Bio-Based Products from Mediterranean Seaweeds: Italian Opportunities and Challenges for a Sustainable Blue Economy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Global Sustainable Bioeconomic Framework
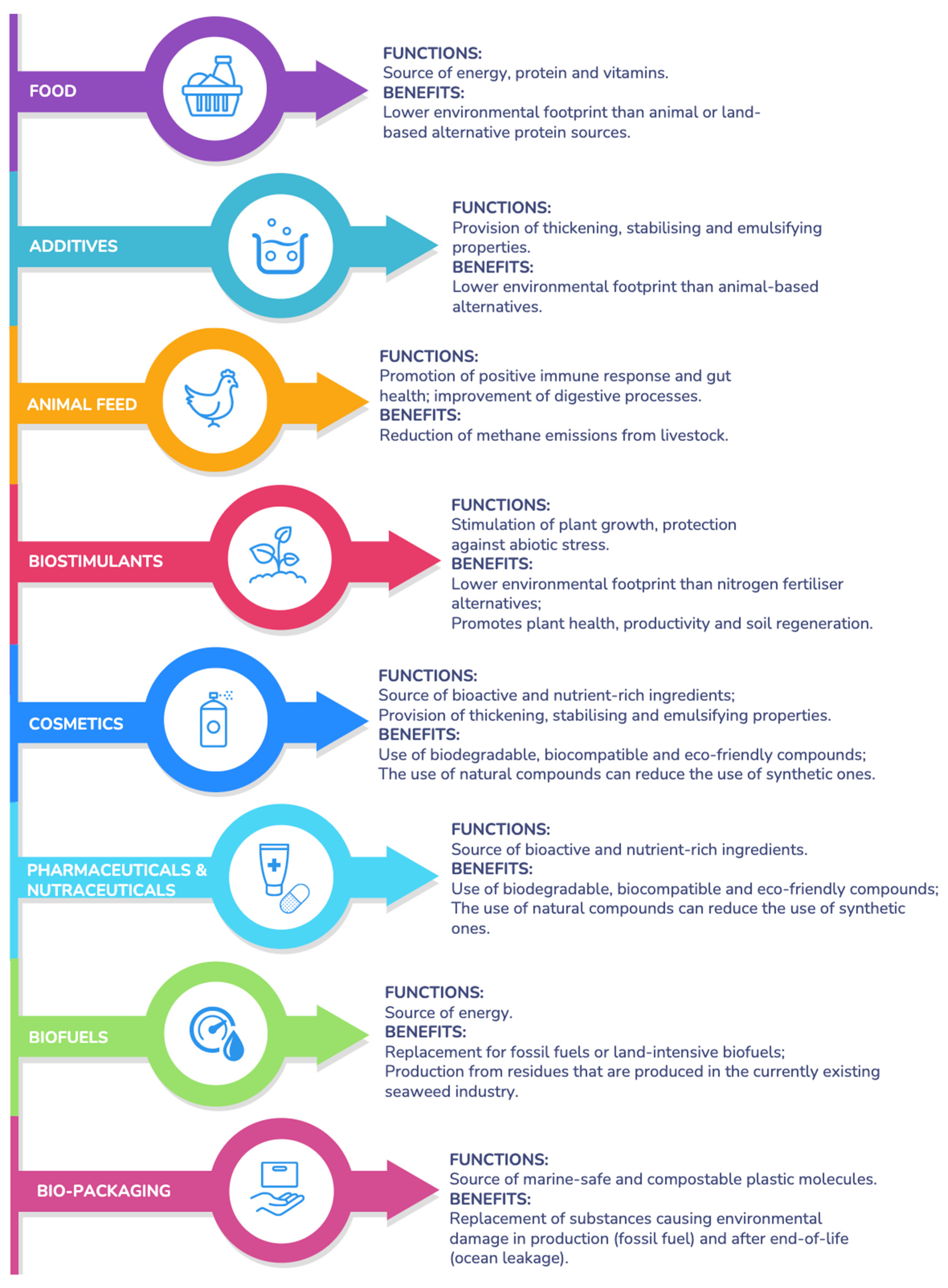
3. The Seaweed Effectiveness: From Ecological Functions to Bioeconomy Contribution
4. Seaweed Research, Production and Use in the Mediterranean Basin
5. Current Status of Seaweeds Production and Research in Italy
5.1. Biodiversity and Traditional Use of Seaweeds
5.2. Research, Harvesting and Industrial Activity of Seaweeds
5.3. Italy’s Commitment to Seaweed Research Projects in the Blue Economy
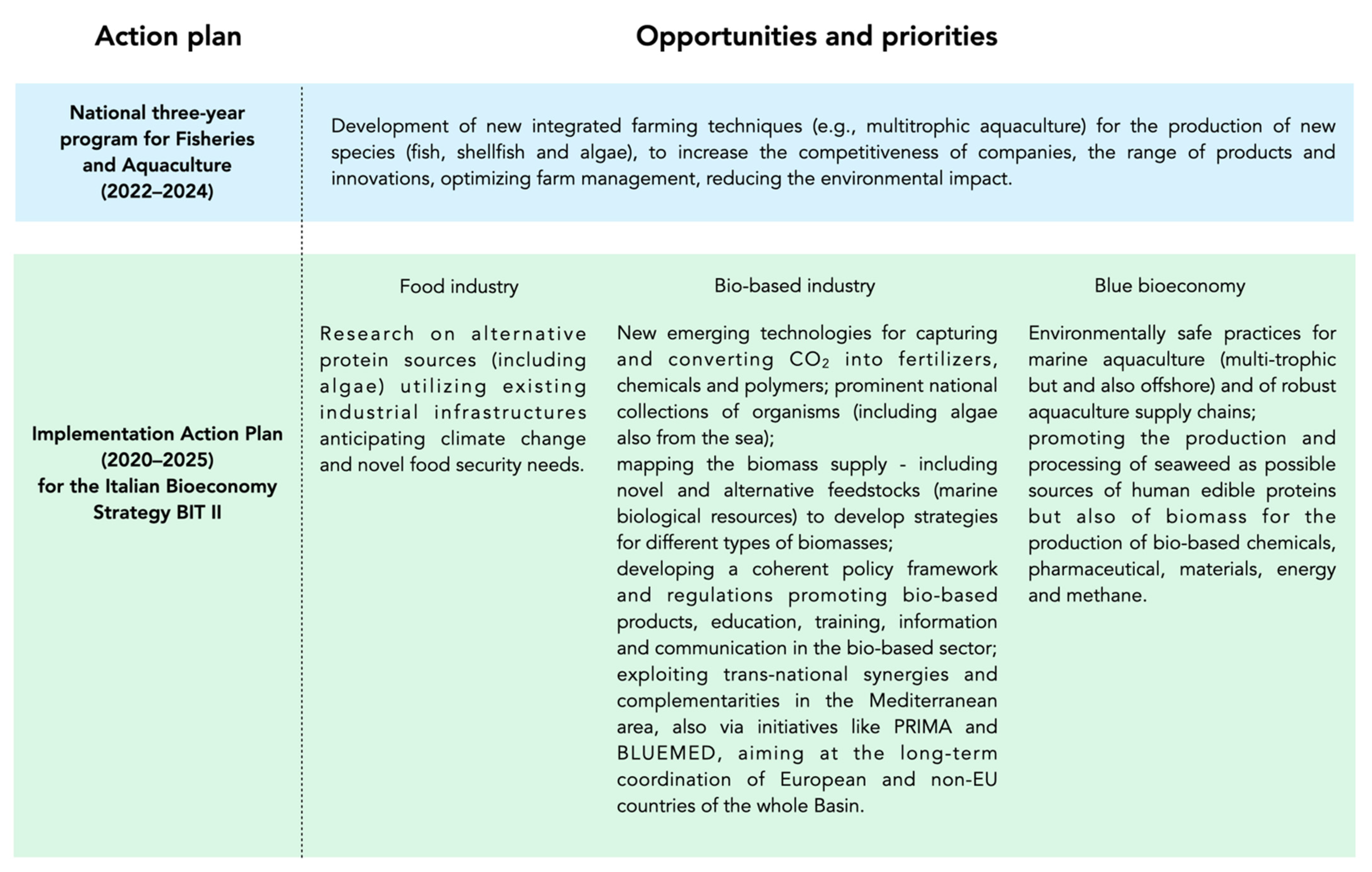
6. European and Italian Strategies and Regulations on Seaweed Bioeconomy
7. Gaps and Perspectives of the Seaweed Based Bioeconomy in Italy
7.1. Research and Development
7.2. Economy
7.3. Resource Management and Conservation
8. Final Remarks
- -
- to invest in research on seaweed biology and farming technologies, also increasing synergy between research and industry;
- -
- to support the production of autochthonous species, which are recognized for their uses, promoting a new seaweed-based supply chain;
- -
- to combine correct environmental management of NISs with economic opportunities;
- -
- to put in place conservation and restoration strategies for seaweeds within MSP with the aim of creating a real, sustainable supply chain; those strategies should include actions of co-participation to promote social and stakeholder acceptance.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Wetlands and Water Synthesis: A Report of the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 68. ISBN 978-1-56973-597-8. [Google Scholar]
- Danley, B.; Widmark, C. Evaluating conceptual definitions of ecosystem services and their implications. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 126, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. European Climate, Infrastructure and Environment Executive Agency. Sustainability Criteria for the Blue Economy: Main Report; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2021; ISBN 978-92-9460-569-6. [Google Scholar]
- Guerry, A.D.; Polasky, S.; Lubchenco, J.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Daily, G.C.; Griffin, R.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Bateman, I.J.; Duraiappah, A.; Elmqvist, T.; et al. Natural capital and ecosystem services informing decisions: From promise to practice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7348–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Directorate-General for Maritime Affairs and Fisheries. Blue Growth Opportunities for Marine and Maritime Sustainable Growth: Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2012; ISBN 978-92-79-25529-8. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Innovation in the Blue Economy: Realising the Potential of Our Seas and Oceans for Jobs and Growth, Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, M.G.; Clemence, M.; McDermott, G.R.; Costello, C.; Gaines, S.D. Five Rules for Pragmatic Blue Growth. Mar. Policy 2016, 87, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament, Council of the European Union Regulation. (EU) 2021/240 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 10 February 2021 Establishing a Technical Support Instrument; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bio-Based Industries Consortium. The European Circular Economy Package—Position of the Bio-Based Industries Consortium. 2015. Available online: http://biconsortium.eu/sites/biconsortium.eu/files/downloads/Biobased_Industries_position_EU_CircularEconomyPackage_NOV2015.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Ellen Macarthur Foundation. Growth within: A Circular Economy Vision for a Competitive Europe. 2015. Available online: https://ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/publications (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions Innovating for Sustainable Growth: A Bioeconomy for Europe; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission, Directorate-General for Environment. A New Circular Economy Action Plan for a Cleaner and More Competitive Europe; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, P.; Levrel, H.; Viard, F.; Frangoudes, K.; Girard, S.; Scemama, P. Ecosystem Services Assessment and Compensation Costs for Installing Seaweed Farms. Mar. Policy 2016, 71, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, M.; Charrier, B.; Araujo, R.; Holdt, S.L.; Bertrand, J.; Rebours, C. PEGASUS Phycomorph Guidelines Seaweed Aquaculture Cost Action; Barbier, M., Charrier, B., Eds.; PHYCOMORPH COST ACTION FA1406: Roscoff, France, 2019; p. 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, H.K.; Milewski, I.; Fast, J.; Kay, L.; Worm, B. Ecosystem-based management of seaweed harvesting. Bot. Mar. 2019, 62, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineur, F.; Arenas, F.; Assis, J.; Davies, A.J.; Engelen, A.H.; Fernandes, F.; Malta, E.; Thibaut, T.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vaz-Pinto, F.; et al. European seaweeds under pressure: Consequences for communities and ecosystem functioning. J. Sea Res. 2015, 98, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lei, J.; Huguenard, K.; Fredriksson, D.W. Wave attenuation by suspended canopies with cultivated kelp (Saccharina latissima). Coast. Eng. 2021, 168, 103947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.L.; Konlechner, T.M.; Ghisalberti, M.; Swearer, S.E. From grey to green: Efficacy of eco-engineering solutions for nature-based coastal defence. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 1827–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, H.E.; Afflerbach, J.C.; Frazier, M.; Halpern, B.S. Blue Growth potential to mitigate climate change through seaweed offsetting. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 3087–3093.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Wu, J.; Xiao, X.; Bruhn, A.; Krause-Jensen, D. Can seaweed farming play a role in climate change mitigation and adaptation? Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaku Canu, D.; Ghermandi, A.; Nunes, P.A.L.D.; Lazzari, P.; Cossarini, G.; Solidoro, C. Estimating the value of carbon sequestration ecosystem services in the Mediterranean Sea: An ecological economics approach. Glob. Environ. Change 2015, 32, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, A.E.; Chiozzini, V.G.; Braga, E.S.; Chow, F. Integrated Multi-Trophic farming system between the green seaweed Ulva lactuca, mussel, and fish: A production and bioremediation solution. