Expanding Horizons: A Review of Sustainability Evaluation Methodologies in the Airport Sector and Beyond
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Sustainability and Sustainability Evaluation
1.2. Airport Sustainability Evaluation
- What are the targets and focuses of current airport sustainability evaluation studies?
- Through which methodological approaches is airport sustainability assessed?
- Which limitations are inherent in the current methodologies, and how might they be effectively mitigated or addressed?
2. Methods, Materials and Content
- Airport sustainability performance evaluation studies: These studies focus on quantifying an airport’s overall sustainability using performance indicators, with an emphasis on the operational phase. This category constitutes more than half of the analyzed airport sustainability evaluation studies, reflecting the diversity of methods employed. A more detailed discussion of this type of study will be provided in Section 3.
- Airport sustainability strategy/measure/project evaluation studies: This category involves quantifying the sustainability impact (either positive or negative) of a specific strategy, measure or project on the airport. Of the six papers, two are review papers [15,16], and two concentrate exclusively on sustainability accounting [17,18]. The remaining two papers integrate both sustainability accounting and assessment. For instance, Dimitriou and Karagkouni [11] applied comprehensive performance benchmarking to assess the sustainability of environmental mitigation strategies at 20 airports in the United States, Asia, and Europe. Similarly, Li and Loo [19] utilized Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) to evaluate the sustainability of two airport infrastructure projects at Hong Kong International Airport.
- Airport terminal sustainability evaluation studies: These articles systematically analyze and evaluate airport terminals’ design, construction, operation, and maintenance, aiming to ensure sustainable performance throughout their life cycle [20,21,22,23,24,25]. Green building rating tools (GBRT) have been identified as the primary method for conducting such research. The most recent articles also revealed hybrid solutions combining GBRT with methods such as the Classification and Regression Tree (CART) model [24] and Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) [21].
- Mono-thematic airport sustainability evaluation studies: These studies are focused on assessing the sustainability of specific subsystems or themes within the entire airport operation. Rather than looking at a specific structure or facility, these studies delve into particular operational areas such as the water management system [26,27], waste management system [28], energy management system [29], and pavement system [30]. Given the distinctive characteristics of each theme, the evaluation methods used in those studies exhibit remarkable diversity and adaptability in addressing the particular challenges associated with each theme.
3. Sustainability Performance Evaluation within the Airport Sector
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
| No. | Citation | Type of Sustainability Study | Theoritical Basis for Accounting | Accounted Dimensions * | No. of Indicators | Assessment Methods | Case Study | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accounting | Accounting and Assessment | Review Paper | Ec | En | O | S | ||||||
| 1 | Dimitriou and Karagkouni [11] | X | 1. literature review | X | 16 | Linear scoring method | Top 5 regional tourist airports in Mediterranean islands | |||||
| 2 | Yangmin et al. [38] | X | 1. Literature review 2. Airport-Industry-City (AIC)’s synergy and sustainability development | X | X | X | X | 18 | Synergetic Measure Model (SMM) | Zhengzhou international airport | ||
| 3 | Kucukvar et al. [39] | X | 1. Literature review | X | X | X | X | 8 | Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) | 30 major international airports | ||
| 4 | Kumar et al. [40] | X | 1. Literature review 2. Delphi method, and panel discussion with experts | X | X | X | 43 | Best worst method (BWM) and VIKOR method | 5 Indian airports | |||
| 5 | Kaya and Erginel [41] | X | 1. Literature review 2. Brainstorming of experts | X | X | 15 | Stepwise Weight Assessment Ratio Analysis (SWARA) | Ankara Esenboga Airport | ||||
| 6 | Greer et al. [42] | X | Not applicable | |||||||||
| 7 | Wang and Song [43] | X | 1. Literature review | X | X | 7 | DEA | 8 Chinese airports and 4 Asian airports | ||||
| 8 | Wan et al. [44] | X | 1. Literature review | X | X | X | X | 55 | Synthetic evaluation method | Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport | ||
| 9 | Lu et al. [45] | X | 1. Literature review 2. Experts’ interviews, and brain storming | X | X | X | 15 | Hybrid Multiple-criteria decision making (MCDM) | 3 Taiwanese airports | |||
| 10 | Carlucci et al. [46] | X | 1. Literature review | X | X | 9 | DEA | 34 Italian airports | ||||
| 11 | Olfat et al. [47] | X | 1. Literature review | X | X | X | X | 9 | Fuzzy dynamic network DEA | 28 Iranian airports | ||
| 12 | Kılkış and Kılkış [37] | X | 1. Literature review 2. Consultation with experts | X | X | 25 | Sustainability ranking index | 9 world busiest and best airports | ||||
| 13 | Adler et al. [36] | X | 1. Literature review | X | X | 7 | DEA | 85 European regional airports | ||||
| 14 | Janic [35] | X | 1. Literature review 2. Effects-benefits and impacts-costs theory | X | X | X | X | 12 | n.a. | n.a. | ||
| 15 | Upham and Mills [34] | X | 1. Literature review | X | X | 10 | n.a. | n.a. | ||||
| 16 | Upham [33] | X | 1. Literature review | X | X | 9 | n.a. | n.a. | ||||
3.2. Assessment Methodologies
- (1)
- Fuzzy Dynamic Network DEA excels as a DEA tool for airport sustainability evaluation, yet enhancing its accuracy demands reduced subjectivity and integration of feedback loops and causal relationships in the sustainability system.
