Diversity and Their Response to Environmental Factors of Prokaryotic Ultraplankton in Spring and Summer of Cihu Lake and Xiandao Lake in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Determination of Physico-Chemical Indicators
2.2. RNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
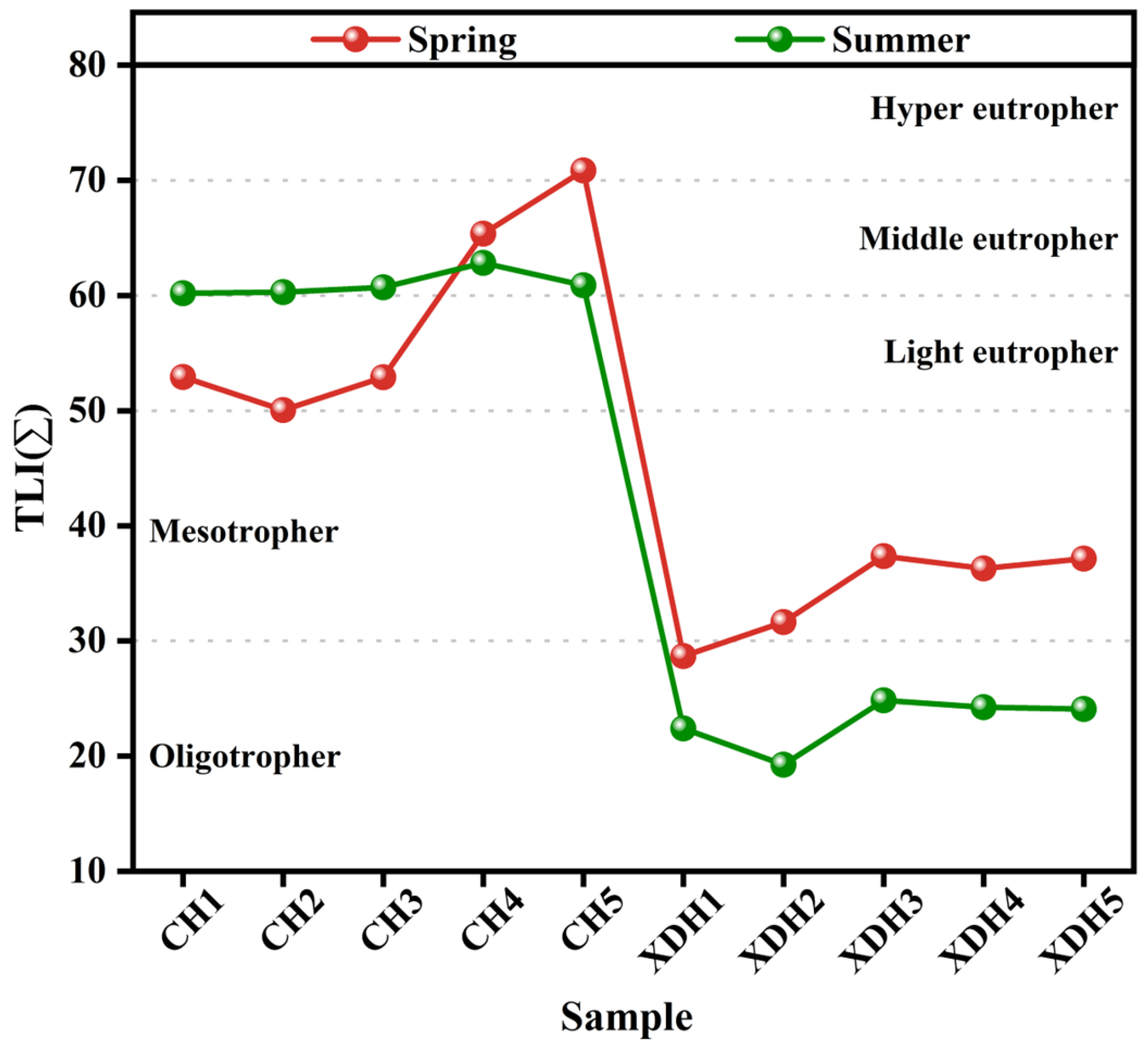
3.1. Spatial–Temporal Variation of Physico-Chemical Indicators
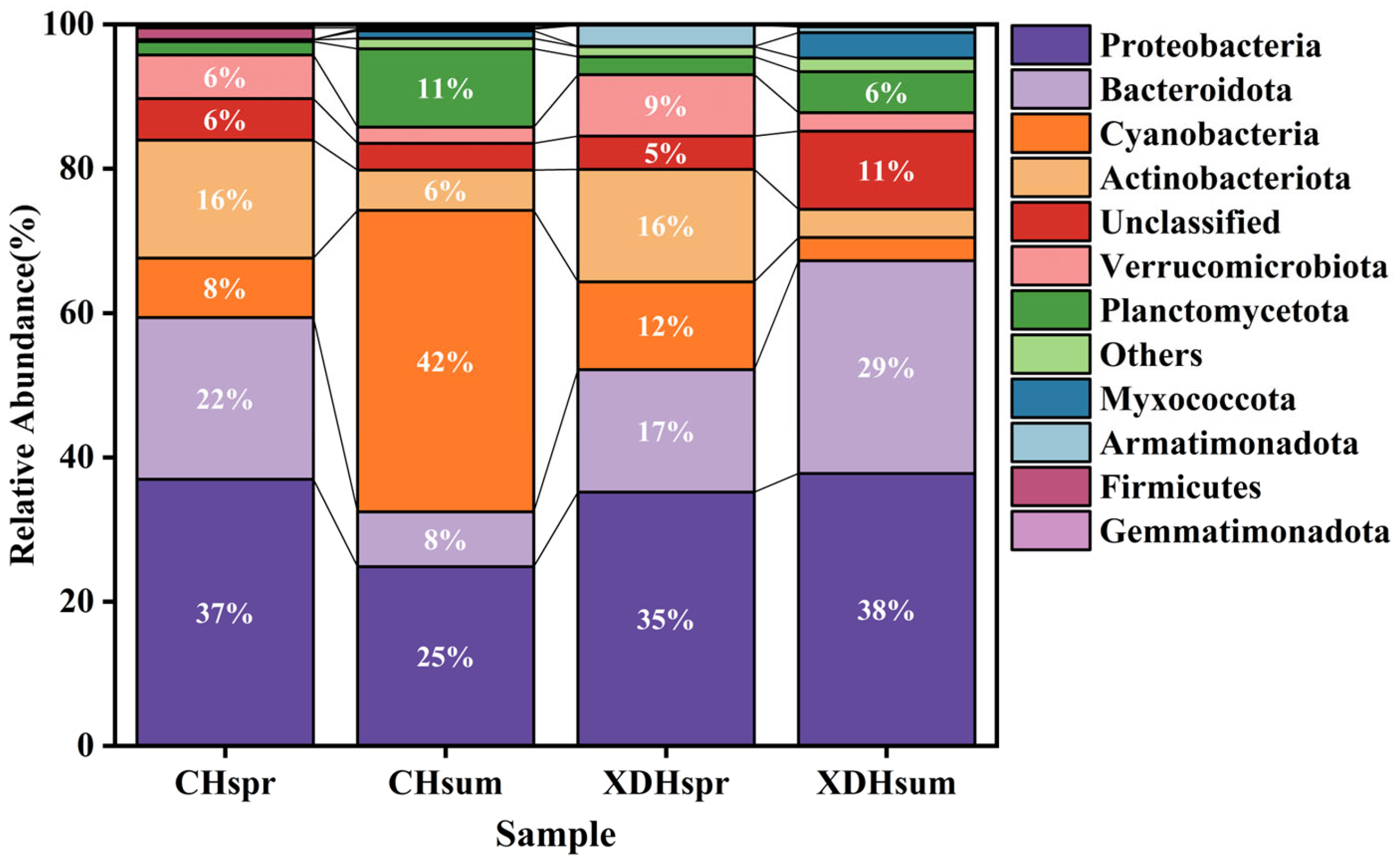
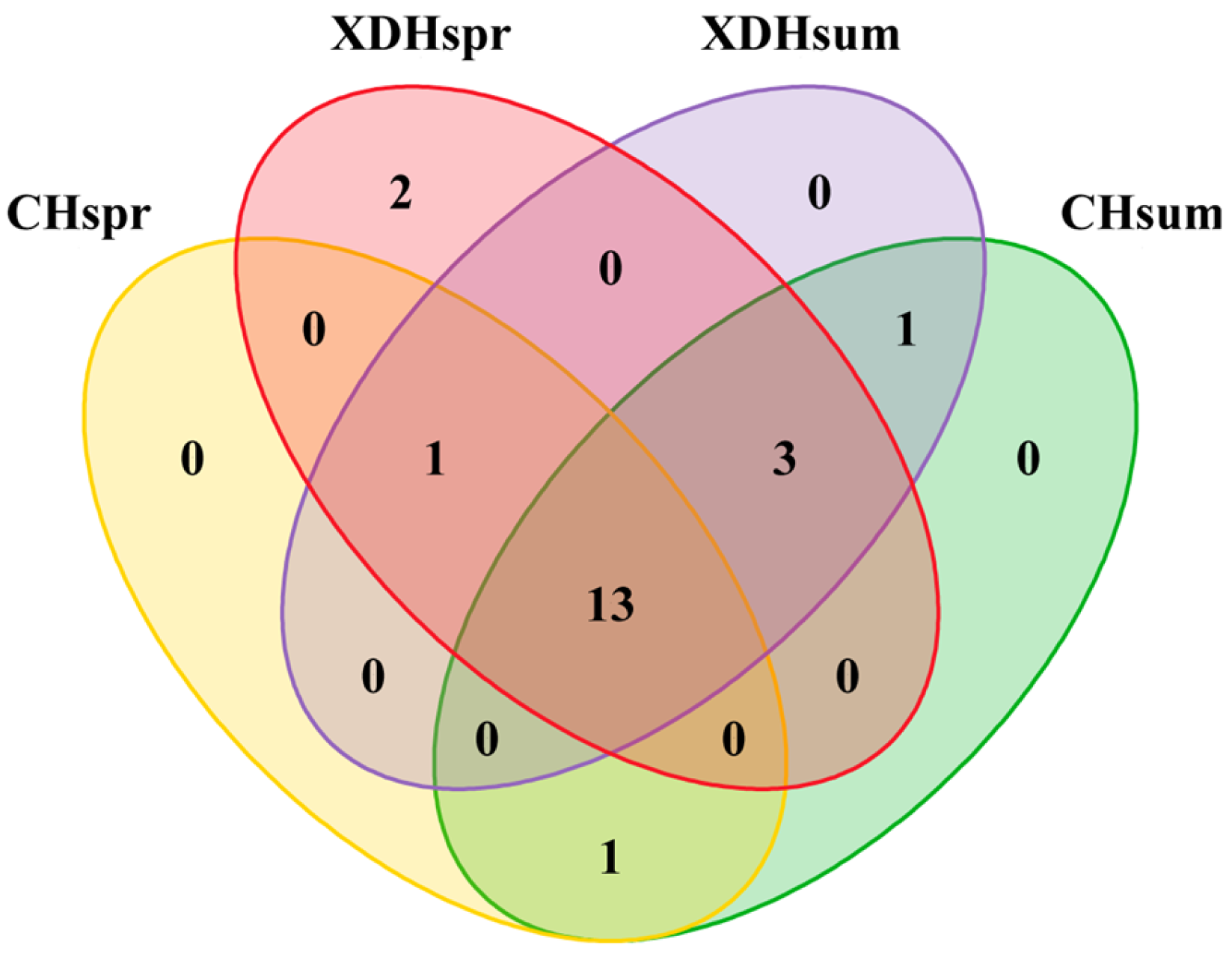
3.2. Components of Prokaryotic Ultraplankton Communities
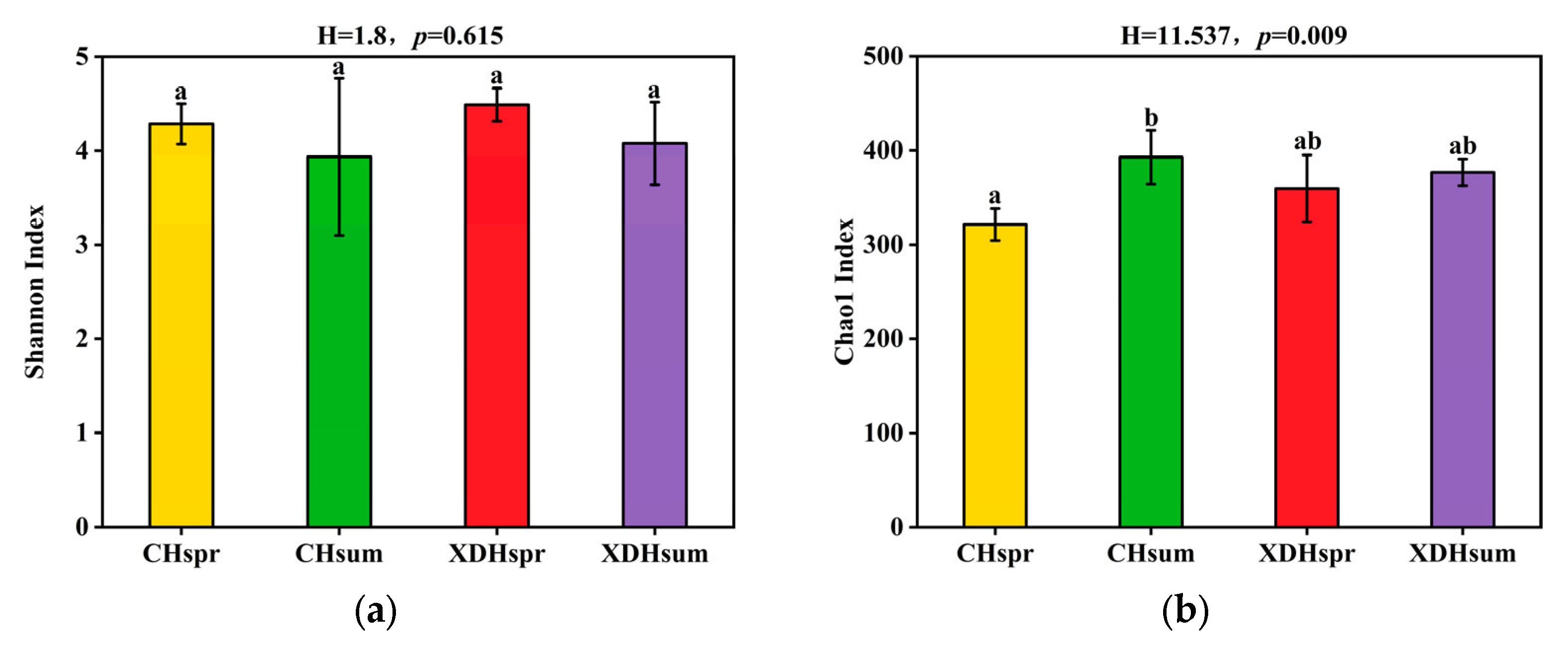
3.3. Analysis of Community Diversity
3.4. Correlation Analysis between Plankton Communities and Environmental Factors
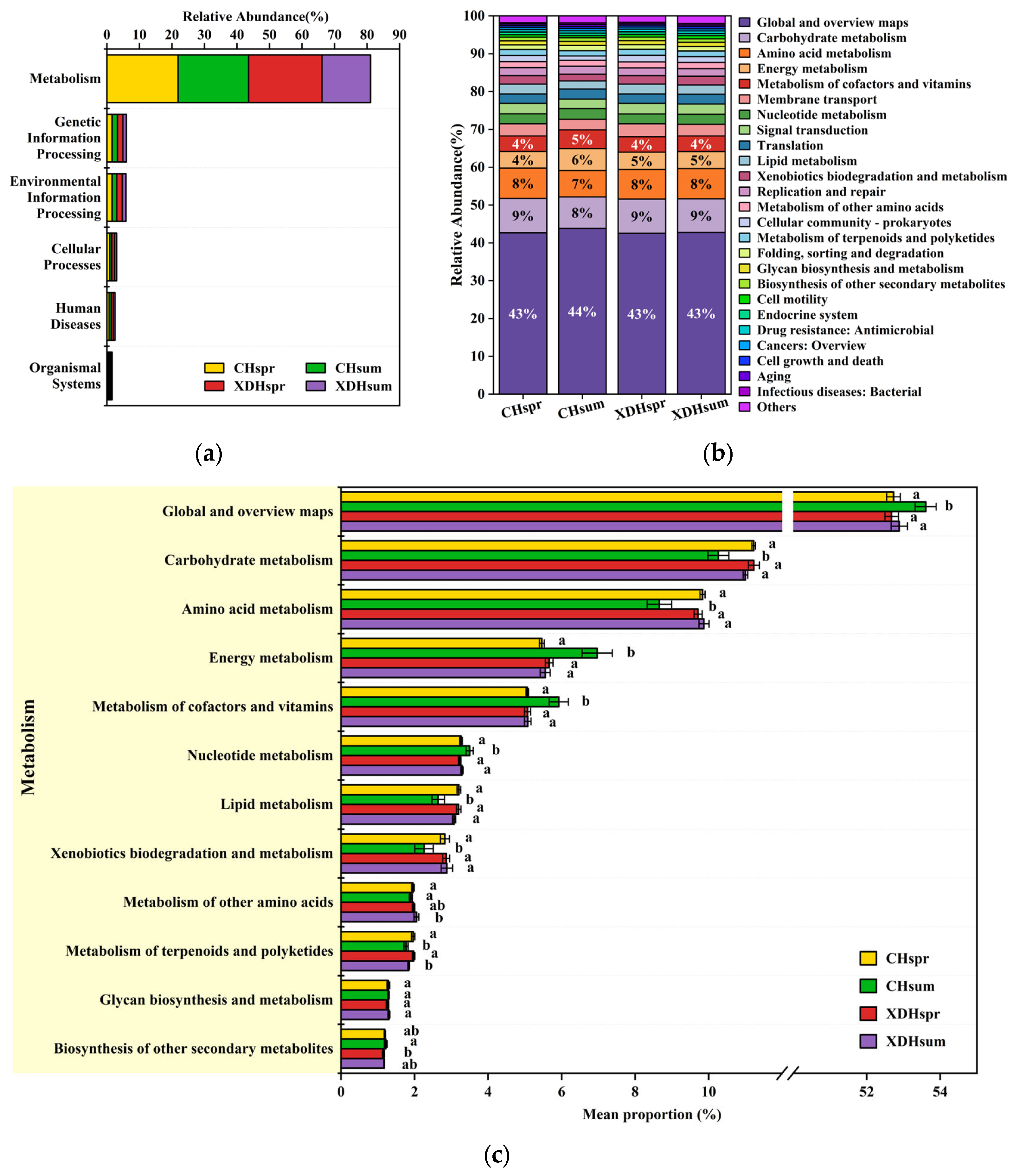
3.5. Functional Prediction of KEGG with PICRUSt
4. Discussion
4.1. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Nutritional Regulations of Cihu Lake and Xiandao Lake
4.2. Changes in the Structural Composition and Diversity of the Plankton Community in Cihu Lake and Xiandao Lake
4.3. Driving Factors of Prokaryotic Ultraplankton Diversity in Cihu Lake and Xiandao Lake
4.4. Functional Prediction Analysis of Prokaryotic Ultraplankton in Cihu Lake and Xiandao Lake
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cosgrove, W.J.; Loucks, D.P. Water management: Current and future challenges and research directions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4823–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancosu, N.; Snyder, R.L.; Kyriakakis, G.; Spano, D. Water scarcity and future challenges for food production. Water 2015, 7, 975–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.L.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.H.; Peng, S.S.; Li, J.S.; Zhou, L.P.; Liu, H.Y.; Ma, Y.C.; Ding, Y.H.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiklomanov, I.A. Appraisal and assessment of world water resources. Water Int. 2000, 25, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Feng, L.; Hou, X.J.; Schurgers, G.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, J. Eutrophication changes in fifty large lakes on the Yangtze Plain of China derived from MERIS and OLCI observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagowati, B.; Ahamad, K.U. A review on lake eutrophication dynamics and recent developments in lake modeling. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2019, 19, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducklow, H.W.; Purdie, D.A.; Williams, P.J.L.; Davies, J.M. Bacterioplankton: A sink for carbon in a coastal marine plankton community. Science 1986, 232, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, J. Bacterioplankton roles in cycling of organic matter: The microbial food web. In Primary Productivity and Biogeochemical Cycles in the Sea; Falkowski, P.G., Woodhead, A.D., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; Volume 43, pp. 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindh, M.V.; Pinhassi, J. Sensitivity of bacterioplankton to environmental disturbance: A review of Baltic Sea field studies and experiments. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunse, C.; Pinhassi, J. Marine bacterioplankton seasonal succession dynamics. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zeng, D.B.; Singh, V.P.; Xu, P.C.; Liu, D.F.; Wang, Y.K.; Zeng, X.K.; Wu, J.C.; Wang, L.C. A multidimension cloud model-based approach for water quality assessment. Environ. Res. 2016, 149, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tromboni, F.; Dodds, W.K. Relationships between land use and stream nutrient concentrations in a highly urbanized tropical region of Brazil: Thresholds and riparian zones. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, J.P.; Francus, P.; Normandeau, A.; Lapointe, F.; Perga, M.E.; Ojala, A.; Schimmelmann, A.; Zolitschka, B. Global spread of hypoxia in freshwater ecosystems during the last three centuries is caused by rising local human pressure. Global Change Biol. 2016, 22, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanza, V.; Pedreros, P.; Laughinghouse IV, H.D.; Félez, J.; Parra, O.; Azócar, M.; Urrutia, R. Association between trophic state, watershed use, and blooms of cyanobacteria in south-central Chile. Limnologica 2019, 75, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Al Osman, M.; Yang, F. An overview on cyanobacterial blooms and toxins production: Their occurrence and influencing factors. Toxin Rev. 2022, 41, 326–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josué, I.I.P.; Cardoso, S.J.; Miranda, M.; Mucci, M.; Ger, K.A.; Roland, F.; Marinho, M.M. Cyanobacteria dominance drives zooplankton functional dispersion. Hydrobiologia 2019, 831, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, L.Z.; You, Q.M.; Pan, Y.D.; Liu, T.T.; Zhou, Y.D.; Zhang, J.Y.; Pang, W.T.; Wang, Q.X. Influence of cyanobacterial blooms and environmental variation on zooplankton and eukaryotic phytoplankton in a large, shallow, eutrophic lake in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.X.; Wu, X.D.; Ge, X.G.; Lin, G.Y.; Zhou, M.D.; Long, Z.J.; Yu, X.H.; Tian, W. Characteristics of dissolved organic matter in lakes with