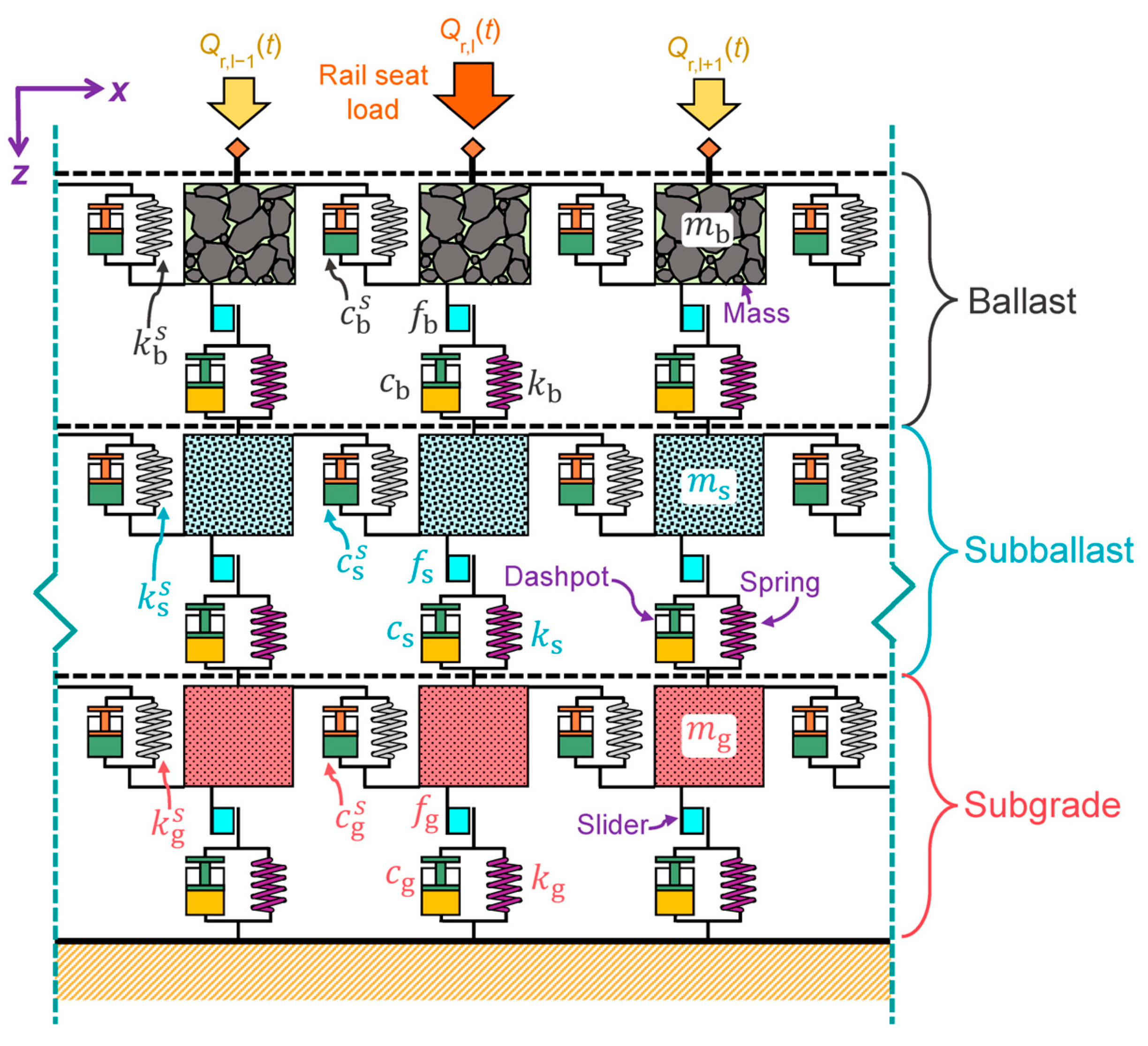
1. Introduction
Rail transport is known for its sustainable attributes, such as emission of lower amounts of greenhouse gases and consumption of less energy than road or air transportation during its operation phase [
1,
2]. However, its construction and maintenance phases can have substantial environmental impacts [
3]. These impacts primarily stem from the extraction, processing and transportation of tremendous quantities of virgin quarried material, use of cement, steel and heavy machinery as well as the generation of waste during construction and maintenance activities [
4,
5].
The carbon footprint of railway infrastructure is expected to rise due to two key factors: (a) the increasing frequency of maintenance and rehabilitation activities, driven by the adoption of heavier axle load in freight trains and the operation of faster passenger trains; (b) the rapid expansion of railway networks, stimulated by urbanization. Addressing these challenges is crucial for enhancing the sustainability of railway transportation. Consequently, the railway industry is actively exploring effective strategies to strengthen track substructure and minimize the requirement for recurrent maintenance. Simultaneously, innovative approaches are being developed to lower the carbon footprint associated with the construction of new tracks, particularly on soils with poor engineering properties. These solutions should not only be cost-effective, but also have minimal impact on the environment, thereby contributing towards sustainable infrastructure development.
One promising approach involves the use of scrap tires in railway track construction and maintenance. With over 1.5 million tires being produced annually, their disposal remains a perplexing problem [
6,
7]. Repurposing them as construction materials in ballasted and ballastless railway tracks can mitigate both financial burdens and the environmental risks associated with their stockpiling or disposal in landfills. Past research has demonstrated that they can be used in various forms, such as whole tires [
8], as mats fabricated from sidewalls or treads [
9] or as aggregates [
10,
11].
Whole scrap tires have been employed in applications like retaining walls, erosion protection systems, breakwaters, and highway crash barriers [
12,
13]. Mats derived from sidewalls or treads have effectively been used to reinforce soil, leveraging their high tensile strength [
9]. For instance, Yoon et al. [
14] reported improved bearing capacity and reduced vertical settlement on reinforcing the soil using tire mats. Aggregates derived from scrap tires have potential applications as fill materials in embankments [
15], backfill for retaining walls [
16], drainage layers in highways [
17] and vibration attenuation materials in railway tracks [
18]. Past studies indicate that these aggregates show comparable performance to conventional materials in embankment and highway applications [
19,
20].
In the context of railway infrastructure, the incorporation of scrap tires in the form of granulated rubber improves the damping properties of track materials [
7,
21] and reduces particle breakage [
22]. For example, Hidalgo-Signes et al. [
18] reported a 95% increase in damping ratio when tire shreds (up to 10%) were mixed with granular soil. Wolfe et al. [
23] found that the use of tire shreds beneath the ballast layer significantly reduced train-induced ground-borne vibrations. Guo et al. [
24] observed that the crumb rubber-ballast mixture exhibits better force distribution compared to pure ballast, due to the cushioning effect provided by rubber particles. This also led to a reduction in the magnitude of contact forces, which can help in minimizing ballast breakage.
Despite these advantages, the addition of rubber aggregates to track materials can also result in reduced shear strength and increased settlement [
25]. For instance, Gong et al. [
22] found that the addition of aggregates derived from scrap tires (up to 10%) to ballast reduced its apparent cohesion and friction angle by 12.8% and 23.8%, respectively. Khoshoei et al. [
26] reported that the vertical settlement increased with a rise in rubber content in rubber aggregate–steel slag ballast mixtures. To address these limitations, stabilizing agents such as polyurethane foam adhesive (PFA) can be employed. As discussed later in this article, the resulting soil–rubber–PFA composite exhibits improved damping properties and reduced plastic deformation. These properties are highly desired for application as a base layer in ballastless railway tracks.
Another sustainable approach is the utilization of artificial inclusions for strengthening the railway track substructure. These inclusions can be cellular, such as geocells, or planar, such as geotextiles, geogrids and geocomposites. Geocells are typically composed of polymer strips joined together at regular intervals, forming a three-dimensional (3D) cellular network that resembles a honeycomb. Similar to geocells, scrap tires can be repurposed as cellular inclusions by connecting multiple units with metal clips, bars or ties [
27].
The cellular inclusions typically reduce the horizontal movement of the infill soil under loading by providing lateral restraint and all-around confinement [
28,
29]. This property is advantageous for ballast and subballast layers of ballasted railway tracks, which are typically subjected to significant lateral deformation or spreading due to limited in-situ confinement. The installation of cellular inclusions in these layers can lead to reduced lateral movement and improved track performance [
30].
It has been observed that reinforcing granular layers using cellular inclusions: (a) promotes uniform stress distribution over a wider subgrade area by increasing the stiffness of infill material [
28,
31]; (b) reduces or redistributes shear stresses at the interface between granular substructure layers and subgrade, depending on their installation location [
32]; (c) enhances the strength and reduces permanent deformation of the infill material [
30,
33]. All these effects contribute to a slower rate of track geometry deterioration, thereby minimizing the need for frequent maintenance operations [
34,
35]. It must be noted that the performance of a reinforced granular layer depends on several factors such as the properties of inclusion, infill material and subgrade soil [
36,
37,
38], position of inclusion within the track [
39] and loading conditions [
40]. A thorough evaluation of these factors is essential prior to their application within the railway track.
Previous field investigations have also demonstrated the effectiveness of cellular inclusions in railway applications. For instance, these inclusions have been shown to: (a) significantly reduce vertical settlement and lateral deformation in ballasted tracks [
41]; (b) mitigate stiffness differences between the softer and stiffer sides of open track–bridge transitions, thereby enhancing their performance [
35]. Despite their significant potential, the incorporation of cellular artificial inclusions in ballasted railway tracks remains elusive, primarily because of the absence of appropriate tools for assessing their effectiveness.
Planar inclusions can be used in pile-supported railway embankments (PSRE) constructed on soils with inferior engineering properties, such as high compressibility and low shear strength. The conventional pile-supported embankments typically require closely spaced piles to effectively transfer loads (self-weight and traffic-induced loads) to the subsoil [
42]. However, closer spacing increases the number of piles, which could increase carbon emissions linked to the use of cement, steel and heavy machinery for their construction and installation. To enhance sustainability, planar inclusions such as geogrids, geocomposites or geotextiles can be employed [
43,
44,
45]. These inclusions enhance the performance of PSRE through mobilization of tensioned membrane effect [
46,
47]. For instance, Liu et al. [
42] reported that the incorporation of a planar inclusion significantly reduced differential settlement between piles and subsoil, as the inclusion carried a part of the load through tension generated within it. Several studies have investigated the role of planar inclusions in improving load-transfer mechanisms in PSRE. Their effectiveness in reducing subsoil settlement and improving load transfer to piles has been shown to depend on factors such as embankment height, pile spacing and pattern, subsoil properties, vehicle speed, inclusion stiffness and the number of inclusion layers [
47,
48,
49,
50,
51]. However, most of these studies overlooked the effect of dynamic train loads on tensile stresses within the inclusions and the associated load-transfer mechanisms.
Despite technological advancements and escalating demands for high-speed and heavy-haul trains, research on effective sustainable approaches to enhance railway track performance under increased loading from these trains remains limited. In addition, there is a need to find sustainable alternatives to natural quarried aggregates for railway track construction and maintenance, due to significant environmental implications stemming from their consumption. Particularly, the utilization of scrap tires and artificial inclusions as sustainable construction materials warrants further investigation.
This article assesses the performance of a novel composite material and two types of artificial inclusions through laboratory, analytical and numerical approaches. These materials have been identified as promising options to enhance the performance and sustainability of railway tracks based on a comprehensive review of alternatives. The article is structured as follows:
Section 2 explores the effectiveness of a novel composite material, made from shredded scrap rubber tires, soil and PFA, as a sustainable base layer in ballastless railway tracks through laboratory investigations. In this composite, the granulated rubber contributes to damping while PFA provides strength and ductility.
Section 3 investigates the adequacy of cellular artificial inclusions in strengthening railway tracks and minimizing the requirement for quarried materials using a computational approach that integrates a geotechnical rheological track model [
52] with a confinement model for artificial inclusions [
40].
