Abstract
Shared parking is an effective means to alleviate the shortage of parking spaces in urban central areas during the morning peak hours. Meanwhile, walking time cost and parking fees are two critical factors affecting shared parking efficiency. Firstly, based on the classic bottleneck model, walking time cost and shared parking fees are added to the model, then the user equilibrium solutions are obtained considering two choices of parking lots: accessorial parking and shared parking. Next, taking the minimum total social cost and the minimum total queue time as the management goals, respectively, the quantitative relationship between parking fee as well as the dispersion degree of the shared parking spaces with the optimal travel pattern is proved. Besides, the rules and methods for the reasonable setting of shared parking fee and the dispersion degree of shared parking spaces layout are proposed. Through the research, it was demonstrated that: (1) differentiated shared parking fee based on the capacity of the accessorial parking lot can reduce both the total social cost and road congestion, while total social cost increases with the dispersion of the layout of shared parking spaces and road congestion decreases with the dispersion of the layout of shared parking spaces; and (2) when derived the optimal travel pattern, it is found that there is an inert zone of shared parking fee, i.e., regardless of adjusting shared parking fee, it had no impact on the determination of the optimal travel pattern. Finally, we put forward policy recommendations combining the numerical examples. Considering the total social cost and congestion, managers can improve the utilization efficiency of shared parking spaces while taking into account social benefits by reasonably setting shared parking fee and the dispersion degree of shared parking spaces layout.
1. Introduction
The equalization of parking resources and parking demand in urban centers is under high pressure. The travel of people and urban development are affected by the problem of difficult parking with the accelerated development of urbanization and the rapid growth of the urban vehicle population. Shared parking is an effective complement to solve the problem of difficult parking in urban centers, with more transparent and accurate parking data, as the level of urban refinement continues to improve.
Sustainable urban transportation systems are essential for economic, environmental and social development, and parking is an essential component of the transportation system. The existing literature on sustainable parking management is extensive and focuses particularly on Park-and-Ride [1], planning and implementation of parklets [2], and Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) [3,4]. There has been a shift in the parking management paradigm from providing adequate parking resources to effectively utilizing available parking resources [5], and shared parking has become a new parking management approach. Shared parking is a solution to the problem of insufficient parking spaces during peak hours by staggering the sharing of unused parking spaces on sites of varying properties during peak parking demand periods. In the existing literature, much of the current literature on shared parking pays particular attention to the allocation of parking spaces [6,7], the utilization of shared parking [8,9,10], and the design for shared parking platform [11,12]. Little research on shared parking has been done at domestic and foreign to study the optimal layout of shared parking spaces (in relation to shared parking walking time) and parking fee strategies. However, the utilization efficiency of most shared parking spaces is low due to factors such as too long walking distance from shared parking spaces or unreasonable parking fee. In this paper, the shared parking walking time cost to work destinations is further considered, and it is analyzed how the shared parking fee and walking time cost affect the optimal layout of shared parking when both accessorial parking lots and shared parking lots exist in urban center.
Walking time cost and parking fee, two important factors in parking management, have always been a concern of traffic managers. Recent evidence suggests that it is of significance to study the parking walking time cost and parking fee. Lu et al. [13] studied daily commuting patterns in linear cities that allow both late arrival in the morning and early departure in the evening in a linear city, and design a combined regime of linear location-dependent parking fee and time-varying road toll to reduce the total social cost of linear cities. Liu [14] investigated the joint equilibrium of departure time and parking location choice for commuters traveling with autonomous vehicles, developed a location-based parking pricing scheme and discussed parking supply with optimal system performance. Research on the subject has been mostly restricted to the impact of location-related parking fee on system performance, ignoring that parking space layout is also an important influencing factor. In this paper, the effects of parking fee and parking space layout on the total social cost and road congestion are further considered, and the rules and methods for the reasonable setting of shared parking fee and the dispersion degree of shared parking spaces layout are proposed.
Based on the above, the main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows. First, based on bottleneck economics, the key parameters of shared parking walking time cost and shared parking fee will be added in the paper based on the traditional shared parking optimization model to analyze the layout optimization of shared parking. Second, the relationship between shared parking fee and accessorial parking fee is considered comprehensively, and pricing strategies under diverse management objectives shared parking fee are further considered. Overall, we focused on how to optimize the walking time cost of shared parking and the pricing of shared parking to achieve the goal of both increasing the efficiency of shared parking utilization and reducing the total social cost and traffic congestion.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews the existing literature relevant to this paper. In Section 3, we illustrate problem description and describe the bottleneck model under two types of travel scenarios. The user equilibrium solution, total social cost, and queue time for the two types of travel scenarios are solved in Section 4. Section 5 explores the optimal travel patterns under two scenarios when the total social cost is minimum or the total queue time is minimum, and solves for the fee margin between the two types of parking lots () and the dispersion between shared parking spaces (). Cases studies are conducted in Section 6, and our work and findings are concluded in Section 7.
2. Literature Review
Shared parking is a novel parking management method that involves sharing available parking places with others who are in need. As a new solution idea to solve the parking difficulty problem, many scholars in domestic and foreign countries have researched this issue. Early examples of research into shared parking include shared parking demand forecasting [15], parking space management strategies [16], and the design of parking platforms [17,18]. In recent years, there has been an increasing amount of literature on allocation for shared parking, several scholars have developed allocation mechanisms for shared parking, such as the global optimal allocation mechanism [19], dynamic allocation mechanism [20], and two-stage matching mechanism [21]. Little research on shared parking has been done at domestic and foreign to study the optimal layout of shared parking spaces and parking fee strategies. This paper further considers the walking time cost from shared parking spaces to work destinations and analyzes how shared parking fee and walking time costs affect the optimal layout of shared parking lots when both accessorial parking lots and shared parking lots exist in the city center.
The walking time cost is considered as an important factor by traffic managers when performing parking optimization. There are relatively few studies in the area of parking walking time, much of the current literature on parking walking time cost pays particular attention to parking cruise [22] and park-and-ride [23]. Wang et al. [24] proposed a mathematical planning model for the layout of public parking lots with the objective of minimizing the walking time of all users and the construction cost of parking lots to ensure the parking demand of users at each time. Recently, Lu et al. [13], Liu [14], Takayama and Kuwahara [25] introduced location-dependent parking fee schemes into parking management studies. In previous studies, parking walking time cost has been used to optimize parking cruises and park-and-rides. One of the important influences on parking utilization is the long walking time, and there is little literature that considers the walking time cost from shared parking to work destinations to study the layout of shared parking spaces and thus optimize the system performance.
Parking fee as an important element of parking management is also a concern for traffic managers, and has been substantially studied in the literature. Amihai and Esko [26], Qian et al. [27,28] investigated parking fees as a tool for traffic management, and explored a variety of parking fee optimization issues. With parking space constraints, Yang et al. [29], Wu et al. [30] and Tang et al. [31] studied parking pricing strategies under parking space competition and evaluated tradable parking management schemes for the morning commute problem. Afterwards, parking permits gradually entered the research perspective of scholars, Zhang et al. [32], Akamatsu and Wada [33], and Xiao et al. [34] and proposed various tradable parking management schemes for the morning commute problem. This paper focuses on how to optimize the shared parking fee from the perspective of the management objectives of minimizing the total social cost and minimizing the degree of road congestion.