- (2)
- Hybrid-MCDM constitutes a useful complementary instrument for evaluating airport sustainability; however, it is inadequate to serve as the predominant methodology.
- (3)
- The SMM offers a more advanced perspective on airport sustainability evaluation compared to the composite indicator approach, but experts’ consultation and stakeholders’ engagement need to be incorporated to form a robust systems-oriented view.
4. Comparative Discussion beyond Airport Sector
- (1)
- The majority of sustainability evaluation papers devise their own approach and criteria, indicating the lack of universally adaptable, well-defined sustainability frameworks.
- (2)
- The preponderance of sustainability evaluation studies predominantly emphasizes the assessment aspect, often neglecting the foundational concept of sustainability accounting.
- (3)
- Certain scholars beyond the airport sector have argued that the traditional understanding of sustainability (which typically segments it into three or four separate dimensions) is losing ground.
- (4)
- The three types of sustainability evaluation methodologies identified by airports are also widely used in other industries; however, a widely accepted consensus among researchers asserts that “no single approach suffices for all contexts”, thus advocating for the use of a combination of methodologies in sustainability evaluation.
- (5)
- Alongside the recognized issue of comprehensiveness, the challenges of trade-offs and compensatory effects further compound the limitations in current sustainability evaluation methodologies.
- (6)
- A consensus has emerged among authors endorsing systems thinking as the future direction for sustainability evaluation.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Büyüközkan, G.; Karabulut, Y. Sustainability performance evaluation: Literature review and future directions. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WCED. Our Common Future, World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED); Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; p. 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Millennium Development Goals and Beyond 2015. Available online: http://www.un.org/millenniumgoals/ (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals: 17 Goals to Transform OUR world. 2023. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/ (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- Ghadimi, P.; Yusof, N.M.; Saman, M.Z.M.; Asadi, M. Methodologies for measuring sustainability of product/process: A review. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 21, 303–326. Available online: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/resources/files/Pertanika%20PAPERS/JST%20Vol.%2021%20(2)%20Jul.%202013/03%20Page%20303-326.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- Turkson, C.; Acquaye, A.; Liu, W.; Papadopoulos, T. Sustainability assessment of energy production: A critical review of methods, measures and issues. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, P.C.; Vassallo, J.M.; Cheung, K. Sustainability Assessment of Transport Infrastructure Projects: A Review of Existing Tools and Methods. Transp. Rev. 2015, 35, 622–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasparatos, A.; El-Haram, M.; Horner, M. A critical review of reductionist approaches for assessing the progress towards sustainability. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2008, 28, 286–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriven, M. Evaluation Thesaurus; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, M.; Surjokusumo, S.; Ma’soem, D.; Johan, J.; Hasyim, C.; Kurniasih, N.; Sukoco, A.; Dhaniarti, I.; Suyono, J.; Sudapet, I.; et al. Business Centre Development Model of Airport Area in Supporting Airport Sustainability in Indonesia. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2018, 954, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, D.; Karagkouni, A. Assortment of Airports’ Sustainability Strategy: A Comprehensiveness Analysis Framework. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decarolis, R. How Sustainability Can Drive Your Airport’s Competitive Advantage. ACI World Insights. 2019. Available online: https://blog.aci.aero/how-sustainability-can-drive-your-airports-competitive-advantage/ (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Desharnais, J. Recovering Sustainably: Why and How Airports Can Initiate, Maintain, or Enhance Their Sustainability Commitments. ACI World Insights. 2021. Available online: https://blog.aci.aero/recovering-sustainably-why-and-how-airports-can-initiate-maintain-or-enhance-their-sustainability-commitments/ (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Pranckutė, R. Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The Titans of Bibliographic Information in Today’s Academic World. Publications 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, A.; Salah, M.; Barakat, M.; Obrecht, M. Airport Sustainability Awareness: A Theoretical Framework. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tłoczyński, D.; Wach-Kloskowska, M.; Martin-Rojas, R. An assessment of airport sustainability measures: A case study of polish airports. Transp. Probl. 2020, 15, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsalud, A.; Ho, D.; Rakas, J. Greenhouse gas emissions mitigation strategies within the airport sustainability evaluation process. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 14, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkomy, A.S.; Sharbatdar, M.K. Identifying Effective Sustainable Development Indicators for Airport Construction Projects: Zahedan International Airport in Iran as Case Study. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2021, 45, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Loo, B.P.Y. Impact analysis of airport infrastructure within a sustainability framework: Case studies on Hong Kong International Airport. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2016, 10, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrulli, P. Green Airport Design Evaluation (GrADE)—Methods and Tools Improving Infrastructure Planning. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 3781–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greer, F.; Horvath, A.; Rakas, J. Life-Cycle Approach to Healthy Airport Terminal Buildings: Spatial-Temporal Analysis of Mitigation Strategies for Addressing the Pollutants that Affect Climate Change and Human Health. Transp. Res. Rec. 2023, 2677, 797–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.S.; Ramdan, A.S. Sustainability in the Design of Passenger Terminals for Airports. IOP Conf. Series Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 745, 012141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, J.; Liu, T.; Yu, R.; Seshadri, K.; Gou, Z. Towards greener airports: Development of an assessment framework by leveraging sustainability reports and rating tools. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 93, 106740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, F.; Seshadri, K.; Yu, R.; Gou, Z. A decision tree-based modeling approach for evaluating the green performance of airport buildings. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 100, 107070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa, S.L.B.; Ribeiro, J.M.P.; Mazon, G.; Schneider, J.; Barcelos, R.L.; Guerra, J.B.S.O.D.A. A Green Airport model: Proposition based on social and environmental management systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 59, 102160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G.; Srisaeng, P.; Wild, G. An Assessment of Airport Sustainability: Part 3—Water Management at Copenhagen Airport. Resources 2019, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancinelli, E.; Canestrari, F.; Graziani, A.; Rizza, U.; Passerini, G. Sustainable Performances of Small to Medium-Sized Airports in the Adriatic Region. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G.; Srisaeng, P.; Wild, G. An Assessment of Airport Sustainability, Part 1—Waste Management at Copenhagen Airport. Resources 2018, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baxter, G.; Srisaeng, P.; Wild, G. An Assessment of Airport Sustainability, Part 2—Energy Management at Copenhagen Airport. Resources 2018, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaki, B.M.; Babashamsi, P.; Shahrir, A.H.; Milad, A.; Abdullah, N.H.; Hassan, N.A.; Yusoff, N.I. The impact of economic analysis methods on project decision-making in airport pavement management. J. Teknol. 2021, 83, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walzberg, J.; Lonca, G.; Hanes, R.J.; Eberle, A.L.; Carpenter, A.; Heath, G.A. Do We Need a New Sustainability Assessment Method for the Circular Economy? A Critical Literature Review. Front. Sustain. 2021, 1, 620047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Murty, H.R.; Gupta, S.K.; Dikshit, A.K. An overview of sustainability assessment methodologies. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 15, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upham, P.J. Selecting Indicators for a Decision Support Tool for Airport Sustainability. 2001. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/227619388 (accessed on 23 May 2023).
