, Z. Water injection softening modeling of hard roof and application in Buertai coal mine. Environ. Earth Sci. 2025, 84, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, T.; Feng, Y.; Cao, J.; Song, Y.; Zhou, G.; Wan, W. Identification of joint probability distribution for thermal parameters of warm frozen clay with incomplete probability information. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2025, 238, 104543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, T.; Fen, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, G. Correlation Characterization Method for Thermal Parameters of Frozen Soil Under Incomplete Probability Information. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2025, 49, 2003–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zou, B.; Tao, Z.; He, M.; Hu, B. Construction and Application of an Intelligent Roof Stability Evaluation System for the Roof-Cutting Non-Pillar Mining Method. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherizadeh, T.; Pinnaduwa, H.S.W.K. Assessment of roof stability in a room and pillar coal mine in the U.S. using three-dimensional distinct element method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 59, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Kong, D.; Zhang, Q. Study on the destabilization and deformation breakage characteristics of the mine roof under repetitive mining of close coal seam group. Comput. Part. Mech. 2024, 11, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qin, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z. How to solve small sample size problems in time-series soil organic carbon mapping: New insights from the Third Law of Geography. Geoderma 2025, 460, 117402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulou, E.; Pavlides, A.; Steiakakis, E.; Varouchakis, A. Geostatistical Analysis of Groundwater Data in a Mining Area in Greece. Hydrology 2024, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Tang, X.; Cao, Z.; Phoon, K. Bayesian model comparison and characterization of bivariate distribution for shear strength parameters of soil. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 95, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R. An Introduction to Copulas; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, T.; Tang, X.; Li, D.; Qi, X. Modeling multivariate distribution of multiple soil parameters using vine copula model. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 118, 103340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Li, J.; Shen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Cui, H. Comprehensive multivariate joint distribution model for marine soft soil based on the vine copula. Comput. Geotech. 2025, 177, 106814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, E.; Pain, A. Efficient Probabilistic Stability Analysis of Geosynthetic Reinforced Slopes Using Collocation-Based Stochastic Response Surface. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04021189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Zhao, J.; Xu, M.; Xu, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, K. Multidimensional seismic fragility analysis of subway station structures using the adaptive bandwidth kernel density estimation and Copula function. Undergr. Space 2025, 22, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Wu, Z. Structural reliability analysis under stochastic seismic excitations and multidimensional limit state based on gamma mixture model and copula function. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2024, 76, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.M.; Morle, D.; Rahimi, A. LayerMix: Enhanced Data Augmentation for Robust Deep Learning. Pattern Recognit. 2026, 172, 112332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Bae, S.H.; Kin, S.T. Effects of mixed sample data augmentation on interpretability of neural networks. Neural Netw. Off. J. Int. Neural Netw. Soc. 2025, 190, 107611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Li, R.; Feng, X.; Li, Z.; Hong, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, S. The research on enhancing LA estimation accuracy across domains for small sample data based on data augmentation and data transfer integration optimization system. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 12, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Zhou, F.; Dai, Y.; Wang, J. A survey of mix-based data augmentation: Taxonomy, methods, applications, and explainability. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, B.; Song, R.; Yang, J. Recursivemix: Mixed learning with history. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (NeurIPS), New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, A.; Monira, M.; Shin, W.; Chung, T.; Bae, S. Saliencymix: A saliency guided data augmentation strategy for better regularization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual Event, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, H.; Zang, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, J. An effective framework with hybrid augmentation for visual reinforcement learning generalization. Neurocomputing 2025, 657, 131602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Liu, C.; Yuan, Z.; Yan, B. Hybrid Data Augmentation Combining Screening-Based MCGAN and Manual Transformation for Few-Shot Tool Wear State Recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 12186–12196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, R.; Zhou, G. Novel evaluation methodology for mechanical behaviour and instability risk of roof structure using limited investigation data. Georisk Assess. Manag. Risk Eng. Syst. Geohazards 2024, 18, 668–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Yang, F.