Tillage Impacts on Initial Soil Erosion in Wheat and Sainfoin Fields under Simulated Extreme Rainfall Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Rainfall Simulator
2.3. Plot Design and Sampling Strategy
2.4. Rainfall Simulation Procedure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Initial Soil Erosion Results
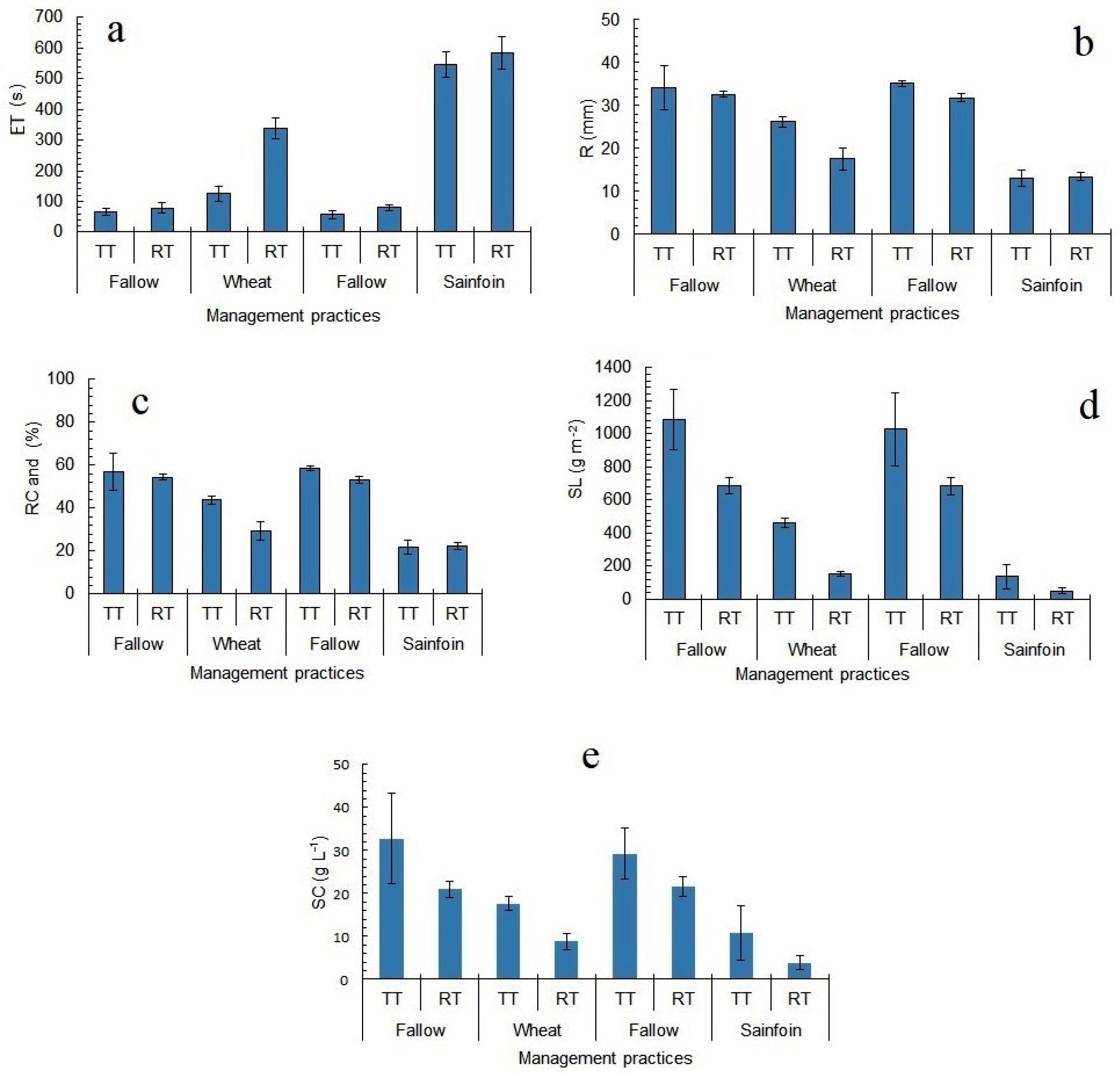
3.2. Effects of Tillage and Crop on Measured Variables
3.3. Determining the Most Suitable Crop and Management System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AWC | available water content for the plant |
| BD | bulk density |
| C | clay content |
| CaCO3 | total calcium carbonate |
| ET | elapsed time to runoff generation |
| FC | field capacity (moisture content at −33 kPa suction) |
| Ksat | saturated hydraulic conductivity |
| pH | soil reaction measured in saturation paste |
| PWP | permanent wilting point (moisture content at −1500 kPa suction) |
| R | total runoff volume |
| RC | runoff coefficient |
| S | sand content |
| SAT | water content in saturation paste |
| SC | sediment concentration |
| SCL | sandy clayey loam |
| Si | silt content (USDA) |
| SL | sandy loam |
| SL | soil loss |
| Slt | total salt content measured in saturation paste |
| SOM | total soil organic matter content |
| WAS | wet aggregate stability of macro-aggregates of 1–2 mm particle size |
References
- Raclot, D.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Louchart, X.; Andrieux, P.; Moussa, R.; Voltz, M. Soil tillage and scale effects on erosion from fields to catchment in a Mediterranean vineyard area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 134, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.K.; Singh, R.J.; Mandal, D.; Kumar, A.; Alam, N.M.; Keesstra, S. Increasing farmer’s income and reducing soil erosion using intercropping in rainfed maize-wheat rotation of Himalaya, India. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.; Mol, G.; de Leeuw, J.; Okx, J.; de Cleen, M.; Visser, S. Soil-related sustainable development goals: Four concepts to make land degradation neutrality and restoration work. Land 2018, 7, 6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, S.; Keesstra, S.; Maas, G.; De Cleen, M. Soil as a Basis to Create Enabling Conditions for Transitions Towards Sustainable Land Management as a Key to Achieve the SDGs by 2030. Sustainability 2019, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Plaza-Bonilla, D.; Arrúe, J.L.; Lampurlanés, J.; Cantero-Martínez, C. Soil organic carbon storage in a no-tillage chronosequence under Mediterranean conditions. Plant Soil 2014, 376, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atucha, A.; Merwin, I.A.; Brown, M.G.; Gardiazabal, F.; Mena, F.; Adriazola, C.; Lehmann, J. Soil erosion, runoff and nutrient losses in an avocado (Perseaamericana Mill) hillside orchard under different groundcover management systems. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhe, A.A.; Barnes, R.T.; Six, J.; Marín-Spiotta, E. Role of soil erosion in biogeochemical cycling of essential elements: Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 46, 521–548. [Google Scholar]