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, F.; Ersanli, E.T. An ecofriendly approach for bioremediation of contaminated water environment: Potential contribution of a coastal seaweed community to environmental improvement. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2018, 20, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, A.; Stanley, A.; Ring, J. Hidden Champion of the Ocean: Seaweed as a Growth Engine for a Sustainable European Future. Seaweed for Europe: 2020. p. 59. Available online: Chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://www.seaweedeurope.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Seaweed_for_Europe-Hidden_Champion_of_the_ocean-Report.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- FAO. The Global Status of Seaweed Production, Trade and Utilization; Food & Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2018; Volume 124, p. 118. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L. A review of the nutrient composition of selected edible seaweeds. In Seaweed: Ecology, Nutrient Composition and Medicinal Uses; Pomin, V.H., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Coimbra, Portugal, 2011; pp. 15–47. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y. Bioactive Seaweeds for Food Applications: Natural Ingredients for Healthy Diets, 1st ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-12-813312-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, D.; Melo, T.; Rey, F.; Meneses, J.; Monteiro, F.L.; Helguero, L.A.; Abreu, M.H.; Lillebø, A.I.; Calado, R.; Domingues, M.R. Valuing bioactive lipids from green, red and brown macroalgae from aquaculture, to foster functionality and biotechnological applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñalver, R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Ros, G.; Amarowicz, R.; Pateiro, M.; Nieto, G. Seaweeds as a Functional Ingredient for a Healthy Diet. Mar Drugs 2020, 18, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, A.J. Medicinal and pharmaceutical uses of seaweed natural products: A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 16, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Jeon, Y.-J. Biological activities and potential cosmeceutical applications of bioactive components from brown seaweeds: A review. Phytochem. Rev. 2011, 10, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Kamthania, M.C.; Kumar, A. Bioactive compounds and properties of seaweeds: A review. Open Access Libr. J. 2014, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.; Flórez-Fernández, N.; Domínguez, H. Integral utilization of red seaweed for bioactive production. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, G.P.; Tavares, W.R.; Sousa, P.M.C.; Pagès, A.K.; Seca, A.M.L.; Pinto, D.C.G.A. Seaweed secondary metabolites with beneficial health effects: An overview of successes in in vivo studies and clinical trials. Mar. Drugs 2019, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Nayak, R.; Patra, S.; Jit, B.P.; Ragusa, A.; Jena, M. Bioactive metabolites from marine algae as potent pharmacophores against oxidative stress-associated human diseases: A comprehensive review. Molecules 2021, 26, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinteus, S.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Alves, C.; Neugebauer, A.; Silva, J.; Thomas, O.P.; Botana, L.M.; Gaspar, H.; Pedrosa, R. Marine invasive macroalgae: Turning a real threat into a major opportunity—The biotechnological potential of Sargassum muticum and Asparagopsis armata. Algal Res. 2018, 34, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunandan, B.L.; Vyas, R.V.; Patel, H.K.; Jhala, Y.K. Perspectives of seaweed as organic fertilizer in agriculture. In Soil Fertility Management for Sustainable Development; Panpatte, D.G., Jhala, Y.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 267–289. ISBN 9789811359033. [Google Scholar]
- Spagnuolo, D.; Russo, V.; Manghisi, A.; Di Martino, A.; Morabito, M.; Genovese, G.; Trifilò, P. Screening on the presence of plant growth regulators in high biomass forming seaweeds from the Ionian Sea (Mediterranean Sea). Sustainability 2022, 14, 3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battacharyya, D.; Zamani Babgohari, M.; Rathor, P.; Prithiviraj, B. Seaweed extracts as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, P.S.; Pahalawattaarachchi, V.; Ranaweera, K.K.D.S. Effect of Seaweed Liquid Fertilizer on Plant Growth of Capsicum annum. Discovery 2016, 52, 723–734. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. World Fertilizer Trends and Outlook to 2019; Food & Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2015; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Kraan, S. Mass-cultivation of carbohydrate rich macroalgae, a possible solution for sustainable biofuel production. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2013, 18, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suutari, M.; Leskinen, E.; Fagerstedt, K.; Kuparinen, J.; Kuuppo, P.; Blomster, J. Macroalgae in biofuel production. Phycol. Res. 2015, 63, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, D.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Macroalgae for biofuels production: Progress and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, R.; Liu, J.J. A strategy for advanced biofuel production and emission utilization from macroalgal biorefinery using superstructure optimization. Energy 2021, 221, 119883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigljević, B.; Liu, J.; Lim, H. Green energy from brown seaweed: Sustainable polygeneration industrial process via fast pyrolysis of S. japonica combined with the Brayton cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 195, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.-T.; Bui, X.-T.; Tran, D.P.H.; Hao Ngo, H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hoang, T.-K.-D.; Nguyen, P.-T.; Nguyen, H.H.; Vo, T.-K.-Q.; Lin, C.; et al. Current application of algae derivatives for bioplastic production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikołajczyk, T.; Wołowska-Czapnik, D. Multifunctional alginate fibres with anti-bacterial properties. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2005, 13, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, M.A.; Becherucci, M.E. Study of the potential use of the invasive marine algae Undaria pinnatifida in the preliminary development of a functional textile. J. Ind. Text. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadhiya, A.; Tyeb, S.; Rathore, K.; Verma, V. Agarose Bioplastic-based drug delivery system for surgical and wound dressings. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A. Sodium alginate solutions: Correlation between rheological properties and spinnability. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 13, 8034–8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axpe, E.; Oyen, M.L. Applications of alginate-based bioinks in 3D bioprinting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhsha, S.; Mbeleck, R.; Xu, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, W.; Xing, M. 3D bioprinting for biomedical devices and tissue engineering: A review of recent trends and advances. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Poza, S.; Leandro, A.; Cotas, C.; Cotas, J.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. The evolution road of seaweed aquaculture: Cultivation technologies and the industry 4.0. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Aguzzi, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Bianchi, C.N.; Corbera, J.; Dailianis, T.; et al. The biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, patterns, and threats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktari, L.; Chebil Ajjabi, L.; De Clerck, O.; Gómez Pinchetti, J.L.; Rebours, C. Seaweeds as a promising resource for blue economy development in Tunisia: Current state, opportunities, and challenges. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 34, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, F.L.; Flores-Moya, A.; Vergara, J.J.; Korbee, N.; Hernández, I. Autochthonous seaweeds. In The Mediterranean Sea; Goffredo, S., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 123–135. ISBN 978-94-007-6703-4. [Google Scholar]
- Korpinen, S.; Klančnik, K.; Peterlin, M.; Nurmi, M.; Laamanen, L.; Zupančič, G.; Popit, A.; Murray, C.; Harvey, T.; Andersen, J.H.; et al. Multiple Pressures and Their Combined Effects in Europe’s Seas; ETC/ICM Technical Report 4/2019; European Topic Centre on Inland, Coastal and Marine Waters: Magdeburg, Germany, 2019; 165p. [Google Scholar]
- Union for the Mediterranean. Towards a Sustainable Blue Economy in the Mediterranean Region. 2021, p. 99. Available online: https://www.euneighbours.eu/en/south/stay-informed/publications/towards-sustainable-blue-economy-mediterranean-region-2021-edition (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Salvador, N.; Gómez Garreta, A.; Lavelli, L.; Ribera, M.A. Antimicrobial activity of Iberian macroalgae. Sci. Mar. 2007, 71, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, N.; Faize, L.; Faize, M.; Nortes, M.D.; Bernardeau, J.; Fernandez, J.M.R.; Burgos, L. Towards the valorization of the invasive seaweeds Caulerpa cylindracea and Asparagopsis taxiformis in the Mediterranean Sea: Applications for in vitro plant regeneration and crop protection. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, M.; Orhan, I.E.; Eren, G.; Okudan, E.S.; Estep, A.S.; Bencel, J.J.; Tabanca, N. Insecticidal activity of forty-seven marine algae species from the Mediterranean, Aegean, and Sea of Marmara in connection with their cholinesterase and tyrosinase inhibitory activity. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 143, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibtissam, C.; Hassane, R.; José, M.-L.; Francisco, D.S.J.; Antonio, G.V.J.; Hassan, B.; Mohamed, K. Screening of antibacterial activity in marine green and brown macroalgae from the coast of Morocco. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Stabili, L.; Acquaviva, M.I.; Angilè, F.; Cavallo, R.A.; Cecere, E.; Del Coco, L.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Gerardi, C.; Narracci, M.; Petrocelli, A. Screening of Chaetomorpha linum lipidic extract as a new potential source of bioactive compounds. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radman, S.; Cikoš, A.-M.; Flanjak, I.; Babić, S.; Čižmek, L.; Šubarić, D.; Čož-Rakovac, R.; Jokić, S.; Jerković, I. Less polar compounds and targeted antioxidant potential (in vitro and in vivo) of Codium adhaerens C. Agardh 1822. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerković, I.; Kranjac, M.; Marijanović, Z.; Šarkanj, B.; Cikoš, A.-M.; Aladić, K.; Pedisić, S.; Jokić, S. Chemical diversity of Codium bursa (Olivi) C. Agardh headspace compounds, volatiles, fatty acids and insight into its antifungal activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trikka, F.; Israel, P.; Koukaras, K.; Argiriou, A. Biochemical characterization of eight Greek algae as candidate species for local seaweed cultivation. Bot. Mar. 2021, 64, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Said, G.F.; El-Sikaily, A. Chemical composition of some seaweed from Mediterranean Sea coast, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 6089–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milović, S.; Kundakovi, T.; Ma, V.; Anti, J.; Grozdani, A.; Stankovi, I.; Stanojkovi, T. Anti α-glucosidase, antitumour, antioxidative, antimicrobial activity, nutritive and health protective potential of some seaweeds from the Adriatic coast of Montenegro. Farmacia 2017, 65, 731–740. [Google Scholar]
- Trentin, R.; Custódio, L.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Moschin, E.; Sciuto, K.; da Silva, J.P.; Moro, I. Exploring Ulva australis Areschoug for possible biotechnological applications: In vitro antioxidant and enzymatic inhibitory properties, and fatty acids contents. Algal Res. 2020, 50, 101980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnabris, K.J.; Elmanama, A.A.; Chihadeh, W.N. Antibacterial activity of four marine seaweeds collected from the coast of Gaza strip, Palestine. Mesopot. J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 28, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, B. Antibacterial activities of methanolic extracts of different seaweeds from Iskenderun Bay, Turkey. Int. J. Second. Metab. 2021, 8, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosanić, M.; Ranković, B.; Stanojković, T. Biological activities of two macroalgae from Adriatic coast of Montenegro. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, M.N.; El-Sayed, A.A.M.; Abd El Latif, H.H.; El-Naggar, N.A.; Shams El-Din, N.G.; Tadros, H.R.Z. Chemical characterization and biochemical activity of polysaccharides isolated from egyptian Ulva fasciata Delile. Oceanologia 2022, 64, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.E.H.; Aboshady, A.M.; Elshobary, M.E. Production and characterization of antimicrobial active substance from some macroalgae collected from Abu-Qir Bay Alexandria, Egypt. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 6847–6858. [Google Scholar]
