Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Coupling Coordination Between Carbon Emission Efficiency and Carbon Balance in the Yellow River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on CEE
2.2. Research on CB
2.3. Research on the Coordinated Development of CEE and CB
2.4. Research Gaps and Contributions
3. Coupling Coordination Mechanism Between CEE and CB
3.1. The Influence of CEE on CB
3.2. The Influence of CB on CEE
4. Materials and Methods
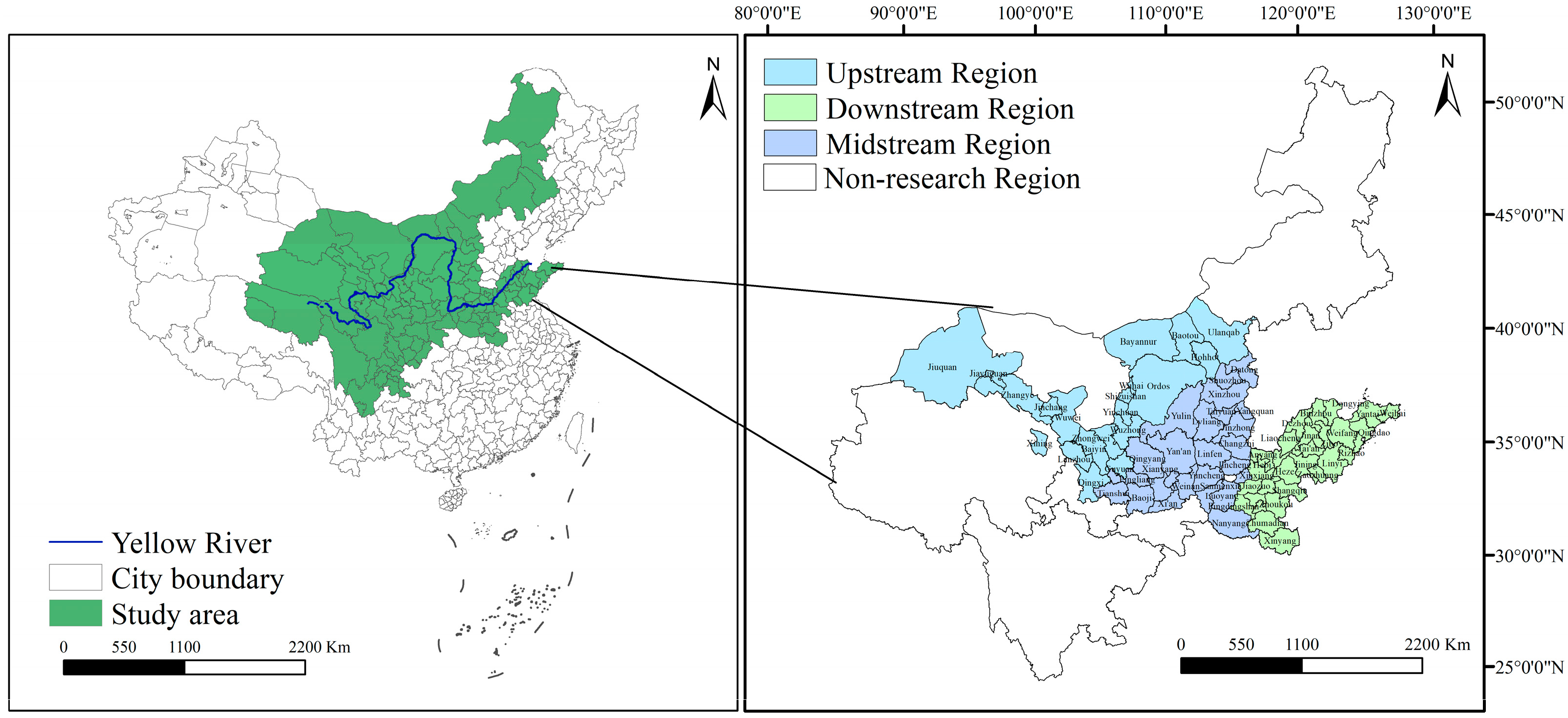
4.1. Study Area
4.2. System of Indicators
4.2.1. Indicators for CEE
4.2.2. Indicators for CB
4.3. Methods
4.3.1. The Super-SBM Model
4.3.2. Carbon Balance Estimation
4.3.3. The Coupling Coordination Model
4.3.4. The Kernel Density Estimation
4.3.5. The Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
4.3.6. Dagum Gini Coefficient and Its Decomposition
4.3.7. Markov Chain Analysis
4.3.8. The Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) Algorithm
4.3.9. The SHAP Value Explanation Algorithm
4.4. Data Sources and Processing
5. Results
5.1. Spatiotemporal Evolution of CEE and CB
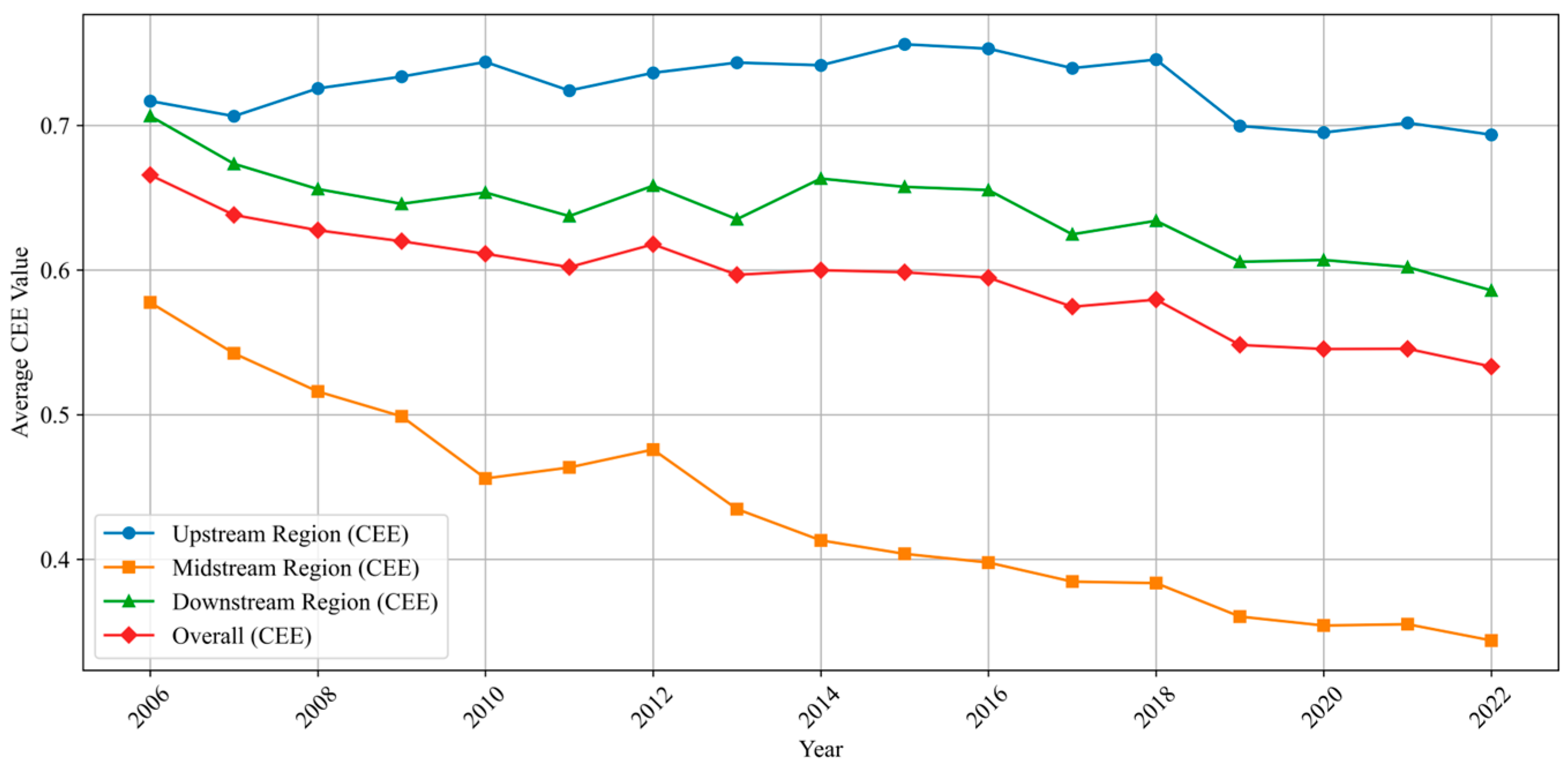
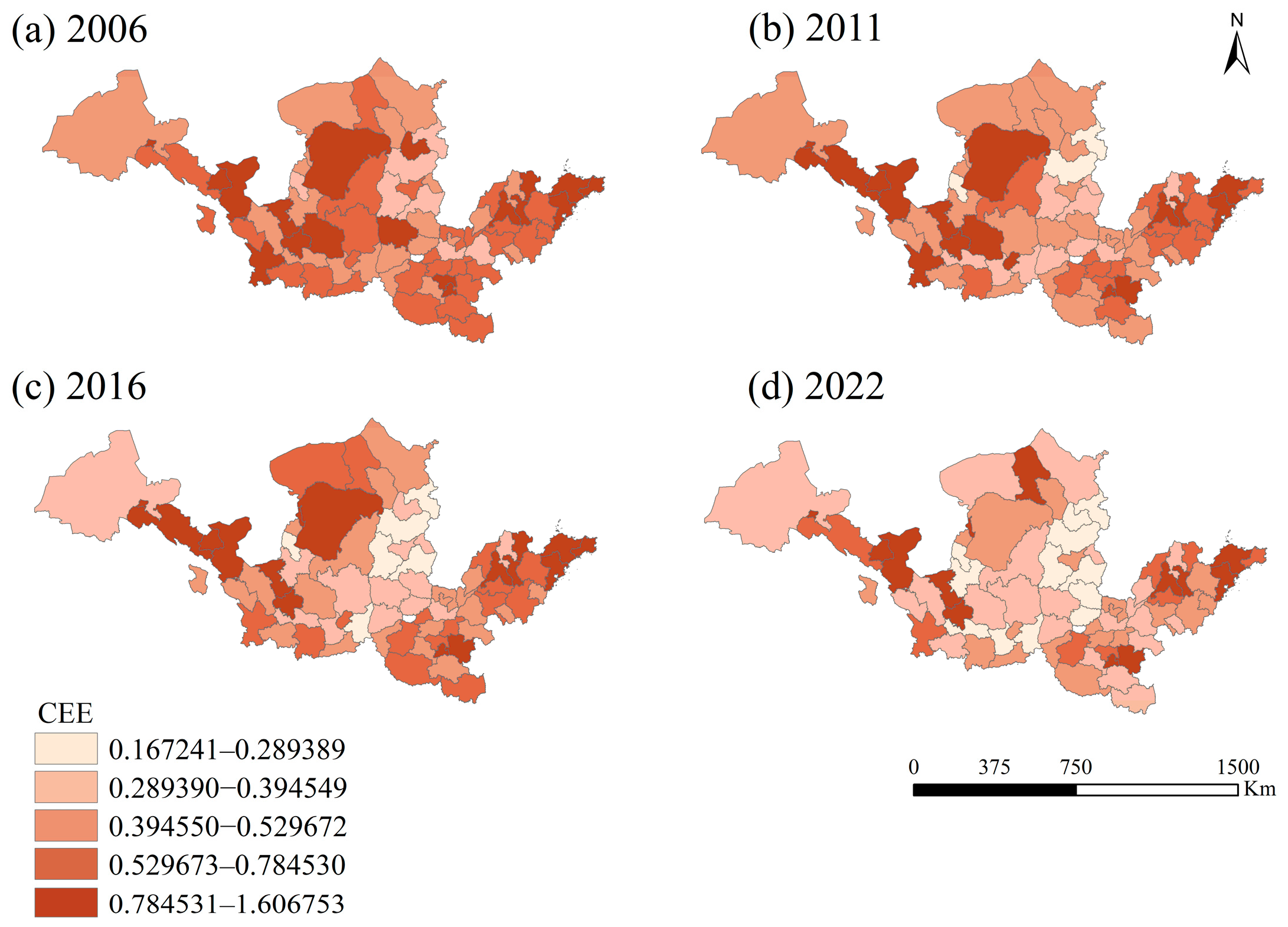
5.1.1. Spatiotemporal Evolution of CEE
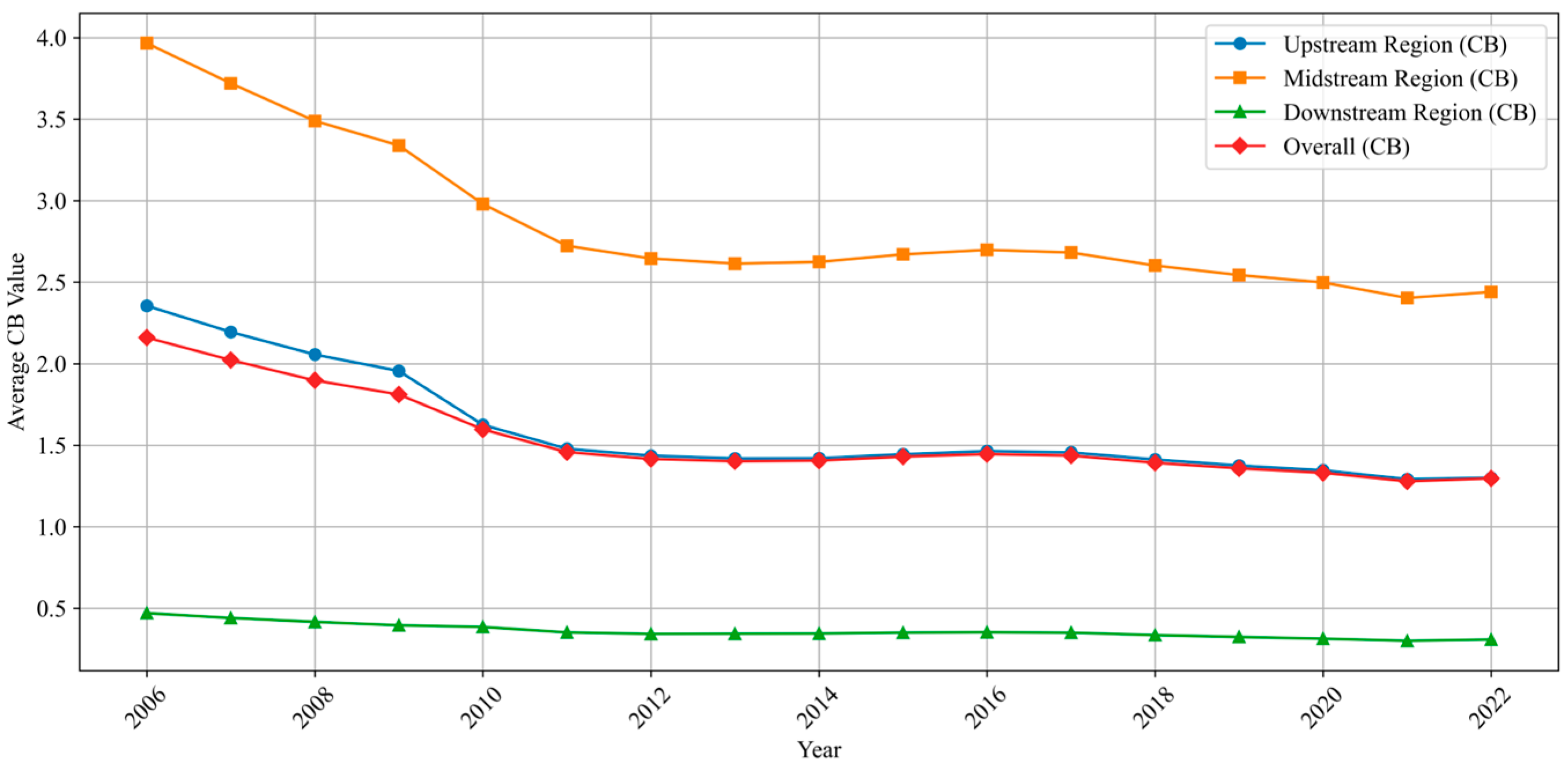
5.1.2. Spatiotemporal Evolution of CB
5.2. The Spatiotemporal Evolution of CCD
5.2.1. The Temporal Evolution of CCD
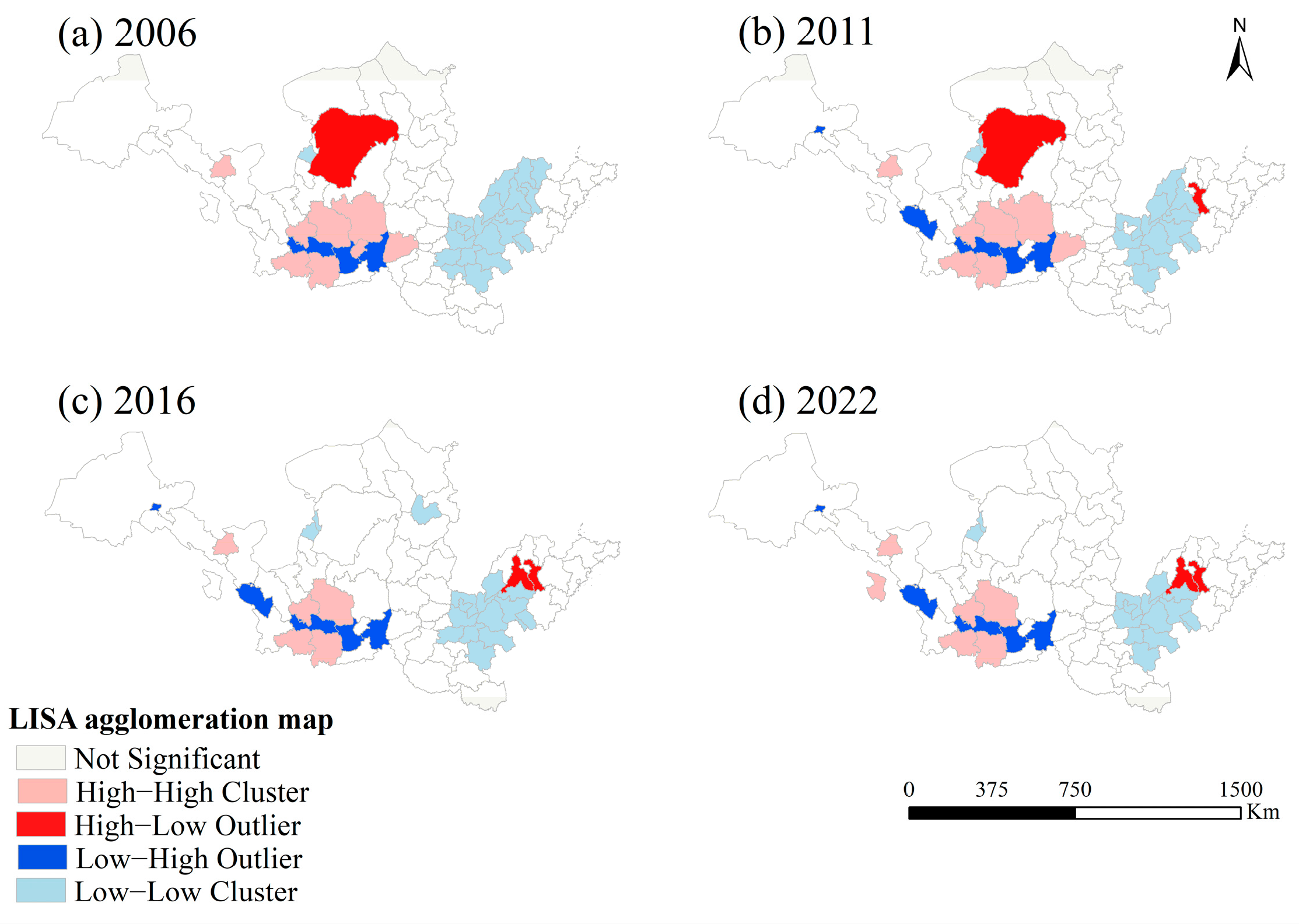
5.2.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the CCD
5.2.3. Spatial Autocorrelation of the CCD
5.2.4. Spatial Disparities of the CCD
5.2.5. Markov Chain Analysis of CCD
5.3. Driving Factors Analysis
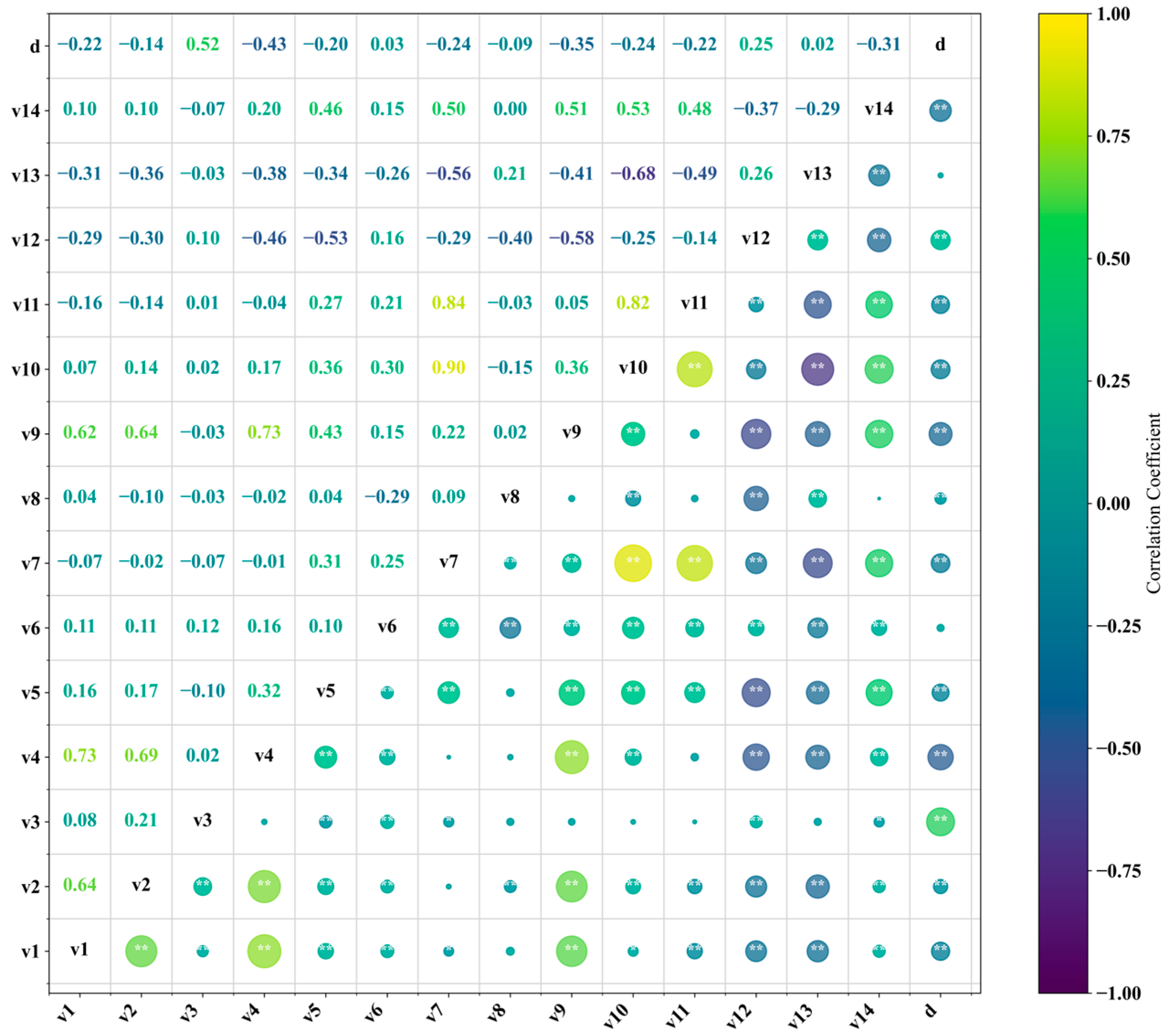
5.3.1. Selection and Correlation of Driving Factors with CCD
5.3.2. Model Selection and Validation
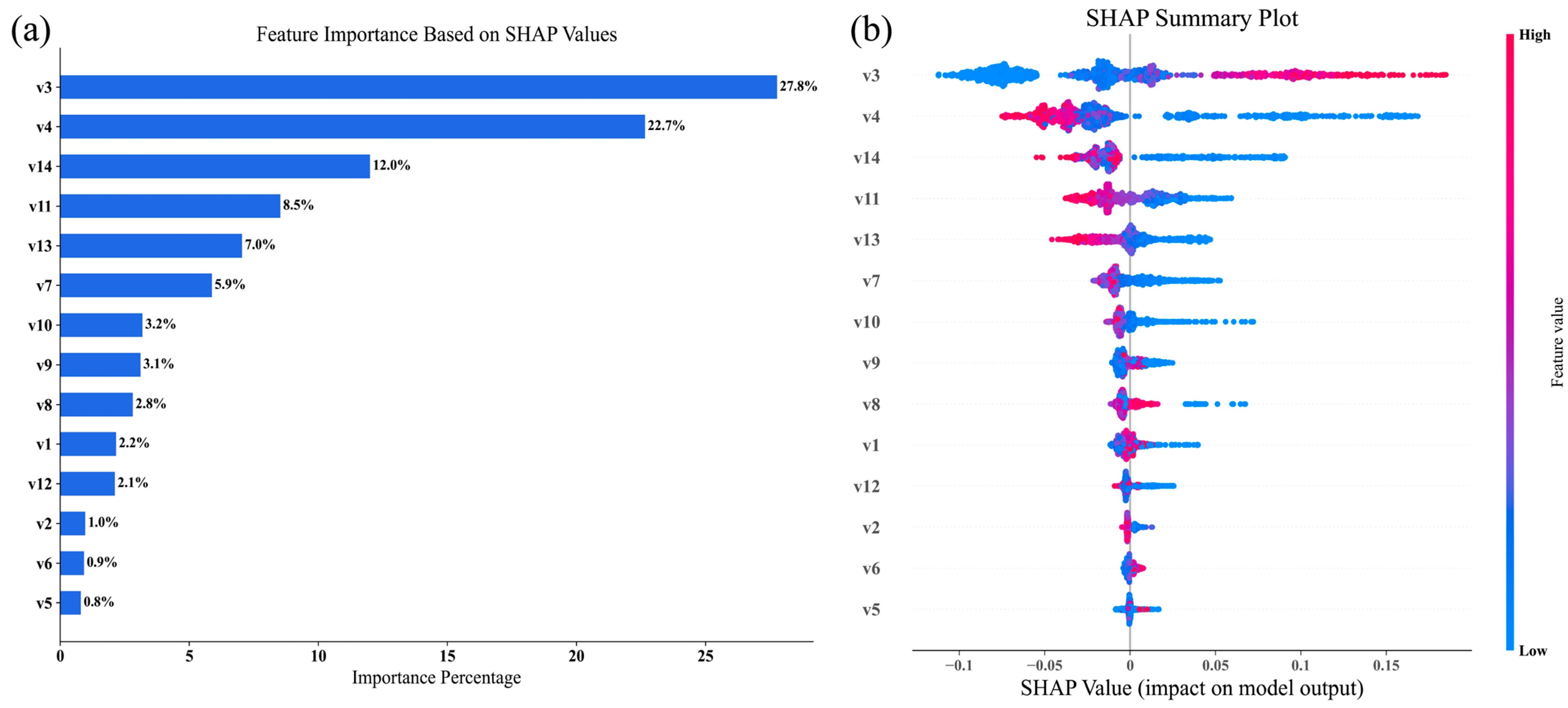
5.3.3. Identification of Key Factors
5.3.4. Single-Factor Importance Impact Analysis
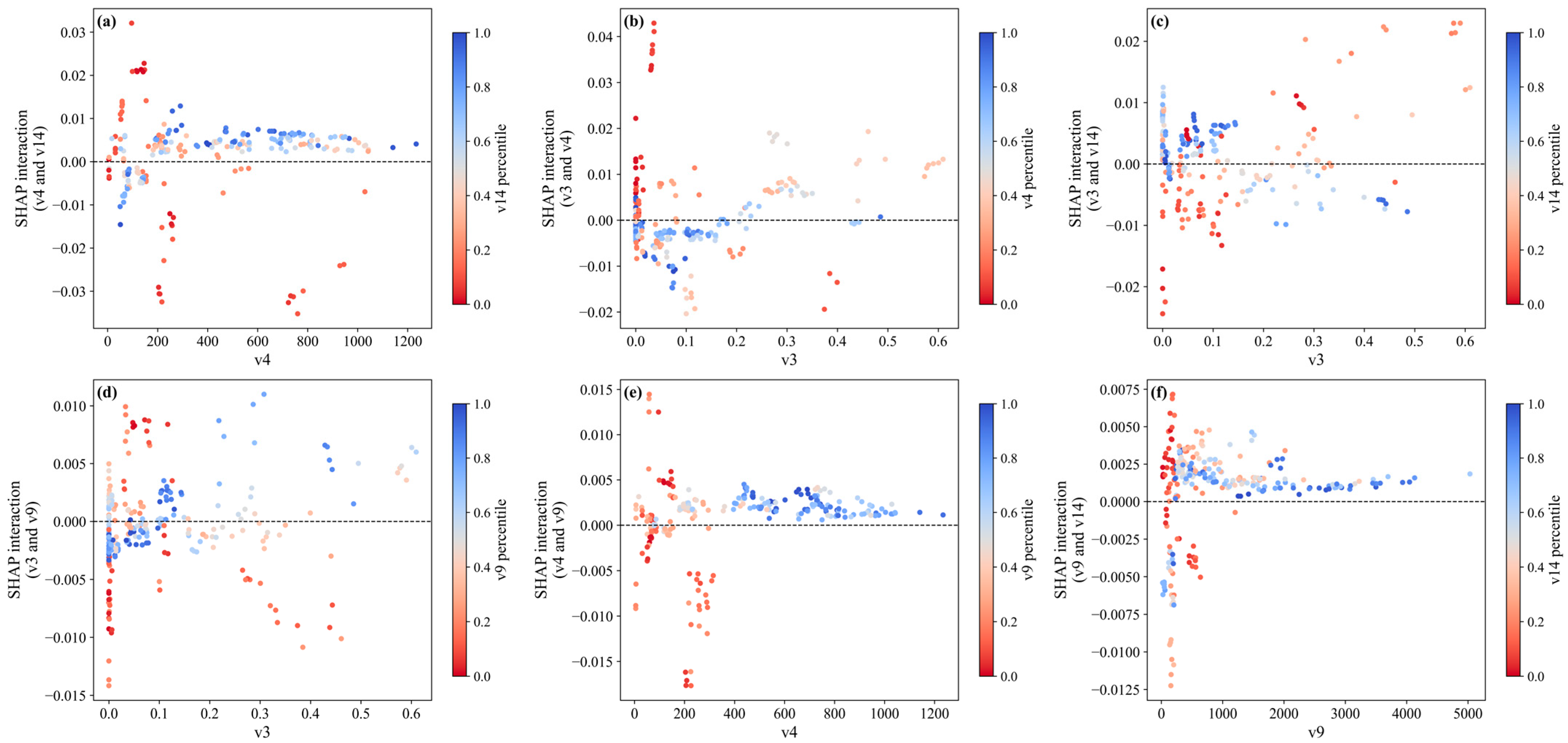
5.3.5. Interaction Analysis of Factors
6. Discussion
6.1. Comparison with Previous Research
6.2. Research Limitations and Future Directions
7. Conclusions and Recommendations
7.1. Research Conclusions
7.2. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, D.; Hu, C.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Deng, P.; Chang, R. A comprehensive analysis of the spatiotemporal dynamics and determinants of carbon emission efficiency in China’s manufacturing sector. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 381, 125269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Fang, S.; Yan, C.; Gong, W.; Wang, C. Research on the impact of digital economy on industrial carbon emission efficiency—An analysis based on spatial threshold model. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 515, 145755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, P. Spatial correlation investigation of carbon emission efficiency in the Yangtze River Delta of China: The role of low-carbon pilot cities. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lan, M. Digital economy and carbon rebound effect: Evidence from Chinese cities. Energy Econ. 2023, 126, 106957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xiong, R.; Ni, T. Spatial network characteristics of carbon balance in urban agglomerations—A case study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei city agglomeration. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 169, 103343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Xu, S.; Zou, A.X. Does green technological diversification impact industrial carbon emissions efficiency? The role of technological specialisation. J. Innov. Knowl. 