This paper is based on the bottleneck model, the classic model used by scholars to analyze congestion pricing, parking optimization, travel behavior, and facility improvements. It was first proposed by Vickrey [35], which describes the departure time choice behavior of commuters during their morning commute. In user equilibrium, commuters cannot reduce their travel costs by changing their departure time. Later Richard et al. [36,37] studied the bottleneck model in detail in the areas of road pricing and parking fee as well as user characteristics. Although the bottleneck model can well characterize the commuting behavior of users during peak hours, it is not very realistic due to excessive assumptions. Thus, many scholars at domestic and overseas have improved the bottleneck model and extended the theoretical and applied research on the model from various dimensions such as different traveler types [28,38], travel pattern selection [39,40], bottleneck capacity [41,42,43], and user activity utility [44,45].
3. Problem Description
The research scenario in this paper is a single-source and single-destination traffic network, in which the residential area and the work destination are connected by an urban road with limited capacity and two types of parking options are available to commuters driving to their work destinations. One of these options is the accessorial parking lot, which is usually a private parking lot attached to the office building, so it is assumed that the walking time from the accessorial parking lot to the work destination is negligible; the other one is the shared parking spaces, since there are not enough parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot, commuters will choose the shared parking spaces around the office building, and commuters have to walk for a while to the work destination after parking. Assuming that the walking time from the nth shared parking space to the work destination is assumed to be linearly increasing, i.e., [37], where denotes the walking time between parking spaces.
In the morning peak commuter traffic network, assuming that there are N commuters commuting by auto vehicles, the total capacity of the two types of parking lots near the work destination can satisfy the parking demand of all commuters, and there are two scenarios depending on whether the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot can satisfy the parking demand of commuters: the first one is scenario A, which indicates that the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot is sufficient, assuming that the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot is , i.e., , so all commuters choose to park in the accessorial parking lot; the other one is scenario B, which indicates that the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot is insufficient, i.e., , and shared parking should be introduced as a supplement. The bottleneck model for the two types of travel scenarios is shown in Figure 1.
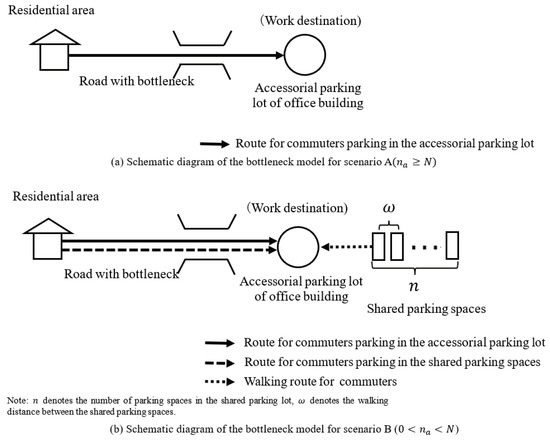
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the bottleneck model under two types of travel scenarios.
The parameters involved are first defined symbolically, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameter Setting.
4. Morning Commute Equilibrium with Parking
Commuters are divided into two categories in the morning peak according to the type of parking they choose: those who choose accessorial parking (without walking time cost) and those who choose shared parking (with walking time cost). Since the free-flow time of commuters is identical during the morning peak, it is assumed that the free-flow time is zero, i.e., . Suppose there are N auto commuters in the morning peak who have the same on-time arrival time , and then the personal travel cost of commuters departing at time t consists of the commute time cost, early or late arrival penalty cost and parking cost, as shown in Equation (1)
where in the commute time cost denotes the queue time at the bottleneck when the commuter departs at time t, denotes the travel cost per unit time; , in the non-punctual arrival penalty cost denotes the penalty cost per unit time for early arrival or late arrival, respectively. Evidently, the relationship is according to the estimates of Small [41]. Assume that the parking fee of the accessorial parking lot is not higher than the shared parking fee , i.e., , and the accessorial parking lot is always preferred when commuters arrive at their destinations. Let as the parking cost that commuters are required to pay when they choose different parking lots, as shown in Equation (2)
where represents the commuter parking in the accessorial parking lot, and the parking cost paid by the commuter who parks in the accessorial parking lot is regardless of whether he or she arrives early or late; while denotes that commuters who park in the shared parking spaces, and the parking cost paid by commuters includes the parking fee for shared parking spaces and the walking time cost for different parking locations, where denotes the walking cost per unit time and [28], as well as the penalty cost or for commuters arriving early or late due to walking time.
Therefore, the personal travel cost for commuters parking in the accessorial parking lot and the personal travel cost for commuters parking in the shared parking spaces can be rewritten as shown in Equations (3) and (4)
4.1. Travel Pattern When There Are Sufficient Parking Spaces in the Accessorial Parking Lot (Scenario A)
In scenario A, there are sufficient parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot to satisfy the demand N of commuters parking, i.e., . The departure time of commuters in scenario A depends on the queue cost at the bottleneck and the penalty cost of off-schedule arrival exclusively. According to Equation (3), the personal travel cost of the first commuter is , the personal travel cost of the on-time arrival commuter is , and the personal travel cost of the last commuter is . According to the user equilibrium principle, the personal travel cost of all commuters in scenario A is identical at the user equilibrium, and the travel pattern of scenario A can be derived, as shown in Figure 2. In this case, the arrival time of the first commuter to depart is given in Equation (5); the departure time of the commuter to arrive on time is given in Equation (6); and the arrival time of the last commuter is given in Equation (7),
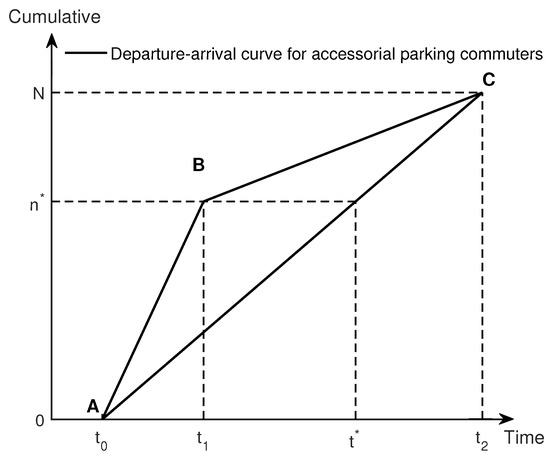
Figure 2.
Travel pattern diagram for scenario A (i.e., sufficient parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot).
The personal travel cost () of commuters in this travel pattern is shown in Equation (8)
Additionally, total travel cost () and total social cost () are shown in Equations (9) and (10), where is the personal travel cost of commuters multiplied by the total number of commuters at user equilibrium, and is equal to the travel cost of all commuters in the system minus the total revenue of the parking lot [27].
