Centrifuge Modeling and the Analysis of Ancient Landslides Subjected to Reservoir Water Level Fluctuation
Abstract
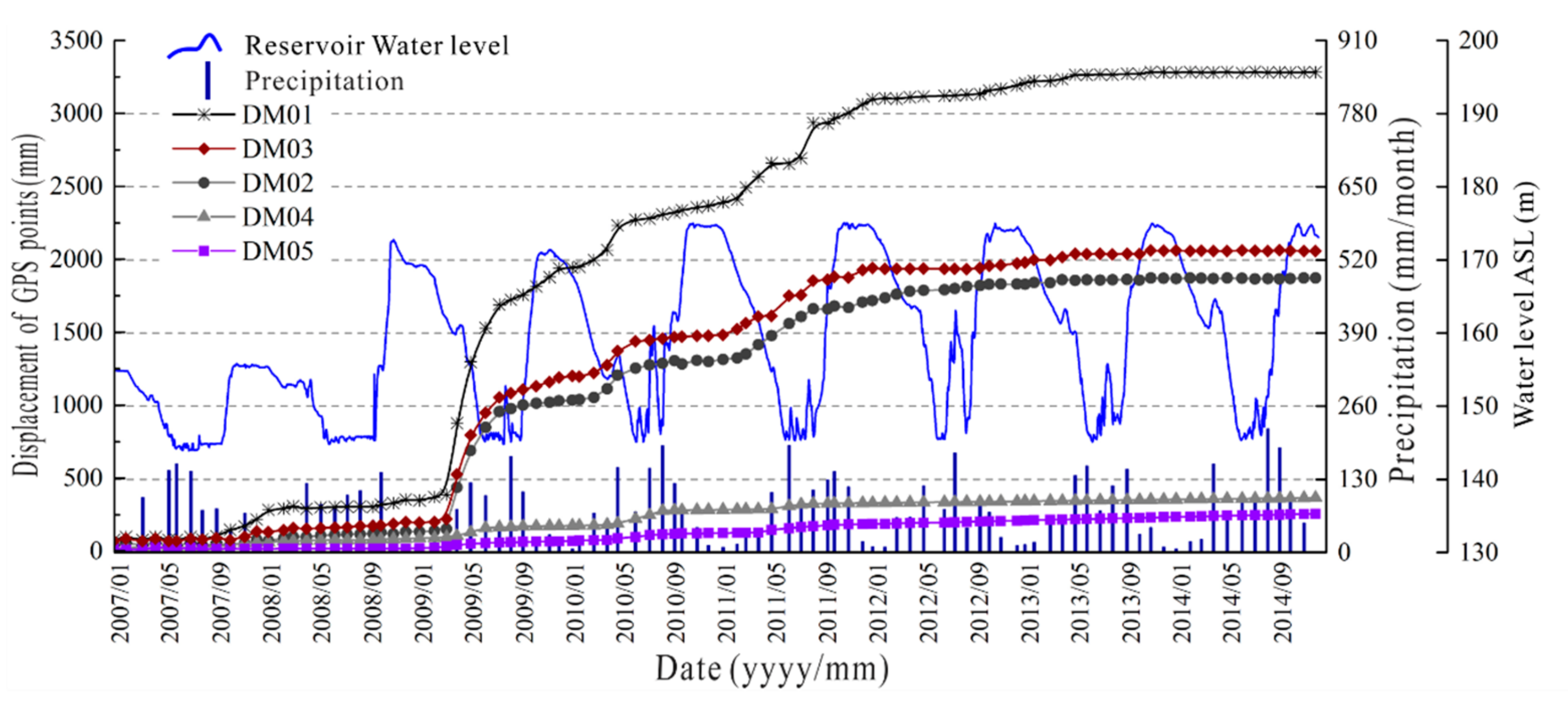
1. Introduction
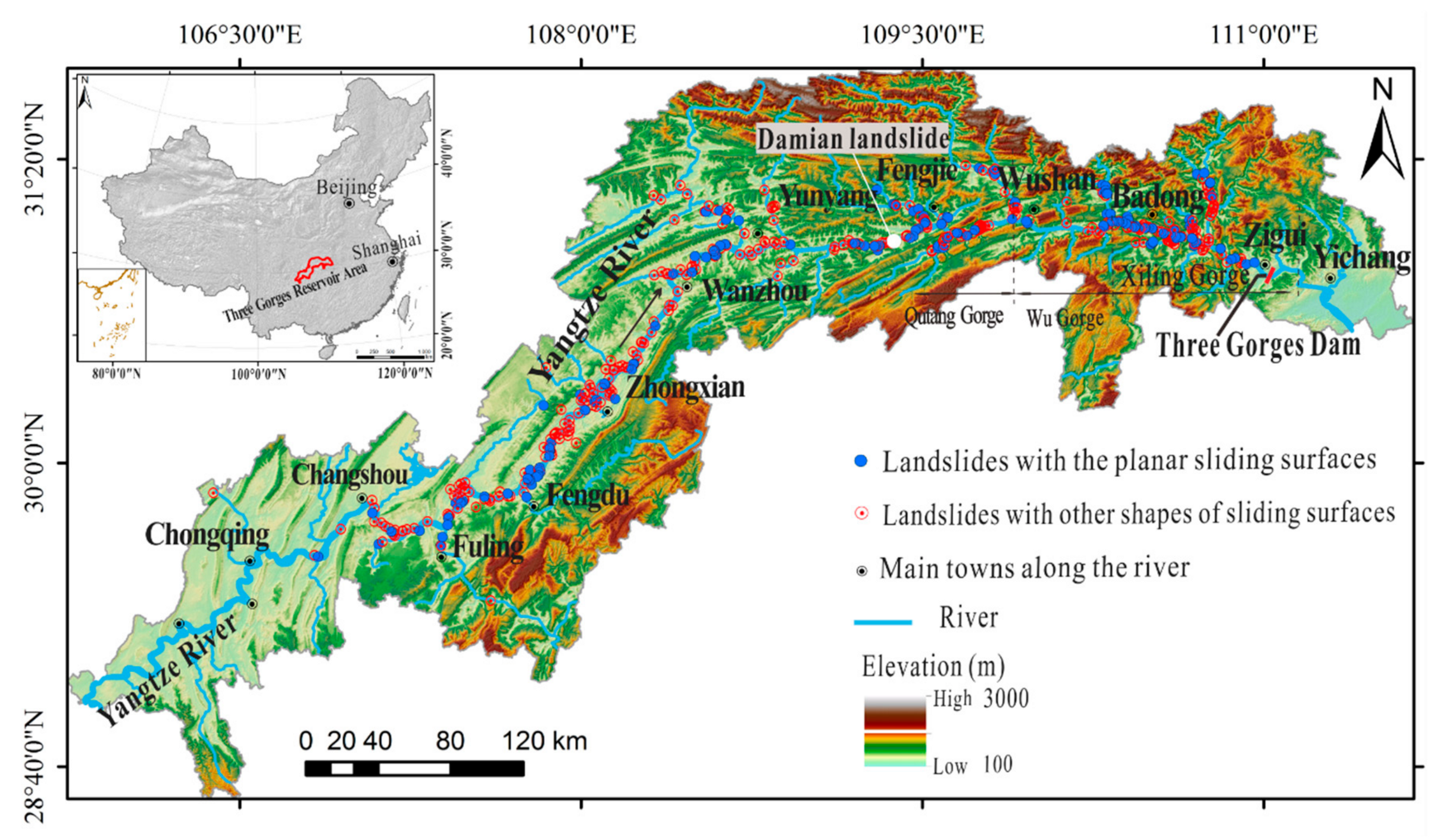
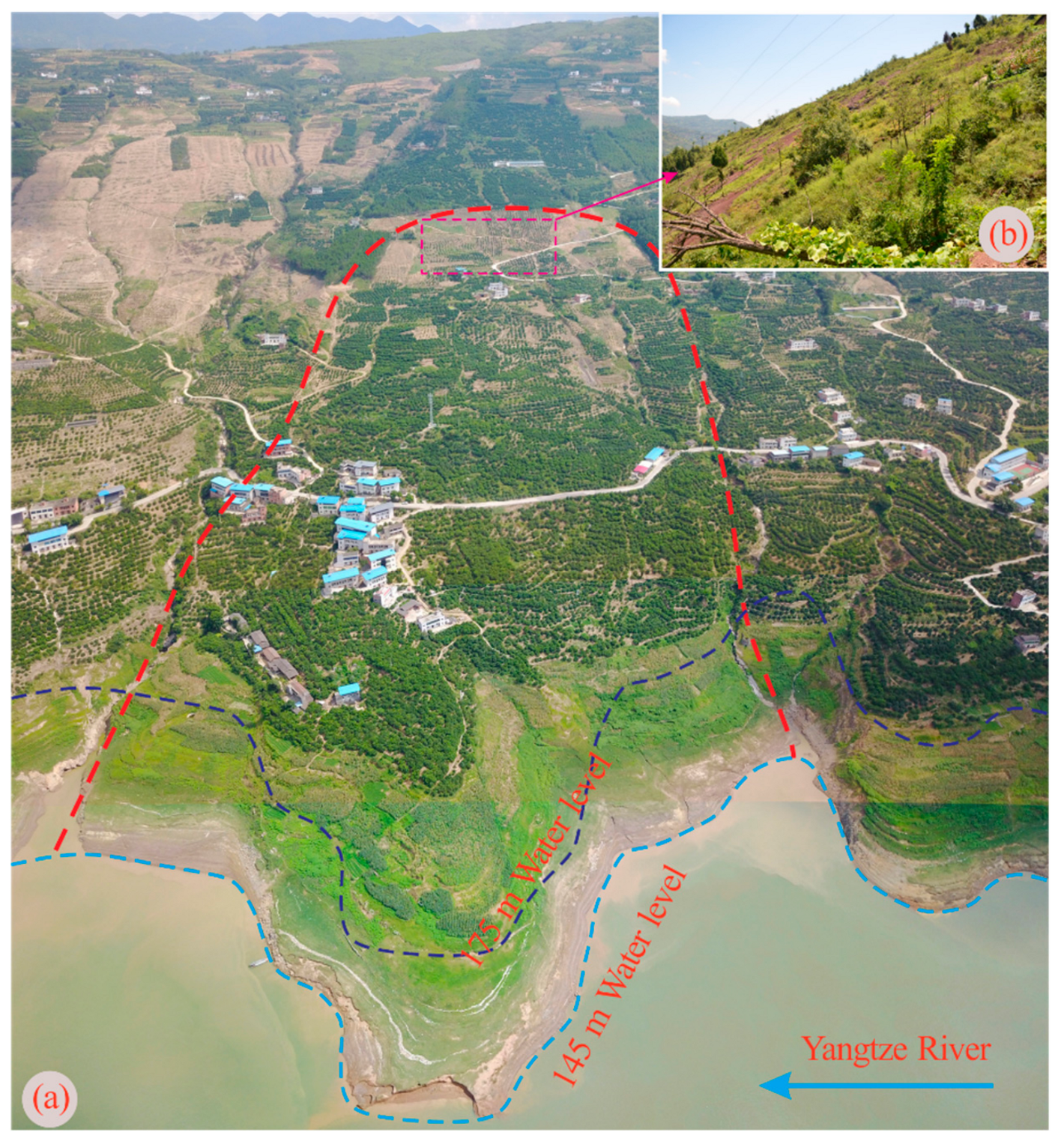
2. Geological Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Principles of Centrifuge Modeling
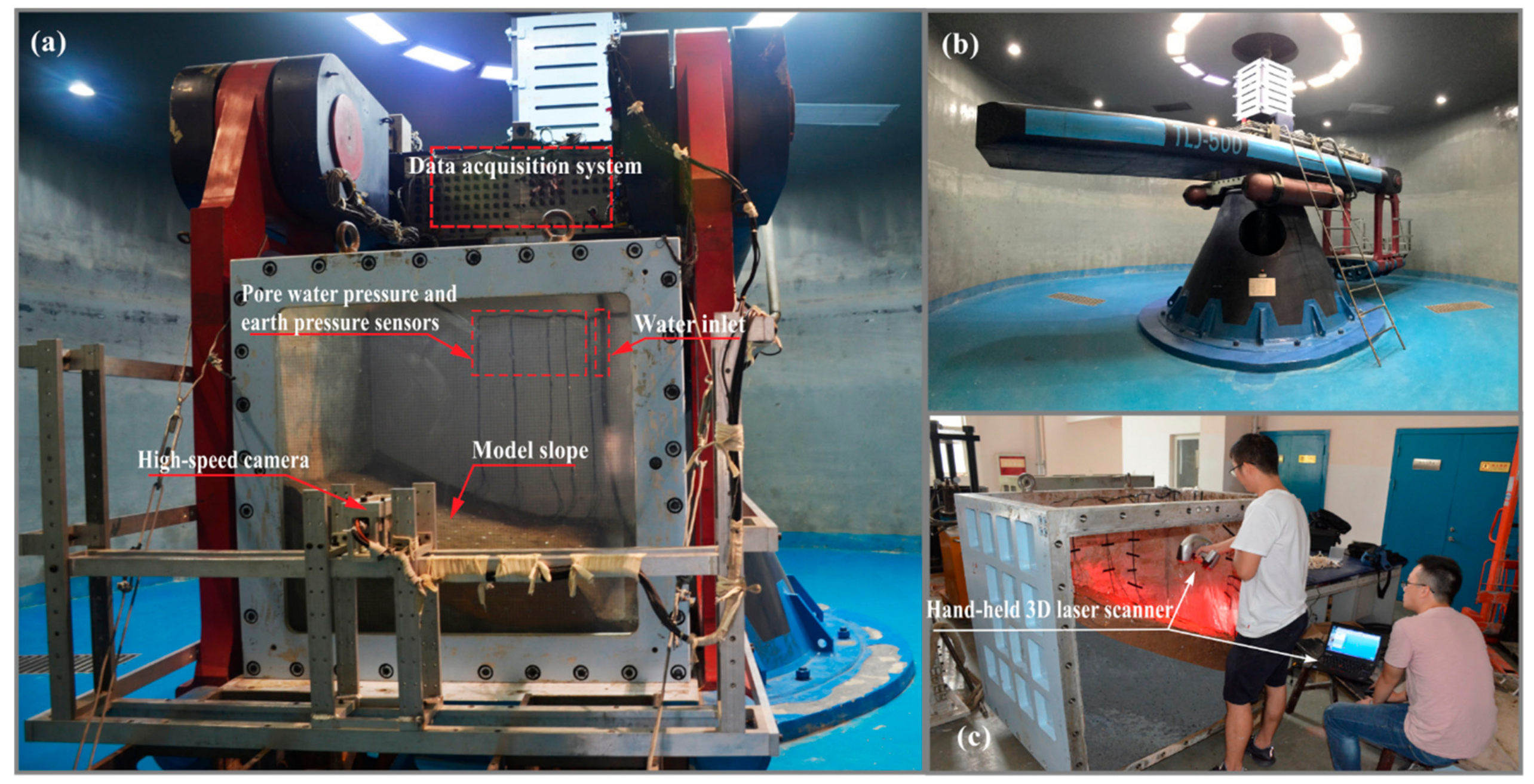
3.2. Centrifuge Facility
3.3. Materials
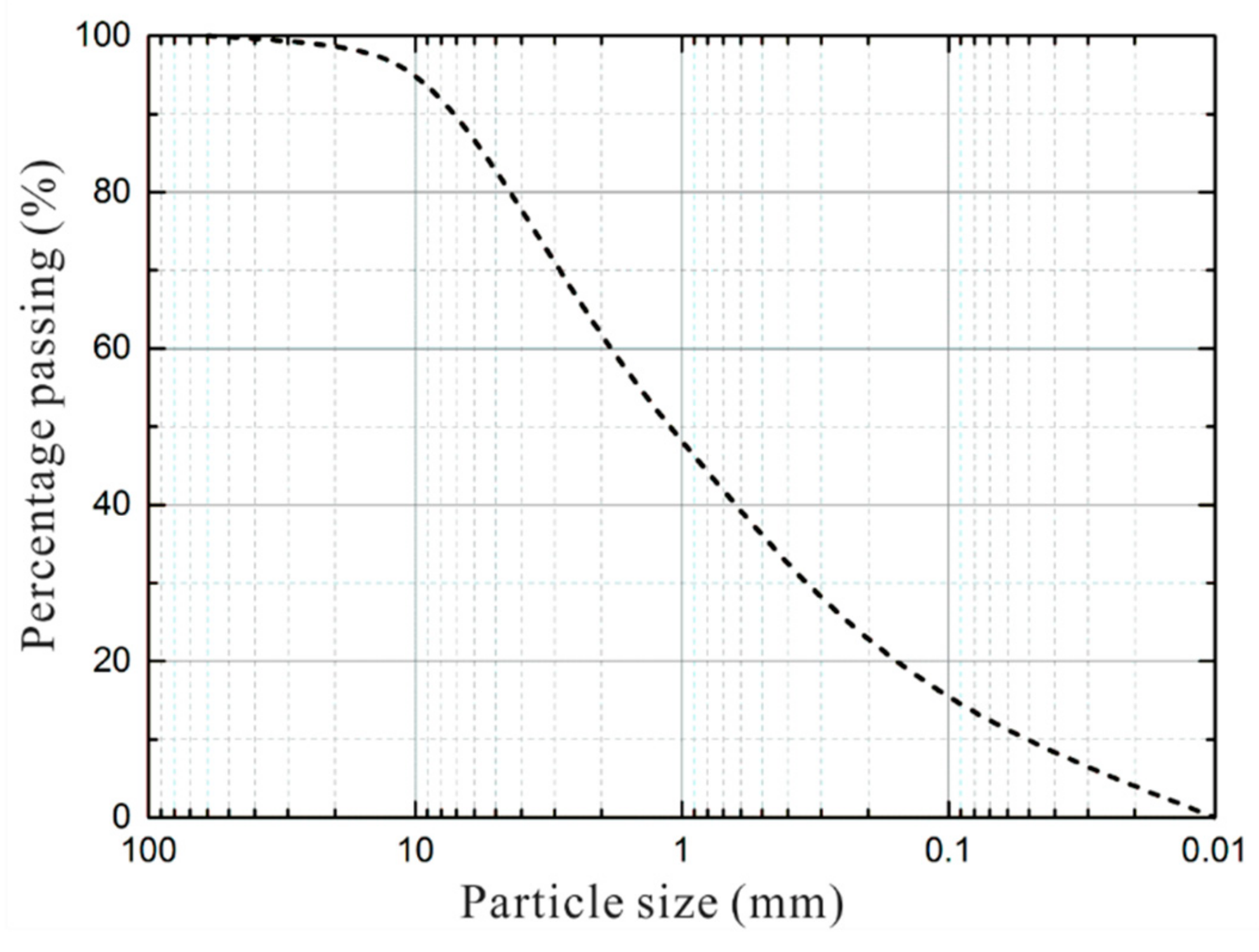
3.3.1. Soil Material
3.3.2. Measurement System
3.4. Methods
3.4.1. Construction of the Model
3.4.2. Test Procedure
4. Results
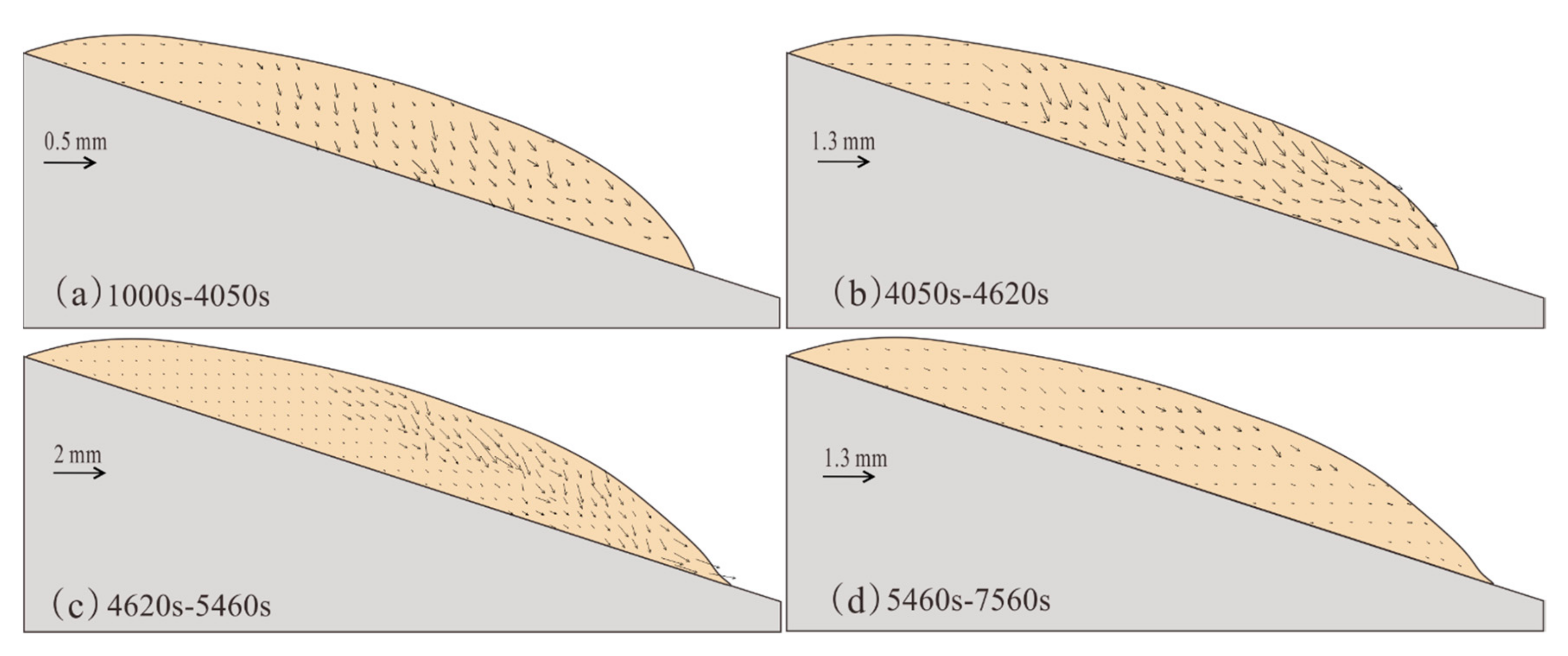
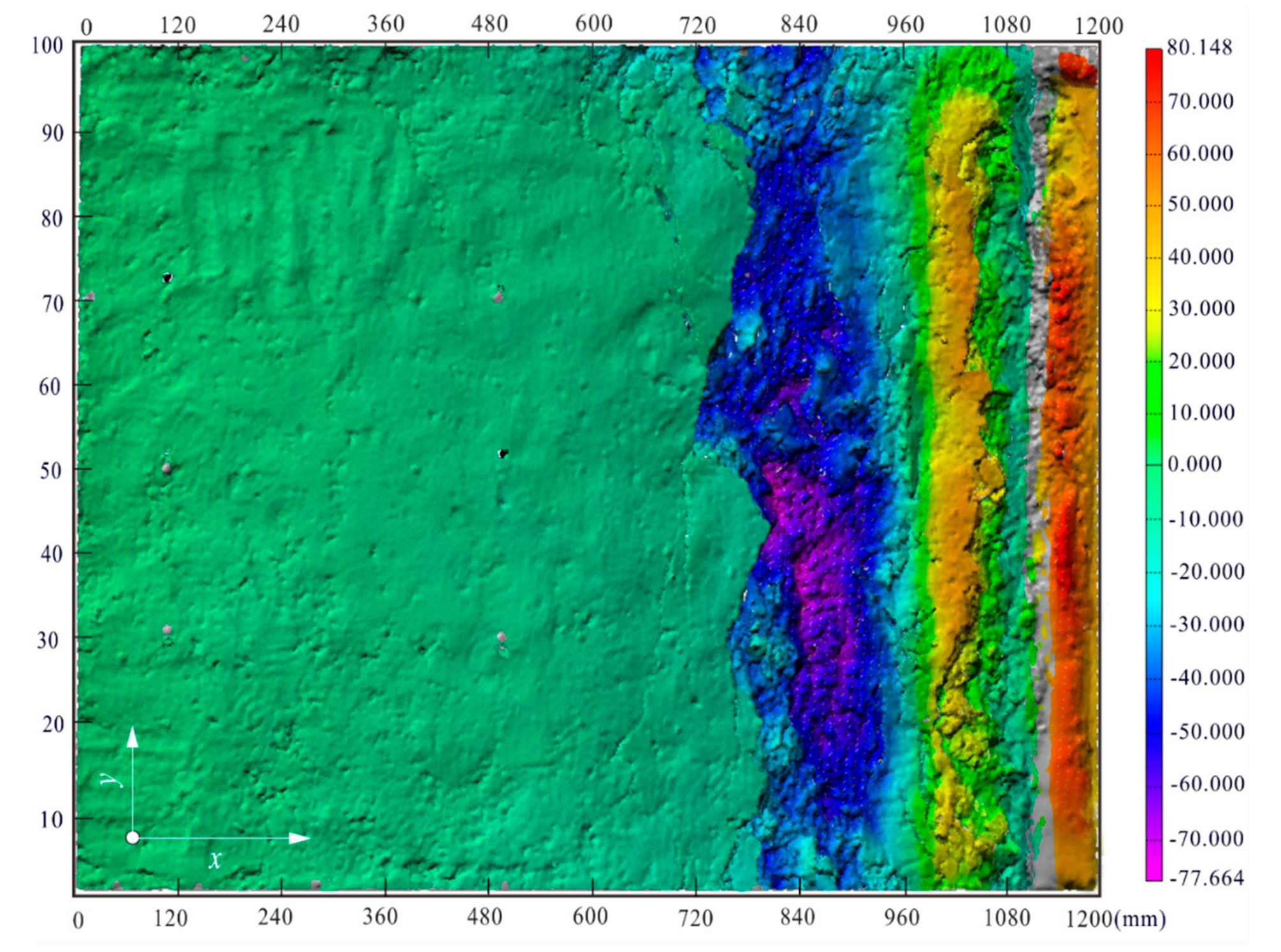
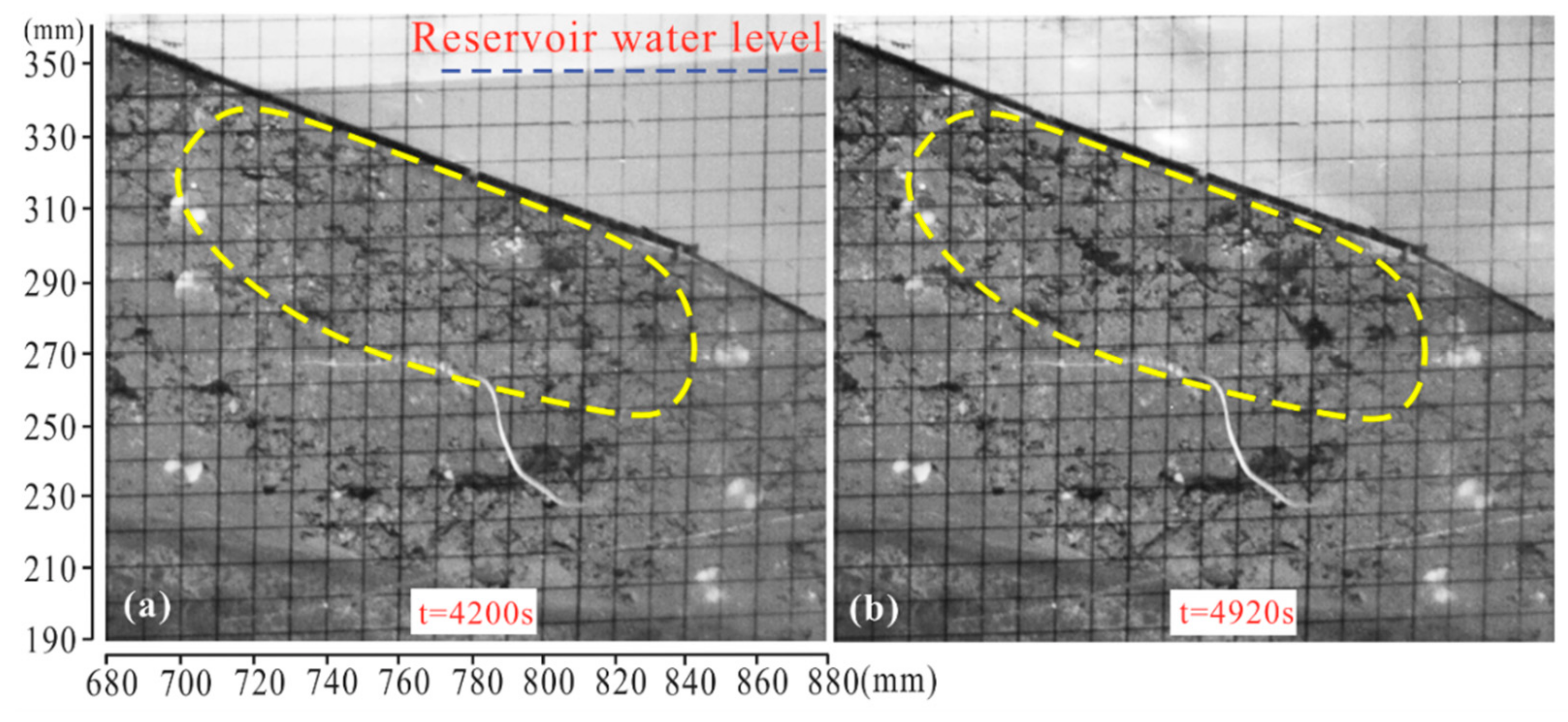
4.1. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Deformation
4.2. Displacement Response
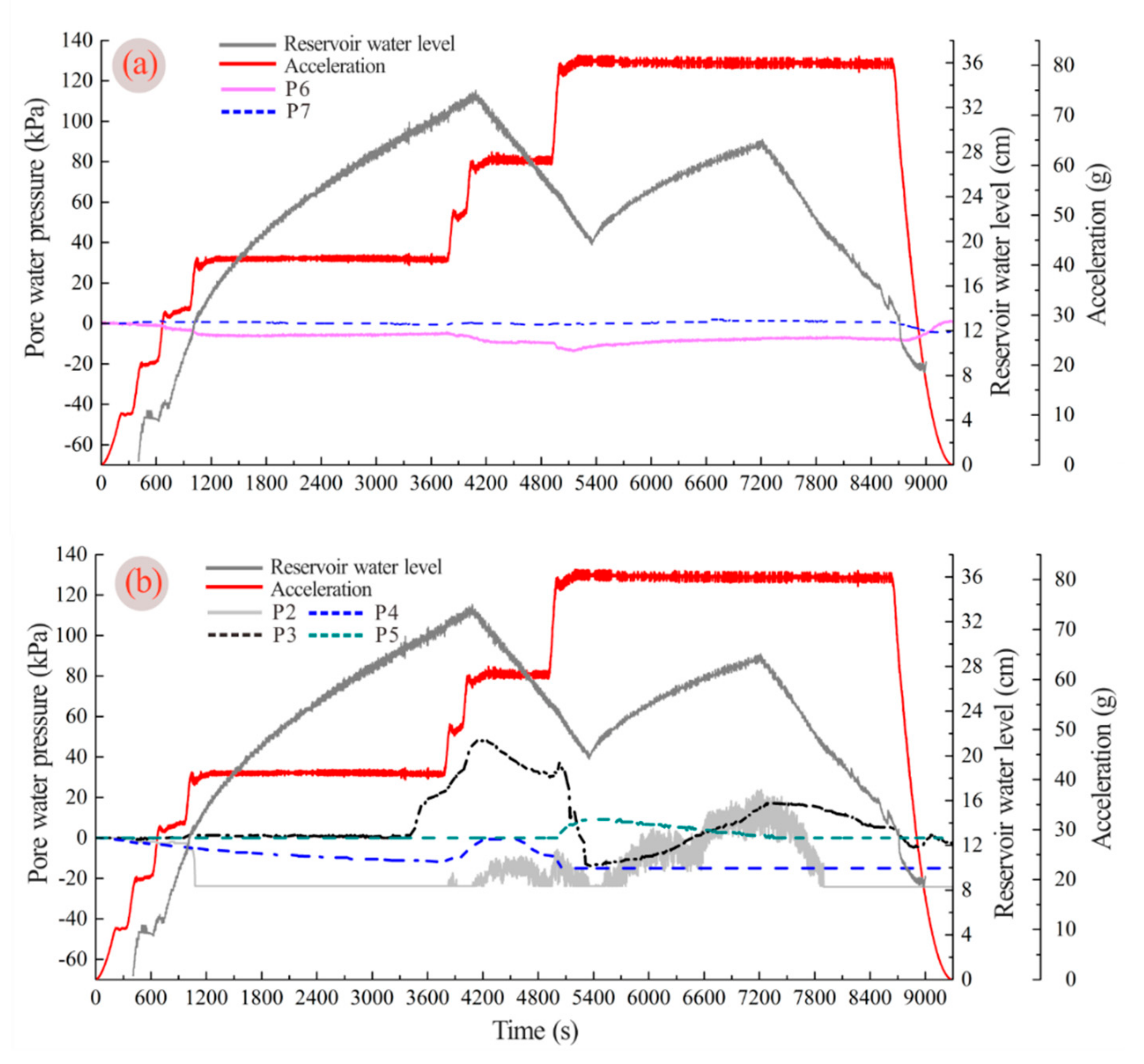
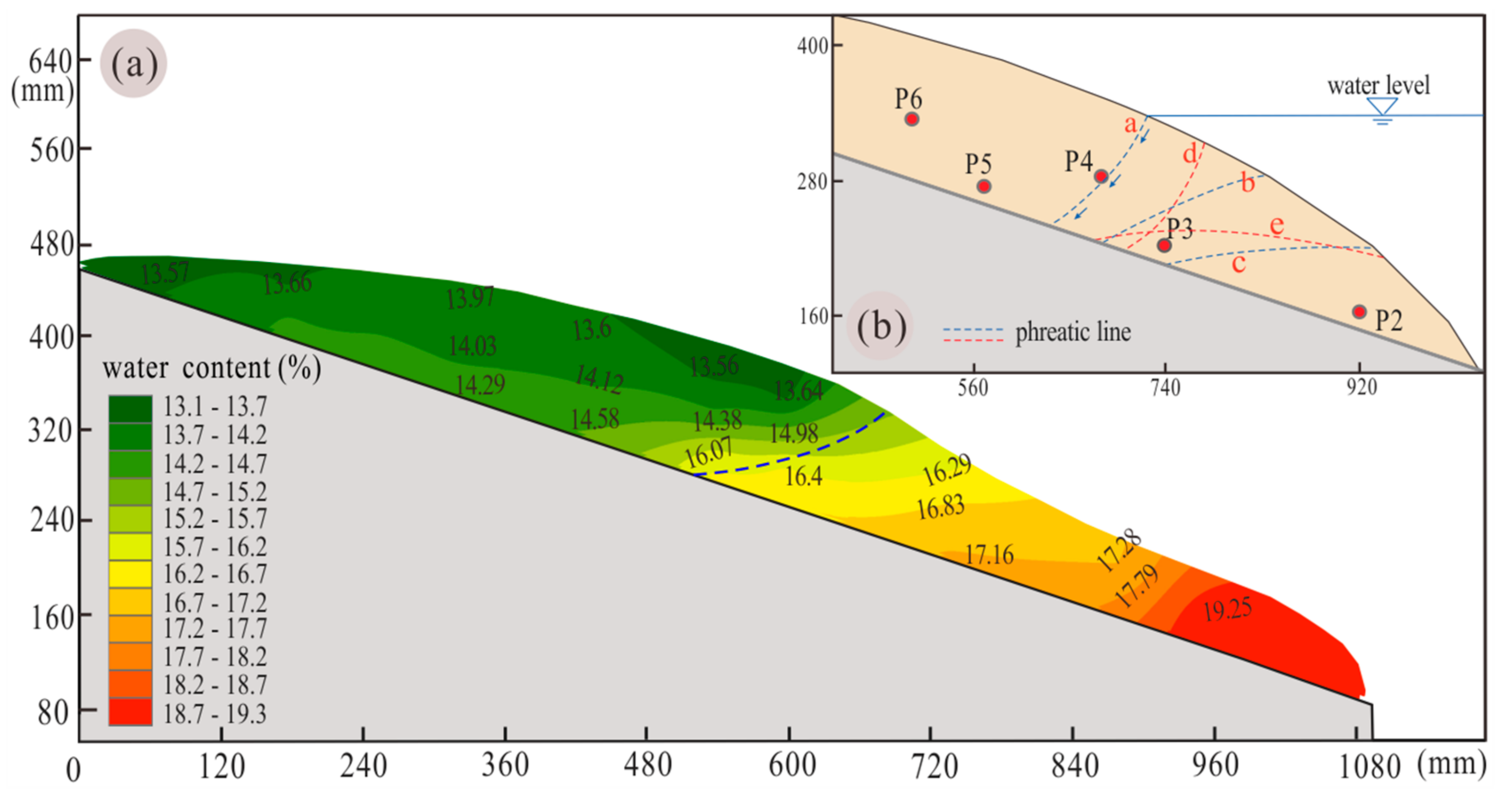
4.3. Pore Pressure and Reservoir Water Infiltration
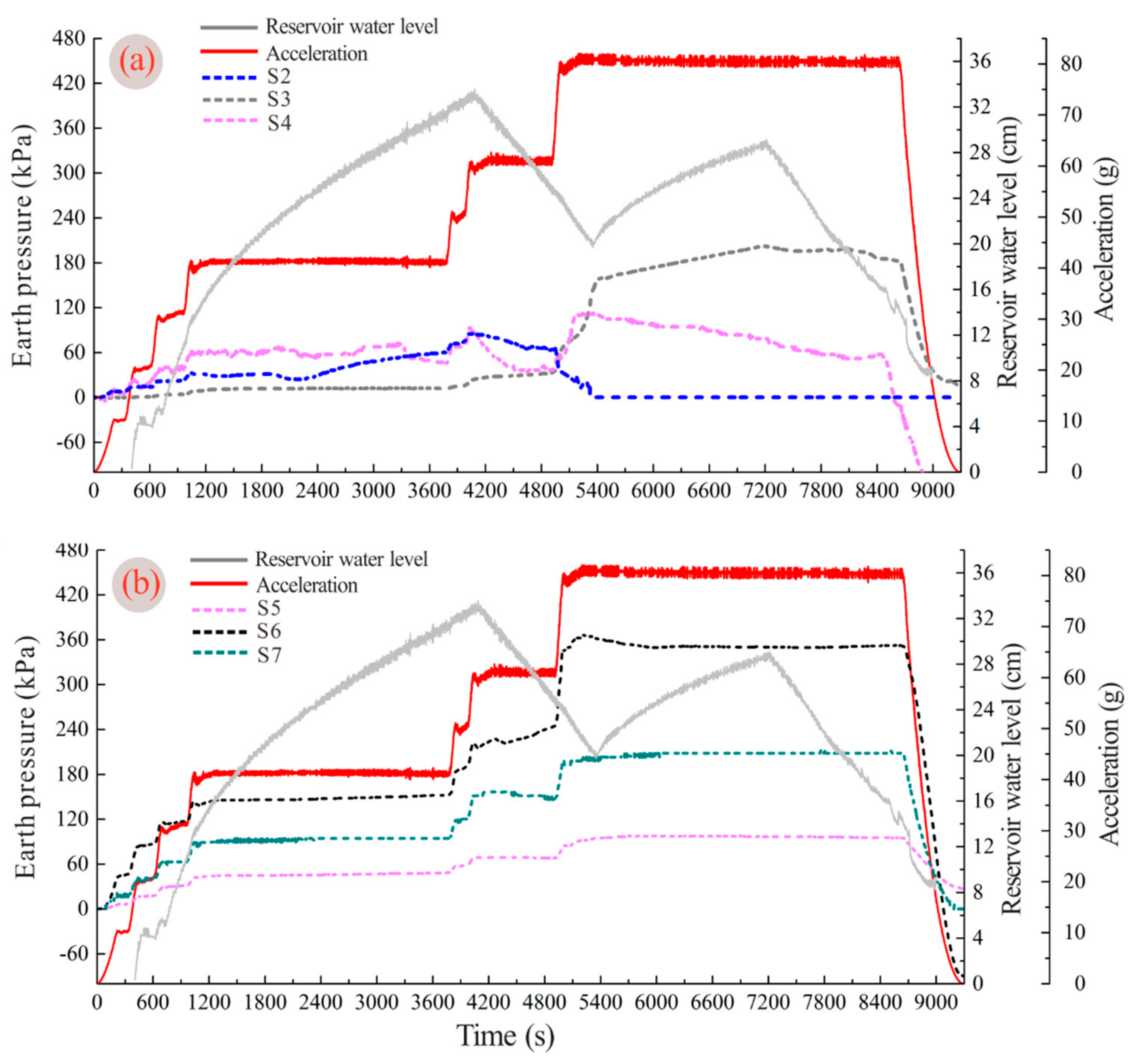
4.4. Earth Pressure
4.5. Failure Mechanism
5. Discussion
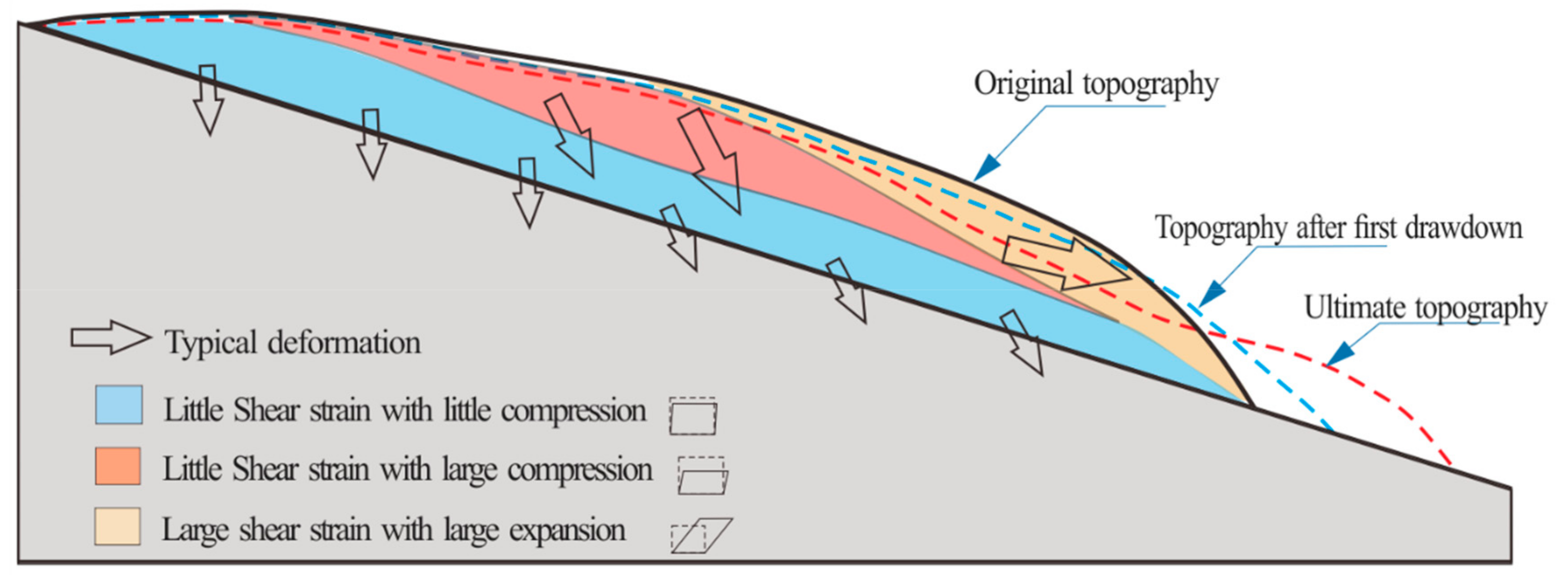
5.1. Self-Adjustment of Deformation
5.2. Seepage Erosion
5.3. Deformation and Failure Modes
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barla, G.; Paronuzzi, P. The 1963 Vajont Landslide: 50th Anniversary. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2013, 46, 1267–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, A.P.; Bromhead, E.N. New, simplified and improved interpretation of the Vaiont landslide mechanics. Landslides 2018, 15, 2001–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibañez, J.P.; Hatzor, Y.H. Rapid sliding and friction degradation: Lessons from the catastrophic Vajont landslide. Eng. Geol. 2018, 244, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaniboni, F.; Tinti, S. The 1963 Vajont Landslide: A Numerical Investigation on the Sliding Surface Heterogeneity. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.F.; Morgenstern, N.R.; Martin, C.D. Expected damage from displacement of slow-moving slides. Landslides 2011, 8, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macciotta, R.; Martin, C.D.; Morgenstern, N.R.; Cruden, D.M. Development and application of a quantitative risk assessment to a very slow moving rock slope and potential sudden acceleration. Landslides 2016, 13, 765–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Lucha, P.; Galve, J.P. Reconstructing the geochronological evolution of large landslides by means of the trenching technique in the Yesa Reservoir (Spanish Pyrenees). Geomorphology 2010, 124, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Meng, X.; Yin, Y.; Dijkstra, T.; Winter, M.; Wasowski, J. Landslide Research in China. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2016, 49, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, X. Real-time monitoring and early warning of landslides at relocated Wushan Town, the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 2010, 7, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yin, K.; Lacasse, S. Displacement prediction in colluvial landslides, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 2013, 10, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; Rengers, N.; Zhu, X. Partial reactivation of a huge deep-seated ancient rock slide: Recognition, formation mechanism, and stability. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 1719–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Hu, X.; Tannant, D.D.; Tan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Response of a landslide to reservoir impoundment in model tests. Eng. Geol. 2018, 247, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Xu, Q.; Huang, R. Site monitoring of suction and temporary pore water pressure in an ancient landslide in the Three Gorges reservoir area, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 5601–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Huang, B.; Wang, W.; Wei, Y.; Ma, X.; Ma, F.; Zhao, C. Reservoir-induced landslides and risk control in Three Gorges Project on Yangtze River, China. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 8, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, Q.; Tang, M.; Iqbal, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, F.; Zhu, D. Characterizing the spatial distribution and fundamental controls of landslides in the three gorges reservoir area, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4275–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, I.; Tu, X.; Gao, W. The Impact of Reservoir Fluctuations on Reactivated Large Landslides: A Case Study. Geofluids 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Gu, D.; Song, Y.; Cen, D.; Zeng, B. Towards a complete understanding of the triggering mechanism of a large reactivated landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Eng. Geol. 2018, 238, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, Q.; He, Y.; Deng, J. Prediction of landslide displacement with an ensemble-based extreme learning machine and copula models. Landslides 2018, 15, 2047–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Gu, D. Influence of filling-drawdown cycles of the Three Gorges reservoir on deformation and failure behaviors of anaclinal rock slopes in the Wu Gorge. Geomorphology 2017, 295, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wang, F.; Yi, Q.; Lu, S. Landslide deformation behavior influenced by water level fluctuations of the Three Gorges Reservoir (China). Eng. Geol. 2018, 247, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Yin, Z.; Cui, D.; Xiang, W. Residual-state creep of clastic soil in a reactivated slow-moving landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Landslides 2018, 15, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabian, A.; Viswanadham, B.V.S.; Ghiassian, H.; Salehzadeh, H. Centrifuge model studies on anchored geosynthetic slopes for coastal shore protection. Geotext. Geomembr. 2012, 34, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Xue, D.; Chen, Q.; Zhai, X.; Huang, M. Centrifuge model test and limit equilibrium analysis of the stability of municipal solid waste slopes. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 3011–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J. Centrifuge modelling of clay slope with montmorillonite weak layer under rainfall conditions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Ling, H.I. Centrifuge Model Simulations of Rainfall-Induced Slope Instability. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2012, 138, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, R.; Qian, J.; Zhang, J.; Qian, J. Effect study of cracks on behavior of soil slope under rainfall conditions. Soils Found. 2012, 52, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wu, S.; Tang, H.; Liang, C. Seismic performance of loess-mudstone slope in TianShui —Centrifuge model tests and numerical analysis. Eng. Geol. 2017, 222, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wu, S.; Tang, H.; Liang, C. Investigation of dormant landslides in earthquake conditions using a physical model. Landslides 2017, 14, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Pei, X.; Wu, H.; Huang, R. Centrifuge model test of an irrigation-induced loess landslide in the Heifangtai loess platform, Northwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Fan, Z.; Wu, D.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, J.; Che, W. Landslides triggered by excavation in the loess plateau of China: A case study of Middle Pleistocene loess slopes. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 171, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, K. Centrifuge modeling and analysis of submarine landslides triggered by elevated pore pressure. Ocean Eng. 2015, 109, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, S.; Fu, C.; Zhong, Q. Centrifugal model tests and numerical simulations for barrier dam break due to overtopping. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, J. Stability analysis of bank slope under conditions of reservoir impounding and rapid drawdown. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2011, 3, 429–437. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, D. Stability analysis of an ancient landslide considering shear strength reduction behavior of slip zone soil. Landslides 2016, 13, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Zhang, G.; Li, B.; Tang, H. Deformation and failure of the Xiaochatou Landslide under rapid drawdown of the reservoir water level based on centrifuge tests. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 76, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Ma, C. Centrifuge modeling of the geotextile reinforced slope subject to drawdown. Geotext. Geomembr. 2018, 46, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, H.; Li, Y. Centrifuge model test on the retrogressive landslide subjected to reservoir water level fluctuation. Eng. Geol. 2018, 245, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiang, W.; Lu, N. Landsliding triggered by reservoir operation: A general conceptual model with a case study at Three Gorges Reservoir. Acta Geotech. 2014, 9, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhengjun, L.; Xiaoxia, S. Changing landscape in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Yangtze River from 1977 to 2005: Land use/land cover, vegetation cover changes estimated using multi-source satellite data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigira, M. Long-term gravitational deformation of rocks by mass rock creep. Eng. Geol. 1992, 32, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godt, J.W.; Baum, R.L.; Savage, W.Z.; Salciarini, D.; Schulz, W.H.; Harp, E.L. Transient deterministic shallow landslide modeling: Requirements for susceptibility and hazard assessments in a GIS framework. Eng. Geol. 2008, 102, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Xu, Q.; Lan, H.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Spatial distribution analysis of landslides triggered by 2008.5.12 Wenchuan Earthquake, China. Eng. Geol. 2010, 116, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, I.; Tu, X.; Xu, L. Landslide Hazards in Reservoir Areas: Case Study of Xiangjiaba Reservoir, Southwest China. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2017, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Take, W.A.; Bolton, M.D.; Wong, P.C.P.; Yeung, F.J. Evaluation of landslide triggering mechanisms in model fill slopes. Landslides 2004, 1, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higo, Y.; Lee, C.; Doi, T.; Kinugawa, T.; Kimura, M.; Kimoto, S.; Oka, F. Study of dynamic stability of unsaturated embankments with different water contents by centrifugal model tests. Soils Found. 2015, 55, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielicke, W.; Stamhuis, E.J. PIVlab—Towards User-friendly, Affordable and Accurate Digital Particle Image Velocimetry in MATLAB. J. Open Res. Softw. 2014, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, R.L. Reservoir-induced landslides. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 1979, 20, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmareka, H.; Mazaevab, O.A.; Kozyrevab, E.A.; Babichevab, V.A.; Tyszkowskia, S.; Rybchenkob, A.A.; Brykałaa, D.; Bartczaka, A.; Słowińskia, M. Impact of large water level fluctuations on geomorphological processes and their interactions in the shore zone of a dam reservoir. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 926–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemer, W. Landslides and Reservoirs (Keynote Paper). In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Landslides, Christchurch, New Zealand, 10–14 February 1992; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 1373–2004. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Xie, M.; Jia, J. Stepped settlement: A possible mechanism for translational landslides. CATENA 2020, 187, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wasowski, J.; Juang, C.H. Geohazards in the three Gorges Reservoir Area, China—Lessons learned from decades of research. Eng. Geol. 2019, 261, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Xu, Q.