2025, 10, 100730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yao, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Xue, A. The impact of innovation-driven industrial clusters on urban carbon emission efficiency: Empirical evidence from China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 121, 106220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Yu, G.; Cao, Y. The impact of industrial structural transformation in the Yangtze River economic belt on the trade-offs and synergies between urbanization and carbon balance. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Pan, J. How do trade-offs between ecological construction and urbanization affect regional carbon balance? A case study from China’s Yellow River Basin. Catena 2024, 247, 108534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Lu, N.; Yang, L. Interaction between carbon emission efficiency and ecological environment from static and dynamic perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Shao, S.; Fan, M.; Chen, S. Regional carbon imbalance within China: An application of the Kaya-Zenga index. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Tang, S.; Zou, J. Administrative division adjustment and carbon intensity: Evidence from County-to-District Reform in China. Cities 2025, 160, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, Q. Does new-type infrastructure improve total factor carbon productivity? Experimental evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 460, 142620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnevisan, B.; Rafiee, S.; Omid, M.; Mousazadeh, H. Applying data envelopment analysis approach to improve energy efficiency and reduce GHG (greenhouse gas) emission of wheat production. Energy 2013, 58, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Li, X.; Long, R.; Liu, X. Regional carbon emission performance in China according to a stochastic frontier model. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Geng, C.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of urban industrial carbon emission efficiency in the Mid-Yangtze River urban agglomeration of China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2024, 135, 103607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, P. Industrialization, urbanization, and carbon emission efficiency of Yangtze River Economic Belt-empirical analysis based on stochastic frontier model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 66914–66929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Liao, X.; Yang, S.; Yu, T. Towards sustainability: Evaluating energy efficiency with a super-efficiency SBM-DEA model across 168 economies. Appl. Energy 2024, 376, 124254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, P.; Yang, J.; Niu, B. Spatiotemporal analysis of carbon emission efficiency across economic development stages and synergistic emission reduction in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Guo, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lin, R.; Wu, H.; Huang, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J. Assessing urban carbon health in China’s three largest urban agglomerations: Carbon emissions, energy-carbon emission efficiency and carbon sinks. Appl. Energy 2025, 383, 125326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liao, Z.; Sun, H. Analysis of Carbon Emission Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin in China: Spatiotemporal Differences and Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Su, C. Spatial-temporal evolution and driving factors of carbon emission efficiency of cities in the Yellow River Basin. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Han, X.; Wang, Q. Do technical differences lead to a widening gap in China’s regional carbon emissions efficiency? Evidence from a combination of LMDI and PDA approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 182, 113361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Study on the efficiency evolution of carbon emissions and factors affecting them in 143 countries worldwide. Urban. Clim. 2025, 59, 102265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Han, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, S.; Zhang, X. The decoupling relationship between land use efficiency and carbon emissions in China: An analysis using the Socio-Ecological Systems (SES) framework. Land. Use Policy 2024, 138, 107055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wu, J.; Sun, J. Analysis of disequilibrium and driving factors of carbon emission efficiency: Evidence from five major urban agglomerations in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 478, 143908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Kim, D. Regional carbon emission efficiency analysis and factor decomposition: Cases from South Korea. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, G. Spatiotemporal differentiation of carbon budget and balance zoning: Insights from the middle reaches of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration, China. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 167, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L. Spatio-temporal evolution and prediction of carbon balance in the Yellow River Basin and zoning for low-carbon economic development. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Jia, J.; Chen, D.; Liu, S. Evolution of spatial network structure for land-use carbon emissions and carbon balance zoning in Jiangxi Province: A social network analysis perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chu, X.; Yang, X.; Jiang, P.; Zhu, J.A.; Cai, Z.; Yu, S. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Land Use Carbon Balance and Its Response to Urbanization: A Case of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Land. 2025, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhan, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, W.; Twumasi-Ankrah, M.J. Analysis of urban carbon balance based on land use dynamics in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 125138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Total-factor carbon emission efficiency of China’s provincial industrial sector and its dynamic evolution. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F. Carbon emissions efficiency and abatement cost under inter-region differentiated mitigation strategies: A modified DDF model. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 532, 121888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wei, Z.; Shahbaz, M.; Zeng, Y. Exploring the dynamics of low-carbon technology diffusion among enterprises: An evolutionary game model on a two-level heterogeneous social network. Energy Econ. 2021, 101, 105399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Feng, R.; Chen, Z. Blue sky defense in low-carbon pilot cities: A spatial spillover perspective of carbon emission efficiency. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, L.; Hao, Y. Dynamic evolution and driving forces of carbon emission efficiency in China: New evidence based on the RBM-ML model. Gondwana Res. 2023, 116, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, X.; Cai, Y. The impact of green finance on carbon emission efficiency. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, X. Did digitalization of manufacturing industry improved the carbon emission efficiency of exports: Evidence from China. Energy Strategy Rev. 2025, 57, 101614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, G.; Song, M.; Fu, S. Carbon emissions trading and corporate energy efficiency: Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Technol. Forecast. Social. Change 2025, 212, 123959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Sun, F.; Hu, Y. Carbon emission efficiency of land use in urban agglomerations of Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: Based on three-stage SBM-DEA model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, K.; Wu, J.; Duan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ren, J.; Yang, Z. Scenario simulation of carbon balance in carbon peak pilot cities under the background of the “dual carbon” goals. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 116, 105910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, L.; Peron, M. The role of carbon tax in the transition from a linear economy to a circular economy business model in manufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 492, 144873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ploeg, F. Why green subsidies are preferred to carbon taxes: Climate policy with heightened carbon tax salience. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2025, 130, 103129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.-T.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Wang, F.-Y.; Xu, M. Carbon capture, utilization, and storage in China’s high-emission industries: Optimal deployment under carbon neutrality goals. Energy 2025, 323, 135774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, F.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Zhang, N.; Song, Z. Multi-objective optimization of non-fossil energy structure in China towards the carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals. Energy 2024, 312, 133643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zang, L.; Schwarz, P.; Yang, H. Achieving China’s carbon neutrality goal by economic growth rate adjustment and low-carbon energy structure. Energy Policy 2023, 183, 113817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, S. A Dynamic Evolution and Spatiotemporal Convergence Analysis of the Coordinated Development Between New Quality Productive Forces and China’s Carbon Total Factor Productivity. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Chen, Y.; Lin, B. Uncovering the role of renewable energy innovation in China’s low carbon transition: Evidence from total-factor carbon productivity. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 101, 107128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Yu, X.; Sun, T.; Pan, T.; Zhong, S. The effects of internet infrastructure on carbon neutrality. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 99, 103964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, C.; Guo, H.; Li, P.; Sun, W. Examining intra-city carbon budget and carbon balance zoning based on firm-level big data: A case study of Nanjing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D. Convergence of energy carbon emission efficiency: Evidence from manufacturing sub-sectors in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 31133–31147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Kasimu, A.; Wei, B.; Zhang, X.; Aizizi, Y.; Chen, J. Spatial and temporal patterns and risk assessment of carbon source and sink balance of land use in watersheds of arid zones in China—A case study of Bosten Lake basin. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zha, H.; Chang, R.