4.2. Travel Patterns Supplemented by Shared Parking When There Is a Shortage of Parking Spaces in the Accessorial Parking Lot (Scenario B)
When the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot is insufficient, i.e., , shared parking is introduced as a supplement. The premise assumes that , i.e., the shared parking fee is not lower than the accessorial parking fee, and the accessorial parking lot is ensured to be used first. Let be the number of commuters who park in the accessorial parking lot, after the first commuters all park in the accessorial parking lot (), the remaining commuters choose the shared parking spaces.
4.2.1. User Equilibrium Solution for Scenario B
According to the user equilibrium principle, commuters who park in the accessorial parking lot and commuters who park in the shared parking spaces have equal personal travel costs in the user equilibrium, i.e., , when no one in the system can unilaterally reduce his or her travel cost by changing his or her departure time or parking options. In this paper, the travel patterns of scenario B are subdivided into five categories (shown in Figure 3) based on whether commuters with two types of parking preferences meet at the bottleneck (whether the bottleneck capacity is wasted) and whether commuters who park in an accessorial parking lot or shared parking spaces when arriving at their work destination on time.
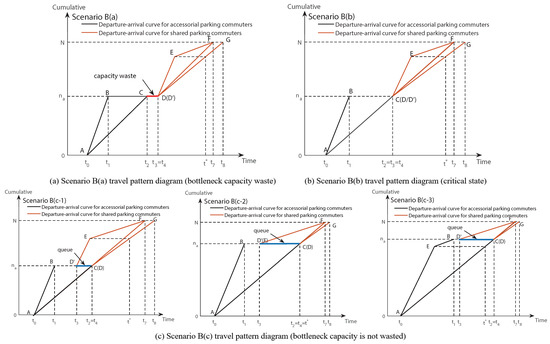
Figure 3.
Travel pattern diagram for scenario B.
In Figure 3, taking Scenario B(a) as an example: for accessorial parking commuters, the segment AB and the segment AC refer to the departure curve from the residential area and the arrival curve to the bottleneck (work destination), respectively. For shared parking commuters, on the other hand, the folded line DEF andv the segment DF represent the departure curve from the residential area and the arrival curve to the bottleneck. Furthermore, the arrival curve to the work destination of shared parking commuters is presented as the segment DG. denotes the departure and arrival time of the first commuter who parks in the accessorial parking lot; denotes the departure time of the last commuter who parks in the accessorial parking lot; denotes the arrival time of the last commuter who parks in the accessorial parking lot at the bottleneck (work destination); indicates the departure time of the first commuter who parks in the shared parking space; denotes the time when the first commuter parking in the shared parking space reaches the bottleneck (work destination); denotes the time when the last commuter parking in the shared parking space reaches the work destination; denotes the time when the commuter reaches the work destination on time.
Scenario B(a): Commute patterns with excess capacity waste, i.e., when the accessorial parking lot has a large fee advantage or the number of parking spaces is minimal, which causes commuters to leave early to compete for parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot, resulting in the waste of bottleneck capacity, as shown in the CD segment marked by the red line in Figure 3a, the last commuter parked in the accessorial parking lot leaves the bottleneck when the first commuter parked in the shared parking space has not reached the bottleneck (). Meanwhile, commuters who park in the accessorial parking lot arrived early (), and subsequent arrivals of shared parking commuters were early () or late ().
Scenario B(b): It is the critical state for scenario B(a) and scenario B(c). The commuters who park in the accessorial parking lot all arrive early (), and commuters who subsequently arrived at the shared parking space were early () or late (), The last commuter who parks in the accessorial parking lot and the first commuter who parks in the shared parking spaces meet exactly at the bottleneck (), and the first commuter who parks in the shared parking spaces does not require a queue, as shown in Figure 3b.
Scenario B(c): Commute patterns with excess queuing delay, as shown in Figure 3c. The commuters are divided into the following three categories according to whether the first commuter who parks in the shared parking spaces arrives early, arrives on time, or arrives late.
(i) Scenario B(c-1): Commuters who park in the accessorial parking lot arrive early (), and commuters who subsequently arrived at the shared parking space were early () or late (), and the first commuter to park in the shared parking spaces reaches the bottleneck before the queue dissipates (as shown by the blue line marking the CD’ segment in scenario B(c-1) in Figure 3c).
(ii) Scenario B(c-2): It is a special case of scenario B(c). The last commuter who parks in the accessorial parking lot happens to arrive on time (), and the first commuter who parks in the shared parking spaces leaves before the queue dissipates (), as shown by the blue line marking the CD’ segment in scenario B(c-2) in Figure 3c, which also arrives on time.
(iii) Scenario B(c-3): Commuters who park in the accessorial parking lot are both early and late (), commuters who park in the shared parking spaces are late (), and the first commuter who parks in the shared parking spaces reaches the bottleneck before the queue dissipates (), as shown by the blue line labeled CD’ in scenario B(c-3) in Figure 3c.
Table 2 is corresponded to the range of parking fee margin between the two types of parking lots for the five travel patterns in Figure 3 under user equilibrium, as well as the range of accessorial parking capacity, where scenarios B(c-2) and B(c-3) appear only when the accessorial parking capacity is larger.

Table 2.
Boundary conditions of different travel patterns under scenario B and the range of parking fee margin and accessorial parking capacity for the two types of parking lots.
4.2.2. Total Social Cost () and Total Queue Time () for Scenario B
According to the user equilibrium principle, the personal travel cost () of each commuter is identical, and the personal travel cost of commuters in each scenario is expressed as a piecewise function with respect to as shown in Equation (12)
where corresponds to the travel pattern of personal travel cost under scenario B(a), corresponds to the travel pattern of personal travel cost under scenario B(b), and when corresponds to the travel pattern of personal travel cost under scenario B(c).
The total social cost of scenario B (), is shown in Equation (13)
where the total social cost is equal to the cost of travel for all commuters in the system, i.e., the total number of commuters multiplied by the personal travel cost in commuter equilibrium, minus the total revenue.
5. Optimal Travel Pattern Solutions under Different Management Objectives
This section explores the optimal travel patterns under two scenarios when the total social cost is the lowest or the total queue time is the lowest, and solves for the fee difference between the two types of parking lots () and the dispersion between shared parking spaces ().
5.1. The Optimal Travel Pattern with the Lowest Total Social Cost
To minimize the total social cost, we first analyze the optimal travel pattern for scenario B. We can derive the following Lemma 1.
Lemma 1.

When the lowest total social cost is the management objective, two types of parking options (accessorial parking and shared parking) are considered, which are divided into three categories according to the range of , and three different total social costs are calculated in (the expressions are shown in column 3 of Table 3). For different accessorial parking capacity (), there is a unique parking fee margin between the two categories and the optimal travel pattern (as shown in Table 3); when and only when , whatever the value of the parking fee margin between the two categories in the interval , it corresponds only to the unique constant total social cost , and the optimal travel pattern cannot be obtained in scenario B(a) in any case.

Table 3.
Optimal parking fee and travel patterns corresponding to different accessorial parking capacities under scenario B at the lowest total social cost.
Proof of Lemma 1.
The proof is shown in Appendix A.1. □
Based on Lemma 1, comparing the total social cost of scenario A and scenario B, we can obtain Proposition 1.
Proposition 1.