- Duguma, L.A.; Hager, H.; Sieghardt, M. Effects of land use types on soil chemical properties in smallholder farmers of central highland Ethiopia. Ecology 2010, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shammary, A.A.G.; Al-Sadoon, J.N.A. Influence of tillage depth, soil mulching systems and fertilizers on some thermal properties of silty clay soil. GJAR 2014, 2, 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoubi, S.; Mokhtari, J.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Zeraatpisheh, M. Erodibility of calcareous soils as influenced by land use and intrinsic soil properties in a semiarid region of central Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, P.; Baker, J.; Sojka, R.E.; Bolan, N.; Desbiolles, J.; Kirkham, M.B.; Ross, C.; Gupta, R. Chapter five—A review of tillage practices and their potential to impact the soil carbon dynamics. Adv. Agron. 2018, 150, 185–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.L.; Daigh, A.L.M. Tillage practices alter the surface energy balance—A review. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-B.; Cai, D.-X.; Hoogmoed, W.B.; Oenema, O.; Perdok, U.D. Potential effect of conservation tillage on sustainable land use: A review of global long-term studies. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampurlanes, J.; Cantero-Martinez, C. Soil bulk density and penetration resistance under different tillage and crop management systems and their relationship with barley root growth. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczko, U.; Bens, O.; Hüttl, R.F. Tillage effects on hydraulic properties and macroporosity in silty and sandy soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gristina, L.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A. No-till durum wheat yield success probability in semi arid climate: A methodological framework. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 181, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani-Harchegani, M.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Asadi, H. Comparing grain size distribution of sediment and original soil under raindrop detachment and raindrop-induced and flow transport mechanism. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, J.; Head, M.; Barraclough, D.; Archer, M.; Scheib, C.; Flight, D.; Voulvoulis, N. Soil quality assessment under emerging regulatory requirements. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Davis, J.; Masselink, R.H.; Casalí, J.; Peeters, E.T.; Dijksma, R. Coupling hysteresis analysis with sediment and hydrological connectivity in three agricultural catchments in Navarre, Spain. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1598–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaez, J.; Lasanta, T.; Ruiz-Flaño, P.; Ortigosa, L. Factors affecting runoff and erosion under simulated rainfall in Mediterranean vineyards. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 93, 324–334. [Google Scholar]
- Buttar, G.S.; Sidhu, H.S.; Singh, V.; Jat, M.L.; Gupta, R.; Singh, Y.; Singh, B. Relay planting of wheat in cotton: An innovative technology for enhancing productivity and profitability of wheat in cotton-wheat production system of South Asia. Exp. Agric. 2013, 49, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Dumlupinar, Z.; Taner, A. Effects of conventional and reduced tillage methods on some traits of wheat in cotton-wheat system. KSU J. Agric Nat. 2018, 21, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crittenden, S.J.; Poot, N.; Heinen, M.; van Balen, D.J.M.; Pulleman, M.M. Soil physical quality in contrasting tillage systems in organic and conventional farming. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 154, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, N.; Miller, P.; Froud-Williams, R. The adoption of non-inversion tillage systems in the United Kingdom and the agronomic impact on soil, crops and the environment: A review. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 108, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soane, B.D.; Ball, B.C.; Arvidsson, J.; Basch, G.; Moreno, F.; Roger-Estrade, J. No-till in northern, western and south-western Europe: A review of problems and opportunities for crop production and the environment. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 118, 66–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, X.; Liu, K.; Li, C. Effects of tillage on soil physical properties and root growth of maize in loam and clay in central China. Plant Soil Environ. 2013, 7, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaisi, M.M.; Yin, X.; Licht, M.A. Soil carbon and nitrogen changes as influenced by tillage and cropping systems in some Iowa soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alba, S.; Lindstrom, M.; Schumacher, T.E.; Malo, D.D. Soil landscape evolution due to soil redistribution by tillage: A new conceptual model of soil catena evolution in agricultural landscapes. Catena 2004, 58, 77–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, R.; Wu, F.; Keesstra, S. Effect of soil surface roughness on infiltration water, ponding and runoff on tilled soils under rainfall simulation experiments. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 179, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansa, J.; Mozafar, A.; Kuhn, G.; Anken, T.; Ruh, R.; Sanders, I.R.; Frossard, E. Soil tillage affects the community structure of mycorrhizal fungi in maize roots. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Gao, M.; Wei, C.; Xie, D.; Pan, G. Tillage effect on organic carbon in a purple paddy soil. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, M.M.; Brye, K.R.; Olk, D.C.; Schmid, B.T. Rice rotation and tillage effects on soil aggregation and aggregate carbon and nitrogen dynamics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, R.; Jantalia, C.P.; Halvorson, A.D. Soil carbon dynamics for irrigated corn under two tillage systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidsson, J.; Etana, A.; Rydberg, T. Crop yield in Swedish experiments with shallow tillage and no-tillage 1983–2012. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 52, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhazo, N.; Chivenge, P.; Chaplot, V. Tillage impact on soil erosion by water: Discrepancies due to climate and soil characteristics. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 230, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, W.S.; Panachuki, E.; De Oliveira, P.T.S.; Menezes, R.S.; Sobrinho, T.A.; De Carvalho, D.F. Effect of soil tillage and vegetal cover on soil water infiltration. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Nadal-Romero, E.; Lana-Renault, N.; Beguería, S. Erosion in Mediterranean landscapes: Changes and future challenges. Geomorphology 2013, 198, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A New European slope length and steepness factor (LS-factor) for modeling soil erosion by water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erpul, G.; Şahin, S.; İnce, K.; Küçümen, A.; Akdağ, M.A.; Demirtaş, İ.; Çetin, E. Turkiye Su Erozyonu Atlasi; General Directorate of Combating Desertification and Erosion: Ankara, Turkey, 2018.
