Potential Impacts of Industrialization on Coastal Fresh Groundwater Resources in Bangladesh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Study Area
2. Methods
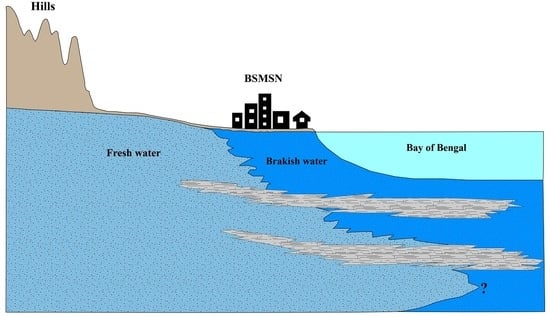
2.1. Aquifer Delineation
2.2. Groundwater Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.4. Hydrogeochemical Types
2.5. Drinking Water Quality (WQI)
2.6. Irrigation Water Quality
3. Results
3.1. Aquifer Framework
3.2. Groundwater Flow Direction
3.3. Physicochemical Characteristics of Groundwater
3.4. Hydrogeochemical Types
3.5. Drinking Water Quality Index
3.6. Irrigation Water Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Groundwater Sustainability for Industrial Abstraction
4.2. Implications of Groundwater Chemistry to Flow System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fienen, M.N.; Arshad, M. The International Scale of the Groundwater Issue. In Integrated Groundwater Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–48. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, M. Global Groundwater? Issues and Solutions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.G.; Scanlon, B.; Döll, P.; Rodell, M.; van Beek, R.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Leblanc, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Edmunds, M.; et al. Ground Water and Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lutz, A.F.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Siderius, C.; Wijngaard, R.R.; Nepal, S.; Shrestha, A.B.; Wester, P.; Biemans, H. South Asian Agriculture Increasingly Dependent on Meltwater and Groundwater. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Burke, J.; Faures, J.M.; Frenken, K.; Hoogeveen, J.; Döll, P.; Portmann, F.T. Groundwater Use for Irrigation—A Global Inventory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1863–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, M.; Stengel, C.; Trang, P.; Hungviet, P.; Sampson, M.; Leng, M.; Samreth, S.; Fredericks, D. Magnitude of Arsenic Pollution in the Mekong and Red River Deltas—Cambodia and Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 372, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendorf, S.; Michael, H.A.; van Geen, A. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Groundwater Arsenic in South and Southeast Asia. Science 2010, 328, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Famiglietti, J.S. The Global Groundwater Crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Jasechko, S.; Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Andreo, B.; Barberá, J.A.; Brielmann, H.; Bouchaou, L.; Charlier, J.-B.; Darling, W.G.; et al. Risk of Groundwater Contamination Widely Underestimated Because of Fast Flow into Aquifers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024492118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammer, H.; Ravenscroft, P. Arsenic in Groundwater: A Threat to Sustainable Agriculture in South and South-East Asia. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanasaki, N.; Yoshikawa, S.; Pokhrel, Y.; Kanae, S. A Global Hydrological Simulation to Specify the Sources of Water Used by Humans. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 789–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alley, W.M.; Healy, R.W.; LaBaugh, J.W.; Reilly, T.E. Flow and Storage in Groundwater Systems. Science 2002, 296, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waibel, M.S.; Gannett, M.W.; Chang, H.; Hulbe, C.L. Spatial Variability of the Response to Climate Change in Regional Groundwater Systems—Examples from Simulations in the Deschutes Basin, Oregon. J. Hydrol. 2013, 486, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; van Beek, L.P.H.; van Kempen, C.M.; Reckman, J.W.T.M.; Vasak, S.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Global Depletion of Groundwater Resources. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L20402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Döll, P.; Müller Schmied, H.; Schuh, C.; Portmann, F.T.; Eicker, A. Global-Scale Assessment of Groundwater Depletion and Related Groundwater Abstractions: Combining Hydrological Modeling with Information from Well Observations and GRACE Satellites. