Stakeholders’ Engagement on Nature-Based Solutions: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
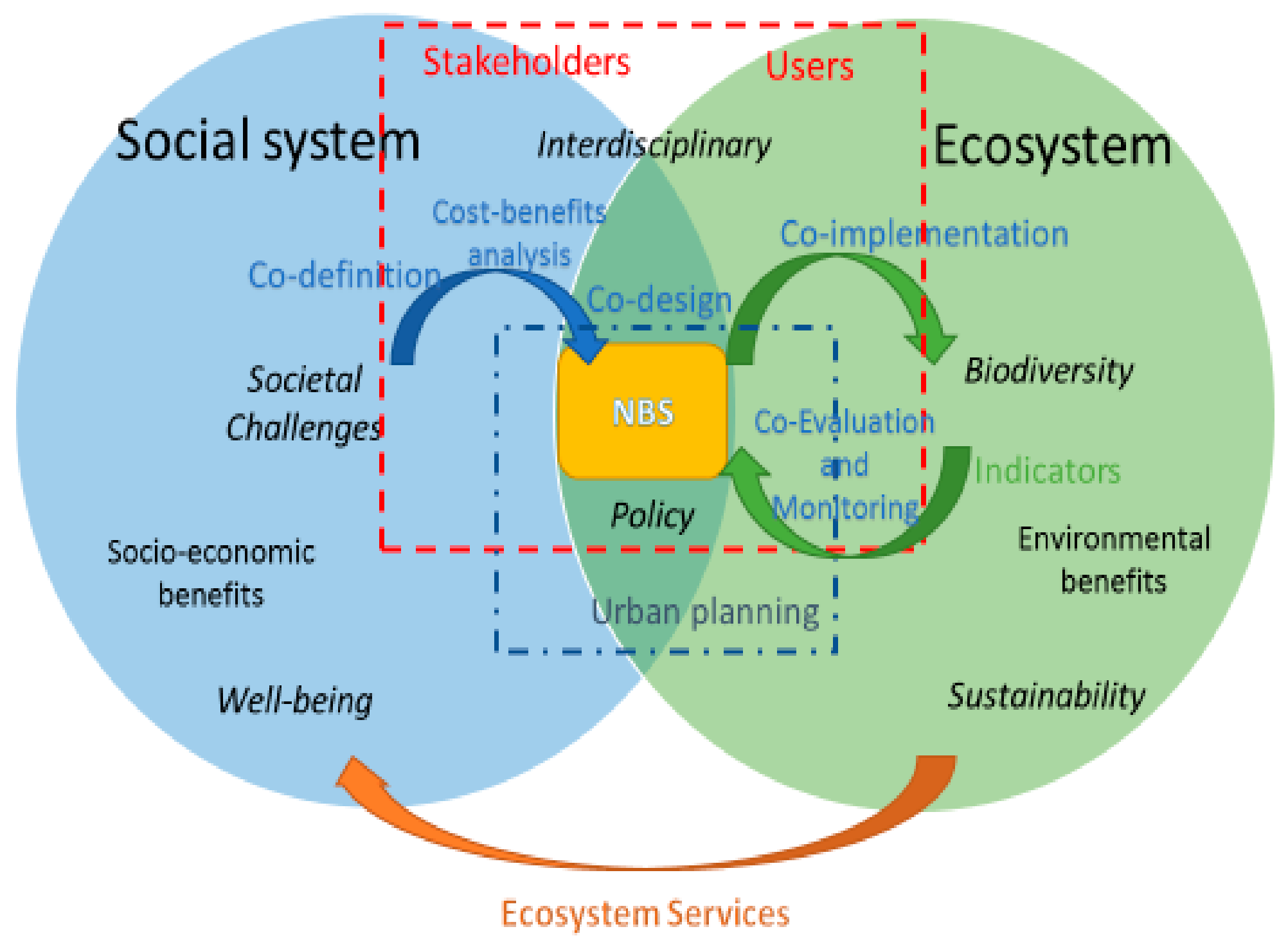
Theoretical Framework and Rationale for the Review
- (RQ1) How are the perceptions, preferences, and perspectives of the citizens and stakeholders taken into consideration in the literature addressing NBS?
- (RQ2) Which motivations trigger the citizens’ and stakeholders’ engagement?
- (RQ3) What are the main benefits and costs sought by citizens and stakeholders resulting from the participation processes of NBS?
- (RQ4) What are the major difficulties and opportunities raised by the engagement of citizens/stakeholders?
- (RQ5) Which approaches are predominant in collaborative governance to involve citizens and stakeholders in participatory processes of NBS?
2. Materials and Methods
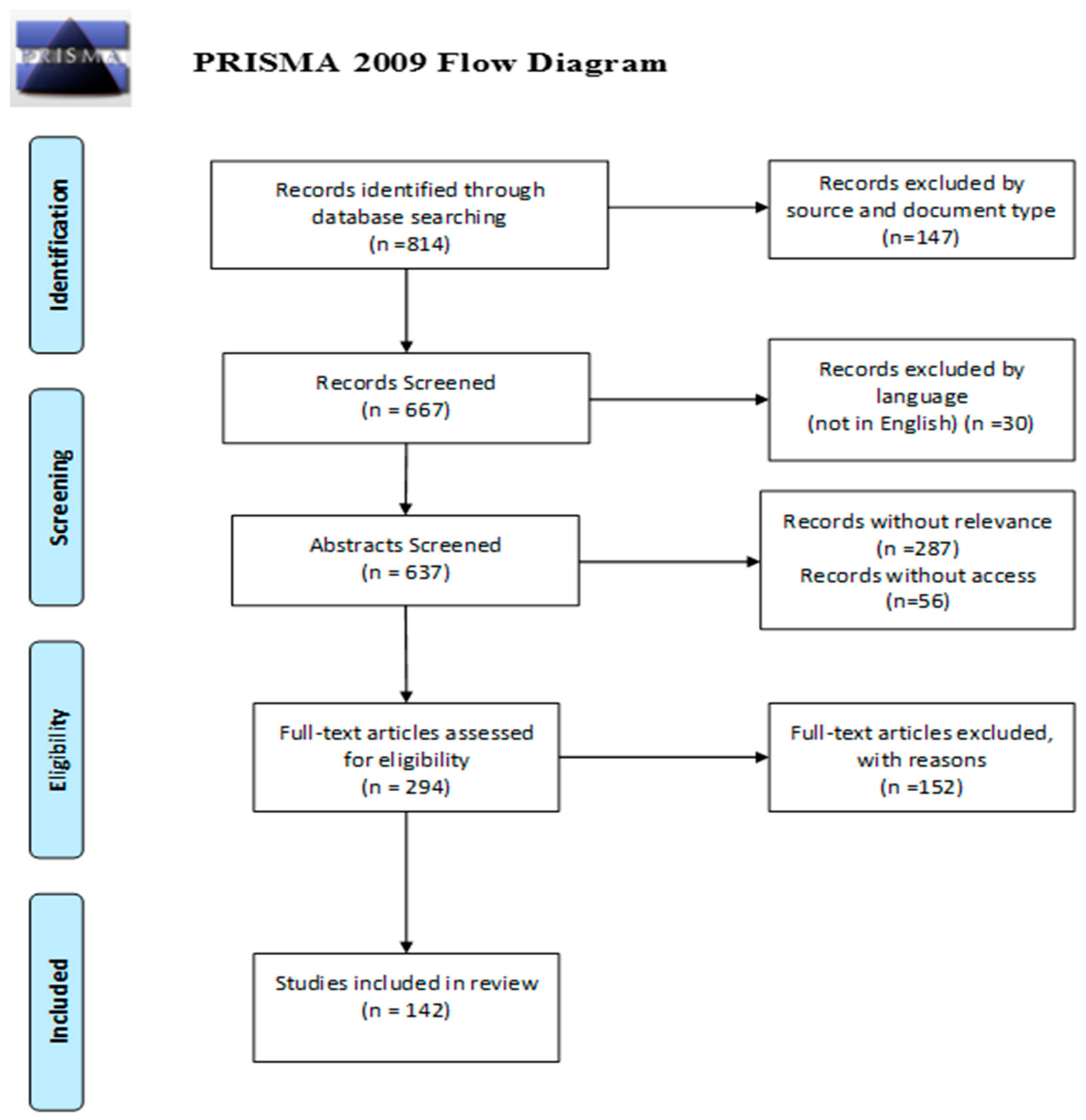
2.1. Identification
2.2. Screening and Eligibility Criteria
- Conceptual articles without evidence of empirical work;
- Not relevant with respect to participatory processes (i.e., without analysis of opportunities and challenges, methods, approaches, motivations, perceptions, and preferences);
- Studies outside the urban context.