- Upham, P.J.; Mills, J.N. Environmental and operational sustainability of airports: Core indicators and stakeholder communication. Benchmarking Int. J. 2005, 12, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janic, M. Developing an indicator system for monitoring, analyzing, and assessing airport sustainability. Eur. J. Transp. Infrastruct. Res. 2010, 10, 206–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, N.; Ülkü, T.; Yazhemsky, E. Small regional airport sustainability: Lessons from benchmarking. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2013, 33, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılkış, Ş.; Kılkış, Ş. Benchmarking airports based on a sustainability ranking index. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 130, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangmin, B.; Shaohong, F.; Yan, L. Assessing the synergy and sustainability of “Airport-Industry-City" (AIC) system in aerotropolis: Evidence from Zhengzhou Aerotropolis in China. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucukvar, M.; Alawi, K.A.; Abdella, G.M.; Bulak, M.E.; Onat, N.C.; Bulu, M.; Yalçıntaş, M. A frontier-based managerial approach for relative sustainability performance assessment of the world’s airports. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 29, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Aswin, A.; Gupta, H. Evaluating green performance of the airports using hybrid BWM and VIKOR methodology. Tour. Manag. 2020, 76, 103941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.K.; Erginel, N. Futuristic airport: A sustainable airport design by integrating hesitant fuzzy SWARA and hesitant fuzzy sustainable quality function deployment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, F.; Rakas, J.; Horvath, A. Airports and environmental sustainability: A comprehensive review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 103007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, W.-K. Sustainable airport development with performance evaluation forecasts: A case study of 12 Asian airports. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2020, 89, 101925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Peng, Q.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Xu, C. Evaluation of Airport Sustainability by the Synthetic Evaluation Method: A Case Study of Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport, China, from 2008 to 2017. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.-T.; Hsu, C.-C.; Liou, J.J.; Lo, H.-W. A hybrid MCDM and sustainability-balanced scorecard model to establish sustainable performance evaluation for international airports. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2018, 71, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, F.; Cirà, A.; Coccorese, P. Measuring and Explaining Airport Efficiency and Sustainability: Evidence from Italy. Sustainability 2018, 10, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olfat, L.; Pishdar, M. Interval type-2 fuzzy dynamic network data envelopment analysis with undesirable outputs considering double frontiers: An application to iran airports’ sustainability evaluation. Int. J. Ind. Eng. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, N.; Golany, B. PCA-DEA: Reducing the curse of dimensionality. In Modeling Data Irregularities and Structural Complexities in Data Envelopment Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, V.; Aparicio, J.; Zhu, J. The curse of dimensionality of decision-making units: A simple approach to increase the discriminatory power of data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 279, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravetz, J. Integrated assessment for sustainability appraisal in cities and regions. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2000, 20, 31–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison-Saunders, A.; Pope, J. Conceptualising and managing trade-offs in sustainability assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2013, 38, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banihabib, M.E.; Chitsaz, N.; Randhir, T.O. Non-compensatory decision model for incorporating the sustainable development criteria in flood risk management plans. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallopín, G. A Systems Approach to Sustainability and Sustainable Development; ECLAC, Sustainable Development and Human Settlements Division: Santiago, Chile, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fiksel, J. Sustainability and resilience: Toward a systems approach. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2006, 2, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

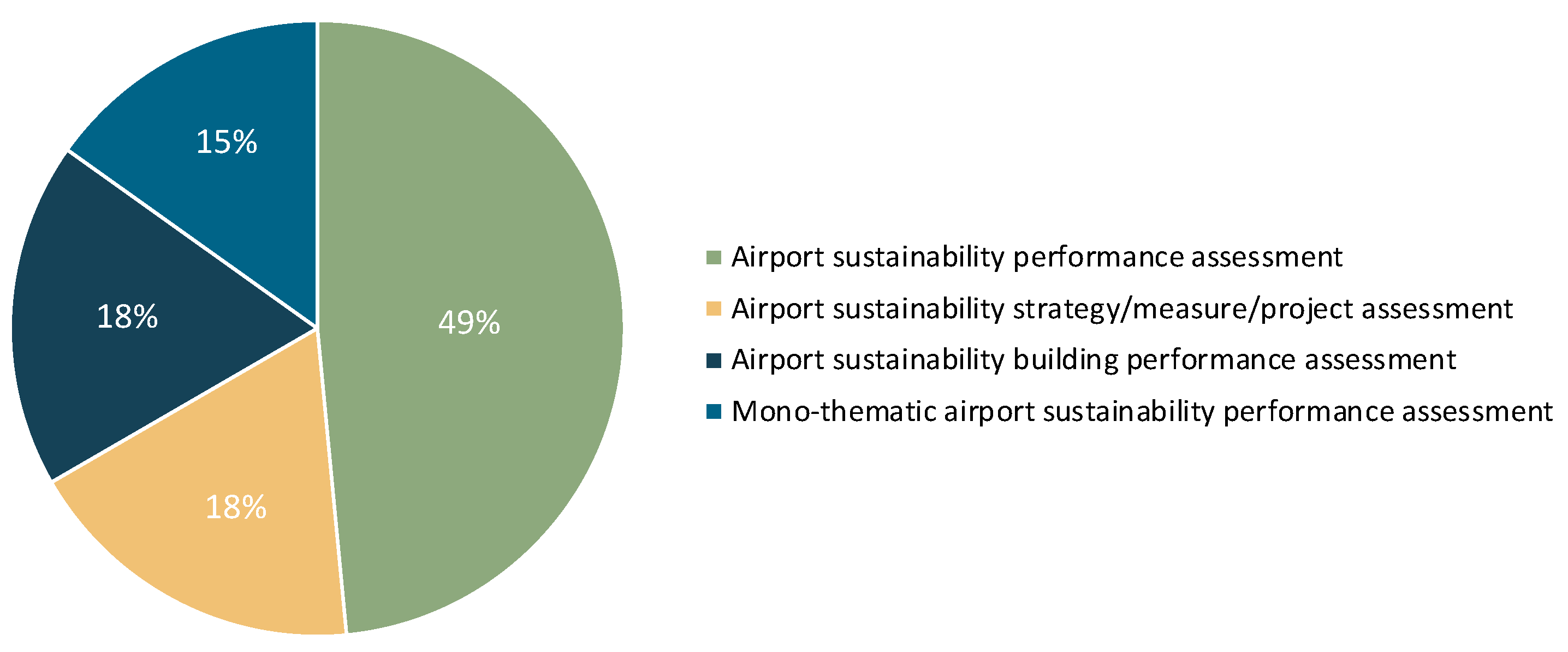

| No. | Citation | Review Period and Quantity | Scope of Review |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Walzberg et al. [31] | Not mentioned | Methods for sustainability performance evaluation in Circular Economy (CE) |
| 2 | Turkson et al. [6] | Not mentioned | Methods for sustainability performance evaluation in energy production system |
| 3 | Büyüközkan and Karabulut [1] | 2007–2018 128 | Methods for sustainability performance evaluation (covering all sectors) |
| 4 | Bueno et al. [7] | Not mentioned | Tools and methods for sustainability performance evaluation of transport infrastructure |
| 5 | Ghadimi et al. [5] | 1987–2012 111 | Tools and methods for sustainability performance evaluation of manufactured product and manufacturing process |
| 6 | Singh et al. [32] | 1998–2018 128 | Sustainable indices applied in policy practice (covering all sectors) |
| 7 | Gasparatos et al. [8] | 2000–2020 92 | Methods for sustainability performance evaluation (covering all sectors) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, X.; Macário, R.; Buyle, S. Expanding Horizons: A Review of Sustainability Evaluation Methodologies in the Airport Sector and Beyond. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11584. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511584
Jia X, Macário R, Buyle S. Expanding Horizons: A Review of Sustainability Evaluation Methodologies in the Airport Sector and Beyond. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11584. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511584
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Xibei, Rosário Macário, and Sven Buyle. 2023. "Expanding Horizons: A Review of Sustainability Evaluation Methodologies in the Airport Sector and Beyond" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11584. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511584
APA StyleJia, X., Macário, R., & Buyle, S. (2023). Expanding Horizons: A Review of Sustainability Evaluation Methodologies in the Airport Sector and Beyond. Sustainability, 15(15), 11584. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511584