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, T.; Xiao, P.; Zheng, W.; Chen, X.; Zhou, K. VS-SMOTE: Leveraging high-value spaces to balance noise control and data diversity for class imbalanced learning. Neurocomputing 2025, 654, 131321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Zhang, H.; Khodadadi, N.; Taffese, W.Z.; Nanni, A. Enhancing bond strength prediction at UHPC-NC interface: A data-driven approach with augmentation and explainability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 451, 138757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarthi, D.; Panimalar, A.; Santhosh, K.S.; Anitha, K. Development of Adaptive Gaussian Filter Based Denoising as an Image Enhancement Technique. Math. Model. Eng. Probl. 2024, 11, 2715–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatouk, K.; Rullière, D.; Bay, X. Sampling large hyperplane-truncated multivariate normal distributions. Comput. Stat. 2023, 39, 1779–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistic model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, C.; Yin, Y.; He, Z.; Du, W.; Wei, G. Research on transparency of coal mine geological conditions based on distributed fiber-optic sensing technology. Deep Undergr. Sci. Eng. 2024, 4, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
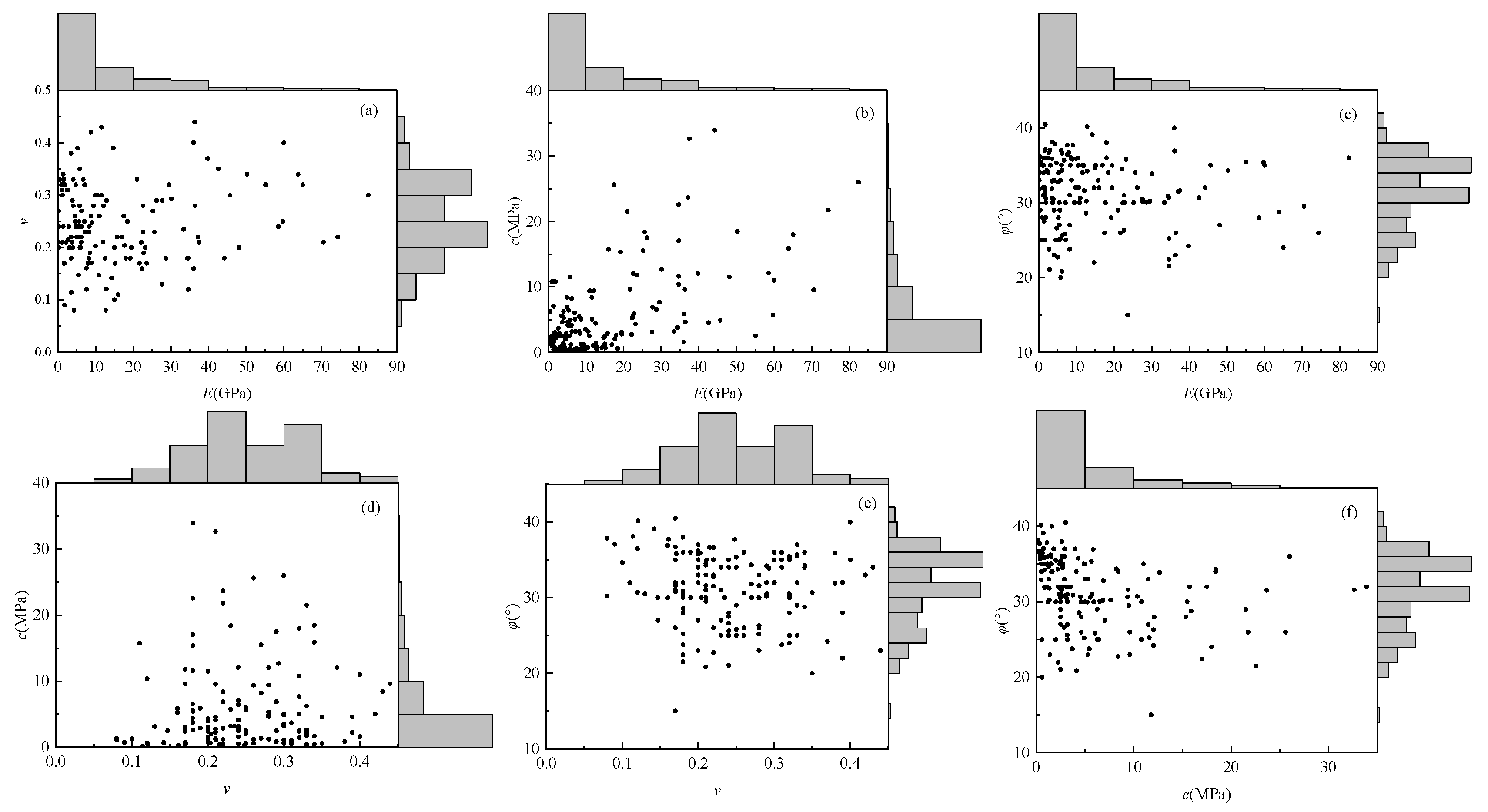
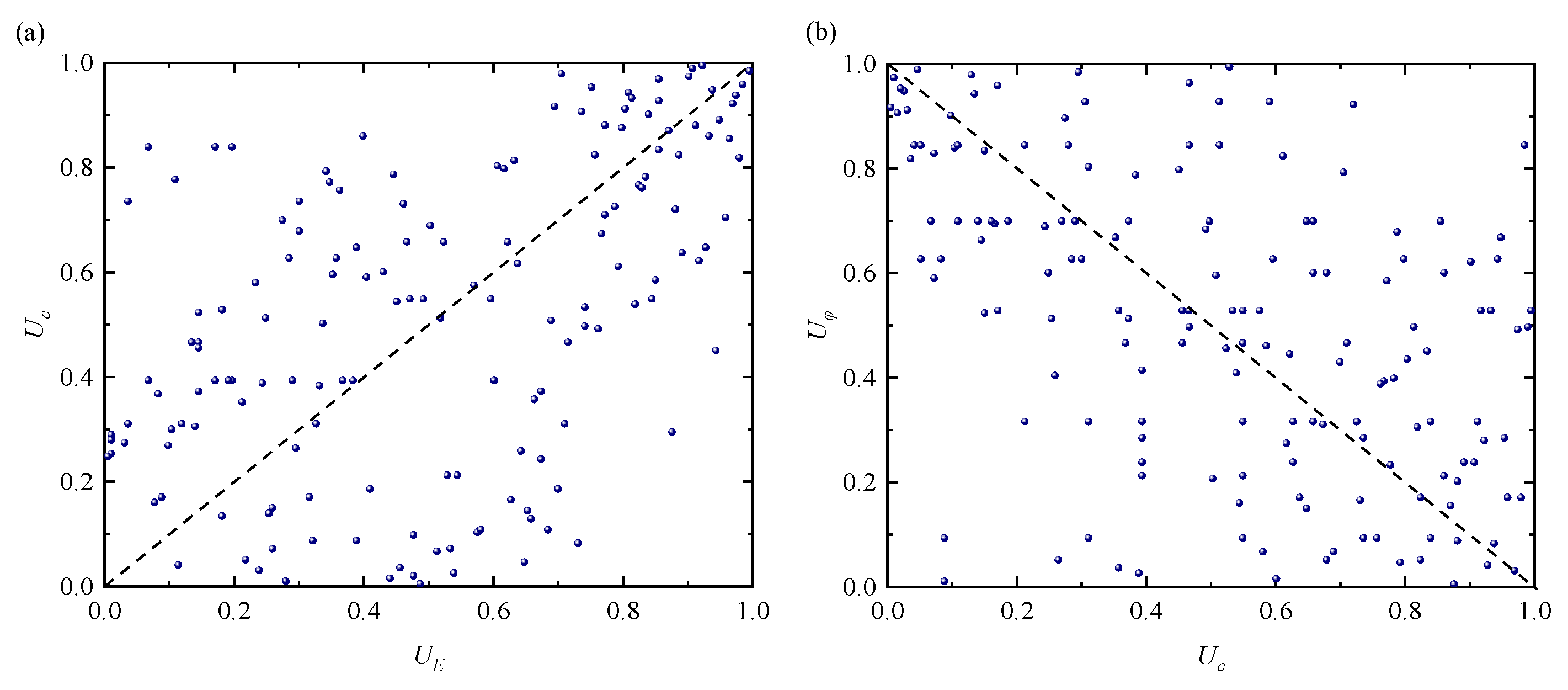
| Name of Coal Mine | Roof Conditions | Number of Measured Data Sets |
|---|---|---|
| Xiadian gold deposits, north China | inclined thick-large orebody | 3 |
| Xinpu phosphate deposit, Lianyungang City | hard rock mass | 4 |
| Yuanjiacun iron mine, Shanxi | Overburden goaf under open pit boundary | 6 |
| 104 regiment coal mine, Xinjiang | steep coal seam mining area | 13 |
| Heilong coal mine, Shanxi | water-sprinkling roof | 3 |
| Qingdong coal mine, Anhui | hard roof | 4 |
| Cangshan iron mine, Shandong | hard rock stratum roof | 3 |
| Zhujiaba copper mine, Yunnan | slightly inclined orebody | 5 |
| a coal mine in southwest China | compound roof | 7 |
| Shennanwa coal mine, Shanxi | compound roof | 12 |
| a coal mine in Guizhou | compound roof | 7 |
| Shilawusu coal mine, Inner Mongolia | large section roadway roof | 9 |
| Xiaotun coal mine, Guizhou | compound roof | 7 |
| Panbei coal mine, Anhui | regenerative roof of large dip angle coal seam | 10 |
| Huangyuchuan coal mine, Inner Mongolia | layered roof | 8 |
| Huainan Panji mining area, Anhui | deep coal-bearing rock series | 17 |
| Linsheng coal mine, Liaoning | hard roof of steeply inclined coal seam | 4 |
| Jingcheng coal mine, Shanxi | water-drenched surrounding rock roof | 3 |
| Heilong coal mine, Shanxi | water-sprinkling roof | 3 |
| Datunsong mine, Yunnan | complex orebody of large goaf | 3 |
| Zhaozhuang mine, Shanxi | compound roof | 6 |
| Dongdong coal mine, Shaanxi | compound roof | 6 |
| Zhujixi coal mine, Anhui | compound roof | 4 |
| Shenzhou coal mine, Shanxi | extra-thick compound roof | 6 |
| Hengsheng coal mine, Shanxi | hard roof | 2 |
| Zhaozhuang mine, Shanxi | layered roof | 4 |
| East Kouzi coal mine, Anhui | component roof | 6 |
| Baode coal mine, Shanxi | thick coal-seam with hard roof | 12 |
| Shuangxin coal mine, InnerMongolia | soft roof | 3 |
| Sanjiaohe coal mine, Shanxi | roof near fault | 7 |
| Ann hill coal mine, Shaanxi | layered roof | 5 |
| Parameter | E | ν | c | φ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| normal | 1638.9 | −455.66 | 1247.7 | 1142.4 |
