Characterizing the Morphological Descriptors of Thirty Seed Sources of Teak (Tectona grandis L.f.) Concerning Sustainable Forestry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Genetic Similarity and Cluster Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Leaf Characterization
3.1.1. Leaf Length and Width
3.1.2. Presence of Petiole
3.1.3. Leaf Shape Attributes
3.1.4. Leaf Margin and Brightness
3.1.5. Leaf Veins
3.1.6. Leaf Color
3.1.7. Leaf Pubescence
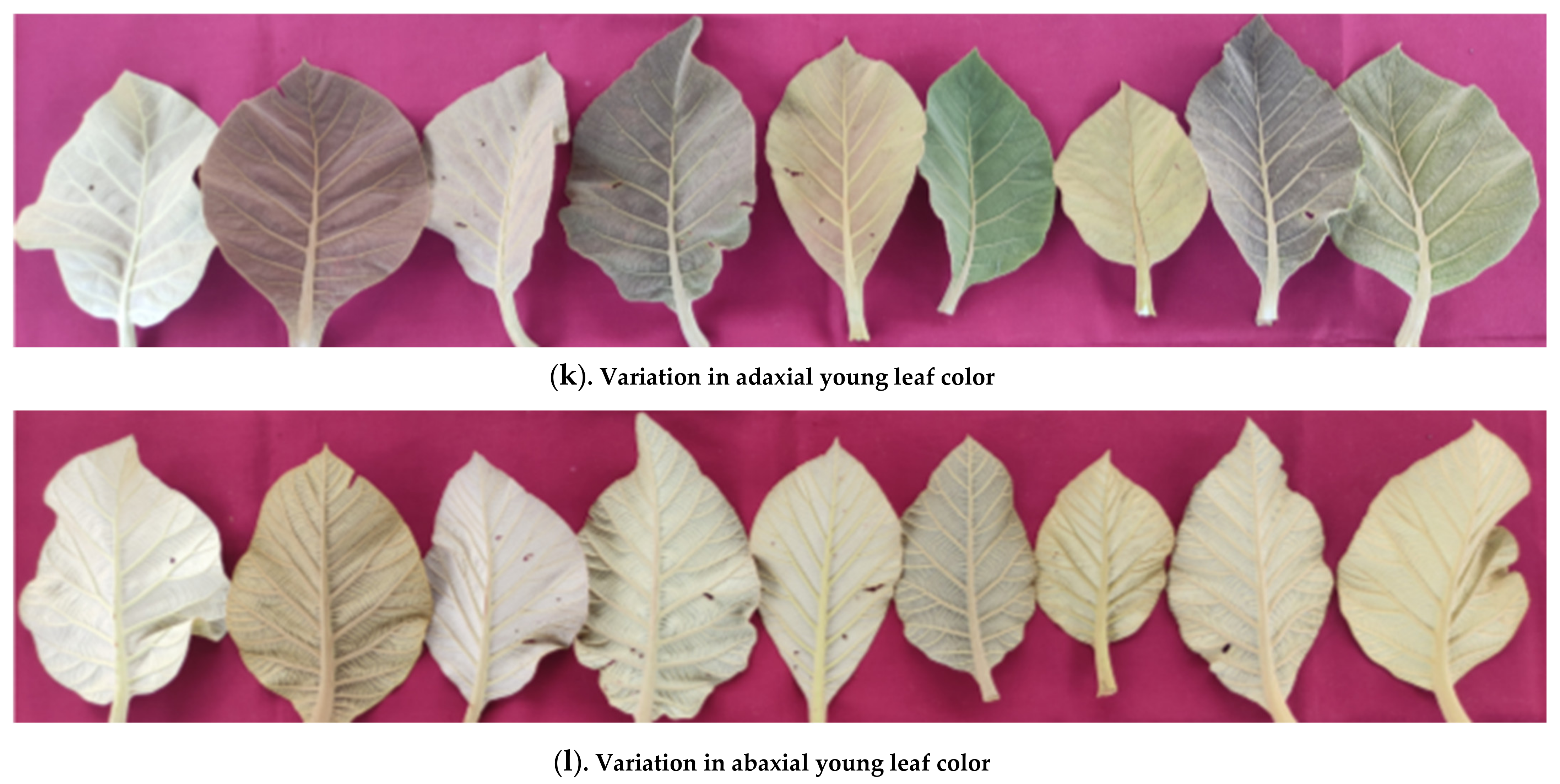
3.1.8. Young Leaf Color
3.2. Stem Characterization
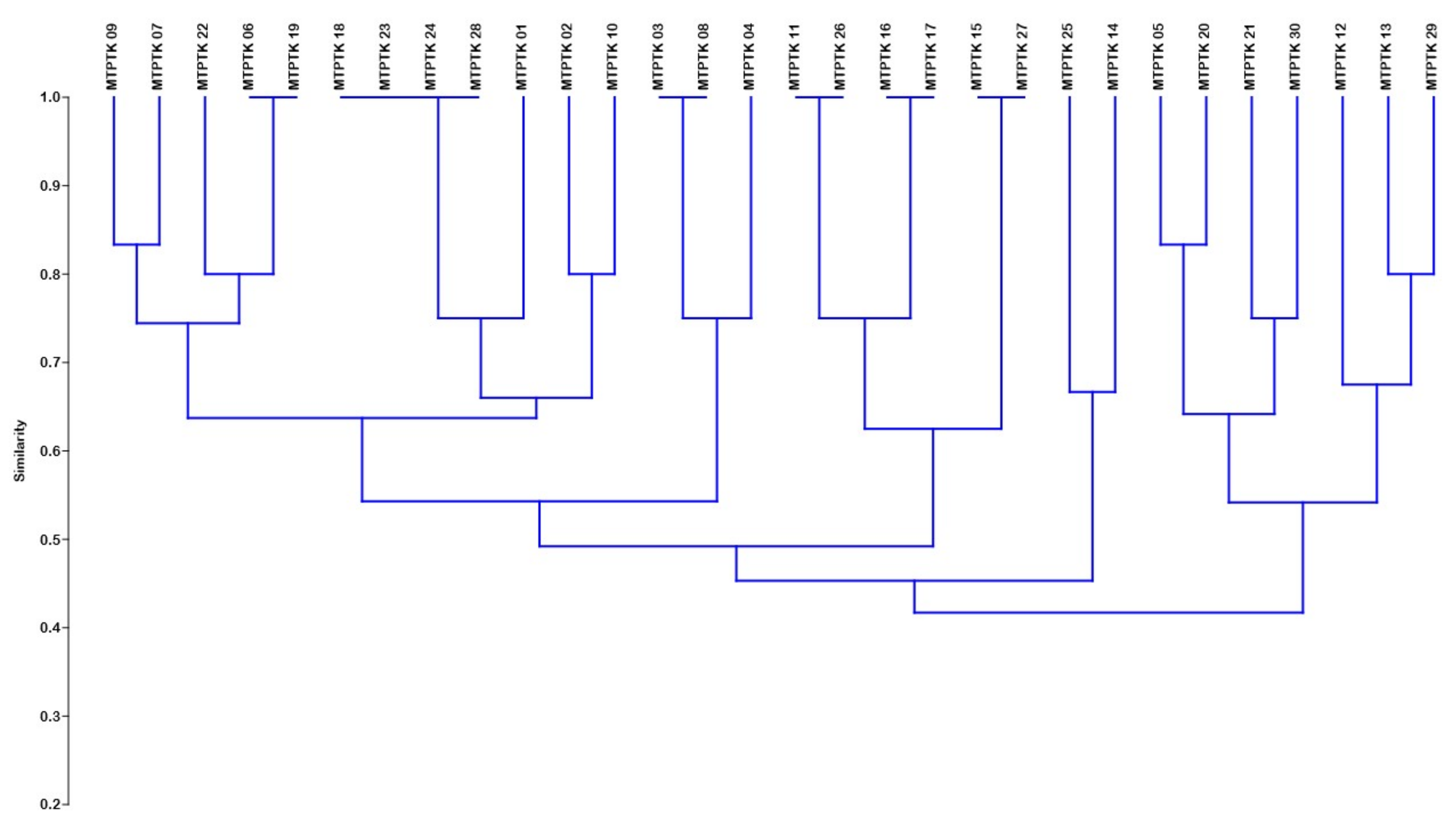
3.3. Genetic Similarity and Cluster Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, K.J. Teak: Some aspects of research and development. RAPA Publ. 1991, 17, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, D.; Brown, C. Teak: A global overview. Unasylva 2000, 51, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Verhaegen, D.; Fofana, I.J.; Logossa, Z.A.; Ofori, D. What is the genetic origin of teak (Tectona grandis L.) introduced in Africa and in Indonesia? Tree Genet. Genomes 2010, 6, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, R. New horizons for teak (Tectona grandis Linn. F.) plantations: The consortium support model (CSM) approach of teak 2000. In Proceedings of the Third Regional Seminar on Teak, Potentials and Opportunities in Marketing and Trade of Plantation Teak: Challenge for the New Millenium, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 31 July–4 August 2001; pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kjaer, E.D.; Kaosa-ard, A.; Suangtho, V.; Etners, T.; Nair, C.T.S. Domestication of teak through tree improvement: Options, potential gains and critical factors. Ph.D. Dissertation, Forestry Research Support Programme for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok University, Bangkok, Thailand, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rajora, O.P.; Rahman, M.H.; Buchert, G.P.; Dancik, B.P. Microsatellite DNA analysis of genetic effects of harvesting in old-growth eastern white pine (Pinus strobus) in Ontario, Canada. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PPV&FR Authority, Protection of Plant Varieties & Farmers’ Rights Authority, India, 2001. Annual Report, Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare Government of India. Available online: www.plantauthority.gov.in (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Shobha, R.N.; Subba, R.L.V.; Viraktamath, B.C.; Mishra, B. National Guideline for the Conduct of Tests for Distinctness, Uniformity and Stability Rice (Oryza sativa L.); DRR (ICAR): Hyderabad, India, 2004.