- Azaza, M.S.; Mensi, F.; Ksouri, J.; Dhraief, M.N.; Brini, B.; Abdelmouleh, A.; Kraïem, M.M. Growth of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) fed with diets containing graded levels of green algae Ulva meal (Ulva rigida) reared in Geothermal waters of Southern Tunisia. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2008, 24, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El Azm, N.; Fleita, D.; Rifaat, D.; Mpingirika, E.Z.; Amleh, A.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Production of bioactive compounds from the sulfated polysaccharides extracts of Ulva lactuca: Post-extraction enzymatic hydrolysis followed by ion-exchange chromatographic fractionation. Molecules 2019, 24, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, H.M.; El-Sheikh, M.A. Antioxidant activity and mineral composition of three Mediterranean common seaweeds from Abu-Qir Bay, Egypt. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.E.-H.A.; Hassanain, M.A.; Darwish, E.M.; Abdel-Rahman, E.H.; Sleem, S.H.; Shaapan, R.M. Molluscicidal effect of some red and green marine algae on Lymnaea natalensis. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2019, 23, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taskin, E.; Ozturk, M.; Kurt, O. Antibacterial activities of some marine algae from the Aegean Sea (Turkey). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6, 2746–2751. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.; Ktari, L.; Ben Redjem Romdhane, Y.; Aoun, B.; Sadok, S.; Boudabous, A.; El Bour, M. Antimicrobial fatty acids from green alga Ulva rigida (Chlorophyta). BioMed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3069595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlila, M.B.; Hichri, A.O.; Mahjoub, M.A.; Mighri, Z.; Mastouri, M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Padina pavonica and Enteromorpha sp. From the Tunisian Mediterranean coast. J. Coast. Life Med. 2017, 5, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazir, M.; Abuhassira, Y.; Robin, A.; Nahor, O.; Luo, J.; Israel, A.; Golberg, A.; Livney, Y.D. Extraction of proteins from two marine macroalgae, Ulva sp. and Gracilaria sp., for food application, and evaluating digestibility, amino acid composition and antioxidant properties of the protein concentrates. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 87, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, Y.; Batran, A. Lipid chemistry of green macroalgae Ulva sp. a potential resource for biotechnological applications in the Southern Mediterranean Sea coast, Alexandria shore, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2014, 18, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Redjem, Y.B.; Ktari, L.; Medhioub, A.; Romdhane, M.S.; Langar, H.; Bour, M.E. Antibacterial and algicidal properties of some brown seaweeds from Northern coasts of Tunisia. Vie Milieu 2013, 63, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Mhadhebi, L.; Laroche-Clary, A.; Robert, J.; Bouraoui, A. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiproliferative activities of organic fractions from the mediterranean brown seaweed Cystoseira sedoides. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 89, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, A.; Jouini, M.; Bel Haj Amor, H.; Mzoughi, Z.; Dridi, M.; Ben Said, R.; Bouraoui, A. phytochemical analysis and evaluation of the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antinociceptive potential of phlorotannin-rich fractions from three mediterranean brown seaweeds. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouafif, C.; Messaoud, C.; Boussaid, M.; Langar, H. Fatty acid profile of Cystoseira C. Agardh (Phaeophyceae, Fucales) species from the Tunisian coast: Taxonomic and nutritional assessments. Cienc. Mar. 2018, 44, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosanić, M.; Ranković, B.; Stanojković, T. Brown macroalgae from the Adriatic Sea as a promising source of bioactive nutrients. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalić Mekinić, I.; Šimat, V.; Botić, V.; Crnjac, A.; Smoljo, M.; Soldo, B.; Ljubenkov, I.; Čagalj, M.; Skroza, D. Bioactive phenolic metabolites from Adriatic brown algae Dictyota dichotoma and Padina pavonica (Dictyotaceae). Foods 2021, 10, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othmani, A.; Bouzidi, N.; Viano, Y.; Alliche, Z.; Seridi, H.; Blache, Y.; El Hattab, M.; Briand, J.-F.; Culioli, G. Anti-microfouling properties of compounds isolated from several mediterranean Dictyota spp. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viano, Y.; Bonhomme, D.; Camps, M.; Briand, J.-F.; Ortalo-Magné, A.; Blache, Y.; Piovetti, L.; Culioli, G. Diterpenoids from the Mediterranean brown alga Dictyota sp. evaluated as antifouling substances against a marine bacterial biofilm. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiboub, O.; Sifaoui, I.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Abderrabba, M.; Mejri, M.; Fernández, J.J.; Piñero, J.E.; Díaz-Marrero, A.R. Spiralyde A, an antikinetoplastid dolabellane from the brown alga Dictyota spiralis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Fuente, G.; Fontana, M.; Asnaghi, V.; Chiantore, M.; Mirata, S.; Salis, A.; Damonte, G.; Scarfì, S. The remarkable antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of the extracts of the brown alga Cystoseira amentacea var. stricta. Mar. Drugs 2020, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radman, S.; Čižmek, L.; Babić, S.; Cikoš, A.-M.; Čož-Rakovac, R.; Jokić, S.; Jerković, I. Bioprospecting of less-polar fractions of Ericaria crinita and Ericaria amentacea: Developmental toxicity and antioxidant activity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Khudir, R.; Ismail, G.A.; Diab, T. Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-tumor activities of Sargassum linearifolium and Cystoseira crinita from Egyptian Mediterranean coast. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 73, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdala-Díaz, R.T.; Cabello-Pasini, A.; Márquez-Garrido, E.; López-Figueroa, F. Intra-thallus variation of phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity, and phenolsulphatase activity in Cystoseira tamariscifolia (Phaeophyceae) from Southern Spain. Cienc. Mar. 2014, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerković, I.; Cikoš, A.-M.; Babić, S.; Čižmek, L.; Bojanić, K.; Aladić, K.; Ul’yanovskii, N.V.; Kosyakov, D.S.; Lebedev, A.T.; Čož-Rakovac, R.; et al. Bioprospecting of less-polar constituents from endemic brown macroalga Fucus virsoides J. Agardh from the Adriatic Sea and targeted antioxidant effects in vitro and in vivo (Zebrafish model). Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellimi, S.; Maalej, H.; Rekik, D.M.; Benslima, A.; Ksouda, G.; Hamdi, M.; Sahnoun, Z.; Li, S.; Nasri, M.; Hajji, M. Antioxidant, antibacterial and in vivo wound healing properties of laminaran purified from Cystoseira barbata seaweed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerzabi-Kanoun, K.; Belyagoubi-Benhammou, N. Antioxidant activity of brown seaweed Padina pavonica (L.) extracts from the Algerian Mediterranean coast. JNPRA 2021, 10, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bouhlal, R.; Riadi, H.; Martínez, J.; Bourgougnon, N. The antibacterial potential of the seaweeds (Rhodophyceae) of the Strait of Gibraltar and the Mediterranean coast of Morocco. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 6365–6372. [Google Scholar]