different eutrophic levels in southeastern Hubei Province, China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 1256–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, F.; Destouni, G. Local flow regulation and irrigation raise global human water consumption and footprint. Science 2015, 350, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Lin, H.M.; Huang, R.R.; Zhai, W.D. Exploring the plankton bacteria diversity and distribution patterns in the surface water of northwest Pacific Ocean by metagenomic methods. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1177401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Ou, D.Y.; Guo, J.Y.; Laws, E.A.; Huang, B.Q. Patterns of relative and quantitative abundances of marine bacteria in surface waters of the subtropical northwest Pacific Ocean estimated with high-throughput quantification sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 599614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Li, Y.Y.; Lin, L.A.; Zheng, B.H.; Ji, M.F.; Li, B.L.; Han, X.M. The seasonal patterns, ecological function and assembly processes of bacterioplankton communities in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 884765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaçin, İ.; Ersoy, Ş.; Doluca, O.; Güngörmüşler, M. Comparing the significance of the utilization of next generation and third generation sequencing technologies in microbial metagenomics. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 264, 127154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Garcia, M.; Swan, B.K.; Poulton, N.J.; Gomez, M.L.; Masland, D.; Sieracki, M.E.; Stepanauskas, R. High-throughput single-cell sequencing identifies photoheterotrophs and chemoautotrophs in freshwater bacterioplankton. ISME J. 2012, 6, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Rio, D.C.; Ares, M.J.; Hannon, G.J.; Nilsen, T.W. Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2010, 2010, pdb.prot5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.S.; Shen, S.L.; Zhou, A.N.; Lyu, H.M. Assessment and management of lake eutrophication: A case study in Lake Erhai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.Q.; Yang, L.Y.; Chen, F.Z.; Zhu, G.W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.Y. Mechanism and control of lake eutrophication. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Leavitt, P.R.; Zhang, Y.B.; Qin, B.Q. Anthropogenic eutrophication of shallow lakes: Is it occasional? Water Res. 2022, 221, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecky, R.E.; Kilham, P. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: A review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 796–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaudani, G.; Vighi, M. The N:P ratio and tests with Selenastrum to predict eutrophication in lakes. Water Res. 1974, 8, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, A.C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am. Sci. 1958, 46, 205–221+230A. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.Q.; Zhou, J.; Elser, J.J.; Gardner, W.S.; Deng, J.M.; Brookes, J.D. Water depth underpins the relative roles and fates of nitrogen and phosphorus in lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3191–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Liang, J.C.; Ma, Y.Q.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y. Bacterial community and eutrophic index analysis of the East Lake. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Z.P.; Chu, Y.X.; Tian, G.M.; He, R. Eutrophic levels and algae growth increase emissions of methane and volatile sulfur compounds from lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.W.; Zeng, H.; Zhou, Q.X.; Hu, X.G.; Qu, Q.; Ouyang, S.H.; Wang, Y.Y. Anthropogenic impacts on the biodiversity and anti-interference ability of microbial communities in lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, M.L.; Li, X.L.; Liu, G.L.; Hua, Y.M.; Zhao, J.W.; Huguet, A.; Li, S.X. Shifts in microbial communities in shallow lakes depending on trophic states: Feasibility as an evaluation index for eutrophication. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Mello, M.M.E.; Van Oosterhout, F.; De Senerpont Domis, L.; Marinho, M.M. Response of natural cyanobacteria and algae assemblages to a nutrient pulse and elevated temperature. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brookes, J.D.; Carey, C.C. Resilience to Blooms. Science 2011, 334, 46–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Qin, H.; Guo, S.D.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.C.; Liang, J.C. Bacterial communities of four adjacent fresh lakes at different trophic status. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2018, 157, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghai, R.; Mizuno, C.M.; Picazo, A.; Camacho, A.; Rodriguez-Valera, F. Key roles for freshwater Actinobacteria revealed by deep metagenomic sequencing. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 6073–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haukka, K.; Kolmonen, E.; Hyder, R.; Hietala, J.; Vakkilainen, K.; Kairesalo, T.; Haario, H.; Sivonen, K. Effect of nutrient loading on bacterioplankton community composition in lake mesocosms. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 51, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrier, V.; Svenning, M.M.; Gründger, F.; Niemann, H.; Dessandier, P.A.; Panieri, G.; Kalenitchenko, D. The impact of methane on microbial communities at Marine Arctic gas hydrate bearing sediment. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.H.; Jiang, W.W.; Meng, S.; He, W.; Wang, G.D.; Guo, E.M.; Yan, Y.S. Polychaete bioturbation alters the taxonomic structure, co-occurrence Network, and functional groups of bacterial communities in the Intertidal Flat. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 86, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessy, L.; Pearman, J.K.; Waters, S.; Vandergoes, M.J.; Wood, S.A. Metagenomic insights to the functional potential of sediment microbial communities in freshwater lakes. Metabarcoding Metagenom. 2022, 6, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, S.; Kuroda, K.; Narihiro, T.; Aoi, Y.; Ozaki, N.; Ohashi, A.; Kindaichi, T. Cometabolism of the superphylum Patescibacteria with anammox bacteria in a long-term freshwater anammox column reactor. Water 2021, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Jiang, C.C.; Xu, S.J.; Zheng, X.X.; Lv, P.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.S.; Zhuang, X.L. Spatiotemporal changes of bacterial communities during a cyanobacterial bloom in a subtropical water source reservoir ecosystem in China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.A.; Kalff, J.; Rasmussen, J.B.; Gasol, J.M. The effect of temperature and algal biomass on bacterial production and specific growth rate in freshwater and marine habitats. Microb. Ecol. 1991, 21, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, T.T.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, T.T.; Li, L.; Qi, P.F. Temporal and spatial variations in the bacterial community composition in Lake Bosten, a large, brackish lake in China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, S.N.; Schindler, D.W. Influence of nitrogen to phosphorus supply ratios and physicochemical conditions on cyanobacteria and phytoplankton species composition in the Experimental Lakes Area, Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1999, 56, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, R.; Nair, K.V.K.; Rao, V.N.R.; Venugopalan, V.P. Nutrient dynamics and successional changes in a lentic freshwater biofilm. Freshwater Biol. 2002, 47, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Alsanea, A.; Barber, M.; Goel, R. High-throughput DNA sequencing reveals the dominance of pico- and other filamentous cyanobacteria in an urban freshwater Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunagawa, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Chaffron, S.; Kultima, J.R.; Labadie, K.; Salazar, G.; Djahanschiri, B.; Zeller, G.; Mende, D.R.; Alberti, A.; et al. Structure and function of the global ocean microbiome. Science 2015, 348, 1261359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Shen, H.; Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Yang, X.; Tao, M.; Ma, Z.M.; Qi, M. Phytoplankton community succession shaping bacterioplankton community composition in Lake Taihu, China. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4169–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Kasai, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Ōmura, S.; Shizuri, Y.; Takahashi, Y. Ilumatobacter fluminis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from the sediment of an estuary. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Jang, J.H.; Kasai, H. Algisphaera agarilytica gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel representative of the class Phycisphaerae within the phylum Planctomycetes isolated from a marine alga. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 105, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvet, P.J.M.; Grimont, P.A.D. Taxonomy of the genus Acinetobacter with the recognition of Acinetobacter baumannii sp. nov., Acinetobacter haemolyticus sp. nov., Acinetobacter johnsonii sp. nov., and Acinetobacter junii sp. nov. and emended descriptions of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and Acinetobacter lwoffii. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1986, 36, 228–240. [Google Scholar]
- Rooney-Varga, J.N.; Giewat, M.W.; Savin, M.C.; Sood, S.; LeGresley, M.; Martin, J.L. Links between phytoplankton and bacterial community dynamics in a coastal marine environment. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muylaert, K.; Van der Gucht, K.; Vloemans, N.; Meester, L.D.; Gillis, M.; Vyverman, W. Relationship between bacterial community composition and bottom-up versus top-down variables in four eutrophic shallow lakes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4740–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, A.N.; Wang, J.W.; Liu, S.F.; Jiang, X.T.; Dang, C.Y.; Ma, T.; Liu, S.T.; Chen, Q.; Xie, S.G.; et al. Integrated biogeography of planktonic and sedimentary bacterial communities in the Yangtze River. Microbiome 2018, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Tang, Q.; Lu, L.