- UPOV. Guideline for the Conduct of the Test for Distinctness, Homogeneity and Stability Banana (Musa acuminate Colla) TG/123/3; International Union for the Protection of new Varieties and plants (UPOV): Geneva, Switzerland, 1989; 26p.
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.B. Applications of bulking in molecular characterization of plant germplasm: A critical review. Plant Genet. Resour. 2003, 1, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.C.D. Caracterização Morfológica e Avaliação do Desenvolvimento Inicial de Clones de Teca (Tectona grandis L.f). Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de Mato Grosso, Cuiabá, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Prasetyawati, C.A.; A’ida, N. Morphological characterization of different provenances of Teak (Tectona grandis L.). In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 308, p. 012062. [Google Scholar]
- Vinothkumar, A.; Anantha Lakshmi, M.; Chandrasekar, R.; Sivakumar, V.; Manokaran, P.; Kolar, A.B. Characterization of morphological diversity in teak (Tectona grandis L.F.) germplasm in India for preparation and implementation of dus testing (Distinct, Uniform and Stable). Int. J. Bot. Stud. 2021, 6, 527–533. [Google Scholar]
- Vinutha, C.S. Morphological characterization of teak (Tectona grandis L.) clones of Karnataka for resistance traits to teak defoliator, Hyblaea puera Cramer. Karnataka J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 27, 367–369. [Google Scholar]
- Gunaga, R.P.; Surendran, T.; Prabhu, H.N. Morphological variation and delineation of teak (Tectona grandis LF) clones of Kerala through leaf character: Implication for seed orchard management. Mysore J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 47, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Alcântara, B.K.; Ortega, E.M.M.; Souza, V.C. Identification of morphological descriptors for characterization of teak (Tectona grandis L. f.). Adv. For. Sci. 2016, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Baretta, M.C. Crescimento e Caracterização Morfológica de Clones de Teca no Sudoeste de Mato Grosso. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universidade Federal Mato Grosso, Cuiabá, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chimello, A.M.; Jesus, J.G.; Teodoro, P.E.; Rossil, A.A.B.; Araújol, K.L.; Marostega, T.N.; Neves, L.G.; Barelli, M.A.A. Morphological descriptors and ISSR molecular markers in the evaluation of genetic variability of Tectona grandis genotypes. Genet. Mol. Res. GMR Ribeirão Preto 2017, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reategui-Betancourt, J.L.; Arriel, D.A.A.; Caldeira, S.F.; Higa, A.R.; Flôres Junior, P.C.; Araujo, S.P.; Marques, R.M.; Corrêa, B.M.B.; Martinez, D.T. Morphological descriptors for the characterization of teak clones (Tectona grandis Lf) in plantations. For. Syst. 2020, 29, 206–218. [Google Scholar]
- George, A.K.; Parthiban, K.T. Vikas Kumar (2016) Development and documentation of descriptors for Jatropha (Jatropha curcas) and their hybrid derivatives. Indian J. Trop. Biodiv. 2016, 24, 2303–2305. [Google Scholar]
- Parthiban, K.T.; Kanagaraj, N.; Palanikumaran, B.; Krishnakumar, N. Development of DUS descriptor for Casuarina genetic resources. Int. J. Genet. 2018, 10, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvan, R.T.; Parthiban, K.T.; Palanikumaran, B. Distinctness, Uniformity and Stability (DUS) Characterization of Neolamarckia Cadamba Genetic Resources. Curr. Agric. Res. J. 2019, 7, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekar, S.; Balasubramanian, A. DUS Descriptors for Registration of Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss.) for Varietal Protection. Trends Biosci. 2014, 7, 2303–2305. [Google Scholar]
- Gnanasekar, S.; Balasubramanian, A. Usefulness of Morphological Characterization for Developing DUS Descriptors in Karanj (Pongamia pinnata (L.) Pierre). Biosciences 2014, 2315, 2315–2318. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, V.; Anandalakshmi, R.; Nicodemus, A.; Warrier, R.R. Guidelines for the Conduct of Test for Distinctiveness, Uniformity and Stability on Eucalypts (Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh. and Eucalyptus tereticornis); Annual Report; Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Authority, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2012.