| lognormal | 1537.9 | −435.62 | 1036.9 | 1166.3 |
| Gumbel | 1662.6 | −405.05 | 1268.4 | 1209.8 |
| Weibull | 1414.2 | −456.45 | 1031.3 | 1129.8 |
| Construction Method | Correlation Coefficients Matrix | Correlation Parameter Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Pearson | ||
| Kendall | ||
| Spearman |
| Method | Parameter | Mean Value | Variance | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured data | E (GPa) | 14.789 | 293.695 | 1.159 |
| ν | 0.249 | 0.005 | 0.295 | |
| c (MPa) | 5.350 | 38.282 | 1.156 | |
| φ (°) | 31.128 | 22.122 | 0.151 | |
| Gaussian_Pearson | E (GPa) | 14.489 | 294.082 | 1.184 |
| ν | 0.252 | 0.006 | 0.305 | |
| c (MPa) | 4.991 | 28.350 | 1.067 | |
| φ (°) | 31.212 | 21.052 | 0.147 | |
| Gaussian_Kendall | E (GPa) | 15.449 | 332.544 | 1.180 |
| ν | 0.246 | 0.006 | 0.306 | |
| c (MPa) | 5.380 | 33.046 | 1.069 | |
| φ (°) | 31.058 | 19.070 | 0.141 | |
| Gaussian_Spearman | E (GPa) | 14.284 | 269.977 | 1.148 |
| ν | 0.247 | 0.005 | 0.295 | |
| c (MPa) | 5.683 | 38.044 | 1.085 | |
| φ (°) | 31.121 | 21.302 | 0.148 | |
| t Copula | E (GPa) | 15.588 | 361.111 | 1.221 |
| ν | 0.246 | 0.008 | 0.367 | |
| c (MPa) | 5.363 | 29.954 | 1.021 | |
| φ (°) | 31.256 | 22.218 | 0.151 |
| Constant Value | γ (kN·m−3) | h0 (m) | n | G (GPa) | k0 | fs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 26.8 | 100 | 1.0 | 10.5 | 1.3 | 1 |
| Data Augmentation Methods | SMOTE | KDE | AGN | MDB | SIA | CMNS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAMDA_balance | 245 (30.3%) | 202 (25.0%) | 160 (19.8%) | 121 (15.0%) | 40 (4.9%) | 40 (4.9%) |
| HAMDA_conservative | 325 (40.2%) | 242 (29.9%) | 121 (15.0%) | 80 (9.9%) | 40 (4.9%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| HAMDA_diverse | 165 (20.4%) | 161 (19.9%) | 161 (19.9%) | 161 (19.9%) | 80 (9.9%) | 80 (9.9%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Wang, T.; Zhu, C.; Xu, Y. Assessment of Soil Structural Stability of Coal Mine Roof Using Multidimensional Elliptical Copula and Data Augmentation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10028. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210028
Cao J, Wang T, Zhu C, Xu Y. Assessment of Soil Structural Stability of Coal Mine Roof Using Multidimensional Elliptical Copula and Data Augmentation. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10028. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210028
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jiazeng, Tao Wang, Chuanqi Zhu, and Ying Xu. 2025. "Assessment of Soil Structural Stability of Coal Mine Roof Using Multidimensional Elliptical Copula and Data Augmentation" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10028. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210028
APA StyleCao, J., Wang, T., Zhu, C., & Xu, Y. (2025). Assessment of Soil Structural Stability of Coal Mine Roof Using Multidimensional Elliptical Copula and Data Augmentation. Sustainability, 17(22), 10028. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210028