When the lowest total social cost is the management objective, there is an optimal travel pattern for each accessorial parking capacity (Lemma 1), and the travel pattern with the lowest total social cost is determined by the value of the dispersion degree ω of shared parking spaces:
(i) When , it is always in scenario A that the optimal travel pattern occurs, i.e., , and the total social cost of scenario B is always higher than that of scenario A.
(ii) When , it is in scenario B that the optimal travel pattern appears, i.e., , and the total social cost of scenario B is no higher than that of scenario A.
Proof of Proposition 1.
The proof is shown in Appendix A.2. □
Proposition 1(i) implies that the optimal total social cost in the system is obtained when all commuters park in the accessorial parking lot, illustrating that the total social cost increases owing to the inconvenience of shared parking facilities. In this case, the manager should establish a sufficient number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot to meet the parking needs of all commuters and discourage the allocation of shared parking spaces. Proposition 1(ii) shows that it is desirable to reduce the total social cost by implementing shared parking policy to take up part of the parking demand of auto commuters in the road network, provided that the distance between shared parking spaces is sufficiently optimized.
5.2. Optimal Travel Pattern with the Shortest Total Queue Time
With the management objective of minimizing the total queue time of commuters, we first analyze the optimal travel pattern for scenario B. We can obtain the following Lemma 2.
Lemma 2.
Minimizing the total queue time of commuters in the system is the management objective. Considering the existence of two types of parking lots (accessorial parking lot and shared parking spaces), a continuous trend is revealed for the total queue time of commuters, i.e., it increases as the parking fee margin between the two types of parking lots increases, then decreases, and finally remains constant (as shown in Figure 4). Additionally, the optimal travel pattern corresponding to the shortest total queue time is related to the capacity of the accessorial parking lot :
(i) When , the optimal travel pattern in scenario B is obtained in scenario B(a) or scenario B(b) (as shown in Figure 4a);
(ii) When , the optimal travel pattern in scenario B is obtained in scenario B(c-3) (as shown in Figure 4b).
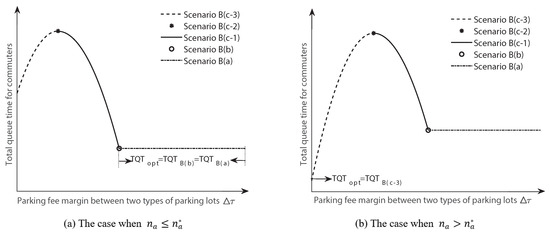
Figure 4.
Trend of total queue time of commuters in the system with the change of travel pattern.
Proof of Lemma 2.
The proof is shown in Appendix A.3. □
Based on Lemma 2, comparing the total queue time for commuters of scenario A and scenario B, we can obtain Proposition 2.
Proposition 2.
With the management objective of minimizing the total queue time of commuters in the system, the optimal travel pattern is determined by the accessorial parking capacity, and there exists an accessorial parking capacity , which can be obtained:
(i) When , the optimal travel pattern definitely appears in scenario A;
(ii) When , the optimal travel pattern necessarily occurs in scenario B(a) or scenario B(b), and the total queue time of commuters in scenarios B(a) and B(b) is identical.
Proof of Proposition 2.
The proof is shown in Appendix A.4. □
The contrast of Propositions 1 and 2 suggest that the total queue time of commuters in scenario B is always smaller than the total queue time of commuters in scenario A, given that regardless of the value of , when considering the management objective of minimizing the total queue time of commuters. That is, when considering parking options in scenario B, it can be visually observed from the travel pattern diagram in the previous section that there are two peaks of traffic at the bottleneck. While in scenario A, there is only one over-concentrated peak in the absence of parking options. The introduction of shared parking enables commuters to have parking options, which essentially separate commuters into different groups so that each group of commuters will travel at a distinct time from the others, thus reducing queue time. Nevertheless, when , the total queue time of commuters in scenario A is lower than that of commuters in scenario B. Since the accessorial parking lot can satisfy the majority of the parking demand, the introduction of shared parking spaces will on the contrary increase road congestion, resulting in little distinction between the two types of travel groups in terms of travel time periods.
6. Numerical Examples
Suppose there are N auto commuters () arriving at their work destinations from their residential areas through the bottleneck during the morning peak hour, and the bottleneck capacity (vehicles/h), the commuters have a joint on-time commute time . The value of unit travel time (yuan/h), the value of unit time for early arrivals (yuan/h), the value of unit time for late arrivals (yuan/h), and the walking cost per unit of time (yuan/h), the parking fee of the accessorial parking lot is (yuan).
6.1. Comparative Analysis of Total Social Cost for Scenario A and Scenario B
With the lowest total social cost as the management objective, we first analyze how to adjust the shared parking fee to achieve the optimal travel pattern in scenario B with different accessorial parking capacities. Then, the optimal travel pattern of scenario B is compared with that of scenario A, and the optimal parking allocation and layout of shared parking spaces under this management objective are discussed respectively concerning the dispersion of shared parking spaces ().
6.1.1. Travel Pattern Analysis for Scenario B with the Lowest Total Social Cost
When we consider the lowest total social cost as the management objective, according to Lemma 1, the optimal parking fee and travel patterns corresponding to different accessorial parking capacities in scenario B are divided into three categories, and the accessorial parking capacity is randomly selected in each of the three categories, and . The variation of the total social cost with the shared parking fee is obtained as shown in Figure 5.
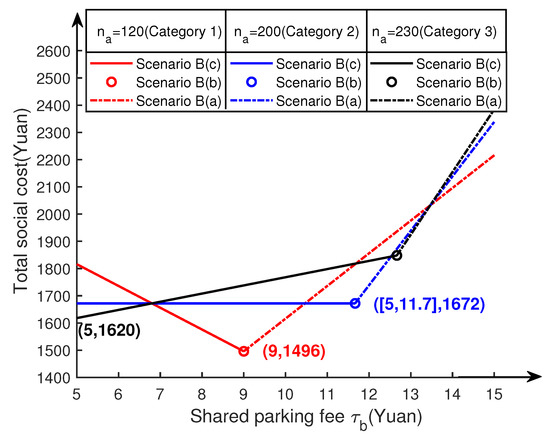
Figure 5.
Impact of shared parking fee on total social cost for scenario B.
It can be seen from Figure 5 and Table 4 that the trend of total social cost with shared parking fee is variable for different categories of accessorial parking capacity. For category 1, when (vehicles) (), the total social cost decreases and then increases with the increase in shared parking fee, and the optimal shared parking fee is 5 yuan, and the total social cost is minimized at 1496 yuan for scenario B(b); secondly, for category 2, when (vehicles) (), the total social cost first remains constant and then increases sharply with the increase in shared parking fee, i.e., the total social cost is minimized at 1672 yuan for both scenario B(b) and B(c-1) in scenario B(c). Finally, for category 3, when (vehicles) (), the total social cost shows two successive increases with the increase in shared parking fee, and the optimal shared parking fee is 5 yuan, which corresponds to the B(c-3) in scenario B(c) at this time, reaching the minimum total social cost of 1620 yuan, thus verifying Lemma 1.