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; An, B. Research on the spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of urbanization and carbon emission efficiency coupling coordination: From the perspective of global countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 360, 121153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, C.; Li, X.; Song, M. The spatial–temporal evolution and influencing factors of the coupling coordination of new-type urbanization and ecosystem services value in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Tian, X. Towards ecological sustainability: The progress and spatio-temporal evolution of green development in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 492, 144912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, W. Analysis of the spatial–temporal evolution and driving factors of carbon emission efficiency in the Yangtze River economic Belt. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yan, K.; Shi, Y.; Lv, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Decrypting resilience: The spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of ecological resilience in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Shi, X. Dynamic evaluation of China’s ecological civilization construction based on target correlation degree and coupling coordination degree. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 93, 106734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Feng, S.; Li, M.; Deng, L.; Fan, Y.; Qian, X. Identifying the combined impact of human activities and natural factors on China’s avian species richness using interpretable machine learning methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Wan, G.; Qin, X. Decoding China’s new-type industrialization: Insights from an XGBoost-SHAP analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 478, 143927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, H. Research on the spatiotemporal evolution and non-stationarity effect of urban carbon balance: Evidence from representative cities in China. Environ. Res. 2024, 252 Pt 1, 118802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Wang, Y.; Ye, T.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Chen, W. Carbon emission efficiency of 284 cities in China based on machine learning approach: Driving factors and regional heterogeneity. Energy Econ. 2024, 129, 107222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Hu, S.; Li, J. Using machine learning to model technological heterogeneity in carbon emission efficiency evaluation: The case of China’s cities. Energy Econ. 2022, 114, 106238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Qi, S.; Chen, J.; Guo, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y. Exploring the spatiotemporal variation of carbon storage on Hainan Island and its driving factors: Insights from InVEST, FLUS models, and machine learning. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, B.; Yao, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Hua, C. Comparative evaluation of multi-scale spatiotemporal variability and drivers of carbon storage: An empirical study from 369 cities, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Cheng, S.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y. What were the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of global land use carbon emission efficiency? A case study of the 136 countries. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wu, B.; Jiang, X. Study on the spatial network structure of energy carbon emission efficiency and its driving factors in Chinese cities. Appl. Energy 2024, 371, 123689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, D.; Zhou, X.; Mi, C.; Wen, H. Insights into geospatial heterogeneity of landslide susceptibility based on the SHAP-XGBoost model. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Niu, Z.; Xu, Y. Impact of Income Inequality on Carbon Emission Efficiency: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, P. Temporal–Spatial Characteristics of Carbon Emissions and Low-Carbon Efficiency in Sichuan Province, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hao, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhen, Z. Spatial-temporal evolution of carbon storage and its driving factors in the Shanxi section of the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Model. 2025, 502, 111039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Duan, Y.; Chen, D.; Wu, X. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Drivers of Carbon Storage from a Sustainable Development Perspective: A Case Study of the Region along the Middle and Lower Yellow River, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, W. Cultivated land use efficiency and its driving factors in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhen, J.; Chen, X. The Spatial Association Network Structure and Influencing Factors of Pollution Reduction and Carbon Emission Reduction Synergy Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, T.; Zhang, P.; Li, G.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, H.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Spatial correlation evolution and prediction scenario of land use carbon emissions in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; Gu, T.; Chen, W. Impact of Urban Expansion on Carbon Emissions in the Urban Agglomerations of Yellow River Basin, China. Land 2024, 13, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Li, L.; Lei, Y.; Wu, S. The performance and influencing factors of high-quality development of resource-based cities in the Yellow River basin under reducing pollution and carbon emissions constraints. Resour. Policy 2024, 88, 104488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, W.; Zhang, X. Spatio-temporal patterns of High-Quality urbanization development under water resource constraints and their key Drivers: A case study in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Meng, Q.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Shen, W. Spatial patterns and evolution trend of coupling coordination of pollution reduction and carbon reduction along the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, W. Analysis of spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and peak forecast of provincial carbon emissions under the dual carbon goal: Considering nine provinces in the Yellow River basin of China as an example. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
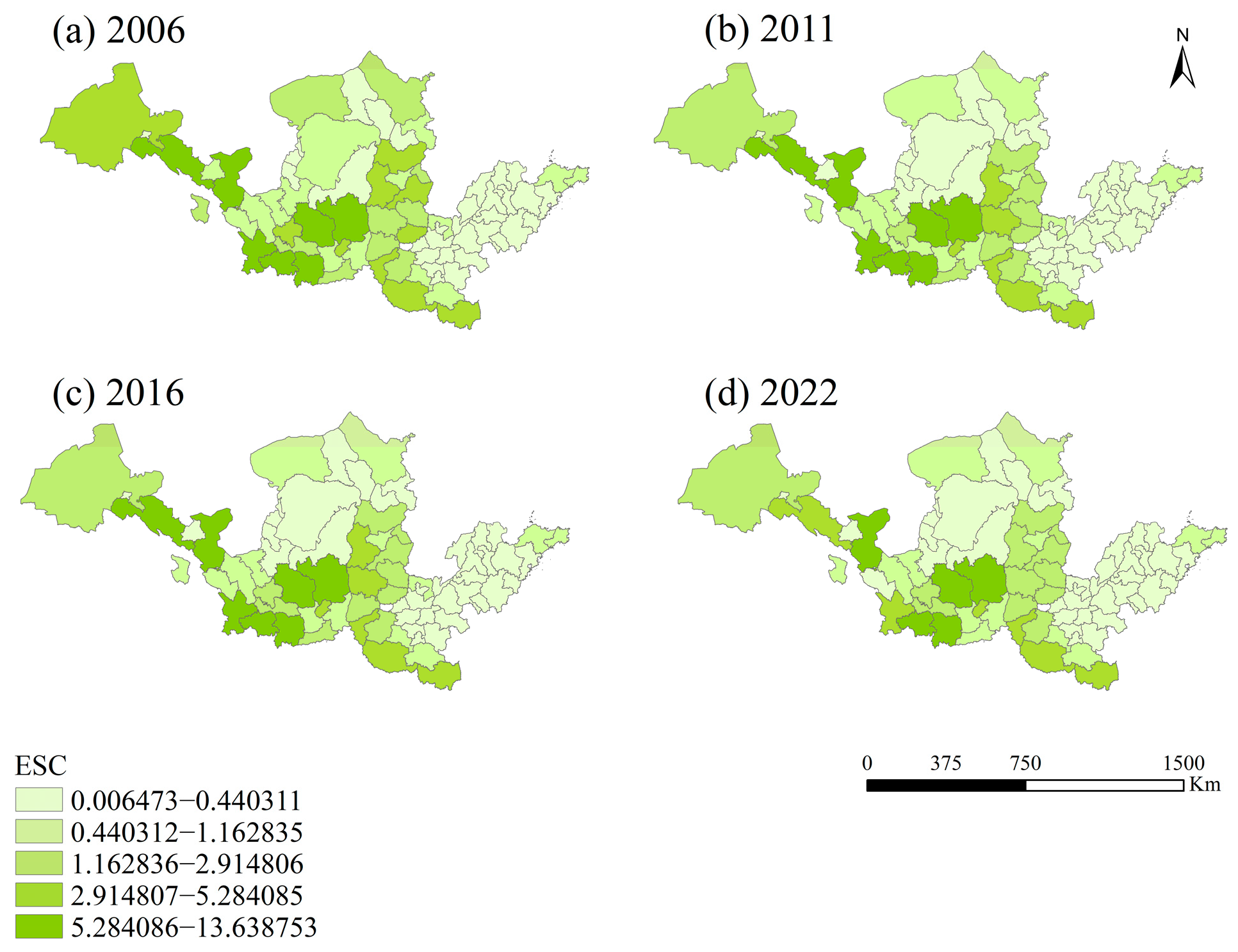
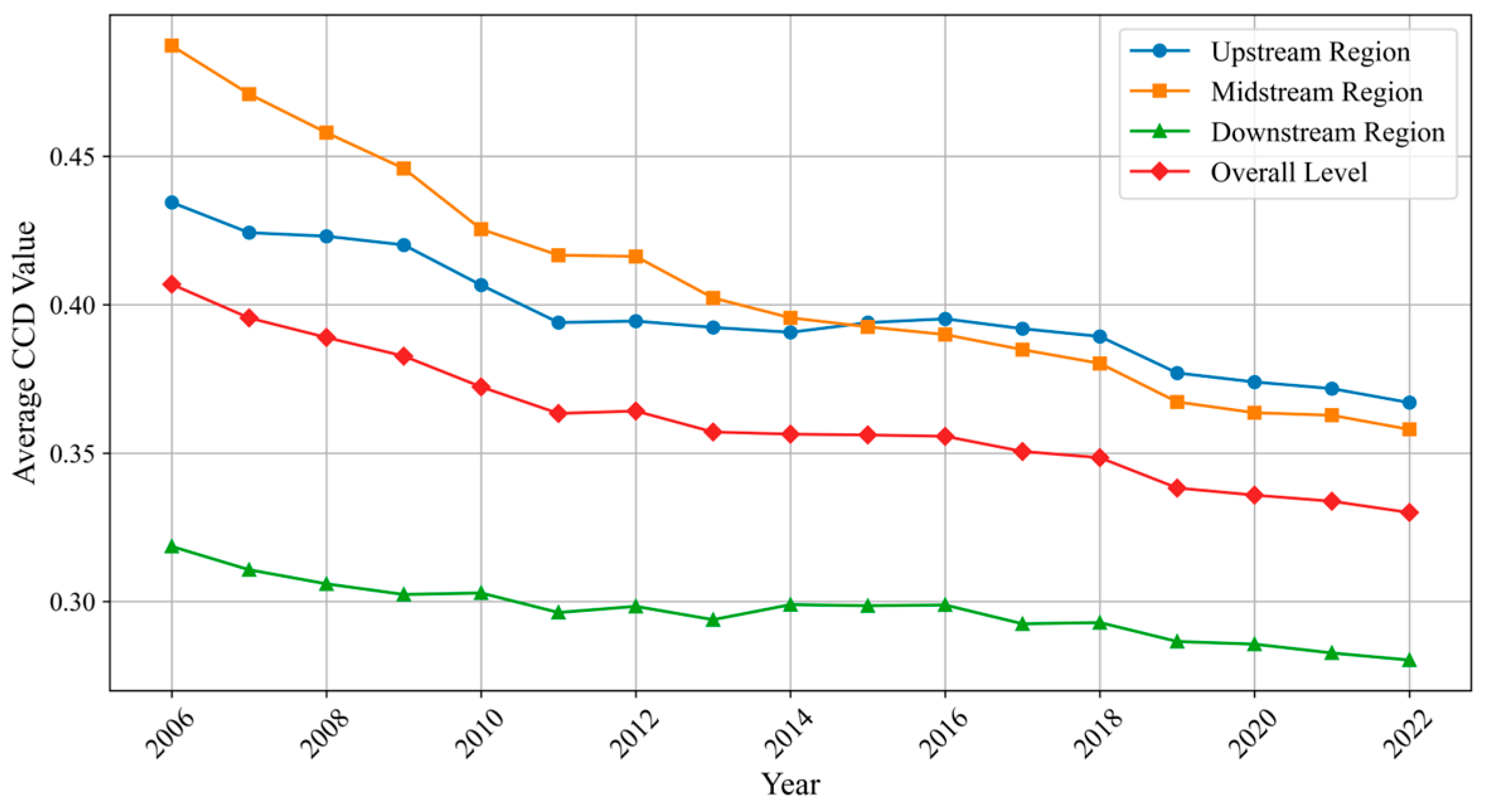
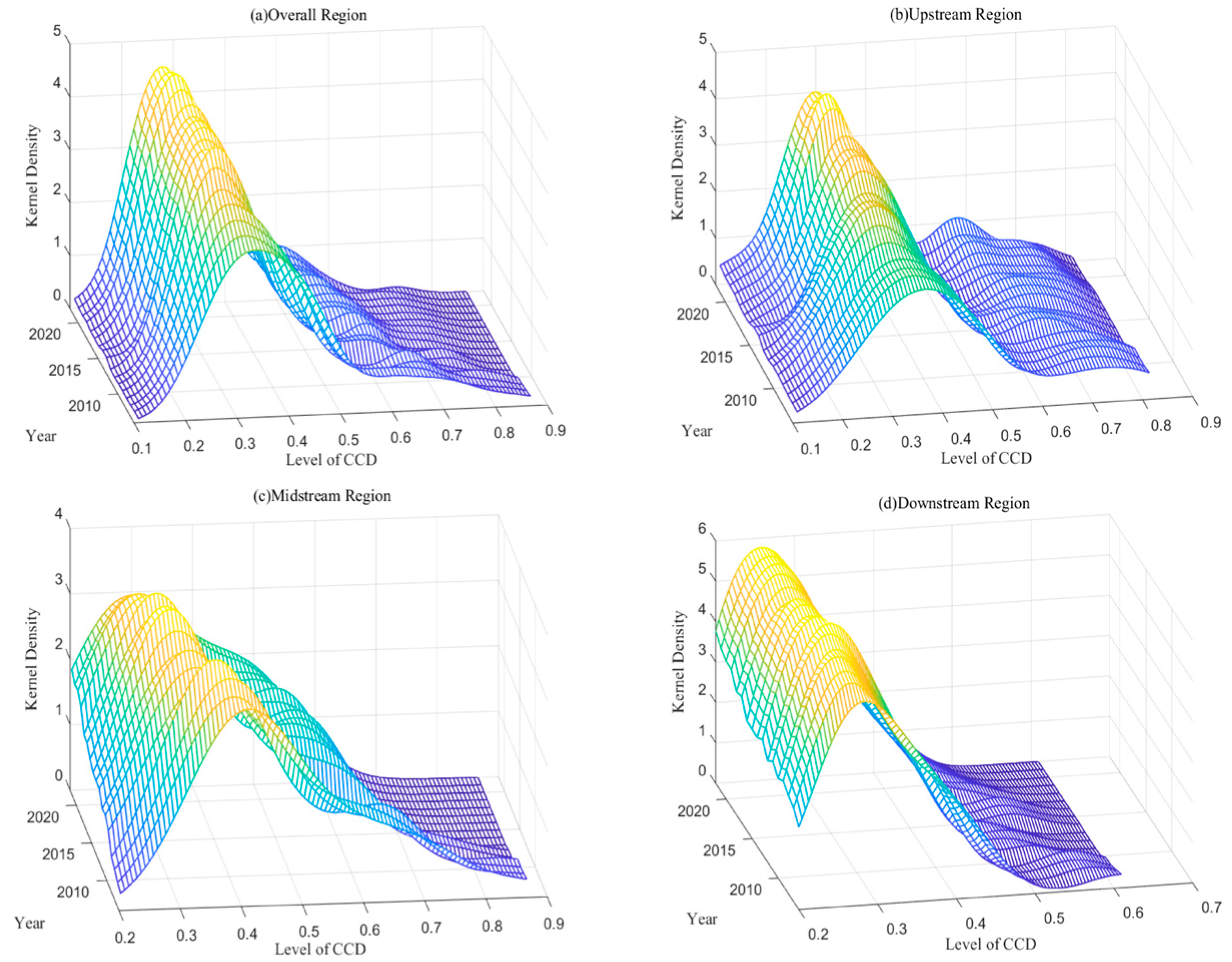
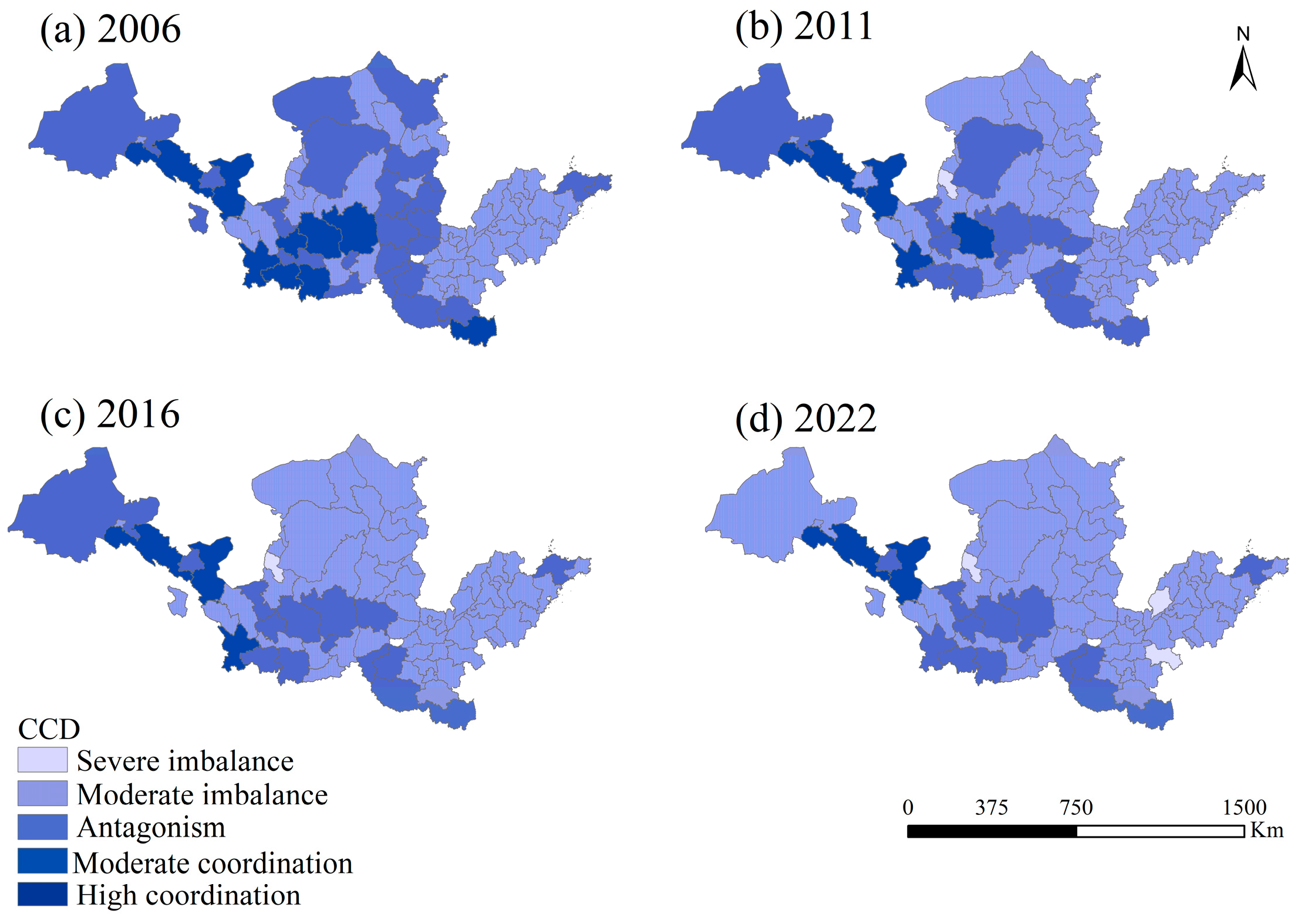


| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Input Indicators | Labor | Number of employees [7]. |
| Capital | Capital input is measured by the capital stock [7]. Capital stock is estimated using the Perpetual Inventory Method, employing the following equation, , where denotes the capital stock (in CNY 100 million); represents the capital depreciation rate, estimated at 9.6% based on existing research; and represents capital flow (in CNY 100 million). | |
| Energy | Referring to existing research, the correlation coefficient between provincial-level data is calculated and applied to city-level data. Nighttime light data at the city level is used to infer city-level energy consumption. ArcGIS is utilized to compute the total DN values for each prefecture-level city in mainland China, from which the simulated energy consumption for each city is estimated and spatialized, ultimately obtaining the total energy consumption data [19]. | |
| Desirable Output | GDP | GDP calculated at constant 2006 prices [19,49]. |