- Prasetyo, E.; Indrioko, S.; Na’iem, M.; Matsui, T.; Matsuo, A.; Suyama, Y.; Tsumura, Y. Genetic diversity and the origin of commercial plantation of Indonesian teak on Java Island. Tree Genet. Genomes 2020, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flôres Junior, P.C.; Ikeda, A.C.; Schuhli, G.S.; Silva, L.D.; Higa, A.R. Repeatability and genetic dissimilarity using biometric traits of black wattle seeds. Adv. For. Sci. 2018, 5, 333–337. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, G.; Muralidharan, E.M. Variation in Photosynthetic Traits and Correlation with Growth in Teak (Tectona grandis Linn.) Clones. Forests 2019, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, M.M.; Ahmad, I.; Farooq, T.H.; Wu, P.; Yousaf, M.S.; Khan, M.W.; Talha, Y.; Ma, X. Effects of pre-sowing treatments on seed germination and Morphological growth of Acacia nilotica and Faidherbia albida. Sci. For. 2019, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.H.; Yan, W.; Chen, X.; Shakoor, A.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Gilani, M.M.; He, Z.; Wu, P. Dynamics of canopy development of Cunninghamia lanceolata mid-age plantation in relation to foliar nitrogen and soil quality influenced by stand density. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.H.; Yan, W.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Tigabu, M.; Gilani, M.M.; Zou, X.H.; Wu, P.F.; City, S.; Buajan, S.; Jinfu, L.; et al. Growth, biomass production and root development of Chinese fir in relation to initial planting density. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 3553–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, M.M.; Tigabu, M.; Liu, B.; Farooq, T.H.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Ramzan, M.; Ma, X. Seed germination and seedling emergence of four tree species of southern China in response to acid rain. J. For. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
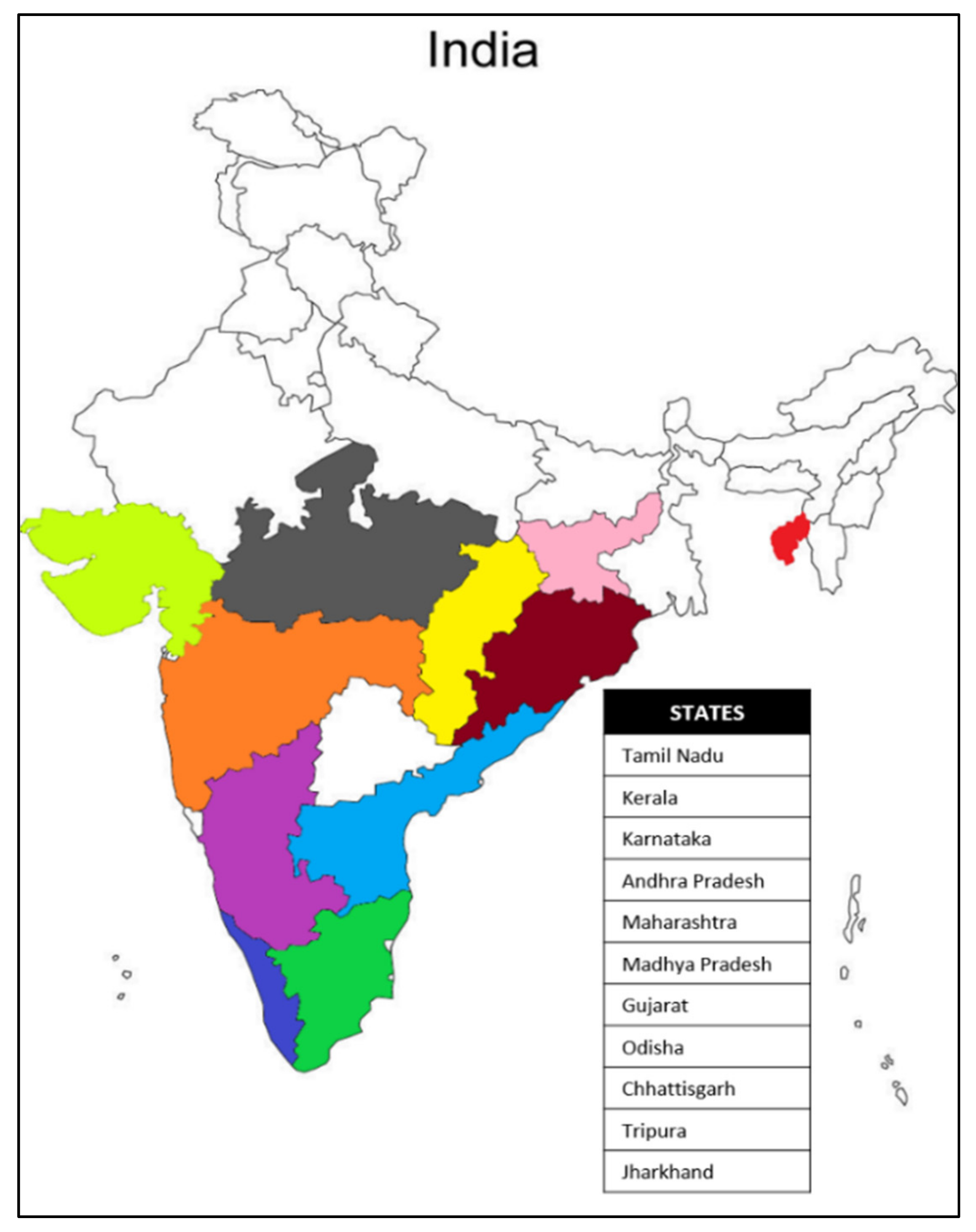


| S.No. | Place | State | Latitude | Longitude | Assigned Number | Source Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nellithurai | Tamil Nadu | 11°17′03″ N | 76°51′55″ E | FCRITK 01 | 1 |
| 2. | Nellithurai | Tamil Nadu | 11°17′01″ N | 76°51′55″ E | FCRITK 02 | 2 |
| 3. | Kallar | Tamil Nadu | 11°20′20″ N | 76°52′31″ E | FCRITK 03 | 3 |
| 4. | Oomapalayam | Tamil Nadu | 11°30′35″ N | 76°91′61″ E | FCRITK 04 | 4 |