Section 4 examines the role of planar inclusions in reducing subsoil settlement and improving load transfer within a PSRE through finite element (FE) simulations. It also highlights the environmental benefits of using planar inclusions in PSRE.
2. Novel Composite Material for Ballastless Railway Tracks
2.1. General
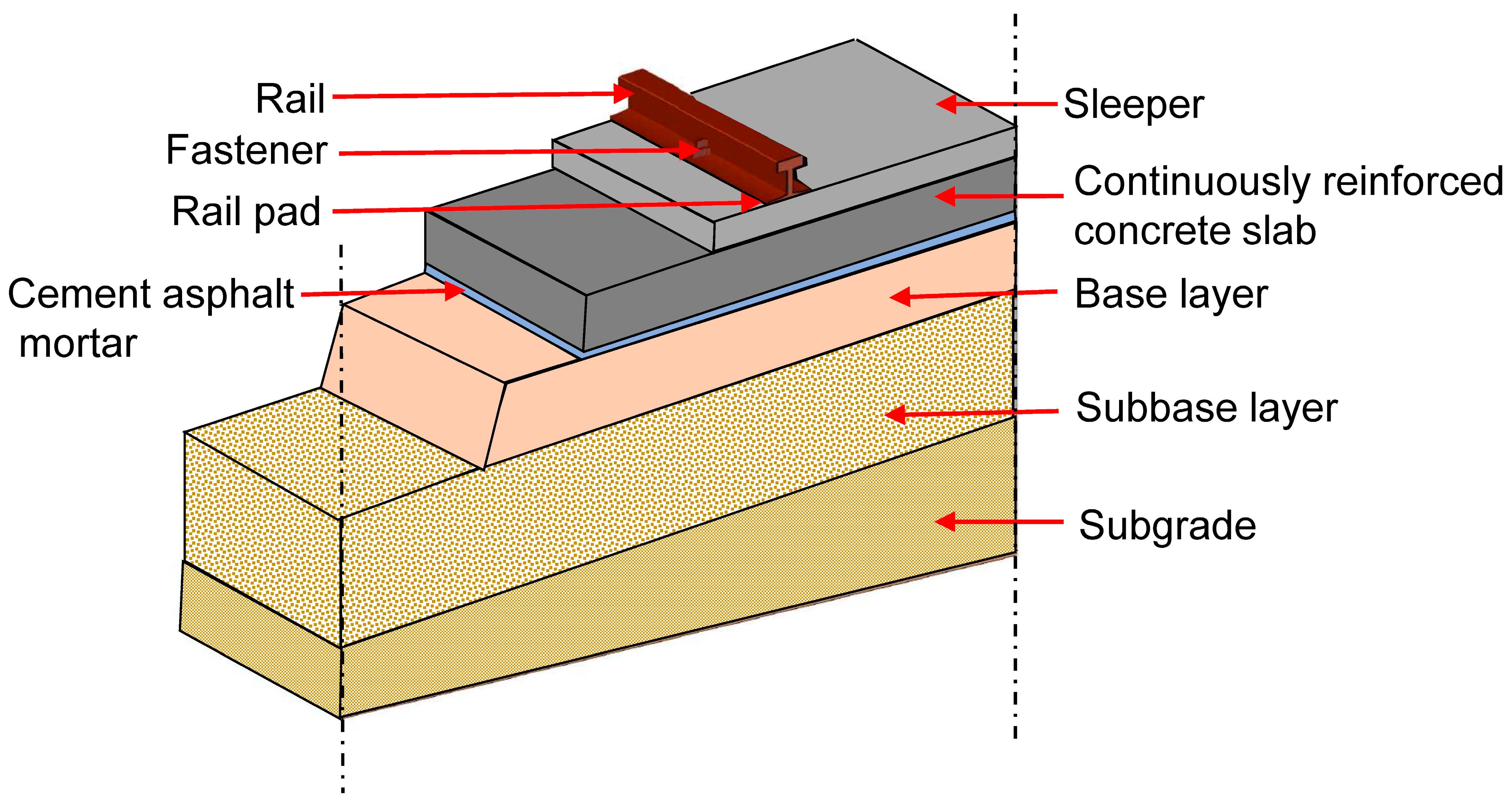
The substructure of ballastless railway tracks typically comprises a concrete slab overlying cement–asphalt mortar, cement or lime-treated base, subbase and subgrade layers, as shown in
Figure 1. While the cement-treated base layer provides adequate structural support, it contributes to the noise and vibration problem commonly associated with this type of track. In addition, although cement and lime enhance strength, they render the base layer brittle and susceptible to cracking. The use of cement also increases the carbon footprint of these tracks. Therefore, a composite material is proposed in this study for application in the base layer of ballastless railway tracks.
2.2. Material Description
The composite proposed in the present study comprises three materials: soil (well-graded gravel), granulated rubber and PFA. All these materials were procured from local suppliers in Australia.
Figure 2 depicts the grain size distribution (GSD) of the soil used in the present study. The terms “upper limit” and “lower limit” in the figure represent the acceptable range for GSD of base material according to the current industry standard [
53]. It can be seen that the soil has a maximum particle size (
dmax) of 19 mm and its gradation conforms to the current industry standard [
53]. The mean particle size (
d50), uniformity coefficient (
Cu) and coefficient of curvature (
Cc) of the soil are 5.3 mm, 62.3 and 3.0, respectively. The specific gravity (
Gs) of the soil is 2.73 (determined in accordance with AS 1289.3.5.1 [
54]).
The granulated rubber was derived from the end-of-life tires from trucks and passenger cars. These tires were first processed using a Tana Shark shredder, which reduced them into small-sized particles. These particles were further processed using another shredder, which removed all metal pieces. Nylon fibers were subsequently removed using a series of granulators. Finally, the scrap rubber was separated into different sizes [
55]. In this study, rubber particles from six different size ranges between 0.075 mm and 13.2 mm have been used to achieve the target GSD shown in
Figure 2. It has a
dmax,
d50,
Cu,
Cc, and
Gs of 13.2 mm, 3.8 mm, 75.0, 2.1, and 1.165, respectively.
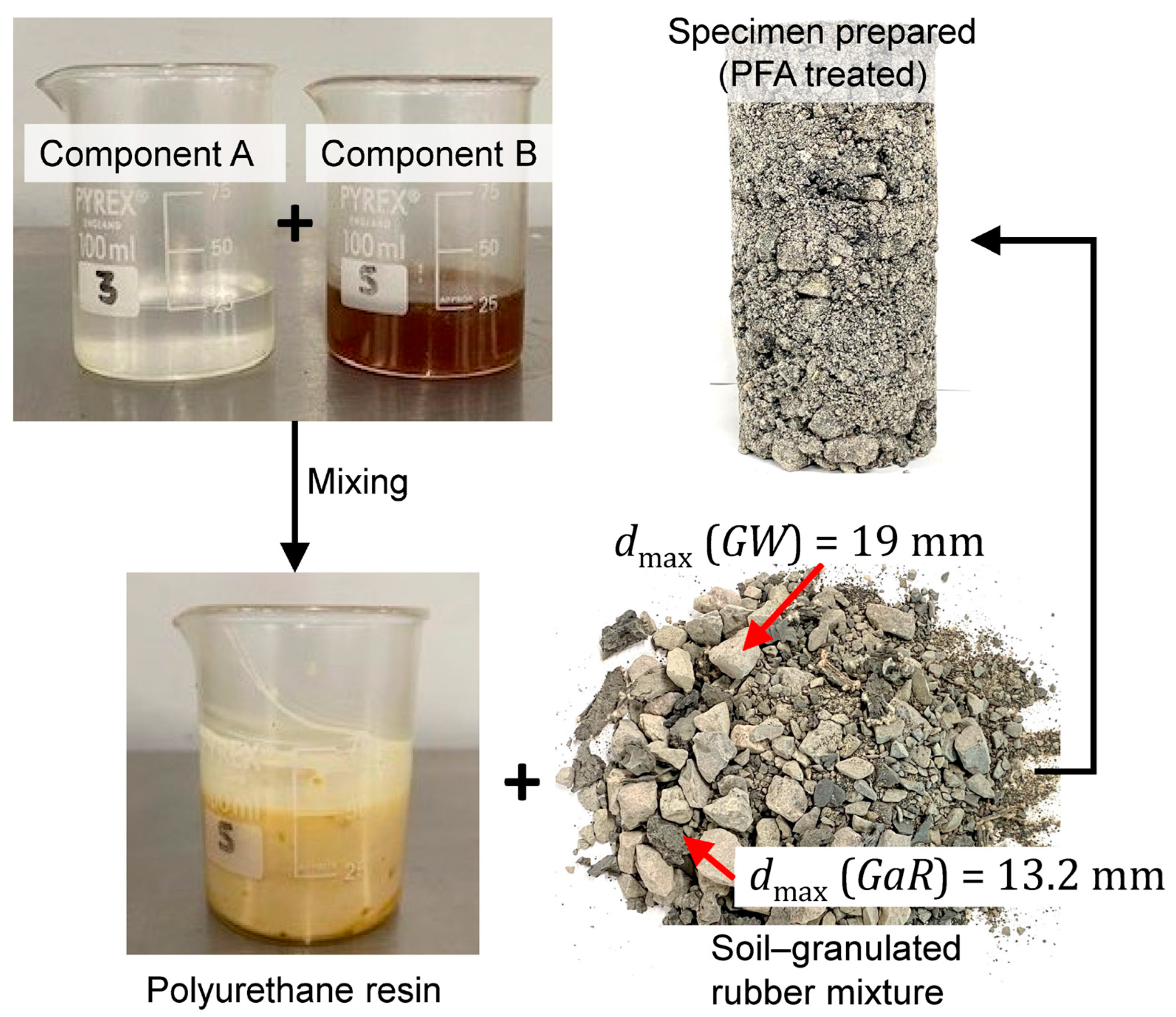
A solvent-free, non-foaming, silicate-modified polyurethane resin, known as PFA, was used in this study. This non-foaming PFA was chosen for its ability to bind the soil and rubber particles without filling the voids, thus providing strength and ductility to the composite mix while not significantly reducing permeability. It comprises two components: A and B (see
Figure 3). Component A is transparent with a light straw color, while Component B is opaque with a dark brown color. The density of component A at 20° C ranges between 1300 and 1500 kg/m
3, whereas component B has a density ranging between 1150 and 1250 kg/m
3. Both components have a flash point greater than 200° C. The viscosity of components A and B varies from 120 to 350 mPa·s, and 50 to 300 mPa·s, respectively.
The sample preparation process of the soil–rubber–PFA mixture is shown in
Figure 3. A 1:1 volume ratio (100:82 by weight) was used to combine components A and B at room temperature (25° C). Vigorous stirring for a few seconds initiated the chemical reaction between the two PFA components. After 30 s of agitation, the PFA was thoroughly mixed for two minutes with the soil–rubber mixture. The mixture was then compacted into five layers using the under-compaction technique to prepare a cylindrical specimen of diameter 100 mm and height 200 mm. More details on sample preparation can be found elsewhere [
56,
57].
It must be noted that the proportion of PFA and rubber granules in this study was fixed at 10% by mass of the mixture. This dosage was identified as optimal based on findings from static direct simple shear (SDSS) and cyclic direct simple shear (CDSS) tests [
58]. In these tests, the percentage of rubber and PFA was varied between 0–25% and 0–20%, respectively. SDSS tests were used to evaluate the performance of mixtures under monotonic loading conditions in terms of cohesion, friction and dilation angles. CDSS tests were used to evaluate the long-term performance of mixtures under repeated loading for 50,000 load cycles under varying shear stress amplitude (50–200 kPa).
The optimum PFA dosage of 10% was based on achieving a significant improvement in strength, reflected by an increase in both cohesion and friction angles, with the most significant improvement occurring for PFA dosages of 7.5–12.5%. Beyond this, any further addition of PFA resulted in only marginal strength improvement. This dosage also triggered maximum dilative behavior, contributing to the highest shear strength, and most importantly, it substantially reduced the residual vertical strain under cyclic loading.