Table 4.
Optimal travel patterns for different accessorial parking capacities under scenario B (with the lowest total social cost as the management objective).
As a result, in order to minimize the total social cost, the shared parking fee should be determined according to the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot, and a higher or lower shared parking fee will increase the total social cost. When the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot is large (category 3), it is recommended to lower the shared parking fee, and when the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot far exceeds the demand (category 1), the shared parking fee should be raised. Moreover, as shown in Figure 5, the optimal pattern is unlikely to be achieved in scenario B(a) (as shown in the dotted line in Figure 5). From the perspective of the total social cost, managers should take into account the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lots to set shared parking fee more precisely.
6.1.2. Comparative Analysis of Total Social Cost for Scenario A and Scenario B
In Figure 6, the total social cost of scenario A is marked with the solid line, and the total social cost of scenario B for different values of is marked with the dotted line. In scenario B, the total social cost shows two different trends with the increase in accessorial parking capacity . (i) When (vehicles) (i.e., ), the total social cost decreases with the increase in the accessorial parking capacity . Regardless of the value of the dispersion of the shared parking spaces, the total social cost of scenario B is consistently larger than the total social cost of scenario A; and (ii) when (vehicles) (i.e., ), the total social cost of scenario B exhibits a parabolic trend of decreasing and then increasing with the increase in accessorial parking capacity . Whether the total social cost of scenario B appears to be lower than that of scenario A at this time is affected by the dispersion degree of the shared parking spaces distribution. From Proposition 1, (i) when (i.e., ), and the walking speed of adults is 5 km/h, and the interval between two adjacent parking spaces is about 12.5 m. At this moment, the total social cost is always higher than the total social cost in scenario A. Therefore, from the perspective of minimizing social travel cost, we should not install shared parking spaces with an average walking interval greater than 12.5 m; (ii) when , (i.e., ), there exists a scenario B where the total social cost of introducing shared parking is lower than that of scenario A. Taking as an example, the total social cost reaches the lowest value of 1495 yuan in scenario B with the number of accessorial parking spaces being 127 vehicles, which is 6.5% optimized compared to scenario A. Hence, the numerical example verifies Proposition 1.
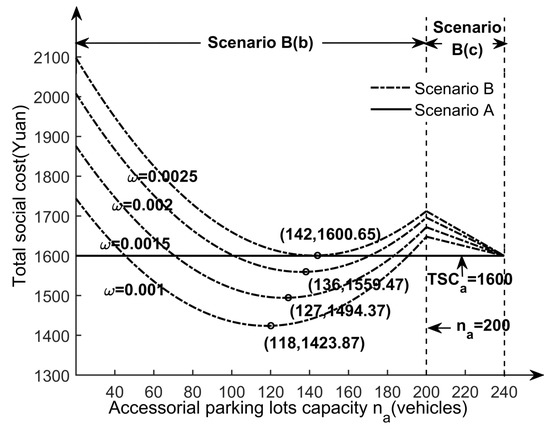
Figure 6.
Comparison of total social cost for scenario A and scenario B with different values of .
Evidently, the dispersion of shared parking spaces has a significant impact on the total travel cost. First of all, when the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot is small, it is feasible to set up shared parking as a supplementary measure, in which case reasonable fees and a compact layout of shared parking spaces can significantly reduce the total social cost. The more compact the layout of shared parking spaces, i.e., the smaller the average distance between parking spaces, the more the shared parking spaces contribute to reducing the total social cost.
6.2. Comparative Analysis of Total Queue Time in Scenario A and Scenario B
With the management objective of minimizing the queue time of the system, we first analyze how to adjust the shared parking fee to achieve the optimal travel pattern under scenario B with different accessorial parking capacities, and then compare the optimal travel pattern of scenario B with that of scenario A. We also discuss the optimal allocation and layout of shared parking spaces under this management objective with respect to the variation of the dispersion of shared parking spaces ().
6.2.1. Analysis of the Optimal Travel Mode for Scenario B with the Lowest Total Queue Time
With the shortest total queue time for commuters as the management objective, the impact of shared parking fee on the total queue time for commuters with different accessorial parking capacities in scenario B is analyzed by randomly selecting the accessorial parking capacity with , and the effect of different shared parking fee on the total queue time for commuters in the system is shown in Figure 7.
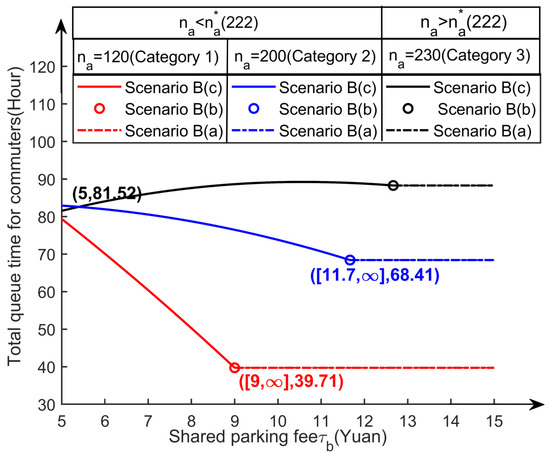
Figure 7.
Impact of shared parking fee on total queue time in scenario B with different accessorial parking capacities.
As can be seen from Figure 7 and Table 5, for category 1, when (vehicles) (), the shortest total queue time is obtained in scenario B(a) or scenario B(b) (as shown by the red circles and dotted lines in Figure 7), and the optimal shared parking fee is greater than or equal to 9 yuan, it results in a shortest total queue time of 39.71 h for the commuter; in category 2, when (vehicles) (), the shortest total queue time is obtained in scenario B(a) or scenario B(b) (as shown by the black circles and dotted lines in Figure 7), and the optimal shared parking fee is greater than or equal to 11.7 yuan, and the shortest total queue time for commuters is 68.41 h, which is 28.7 h more than the total queue time in category 1, i.e., 72.27% longer; for category 3, when (vehicles) (), the optimal travel pattern in scenario B is obtained in the B(c-3) of scenario B(c) (as shown by the black solid line in Figure 7), and the corresponding optimal shared parking fee is 5 yuan, and the total queue time of commuters is 81.52 yuan, which is 105.29% more than that of category 1. Therefore, the numerical example verifies Lemma 2.

Table 5.
Optimal travel patterns for different accessorial parking capacities under scenario B (with the shortest total queue time for commuters as the management objective).
Consequently, the fewer the number of parking spaces in an accessorial parking lot, the more effective the shared parking can be in reducing traffic congestion, i.e., reducing the average queue time, and even reducing the total queue time by more than half. When setting shared parking fee in terms of the shortest total queue time for commuters, the optimal fee tends to increase and then decrease as the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot increases. When the capacity of the accessorial parking lot is small (as shown by the red and blue lines in Figure 7), it is recommended that the shared parking fee be higher than that of the accessorial parking lot, but when the shared parking fee is too large, there is no impact on the total queue time of commuters regardless of the change in shared parking fee; when the capacity of the accessorial parking lot is larger (as shown by the black line in Figure 7), it is suggested that shared parking fee be reduced to at least equal the accessorial parking fee. Accordingly, a reasonable shared parking fee can be set in terms of the capacity of different accessorial parking spaces in order to minimize the queue time on the road, improve the efficiency of road utilization and reduce the congestion degree of the road.