| 5. | Kallar | Tamil Nadu | 11°20′23″ N | 76°52′20″ E | FCRITK 05 | 5 |
| 6. | Kallar RF | Tamil Nadu | 11°20′24″ N | 76°52′36″ E | FCRITK 06 | 6 |
| 7. | Agartala | Tripura | 23°83′15″ N | 91°28′68″ E | FCRITK 07 | 7 |
| 8. | Nellithurai | Tamil Nadu | 11°16′56″ N | 76°51′58″ E | FCRITK 08 | 8 |
| 9. | Vilamarathur | Tamil Nadu | 11°15′50″ N | 76°50′52″ E | FCRITK 09 | 9 |
| 10. | Salem | Tamil Nadu | 11°66′43″ N | 78°14′60″ E | FCRITK 10 | 10 |
| 11. | Burliyar | Tamil Nadu | 11°34′37″ N | 76°84′04″ E | FCRITK 11 | 11 |
| 12. | Chandrapur | Maharashtra | 19°96′15″ N | 79°29′61″ E | FCRITK 12 | 12 |
| 13. | Chandrapur | Maharashtra | 19°96′15″ N | 79°29′61″ E | FCRITK 13 | 13 |
| 14. | Chandrapur | Maharashtra | 19°96′15″ N | 79°29′61″ E | FCRITK 14 | 14 |
| 15. | Chandrapur | Maharashtra | 19°96′15″ N | 79°29′61″ E | FCRITK 15 | 15 |
| 16. | Chandrapur | Maharashtra | 19°96′15″ N | 79°29′61″ E | FCRITK 16 | 16 |
| 17. | Chandrapur | Maharashtra | 19°96′15″ N | 79°29′61″ E | FCRITK 17 | 17 |
| 18. | Tanjore | Tamil Nadu | 10°78′70″ N | 79°13′78″ E | FCRITK 18 | 18 |
| 19. | Rairakhol | Odisha | 21°04′12″ N | 84°20′60″ E | FCRITK 19 | 19 |
| 20. | Dang | Gujarat | 20°82′54″ N | 73°70′07″ E | FCRITK 20 | 20 |
| 21. | Nilambur | Kerala | 11°28′55″ N | 76°23′86″ E | FCRITK 21 | 21 |
| 22. | Parambikulam | Kerala | 10°37′78″ N | 76°76′42″ E | FCRITK 22 | 22 |
| 23. | Thenmala | Kerala | 8°96′32″ N | 77°06′51″ E | FCRITK 23 | 23 |
| 24. | Shivamogga | Karnataka | 13°92′99″ N | 75°56′81″ E | FCRITK 24 | 24 |
| 25. | Valsad | Gujarat | 20°59′92″ N | 72°93′42″ E | FCRITK 25 | 25 |
| 26. | Dandeli | Karnataka | 15°23′61″ N | 74°61′73″ E | FCRITK 26 | 26 |
| 27. | Khandwa | Madhya Pradesh | 21°83′14″ N | 76°34′98″ E | FCRITK 27 | 27 |
| 28. | Vizianagaram | Andra Pradesh | 18°10′67″ N | 83°39′56″ E | FCRITK 28 | 28 |
| 29. | Raipur | Chhattisgarh | 21°25′14″ N | 81°62′96″ E | FCRITK 29 | 29 |
| 30. | Ranchi | Jharkhand | 23°34′41″ N | 85°30′96″ E | FCRITK 30 | 30 |
| S.No | Characteristics | Levels of Expression | Distribution of Classes | Source Code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Leaf Length (cm) | 40–50 cm | 5 (16.7%) | 1, 4, 6, 18, 28 | |
| 50–60 cm | 15 (50%) | 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26 | |||
| >60 cm | 10 (33.3%) | 5, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 25, 27, 29, 30 | |||