The residual vertical strain under cyclic loading remained low for rubber content of up to 15% but increased thereafter. In contrast, the damping ratio consistently increased with an increase in rubber content. An optimum rubber content of 10–20% was found to achieve desirable damping properties with the least negative impact on other characteristics, viz., cohesion, friction angle and shear modulus.
Thus, the optimum dosages of 10% PFA and 10% rubber adopted in this study were based on achieving a favorable balance of increased shear strength, minimized residual vertical strains, and enhanced damping. More details on the determination of optimum dosages of PFA and rubber are available in [
58]. Furthermore, the obtained optimum dosage of rubber and PFA are in line with previous studies on scrap rubber, e.g., [
7,
59], which recommend optimum rubber dosage of 5–10%, and studies on PFA, e.g., [
60,
61], which recommend optimum PFA dosages of 5–15%.
2.3. Testing Procedure
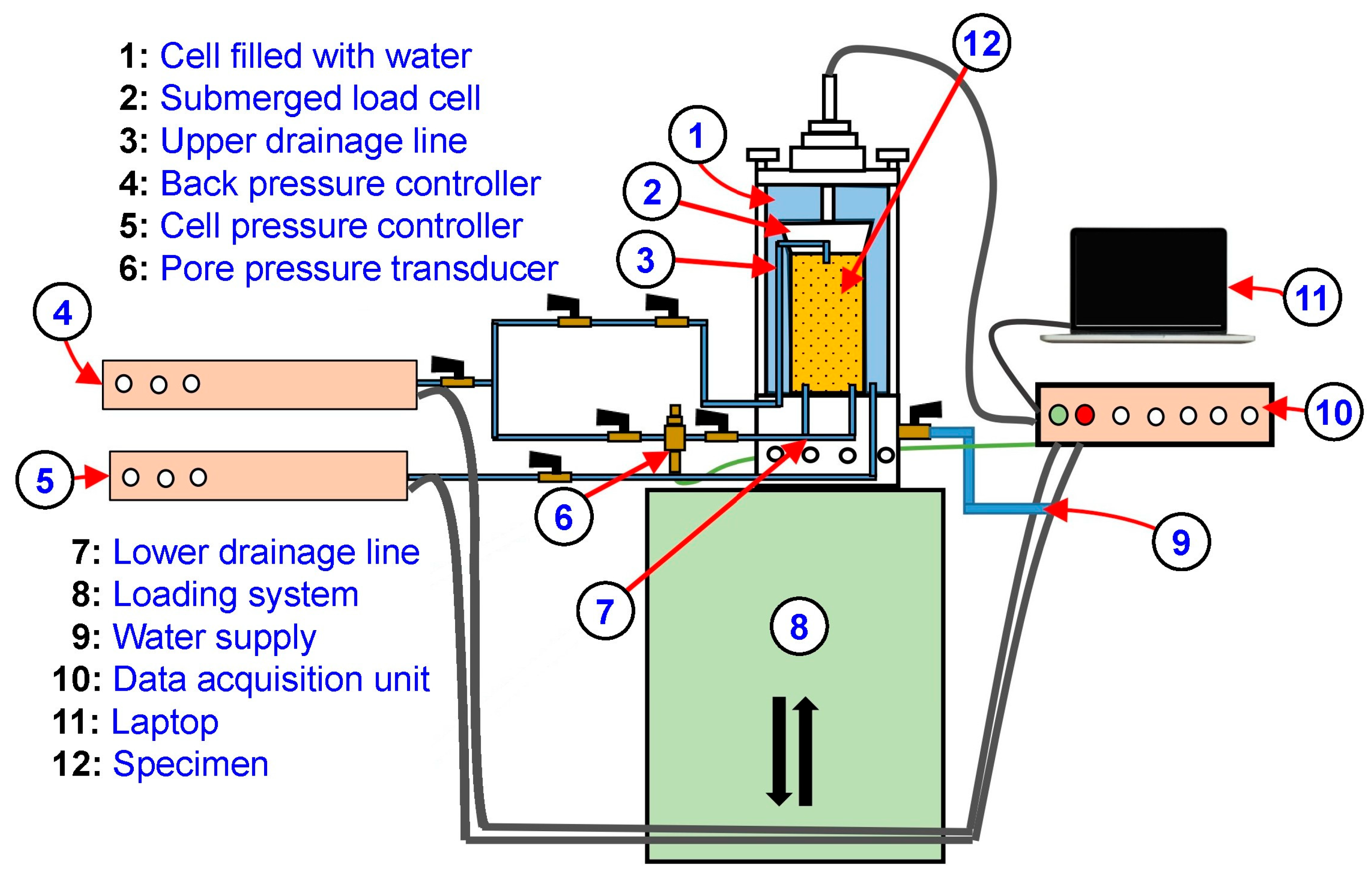
Cyclic triaxial tests were performed to study the behavior of the soil–rubber–PFA composite under repeated loading conditions. The advanced triaxial testing equipment used in the present study is illustrated in
Figure 4. Train loading was replicated by applying stress-controlled sinusoidal load cycles at a frequency (
f) of 4 Hz. This frequency was determined based on the speed of trains and spacing between bogies, using the formula
f =
Vt/(3.6
λ)
, where
Vt represents speed (km/h) and
λ denotes spacing between bogies (m) [
62,
63]. The bogie spacing and train speed were considered 18 m and 260 km/h, respectively, which represents a cyclic frequency of 4 Hz.
A cyclic deviatoric stress amplitude (
qcyc) of 300 kPa was selected, which represents the stress level beneath the concrete slab of a ballastless track, as computed using FE analyses [
63]. An effective confining stress (
σ′
3) of 10 and 50 kPa was selected to reflect conditions pertinent to ballastless railway tracks. Undrained loading conditions were chosen to replicate the high-speed track environment. The triaxial specimens were subjected to 50,000 load cycles (
N) or until a vertical strain (
εv) of 20% was reached, whichever occurred first.
In addition to the ternary mixture of soil, rubber and PFA, cyclic triaxial tests were conducted on binary mixtures, viz., soil–rubber, soil–PFA, and untreated soil for comparison purposes.
2.4. Results from Cyclic Triaxial Tests
2.4.1. Accumulation of Residual Vertical Strain
Figure 5 illustrates the accumulation of residual vertical strain (
) with the number of load cycles (
N) for untreated soil and three mixtures at varying confinement levels (
σ′
3 = 10 and 50 kPa). It can be observed that as
σ′
3 increased,
decreased for all four samples. At
σ′
3 = 10 kPa, the untreated soil failed after 260 cycles (
~20%), as shown in
Figure 5a. When 10% rubber granules were added to the soil (without PFA treatment),
significantly increased, and the sample failed after
N = 9. This abrupt failure can be attributed to reduced gravel particle interlock and the enhanced interparticle mobility provided by rubber particles. This increased
upon rubber incorporation under cyclic loading is consistent with previous studies [
25,
26,
65,
66,
67]. When PFA was added to the untreated soil and the soil–rubber mixture,
decreased significantly, and both these samples withstood 50,000 cycles. Soil–PFA and soil–rubber–PFA mixtures exhibited
of 0.17% and 0.98%, respectively, at the end of test. All samples, except the soil–rubber mixture, withstood 50,000 cycles at higher confinement, i.e.,
σ′
3 = 50 kPa (
Figure 5b). The soil–rubber–PFA mixture exhibited
of 0.29% after 50,000 cycles at
σ′
3 = 50 kPa. These results indicate that the composite material will not undergo excessive deformation under train-induced repeated loading.
2.4.2. Pore Water Pressure Variations
Figure 6 illustrates the variation of change in pore water pressure (Δ
u) with
N at
σ′
3 = 10 and 50 kPa. It is apparent that at
σ′
3 = 10 kPa, Δ
u remains negligible (≤10 kPa) for soil–PFA and soil–rubber–PFA mixtures. The untreated soil exhibits negative Δ
u during the initial stages, which decreases with an increase in
N. However, for the soil–rubber mixture, Δ
u becomes more negative with an increase in
N.
Under low confinement, the rubber particles might prevent the soil particles from rearranging into a denser packing. This creates temporary voids, which result in the observed negative pore water pressure. This negative Δ
u then reduces as the rigid soil particles gradually migrate into the spaces created by the deformed rubber. A similar pattern was reported by Madhusudhan et al. [
68] for a rubber–sand mixture.
At σ′3 = 50 kPa, untreated soil shows a sharp rise in Δu within the first 1000 cycles, while Δu for the soil–rubber–PFA mixture increased gradually. A drop in Δu for this mixture after N = 4000 suggests dilation due to PFA cementation. The soil–PFA mixture exhibits minimal Δu, whereas Δu for the soil–rubber–PFA mixture reached ≈5 kPa and 1 kPa at σ′3 = 10 and 50 kPa, respectively, after N = 50,000.
These results highlight that PFA reduces cumulative deformation and excess pore water pressure buildup; thus, its application in the base layer will improve the performance of track substructure irrespective of the confinement levels.
2.4.3. Shear Modulus and Damping Ratio Variations
Evaluation of shear modulus (
G) and damping ratio (
DR) of track materials is essential to understand their behavior under train-induced dynamic loading. The
G values are computed using Equation (1) [
69].
where
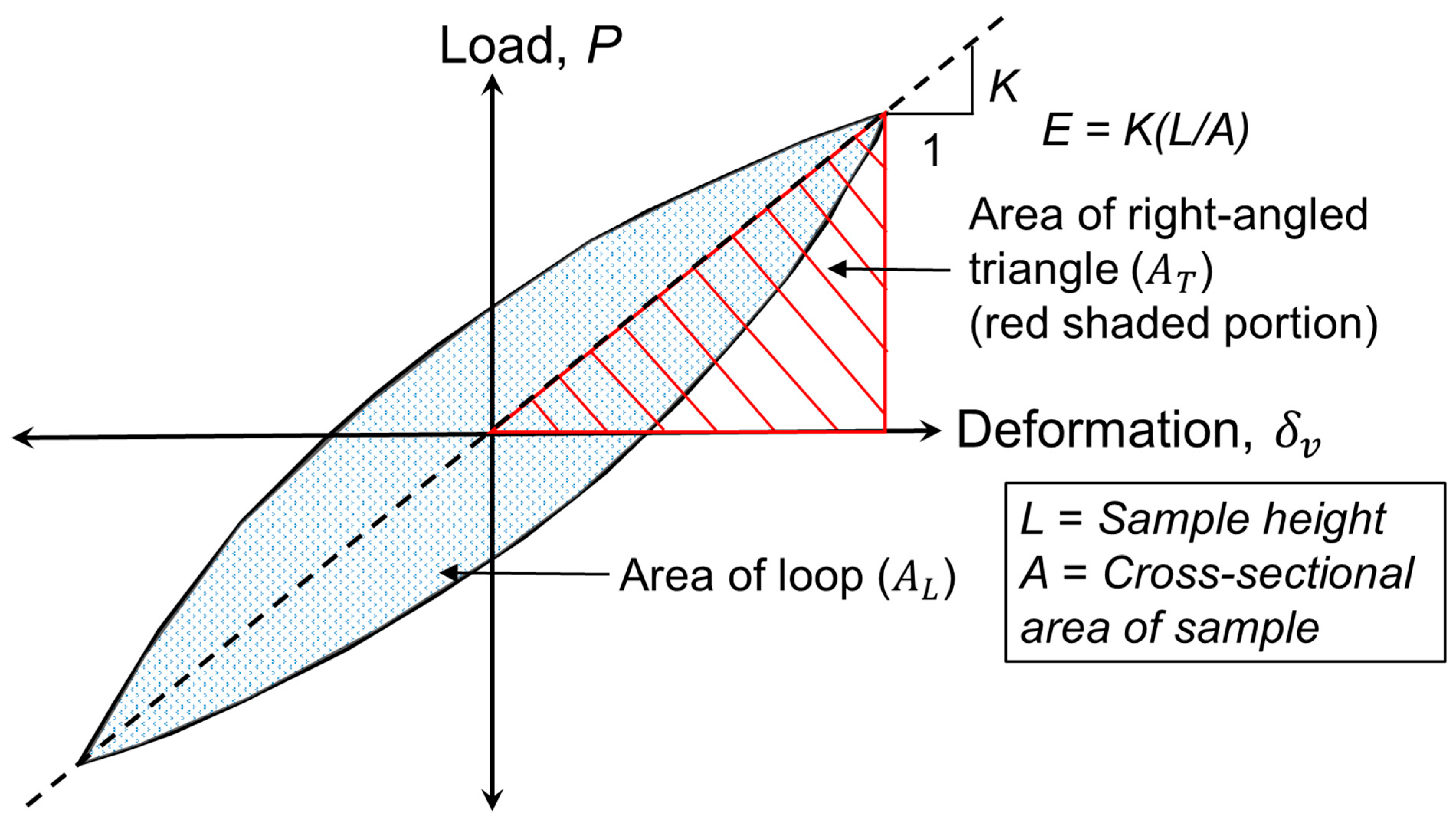
E is the elastic modulus calculated using the slope of the line passing through the extreme points of the hysteresis loop, as shown in
Figure 7;
ν is Poisson’s ratio (considered 0.5 for the undrained specimen). It must be noted that
G computed in the present study is the secant shear modulus (
Gsec) but is referred to as shear modulus for simplicity.