- Mofeed, J.; Deyab, M.; Mohamed, A.; Moustafa, M.; Negm, S.; El-Bilawy, E. Antimicrobial activities of three seaweeds extract against some human viral and bacterial pathogens. Biocell 2022, 46, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslin, C.; Lahaye, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Chermann, J.-C. In vitro anti-HIV activity of sulfated cell-wall polysaccharides from gametic, carposporic and tetrasporic stages of the Mediterranean red alga Asparagopsis armata. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhlal, R.; Riadi, H.; Bourgougnon, N. Antibacterial activity of the exctracts of Rhodophyceae from the Atlantic and the Mediterranean coasts of Morocco. JMBFS 2013, 9, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar]
- Hmani, I.; Ktari, L.; Ismail, A.; M’dallel, C.; El Bour, M. Assessment of the antioxidant and antibacterial properties of red algae (Rhodophyta) from the North coast of Tunisia. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2021, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saim, S.; Sahnouni, F.; Bouhadi, D.; Kharbouche, S. The antimicrobial activity of two marine red algae collected from Algerian West coast. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 7, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capillo, G.; Savoca, S.; Costa, R.; Sanfilippo, M.; Rizzo, C.; Lo Giudice, A.; Albergamo, A.; Rando, R.; Bartolomeo, G.; Spanò, N.; et al. New insights into the culture method and antibacterial potential of Gracilaria gracilis. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, R.; Acquaviva, M.; Stabili, L.; Cecere, E.; Petrocelli, A.; Narracci, M. Antibacterial activity of marine macroalgae against fish pathogenic Vibrio species. Open Life Sci. 2013, 8, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabili, L.; Acquaviva, M.I.; Biandolino, F.; Cavallo, R.A.; De Pascali, S.A.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Narracci, M.; Petrocelli, A.; Cecere, E. The lipidic extract of the seaweed Gracilariopsis longissima (Rhodophyta, Gracilariales): A potential resource for biotechnological purposes? New Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaballi, I.; Saad, H.B.; Bkhairia, I.; Cherif, B.; Kallel, C.; Boudawara, O.; Droguet, M.; Magné, C.; Hakim, A.; Amara, I.B. cytoprotective effects of the red marine alga Chondrus canaliculatus against maneb-induced hematotoxicity and bone oxidative damages in adult rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 184, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaballi, I.; Sallem, I.; Feki, A.; Cherif, B.; Kallel, C.; Boudawara, O.; Jamoussi, K.; Mellouli, L.; Nasri, M.; Amara, I.B. Polysaccharide from a Tunisian red seaweed Chondrus canaliculatus: Structural characteristics, antioxidant activity and in vivo hemato-nephroprotective properties on maneb induced toxicity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chérif, W.; Bour, M.E.; Yahia-Kefi, O.D.; Ktari, L. Screening de l’activité anti-microfouling d’algues vertes récoltées sur la côte nord tunisienne. Bull. Inst. Natn. Scien. Tech. Mer Salammbô 2011, 38, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Stabili, L.; Cecere, E.; Falzone, M.; Giangrande, A.; Laterza, F.; Licciano, M.; Notarangelo, M.; Petrocelli, A.; Portacci, G.; Santamaria, F.; et al. Un mangime innovativo da policheti e macroalghe per l’allevamento di stadi giovanili di Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus, 1758). Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2016, 23, 167–168. [Google Scholar]
- Chiboub, O.; Ktari, L.; Sifaoui, I.; López-Arencibia, A.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Mejri, M.; Valladares, B.; Abderrabba, M.; Piñero, J.E.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. In vitro amoebicidal and antioxidant activities of some Tunisian seaweeds. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 183, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Abotaleb, S.; Gheda, S.; Alam, N.; ELMehalawy, A. In vitro assessment of antimicrobial, antioxidant and anticancer activities of some marine macroalgae. Egypt. J. Bot. 2020, 60, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktari, L.; Guyot, M. An anti-inflammatory compound from the green alga Ulva rigida collected from Tunisian coasts. Electron. J. Nat. Subs. 2006, 1, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Yaich, H.; Garna, H.; Bchir, B.; Besbes, S.; Paquot, M.; Richel, A.; Blecker, C.; Attia, H. Chemical composition and functional properties of dietary fibre extracted by englyst and prosky methods from the alga Ulva lactuca collected in Tunisia. Algal Res. 2015, 9, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čagalj, M.; Skroza, D.; Razola-Díaz, M.d.C.; Verardo, V.; Bassi, D.; Frleta, R.; Generalić Mekinić, I.; Tabanelli, G.; Šimat, V. Variations in the composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Cystoseira compressa during seasonal growth. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheda, S.; Naby, M.A.; Mohamed, T.; Pereira, L.; Khamis, A. Antidiabetic and antioxidant activity of phlorotannins extracted from the brown seaweed Cystoseira compressa in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22886–22901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellimi, S.; Kadri, N.; Barragan-Montero, V.; Laouer, H.; Hajji, M.; Nasri, M. Fucans from a Tunisian brown seaweed Cystoseira barbata: Structural characteristics and antioxidant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 66, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Saad, H.; Kharrat, N.; Krayem, N.; Boudawara, O.; Boudawara, T.; Zeghal, N.; Ben Amara, I. Biological properties of Alsidium corallinum and its potential protective effects against damage caused by potassium bromate in the mouse liver. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3809–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Saïd, R.; Romdhane, M.S.; El Abed, A.; M’rabet, R. Temporal variation of some biometric parameters, agar-agar and quality of Gelidium spinosum (S.G. Gmelin) P.C. Silva (Rhodophyta, Rhodophyceae, Gelidiales) from Monastir coasts (Tunisia). Cah. Biol. Mar. 2011, 1, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, N.A.; Mohd Tahir, S.; Yahya, N.; Abdul Wahid, M.F.; Khairuddin, N.E.; Hashim, I.; Rosli, N.; Abdullah, M.A. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable starch-based bioplastics. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 846, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktari, L.; Blond, A.; Guyot, M. 16β-Hydroxy-5α-Cholestane-3,6-Dione, a novel cytotoxic oxysterol from the red alga Jania rubens. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 2563–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhlal, R.; Haslin, C.; Chermann, J.-C.; Colliec-Jouault, S.; Sinquin, C.; Simon, G.; Cerantola, S.; Riadi, H.; Bourgougnon, N. Antiviral activities of sulfated polysaccharides isolated from Sphaerococcus coronopifolius (Rhodophytha, Gigartinales) and Boergeseniella thuyoides (Rhodophyta, Ceramiales). Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1187–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armeli Minicante, S.; Carlin, S.; Stocco, M.; Sfriso, A.; Capelli, G.; Montarsi, F. Preliminary results on the efficacy of macroalgal extracts against larvae of Aedes albopictus. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2017, 33, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, G.; Alisi, C.; Sprocati, A.R.; Massi, E.; Ciccoli, R.; Lenzi, M.; Wang, A.; Cremisini, C. Anaerobic digestion of macroalgal biomass and sediments sourced from the Orbetello Lagoon, Italy. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 42, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.S.; Israel, A.; Palatnik, R.R.; Zilberman, D.; Golberg, A. Integrated biorefinery process for sustainable fractionation of Ulva ohnoi (Chlorophyta): Process optimization and revenue analysis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemodanov, A.; Jinjikhashvily, G.; Habiby, O.; Liberzon, A.; Israel, A.; Yakhini, Z.; Golberg, A. Net primary productivity, biofuel production and CO2 emissions reduction potential of Ulva sp. (Chlorophyta) biomass in a coastal area of the Eastern Mediterranean. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 148, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latique, S.; Elouaer, M.A.; Chernane, H.; Hannachi, C.; Elkaoua, M. Effect of seaweed liquid extract of Sargassum vulgare on growth of durum wheat seedlings (Triticum durum L.) under salt stress. IJIAS 2014, 7, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Marinho-Soriano, E. Polysaccharides from the red seaweed Gracilaria dura (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta). Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Said, R.; Mensi, F.; Majdoub, H.; Ben Said, A.; Ben Said, B.; Bouraoui, A. Effects of depth and initial fragment weights of Gracilaria gracilis on the growth, agar yield, quality, and biochemical composition. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francavilla, M.; Manara, P.; Kamaterou, P.; Monteleone, M.; Zabaniotou, A. Cascade approach of red macroalgae Gracilaria gracilis sustainable valorization by extraction of phycobiliproteins and pyrolysis of residue. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neifar, M.; Chatter, R.; Chouchane, H.; Genouiz, R.; Jaouani, A.; Slaheddine Masmoudi, A.; Cherif, A. Optimization of enzymatic saccharification of Chaetomorpha linum biomass for the production of macroalgae-based third generation bioethanol. AIMS Bioeng. 2016, 3, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.; Veneziano, V.; Orlando-Bonaca, M. Comparative assessment of trace element accumulation and biomonitoring in seaweed Ulva lactuca and seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohy, E.; Din, S.; Noaman, N.; Zaky, S. Removal of some pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds by the marine macroalgae Pterocladia capillacea and Ulva lactuca. Egypt. J. Bot. 2017, 57, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ajjabi Chebil, L.; Sadok, S. La macroalgue verte Ulva sp. pour la production du bioéthanol: Optimisation et caractérisation. Bull. Inst. Nat. Sci. Tech. Mer. Salammbô 2015, 42, 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Karray, R.; Karray, F.; Loukil, S.; Mhiri, N.; Sayadi, S. Anaerobic codigestion of Tunisian green macroalgae Ulva rigida with sugar industry wastewater for biogas and methane production enhancement. Waste Manag. 2016, 61, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A.; El-Sikaily, A.; Khaled, A.; Abdelwahab, O. Removal of toxic chromium from aqueous solution, wastewater and saline water by marine red alga Pterocladia capillacea and its activated carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 8, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, A.H.; Camus, C.; Infante, J.; Neori, A.; Israel, Á.; Hernández-González, M.C.; Pereda, S.V.; Gomez-Pinchetti, J.L.; Golberg, A.; Tadmor-Shalev, N.; et al. Seaweed production: Overview of the global state of exploitation, farming and emerging research activity. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 52, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.; Vázquez Calderón, F.; Sánchez López, J.; Azevedo, I.C.; Bruhn, A.; Fluch, S.; Garcia Tasende, M.; Ghaderiardakani, F.; Ilmjärv, T.; Laurans, M.; et al. Current status of the algae production industry in Europe: An emerging sector of the Blue Bioeconomy. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 626389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Marques, A.; Nunes, M.L. Mediterranean aquaculture in a changing climate. In The Mediterranean Sea; Goffredo, S., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 605–616. ISBN 978-94-007-6703-4. [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander, M. Israeli R&D activities in seaweed cultivation. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2008, 56, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neori, A.; Shpigel, M.; Guttman, L.; Israel, A. Development of polyculture and Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA) in Israel: A review. IJA 2017, 68, 20874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, A.; Golberg, A.; Neori, A. The seaweed resources of Israel in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Bot. Mar. 2019, 63, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzen, L.; Abelson, A.; Israel, A. Growth, protein and carbohydrate contents in Ulva rigida and Gracilaria bursa-pastoris integrated with an offshore fish farm. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaka, S.; Moawad, M. Ecology and biochemical composition of a newly reported non-indigenous red alga, Grateloupia gibbesii, in the Mediterranean Sea, with reference to edible red seaweeds. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.M.; Ashour, M.; Soliman, A.A.F.; Hassanien, H.A.; Alsanie, W.F.; Gaber, A.; Elshobary, M.E. The potential of a new commercial seaweed extract in stimulating morpho-agronomic and bioactive properties of Eruca vesicaria (L.) Cav. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnari, G.; Giaccone, G.; Cormaci, M.; Alongi, G.; Catra, M.; Nisi, A.; Serio, D. Macrophytobenthos. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2010, 17, 801–828. [Google Scholar]