| 2 | Leaf width (cm) | 30–40 cm | 5 (16.7%) | 1, 4, 6, 18, 24 | |
| 40–50 cm | 17 (56.7%) | 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 26, 28 | |||
| 50–60 cm | 8 (26.6%) | 2 14, 15, 16, 25, 27, 29, 30 | |||
| 3 | Presence of Petiole | Petiolate | 26 (86.7%) | 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29 | |
| Sessile | 4 (13.3%) | 1, 5, 21, 30 | |||
| 4 | Petiole length (cm) | 2–4 cm | 4 (15.4%) | 6, 8, 11, 26 | |
| 4–6 cm | 9 (34.6%) | 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, 13, 17, 22, 29 | |||
| >6 cm | 13 (50%) | 10, 12, 14, 15, 16, 18, 19, 20, 23, 24, 25, 27, 28 | |||
| 5 | Leaf Shape | Ovate | 30 (100%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | |
| 6 | Shape of Leaf Apex | Acute | 30 (100%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | |
| 7 | Shape of Leaf Base | Obtuse | 22 (73.4%) | 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29 | |
| Cuneate | 4 (13.3%) | 6, 9, 11, 13 | |||
| Attenuated | 4 (13.3%) | 1, 5, 21, 30 | |||
| 8 | Leaf Texture | Glabrous | 5 (16.7%) | 9, 19, 21, 26, 28 | |
| Coriaceous | 13 (43.3%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 18, 22, 23, 24 | |||
| Scabrous | 12 (40%) | 5, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 20, 25, 27, 29, 30 | |||
| 9 | Phyllotaxy | Opposite | 30 (100%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | |
| 10 | Leaf Attitude | Bending | 13 (43.3%) | 5, 6, 7, 9, 12, 13, 19, 20, 21, 22, 25, 29, 30 | |
| Horizontal | 17 (56.7%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 10, 11, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 23, 24, 26, 27, 28 | |||
| 11 | Leaf Margin | Whole | 30 (100%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | |
| 12 | Leaf Margin Undulation | Low | 24 (80%) | 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 13, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | |
| Medium | 6 (20%) | 3, 4, 8, 12, 14, 25 | |||
| 13 | Leaf Brightness | Present | 12 (40%) | 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10, 18, 19, 23, 24, 28 | |
| Absent | 18 (60%) | 2, 5, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 20, 21, 22, 25, 26, 27, 29, 30 | |||
| 14 | Leaf Venation | Touches the margin | 30 (100%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | |
| 15 | Leaf Main Vein | Touches the margin | 30 (100%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | |
| 16 | Leaf Veins | Tertiary | 6 (20%) | 2, 5, 7, 9, 10, 20 | |
| Quaternary | 24 (80%) | 1, 3, 4, 6, 8, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | |||
| 17 | Leaf Vein Color | Light yellow | 2 (6.7%) | 3, 6 | |
| Yellowish green | 9 (30%) | 2, 5, 14, 15, 16, 17, 20, 21, 22 | |||
| Light yellowish green | 19 (63.3%) | 1, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 18, 19, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | |||
| 18 | Leaf Color | Adaxial | Dark green | 26 (86.7%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 14, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 28, 29, 30 |
| Light green | 4 (13.3%) | 12, 13, 15, 27 | |||
| Abaxial | Greyish green | 8 (26.6%) | 1, 3, 11, 16, 17, 19, 20, 26 | ||
| Light greyish green | 3 (10%) | 2, 25, 27 | |||
| Light green | 16 (53.4%) | 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 14, 15, 18, 21, 22, 23, 24, 28, 30 | |||
| Light yellowish green | 3 (10%) | 12, 13, 29 | |||
| 19 | Leaf Pubescence | Adaxial | Absent | 30 (100%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 |
| Abaxial | Present | 11 (36.7%) | 4, 5, 12, 13, 15, 16, 17, 20, 27, 29, 30 | ||
| Absent | 19 (63.3%) | 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 14, 18, 19, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 28 | |||
| 20 | Young Leaf Color | Adaxial | Greyish green | 3 (10%) | 1, 18, 28 |
| Light greenish brown | 10 (33.3%) | 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 11, 15, 16, 24, 27 | |||
| Dark greenish brown | 4 (13.3%) | 13, 22, 25, 29 | |||
| Light brown | 6 (20%) | 3, 6, 7, 19, 23, 26 | |||
| Dark brown | 3 (10%) | 12, 20, 30 | |||
| Green | 2 (6.7%) | 14, 17 | |||
| Purplish green | 2 (6.7%) | 9, 21 | |||
| Abaxial | Light greyish green | 2 (6.7%) | 1, 18 | ||
| Light greenish brown | 13 (43.3%) | 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 15, 16, 22, 24, 29, 30 | |||
| Greenish brown | 5 (16.7%) | 3, 12, 13, 20, 27 | |||
| Light green | 4 (13.3%) | 14, 17, 25, 28 | |||
| Light brown | 4 (13.3%) | 7, 19, 23, 26 | |||
| Light purplish green | 2 (6.7%) | 9, 21 | |||
| S.No. | Characteristics | Levels of Expression | Distribution of Classes | Source Code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No. of Internodes (measured from 1 m above the ground level) | 4–5 | 12 (40%) | 1, 3, 6, 7, 14, 16, 17, 22, 25, 27, 29, 30 | |