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Body of Research
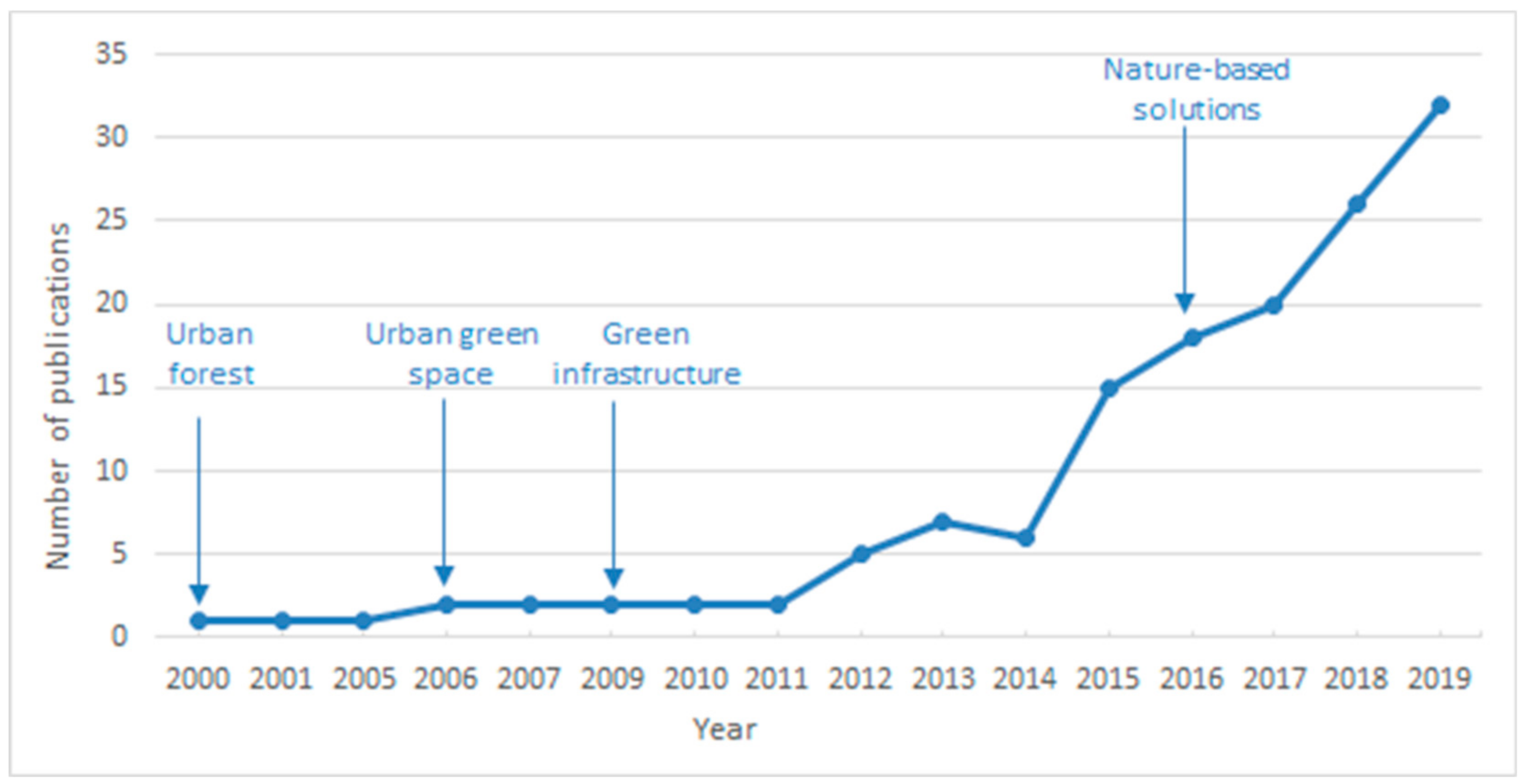
3.1.1. Temporal Progression of the Research on the Issue
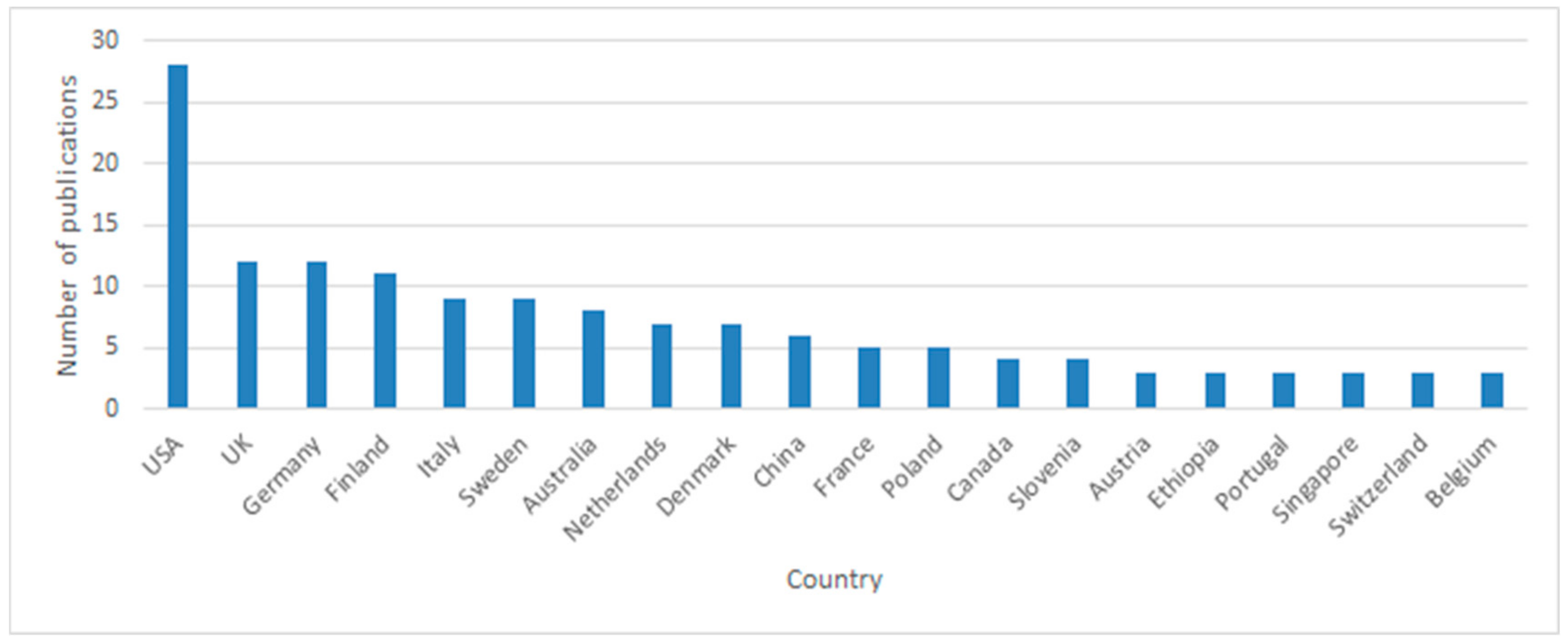
3.1.2. Geographical Distribution of Research on the Issue
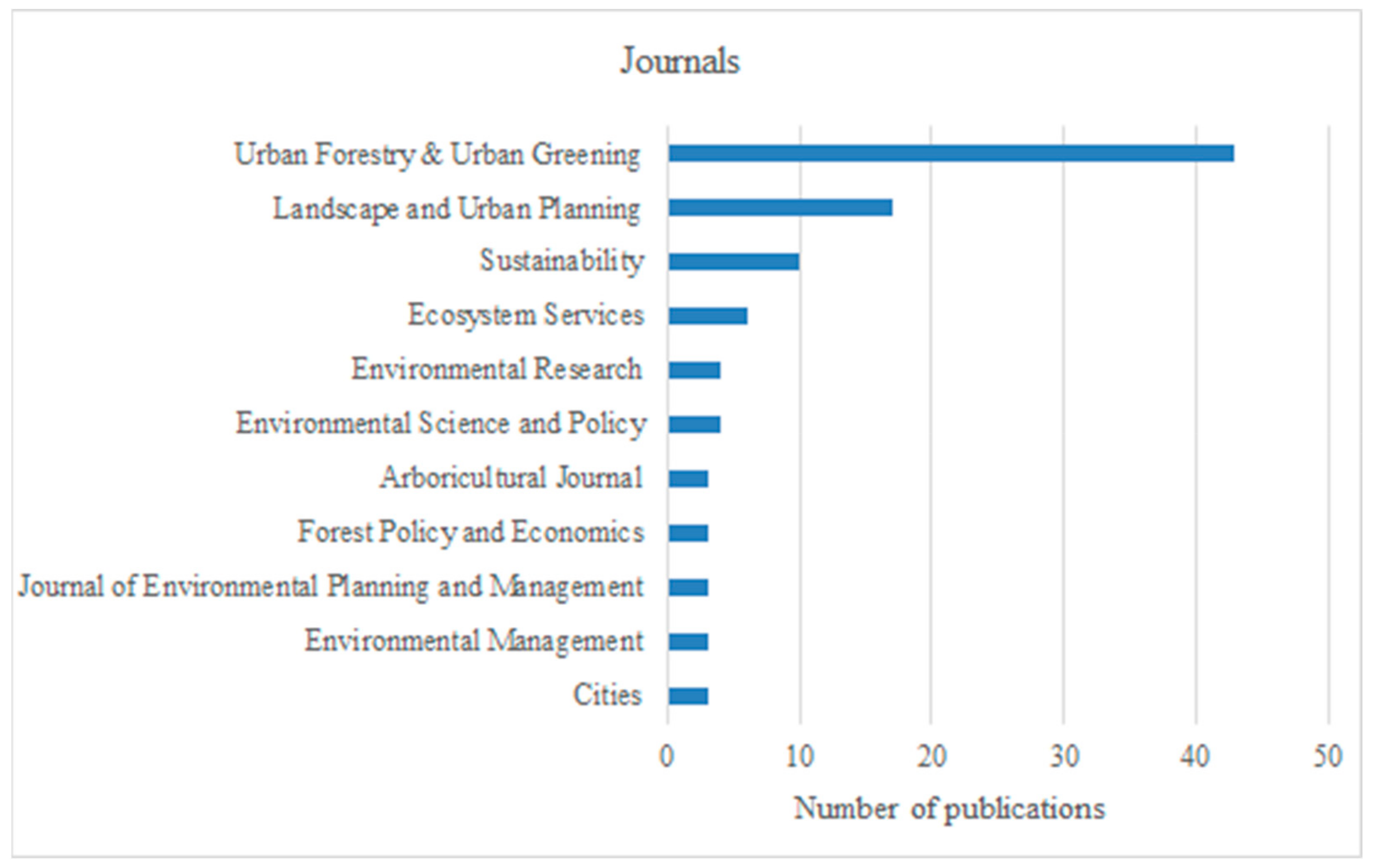
3.1.3. Coverage of the Issue by Journals
3.1.4. General Focus of the Articles
3.2. Citizens’ and Stakeholders’ Perceptions, Preferences, and Perspectives
3.2.1. Perceived Benefits and Costs
Perceptions of the Benefits
Perception of the Risks That Can Cause Costs/Disservices
3.2.2. Preferred Attributes for the Design of NBS
3.2.3. Perspectives on the NBS Challenges
3.3. Citizens’ and Stakeholders’ Participation in the Processes of NBS
3.3.1. Opportunities and Challenges Found in the NBS Practices
Opportunities
Challenges
3.3.2. Identified Drivers/Motivations for Public Participation
3.3.3. Methods, Tools, and Frameworks
3.3.4. Collaborative Governance and Actors’ Interactions Through the Decision-Making Process
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The lack of research applied to countries of southern Europe (which are in the forefront of climate changes) as well as the almost nonexistent research applied to Africa and South America, which preclude the establishment of a comprehensive theoretical and empirical knowledge of the participation processes during their several steps from the conceptualization to the implementation and management of NBS.
- Despite the bulk of the literature dealing with perceptions, preferences, and perspectives of citizens and stakeholders engaged in participation processes of NBS and their anticipated benefits, only a few studies pay attention to economic benefits and those raising the quality of life in cities.
- Few studies looked at the risks perceived by citizens and stakeholders due their involvement in NBS, and in particular, how NBS are perceived as contributing to reduce social injustice.
- Remaining to be explored is the possibility of using the participatory process in NBS to prevent conflicts between the various interests involved.
- New studies are needed aiming to interconnect the theoretical conceptions and the practice of participation processes in NBS, in order to adjust the citizens’ and stakeholders’ expected difficulties and the ones faced in reality—mitigating, in accordance, eventual frustrations of those involved and promoting the maintenance of collaboration during the life cycle of the implemented NBS as well as in future projects.