- Servello, G.; Andaloro, F.; Azzurro, E.; Castriota, L.; Catra, M.; Chiarore, A.; Crocetta, F.; D’Alessandro, M.; Denitto, F.; Froglia, C.; et al. Marine alien species in Italy: A contribution to the implementation of descriptor D2 of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2019, 20, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrini, M.; Molento, M.B.; Mancini, S.; della Cuna, F.S.R.; Furnari, G.; Serio, D.; Cornara, L.; Perrucci, S. Evaluation of the anthelmintic properties of a traditional remedy based on a mixture of red algae using an in vitro assay on gastrointestinal nematodes of donkeys. Open J. Chem. 2021, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armeli Minicante, S.; Birello, G.; Sigovini, M.; Minuzzo, T.; Perin, A.; Ceregato, A. Building a natural and cultural heritage repository for the storage and dissemination of knowledge: The Algarium Veneticum and the Archivio di Studi Adriatici (ISMAR-CNR) case-study. J. Libr. Metadata 2017, 17, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, F. Possibilità di reale sfruttamento dei vegetali marini delle coste italiane. In Atti della Società Toscana di Scienze Naturali. Memorie; Arti Grafiche Pacini Mariotti: Pisa, Italy, 1979; Volume LXXXVI, pp. 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, G.; Tedone, L.; Hamann, M.T.; Morabito, M. The Mediterranean red alga Asparagopsis: A source of compounds against Leishmania. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, G.; Faggio, C.; Gugliandolo, C.; Torre, A.; Spanò, A.; Morabito, M.; Maugeri, T.L. In vitro evaluation of antibacterial activity of Asparagopsis taxiformis from the Straits of Messina against pathogens relevant in aquaculture. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 73, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, G.; Leitner, S.; Armeli Minicante, S.; Lass-Flörl, C. The Mediterranean red alga Asparagopsis taxiformis has antifungal activity against Aspergillus species. Mycoses 2013, 56, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, F.; Genovese, G.; Bruno, F.; Castelli, G.; Piazza, M.; Migliazzo, A.; Armeli Minicante, S.; Manghisi, T.; Morabito, M. Effectiveness of red alga Asparagopsis taxiformis extracts against Leishmania infantum. Open Life Sci. 2015, 10, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, C.; Genovese, G.; Morabito, M.; Faggio, C.; Pagano, M.; Spanò, A.; Zammuto, V.; Minicante, S.; Manghisi, A.; Cigala, R.; et al. Potential antibacterial activity of marine macroalgae against pathogens relevant for aquaculture and human health. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 11, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, F.; Di Caro, G.; Gugliandolo, C.; Spanò, A.; Faggio, C.; Genovese, G.; Morabito, M.; Russo, A.; Barreca, D.; Fazio, F.; et al. preliminary study on the in vitro and in vivo effects of Asparagopsis taxiformis bioactive phycoderivates on teleosts. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armeli Minicante, S.; Michelet, S.; Bruno, F.; Castelli, G.; Vitale, F.; Sfriso, A.; Morabito, M.; Genovese, G. Bioactivity of Phycocolloids against the Mediterranean Protozoan Leishmania infantum: An Inceptive Study. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggio, C.; Pagano, M.; Morabito, M.; Armeli Minicante, S.; Arfuso, F.; Genovese, G. In vitro assessment of the effect of Undaria pinnatifida extracts on erythrocytes membrane integrity and blood coagulation parameters of Equus caballus. J. Coast. Life Med. 2014, 2, 614–616. [Google Scholar]
- Faggio, C.; Morabito, M.; Armeli Minicante, S.; Lo Piano, G.; Pagano, M.; Genovese, G. Potential use of polysaccharides from the brown alga Undaria pinnatifida as anticoagulants. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2015, 58, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francavilla, M.; Kamaterou, P.; Intini, S.; Monteleone, M.; Zabaniotou, A. Cascading microalgae biorefinery: Fast pyrolysis of Dunaliella tertiolecta lipid extracted-residue. Algal Res. 2015, 11, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogero, G.; Citro, I.; Di Marco, G.; Armeli Minicante, S.; Morabito, M.; Genovese, G. Brown seaweed pigment as a dye source for photoelectrochemical solar cells. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francavilla, M.; Franchi, M.; Monteleone, M.; Caroppo, C. The red seaweed Gracilaria gracilis as a multi products source. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3754–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armeli Minicante, S.; Ambrosi, E.; Back, M.; Barichello, J.; Cattaruzza, E.; Gonella, F.; Scantamburlo, E.; Trave, E. Development of an eco-protocol for seaweed chlorophylls extraction and possible applications in Dye Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 295–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Croce, N.; Cattaneo Vietti, R.; Danovaro, R. Ecologia e Protezione Dell’ambiente Marino Costiero; UTET: Torino, Italy, 2005; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Petrocelli, A.; Cecere, E. A 20-year update on the state of seaweed resources in Italy. Bot. Mar. 2019, 62, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission, Directorate-General for Research and Innovation. A Sustainable Bioeconomy for Europe: Strengthening the Connection between Economy, Society and the Environment: Updated Bioeconomy Strategy; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fava, F.; Gardossi, L.; Brigidi, P.; Morone, P.; Carosi, D.A.R.; Lenzi, A. The bioeconomy in italy and the new national strategy for a more competitive and sustainable country. New Biotechnol. 2021, 61, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bioeconomy Coordination Board (NBCB) of the Presidency of Council of Ministers Implementation Action Plan (2020–2025) for the Italian Bioeconomy Strategy BIT II 2021. Available online: https://knowledge4policy.ec.europa.eu/node/38121_de (accessed on 7 March 2022).