| 5–6 | 8 (26.6%) | 9, 10, 12, 15, 19, 20, 23, 26 | |||
| >6 | 10 (33.3%) | 2, 4, 5, 8, 11, 13, 18, 21, 24, 28 | |||
| 2 | Internodal Length (measured from 1 m above the ground level) | 13–16 cm | 11 (36.7%) | 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 15,18, 21, 28 | |
| 16–19 cm | 10 (33.3%) | 1, 2, 5, 7, 10, 19, 20, 23, 24, 26 | |||
| >19 cm | 9 (30%) | 13, 14, 16, 17, 22, 25, 27, 29, 30 | |||
| 3 | Trunk spots | Present | 30 (100%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | |
| 4 | Trunk Color | Base | Grey | 30 (100%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 |
| Middle | Light green | 2 (6.7%) | 12, 17 | ||
| Dark green | 20 (66.7%) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 14, 18, 19, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30 | |||
| Greyish green | 8 (26.6%) | 5, 11, 13, 15, 16, 20, 25, 29 | |||
| Top | Light green | 6 (20%) | 1, 6, 7, 17, 18, 27 | ||
| Green | 17 (56.7%) | 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14, 19, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26, 28, 30 | |||
| Greyish green | 7 (23.3%) | 11, 12, 15, 16, 20, 25, 29 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
M. V., J.V.; K. T., P.; S., U.K.; S., R.; Kumar, U.; Farooq, T.H. Characterizing the Morphological Descriptors of Thirty Seed Sources of Teak (Tectona grandis L.f.) Concerning Sustainable Forestry. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912012
M. V. JV, K. T. P, S. UK, S. R, Kumar U, Farooq TH. Characterizing the Morphological Descriptors of Thirty Seed Sources of Teak (Tectona grandis L.f.) Concerning Sustainable Forestry. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912012
Chicago/Turabian StyleM. V., Jawahar Vishnu, Parthiban K. T., Umesh Kanna S., Radhakrishnan S., Uttam Kumar, and Taimoor Hassan Farooq. 2022. "Characterizing the Morphological Descriptors of Thirty Seed Sources of Teak (Tectona grandis L.f.) Concerning Sustainable Forestry" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912012
APA StyleM. V., J. V., K. T., P., S., U. K., S., R., Kumar, U., & Farooq, T. H. (2022). Characterizing the Morphological Descriptors of Thirty Seed Sources of Teak (Tectona grandis L.f.) Concerning Sustainable Forestry. Sustainability, 14(19), 12012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912012