The
DR is calculated using the area of the hysteresis loop and the right-angled triangle (representing the maximum energy stored during a load cycle) (see
Figure 7). This
DR represents the capacity of a soil to dissipate energy for each loading cycle [
70] and can be computed using Equation (2).
where
and
= areas enclosed by the hysteresis loop and the right-angled triangle (refer to
Figure 7), respectively.
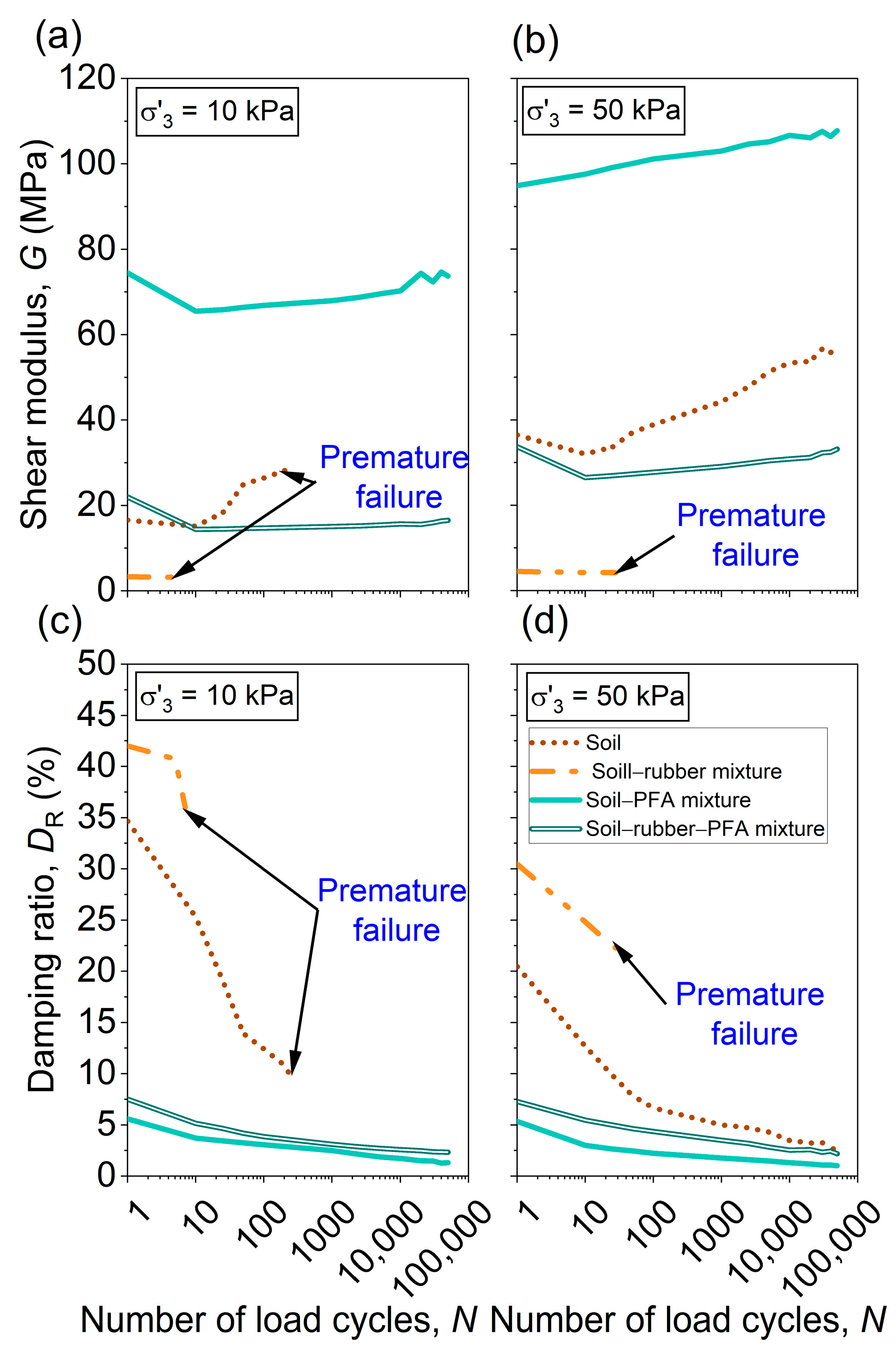
Figure 8 illustrates the variation in G and
DR with
N for untreated soil and the three mixtures under
σ′
3 of 10 and 50 kPa. It is apparent that the incorporation of rubber to untreated soil increases
DR but reduces
G. Conversely,
G increases upon adding PFA to untreated soil while
DR decreases. The confining pressure also influences both
G and
DR, with higher
σ′
3 leading to increased
G and reduced
DR.
To quantify the individual effects of adding rubber and PFA on the behavior of different mixtures, their dynamic properties (G and DR) are compared at the 10th loading cycle under σ′3 = 10 kPa. This comparison reveals that the addition of rubber to soil primarily enhances its energy dissipation capacity, with 61% increase in DR at 10% rubber content compared to untreated soil. However, this improvement in damping is accompanied by a substantial reduction in stiffness (a 79% decrease in G). In contrast, PFA acts as a stabilizing agent that significantly increases the stiffness of the mixture, with a 333% increment in G value at 10% PFA content compared to untreated soil. However, this stiffness improvement is accompanied by a significant reduction in energy dissipation capacity, as indicated by an 85% decrease in DR.
Interestingly, the ternary mixture (soil–rubber–PFA) demonstrates a balanced performance. Compared to the soil–PFA mixture, this mix achieved a 39.4% improvement in DR with a 78% decrease in G value. Despite the reduction in G, the mixture showed superior long-term stability and withstood 50,000 cycles with minimal deformation ( = 0.98%), thereby outperforming the binary mixtures (soil–rubber and soil–PFA).
2.4.4. Permeability
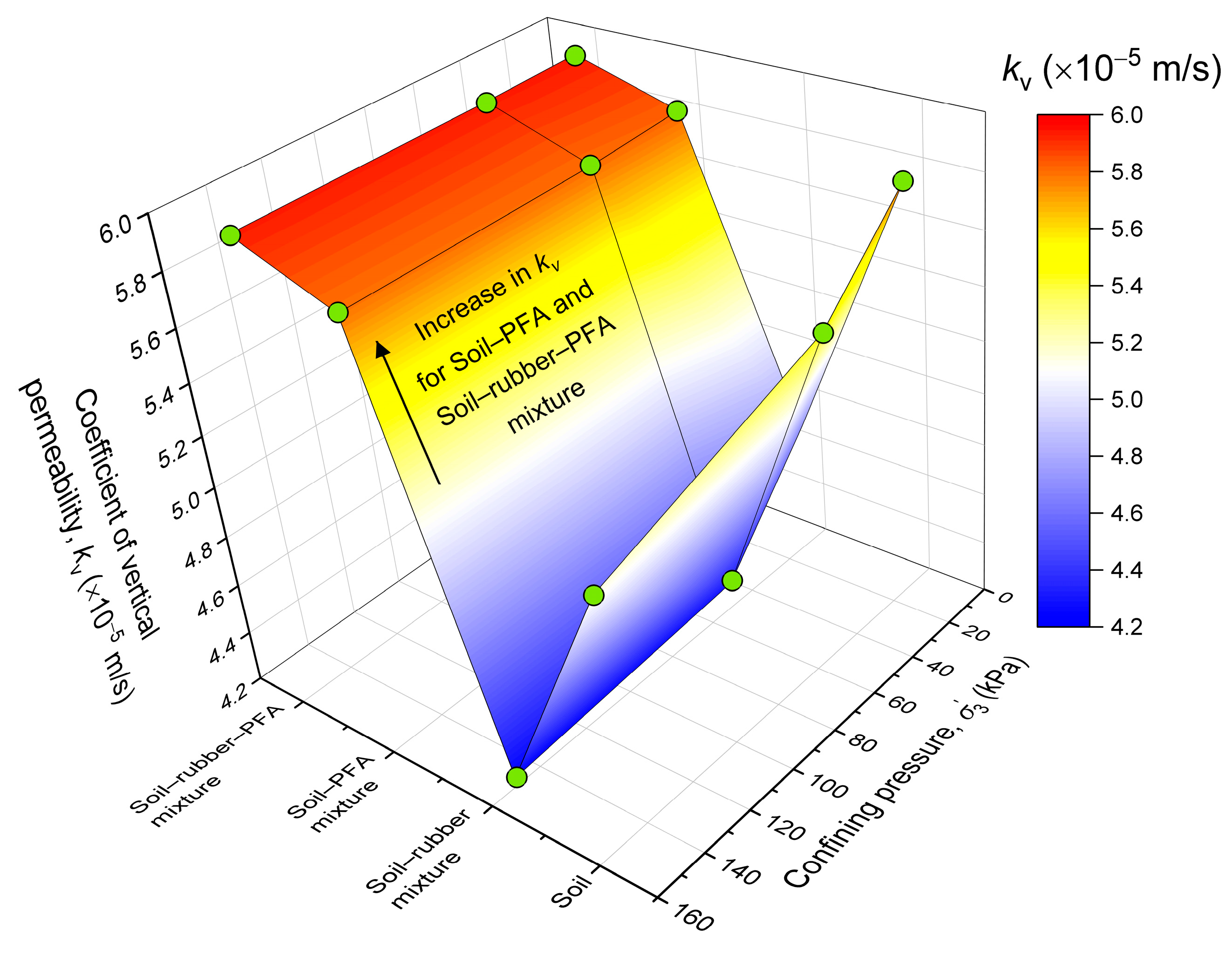
The coefficient of vertical permeability for different mixtures was also determined at the end of the consolidation stage before cyclic loading. After completion of the consolidation stage, a significant reduction in was observed for untreated soil and soil–rubber mixture. This reduction in was due to a decrease in the void ratio of the sample, which occurs during consolidation. The reduction in increased with an increase in . Insignificant changes in were observed for the soil–PFA and soil–rubber–PFA mixtures. Also, did not influence of these PFA-treated mixtures. Thus, using these treated mixtures in the base layer of ballastless railway tracks would avoid the build-up of excess pore pressure by offering an uninterrupted water flow under varying confinement levels.