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5698–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konikow, L.F.; Kendy, E. Groundwater Depletion: A Global Problem. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrard, N.; Foster, T.; Willetts, J. Groundwater as a Source of Drinking Water in Southeast Asia and the Pacific: A Multi-Country Review of Current Reliance and Resource Concerns. Water 2019, 11, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.-J.; Zhu, D. Water Security of the Megacities in the Yangtze River Basin: Comparative Assessment and Policy Implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudduha, M.; Taylor, R.G.; Ahmed, K.M.; Zahid, A. The Impact of Intensive Groundwater Abstraction on Recharge to a Shallow Regional Aquifer System: Evidence from Bangladesh. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudduha, M.; Joseph, G.; Haque, S.S.; Khan, M.R.; Zahid, A.; Ahmed, K.M.U. Multi-Hazard Groundwater Risks to Water Supply from Shallow Depths: Challenges to Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals in Bangladesh. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoque, M.A.; Hoque, M.M.; Ahmed, K.M. Declining Groundwater Level and Aquifer Dewatering in Dhaka Metropolitan Area, Bangladesh: Causes and Quantification. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshfika, M.; Biswas, S.; Mondal, M.S. Assessing Groundwater Level Declination in Dhaka City and Identifying Adaptation Options for Sustainable Water Supply. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.G.M.; Allinson, G.; Stagnitti, F.; Tanaka, A.; Westbrooke, M. Arsenic Contamination in Bangladesh Groundwater: A Major Environmental and Social Disaster. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2002, 12, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, R.B.; Ashfaque, K.N.; Badruzzaman, A.B.M.; Ashraf Ali, M.; Shoemaker, J.K.; Harvey, C.F. Anthropogenic Influences on Groundwater Arsenic Concentrations in Bangladesh. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, K.J.; Ong, L.A.; Achi, N.E.; Ahmed, K.M.; Khan, M.R. Bangladesh MICS 2019: Water Quality Thematic Report; Dhaka, 2021. Available online: https://psb.gov.bd/policies/wqtr2019.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2022).
- Ayers, J.C.; Goodbred, S.; George, G.; Fry, D.; Benneyworth, L.; Hornberger, G.; Roy, K.; Karim, M.R.; Akter, F. Sources of Salinity and Arsenic in Groundwater in Southwest Bangladesh. Geochem. Trans. 2016, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehin, M.; Chowdhury, M.M.A.; Clarke, D.; Mondal, S.; Nowreen, S.; Jahiruddin, M.; Haque, A. Mechanisms and Drivers of Soil Salinity in Coastal Bangladesh. In Ecosystem Services for Well-Being in Deltas; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 333–347. [Google Scholar]
- Ravenscroft, P.; McArthur, J.M.; Hoque, M.A. Stable Groundwater Quality in Deep Aquifers of Southern Bangladesh: The Case against Sustainable Abstraction. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 454–455, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, P.K.; Froehlich, K.; Basu, A.R.; Poreda, R.J.; Kulkarni, K.M.; Tarafdar, S.A.; Ali, M.; Ahmed, N.; Hussain, A.; Rahman, M.; et al. A Report on Isotope Hydrology of Groundwater in Bangladesh: Implications for Characterization and Mitigation of Arsenic in Groundwater; INIS-XA-648; International Atomic Energy Agency, Department of Technical Co-operation: Vienna, Austria, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Mohsenipour, M.; Asgari, H. Impact of Landuse on Groundwater Quality of Bangladesh. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 4, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.E. An Overview of Groundwater Quality in Bangladesh. In Groundwater of South Asia; Mukherjee, A., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 205–232. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.R.; Koneshloo, M.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Ahmed, K.M.; Bostick, B.C.; Mailloux, B.J.; Mozumder, R.H.; Zahid, A.; Harvey, C.F.; Van Geen, A.; et al. Megacity Pumping and Preferential Flow Threaten Groundwater Quality. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knappett, P.S.K.; Mailloux, B.J.; Choudhury, I.; Khan, M.R.; Michael, H.A.; Barua, S.; Mondal, D.R.; Steckler, M.S.; Akhter, S.H.; Ahmed, K.M.; et al. Vulnerability of Low-Arsenic Aquifers to Municipal Pumping in Bangladesh. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mozumder, M.R.H.; Michael, H.A.; Mihajlov, I.; Khan, M.R.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Bostick, B.C.; Mailloux, B.J.; Ahmed, K.M.; Choudhury, I.; Koffman, T.; et al. Origin of Groundwater Arsenic in a Rural Pleistocene Aquifer in Bangladesh Depressurized by Distal Municipal Pumping. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Khan, A.Q. Urbanization and Environmental Degradation: Evidence from Four SAARC Countries-Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2016, 35, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capps, K.A.; Bentsen, C.N.; Ramírez, A. Poverty, Urbanization, and Environmental Degradation: Urban Streams in the Developing World. Freshw. Sci. 2015, 35, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Gao, Z.; Ning, J.; Bi, X.; Wang, Q. Impact of Progressive Urbanization and Changing Cropping Systems on Soil Erosion and Net Primary Production. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, S. Subsurface Pollution in Asian Megacities. In Groundwater and Subsurface Environments; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2011; pp. 159–184. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, F.; Bendimerad, F.; Sinha, R. Megacities—Megarisks. Nat. Hazards 2007, 42, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodrud-Doza, M.; Islam, S.M.D.-U.; Rume, T.; Quraishi, S.B.; Rahman, M.S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.H. Groundwater Quality and Human Health Risk Assessment for Safe and Sustainable Water Supply of Dhaka City Dwellers in Bangladesh. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.J.; Onodera, S.; Shimizu, Y. An Overview of the Effects of Urbanization on the Quantity and Quality of Groundwater in South Asian Megacities. Limnology 2013, 14, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, Y.; Hosono, T.; Onodera, S.; Siringan, F.; Buapeng, S.; Delinom, R.; Yoshimizu, C.; Tayasu, I.; Nagata, T.; Taniguchi, M. Sources of Nitrate and Ammonium Contamination in Groundwater under Developing Asian Megacities. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, S.; Saito, M.; Sawano, M.; Hosono, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Shimada, J.; Umezawa, Y.; Lubis, R.F.; Buapeng, S.; Delinom, R. Effects of Intensive Urbanization on the Intrusion of Shallow Groundwater into Deep Groundwater: Examples from Bangkok and Jakarta. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Leal, J.A.; Noyola Medrano, C.; Tapia Silva, F.O. Aquifer Vulnerability and Groundwater Quality in Mega Cities: Case of the Mexico Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors on Surface and Groundwater Quality in Rural and Urban Areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, P.A.; Anornu, G.K.; Gibrilla, A.; Owusu-Ansah, E.d.-G.J.; Ganyaglo, S.Y.; Egbi, C.D. Spatial Distributions and Probabilistic Risk Assessment of Exposure to Heavy Metals in Groundwater in a Peri-Urban Settlement: Case Study of Atonsu-Kumasi, Ghana. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutiani, R.; Kulkarni, D.B.; Khanna, D.R.; Gautam, A. Water Quality, Pollution Source Apportionment and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Groundwater of an Industrial Area in North India. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.T.M.T.; Paul, M.; Bhoumik, N.; Hassan, M.; Alam, M.K.; Aktar, Z. Heavy Metal Pollution Assessment in the Groundwater of the Meghna Ghat Industrial Area, Bangladesh, by Using Water Pollution Indices Approach. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, Mechanism and Health Effects of Some Heavy Metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GoB. Bangladesh Economic Review 2021; GoB: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Bussi, G.; Peters, R.; Hossain, M.A.; Softley, L.; Shawal, S.; Jin, L.; Rampley, C.P.N.; Holdship, P.; Hope, R.; et al. Modelling Heavy Metals in the Buriganga River System, Dhaka, Bangladesh: Impacts of Tannery Pollution Control. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.S.; Han, B.; Al-Mizan; Pichtel, J. Assessment of Soil and Groundwater Contamination at a Former Tannery District in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1905–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BEZA. Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Shilpanagar, Mirsarai-Sitakundu-Sonagazi, Chattogram-Feni; Prime Minister’s Office: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- IWM. Environmental and Social Assessment (ESA), Bangladesh Economic Zones Authority (BEZA), Final Report; IWM: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. Population and Housing Census 2011; Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chadha, D.K. A Proposed New Diagram for Geochemical Classification of Natural Waters and Interpretation of Chemical Data. Hydrogeol. J. 1999, 7, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation of Water-Analyses. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durov, S.A. Natural Waters and Graphical Representation of Their Composition: Doklady Akademii Nauk. Union Sov. Social. Repub. 1948, 59, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R.K. An Index Number System for Rating Water Quality. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1965, 37, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedi, M.; Abessi, O.; Sharifi, F.; Meraji, H. Development of Groundwater Quality Index. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 163, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P.; Dobhal, R. Water Quality Assessment in Terms of Water Quality Index. Am. J. Water Resour. 2013, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packialakshmi, S.; Deb, M.; Chakraborty, H. Assessment of Groundwater Quality Index in and around Sholinganallur Area, Tamil Nadu. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaei, A.; Hassani, H.; Tziritis, E.; Fard Mousavi, S.B.; Jabbari, N. Hydrochemical Characterization and Evaluation of Groundwater Quality in Dalgan Basin, SE Iran. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Agriculture Handbook No 60; United States Salinity Laboratory, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, L. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; No. 969; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Bauder, J.W.; Brock, T.A. Irrigation Water Quality, Soil Amendment, and Crop Effects on Sodium Leaching. Arid L. Res. Manag. 2001, 15, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, V.E.A.; Groen, J.; Kooi, H.; Person, M.; Ge, S.; Edmunds, W.M. Offshore Fresh Groundwater Reserves as a Global Phenomenon. Nature 2013, 504, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, H.A.; Scott, K.C.; Koneshloo, M.; Yu, X.; Khan, M.R.; Li, K. Geologic Influence on Groundwater Salinity Drives Large Seawater Circulation through the Continental Shelf. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- BGS; DPHE. Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater in Bangladesh; British Geological Survey Technical Report WC/00/19; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2001; Volume 4, pp. 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Tokunaga, T.; Yamanaka, T. Origin and Evolutionary Processes of Deep Groundwater Salinity in Southwestern Coastal Region of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna Delta, Bangladesh. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 36, 100854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Implications of Climate Change for Fresh Groundwater Resources in Coastal Aquifers in Bangladesh; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.R. Groundwater Chemistry of Mirsharai Upazila Chattogram, HydroShare. 2022. Available online: http://www.hydroshare.org/resource/ce9529d9678e4f988739aab517acf1b2 (accessed on 5 June 2022).