6.2.2. Comparative Analysis of Total Queue Time of Commuters in Scenario A and Scenario B
The dotted lines in Figure 8 demonstrate the trend of the total queue time of commuters in scenario B as the capacity of the accessorial parking lot increases for different values of (the dispersion of the shared parking spaces), while the solid lines show the total queue time of commuters in scenario A. There are two cases bounded by (vehicles): (i) when the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot is greater than 219 vehicles, the total queue time in the system in scenario B is usually higher than that in scenario A, and (ii) when the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot is less than 219 vehicles, the total queue time in scenario B is constantly lower than that in scenario A. Moreover, as increases, the total queue time of commuters on the road decreases, which implies that the more discrete the distribution of shared parking spaces is, the more it contributes to reducing congestion on the road and relieving traffic pressure. For instance, when and (vehicles), the total queue time of commuters in the corresponding system is 29.06 h, which is 60.68% less than the queue time of 80 h in scenario A. It confirms Proposition 2.
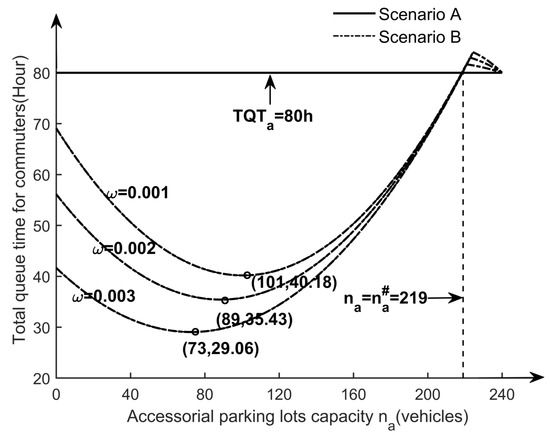
Figure 8.
Comparison of total queue time for scenario A and scenario B with different values of .
For the impact of the dispersion of shared parking layout on total queue time and total social cost, as a discrete shared parking layout reduces traffic congestion but increases the total social cost. In addition, it is necessary for the layout of shared parking spaces to take into account the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot as well. When there is a large shortage of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot, commuters compete for parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot, which leads to greater road congestion, and the shared parking spaces can effectively alleviate the competition for limited resources, thus reducing the total road queue time. Additionally, the more discrete the distribution of shared parking, the more it contributes to delaying the departure time of commuters, thus reducing traffic congestion. However, the unit travel cost of commuters and the total social cost are raised. Accordingly, the setting of shared parking spaces should be based on both the total social cost and the cost of road congestion.
6.3. Comparative Analysis of Total Social Cost and Total Queue Time under Different Management Objectives
From the previous analysis, we can conclude that the tendency of the shared parking fee () to the total social cost and the total queue time is the same, while the tendency of the shared parking dispersion () to the total social cost and the total queue time is opposite, thereby comparing the impact of different management objectives on the selection of critical parameters in this section. The accessorial parking capacity of (vehicles) is used to analyze the impact of the variation of shared parking fee and the dispersion of shared parking spaces layout on the total social cost and the total queue time, as shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10.
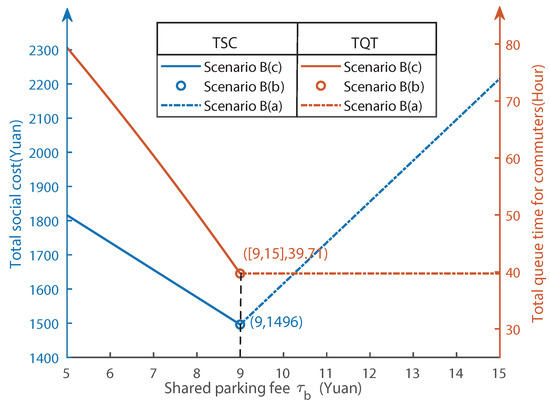
Figure 9.
Relationship between total social cost and total queue time with shared parking fee in scenario B.
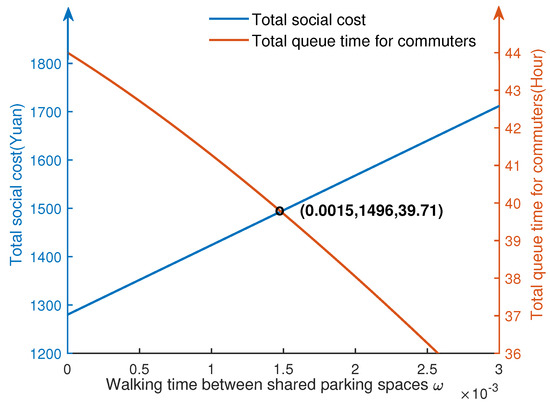
Figure 10.
Relationship between total social cost and total queue time for commuters with the discrete degree of space layout of shared parking spaces in scenario B.
When the dispersion of shared parking is constant, i.e., , and the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot (vehicles) (,), the relationship between total social cost and total queue time for commuters with shared parking fee is depicted in Figure 9. The total social cost and the total queue time are depicted by the blue and orange lines, respectively, both showing a decreasing trend when the shared parking fee is less than 9 yuan. However, when the fee is greater than 9 yuan, the total social cost increases rapidly while the total queue time remains constant. In Figure 9, scenario B(a), scenario B(b), and scenario B(c) are marked with dotted lines, circles, and solid lines separately. The minimum total social cost and the minimum total queue time both appear in scenario B(b), which are 1496 yuan and 39.71 h, respectively, corresponding to a shared parking fee of 9 yuan. The results indicate that shared parking fee is a key parameter that can be regulated to switch scenarios. Total social cost and total queue time can be reduced simultaneously until the shared parking fee is .
When the shared parking fee is constant, i.e., (yuan), as the dispersion of the layout of shared parking spaces () increases, the total social cost increases and the total queue time decreases, which are shown in blue and orange line separately in Figure 10. When h, the total social cost is 1496 yuan and the total queue time is 39.71 h, which refers to the optimal scenario for both the total social cost and road congestion management objectives. Further analysis showed that an overly dispersed shared parking layout results in excessive total social cost, while an overly compact shared parking layout leads to excessive total queue time.
7. Concluding Remarks
The shared parking walking time cost and shared parking fee are significant factors that affect the efficiency of shared parking utilization. Based on the principle of the bottleneck model, an optimal layout model of shared parking spaces is established in this study. The user equilibrium solution of the travel mode supplemented by shared parking spaces is solved when there are not sufficient parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot; the quantitative relationship among shared parking fee, the dispersion of the layout and the optimal travel pattern is proved when the total social cost and the total queue time are minimized as the management objectives, respectively. The rules and methods for setting the shared parking fee, the dispersion of the layout and the optimal travel pattern are proposed.
