Exploring the Impact of Female Student’s Digital Intelligence on Sustainable Learning and Digital Mental Well-Being: A Case Study of Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Adaptive Online Learning (AOL) and Constructivist Learning Theory
2.2. Student Digital Intelligence (SDI)
2.3. Sustainable Learning (SLR)
2.4. Moderating Role of Innovative Teaching
2.5. Mediating Role of Student’s Digital Intelligence
3. Methodology
3.1. Questionnaire Design and Distribution
3.2. Target Population and Sampling Technique
3.3. Data Collection and Cleaning
3.4. Data Analysis Method
4. Data Analysis
4.1. Measurement Model
4.2. Structural Model and Discussion
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Practical Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, N.; Muhammad, K.; Hussain, T.; Nasir, M.; Munsif, M.; Imran, A.S.; Sajjad, M. An adaptive game-based learning strategy for children road safety education and practice in virtual space. Sensors 2021, 21, 3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, R.; Mora, D.; Cirqueira, D.; Helfert, M.; Bezbradica, M.; Werth, D.; Weitzl, W.J.; Riedl, R.; Auinger, A. Enhancing brick-and-mortar store shopping experience with an augmented reality shopping assistant application using personalized recommendations and explainable artificial intelligence. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2023, 17, 273–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, C.; Iannuzzi, E.; di Santo, N.; Sisto, R. Food delivery, ghost kitchens and virtual restaurants: Temporary or long-lasting game changers? Br. Food J. 2023, 125, 2217–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlister, A.R.; Alhabash, S.; Yang, J. Artificial intelligence and ChatGPT: Exploring Current and potential future roles in marketing education. J. Mark. Commun. 2024, 30, 166–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahri, N.A.; Al-Rahmi, W.M.; Almogren, A.S.; Yahaya, N.; Vighio, M.S.; Al-maatuok, Q.; Al-Rahmi, A.M.; Al-Adwan, A.S. Acceptance of mobile learning technology by teachers: Influencing mobile self-efficacy and 21st-century skills-based training. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, S.A.; Alhumaid, K.; Alfaisal, A.M.; Aljanada, R.A.; Alfaisal, R. Adoption of 3D Holograms in Science Education: Transforming Learning Environments. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 70984–70998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorea, I.; Cioca, M.; Oancea, R.; Gorski, A.-T.; Gorski, H.; Tudorache, P. Adaptive learning using artificial intelligence in e-learning: A literature review. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minn, S. AI-assisted knowledge assessment techniques for adaptive learning environments. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Christensen, C.; Cui, W.; Tong, R.; Yarnall, L.; Shear, L.; Feng, M. When adaptive learning is effective learning: Comparison of an adaptive learning system to teacher-led instruction. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2023, 31, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabudi, T.; Pappas, I.; Olsen, D.H. AI-enabled adaptive learning systems: A systematic mapping of the literature. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Renard, A. A Society of Young Women: Opportunities of Place, Power, and Reform in Saudi Arabia; Stanford University Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aldossari, M.; Calvard, T. The politics and ethics of resistance, feminism and gender equality in Saudi Arabian organizations. J. Bus. Ethics 2022, 181, 873–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, K.; Nasr, O.A.; Miladi, M.N.; Fatima, H.; Shahwar, S.; Naveed, Q.N. Potentialities and priorities for higher educational development in Saudi Arabia for the next decade: Critical reflections of the vision 2030 framework. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besser, A.; Flett, G.L.; Zeigler-Hill, V. Adaptability to a sudden transition to online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: Understanding the challenges for students. Scholarsh. Teach. Learn. Psychol. 2022, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokhan, A.; Chand, A.A.; Singh, V.; Mamun, K.A. Increased digital resource consumption in higher educational institutions and the artificial intelligence role in informing decisions related to student performance. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Tang, J.; Roll, I.; Fels, S.; Yoon, D. The impact of artificial intelligence on learner–instructor interaction in online learning. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2021, 18, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; He, Y.; Xue, Q. Progress, challenges and countermeasures of adaptive learning. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2021, 24, 238–255. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Eliyahu, A. Sustainable learning in education. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, N.S. The significance of digital learning for sustainable development in the post-COVID19 world in Saudi Arabia’s higher education institutions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, S. Identifying world types to deliver gameful experiences for sustainable learning in the metaverse. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifenthaler, D.; Yau, J.Y.-K. Utilising learning analytics to support study success in higher education: A systematic review. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2020, 68, 1961–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Xia, Q. Research landscape of adaptive learning in education: A bibliometric study on research publications from 2000 to 2022. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, S.; Mascheroni, G.; Stoilova, M. The outcomes of gaining digital skills for young people’s lives and wellbeing: A systematic evidence review. New Media Soc. 2023, 25, 1176–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhalafawy, W.S.; Najmi, A.H.; Zaki, M.Z.T.; Alharthi, M.A. Design an Adaptive Mobile Scaffolding System According to Students’ Cognitive Style Simplicity vs Complexity for Enhancing Digital Well-Being. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. 2021, 15, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haim, K.; Aschauer, W. Innovative FOCUS: A Program to Foster Creativity and Innovation in the Context of Education for Sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivarajah, R.T.; Curci, N.E.; Johnson, E.M.; Lam, D.L.; Lee, J.T.; Richardson, M.L. A review of innovative teaching methods. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, F.; Murad, H.S. Innovative teaching has a positive impact on the performance of diverse students. SAGE Open 2017, 7, 2158244017734022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Yu, B. Developing intercultural competence in college business English students: A study of innovative teaching in China. Int. J. Intercult. Relat. 2023, 92, 101747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi-Karim, M.; Bali, A.O.; Rached, K. Online education via media platforms and applications as an innovative teaching method. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsuwaida, N. Women’s Education in Saudi Arabia. J. Int. Educ. Res. 2016, 12, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, F.; Belas, J.; Santoro, G.; Alam, G.M. The role of open innovation in fostering SMEs’ business model innovation during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Knowl. Manag. 2023, 27, 1562–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, F.; Jiao, P. Artificial intelligence in education: The three paradigms. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, B.A. Participations and Interactions: A study of emerging art practices in Saudi Arabia supported by the Saudi Vision 2030. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Reading, Reading, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kem, D. Personalised and adaptive learning: Emerging learning platforms in the era of digital and smart learning. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Hum. Res. 2022, 5, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, K.; Hussein, H.; Arrona-Palacios, A.; Quintero, H.N.; Ortega, L.O.P.; Sanchez, A.L.; Ortiz, E.A.; Escamilla, J.; Hosseini, S. Impact of digital technologies upon teaching and learning in higher education in Latin America: An outlook on the reach, barriers, and bottlenecks. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 2291–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bada, S.O.; Olusegun, S. Constructivism learning theory: A paradigm for teaching and learning. J. Res. Method Educ. 2015, 5, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Fosnot, C.T. Constructivism: Theory, Perspectives, and Practice; Teachers College Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, S. The applications of constructivist learning theory and social learning theory on adult continuous development. Perform. Improv. 2021, 60, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, I.; Shamir-Inbal, T.; Avdiel, O. How does the pedagogical design of a technology-enhanced collaborative academic course promote digital literacies, self-regulation, and perceived learning of students? Internet High. Educ. 2020, 45, 100722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strielkowski, W.; Grebennikova, V.; Lisovskiy, A.; Rakhimova, G.; Vasileva, T. AI-driven adaptive learning for sustainable educational transformation. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 33, 1921–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcombe, L. AI chatbots in digital mental health. Informatics 2023, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liverpool, S.; Mota, C.P.; Sales, C.M.D.; Čuš, A.; Carletto, S.; Hancheva, C.; Sousa, S.; Cerón, S.C.; Moreno-Peral, P.; Pietrabissa, G. Engaging children and young people in digital mental health interventions: Systematic review of modes of delivery, facilitators, and barriers. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e16317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnok, K.; Wannapiroon, P.; Nilsook, P. DTL-eco system by digital storytelling to develop knowledge and digital intelligence for teacher profession students. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2020, 10, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Do, K.-H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.H.; Lim, Y.-S. What should medical students know about artificial intelligence in medicine? J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2019, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden, C.A.; Chisom, O.N.; Adeniyi, I.S. Promoting digital literacy and social equity in education: Lessons from successful initiatives. Int. J. Manag. Entrep. Res. 2024, 6, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Llorente, A.M.P.; Gómez, M.C.S. Digital competence in higher education research: A systematic literature review. Comput. Educ. 2021, 168, 104212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z. The effects of gender, educational level, and personality on online learning outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2021, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almulla, M.A.; Al-Rahmi, W.M. Integrated social cognitive theory with learning input factors: The effects of problem-solving skills and critical thinking skills on learning performance sustainability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premlatha, K.R.; Geetha, T.V. Learning content design and learner adaptation for adaptive e-learning environment: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2015, 44, 443–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, N.N.; Rothenberger, D. From burnout to well-being: A focus on resilience. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2019, 32, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadbent, J.; Panadero, E.; Lodge, J.M.; de Barba, P. Technologies to enhance self-regulated learning in online and computer-mediated learning environments. In Handbook of Research in Educational Communications and Technology: Learning Design; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.H.; Lin, M.P.-C.; Hajian, S.; Wang, Q.Q. Educational design principles of using AI chatbot that supports self-regulated learning in education: Goal setting, feedback, and personalization. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Self-determination theory. Handb. Theor. Soc. Psychol. 2012, 1, 416–436. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I.U.; Hameed, Z.; Yu, Y.; Islam, T.; Sheikh, Z.; Khan, S.U. Predicting the acceptance of MOOCs in a developing country: Application of task-technology fit model, social motivation, and self-determination theory. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 964–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.J.; Marôco, A.L.; Gonçalves, S.P.; Machado, A.d.B. Digital learning is an educational format towards sustainable education. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, N.; Fake, H.; Zhang, Z. Student perspectives of technology use for learning in higher education. RIED-Rev. Iberoam. Educ. A Distancia 2019, 22, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshari, M.; Almunawar, M.N.; Shahrill, M.; Wicaksono, D.K.; Huda, M. Smartphones usage in the classrooms: Learning aid or interference? Educ. Inf. Technol. 2017, 22, 3063–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cismaru, D.-M.; Gazzola, P.; Ciochina, R.S.; Leovaridis, C. The rise of digital intelligence: Challenges for public relations education and practices. Kybernetes 2018, 47, 1924–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurutdinova, A.R.; Perchatkina, V.G.; Zinatullina, L.M.; Zubkova, G.I.; Galeeva, F.T. Innovative teaching practice: Traditional and alternative methods (challenges and implications). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2016, 11, 3807–3819. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, R.; Coughlan, T.; Egelandsdal, K.; Gaved, M.; Herodotou, C.; Hillaire, G.; Jones, D.; Jowers, I.; Kukulska-Hulme, A.; McAndrew, P.; et al. Innovating Pedagogy 2019: Open University Innovation Report 7; The Open University: Milton Keynes, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, B.; Goh, G. Digital entrepreneurs in artificial intelligence and data analytics: Who are they? J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoc, M.L.; Sawicka, A.; Weichbroth, P. Artificial Intelligence Technologies in Education: Benefits, Challenges and Strategies of Implementation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 37–58. [Google Scholar]
- Vuorre, M.; Orben, A.; Przybylski, A.K. There is no evidence that associations between adolescents’ digital technology engagement and mental health problems have increased. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2021, 9, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Batanero, J.-M.; Román-Graván, P.; Reyes-Rebollo, M.-M.; Montenegro-Rueda, M. Impact of educational technology on teacher stress and anxiety: A literature review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drigas, A.; Papanastasiou, G.; Skianis, C. The school of the future: The role of digital technologies, metacognition and emotional intelligence. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2023, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishtiaq, M. Book Review Creswell, J.W. (2014). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative and Mixed Methods Approaches. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2019, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lekawael, R.F.J. The impact of smartphone and internet usage on English language learning. Engl. Rev. J. Engl. Educ. 2017, 5, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shelle, G.; Earnesty, D.; Pilkenton, A.; Powell, E. Adaptive learning: An innovative method for online teaching and learning. J. Ext. 2018, 56, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakin, M.; Linden, K. Adaptive e-learning platforms can improve student performance and engagement in dental education. J. Dent. Educ. 2021, 85, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, R. Determining the role of innovative teaching practices, sustainable learning, and the adoption of e-learning tools in leveraging academic motivation for students’ mental well-being. BMC Psychol. 2024, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na-Nan, K.; Roopleam, T.; Wongsuwan, N. Validation of a digital intelligence quotient questionnaire for employee of small and medium-sized Thai enterprises using exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. Kybernetes 2020, 49, 1465–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, A.A.; Abdul Razak, N.; Qasem, Y.A.M.; Saeed Mohammed, M.A. Intercultural learning challenges affecting international students’ sustainable learning in Malaysian higher education institutions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etikan, I.; Musa, S.A.; Alkassim, R.S. Comparison of convenience sampling and purposive sampling. Am. J. Theor. Appl. Stat. 2016, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Hair, J.F. Partial least squares structural equation modeling. In Handbook of Market Research; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 587–632. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonysamy, L.; Koo, A.C.; Hew, S.H. Self-regulated learning strategies in higher education: Fostering digital literacy for sustainable lifelong learning. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 2393–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.L.; Council, M.L. Distance learning in the era of COVID-19. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2021, 313, 389–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Kim, D.-g. Perception of instructor presence and its effects on learning experience in online classes. J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Res. 2020, 19, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthonysamy, L.; Ah Choo, K.; Soon Hin, H. Investigating Self-Regulated Learning Strategies for Digital Learning Relevancy. Malays. J. Learn. Instr. 2021, 18, 29–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, M.L.; Agus, M.; Penna, M.P. Emotional intelligence, self-regulation, smartphone addiction: Which relationship with student well-being and quality of life? Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, R.K.; Al Sabbah, S.; Al-Jarrah, M.; Senior, J.; Almomani, J.A.; Darwish, A.; Albannay, F.; Al Naimat, A. The mediating effect of digital literacy and self-regulation on the relationship between emotional intelligence and academic stress among university students: A cross-sectional study. BMC Med. Educ. 2024, 24, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self-Determination Theory: Basic Psychological Needs in Motivation, Development, and Wellness; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.; Koehler, M.J. Technological pedagogical content knowledge: A framework for teacher knowledge. Teach. Coll. Rec. 2006, 108, 1017–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodyear, P.; Retalis, S. Technology-Enhanced Learning: Design Patterns and Pattern Languages; BRILL: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kineshanko, M.K.; Jugdev, K. Enhancing digital intelligence through communities of learning. In On the Line: Business Education in the Digital Age; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, M.-C.; Tu, Y.-L.; Kao, M.-C. Applying deep learning image recognition technology to promote environmentally sustainable behavior. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 31, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Qadri, M.A.; Suman, R. Understanding the role of digital technologies in education: A review. Sustain. Oper. Comput. 2022, 3, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, F. On the issues of digital competence in educational contexts–a review of literature. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2018, 23, 1005–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymakamoglu, S.E. Teachers’ Beliefs, Perceived Practice and Actual Classroom Practice in Relation to Traditional (Teacher-Centered) and Constructivist (Learner-Centered) Teaching (Note 1). J. Educ. Learn. 2018, 7, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Garza, V.; Keicher, A.; Popov, V. Predicting high school teacher use of technology: Pedagogical beliefs, technological beliefs and attitudes, and teacher training. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2019, 24, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Demographic Variable | Category | Frequency (N = 284) |
|---|---|---|
| Age Group | 18–23 years | 198 |
| 24–28 years | 66 | |
| 29+ years | 20 | |
| Education Level | Bachelor’s | 201 |
| Master’s | 83 | |
| Family Income (Monthly) | Below 50,000 SAR | 63 |
| 50,000–100,000 SAR | 167 | |
| 100,001–150,000 SAR | 46 | |
| Above 150,000 SAR | 8 |
| Constructs | Item Code | Factor Loadings | Cronbach’s Alpha | Composite Reliability | Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Online Learning | AOL1 | 0.791 | 0.886 | 0.910 | 0.591 |
| AOL2 | 0.726 | ||||
| AOL3 | 0.742 | ||||
| AOL4 | 0.815 | ||||
| AOL5 | 0.815 | ||||
| AOL6 | 0.750 | ||||
| AOL7 | 0.738 | ||||
| Innovative Teaching | INT1 | 0.650 | 0.812 | 0.876 | 0.641 |
| INT2 | 0.872 | ||||
| INT3 | 0.776 | ||||
| INT4 | 0.883 | ||||
| Digital Mental Well-Being | MWB1 | 0.868 | 0.919 | 0.933 | 0.666 |
