Performance Evaluation of a Novel Pilot-Scale Wet Electrostatic Precipitator in a Bio-Drying-Assisted Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) Generation Plant: Particulate Matter (PM) Collection Efficiency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
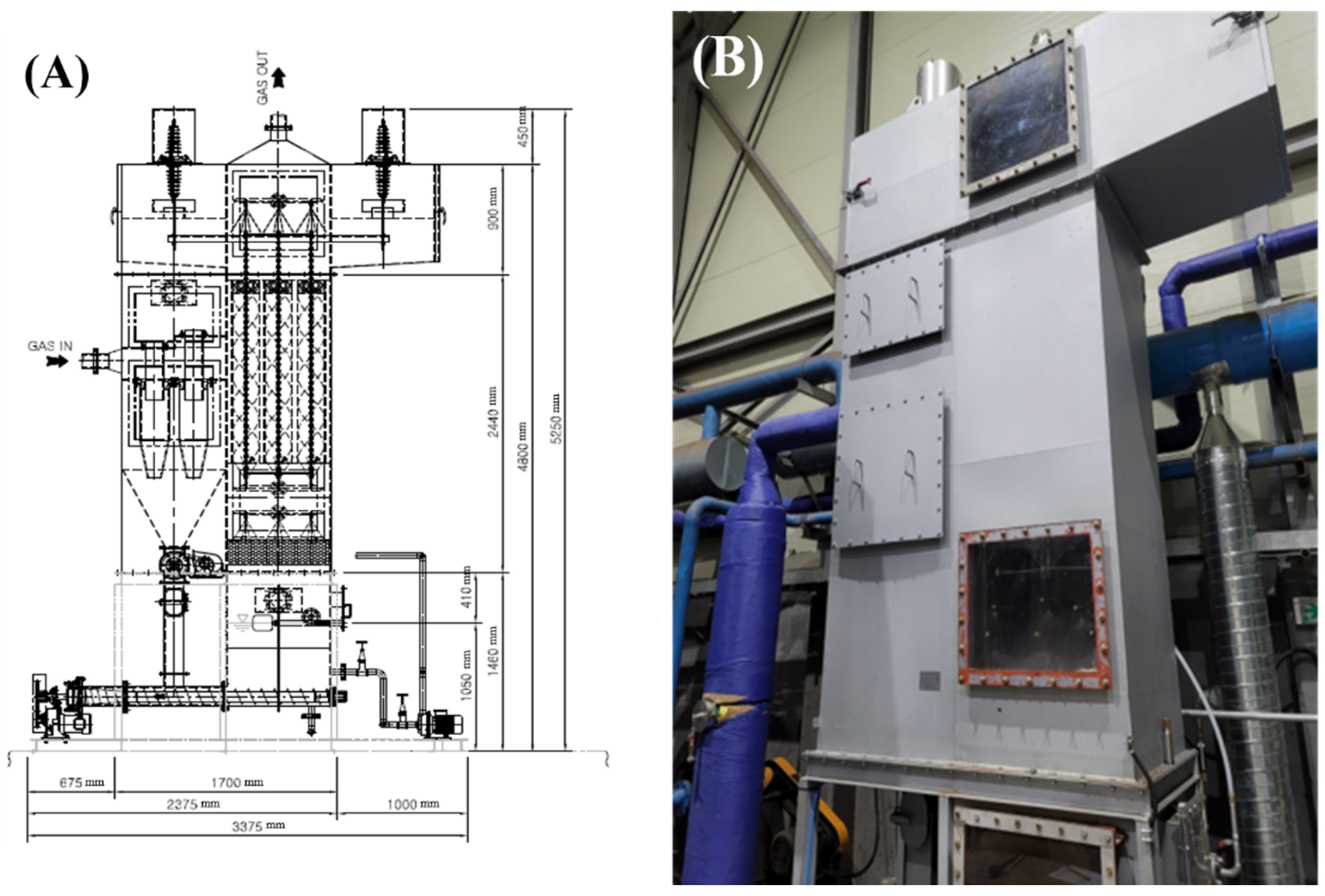
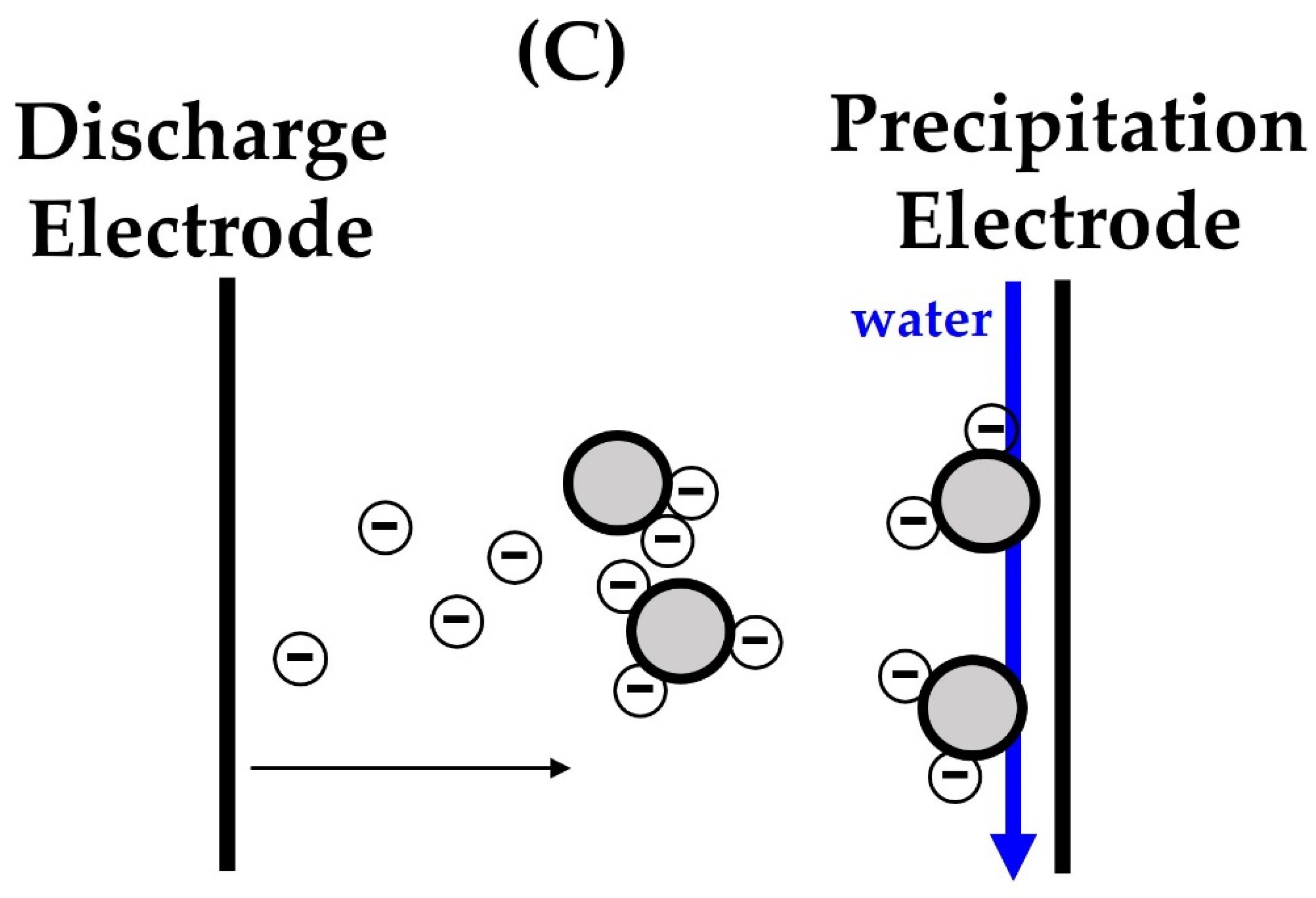
2.1. Wet Electrostatic Precipitator
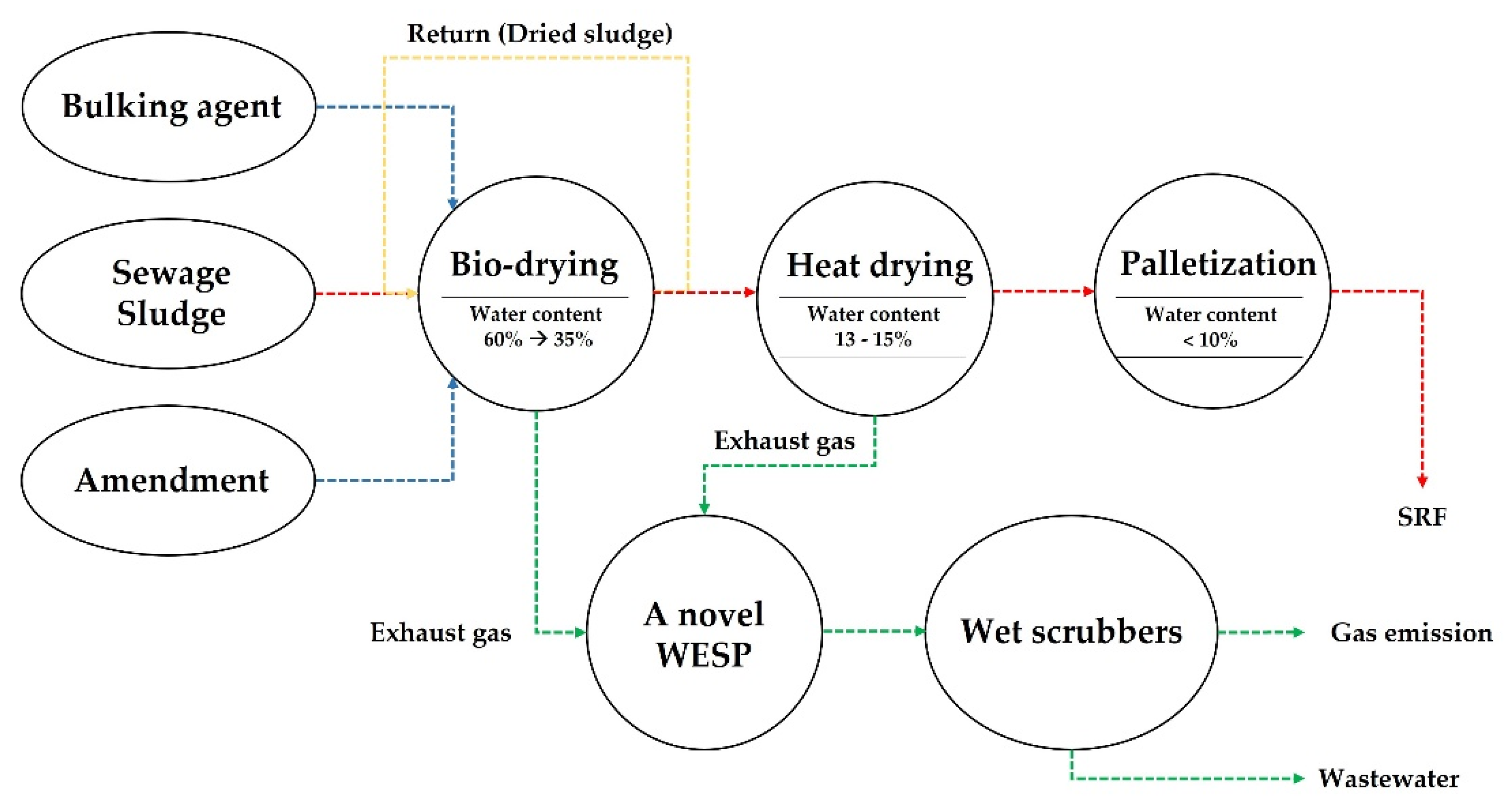
2.2. A Pilot-Scale Bio-Drying-Assisted SRF Generation Plant with the WESP