- GDCDE. Türkiye’ de Yağışların Özelliklerive Yenilenmiş Evrensel Toprak Kayıpları Eşitliği (YETKE) R Faktörü; Turkish Republic Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, General Directorate of Combating Desertification and Erosion: Ankara, Turkey, 2016.
- Baiamonte, G.; Minacapilli, M.; Novara, A.; Gristina, L. Time scale effects and interactions of rainfall erosivity and cover management factors on vineyard soil loss erosion in the semi-arid area of southern Sicily. Water 2019, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Terol, E.; Mora, G.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Cerdà, A. Vicia sativa Roth. can reduce soil and water losses in recently planted vineyards (Vitis vinifera L.). Earth Syst. Environ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSMS. Available online: https://mgm.gov.tr/eng/forecast-cities.aspx (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Ozturk, M.Z.; Çetinkaya, G.; Aydin, S. Climate types of Turkey according to Köppen-Geiger climate classification. J. Geogr. 2017, 35, 17–27. Available online: http://dergipark.gov.tr/download/article-file/370152 (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Soil Survey Staff. Key to Soil Taxonomy, 12th ed.; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), NRSC, United States Printing Office: Washington DC, USA, 2014.
- Karakus, N. The Formation, Classification and Mapping of Mersin Tarsus Topcu Creek Basin Soils. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Natural and Applied Sciences, Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University, Kahramanmaras, Turkey, 12 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yakupoglu, T.; Dindaroglu, T.; Akay, A.E.; Kusvuran, K.; Alma, V.; Gundogan, R. The effect of traditional and reduced tillage systems on the sediment yield of plots constructed in the Mediterranean climate zone caused by natural rainfall. Int. J. Glob. Warm. 2020, 24, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, N. Soil Conservation; B.T. Batsford Limited: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.; Pohl, M.; Alewell, C.; Körner, C.; Rixen, C. Interrill erosion at disturbed alpine sites: Effects of plant functional diversity and vegetation cover. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2010, 11, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nciizah, A.D.; Wakindiki, I.I.C. Rainfall pattern effects on crusting, infiltration and erodibility in some African soils with various texture and mineralogy. Water SA 2014, 40, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe, E.; Bek, Y.; Sahin, M. SPSS’ de Cozumleriile Istatistiksel Yontemler II; No. 73; KSU: Kahramanmaras, Turkey, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nearing, M.A.; Pruski, F.F.; O’Neal, M.R. Expected climate change impacts on soil erosion rates: A review. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 59, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nearing, M.A. Potential changes in rainfall erosivity in the U.S. with climate change during the 21st century. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2001, 59, 43–50. Available online: http://www.jswconline.org/content/56/3/229.abstractT (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Pfeifer, R.A.; Habeck, M. Farm level economic impacts of climate change. In Effects of Climate Change and Variability on Agricultural Production Systems; Doering, O.C., Randolph, J.C., Southworth, J., Pfeifer, R.A., Eds.; Kluwer Academic: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ruiz, J.M. The effects of land uses on soil erosion in Spain: A review. Catena 2010, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C. Soil losses in rainfed Mediterranean vineyards under climate changes scenarios. The effects of drainage terraces. Agriculture 2016, 1, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, C.; Lourenço, A.; Guimaraes, M.d.F.; Fonsecac, I.C.B. Aggregate stability under different soil management systems in a red latosol in the state of Parana, Brazil. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 65, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiec, J.; Kus, J.; Slowinska-Jurkiewicz, A.; Nosalewicz, A. Soil porosity and water infiltration as influenced by tillage methods. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 89, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haene, K.; Vermang, J.; Cornelis, W.M.; Leroy, B.L.M.; Schiettecatte, W.; De Neve, S.; Gabriels, D.; Hofman, G. Reduced tillage effects on physical properties of silt loam soils growing root crops. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 99, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, B.D.; Vandenbygaart, B. Conservation tillage and depth stratification of porosity and soil organic matter. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 66, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamen, T.; Alakukku, L.; Pires, S.; Sommer, C.; Spoor, G.; Tijink, F.; Weisskopf, P. Prevention strategies for field traffic-induced subsoil compaction: A review: Part 2. Equipment and field practices. Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 73, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, A.; Crescimanno, M.; Gristina, L.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A. Actual provision as an alternative criterion to improve the efficiency of payments for ecosystem services for C sequestration in semiarid vineyards. Agric. Syst. 2016, 144, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkholm, L.J.; Hansen, E.M.; Olesen, J.E. The effect of tillage intensity on soil structure and winter wheat root/shoot growth. Soil Use Manag. 2008, 24, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Cornelis, W.M.; Gabriels, D.; Schiettecatte, W.; De Neve, S.; Lu, J.; Buysse, T.; Wu, H.; Cai, D.; Jin, J.; et al. Soil management effects on runoff and soil loss from field rainfall simulation. Catena 2008, 75, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulenard, J.; Podwojewski, P.; Janeau, J.L.; Collinet, J. Runoff and soil erosion under rainfall simulation of Andisols from the Ecuadorian Páramo: Effect of tillage and burning. Catena 2001, 45, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.L.; Jastrow, J.D. Physical and chemical protection in hierarchical soil aggregates regulates soil carbon and nitrogen recovery in restored perennial grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cates, A.M.; Ruark, M.D.; Hedtcke, J.L.; Posner, J.L. Long-term tillage, rotation and perennialization effects on particulate and aggregate soil organic matter. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entz, M.H.; Bullied, W.J.; Katepa-Mupondwa, F. Rotational benefits of forage crops in Canadian prairie cropping systems. J. Prod. Agric. Abstr. Res. 2013, 8, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Gonzalez, J.L. Influence of organic amendments on soil structure and soil loss under simulated rain. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 93, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthes, B.; Albrecht, A.; Asseline, J.; De Noni, G.; Roose, E. Relationships between soil erodibility and topsoil aggregate stability on carbon content in a cultivated Mediterranean highland (Aveyron, France). Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1999, 30, 1929–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Figueiredo, T.; Poesen, J. Effects of surface rock fragments characteristics on interrill runoff and erosion of a silty loam soil. Soil Till. Res. 1998, 46, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; De Luna, E.; Franca, A.; Nachtergaele, J.; Govers, G. Concentrated flow erosion rates as affected by rock fragment cover and initial soil moisture content. Catena 1999, 36, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Luo, H.; Xie, Y. Effects of rock fragment content, size and cover on soil erosion dynamics of spoil heaps through multiple rainfall events. Catena 2019, 172, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
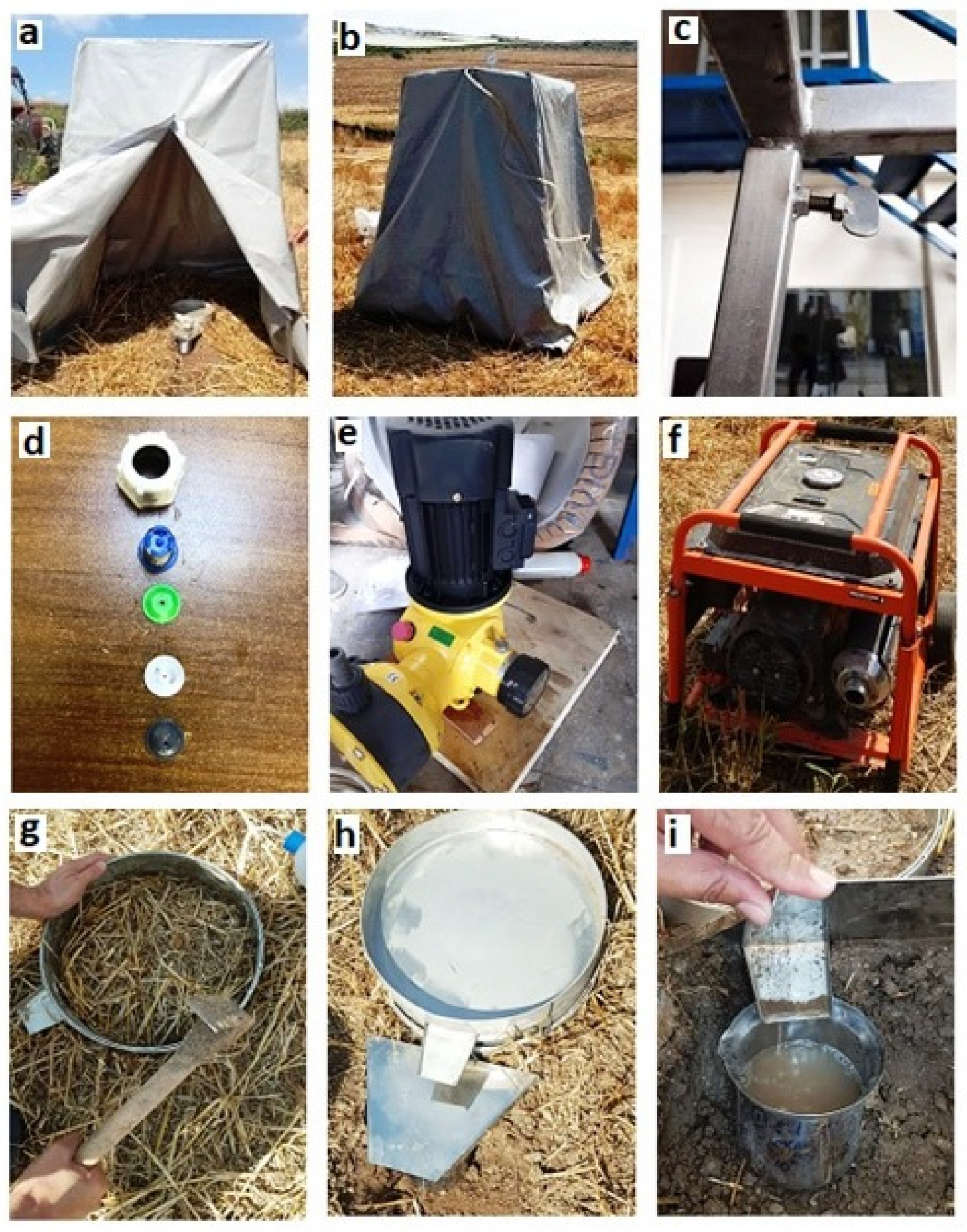



| Location | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII | VIII | IX | X | XI | XII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K.maras (°C) | 4.7 | 6.1 | 10.3 | 15.0 | 19.9 | 24.8 | 28.2 | 28.3 | 24.9 | 18.7 | 11.7 | 6.6 |
| K.maras (mm) | 122 | 112 | 95 | 73 | 38 | 8.6 | 2.7 | 2.2 | 11 | 45 | 78 | 130 |
| Tarsus (°C) | 9.9 | 10.7 | 13.6 | 17.3 | 21 | 24.7 | 27.4 | 27.8 | 26 | 21.8 | 16.6 | 11.9 |
| Tarsus (mm) | 128 | 92 | 70 | 50 | 40 | 18 | 9 | 6 | 12 | 48 | 83 | 144 |
| Soil Property | Location | |
|---|---|---|
| Tarsus | Kahramanmaras | |
| C (g kg−1) | 170 | 280 |
| Si (g kg−1) | 180 | 250 |
| S (g kg−1) | 650 | 470 |
| Textural class | SL | SCL |
| pH | 7.52 | 6.65 |
| Salt (g kg−1) | 0.7 | 1.0 |
| SOM (g kg−1) | 25.0 | 28.3 |
| CaCO3 (g kg−1) | 92 | 75 |
| FC (cm3cm−3) | 0.21 | 0.32 |
| PWP (cm3cm−3) | 0.12 | 0.19 |
| AWC (cm3cm−3) | 0.09 | 0.13 |
| SAT (cm3cm−3) | 0.43 | 0.46 |
| BD (Mg m−3) | 1.55 | 1.38 |
| WAS (%) | 29.1 | 76.1 |
| Ksat (cm h−1) | 2.61 | 5.70 |
| Surface stoniness (%) | 2 | 15 |
| Locations | Variables | Min. | Max. | Mean | Std. Dev. | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tarsus (N = 24) | ET (s) | 42 | 622 | 234 | 215 | 0.825 | −1.088 |