| Indexing Parameter | Unit | Standard | Weight (wi) | Relative Weight (Wi) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 6.5–8.5 | 2 | 0.0444 |
| TDS | mg/L | 1000 | 5 | 0.1111 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 400 | 3 | 0.0667 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 600 | 5 | 0.1111 |
| NO3− | mg/L | 10 | 5 | 0.1111 |
| F− | mg/L | 1 | 5 | 0.1111 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 75 | 2 | 0.0444 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 35 | 2 | 0.0444 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 200 | 2 | 0.0444 |
| K+ | mg/L | 12 | 2 | 0.0444 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 200 | 2 | 0.0444 |
| Fe | mg/L | 1 | 2 | 0.0444 |
| Mn | mg/L | 0.1 | 3 | 0.0667 |
| As | µg/L | 50 | 5 | 0.1111 |
| Total | 45 | 1.0000 | ||
| Parameters | Min | Max | Mean | SD | WHO Guidelines |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 21.5 | 30.5 | 26.5 | 3.7 | - |
| pH | 5.04 | 7.90 | 6.90 | 0.57 | 6.5–9.2 |
| EC (µS/cm), 25 °C | 60 | 9540 | 1628 | 2086 | - |
| Eh (mV) | −167 | −195 | −52 | −83 | 850 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 65 | 7114 | 1126 | 1359 | 1000 |
| Sodium (mg/L) | 2.10 | 1748 | 236.4 | 340.5 | 200 |
| Potassium (mg/L) | 0.62 | 20.19 | 4.95 | 4.70 | 200 |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 5.44 | 171.7 | 28.48 | 30.58 | 200 |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | 6.67 | 280.1 | 50.83 | 57.59 | 150 |
| Bicarbonate (mg/L) | 45.75 | 799.8 | 375.0 | 195.6 | 125–350 |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 1.38 | 3720 | 393.3 | 755.8 | 250 |
| Nitrate (mg/L) | 0.07 | 13.35 | 2.64 | 3.01 | 50 |
| Sulphate (mg/L) | 0.11 | 443.8 | 29.6 | 78.4 | 250 |
| Manganese (mg/L) | <DL | 2.45 | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.1 |
| Iron (mg/L) | 0.05 | 10.14 | 2.34 | 2.60 | 0.3 |
| Fluoride (mg/L) | <DL | 0.65 | 0.28 | 0.15 | 1.5 |
| Bromide (mg/L) | <DL | 17.3 | 1.37 | 3.09 | - |
| Phosphate (mg/L) | <DL | 9.80 | 0.97 | 1.97 | 0.3 |
| Nitrite (mg/L) | <DL | 0.42 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.5 |
| Arsenic (µg/L) | <DL | 1000 | 131.3 | 213.2 | 10 |
| Hardness | 41 | 1501 | 280 | 308 | - |
| %Na | 8.12 | 83.41 | 51.59 | 20.39 | - |
| SAR | 0.13 | 19.62 | 5.07 | 4.85 | - |
| >DL Less than the detection limit | |||||
| Groundwater Quality Range | Groundwater Quality | No. of Shallow Wells | No. of Deep Wells |
|---|---|---|---|
| <50 | Excellent | 2 | 20 |
| 50–100 | Good | 1 | 6 |
| 100–200 | Poor | 8 | - |
| 200–300 | Very poor | 7 | - |
| >300 | Unsuitable for drinking | 3 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.R.; Hasan, F.; Islam, M.; Chowdhury, M.; Sadeak, S.; Amin, A.; Hossain, F.; Ahmed, K.M. Potential Impacts of Industrialization on Coastal Fresh Groundwater Resources in Bangladesh. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148704
Khan MR, Hasan F, Islam M, Chowdhury M, Sadeak S, Amin A, Hossain F, Ahmed KM. Potential Impacts of Industrialization on Coastal Fresh Groundwater Resources in Bangladesh. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148704
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Mahfuzur R, Fuad Hasan, Majidul Islam, Masuma Chowdhury, Sumiya Sadeak, Al Amin, Farhad Hossain, and Kazi Matin Ahmed. 2022. "Potential Impacts of Industrialization on Coastal Fresh Groundwater Resources in Bangladesh" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148704
APA StyleKhan, M. R., Hasan, F., Islam, M., Chowdhury, M., Sadeak, S., Amin, A., Hossain, F., & Ahmed, K. M. (2022). Potential Impacts of Industrialization on Coastal Fresh Groundwater Resources in Bangladesh. Sustainability, 14(14), 8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148704