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Izaguirre, I.; Li, Z. Changes in planktonic and sediment bacterial communities under the highly regulated dam in the mid-part of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Beiko, R.G.; Langille, M.G.I. Predicting the functional potential of the microbiome from marker genes using PICRUSt. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1849, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, J.L.; Liu, X.J.; Charron, C.S.; Novotny, J.A.; Jeffery, E.H.; Seifried, H.E.; Ross, S.A.; Miller, M.J.; Swanson, K.S.; Holscher, H.D. Broccoli consumption affects the human gastrointestinal microbiota. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 63, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelusmond, J.R.; Strathmann, T.J.; Cupples, A.M. The identification of carbamazepine biodegrading phylotypes and phylotypes sensitive to carbamazepine exposure in two soil microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, W.K.; Li, X.C.; Gao, G.; Jiang, J.H. Linking bacterial community shifts with changes in the dissolved organic matter pool in a eutrophic lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluseyi Osunmakinde, C.; Selvarajan, R.; Mamba, B.B.; Msagati, T.A.M. Profiling bacterial diversity and potential pathogens in wastewater treatment plants using high-throughput sequencing analysis. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Robb, C.S.; Unfried, F.; Kappelmann, L.; Markert, S.; Song, T.; Harder, J.; Avcı, B.; Becher, D.; Xie, P.; et al. Alpha- and beta-mannan utilization by marine Bacteroidetes. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 4127–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, F.; Qu, X.D.; Elser, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Chu, L.M. Taxonomic and functional differences between microbial communities in Qinghai Lake and its input streams. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

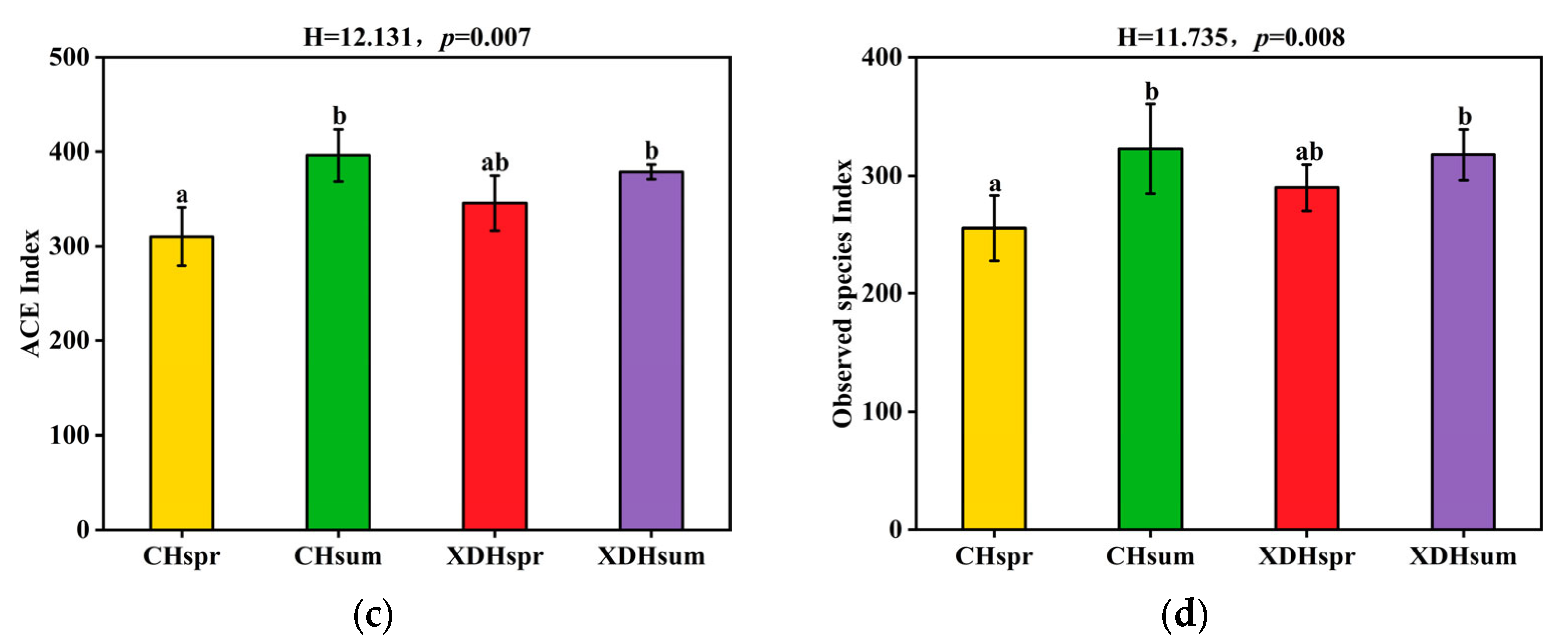
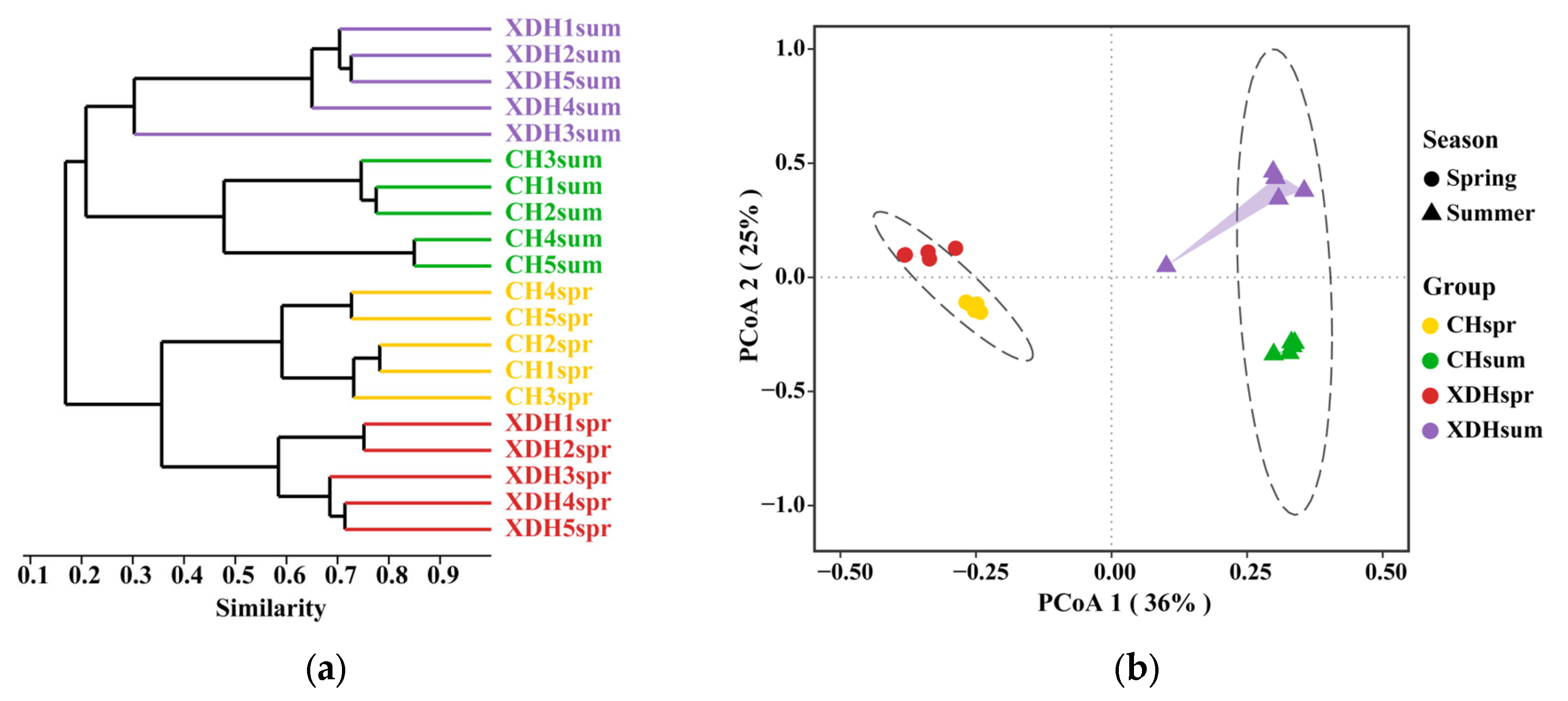
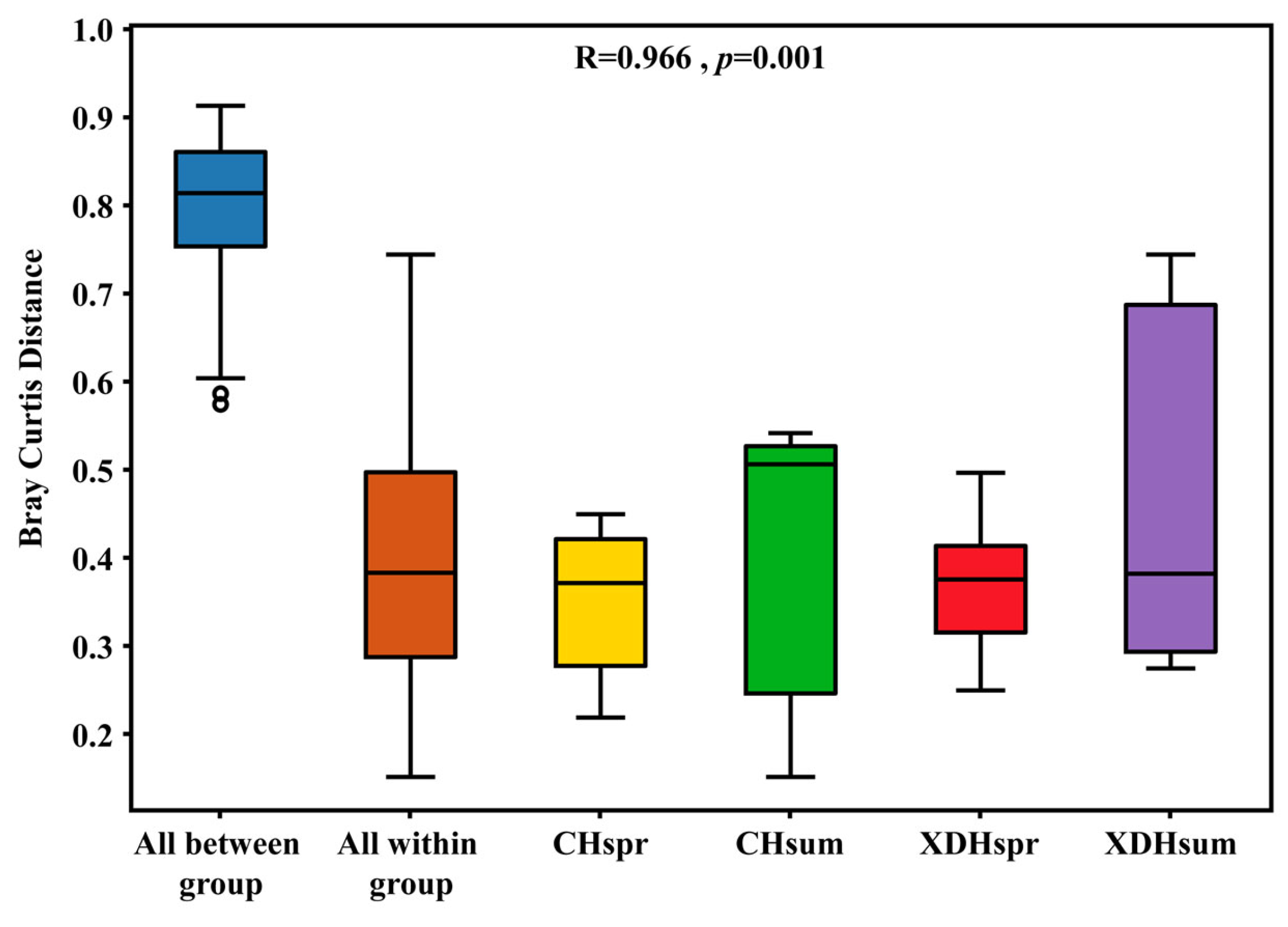
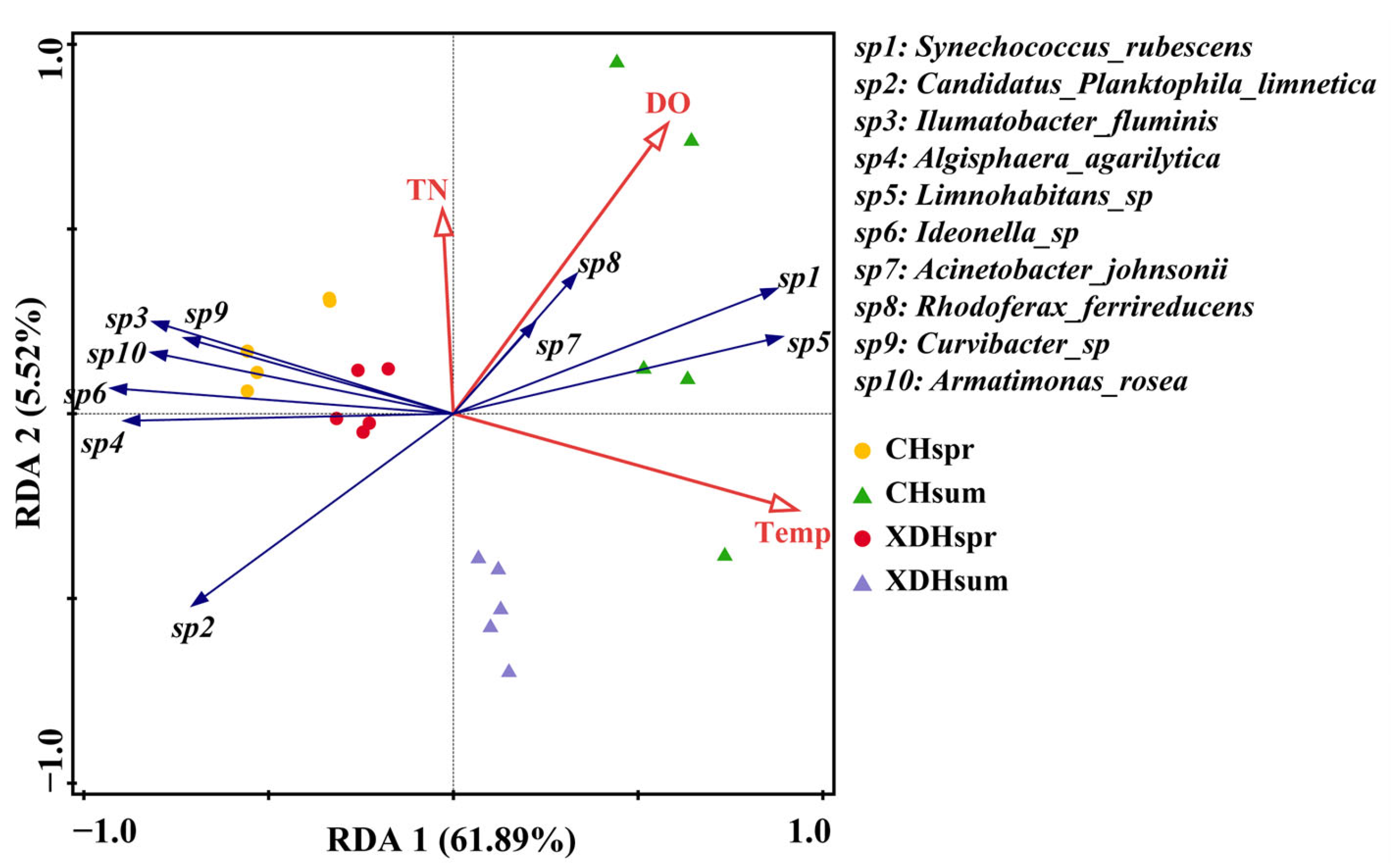
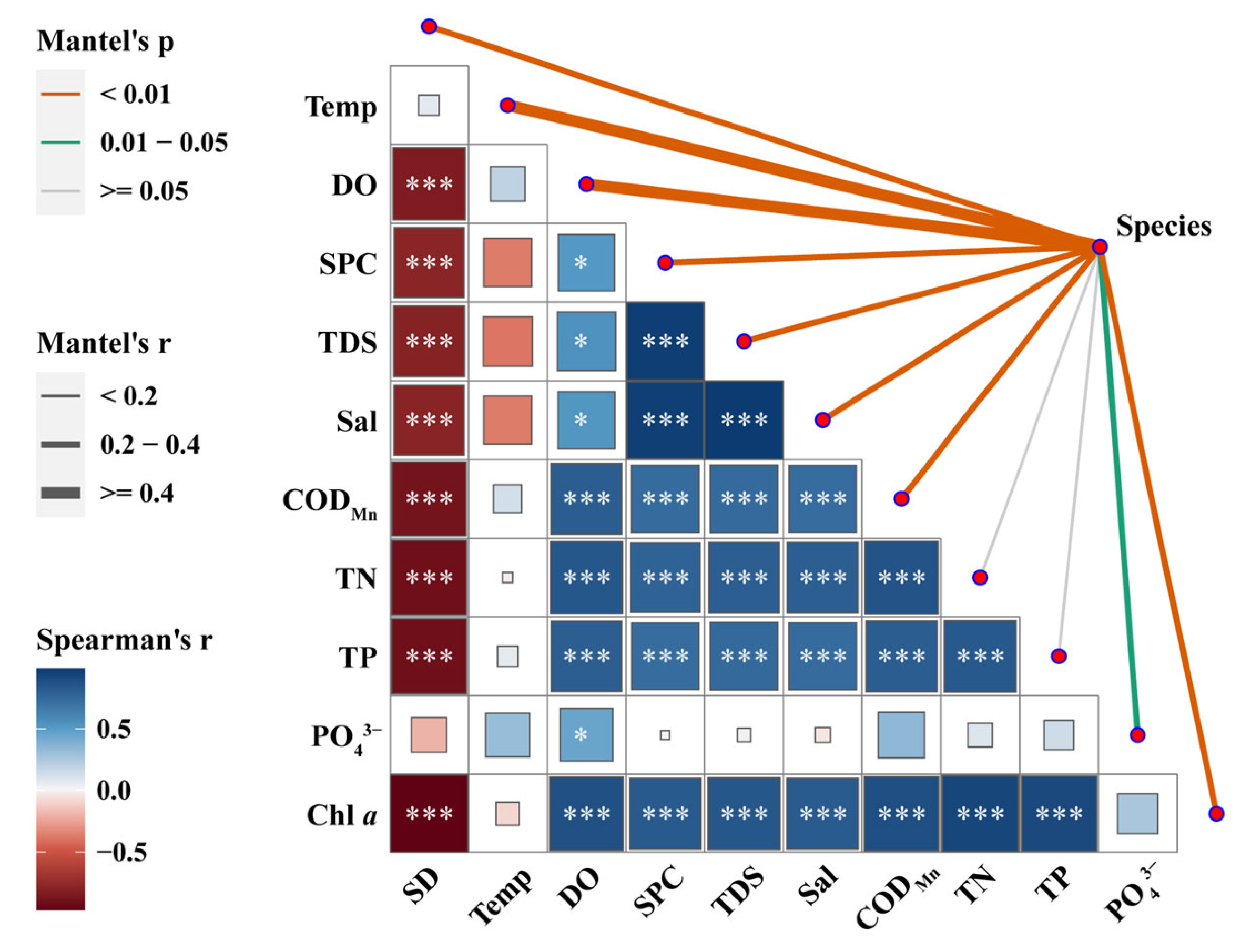
| CHspr | CHsum | XDHspr | XDHsum | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD (m) | 0.57 ± 0.08 a | 0.45 ± 0.01 a | 2.62 ± 0.33 ab | 5.06 ± 0.74 b | 0.001 |
| Temp (℃) | 22.64 ± 0.28 a | 29.99 ± 0.43 b | 25.53 ± 0.06 ac | 28.49 ± 0.06 bc | <0.001 |
| DO (mg/L) | 9.47 ± 0.50 ab | 11.78 ± 0.53 a | 8.94 ± 0.17 ab | 8.27 ± 0.09 b | 0.002 |