| Undesired Output | CEs | CE data sourced from the Center for Global Environmental Research (CGER) [50]. |
| Land Use Type | Carbon Sequestration Coefficient (t/hm2) |
|---|---|
| Forest Land | 0.644 |
| Grassland | 0.022 |
| Water Bodies | 0.253 |
| Unused Land | 0.005 |
| Year | Global Moran’s I | Z-Values | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 0.361 | 4.734 | 0.000 |
| 2007 | 0.353 | 4.627 | 0.000 |
| 2008 | 0.346 | 4.556 | 0.000 |
| 2009 | 0.331 | 4.366 | 0.000 |
| 2010 | 0.327 | 4.302 | 0.000 |
| 2011 | 0.324 | 4.274 | 0.000 |
| 2012 | 0.322 | 4.245 | 0.000 |
| 2013 | 0.331 | 4.349 | 0.000 |
| 2014 | 0.349 | 4.578 | 0.000 |
| 2015 | 0.347 | 4.557 | 0.000 |
| 2016 | 0.341 | 4.491 | 0.000 |
| 2017 | 0.336 | 4.426 | 0.000 |
| 2018 | 0.334 | 4.401 | 0.000 |
| 2019 | 0.359 | 4.729 | 0.000 |
| 2020 | 0.356 | 4.690 | 0.000 |
| 2021 | 0.352 | 4.645 | 0.000 |
| 2022 | 0.345 | 4.552 | 0.000 |
| Year | Gini Coefficient | Rate of Contribution (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | Gw | Gnb | Gt | Gw | Gnb | Gt | |
| 2006 | 0.197 | 0.054 | 0.097 | 0.046 | 27.478 | 49.193 | 23.330 |
| 2007 | 0.197 | 0.055 | 0.095 | 0.048 | 27.687 | 48.072 | 24.241 |
| 2008 | 0.195 | 0.054 | 0.092 | 0.049 | 27.687 | 47.178 | 25.136 |
| 2009 | 0.197 | 0.055 | 0.088 | 0.053 | 28.119 | 44.841 | 27.039 |
| 2010 | 0.186 | 0.053 | 0.078 | 0.056 | 28.382 | 41.680 | 29.938 |
| 2011 | 0.185 | 0.053 | 0.078 | 0.054 | 28.602 | 42.097 | 29.301 |
| 2012 | 0.184 | 0.053 | 0.076 | 0.054 | 28.848 | 41.505 | 29.647 |
| 2013 | 0.180 | 0.052 | 0.072 | 0.056 | 28.742 | 40.022 | 31.236 |
| 2014 | 0.181 | 0.053 | 0.064 | 0.064 | 29.195 | 35.617 | 35.188 |
| 2015 | 0.181 | 0.053 | 0.064 | 0.064 | 29.328 | 35.177 | 35.495 |
| 2016 | 0.180 | 0.053 | 0.064 | 0.063 | 29.520 | 35.557 | 34.923 |
| 2017 | 0.181 | 0.053 | 0.067 | 0.061 | 29.340 | 36.948 | 33.712 |
| 2018 | 0.178 | 0.053 | 0.065 | 0.061 | 29.477 | 36.402 | 34.121 |
| 2019 | 0.181 | 0.054 | 0.063 | 0.065 | 29.685 | 34.605 | 35.710 |
| 2020 | 0.181 | 0.054 | 0.061 | 0.065 | 29.861 | 33.972 | 36.167 |
| 2021 | 0.179 | 0.053 | 0.062 | 0.063 | 29.644 | 34.985 | 35.370 |
| 2022 | 0.181 | 0.054 | 0.062 | 0.065 | 29.796 | 34.056 | 36.147 |
| Average | 0.185 | 0.053 | 0.073 | 0.058 | 28.907 | 39.524 | 31.571 |
| Year | Differences Within the Region | Differences Between Regions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | Down | Mid | Up Down | Up Mid | Down Mid | |
| 2006 | 0.209 | 0.136 | 0.158 | 0.217 | 0.192 | 0.231 |
| 2007 | 0.211 | 0.134 | 0.161 | 0.218 | 0.194 | 0.228 |
| 2008 | 0.210 | 0.129 | 0.160 | 0.219 | 0.192 | 0.222 |
| 2009 | 0.213 | 0.129 | 0.171 | 0.221 | 0.196 | 0.220 |
| 2010 | 0.215 | 0.124 | 0.156 | 0.211 | 0.192 | 0.200 |
| 2011 | 0.210 | 0.119 | 0.165 | 0.204 | 0.192 | 0.201 |
| 2012 | 0.206 | 0.116 | 0.169 | 0.200 | 0.192 | 0.198 |
| 2013 | 0.203 | 0.118 | 0.159 | 0.201 | 0.186 | 0.192 |
| 2014 | 0.215 | 0.123 | 0.156 | 0.206 | 0.191 | 0.183 |
| 2015 | 0.211 | 0.124 | 0.160 | 0.207 | 0.190 | 0.183 |
| 2016 | 0.205 | 0.125 | 0.163 | 0.203 | 0.189 | 0.183 |
| 2017 | 0.207 | 0.126 | 0.159 | 0.206 | 0.188 | 0.183 |
| 2018 | 0.204 | 0.125 | 0.159 | 0.203 | 0.187 | 0.179 |
| 2019 | 0.211 | 0.126 | 0.162 | 0.204 | 0.193 | 0.179 |
| 2020 | 0.213 | 0.123 | 0.166 | 0.202 | 0.195 | 0.178 |
| 2021 | 0.21 | 0.122 | 0.161 | 0.202 | 0.192 | 0.177 |
| 2022 | 0.211 | 0.124 | 0.166 | 0.203 | 0.194 | 0.179 |
| Average | 0.210 | 0.125 | 0.162 | 0.207 | 0.191 | 0.195 |
| t/(t + 1) | I | II | III | IV | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.9828 | 0.0172 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 290 |
| II | 0.0614 | 0.9249 | 0.0137 | 0.0000 | 293 |
| III | 0.0000 | 0.0795 | 0.9139 | 0.0066 | 302 |