| MWB2 | 0.857 | ||||
| MWB3 | 0.868 | ||||
| MWB4 | 0.790 | ||||
| MWB5 | 0.790 | ||||
| MWB6 | 0.763 | ||||
| MWB7 | 0.767 | ||||
| Student’s Digital Intelligence | SDI1 | 0.687 | 0.873 | 0.899 | 0.527 |
| SDI2 | 0.713 | ||||
| SDI3 | 0.688 | ||||
| SDI4 | 0.773 | ||||
| SDI5 | 0.692 | ||||
| SDI6 | 0.766 | ||||
| SDI7 | 0.752 | ||||
| SDI8 | 0.729 | ||||
| Sustainable Learning | SLR1 | 0.864 | 0.950 | 0.960 | 0.799 |
| SLR2 | 0.898 | ||||
| SLR3 | 0.897 | ||||
| SLR4 | 0.912 | ||||
| SLR5 | 0.887 | ||||
| SLR6 | 0.903 |
| HTMT Ratio | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Adaptive Online Learning | |||||
| 2. Innovative Teaching | 0.162 | ||||
| 3. Digital Mental Well-Being | 0.356 | 0.326 | |||
| 4. Student’s Digital Intelligence | 0.594 | 0.426 | 0.619 | ||
| 5. Sustainable Learning | 0.473 | 0.383 | 0.696 | 0.714 | |
| Fornell-Larker Criterion | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1. Adaptive Online Learning | 0.769 | ||||
| 2. Innovative Teaching | 0.149 | 0.800 | |||
| 3. Digital Mental Well-Being | 0.374 | 0.290 | 0.816 | ||
| 4. Student’s Digital Intelligence | 0.536 | 0.380 | 0.596 | 0.726 | |
| 5. Sustainable Learning | 0.454 | 0.346 | 0.687 | 0.682 | 0.894 |
| Relationships | β | SD | t | p Values | Decision | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
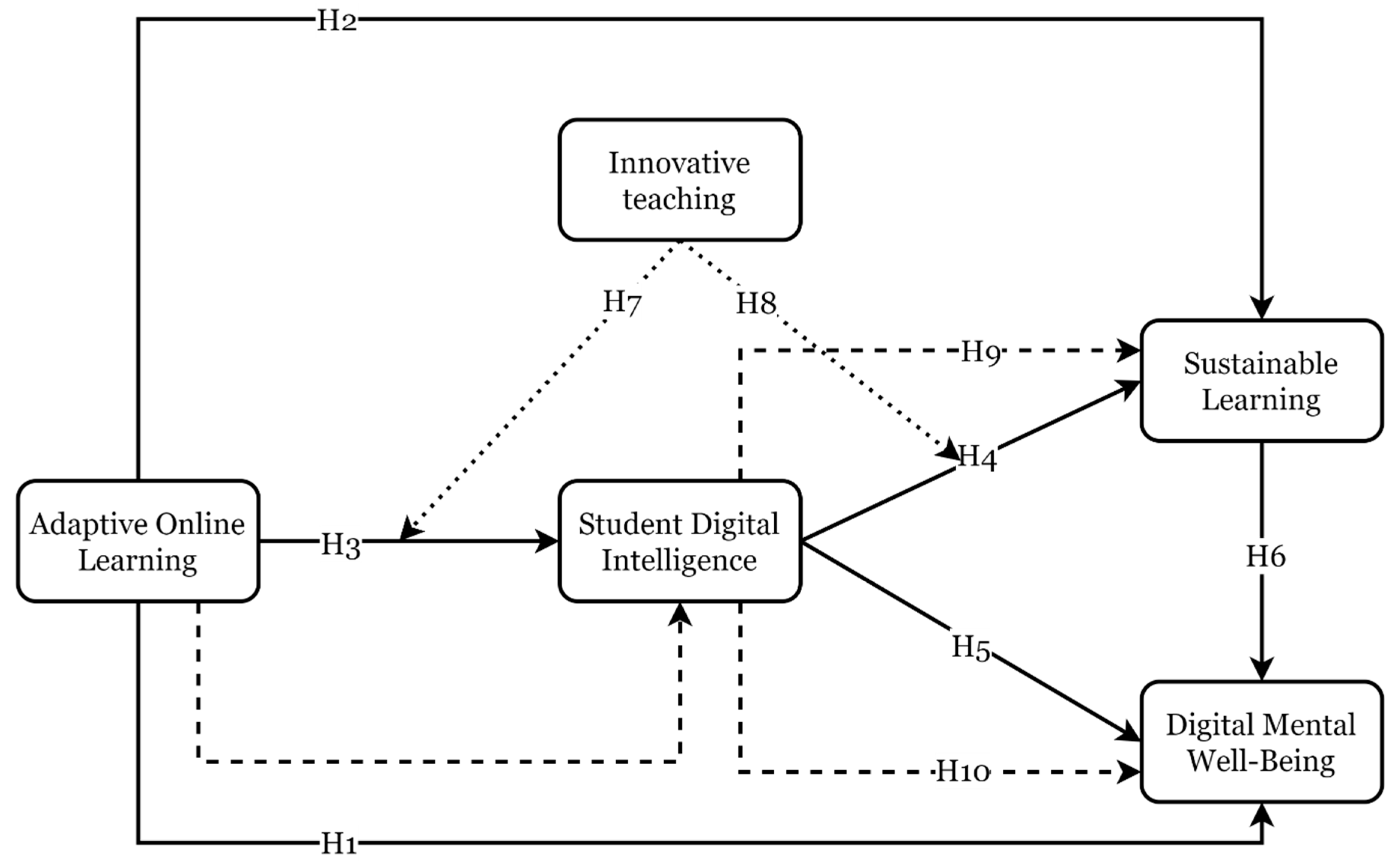
| H1 | Adaptive Online Learning → Digital Mental Well-Being | 0.010 | 0.051 | 0.205 | 0.837 | Not Supported |
| H2 | Adaptive Online Learning → Sustainable Learning | 0.106 | 0.057 | 1.876 | 0.061 | Not Supported |
| H3 | Adaptive Online Learning → Student’s Digital Intelligence | 0.488 | 0.069 | 7.040 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H4 | Student’s Digital Intelligence → Sustainable Learning | 0.595 | 0.057 | 10.379 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H5 | Student’s Digital Intelligence → Digital Mental Well-Being | 0.236 | 0.076 | 3.105 | 0.002 | Supported |
| H6 | Sustainable Learning → Digital Mental Well-Being | 0.521 | 0.067 | 7.738 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H7 | Innovative Teaching × Adaptive Online Learning → Student’s Digital Intelligence | 0.183 | 0.076 | 2.397 | 0.017 | Supported |
| H8 | Innovative Teaching × Student’s Digital Intelligence → Sustainable Learning | 0.084 | 0.042 | 2.020 | 0.043 | Supported |
| Relationships | β | SD | t | p Values | Decision | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H9 | Adaptive Online Learning → Student’s Digital Intelligence → Sustainable Learning | 0.290 | 0.049 | 5.958 | 0.000 | Full Mediation |
| H10 | Adaptive Online Learning → Student’s Digital Intelligence → Digital Mental Well-Being | 0.115 | 0.042 | 2.720 | 0.007 | Full Mediation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alruwaili, N.M.; Ali, Z.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Butt, A.H.; Ahmad, H.; Ali, R.; Alsalem, S.H. Exploring the Impact of Female Student’s Digital Intelligence on Sustainable Learning and Digital Mental Well-Being: A Case Study of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6632. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146632
Alruwaili NM, Ali Z, Siddiqui MS, Butt AH, Ahmad H, Ali R, Alsalem SH. Exploring the Impact of Female Student’s Digital Intelligence on Sustainable Learning and Digital Mental Well-Being: A Case Study of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6632. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146632
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlruwaili, Norah Muflih, Zaiba Ali, Mohd Shuaib Siddiqui, Asad Hassan Butt, Hassan Ahmad, Rahila Ali, and Shaden Hamad Alsalem. 2025. "Exploring the Impact of Female Student’s Digital Intelligence on Sustainable Learning and Digital Mental Well-Being: A Case Study of Saudi Arabia" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6632. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146632
APA StyleAlruwaili, N. M., Ali, Z., Siddiqui, M. S., Butt, A. H., Ahmad, H., Ali, R., & Alsalem, S. H. (2025). Exploring the Impact of Female Student’s Digital Intelligence on Sustainable Learning and Digital Mental Well-Being: A Case Study of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 17(14), 6632. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146632