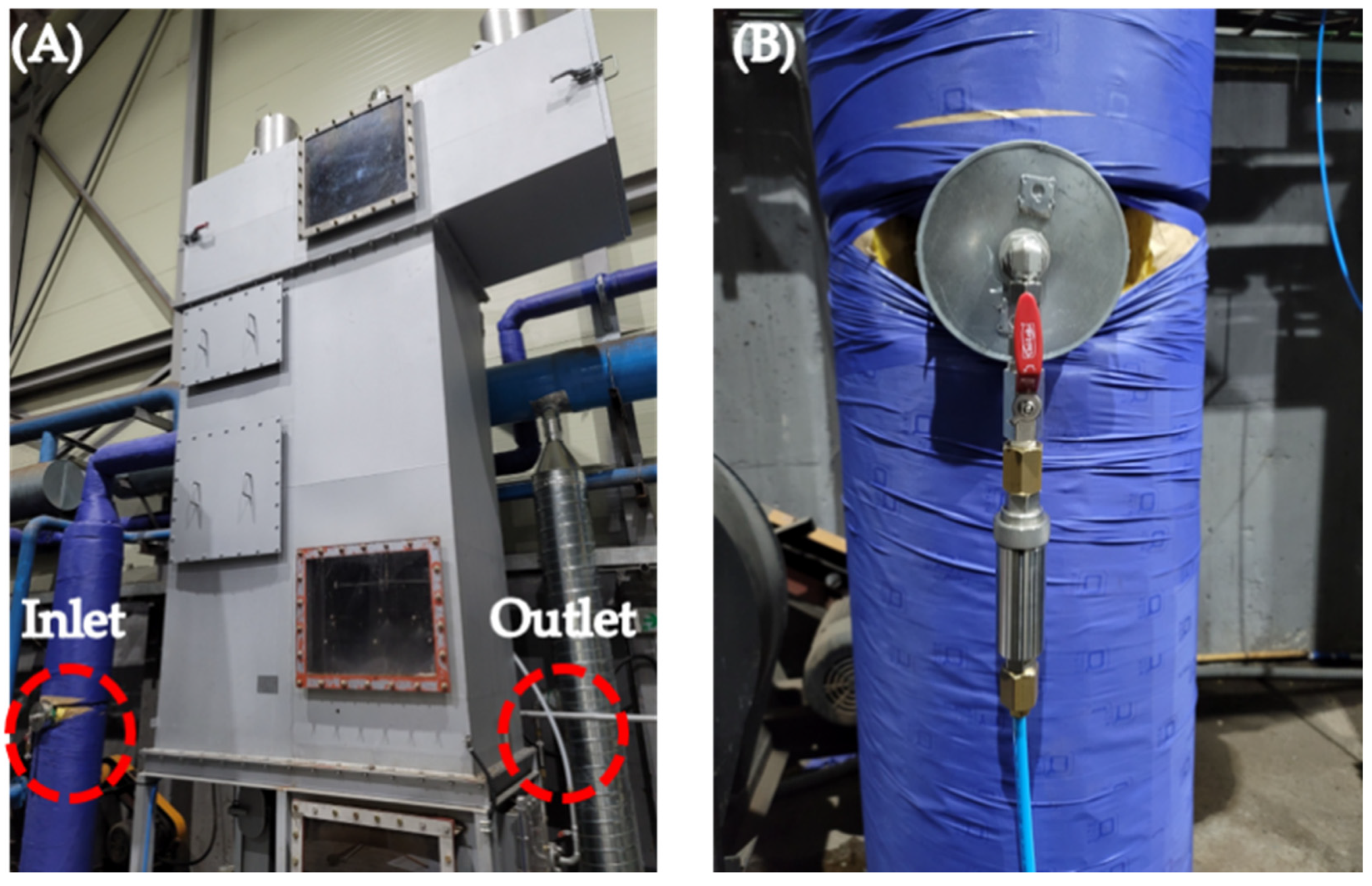
2.3. PM Collection Efficiency Test
2.4. PM10 Collection Efficiency Test
3. Result and Discussion
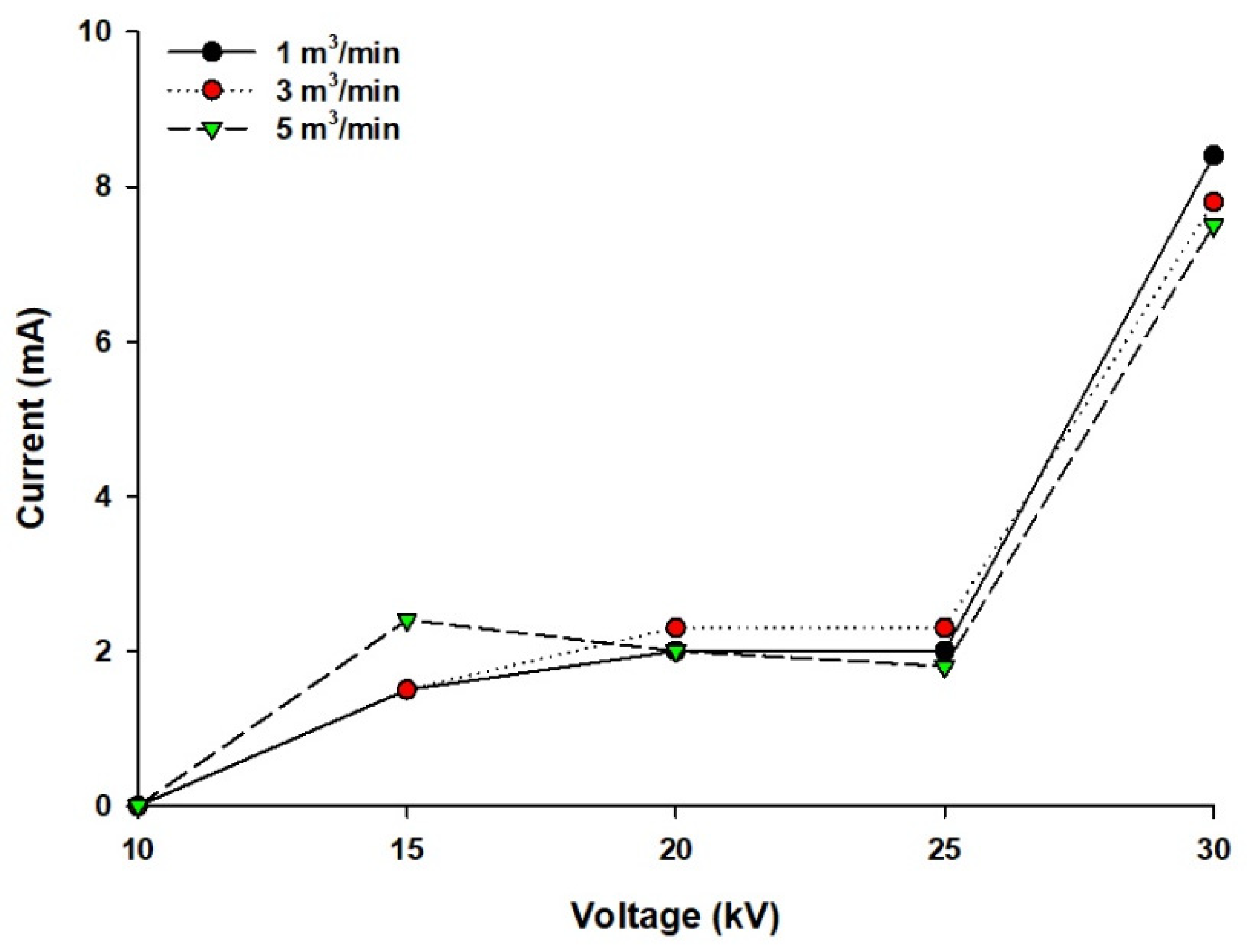
3.1. Voltage–Current Relationship in the Novel Pilot-Scale WESP
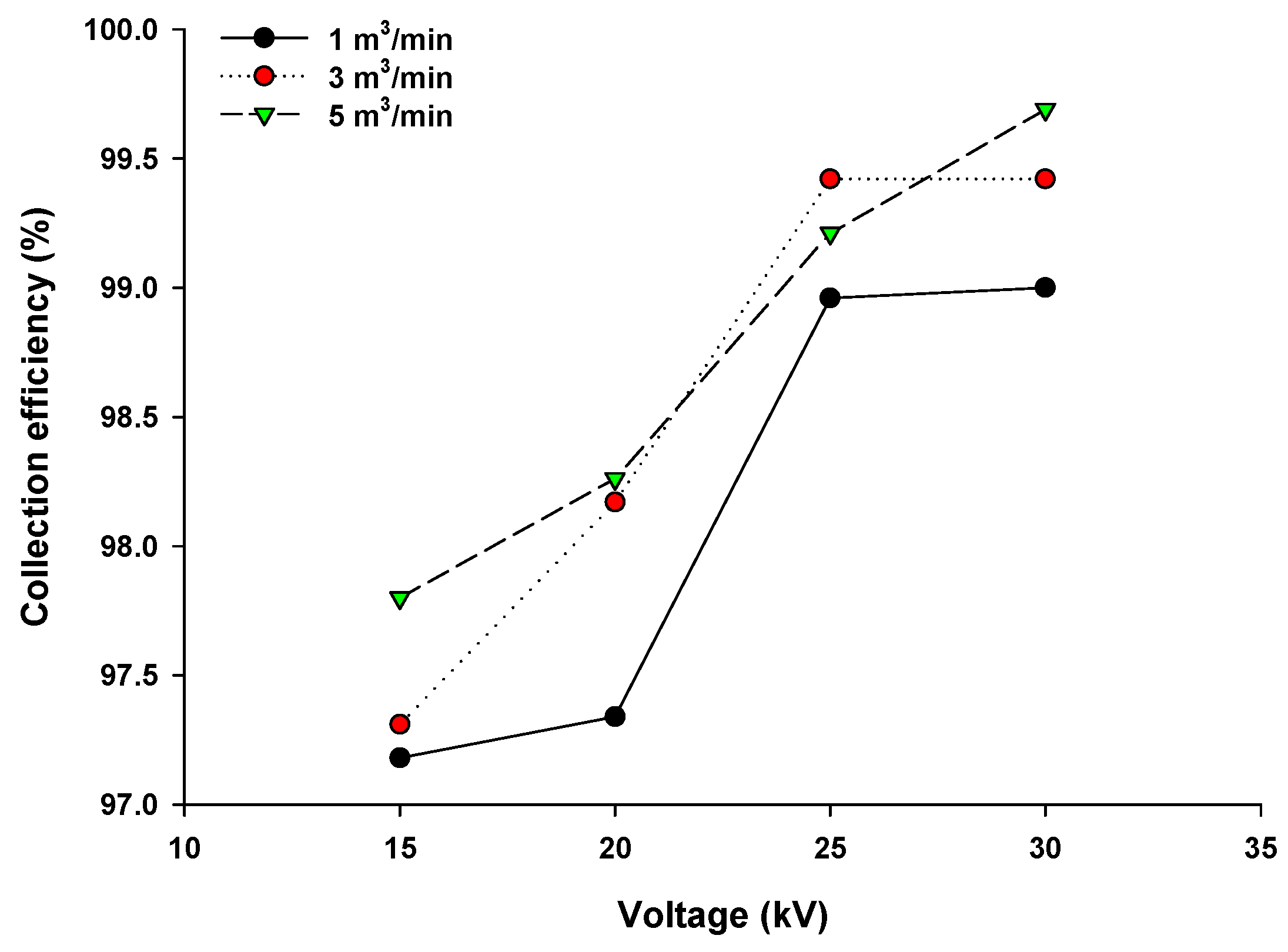
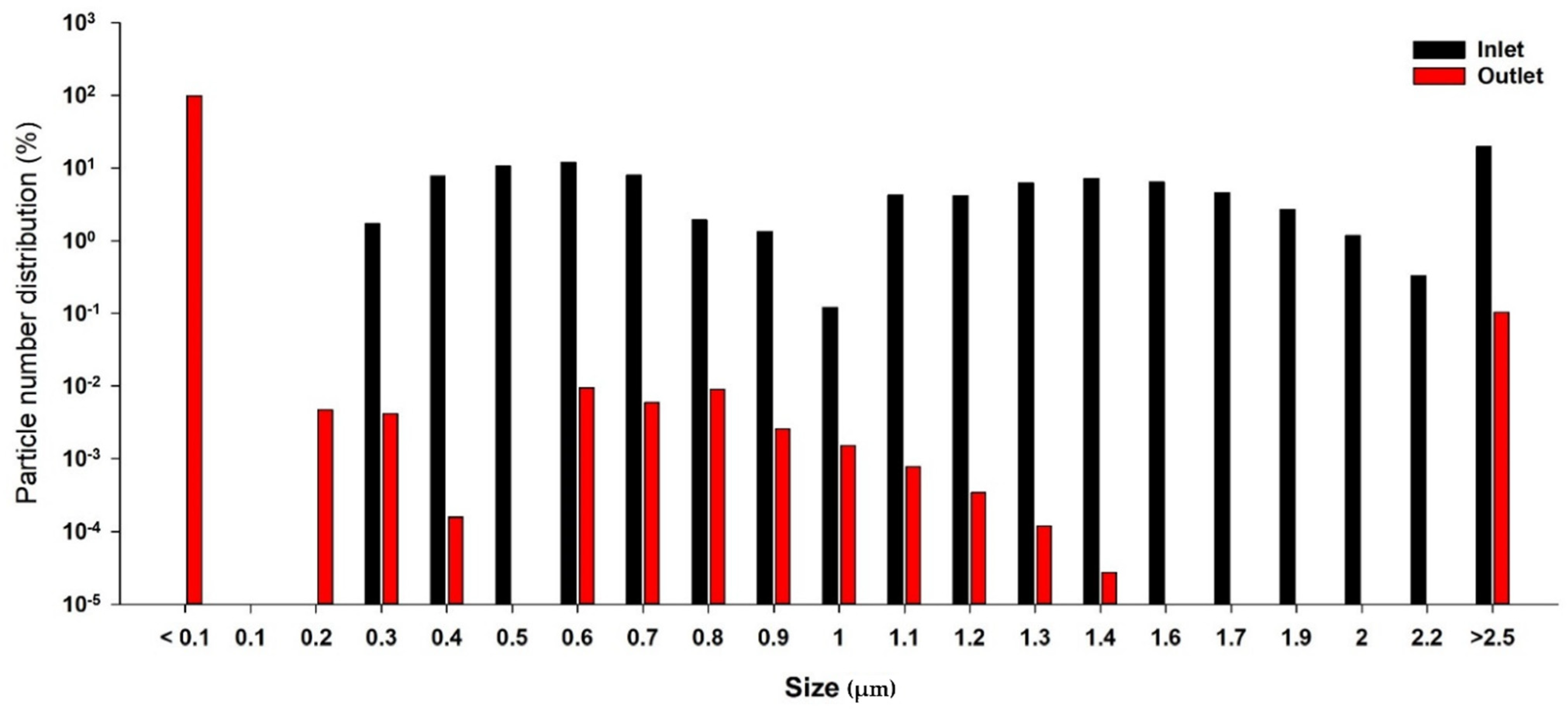
3.2. PM Collection Efficiency
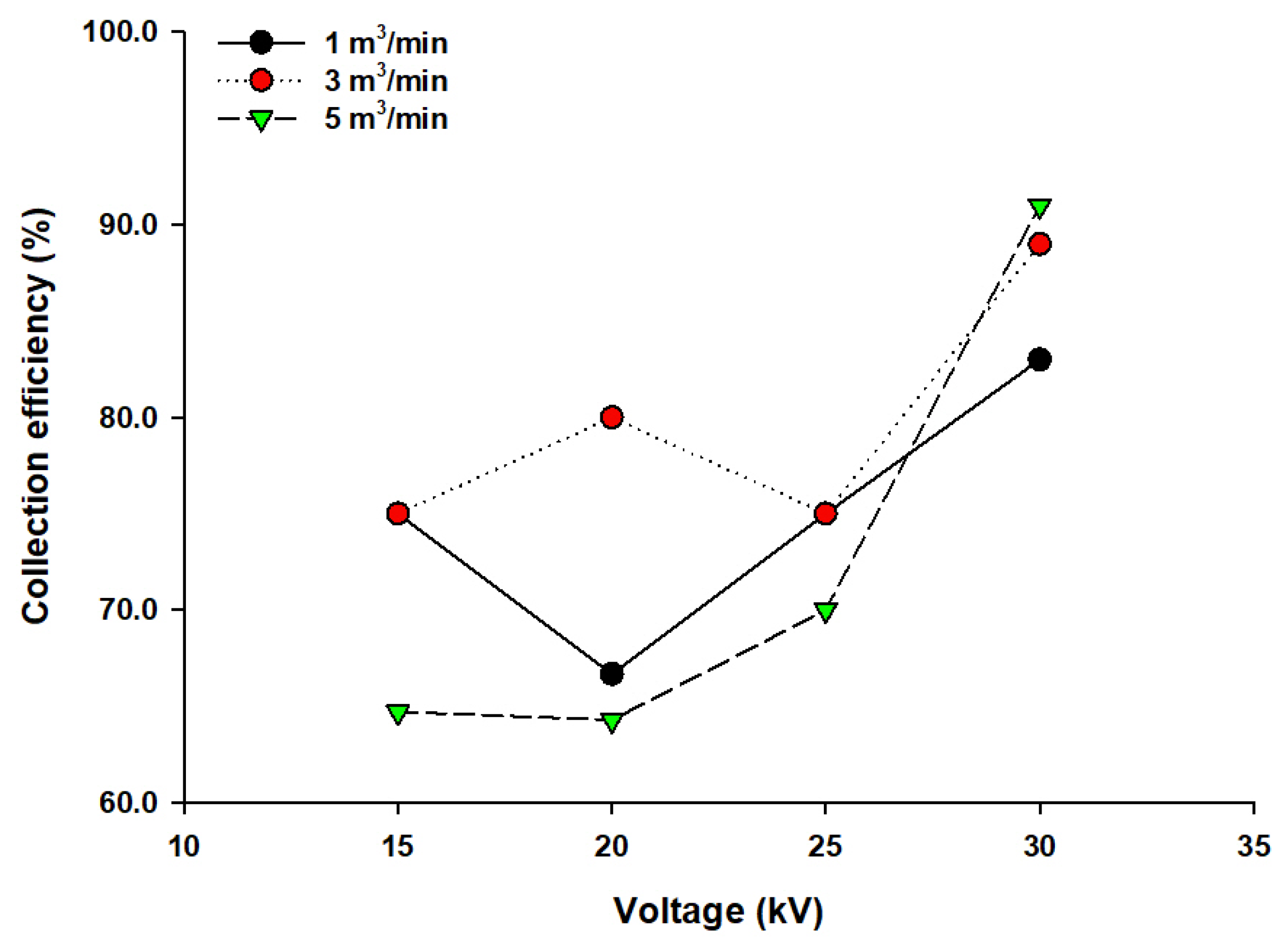
3.3. PM10 Collection Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ozcan, B.; Tzeremes, P.G.; Tzeremes, N.G. Energy consumption, economic growth and environmental degradation in OECD countries. Econ. Model. 