| SPC (uS/cm) | 431.38 ± 9.16 a | 349.74 ± 10.27 ab | 194.80 ± 4.74 b | 187.64 ± 2.30 b | 0.001 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 280.20 ± 5.98 a | 224.00 ± 3.51 ab | 126.6 ± 3.17 b | 116.20 ± 2.62 b | 0.001 |
| Sal (psu) | 0.21 ± 0.00 a | 0.16 ± 0.00 ab | 0.09 ± 0.00 b | 0.08 ± 0.00 b | 0.001 |
| TN (mg/L) | 0.88 ± 0.26 a | 0.63 ± 0.06 a | 0.27 ± 0.06 ab | 0.13 ± 0.02 b | 0.002 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.32 ± 0.25 ab | 0.17 ± 0.01 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 bc | 0.02 ± 0.00 c | 0.001 |
| TN/TP | 7.88 ± 1.87 a | 3.75 ± 0.35 a | 9.42 ± 2.29 a | 6.48 ± 1.52 a | 0.217 |
| PO43− (mg/L) | 0.02 ± 0.01 ab | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.003 |
| Chl a (μg/L) | 55.71 ± 17.12 a | 55.07 ± 5.42 a | 6.01 ± 0.52 ab | 1.01 ± 0.19 b | 0.001 |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 6.30 ± 0.51 a | 7.40 ± 0.12 a | 2.24 ± 0.06 ab | 1.89 ± 0.07 b | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, C.; Sun, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Ding, H.; Tang, R.; Hou, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, X. Diversity and Their Response to Environmental Factors of Prokaryotic Ultraplankton in Spring and Summer of Cihu Lake and Xiandao Lake in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11532. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511532
Lan C, Sun L, Hu Y, Zhang Y, Xu J, Ding H, Tang R, Hou J, Li Y, Wu X. Diversity and Their Response to Environmental Factors of Prokaryotic Ultraplankton in Spring and Summer of Cihu Lake and Xiandao Lake in China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11532. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511532
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Cong, Lili Sun, Yihan Hu, Yan Zhang, Jinjing Xu, Heng Ding, Rong Tang, Jianjun Hou, Yuntao Li, and Xiaodong Wu. 2023. "Diversity and Their Response to Environmental Factors of Prokaryotic Ultraplankton in Spring and Summer of Cihu Lake and Xiandao Lake in China" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11532. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511532
APA StyleLan, C., Sun, L., Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., Xu, J., Ding, H., Tang, R., Hou, J., Li, Y., & Wu, X. (2023). Diversity and Their Response to Environmental Factors of Prokaryotic Ultraplankton in Spring and Summer of Cihu Lake and Xiandao Lake in China. Sustainability, 15(15), 11532. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511532