| IV | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0602 | 0.9398 | 299 |
| Domain Type | t/t + 1 | I | II | III | IV | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | I | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 118 |
| II | 0.0417 | 0.9583 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 24 | |
| III | 0.0000 | 0.1111 | 0.8889 | 0.0000 | 18 | |
| IV | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0 | |
| II | I | 0.9692 | 0.0308 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 130 |
| II | 0.0855 | 0.8889 | 0.0256 | 0.0000 | 117 | |
| III | 0.0000 | 0.0575 | 0.9425 | 0.0000 | 87 | |
| IV | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.1667 | 0.8333 | 6 | |
| III | I | 0.9730 | 0.0270 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 37 |
| II | 0.0513 | 0.9359 | 0.0128 | 0.0000 | 78 | |
| III | 0.0000 | 0.0853 | 0.9147 | 0.0000 | 129 | |
| IV | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0734 | 0.9266 | 109 | |
| IV | I | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 5 |
| II | 0.0405 | 0.9595 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 74 | |
| III | 0.0000 | 0.0882 | 0.8824 | 0.0294 | 68 | |
| IV | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0489 | 0.9511 | 184 |
| Indicator | Measurement Indicator | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Annual average temperature [67] | °C (degrees Celsius) |
| Precipitation | Annual average precipitation [67] | mm (millimeters) |
| Forest scale | Forest coverage rate [66] | % |
| Population density | Year-end registered population/administrative area land area [68] | persons/km2 |
| Degree of openness | Total import and export/regional GDP [24] | % |
| Tech development | Science and technology expenditure/government fiscal expenditure [24] | % |
| Economic development | Per capita GDP at constant prices [59] | CNY |
| Scale of secondary industry | Secondary industry output/GDP [69] | % |
| Industrial enterprise scale | Number of industrial enterprises above a designated size [16] | count |
| Resident consumption | Per capita retail sales of consumer goods [69] | CNY/person |
| Urbanization | Urban resident population/total resident population [59] | % |
| Government intervention | Local government science and technology expenditure/GDP [70] | % |
| Energy intensity | Energy consumption per unit of GDP [16] | 10,000 tons standard coal/CNY 100 million |
| Energy structure | Total electricity consumption [24] | 100 million kWh |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Li, S. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Coupling Coordination Between Carbon Emission Efficiency and Carbon Balance in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5975. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135975
Wang S, Li S. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Coupling Coordination Between Carbon Emission Efficiency and Carbon Balance in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):5975. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135975
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Silu, and Shunyi Li. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Coupling Coordination Between Carbon Emission Efficiency and Carbon Balance in the Yellow River Basin" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 5975. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135975
APA StyleWang, S., & Li, S. (2025). Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Coupling Coordination Between Carbon Emission Efficiency and Carbon Balance in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability, 17(13), 5975. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135975