Firstly, the optimal setting of a shared parking lot should be based on the number of parking in the accessorial parking lot. When the gap of parking space in the accessorial parking lot is small, compact parking spaces should be selected for shared parking, and a parking fee can be set as low as possible to encourage commuters to use the shared parking spaces as a parking supplement. Moreover, managers can take appropriate price subsidies to guide and encourage shared parking, which helps to reduce the total social cost and the traffic congestion cost.
Secondly, when there is a large parking gap in the accessorial parking lot, the total social cost and the total queue time can be reduced significantly by increasing shared parking fee appropriately. However, the dispersion of shared parking spaces distribution has the opposite effect between total social cost and total queue time, namely, a more compact shared parking spaces distribution can reduce total social cost but greatly increase road traffic congestion. On the contrary, although the higher degree of dispersion of shared parking spaces increases the total social cost, it greatly alleviates traffic congestion. Therefore, the number of parking spaces in the accessorial parking lot and road traffic congestion conditions should be considered in the optimal layout of shared parking spaces.
Finally, the shared parking fee has a certain impact on the total social cost, nevertheless, when the value of is and in such condition the travel modes are scenario B(a) and scenario B(c), there is a pricing inertia region, that is, no matter how to adjust shared parking fee, it has no effect on the total social cost. At that time, it should be considered to change the dispersion degree of the layout of shared parking spaces to reduce the total travel cost. While taking the total queue time of commuters as the management objective, the travel pattern is scenario B(a) and scenario B(b), there is a pricing inertia region as well. In the meantime, road congestion can also be reduced by adjusting the dispersion degree of shared parking spaces reasonably.
In summary, this paper mainly studies the layout optimization of shared parking spaces when the capacity of the accessorial parking lot is insufficient. Two essential factors have been taken into consideration, one is the shared parking fee, the other is shared parking walking time cost. The conclusions of quantitative analysis have certain management suggestions for improving the use efficiency of existing shared parking projects and guiding the optimization of the layout of shared parking spaces.
However, there are some limitations in this paper: Urban transportation is a complex, stochastic and hybrid system, and the actual traffic and travel scenarios are even more complicated. For example, the importance of public transportation in daily commuting is ignored. Moreover, the parking duration of shared parking and parking reservations are not taken into account. In future studies, the public transport mode in the road network and the specific attributions of shared parking reservations should be further considered.
Author Contributions
The authors confirm contributions to the paper as follows: conceptualization, Y.J.; methodology, Y.J., X.L. and J.W.; validation, X.L. and X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.J., X.L. and H.J.; writing—review and editing, Y.J., H.J. and X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Fund Projects (20DZ1202703, 21DZ1203803).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Proof of Lemma 1
This section proves Lemma 1.
Based on the equilibrium solution of commuters for each travel mode obtained in Section 3, the total social cost is obtained as a segmental function of the difference in fee margin between the two types of parking lots, , as expressed in Equation (A1)
Since , the corresponding travel mode is the critical scenario B(b), when , the is continuous, where when the corresponding travel pattern is the total social cost function under scenario B(a), and when the corresponding travel pattern is the total social cost function under scenario B(c). The derivation of the total social cost function with respect to the fee of the two types of parking lots is shown in Equation (A2)
When , the first derivative is larger than zero, and there is no optimal solution for scenario B(a). Therefore, from the perspective of minimizing the total social cost, the margin between the two types of parking fee should not be too large, otherwise, the bottleneck capacity will be wasted and the total social cost will increase, hence only scenario B(b) and scenario B(c) are discussed here. When , the first derivative results need to be discussed situationally.
(i) When , since , the achievable travel patterns are scenario B(b) and scenario B(c-1), and the derivation result , so the optimal parking fee under the minimized total social cost is , and the corresponding optimal travel pattern is scenario B(b), as shown in Figure 3b;
(ii) When , similarly, since , the achievable travel modes are scenario B(b), scenario B(c-1), and the derivation result , the optimal parking fee is not unique, so the optimal parking fee under the minimized total social cost ranges from , which corresponds to the optimal travel pattern of scenario B(b) or scenario B(c-1), as shown in Figure 3b and scenario (c-1) of Figure 3c;
(iii) When , because , the travel pattern can be formed in scenario B(b) and scenario B(c), and the derivation result , the optimal parking fee under the minimized total social cost is . When , the corresponding optimal travel pattern is scenario B(c-1), as shown in scenario (c-1) of Figure 3c; when , the corresponding optimal travel pattern is scenario B(c-2), as shown in scenario (c-2) of Figure 3c; when , the corresponding optimal travel pattern is scenario B(c-3), as shown in scenario (c-3) of Figure 3c.
Appendix A.2. Proof of Proposition 1
This section proves Proposition 1.
According to the optimal travel pattern of scenario B derived from Lemma 1, when , it is known that the total social cost of scenario B under category 2 and category 3 is always higher than the total social cost of scenario A, as shown in Equation (A3)
For category 1, the total social cost in category 1 is shown in Equation (A4)
It is simple to prove that is a convex function with respect to , which obtains the optimal value at , and the corresponding is shown in Equation (A5)
The difference between the total social cost of scenario B(a) and the total social cost of scenario A yields , as shown in Equation (A6)
When , , the optimal travel mode is scenario A; when , , the optimal travel mode corresponds to scenario B(b).
Appendix A.3. Proof of Lemma 2
This section proves Lemma 2.
Here, according to the commuter equilibrium solution, the queue time under different conditions of scenario B can be derived, and from the travel pattern diagram under different conditions of Figure 3, it can be concluded that the total queue time () of commuters in the system can be expressed as a segmented function of the difference between the two types of parking fee, as shown in Equation (A7)
where the expressions of , , are shown in Equations (A8)–(A10)
Since when , and when , TQT can be obtained continuously. The first partial derivatives of and with respect to the difference between the two types of parking fee are obtained as shown in Equations (A11) and (A12)
The second derivative is further derived as shown in Equations (A13) and (A14)
The second derivative results in less than zero to obtain and as concave functions with respect to the difference in fee between the two types of parking lots, with maximum values at the stationary points where the first derivative equals zero, while the minimum system commuter queue time will depend on the comparison of the boundary solutions of and .
Let the minimum system queue time , when , the expression of the minimum system queue time is shown in Equation (A15)
or , the expression for the minimum system queue time is shown in Equation (A16)
The value of can be solved by the iterative method. Let there exist an accessorial parking capacity , so that , and the optimal travel pattern is selected at the left or right boundary. If the left side of the equation is smaller than the right side, the optimal travel mode is obtained in scenario B(c-3), and the value of should be reduced. On the contrary, increase the value of until both sides of the equation are identical to obtain the final equilibrium solution.
Appendix A.4. Proof of Proposition 2
This section proves Proposition 2.
The total queue time of commuters in the system of scenario A is shown in Figure 2, and the total queue time area in the system is the triangular area enclosed by ABC. According to the relevant parameters, the total queue time of commuters in the system () can be expressed as shown in Equation (A17)
From the total queue time of commuters under scenario B with optimal fee in Lemma 2, when , it follows that the queue time of scenario B with is always higher than that of scenario A, i.e., ; when , .