The
kv values for different mixtures after consolidation under various
, are illustrated in
Figure 9. It can be observed that the
kv of soil is
m/s after consolidation under
of 10 kPa, and it decreases to
m/s with the addition of 10% rubber. Madhusudhan et al. [
71] and Masad et al. [
72] also noted a decrease in
kv with the addition of rubber to soil. Soil–PFA and soil–rubber–PFA mixtures exhibit
kv of
m/s and
m/s, respectively, which are similar to untreated soil. PFA was added to the soil–rubber mixture to bind the soil and rubber particles together. This prevented the particles from moving during the saturation stage and made it easier for water to flow. Therefore, the soil–rubber–PFA mixture did not show a decrease in
kv. Notably, non-foaming PFA was utilized in the present study at an ideal dosage that was adequate to cover the particles without filling in the gaps, which could have decreased the permeability.
2.5. Limitations and Future Scope
A direct comparison of the performance of the novel composite with cement-treated soil was beyond the scope of this study due to the limitations of the testing equipment. Such a comparison would have enabled a more comprehensive evaluation of the performance of the composite, and it will be addressed in future research. This study also did not explore the micro-level interactions between soil, rubber particles and PFA within the proposed composite material. Understanding these interactions is essential for gaining deeper insights into the long-term performance of this material under varying mechanical and environmental loading conditions. Future investigations shall address this limitation by conducting microstructural analysis using techniques such as scanning electron microscopy. In addition, advanced modeling approaches, such as the discrete element (DE) method, would be employed to simulate particle-scale interactions and accurately predict the mechanical behavior of this material.
2.6. Concluding Remarks
This section assessed the effectiveness of a novel composite material, comprising soil, aggregates derived from discarded tires, and PFA, in enhancing the performance and sustainability of the railway tracks through laboratory investigations. The main findings from this section are as follows:
The novel composite material demonstrates strong potential as a sustainable base layer for ballastless railway tracks. This composite exhibited negligible cumulative residual vertical strain (0.29–0.98%) and minimal residual pore water pressure (~1–10 kPa) after 50,000 load cycles.
The composite showed superior damping performance for vibration attenuation and a high permeability, reflecting improved drainage.
These findings highlight that the proposed soil–rubber–PFA composite offers a sustainable alternative for the base layer in ballastless railway tracks. This novel composite contributes to sustainability by:
Promoting utilization of a significant industrial waste stream through repurposing of granulated rubber from end-of-life tires, thereby alleviating landfill burden.
Substituting carbon-intensive cement with a polyurethane-based resin (i.e., PFA), which significantly reduces the embodied carbon and overall greenhouse gas emissions linked to the construction of track substructure.
These environmental benefits are achieved while ensuring the novel composite meets the engineering performance criteria for ballastless railway tracks. Thus, the composite presents an effective solution that integrates high performance with environmental stewardship. It must be noted that a quantitative assessment of the reduction in carbon footprint achieved using the novel composite is beyond the scope of this study and is a subject of future research.
4. Using Planar Artificial Inclusions in Railway Embankments
4.1. General
Planar artificial inclusions can be installed at the base of pile-supported embankments (PSE) to enhance their performance and sustainability. These embankments are typically used in areas where subgrade soil possesses unfavorable engineering characteristics, such as high compressibility and low shear strength. In PSEs, the fill material shows higher settlement between the piles due to the stiffness differences [
93]. However, a shear resistance mechanism, called soil arching, is developed within the fill, which limits this settlement, and most of the train-induced load is transferred to the piles [
94,
95]. The incorporation of planar inclusions could improve this load-transfer mechanism by virtue of the tensioned-membrane effect [
46].
Several studies have explored the effect of planar inclusions on the load-transfer behavior in PSE. Cao et al. [
47] conducted model tests to study the effect of factors such as relative settlement between subsoil and piles, height of embankment, and clear pile spacing on the soil arching mechanism. Their findings revealed that soil arching was completely mobilized when the relative settlement between the pile and subsoil reaches 6 to 8 mm. Moreover, differential settlement decreased as the embankment height to clear pile spacing ratio increased. The use of a planar inclusion further enhanced the soil arching effect. Lang et al. [
48] performed 3D FE analyses to study the long-term load transfer mechanism in pile-supported highway embankments under traffic-induced loading. Their results indicated that factors such as traffic loading type, vehicle speed, pile spacing, and the number of inclusion layers substantially influence the load distribution over time.
Pan et al. [
96] carried out field tests to monitor the evolution of soil arching and deformation in soil, piles, and planar inclusions during both the construction and equilibrium phases of embankments. Their findings suggested that three stages of soil arching evolution occurred with increasing fill height. Soil arching was completely mobilized when the pile–soil settlement ratio attained a minimum value, corresponding to a differential settlement of approximately 1% of the net pile spacing. Strain in inclusions primarily developed in the early stage of filling, with a progressive reduction in strain accumulation during subsequent filling stages. Ye et al. [
49] conducted numerical analyses on various pile layouts and found that a triangular arrangement enhanced the load transfer mechanism. Furthermore, in multi-layered inclusions, the bottom layer played a critical role in load distribution. Li et al. [
97] investigated the load-transfer behavior in PSE through a modified FE model, which was validated using field test data. Their findings revealed that pile spacing significantly influenced load-transfer behavior in PSE, thereby affecting the long-term performance and sustainability of railway infrastructure.
This review of existing studies suggests that integrating planar inclusion layers in PSE can improve their performance and contribute to sustainability by reducing the number of piles required. However, limited research has focused on the impact of train loading on the tensile stresses in planar inclusions and the load-transfer mechanisms. Therefore, the next section investigates the effectiveness of a planar artificial inclusion, specifically a geogrid, in enhancing the soil arching within a PSRE.
4.2. Numerical Modelling of Pile-Supported Embankment
A pile-supported embankment with and without a planar inclusion layer was analyzed under two-dimensional (2D) plane strain conditions using the FE method.
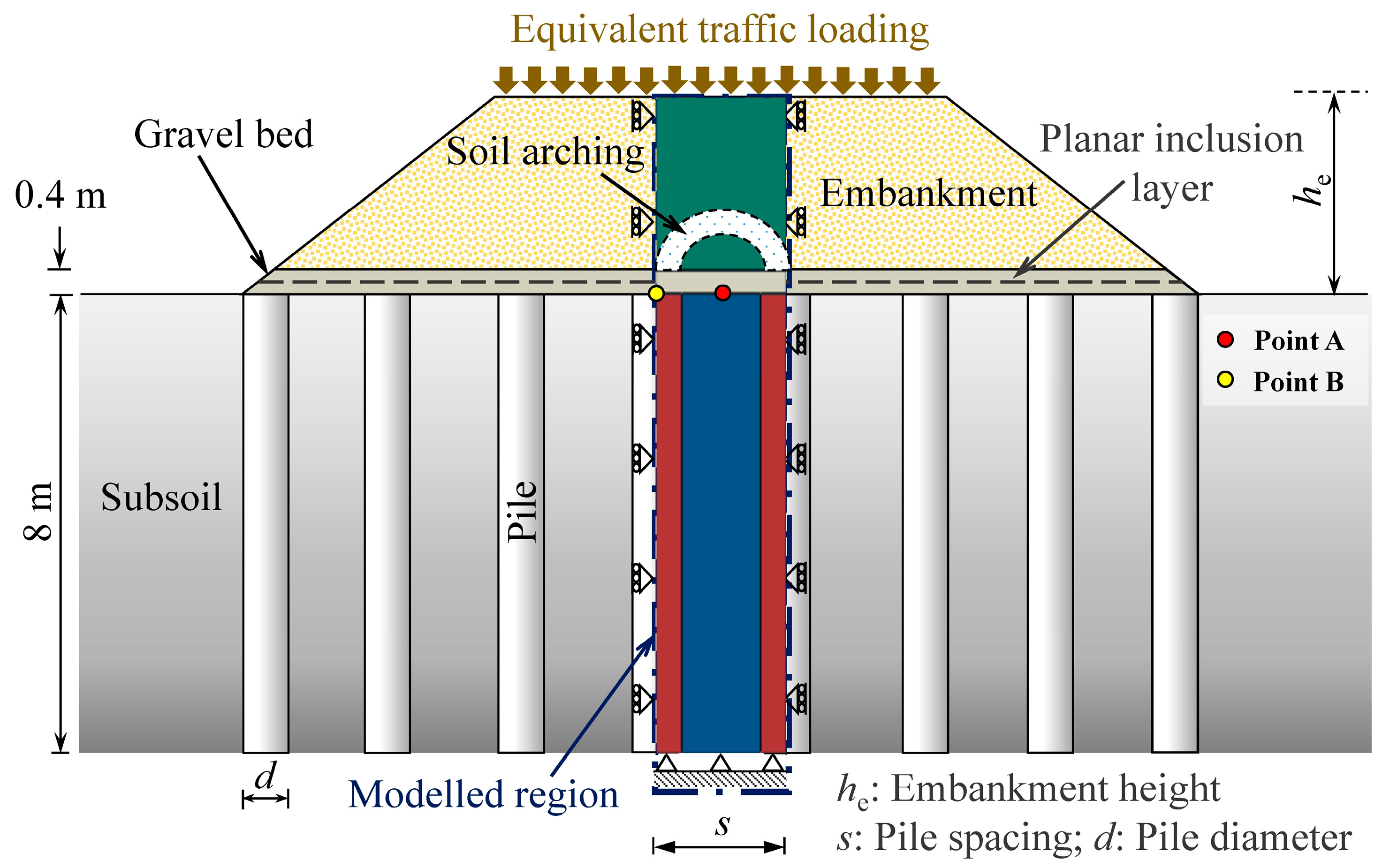
Figure 17 presents a schematic representation of a pile-supported railway embankment (PSRE) with a planar inclusion layer at the bottom, highlighting the soil arches and the modelled region. The spacing (
s) and diameter (
d) of the piles were chosen as 2–3.5 m and 1 m, respectively, and these piles extended to a depth of 8 m in the subsoil. The height of the embankment (
he), incorporating a 0.4 m thick gravel layer, was considered to be 3.5 m. The planar inclusion was a PP biaxial geogrid with a stiffness of 1 kN/m, which was embedded at the mid-depth (0.2 m) of the gravel layer. To simulate train-induced loads and the weight of the railway track, an equivalent dynamic loading was exerted on the embankment surface. The bottom and side boundaries of the FE model were constrained, with the bottom fully fixed and the sides normally fixed [
98].
Table 3 summarizes the values of material parameters employed in the numerical simulations to investigate the load-transfer behavior in PSRE.
Eight-noded, quadratic solid elements (CPE8R) with reduced integration were used for discretizing the FE model of PSRE. The interaction between soil and pile was modelled using a “hard” normal contact and a penalty-based tangential contact with a friction coefficient of 0.7. The FE modelling process began with the application of geostatic loading to generate the initial stresses in the subsoil, followed by sequential construction of the gravel bed, rigid piles, and embankment. Once full geometry was created, an equivalent dynamic-load-simulating railway track self-weight and train movement was exerted on the embankment surface.
Detailed information on the 3D to 2D conversion method, applied loading and model validation is available elsewhere (see, for, e.g., [
99]). In the present study, the influence of embankment fill parameters, including
he, elastic modulus (
Ee), effective friction angle (
ϕ′), and pile spacing (
s) on the soil arching mechanism and tensile stresses generated in the planar inclusion is investigated.