2020, 84, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Stafford Smith, M.; O’Brien, K.; Zsolnai, L. Transforming Sustainability Science to Generate Positive Social and Environmental Change Globally. One Earth 2020, 2, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdiwansyah, M.; Husin, A.; Nasaruddin, M.Z.; Muhibbuddin, A. A critical review of the integration of renewable energy sources with various technologies. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2021, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Seo, Y.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Yang, W.S.; Oh, J.H.; Gu, J.H. Development of 8 ton/day gasification process to generate electricity using a gas engine for solid refuse fuel. Waste Manag. 2020, 113, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjoo, A.; Gakenia Kaigutha, L.; Vaziri Rad, M.A.; Marzband, M.; Davarpanah, A.; Denai, M. A Technical analysis investigating energy sustainability utilizing reliable renewable energy sources to reduce CO2 emissions in a high potential area. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Tang, Y. Enhancing food security and environmental sustainability: A critical review of food loss and waste management. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 4, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debrah, J.K.; Vidal, D.G.; Dinis, M.A.P. Raising awareness on solid waste management through formal education for sustainability: A developing countries evidence review. Recycling 2021, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Rios, C.; Hofmann, A.; Mackenzie, N. Sustainability-oriented innovations in food waste management technology. Sustainability 2021, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Cha, J. Towards improved circular economy and resource security in South Korea. Sustainability 2021, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewage Information System. Available online: www.hasudoinfo.or.kr (accessed on 2 March 2022).