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Iqbal, J.; Fu, X.; Huang, X.; Cheng, W. Activity law and hydraulics mechanism of landslides with different sliding surface and permeability in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Eng. Geol. 2019, 260, 105212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, Z.; Peng, X.; Araiba, K.; Wang, G. Movement of the Shuping landslide in the first four years after the initial impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam Reservoir, China. Landslides 2008, 5, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhungana, P.; Wang, F. The relationship among the premonitory factors of landslide dam failure caused by seepage: An experimental study. Geoenviron. Disasters 2019, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, L. Study on the Hydraulic Parameters of Woshaxi Landslide Soils during Water Level Drawdown of Three Gorges Reservoir. Geofluids 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Miao, F.; Xie, Y.; Leo, C. Hazard Prediction for Baishuihe Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir during the Extreme Rainfall Return Period. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 5021–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Jin, X.; Huang, D. Long-term coupled effects of hydrological factors on kinematic responses of a reactivated landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Eng. Geol. 2019, 261, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
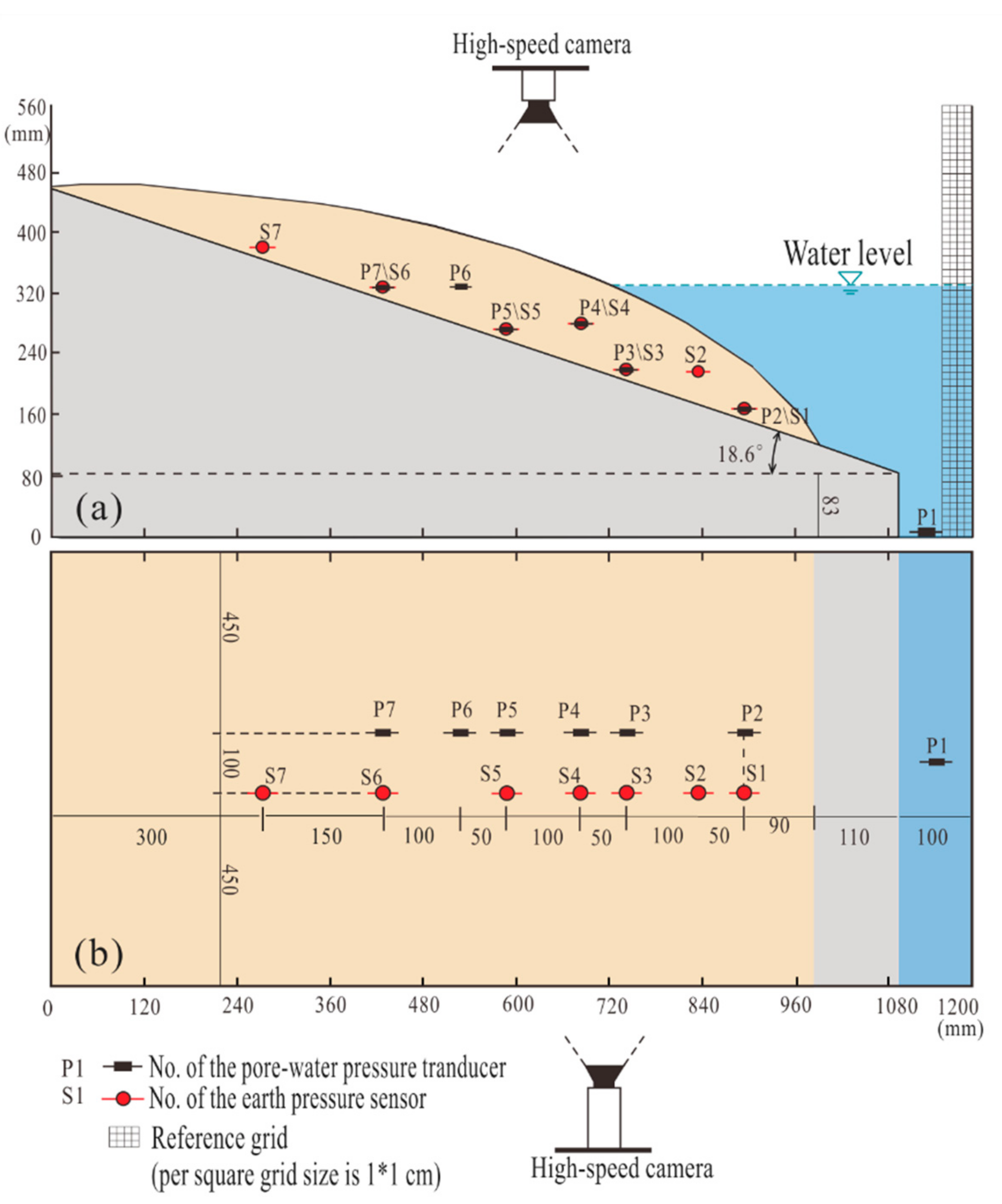
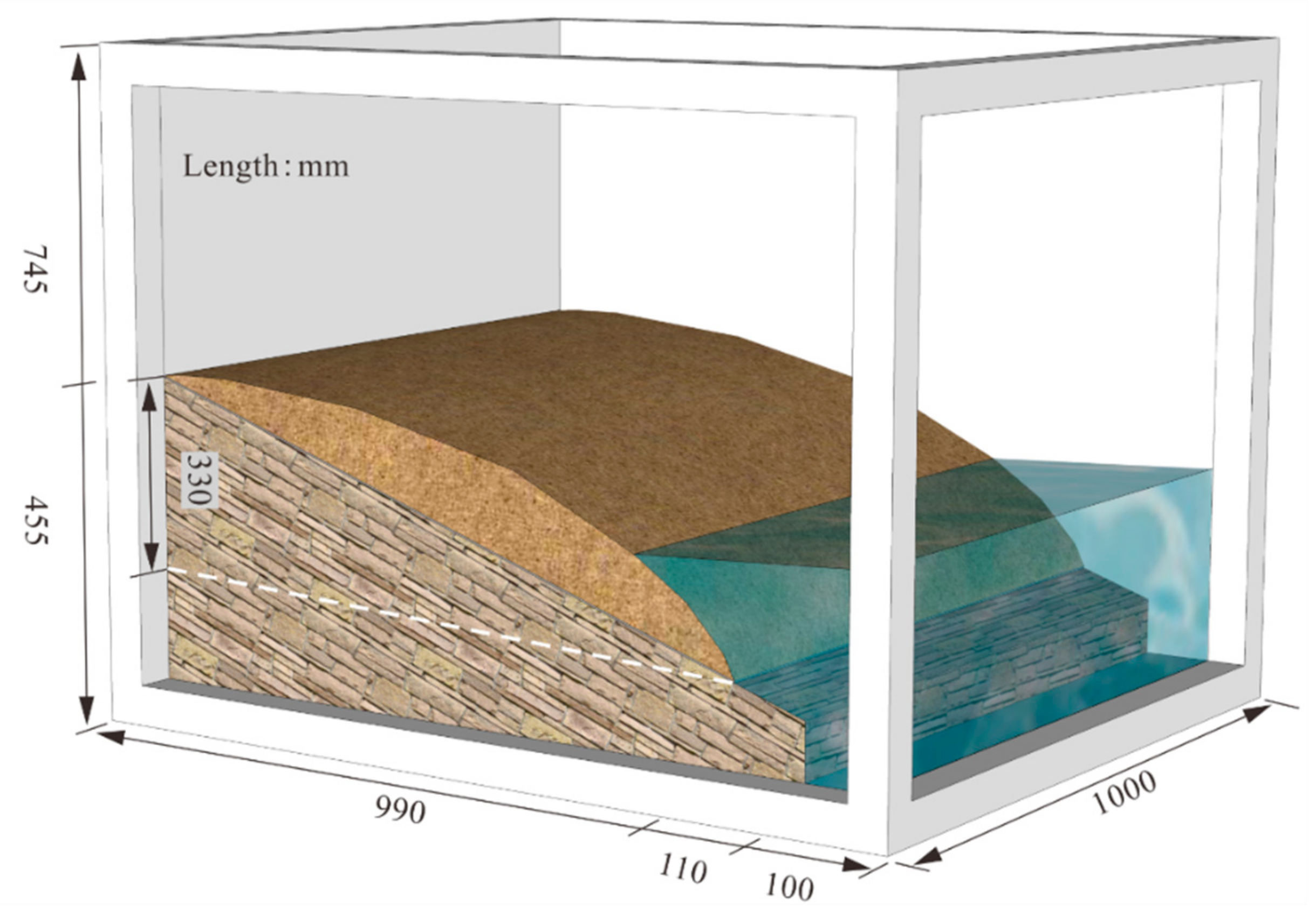
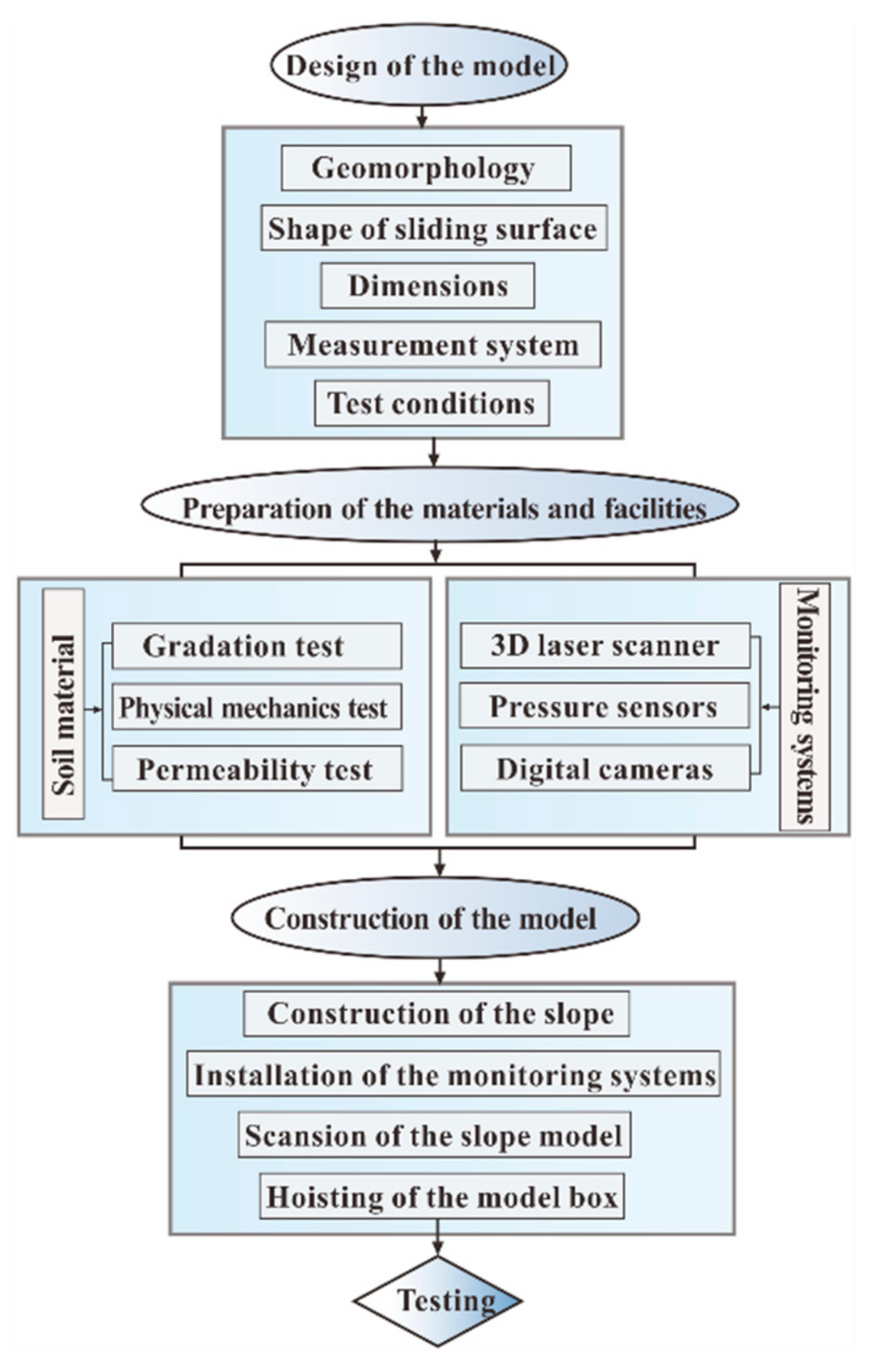
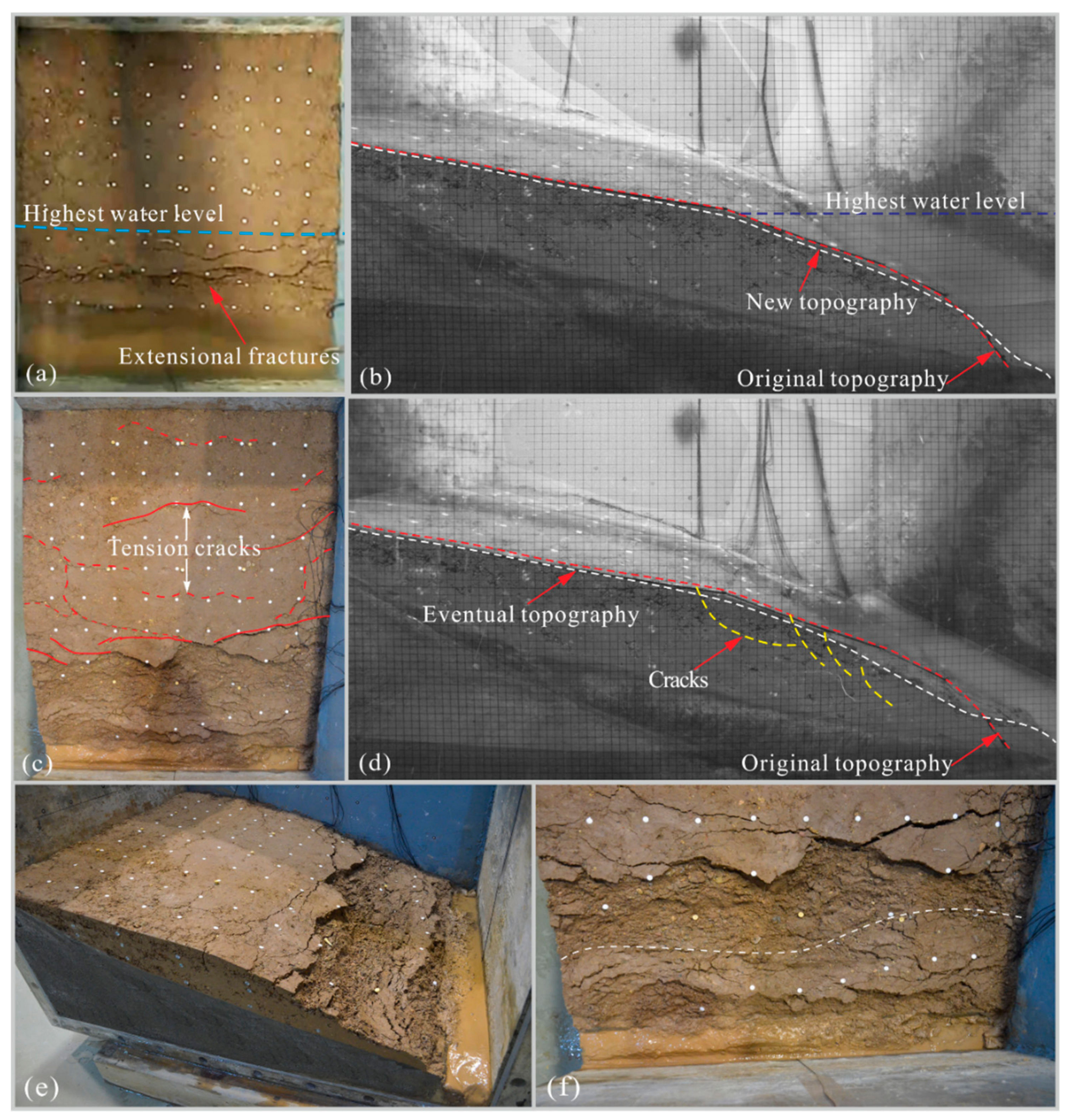
| Type | Physical Quantity | Dimension | Centrifuge Model (ng) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical dimension | Length | L | 1/n |
| Displacement | L2 | n2 | |
| Material properties | Density | ML−3 | 1 |
| Unit weight | ML−2T−2 | n3 | |
| Cohesion | ML−1T−2 | 1 | |