4.3. Results and Discussion
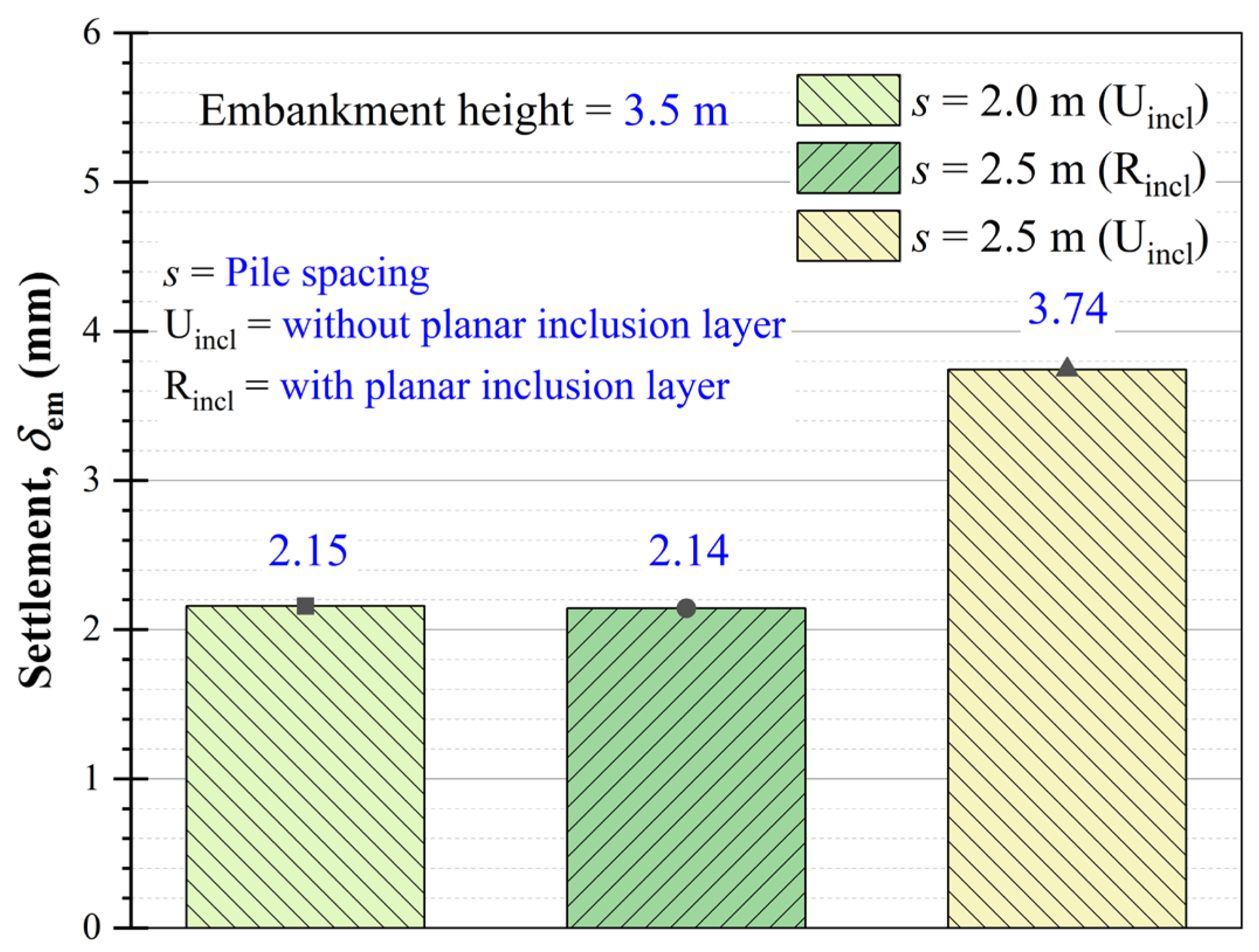
Figure 18 illustrates the effect of pile spacing on the settlement in embankment fill. In the absence of reinforcement, the settlement at Point A (at
Dtd = 0) increases from 6.3 to 12 mm as
s increases from 2 to 3.5 m. To mitigate this settlement, a planar inclusion layer can be introduced at the mid-depth of the gravel bed. This inclusion reduces the vertical stress at Point A (see
Figure 19) by virtue of the tensioned membrane effect and consequently decreases the settlement.
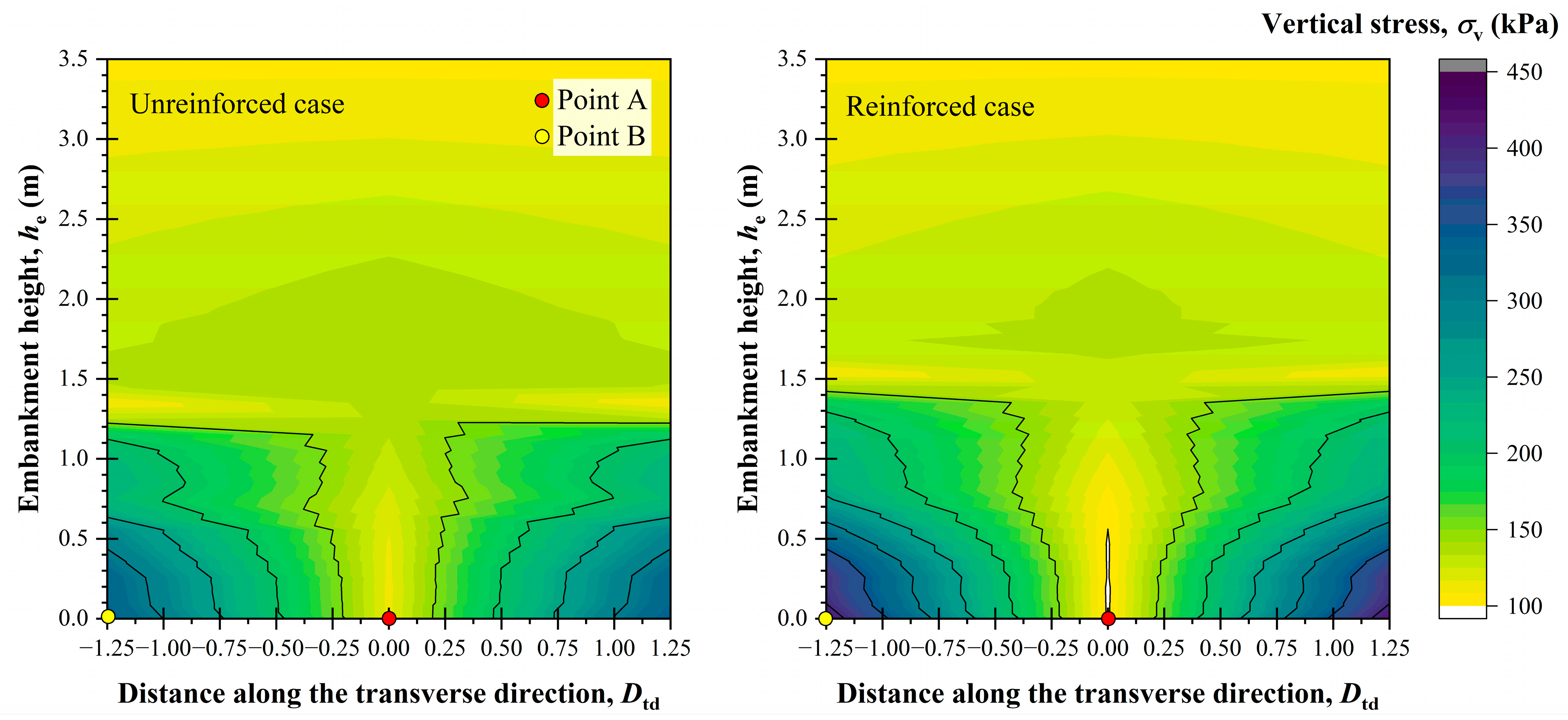
Figure 19 illustrates the vertical stress distribution contours for both a conventional embankment (i.e., without inclusion layer) and the one reinforced with a planar inclusion layer. These contours represent the transmission of vertical stresses from the top to the base of the embankment. It must be noted that the height of the embankment and spacing of piles for this analysis are set at 3.5 and 2.5 m, respectively.
It can be seen in
Figure 19 that the vertical stress for the unreinforced case initially increases from
he = 3.5 to 2 m and then decreases from 2 to 0.5 m along a section passing through point A. Meanwhile, the vertical stress progressively increases from the embankment top to the bottom along a section passing through point B. Thus, the vertical stress within the embankment fluctuates, decreasing at Point A and increasing at Point B, within the height range of 0.5 to 2 m. This region is referred to as the load transfer zone.
For the reinforced case, the vertical stress distribution follows a similar trend to that of the unreinforced case. However, a notable difference is observed in the magnitude of vertical stress at key points. At point A, the vertical stress is reduced by approximately 10%, whereas at point B, it is elevated by 19% compared to the unreinforced case. This variation is primarily ascribed to the development of tensile forces within the inclusion layer, which enhances load redistribution and improves the efficiency of the load-transfer mechanism.
It is apparent from
Figure 20 that the use of planar inclusions reduces the settlement at the embankment top by around 43% at a pile spacing of 2.5 mm. A similar reduction in settlement with the incorporation of inclusions was reported in [
100,
101]. It is important to note that by using planar inclusions in the base of PSRE, it is feasible to increase the spacing of the piles without compromising the embankment performance, as illustrated in
Figure 20. It is evident from the figure that the settlement at the embankment crest with 2 m pile spacing (unreinforced case) is similar to the reinforced case with a 2.5 m pile spacing. This indicates that similar performance can be achieved with wider pile spacing when planar inclusions are used, implying fewer piles are needed. This could potentially reduce the amount of concrete required as well as lower the carbon footprint and overall construction cost.
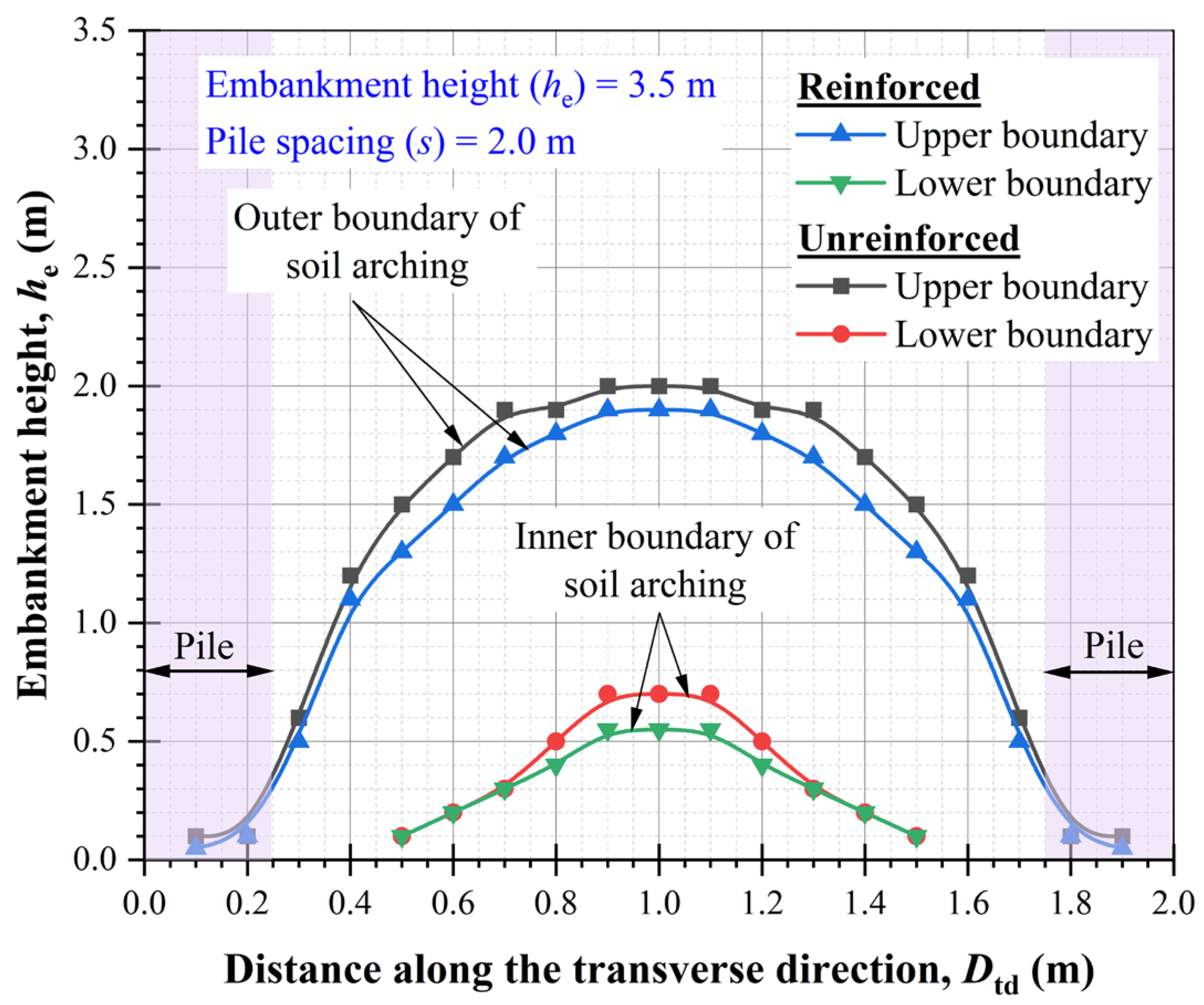
Figure 21 illustrates the formation of soil arches within the embankment, highlighting both their outer and inner boundaries. To depict the shape of the soil arch, multiple vertical planes perpendicular to the transverse direction are analyzed. The heights corresponding to the minimum and maximum vertical stresses along each vertical plane define the inner and outer boundaries of the soil arch, respectively.