- Hong, J.H.; Kim, J.; Son, W.; Shin, H.; Kim, N.; Lee, W.K.; Kim, J. Long-term energy strategy scenarios for South Korea: Transition to a sustainable energy system. Energy Policy 2019, 127, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G. Yearbook of International Environmental Law; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; Volume 29, pp. 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Monteiro, E.; Silva, V.; Rouboa, A. Co-gasification and recent developments on waste-to-energy conversion: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 380–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.S.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.H.; Joo, J.C.; Ohm, T.I. Combustion characteristics of solid refuse fuel derived from mixture of food and plastic wastes. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Wnukowski, M.; Krochmalny, K.; Kowal, M.; Baranowski, M.; Zgóra, J.; Czerep, M.; Ostrycharczyk, M.; Niedzwiecki, L. The staged thermal conversion of sewage sludge in the presence of oxygen. J. Energy Resour. Technol. Trans. ASME 2019, 141, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Połomka, J.; Jędrczak, A. RDF from Compost-Like-Output’s Produced in the MBT installation in the case of Marszów, Poland. Energies 2020, 13, 4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarc, R.L. Manufacturing of Solid Recovered Fuels (SRF) for Energy Recovery Processes. Waste Manag. 2016, 6, 401–416. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.R.; Lee, D.H. Effect of Aeration Strategy on Moisture Removal in Bio-Drying Process with Auto-Controlled Aeration System. Dry. Technol. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, G.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Matsuto, T.; Tojo, Y.; Park, J.R. Simultaneous Effects of Airflow and Temperature Increase on Water Removal in Bio-Drying. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 224, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, W.; Wu, D.; Shao, L. Energy Balance of a Biodrying Process for Organic Wastes of High Moisture Content: A Review. Dry. Technol. 2013, 31, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Tan, H.; Xiong, Y.; Mikulčić, H.; Vujanović, M.; Wang, X.; Duić, N. Improving the removal of particles and trace elements from coal-fired power plants by combining a wet phase transition agglomerator with wet electrostatic precipitator. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bologa, A.; Paur, H.R.; Seifert, H.; Wäscher, T.; Woletz, K. Novel wet electrostatic precipitator for collection of fine aerosol. J. Electrostat. 2009, 67, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.Y.; Tsai, C.J.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, T.M.; Li, S.N. An efficient single-stage wet electrostatic precipitator for fine and nanosized particle control. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, M.; Hayafune, Y.; Sugamiya, R.; Nakagawa, Y.; Makishima, K. Pyrolysis of municipal solid waste in Japan. J. Energy Resour. Technol. Trans. ASME 1984, 106, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment. South Korea, Clean Air Conservation Act. Article 7, Ministry of Environment Notice 2011-132, Official Air Pollution Test Method; South Korea Ministry of Environment: Seoul, Korea, 2011.
- Ministry of Environment, KEITI. Report on Domestic IP Environment Trends. Fine Dust in Exhaus Gas Measurement; Ministry of Environment, KEITI: Seoul, Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Liu, S.; Guo, Y.; Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, D.; Gao, X. A combined wet electrostatic precipitator for efficiently eliminating fine particle penetration. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 180, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwat, B.; Machnik, R.; Niedźwiedzki, J.; Nogaj, M. Selecting operating parameters of an electrostatic precipitator decreasing emission of solid fuels fly ashes. Eksploat. Niezawodn. 