| Internal friction angle | – | 1 | |
| Stress | ML−2T−2 | 1 | |
| Strain | – | 1 | |
| Seepage parameters | Seepage time | T | 1/n2 |
| Seepage velocity | LT−1 | 1/n |
| Effective Radius | 4.50 (m) |
|---|---|
| Space of the utilized box (L × W × H) | 1200 × 1000 × 1000 (mm) |
| Allowable weight of the model | 500 (kg) |
| Test capacity | 80 (g/t) |
| Maximum centrifugal acceleration | 500 (g) |
| Soil Type | Density (g/cm3) | Water Content (%) | Cohesion (kPa) | Internal Friction Angle (°) | Permeability Coefficient (10−6 m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | 2.1 | 14 | 32.8 | 22.5 | 1.6 |
| Phreatic Line | Time (s) | Water Level Elevation (cm) | Water Level Variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 4200 | 33.2 | First impoundment |
| b | 4600 | 28.2 | First drawdown |
| c | 5300 | 22.1 | First drawdown |
| d | 7190 | 29.4 | Second impoundment |
| e | 7900 | 22 | Second drawdown |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Xu, Q.; Tang, M.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Wei, Y. Centrifuge Modeling and the Analysis of Ancient Landslides Subjected to Reservoir Water Level Fluctuation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052092
Li S, Xu Q, Tang M, Li H, Yang H, Wei Y. Centrifuge Modeling and the Analysis of Ancient Landslides Subjected to Reservoir Water Level Fluctuation. Sustainability. 2020; 12(5):2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052092
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Songlin, Qiang Xu, Minggao Tang, Huajin Li, He Yang, and Yong Wei. 2020. "Centrifuge Modeling and the Analysis of Ancient Landslides Subjected to Reservoir Water Level Fluctuation" Sustainability 12, no. 5: 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052092
APA StyleLi, S., Xu, Q., Tang, M., Li, H., Yang, H., & Wei, Y. (2020). Centrifuge Modeling and the Analysis of Ancient Landslides Subjected to Reservoir Water Level Fluctuation. Sustainability, 12(5), 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052092