In an unreinforced embankment, at a section along point A (see
Figure 17), the maximum vertical stress corresponding to the outer boundary of the soil arch is observed at
he = 2 m. Meanwhile, the inner boundary of the soil arch is identified at a height of 0.7 m, resulting in a load transfer zone of 1.3 m. This zone becomes thinner along the section at point B and deviates from the semicircular arching pattern proposed by Hewlett and Randolph [
93]. Instead, it aligns more closely with the multi-shell arching theory suggested by Kempfert et al. [
102], indicating a more complex load redistribution mechanism.
In the reinforced case, a similar trend is observed, with a 5% increase in the load transfer zone at a section along point A. This indicates that the reinforcement effectively improves stress distribution within the embankment without altering the fundamental arching behavior. This observation is ascribed to the tensioned membrane effect, wherein the inclusion layer mobilizes tensile forces that counteract vertical deformation. However, the magnitude of tension in the inclusion layer depends on various factors, including the stiffness and tensile strength of the material, depth and position of the inclusions within the granular bed, the spacing and geometry of piles, and the characteristics of the overlying embankment fill. These parameters collectively govern the extent to which inclusions can redistribute stress and reduce settlement.
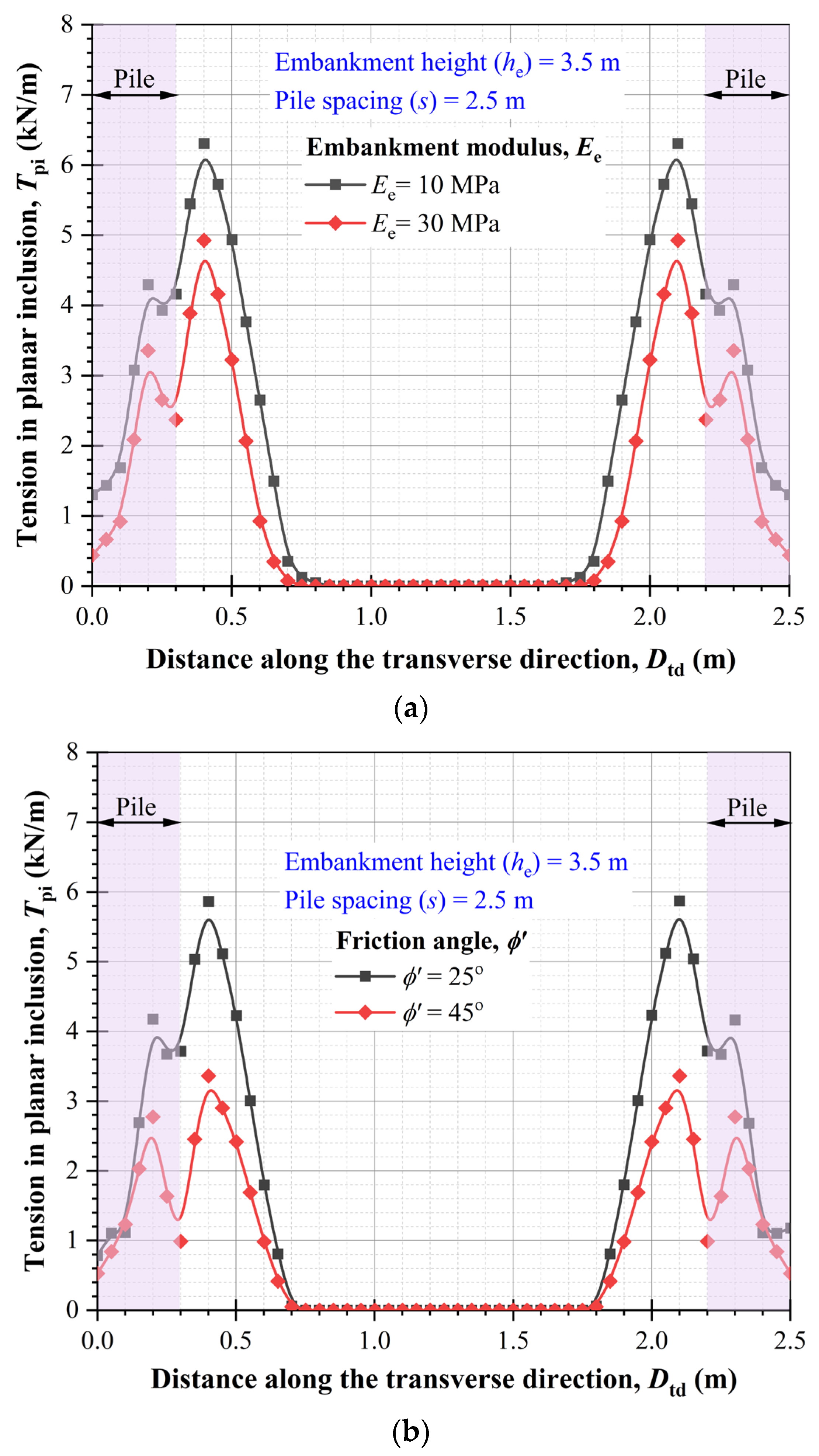
Figure 22 illustrates how tension developed in the inclusions (
Tpi) varies with the properties of embankment fill material, such as elastic modulus (
Ee) and friction angle (
ϕ′). The results indicate that as
Ee increases from 10 to 30 MPa, the tensile stresses in the inclusions significantly decrease by up to 35%. Similarly, an increase in
ϕ′ from 25° to 45° leads to a reduction in
Tpi by approximately 54%. This reduction in tension can be ascribed to the improved strength and stiffness of the embankment fill, which minimizes settlement, and consequently, the demand for planar reinforcement. These findings suggest that when
Ee and
ϕ′ are sufficiently high, the contribution of inclusions to load transfer is diminished. Therefore, planar reinforcement is more effective for embankments constructed using fill with a smaller modulus and friction angle.
4.4. Limitations and Future Scope
In this study, a 2D FE method was employed to investigate the behavior of pile-supported railway embankments with planar artificial inclusions. While the 2D FE approach provides reasonably accurate predictions more quickly than 3D FE analysis, it is unable to capture the influence of factors such as embankment slope, moving loads, and non-uniform stress-distribution within the inclusion layer. Future studies shall address this limitation by using 3D FE analysis, which can more accurately predict the performance of pile-supported railway embankments under realistic geometry and loading conditions.
4.5. Concluding Remarks
This section investigated the effectiveness of a planar artificial inclusion in enhancing the load transfer mechanism within a pile-supported railway embankment (PSRE) using 2D FE analysis. The main findings from this section are as follows:
The incorporation of planar inclusions at the base of the PSRE improved the load-transfer mechanism by reducing the magnitude of stress transmitted to the subsoil. This improvement is primarily attributed to the tensioned membrane effect within the inclusion layer, which facilitates better load distribution and reduces differential settlement.
The use of planar inclusions could reduce the number of piles required for PSRE construction, thereby curtailing the carbon emissions associated with piling operations.
By reinforcing the embankment, the inclusion layer effectively mobilizes soil arching, leading to enhanced stability and long-term performance of the railway track. This improvement not only optimizes structural performance but could also contribute to the sustainability of transport infrastructure by minimizing maintenance needs and extending service life.
5. Conclusions
This study assessed the effectiveness of three approaches in enhancing the performance and sustainability of railway track infrastructure: (a) a novel composite material comprising soil, aggregates derived from discarded rubber tires and PFA; (b) cellular artificial inclusions; (c) planar artificial inclusions.
Laboratory investigations revealed that the soil–rubber–PFA composite exhibits excellent mechanical performance, including low residual strain (0.29–0.98%), minimal pore water pressure (~1–10 kPa), adequate damping and high permeability (~ m/s). Its use would promote sustainability by repurposing scrap tires and substituting carbon-intensive cement with PFA, thereby reducing environmental impact while meeting engineering requirements for ballastless track applications.