2018, 20, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D.; Höflinger, W.; Lisberger, M. Influence of Gas Distribution, Field Velocity and Power Supply Technique for Small Scale Industrial Esp’s. Int. J. Plasma Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, A.E.; Guerra, V.G. Effect of low gas velocity on the nanoparticle collection performance of an electrostatic precipitator. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Su, H.; Ho, H.C.; Song, Y.; Zheng, H.; Hossain, M.Z.; Khan, M.A.; Bogale, D.; Zhang, H.; et al. Ambient Particulate Matter (PM1, PM2.5, PM10) and Childhood Pneumonia: The Smaller Particle, the Greater Short-Term Impact? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Sheng, Z.; He, Q.; Wu, K. Characteristics of condensable particulate matter before and after wet flue gas desulfurization and wet electrostatic precipitator from ultra-low emission coal-fired power plants in China. Fuel 2020, 278, 118206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.V.; Dunn, P.F. Controlled production of droplets by in-flight electrospraying. Langmuir 2010, 26, 15807–15813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukeran, A.; Sawano, H.; Yasumoto, K. Collection characteristic of nanoparticles emitted from a diesel engine with residual fuel oil and light fuel oil in an electrostatic precipitator. Energies 2019, 12, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvo, A.I.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Teixeira, E.R.; Alves, C.; Nunes, T.; Duarte, M.; Coz, E.; Custodio, D.; Castro, A.; Artiñano, B.; et al. Particulate emissions from the co-combustion of forest biomass and sewage sludge in a bubbling fluidised bed reactor. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 114, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
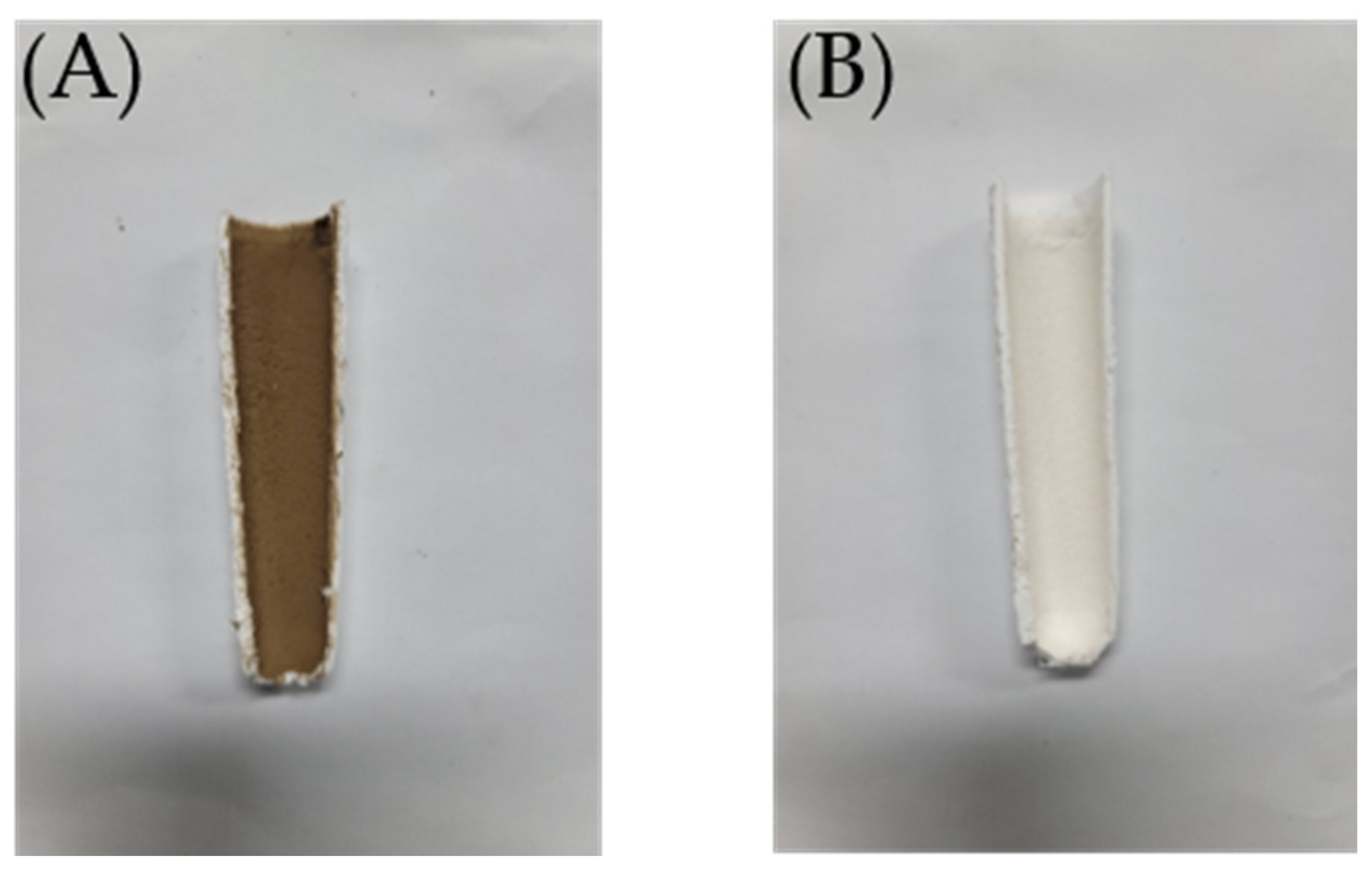

| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Water content (%) | 81.8 |
| Combustible volatile matter (%) | 14.4 |
| Ash content (%) | 3.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-S.; Jo, H.; Park, Y.; Han, U.; Thapa, A.; Kim, K.; Choi, D.H.; Park, G.J.; Cho, S.-K. Performance Evaluation of a Novel Pilot-Scale Wet Electrostatic Precipitator in a Bio-Drying-Assisted Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) Generation Plant: Particulate Matter (PM) Collection Efficiency. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8702. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148702
Kim M-S, Jo H, Park Y, Han U, Thapa A, Kim K, Choi DH, Park GJ, Cho S-K. Performance Evaluation of a Novel Pilot-Scale Wet Electrostatic Precipitator in a Bio-Drying-Assisted Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) Generation Plant: Particulate Matter (PM) Collection Efficiency. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8702. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148702
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Sang, Hongmok Jo, Yeongmi Park, Uijeong Han, Ajay Thapa, Kyunghyun Kim, Du Hyeong Choi, Gwang Jo Park, and Si-Kyung Cho. 2022. "Performance Evaluation of a Novel Pilot-Scale Wet Electrostatic Precipitator in a Bio-Drying-Assisted Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) Generation Plant: Particulate Matter (PM) Collection Efficiency" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8702. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148702
APA StyleKim, M.-S., Jo, H., Park, Y., Han, U., Thapa, A., Kim, K., Choi, D. H., Park, G. J., & Cho, S.-K. (2022). Performance Evaluation of a Novel Pilot-Scale Wet Electrostatic Precipitator in a Bio-Drying-Assisted Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) Generation Plant: Particulate Matter (PM) Collection Efficiency. Sustainability, 14(14), 8702. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148702