| R (mm) | 10.9 | 38.0 | 25.5 | 9.17 | −0.334 | −1.554 | |
| SL (g m−2) | 38 | 1251 | 535.83 | 395.61 | 0.307 | −1.090 | |
| SC (g L−1) | 0.97 | 3.70 | 2.44 | 0.819 | −0.254 | −0.871 | |
| RC (%) | 18 | 63 | 42.54 | 15.220 | −0.322 | −1.559 | |
| Kahramanmaras (N = 24) | ET (s) | 166 | 654 | 323 | 160 | 0.861 | −0.277 |
| R (mm) | 2.0 | 14.3 | 6.85 | 4.04 | 0.589 | −0.968 | |
| SL (g m−2) | 2.0 | 37.3 | 18.27 | 12.02 | −0.036 | −1.634 | |
| SC (g L−1) | 2.6 | 44.1 | 18.21 | 2.139 | 0.451 | 0.211 | |
| RC (%) | 3.0 | 24.0 | 11.41 | 6.736 | 0.528 | −1. |
| Location | Management Practices | Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET | R | SL | SC | RC | ||
| Tarsus | Tillage (A) | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| Crop (B) | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| A × B | *** | ** | * | ns | ** | |
| Kahramanmaras | Tillage (A) | *** | *** | *** | ns | *** |
| Crop (B) | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| A × B | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | |
| Location | Variation Sources | Mean Values of Measured Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET (s) | R (mm) | SL (g m−2) | SC (g L−1) | RC (%) | ||
| Tarsus | Fallow | 70.67c | 33.43a | 871.33a | 26.18a | 57.7a |
| Wheat | 232.33b | 21.95b | 307.02b | 13.20b | 36.5b | |
| Sainfoin | 564.83a | 13.32c | 93.68c | 7.28c | 22.3c | |
| Kahramanmaras | Fallow | 188.17c | 10.18a | 29.21a | 3.00a | 17.0a |
| Wheat | 384.50b | 4.53b | 11.25b | 2.43b | 7.7b | |
| Sainfoin | 533.33a | 2.53c | 3.45c | 1.33c | 4.0c | |
| Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET (s) | R (mm) | SL (g m−2) | SC (ppm) | RC (%) |
| ns | *** | *** | *** | *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yakupoglu, T.; Gundogan, R.; Dindaroglu, T.; Kusvuran, K.; Gokmen, V.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; Cerdà, A. Tillage Impacts on Initial Soil Erosion in Wheat and Sainfoin Fields under Simulated Extreme Rainfall Treatments. Sustainability 2021, 13, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020789
Yakupoglu T, Gundogan R, Dindaroglu T, Kusvuran K, Gokmen V, Rodrigo-Comino J, Gyasi-Agyei Y, Cerdà A. Tillage Impacts on Initial Soil Erosion in Wheat and Sainfoin Fields under Simulated Extreme Rainfall Treatments. Sustainability. 2021; 13(2):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020789
Chicago/Turabian StyleYakupoglu, Tugrul, Recep Gundogan, Turgay Dindaroglu, Kadir Kusvuran, Veysel Gokmen, Jesus Rodrigo-Comino, Yeboah Gyasi-Agyei, and Artemi Cerdà. 2021. "Tillage Impacts on Initial Soil Erosion in Wheat and Sainfoin Fields under Simulated Extreme Rainfall Treatments" Sustainability 13, no. 2: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020789
APA StyleYakupoglu, T., Gundogan, R., Dindaroglu, T., Kusvuran, K., Gokmen, V., Rodrigo-Comino, J., Gyasi-Agyei, Y., & Cerdà, A. (2021). Tillage Impacts on Initial Soil Erosion in Wheat and Sainfoin Fields under Simulated Extreme Rainfall Treatments. Sustainability, 13(2), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020789