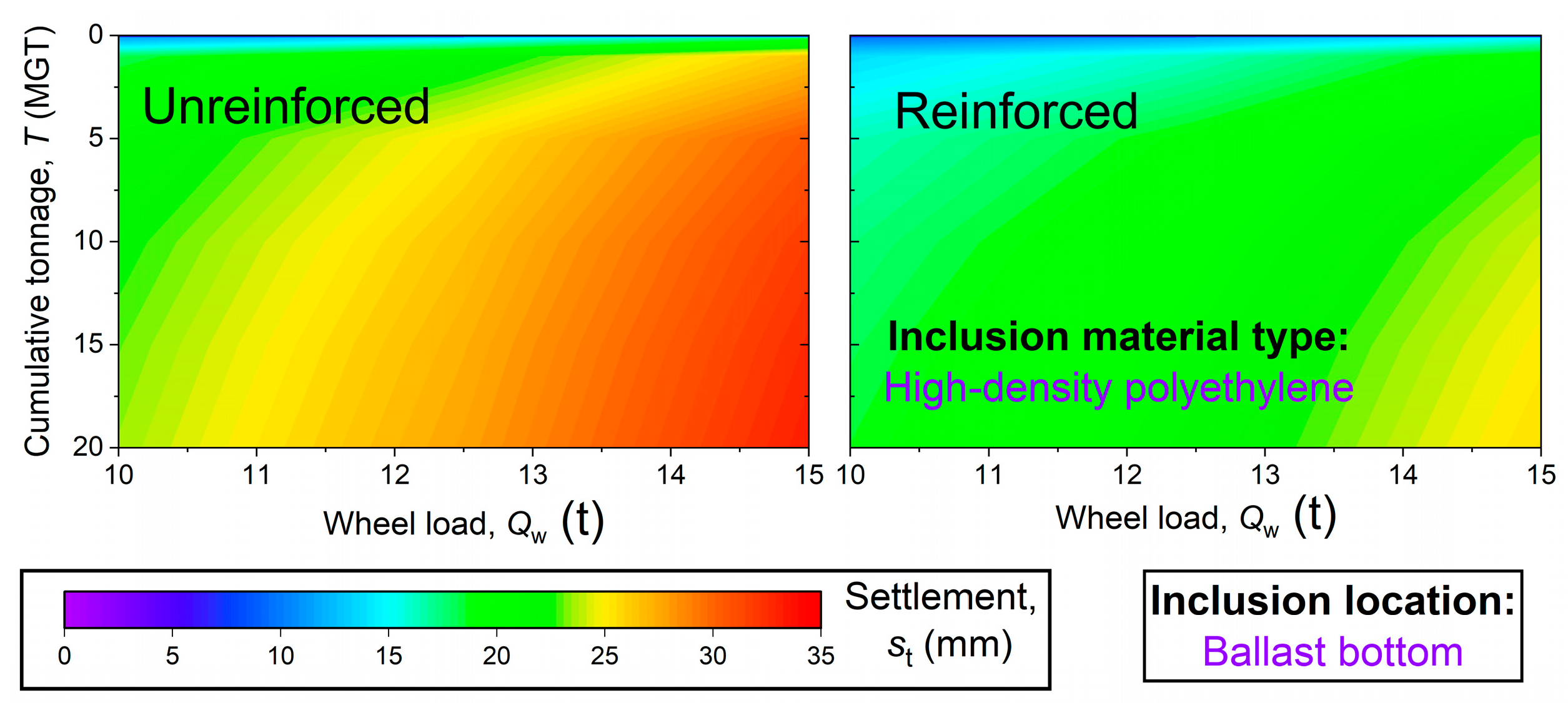
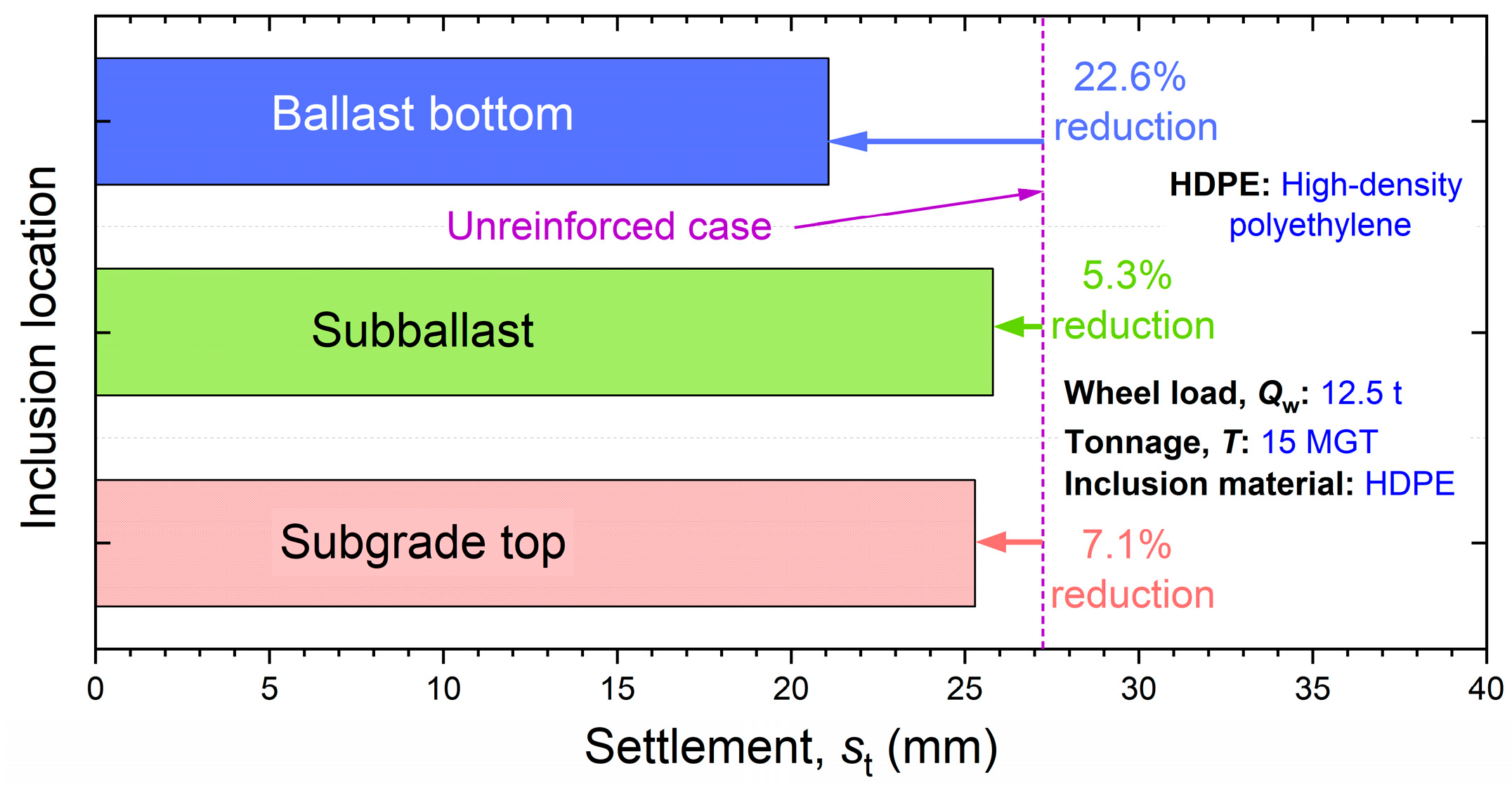
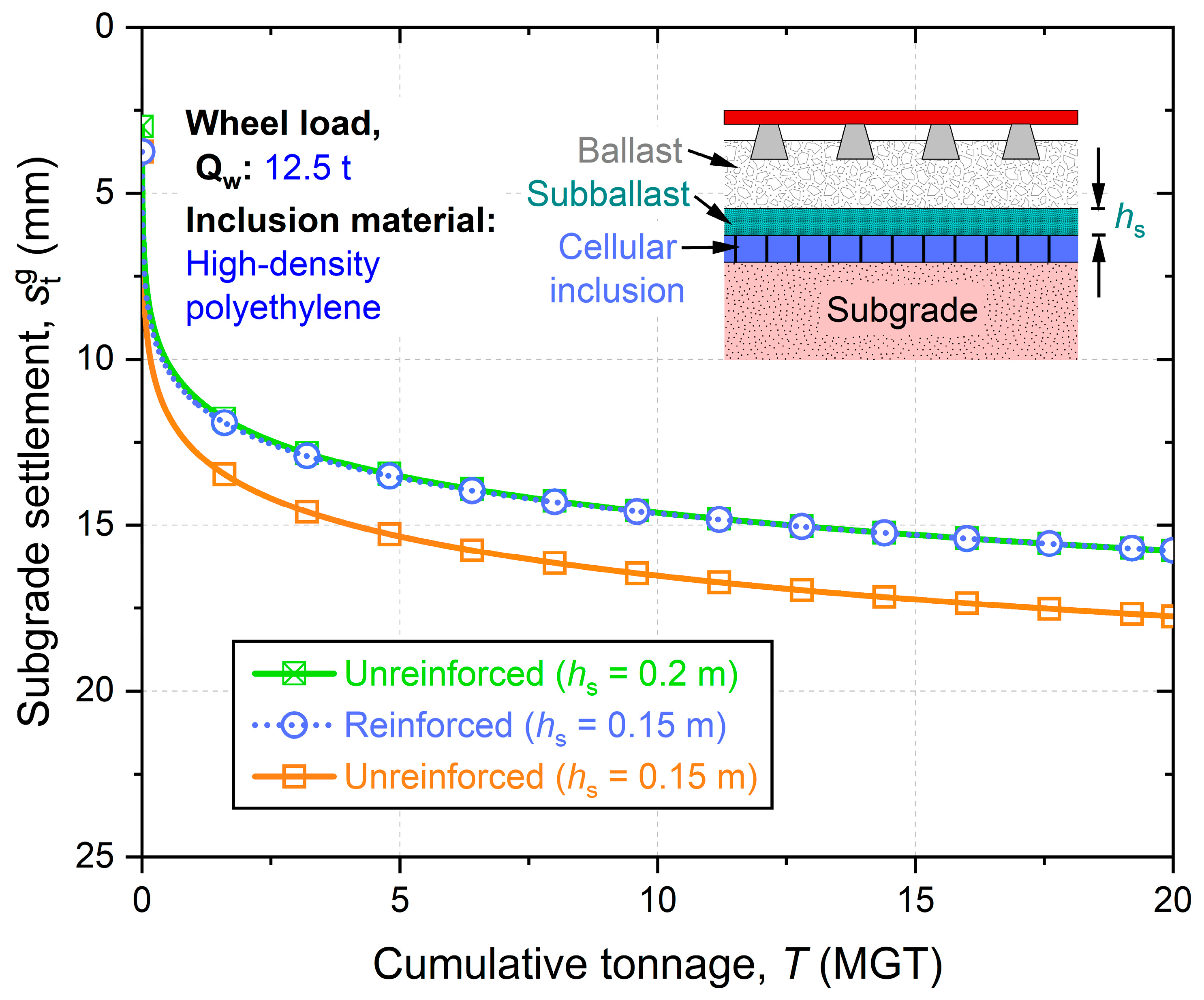
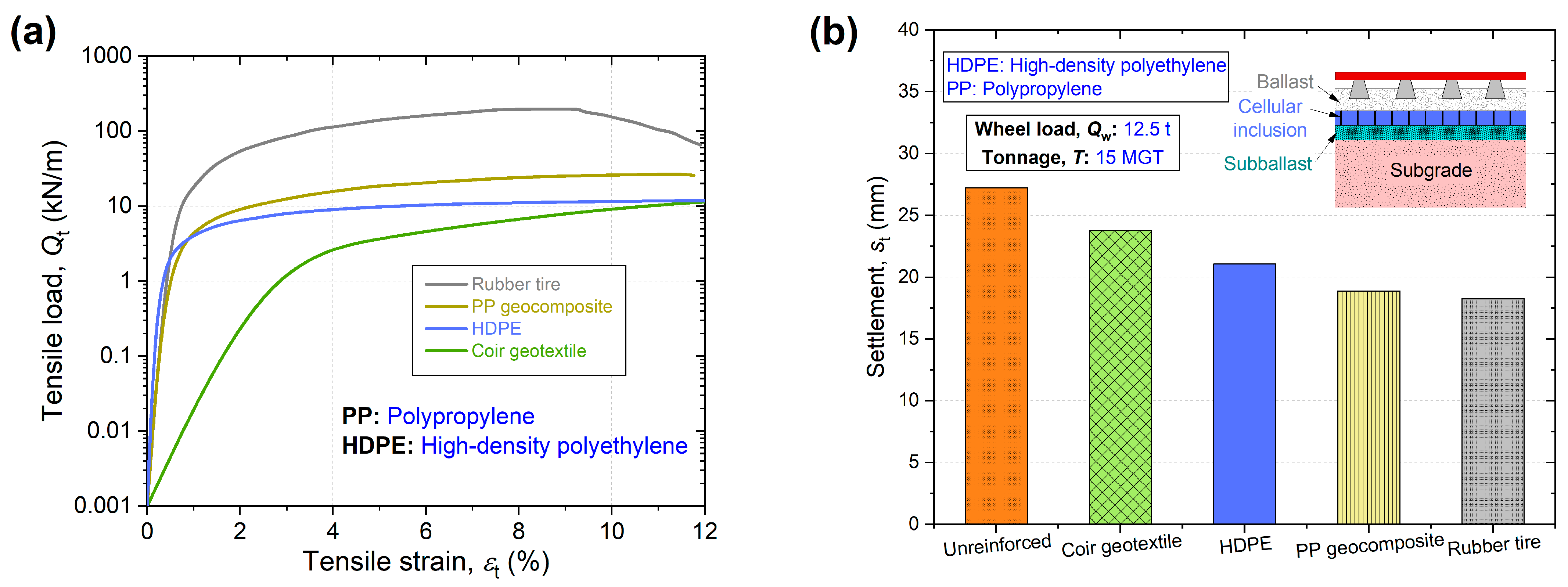
Results from a rheological computational approach highlighted that the use of cellular artificial inclusions could significantly reduce cumulative settlement (by up to 33%) and material usage in ballasted railway tracks. This could potentially lead to lower maintenance requirements and reduced carbon emissions. Their effectiveness under higher load levels demonstrates their potential for enhancing the resilience of railway infrastructure against future load escalation.
Finite element analyses of pile-supported railway embankments showed that planar artificial inclusions improve the load transfer to the piles through the tensioned membrane effect and reduce the subsoil stress and settlement. Their use enabled wider pile spacing, which could lead to fewer piles, lower concrete usage and reduced carbon emissions, without compromising the stability of the PSRE.
These techniques show strong potential for enhancing the long-term resilience and sustainability of railway infrastructure. Their integration into future designs could enable high-performing systems with lower carbon footprints as well as greater adaptability to future load escalation and climate-related impacts.