Similar to the solution of , can also be obtained by an iterative method. Let there exist an accessorial parking capacity of , corresponding to , when , , conversely, when , . It is summarized in the case shown in Table A1.

Table A1.
Optimal travel pattern selection within the capacity range of different accessorial parking lots .
Table A1.
Optimal travel pattern selection within the capacity range of different accessorial parking lots .
| Optimal Travel Pattern for Scenario B | Optimal Travel Pattern under Scenario A and Scenario B Comparison | |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario B(a) or Scenario B(b) | Scenario B(a) or Scenario B(b) | |
| Scenario B(a) or Scenario B(b) | Scenario A | |
| Scenario B(c-3) | Scenario A |
1 The optimal travel pattern is chosen with the objective of minimizing the total queue time of commuters in the system.
References
- Ortega, J.; Moslem, S.; Palaguachi, J.; Ortega, M.; Campisi, T.; Torrisi, V. An integrated multi criteria decision making model for evaluating park-and-ride facility location issue: A case study for cuenca city in ecuador. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, T.; Caselli, B.; Rossetti, S.; Torrisi, V. The evolution of sustainable mobility and urban space planning: Exploring the factors contributing to the regeneration of car parking in living spaces. Transp. Res. Procedia 2022, 60, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.H.K.; Liu, C.Y.; Sahoo, J.; Jin, M.H.; Lin, S.H. Agile urban parking recommendation service for intelligent vehicular guiding system. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2014, 6, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, V.; Ignaccolo, M.; Inturri, G. Innovative transport systems to promote sustainable mobility: Developing the model architecture of a traffic control and supervisor system. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2018, 622–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman, T. Parking Management Principles, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. A parking space allocation method to make a shared parking strategy for appertaining parking lots of public buildings. Sustainability 2019, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Long, X.; Wang, J.; He, L. Research on parking sharing strategies considering user overtime parking. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q. Floating charge method based on shared parking. Sustainability 2019, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.; Guan, H.; Wei, H.; Liu, S. Mathematical modeling and heuristic approaches to optimize shared parking resources: A case study of Beijing, China. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2021, 9, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Wu, D.; Liu, H. Bi-level programming model for resource-shared parking lots allocation. Transp. Lett. 2019, 12, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Waller, S.T. On integrating carsharing and parking sharing services. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2020, 142, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Dong, J.; Lai, Z.; Feng, Q. Optimal allocation of shared parking spaces for hospital parkers considering parking choice behavior under bounded rationality. Transp. Lett. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.S.; Huang, H.J.; Guo, R.Y.; Xiong, F. Linear location-dependent parking fees and integrated daily commuting patterns with late arrival and early departure in a linear city. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2021, 150, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. An equilibrium analysis of commuter parking in the era of autonomous vehicles. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 92, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Peng, B.; Dai, L.; Chen, Y. Parking demand forecasting of urban comprehensive development blocks involving shared parking and location conditions. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Transportation Engineering, American Society of Civil Engineers, Chengdu, China, 23–25 July 2011; pp. 829–834. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.X.; Cheng, M.; Kong, X.T.R.; Yang, H.; Huang, G.Q. Private parking slot sharing. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2016, 93, 596–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Guan, H.; Wang, P. Data-driven robust optimal allocation of shared parking spaces strategy considering uncertainty of public users’ and owners’ arrival and departure: An agent-based approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 24182–24195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Chu, F.; Saidani, N.; Chen, H.; Zhou, W. IoT-based location and quality decision-making in emerging shared parking facilities with competition. Decis. Support Syst. 2020, 134, 113301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, J. A simple reservation and allocation model of shared parking lots. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 71, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangbin, N.; Zhenzhou, Y.; Zhenyu, H.; Yang, Y. A novel reservation-based allocation mechanism of private parking slots sharing. In Proceedings of the ASCE International Conference on Transportation and Development (ASCE ICTD), Seattle, DC, USA, 26–29 May 2020; pp. 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Cai, X.; Ni, D.; Chu, F.; He, H. Two-stage matching-and-scheduling algorithm for real-time private parking-sharing programs. Comput. Oper. Res. 2021, 125, 105083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.-J.; Guan, H.; Wang, P.; Shahinpoor, N. Analysis of parking cruising behaviour and parking location choice. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2020, 43, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Chien, S.; Hu, D. Optimizing coordinated transfer with probabilistic vehicle arrivals and passengers’ walking time. J. Adv. Transp. 2017, 50, 2306–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Chen, Q. Model for public car park layout based on dynamic multiperiodic parking demands. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 04018031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, Y.; Kuwahara, M. Scheduling preferences, parking competition, and bottleneck congestion: A model of trip timing and parking location choices by heterogeneous commuters. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 117, 102677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amihai, G.; Esko, N. Parking fees and congestion. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 1992, 22, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, H.M. The economics of parking provision for the morning commute. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 17, 612–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, Z.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, H.M. Managing morning commute traffic with parking. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2012, 46, 894–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. On the morning commute problem with bottleneck congestion and parking space constraints. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2013, 58, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, F.; Dixit, V. A New Flexible Parking Reservation Scheme for the Morning Commute under Limited Parking Supplies. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2021, 21, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.Y.; Tian, L.J.; Wang, D.Z.W. Multi-modal morning commute with endogenous shared autonomous vehicle penetration considering parking space constraint. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 151, 102354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Huang, H.J. Improving travel efficiency by parking permits distribution and trading. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2011, 45, 1018–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, T.; Wada, K. Tradable network permits: A new scheme for the most efficient use of network capacity. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2017, 79, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, L.L.; Liu, T.L.; Huang, H.J. Tradable permit schemes for managing morning commute with carpool under parking space constraint. Transportation 2019, 48, 1563–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickrey, W.S. Congestion theory and transport investment. Am. Econ. Rev. 1969, 59, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, A. Spatial competition between parking garages and downtown parking policy. Transp. Policy 2006, 13, 458–469. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, A.; Andre, d.P.; Robin, L. A temporal and spatial equilibrium analysis of commuter parking. North-Holland 1991, 45, 884. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. Analysis of the time-varying pricing of a bottleneck with elastic demand using optimal control theory. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 1997, 31, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, E.J.; Daganzo, C.F. Morning commute with competing modes and distributed demand: User equilibrium, system optimum, and pricing. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2012, 46, 1519–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Palma, A.; Lindsey, R.; Monchambert, G. The economics of crowding in rail transit. J. Urban Econ. 2017, 101, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, K.A. The scheduling of consumer activities: Work trips. Am. Econ. Rev. 1982, 72, 467–479. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Xue, Y.; Long, J.; Gao, Z. A single-step-toll equilibrium for the bottleneck model with dropped capacity. Transp. B Transp. Dyn. 2014, 4, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.D. Pareto improvements from Lexus Lanes: The effects of pricing a portion of the lanes on congested highways. J. Public Econ. 2018, 158, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.C.; Lam, W.H.K.; Wong, S.C. Bottleneck model revisited: An activity-based perspective. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2014, 68, 262–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.C.; Zhang, L. The two-mode problem with bottleneck queuing and transit crowding: How should congestion be priced using tolls and fares? Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2020, 138, 46–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).