- Barrento, S.; Camus, C.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Buschmann, A.H. Germplasm banking of the giant kelp: Our biological insurance in a changing environment. Algal Res. 2016, 13, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, E.; Tamburello, L.; Verdura, J.; Guarnieri, G.; Medrano, A.; Linares, C.; Hereu, B.; Garrabou, J.; Cerrano, C.; Galobart, C.; et al. A Roadmap for the restoration of Mediterranean macroalgal forests. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 709219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburello, L.; Papa, L.; Guarnieri, G.; Basconi, L.; Zampardi, S.; Scipione, M.B.; Terlizzi, A.; Zupo, V.; Fraschetti, S. Are we ready for scaling up restoration actions? An insight from Mediterranean macroalgal canopies. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangrande, A.; Gravina, M.F.; Rossi, S.; Longo, C.; Pierri, C. Aquaculture and restoration: Perspectives from Mediterranean Sea experiences. Water 2021, 13, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armeli Minicante, S.; De Lazzari, A.; Lucertini, G. Management of invasive alien species: Turning threats into new opportunities. In Governing Future Challenges in Mediterranean Protected Areas; Alfarè, L.T., Ruoss, E., Eds.; CNR Edition: Roma, Italy, 2020; p. 156. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, M.D.; Kraan, S.; Domínguez, H. Seaweed biorefinery. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 335–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Country | Industry Name | Value Chain | Species | Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| France | Eranova | Farming and harvesting; applications | Ulva sp. | Bioplastics |
| Israel | Seakura Ltd. | Farming and harvesting; applications | Ulva sp.; Gracilaria sp. | Nutraceuticals |
| Israel | Sealaria Ltd. | Farming and harvesting; applications | Gracilaria sp. | Nutraceuticals and cosmetics |
| Israel | Y.A. Maof | Farming and harvesting | Sargassum sp. * | Biogas |
| Israel | Biotic | Applications | Bioplastics | |
| Israel | Algaeing | Applications | seaweeds | Textile |
| Italy | FAVINI | Applications | Ulva sp. *; Gracilaria sp. * | Paper |
| Italy | South Agro | Farming and harvesting; applications | Ascophyllum nodosum *; Macrocystis sp. *; Laminaria digitata *; green and red seaweeds | Biostimulants and Biofertilizers |
| Italy | Guam | Applications | Laminaria digitata *; Fucus sp. *; Undaria pinnatifida * | Cosmetics |
| Italy | Consonni Bioalghe | Applications | Ulva sp. *; Fucus sp. *; Undaria pinnatifida *; Palmaria palmata *; Chondrus crispus *; Laminaria sp. *; Lithothamnum calcareum *; Saccharina latissima *; Porphyra sp. *; Himanthalia elongata * | Nutraceuticals and cosmetics |
| Italy | Aboca | Applications | Fucus vesiculosus * | Nutraceuticals |
| Italy | B&V Italy | Applications | Gracilaria sp. *; Gelidium sp. *; Pterocladia sp. * | Hydrocolloids |
| Italy | Prodotti Arca | Applications | Ascophyllum nodosum * | Nutrition and zootechnical products |
| Italy | Java Biocolloid Europe | Farming and harvesting; applications | Gracilaria sp. *; Gelidium sp. * | Hydrocolloids |
| Italy | Specialagri | Applications | brown seaweeds * | Biostimulants and biofertilizers |
| Italy | Forfoods | Applications | Ulva spp. | Food |
| Slovenia | EKOGEA | Applications | Ascophyllum nodosum * | Biostimulants |
| Spain | Mediterranean Algae | Farming and harvesting | Ulva lactuca | Cosmetic products; alimentation; biofertilizers |
| Tunisia | SELT Marine Group | Farming and harvesting; applications | Gracilaria sp.; Gelidium sesquipedale; Kappaphycus alvarezii *; Eucheuma spinosum *; Ulva lactuca | Hydrocolloids |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Armeli Minicante, S.; Bongiorni, L.; De Lazzari, A. Bio-Based Products from Mediterranean Seaweeds: Italian Opportunities and Challenges for a Sustainable Blue Economy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095634
Armeli Minicante S, Bongiorni L, De Lazzari A. Bio-Based Products from Mediterranean Seaweeds: Italian Opportunities and Challenges for a Sustainable Blue Economy. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095634
Chicago/Turabian StyleArmeli Minicante, Simona, Lucia Bongiorni, and Amelia De Lazzari. 2022. "Bio-Based Products from Mediterranean Seaweeds: Italian Opportunities and Challenges for a Sustainable Blue Economy" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095634
APA StyleArmeli Minicante, S., Bongiorni, L., & De Lazzari, A. (2022). Bio-Based Products from Mediterranean Seaweeds: Italian Opportunities and Challenges for a Sustainable Blue Economy. Sustainability, 14(9), 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095634