- Future research should evaluate the contribution of participatory processes for the quality of decisions, the building of public trust in the decision-making process, and for the success of implemented social-learning strategies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Towards an EU Research and Innovation Policy Agenda for Nature-Based Solutions & Re-Naturing Cities: Final Report of the Horizon 2020 Expert Group on Nature-Based Solutions and Re-Naturing Cities; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lafortezza, R.; Sanesi, G. Nature-based solutions: Settling the issue of sustainable urbanization. Environ. Res. 2018, 172, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, F.; Gou, Z.; Lau, S.S.Y.; Lau, S.K.; Chung, K.H.; Zhang, J. From biophilic design to biophilic urbanism: Stakeholders’ perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauleit, S.; Zölch, T.; Hansen, R.; Randrup, T.B.; van den Bosch, C.K. Nature-Based Solutions and Climate Change—Four Shades of Green; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lafortezza, R.; Chen, J.; van den Bosch, C.K.; Randrup, T.B. Nature-based solutions for resilient landscapes and cities. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobedo, F.J.; Giannico, V.; Jim, C.Y.; Sanesi, G.; Lafortezza, R. Urban forests, ecosystem services, green infrastructure and nature-based solutions: Nexus or evolving metaphors? Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 37, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, H.; Balian, E.; Azevedo, M.N.; Beumer, V.; Brodin, T.; Claudet, J.; Fady, B.; Grube, M.; Keune, H.; Lamarque, P.; et al. Nature-based solutions: New influence for environmental management and research in Europe. GAIA 2015, 24, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, C.M.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Kabisch, N.; Berry, P.; Breil, M.; Nita, M.R.; Geneletti, D.; Calfapietra, C. A framework for assessing and implementing the co-benefits of nature-based solutions in urban areas. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 77, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.; de Baro, M.E.Z. Green infrastructure in the urban environment: A systematic quantitative review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabi, S.E.; Han, Q.; Romme, A.G.; de Vries, B.; Wendling, L. Key Enablers of and Barriers to the Uptake and Implementation of Nature-Based Solutions in Urban Settings: A Review. Resources 2019, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, R.W.; Bussey, S.C. Urban forest landscapes in the UK—progressing the social agenda. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2000, 52, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, M.; Tyrväinen, L. Evaluation of collaborative urban forest planning in Helsinki, Finland. Urban For. Urban Green. 2005, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabelis, A.A.; Maksymiuk, G. Public participation in green urban policy: Two strategies compared. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Manag. 2009, 5, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabisch, N.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Pauleit, S.; Naumann, S.; Davis, M.; Artmann, M.; Haase, D.; Knapp, S.; Korn, H.; Stadler, J.; et al. Nature-based solutions to climate change mitigation and adaptation in urban areas: Perspectives on indicators, knowledge gaps, barriers, and opportunities for action. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.; Simpson, G.D. Public green infrastructure contributes to city livability: A systematic quantitative review. Land 2018, 7, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramanan, V.; Packman, A.I.; Peters, D.R.; Lopez, D.; McCuskey, D.J.; McDonald, R.I.; Miller, W.M.; Young, S.L. A systematic review of the human health and social well-being outcomes of green infrastructure for stormwater and flood management. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuniga-Teran, A.A.; Gerlak, A.K. A multidisciplinary approach to analyzing questions of justice issues in urban greenspace. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, C.; Schröter, B.; Haase, D.; Brillinger, M.; Henze, J.; Herrmann, S.; Gottwald, S.; Guerrero, P.; Nicolas, C.; Matzdorf, B. Addressing societal challenges through nature-based solutions: How can landscape planning and governance research contribute? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 182, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijs, A.E.; Mattijssen, T.J.; Van der Jagt, A.P.; Ambrose-Oji, B.; Andersson, E.; Elands, B.H.; Steen Møller, M. Active citizenship for urban green infrastructure: Fostering the diversity and dynamics of citizen contributions through mosaic governance. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2016, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fors, H.; Molin, J.F.; Murphy, M.A.; van den Bosch, C.K. User participation in urban green spaces—For the people or the parks? Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, L.; Ajewole, O. Public perceptions of urban forests in Ibadan, Nigeria: Implications for environmental conservation. Arboric. J. 2001, 25, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanesi, G.; Chiarello, F. Residents and urban green spaces: The case of Bari. Urban For. Urban Green. 2006, 4, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.Y.; Chen, W.Y. Perception and attitude of residents toward urban green spaces in Guangzhou (China). Environ. Manag. 2006, 38, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forzieri, G.; Alessandra, B.; e Silva, F.B.; Herrera, M.A.M.; Leblois, A.; Lavalle, C.; Jeroen, C.J.H.; Feyen, L. Escalating impacts of climate extremes on critical infrastructures in Europe. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2018, 48, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelleri, L.; Kua, H.W.; Sánchez, J.P.R.; Md Nahiduzzaman, K.; Thondhlana, G. Are people responsive to a more sustainable, decentralized, and user-driven management of urban metabolism? Sustainability 2016, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhill, K.; Smardon, R. Gaining ground: Green infrastructure attitudes and perceptions from stakeholders in Syracuse, New York. Environ. Pract. 2012, 14, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, S.J.; Larson, L.R.; Shafer, C.S.; Hallo, J.C.; Fernandez, M. Greenway use and preferences in diverse urban communities: Implications for trail design and management. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 172, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Arvai, V. Engaging urban nature: Improving our understanding of public perceptions of the role of biodiversity in cities. Urban Ecosyst. 2019, 22, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchel, S.; Frantzeskaki, N. Citizens’ voice: A case study about perceived ecosystem services by urban park users in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.M.; Montalto, F.A. Stakeholder perceptions of the ecosystem services provided by Green Infrastructure in New York City. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 37, 100928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, D.; Arndt, T. Investigating perception of green structure configuration for afforestation in urban brownfield development by visual methods-A case study in Leipzig, Germany. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 15, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.L. Park user preferences for establishing a sustainable forest park in Taipei, Taiwan. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barau, A.S. Perceptions and contributions of households towards sustainable urban green infrastructure in Malaysia. Habitat Int. 2015, 47, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conedera, M.; Del Biaggio, A.; Seeland, K.; Moretti, M.; Home, R. Residents’ preferences and use of urban and peri-urban green spaces in a Swiss mountainous region of the Southern Alps. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Nielsen, A.B. Are perceived sensory dimensions a reliable tool for urban green space assessment and planning? Landsc. Res. 2015, 40, 834–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, C.D.D.; Byrne, J.A.; Ueda, H.; Lo, A.Y. “It’s real, not fake like a park”: Residents’ perception and use of informal urban green-space in Brisbane, Australia and Sapporo, Japan. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 143, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, L.R.; Keith, S.J.; Fernandez, M.; Hallo, J.C.; Shafer, C.S.; Jennings, V. Ecosystem services and urban greenways: What’s the public’s perspective? Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 22, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, C.D.; Oke, C.; Hehir, A.; Gordon, A.; Wang, Y.; Bekessy, S.A. Capturing residents’ values for urban green space: Mapping, analysis and guidance for practice. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 161, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpilo, S.; Virtanen, T.; Saukkonen, T.; Lehvävirta, S. More than A to B: Understanding and managing visitor spatial behaviour in urban forests using public participation GIS. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, T.; Tampakis, S.; Karanikola, P.; Karipidou-Kanari, A.; Kantartzis, A. The usage and perception of pedestrian and cycling streets on residents’ well-being in Kalamaria, Greece. Land 2018, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenat, S.; Dougill, A.J.; Kunin, W.E.; Dallimer, M. Untangling the motivations of different stakeholders for urban greenspace conservation in sub-Saharan Africa. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 36, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwedla, N.; Shackleton, C.M. Perceptions and preferences for urban trees across multiple socio-economic contexts in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 189, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckham, S.C.; Duinker, P.N.; Ordóñez, C. Urban forest values in Canada: Views of citizens in Calgary and Halifax. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Soeung, B. An assessment of the knowledge and demand of young residents regarding the ecological services of urban green spaces in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Sustainability 2016, 8, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, N.; Fritz, M.; Freitas, T.; de Boissezon, B.; Vandewoestijne, S. Nature-Based Solutions in the EU: Innovating with nature to address social, economic and environmental challenges. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, C.; Xia, B.; de Groot, R. Perception of urban environmental risks and the effects of urban green infrastructures (UGIs) on human well-being in four public green spaces of Guangzhou, China. Environ. Manag. 2018, 62, 500–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, T.K.; Zhe Han, S.S.; Lechner, A.M. Urban green space and well-being in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 36, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwierzchowska, I.; Hof, A.; Iojă, I.C.; Mueller, C.; Poniży, L.; Breuste, J.; Mizgajski, A. Multi-scale assessment of cultural ecosystem services of parks in Central European cities. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 30, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashu, K.; Gebre-Egziabher, T.; Wubneh, M. Local communities’ perceptions and use of urban green infrastructure in two Ethiopian cities: Bahir Dar and Hawassa. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2020, 63, 287–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, E.; Bruggeman, A.; Poulou, D.; Zoumides, C.; Eliades, M. Linear parks along urban rivers: Perceptions of thermal comfort and climate change adaptation in Cyprus. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.A.; Schulz, C. Do ecosystem services provide an added value compared to existing forest planning approaches in Central Europe? Ecol. Soc. 2017, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwartz, A.; Turbé, A.; Simon, L.; Julliard, R. Enhancing urban biodiversity and its influence on city-dwellers: An experiment. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 171, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kotze, D.J.; Vierikko, K.; Niemelä, J. What makes urban greenspace unique—Relationships between citizens’ perceptions on unique urban nature, biodiversity and environmental factors. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, T.M.; Yip, V. Assessing residents’ reactions to urban forest disservices: A case study of a major storm event. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 153, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Nagendra, H. Factors influencing perceptions and use of urban nature: Surveys of park visitors in Delhi. Land 2017, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.O.; da Silva, I.M.; Teixeira, C.P.; Costa, L. Between tree lovers and tree haters. Drivers of public perception regarding street trees and its implications on the urban green infrastructure planning. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 37, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostoić, S.K.; van den Bosch, C.C.; Vuletić, D.; Stevanov, M.; Živojinović, I.; Mutabdžija-Bećirović, S.; Lazarević, J.; Stojanova, B.; Blagojević, D.; Stojanovska, M.; et al. Citizens’ perception of and satisfaction with urban forests and green space: Results from selected Southeast European cities. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 23, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnema, S.; Sedaghathoor, S.; Allahyari, M.S.; Damalas, C.A.; Bilali, H. El Preferences and emotion perceptions of ornamental plant species for green space designing among urban park users in Iran. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 39, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantopoulos, G.; Varras, G.; Chiotelli, E.; Fotia, K.; Batou, M. Public perceptions and attitudes toward green infrastructure on buildings: The case of the metropolitan area of Athens, Greece. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 34, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.C.; Park, M.S.; Youn, Y.C. Preferences of urban dwellers on urban forest recreational services in South Korea. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Sun, Z.; Bao, Z. Landscape perception and recreation needs in urban green space in Fuyang, Hangzhou, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, J.W.R.; Tynon, J.F.; Ries, P.; Rosenberger, R.S. Public attitudes about urban forest ecosystem services management: A case study in Oregon cities. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 17, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnberger, A.; Allex, B.; Eder, R.; Ebenberger, M.; Wanka, A.; Kolland, F.; Wallner, P.; Hutter, H.P. Elderly resident’s uses of and preferences for urban green spaces during heat periods. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 21, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkzen, M.L.; van Teeffelen, A.J.A.; Verburg, P.H. Green infrastructure for urban climate adaptation: How do residents’ views on climate impacts and green infrastructure shape adaptation preferences? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 157, 106–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzyk-Kaszyńska, A.; Czepkiewicz, M.; Kronenberg, J. Eliciting non-monetary values of formal and informal urban green spaces using public participation GIS. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 160, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Azcárraga, C.; Diaz, D.; Zambrano, L. Characteristics of urban parks and their relation to user well-being. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 189, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Yue, Z.E.J.; Ling, S.K.; Tan, H.H.V. It’s ok to be wilder: Preference for natural growth in urban green spaces in a tropical city. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 38, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramer, H.; Nelson, K.C.; Spivak, M.; Watkins, E.; Wolfin, J.; Pulscher, M.L. Exploring park visitor perceptions of ‘flowering bee lawns’ in neighborhood parks in Minneapolis, MN, US. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 189, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caula, S.; Hvenegaard, G.T.; Marty, P. The influence of bird information, attitudes, and demographics on public preferences toward urban green spaces: The case of Montpellier, France. Urban For. Urban Green. 2009, 8, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanikola, P.; Panagopoulos, T.; Tampakis, S. Weekend visitors’ views and perceptions at an urban national forest park of Cyprus during summertime. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2017, 17, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menconi, M.E.; Grohmann, D. Participatory retrofitting of school playgrounds: Collaboration between children and university students to develop a vision. Think. Sk. Creat. 2018, 29, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, I.; Barker, A. Barriers and opportunities of combining social and ecological functions of urban greenspaces—Users’ and landscape professionals’ perspectives. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 39, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, D.; Thapa, H.B. Participatory urban forestry in Nepal: Gaps and ways forward. Urban For. Urban Green. 2012, 11, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, M.; Koburger, A.; Dolowitz, D.P.; Medearis, D.; Nickel, D.; Shuster, W. Perspectives on the use of green infrastructure for stormwater management in cleveland and milwaukee. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyle, H.; Jorgensen, A.; Warren, P.; Dunnett, N.; Evans, K. “Not in their front yard” The opportunities and challenges of introducing perennial urban meadows: A local authority stakeholder perspective. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 25, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, C.; Phelan, K.; Dodson, J. The role of water utilities in urban greening: A case study of Melbourne, Australia. Util. Policy 2018, 53, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshkar, S.; Balfors, B.; Wärnbäck, A. Planning for green qualities in the densification of suburban Stockholm—Opportunities and challenges. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2018, 61, 2613–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onori, A.; Lavau, S.; Fletcher, T. Implementation as more than installation: A case study of the challenges in implementing green infrastructure projects in two Australian primary schools. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, Y.; Terefe, H.; Pauleit, S. Urban green spaces use and management in rapidly urbanizing countries: The case of emerging towns of Oromia special zone surrounding Finfinne, Ethiopia. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 43, 126357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, M.B.; Mekonnen, A.B. Understanding the local values of trees and forests: A strategy to improve the urban environment in Hawassa City, Southern Ethiopia. Arboric. J. 2019, 41, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živojinović, I.; Wolfslehner, B. Perceptions of urban forestry stakeholders about climate change adaptation—A Q-method application in Serbia. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähde, E.; Di Marino, M. Multidisciplinary collaboration and understanding of green infrastructure Results from the cities of Tampere, Vantaa and Jyväskylä (Finland). Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 40, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rall, E.L.; Kabisch, N.; Hansen, R. A comparative exploration of uptake and potential application of ecosystem services in urban planning. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 16, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marino, M.; Tiitu, M.; Lapintie, K.; Viinikka, A.; Kopperoinen, L. Integrating green infrastructure and ecosystem services in land use planning. Results from two Finnish case studies. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, J.F.; Dupras, J.; Messier, C.; Lechowicz, M.; Dagenais, D.; Paquette, A.; Jaeger, J.A.G.; Gonzalez, A. Moving forward in implementing green infrastructures: Stakeholder perceptions of opportunities and obstacles in a major North American metropolitan area. Cities 2018, 81, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.F. Planting the living city: Best practices in planning green infrastructure—Results from major U.S. cities. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2011, 77, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.J.; Wu, C.T.; Huang, F.T. Fostering multi-functional urban agriculture: Experiences from the champions in a revitalized farm pond community in Taoyuan, Taiwan. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fors, H.; Jansson, M.; Nielsen, A.B. The impact of resident participation on urban woodland quality-a case study of Sletten, Denmark. Forests 2018, 9, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, R.W.; Huff, E.S.; Bloniarz, D.V.; DeStefano, S.; Nicolson, C.R. Exploring the characteristics of successful volunteer-led urban forest tree committees in Massachusetts. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 34, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozová, M.; Dobšinská, Z.; Pauditšová, E.; Tomčíková, I.; Rakytová, I. Network and participatory governance in urban forestry: An assessment of examples from selected Slovakian cities. For. Policy Econ. 2018, 89, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugolini, F.; Sanesi, G.; Steidle, A.; Pearlmutter, D. Speaking “Green”: A worldwide survey on collaboration among stakeholders in urban park design and management. Forests 2018, 9, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolf, W.; Pauleit, S.; Wiggering, H. A stakeholder approach, door opener for farmland and multifunctionality in urban green infrastructure. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 40, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.; James, P. Considerations in the valuation of urban green space: Accounting for user participation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 21, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.; James, P. User participation in urban green commons: Exploring the links between access, voluntarism, biodiversity and well being. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 15, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.K.; Brinkmeyer, D.; Karle, S.J.; Cremer, K.; Huttner, E.; Seebauer, M.; Nowikow, U.; Schütze, B.; Voigt, P.; Völker, S.; et al. Biodiverse edible schools: Linking healthy food, school gardens and local urban biodiversity. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 40, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskell, C.; Allred, S.B. Residents’ beliefs about responsibility for the stewardship of park trees and street trees in New York City. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 120, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulsrud, N.M.; Hertzog, K.; Shears, I. Innovative urban forestry governance in Melbourne? Investigating “green placemaking” as a nature-based solution. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travaline, K.; Montalto, F.; Hunold, C. Deliberative Policy Analysis and Policy-making in Urban Stormwater Management. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2015, 17, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.; Armitage, R.P.; James, P. Appraisal of social-ecological innovation as an adaptive response by stakeholders to local conditions: Mapping stakeholder involvement in horticulture orientated green space management. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 18, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmeziti, A.; Cherqui, F.; Kaufmann, B. Improving the multi-functionality of urban green spaces: Relations between components of green spaces and urban services. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, E.; Wamsler, C. Collaborative governance for climate change adaptation: Mapping citizen–municipality interactions. Environ. Policy Gov. 2018, 28, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, J.J. Infrastructure and institutions: Stakeholder perspectives of stormwater governance in Chicago. Cities 2017, 66, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattijssen, T.J.M.; van der Jagt, A.P.N.; Buijs, A.E.; Elands, B.H.M.; Erlwein, S.; Lafortezza, R. The long-term prospects of citizens managing urban green space: From place-making to place-keeping? Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 26, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, C.A.; Andres, L.; Baidoo, P.; Eshun, J.K.; Antwi, K.B. Community Participation in Urban Planning: The Case of Managing Green Spaces in Kumasi, Ghana. Urban Forum 2017, 28, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jensen, M.B. Green infrastructure for sustainable urban water management: Practices of five forerunner cities. Cities 2018, 74, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaki, K. Role of social networks in urban forest management collaboration: A case study in northern Japan. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 18, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asah, S.T.; Blahna, D.J. Motivational functionalism and urban conservation stewardship: Implications for volunteer involvement. Conserv. Lett. 2012, 5, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.Z. Attitude and willingness toward participation in decision-making of urban green spaces in China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2012, 11, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, S.; Namiranian, M.; Feghhi, J.; Fami, H.S. Factors encouraging and restricting participation in urban forestry (Case study of Tehran, Iran). Arboric. J. 2015, 37, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beery, T. Engaging the private homeowner: Linking climate change and green stormwater infrastructure. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fors, H.; Wiström, B.; Nielsen, A.B. Personal and environmental drivers of resident participation in urban public woodland management—A longitudinal study. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 186, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.; Enqvist, J.P.; Tengö, M. Place-making to transform urban social–ecological systems: Insights from the stewardship of urban lakes in Bangalore, India. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 14, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, O.O.; Shuster, W.D.; Rhea, L.K.; Garmestani, A.S.; Thurston, H.W. Identification and induction of human, social, and cultural capitals through an experimental approach to stormwater management. Sustainability 2012, 4, 1669–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, O.; Home, R.; Kizos, T. Digging for the roots of urban gardening behaviours. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 34, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberherr, E.; Green, O.O. Green infrastructure through citizen stormwater management: Policy instruments, participation and engagement. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.C. An empirical study of spatial-temporal growth patterns of a voluntary residential green infrastructure program. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2018, 61, 1363–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, N.; Simpson, T.; Orlove, B.; Dowd-Uribe, B. Environmental and social dimensions of community gardens in East Harlem. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 183, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romolini, M.; Ryan, R.L.; Simso, E.R.; Strauss, E.G. Visitors’ attachment to urban parks in Los Angeles, CA. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 41, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.R. Impact of ecological disturbance on awareness of urban nature and sense of environmental stewardship in residential neighborhoods. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 101, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzalan, N.; Muller, B. The Role of social media in green infrastructure planning: A case study of neighborhood participation in park siting. J. Urban Technol. 2014, 21, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, P.; Møller, M.S.; Olafsson, A.S.; Snizek, B. Revealing cultural ecosystem services through instagram images: The potential of social media volunteered geographic information for urban green infrastructure planning and governance. Urban Plan. 2016, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwartz, A.; Cheval, H.; Simon, L.; Julliard, R. Virtual garden computer program for use in exploring the elements of biodiversity people want in cities. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 27, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, M.S.; Olafsson, A.S.; Vierikko, K.; Sehested, K.; Elands, B.; Buijs, A.; van den Bosch, C.K. Participation through place-based e-tools: A valuable resource for urban green infrastructure governance? Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 40, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse, G.; Konijnendijk, C.C. Communication between science, policy and citizens in public participation in urban forestry-Experiences from the Neighbourwoods project. Urban For. Urban Green. 2007, 6, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, T.L.; Elmore, V.; Strong, A.; Bennett-Martin, P.; Finnie, J.; Parkman, J.; Harris, T.; Singh, J.; Edwards, L.; Reed, J. Mapping non-native invasive species and accessibility in an urban forest: A case study of participatory mapping and citizen science in Atlanta, Georgia. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 56, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, C.M.; Gottwald, S.; Kuoppa, J.; Kyttä, M. Integrating multiple elements of environmental justice into urban blue space planning using public participation geographic information systems. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 153, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rall, E.; Hansen, R.; Pauleit, S. The added value of public participation GIS (PPGIS) for urban green infrastructure planning. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 40, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Xiang, J.; Tao, Y.; Tong, C.; Che, Y. Mapping the social values for ecosystem services in urban green spaces: Integrating a visitor-employed photography method into SolVES. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 38, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuenschwander, N.; Wissen Hayek, U.; Grêt-Regamey, A. Integrating an urban green space typology into procedural 3D visualization for collaborative planning. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2014, 48, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, K.; Åkerlund, U.; Konijnendijk, C.C.; Alekseev, A.; Caspersen, O.H.; Guldager, S.; Kuznetsov, E.; Mezenko, A.; Selikhovkin, A. Implementing urban greening aid projects—The case of St. Petersburg, Russia. Urban For. Urban Green. 2007, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, A.; Heikkilä, J.; Malmivaara-Lämsä, M.; Löfström, I. Case Puijo-Evaluation of a participatory urban forest planning process. For. Policy Econ. 2014, 45, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturiale, L.; Scuderi, A. The evaluation of green investments in urban areas: A proposal of an eco-social-green model of the city. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, C.C.; van der Jagt, A.P.N.; Barbour, S.; Smith, M.; Moseley, D. A spatial framework for targeting urban planning for pollinators and people with local stakeholders: A route to healthy, blossoming communities? Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assmuth, T.; Hellgren, D.; Kopperoinen, L.; Paloniemi, R.; Peltonen, L. Fair blue urbanism: Demands, obstacles, opportunities and knowledge needs for just recreation beside Helsinki Metropolitan Area waters. Int. J. Urban Sustain. Dev. 2017, 9, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Jagt, A.P.N.; Smith, M.; Ambrose-Oji, B.; Konijnendijk, C.C.; Giannico, V.; Haase, D.; Lafortezza, R.; Nastran, M.; Pintar, M.; Železnikar, Š.; et al. Co-creating urban green infrastructure connecting people and nature: A guiding framework and approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann-Matthies, P.; Brieger, H. Does urban gardening increase aesthetic quality of urban areas? A case study from Germany. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 17, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Hall, M. Coupling human preferences with biophysical processes: Modeling the effect of citizen attitudes on potential urban stormwater runoff. Urban Ecosyst. 2016, 19, 1433–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasooriya, V.M.; Ng, A.W.M.; Muthukumaran, S.; Perera, B.J.C. Multi Criteria Decision Making in Selecting Stormwater Management Green Infrastructure for Industrial Areas Part 1: Stakeholder Preference Elicitation. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafortezza, R.; Giannico, V. Combining high-resolution images and LiDAR data to model ecosystem services perception in compact urban systems. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordström, E.M.; Eriksson, L.O.; Öhman, K. Integrating multiple criteria decision analysis in participatory forest planning: Experience from a case study in northern Sweden. For. Policy Econ. 2010, 12, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beumer, C.; Martens, P. Biodiversity in my (back)yard: Towards a framework for citizen engagement in exploring biodiversity and ecosystem services in residential gardens. Sustain. Sci. 2015, 10, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, E.C.; Lamond, J.E.; Thorne, C.R. Learning and Action Alliance framework to facilitate stakeholder collaboration and social learning in urban flood risk management. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 80, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Lindberg, S.; Nielsen, A.B. Is biodiversity attractive?—On-site perception of recreational and biodiversity values in urban green space. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 119, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosol, M. Public Participation in post-fordist urban green space governance: The case of community gardens in Berlin. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2010, 34, 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faehnle, M.; Bäcklund, P.; Tyrväinen, L.; Niemelä, J.; Yli-Pelkonen, V. How can residents’ experiences inform planning of urban green infrastructure? Case Finland. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 130, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skandrani, Z.; Prévot, A.C. Beyond green-planning political orientations: Contrasted public policies and their relevance to nature perceptions in two European capitals. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 52, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi, D.; Pennisi, G.; Rizzati, N.; Magrefi, F.; Bazzocchi, G.; Mezzacapo, U.; Stefani, M.C.; Sanyé-Mengual, E.; Orsini, F.; Gianquinto, G. Towards regenerated and productive vacant areas through urban horticulture: Lessons from Bologna, Italy. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, J.; Pietrzyk-Kaszyńska, A.; Zbieg, A.; Żak, B. Wasting collaboration potential: A study in urban green space governance in a post-transition country. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 62, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifflett, S.D.; Newcomer-Johnson, T.; Yess, T.; Jacobs, S. Interdisciplinary collaboration on green infrastructure for urban watershed management: An Ohio case study. Water 2019, 11, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvejić, R.; Železnikar, Š.; Nastran, M.; Rehberger, V.; Pintar, M. Urban agriculture as a tool for facilitated urban greening of sites in transition: A case study. Urbani Izziv 2015, 26, S84–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome, G. Defining community-scale green infrastructure. Landsc. Res. 2017, 42, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Jagt, A.P.N.; Szaraz, L.R.; Delshammar, T.; Cvejić, R.; Santos, A.; Goodness, J.; Buijs, A. Cultivating nature-based solutions: The governance of communal urban gardens in the European Union. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanovič, N.P. Green infrastructure and urban revitalisation in Central Europe: Meeting environmental and spatial challenges in the inner city of Ljubljana, Slovenia. Urbani izziv 2015, 26, 50–64. [Google Scholar]
- Simić, I.; Stupar, A.; Djokić, V. Building the green infrastructure of Belgrade: The importance of community greening. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijs, A.; Hansen, R.; Van der Jagt, S.; Ambrose-Oji, B.; Elands, B.; Lorance Rall, E.; Mattijssen, T.; Pauleit, S.; Runhaar, H.; Stahl Olafsson, A.; et al. Mosaic governance for urban green infrastructure: Upscaling active citizenship from a local government perspective. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 40, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugolini, F.; Massetti, L.; Sanesi, G.; Pearlmutter, D. Knowledge transfer between stakeholders in the field of urban forestry and green infrastructure: Results of a European survey. Land Use Policy 2015, 49, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifman, L.A.; Herrmann, D.L.; Shuster, W.D.; Ossola, A.; Garmestani, A.; Hopton, M.E. Situating green infrastructure in context: A framework for adaptive socio-hydrology in cities. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 10139–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzeskaki, N. Seven lessons for planning nature-based solutions in cities. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 93, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
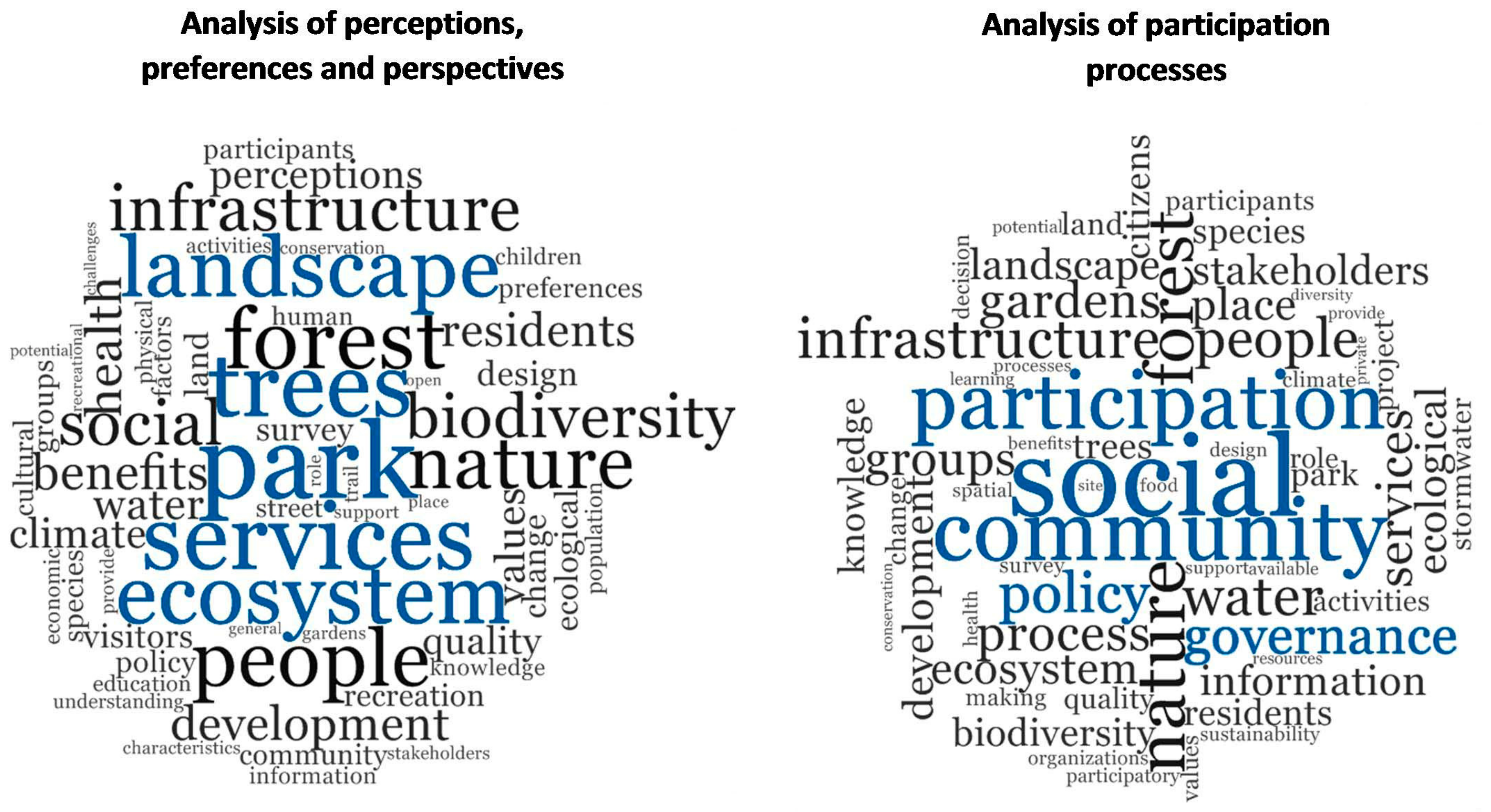
| Area | Sub-Area | Aim |
|---|---|---|
| Analysis of perceptions, preferences and perspectives on NBS (n = 65) | Benefits and costs (n = 35) | Focus on citizen and/or stakeholder perceptions of benefits and costs of NBS |
| Attributes (n = 16) | Focus on citizen and/or stakeholder preferences of specific attributes and design of NBS | |
| NBS challenges (n = 14) | Focus on citizen and/or stakeholder viewpoints of challenges on NBS implementation | |
| Analysis of participation processes on NBS (n = 77) | Drivers and motivations (n = 14) | Analyzes drivers and motivation for participation |
| Methods, tools, and frameworks (n = 26) | Analyzes methods, tools, or frameworks for participation | |
| Collaborative governance and interactions (n = 17) | Analyzes participation in terms of governance and existing interactions | |
| Challenges and opportunities (n = 20) | Analyzes challenges and opportunities presented in the participatory process |
| Perceived Benefits (n = 34) | Authors | |
|---|---|---|
| Social Benefits (n = 27) | Aesthetics, scenic views and proximity to nature (n = 13) | Coles and Bussey 2000 [11]; Huang 2014 [32]; Barau 2015 [33]; Buchel and Frantzeskaki 2015 [29]; Conedera et al. 2015 [34]; Qiu and Nielsen 2015 [35]; Rupprecht et al. 2015 [36]; Larson et al. 2016 [37]; Ives et al. 2017 [38]; Korpilo et al. 2018 [39]; Panagopoulos et al. 2018 [40]; Campbell-Arvai 2019 [28]; Guenat et al. 2019 [41]. |
| Quality of life (n = 4) | Sanesi and Chiarello 2006 [22]; Conedera et al. 2015 [36]; Panagopoulos et al. 2018 [40]; Gwedla and Shackleton 2019 [42]. | |
| Physical and mental well-being (n = 12) | Coles and Bussey 2000 [11]; Peckham et al. 2013 [43]; Buchel and Frantzeskaki 2015 [29]; Yen et al. 2016 [44]; Faivre et al. 2017 [45]; Duan et al. 2018 [46]; Keith et al. 2018 [27]; Nath et al. 2018 [47]; Panagopoulos et al. 2018 [40]; Zwierzchowska et al. 2018 [48]; Campbell-Arvai 2019 [28]; Gashu et al. 2020 [49]. | |
| Sociocultural (n = 6) | Huang 2014 [32]; Barau 2015 [33]; Buchel and Frantzeskaki 2015 [29]; Conedera et al. 2015 [34]; Zwierzchowska et al. 2018 [48]; Gashu et al. 2020 [49]. | |
| Recreational and exercise (n = 10) | Popoola and Ajewole 2001 [21]; Barnhill and Smardon 2012 [26]; Buchel and Frantzeskaki 2015 [29]; Giannakis et al. 2016 [50]; Larson et al. 2016 [37]; Yen et al. 2016 [44]; Ives et al. 2017 [38]; Keith et al. 2018 [27]; Meyer and Schulz 2018 [51]; Nath et al. 2018 [47]. | |
| Environmental Benefits (n = 21) | Biodiversity and wildlife (n = 9) | Peckham et al. 2013 [43]; Shwartz et al. 2014 [52]; Rupprecht et al. 2015 [36]; Giannakis et al. 2016 [50]; Meyer and Schulz 2017 [51]; Korpilo et al. 2018 [39]; Campbell-Arvai 2019 [28]; Wang et al. 2019 [53]. |
| Shade (n = 5) | Conway and Yip 2016 [54]; Paul and Nagendra 2017 [55]; Fernandes et al. 2019 [56]; Guenat et al. 2019 [41]; Gwedla and Shackleton 2019 [42]. | |
| Better air quality and climate regulation (n = 13) | Sanesi and Chiarello [22]; Peckham et al. 2013 [43]; Buchel and Frantzeskaki 2015 [29]; Rupprecht et al. 2015 [36]; Conway and Yip 2016 [54]; Giannakis et al. 2016 [50]; Yen et al. 2016 [44]; Faivre et al. 2017 [45]; Paul and Nagendra 2017 [55]; Duan et al. 2018 [46]; Fernandes et al. 2019 [56]; Guenat et al. 2019 [41]; Miller and Montalto 2019 [30]. | |
| Water runoff mitigation (n = 3) | Barnhill and Smardon 2012 [26]; Paul and Nagendra 2017 [55]; Miller and Montalto 2019 [30]. | |
| Economic Benefits (n = 8) | Food provision (n = 3) | Barau 2015 [33]; Guenat et al. 2019 [41]; Gwedla and Shackleton 2019 [42]. |
| Wood provision (n = 2) | Popoola and Ajewole 2001 [21]; Meyer and Schulz 2017 [51]. | |
| Increase in property value (n = 3) | Jim and Chen 2006 [23]; Yen et al. 2016 [44]; Panagopoulos et al. 2018 [40]. | |
| Perceived Risks (n = 9) | Authors |
|---|---|
| Danger (e.g., crime and vandalism) (n = 6) | Sanesi and Chiarello 2006 [22]; Ostoić et al. 2017 [57]; Keith et al. 2018 [27]; Campbell-Arvai 2019 [28]; Fernandes et al. 2019 [56]; Gwedla and Shackleton [42]. |
| Dirtiness (e.g., leaves in autumn or bird excrement) (n = 4) | Conway and Yip 2016 [54]; Ostoić et al. 2017 [57]; Fernandes et al. 2019 [56]; Gwedla and Shackleton 2019 [42]. |
| Attraction of unwanted animals/insects (n = 3) | Jim and Chen 2006 [23]; Conway and Yip 2016 [54]; Campbell-Arvai 2019 [28]. |
| Limited Access/Environmental injustice (n = 2) | Ostoić et al. 2017 [57]; Keith et al. 2018 [27]. |
| Damage (e.g., person, property) (n = 2) | Conway and Yip 2016 [54]; Campbell-Arvai 2019 [28]. |
| Allergies (n = 1) | Gwedla and Shackleton 2019 [42]. |
| Economic costs (e.g., construction and maintenance) (n = 2) | Conway and Yip 2016 [54]; Campbell-Arvai 2019 [28]. |
| Invasive species of plants (n = 1) | Campbell-Arvai 2019 [28] |
| Contamination (e.g., soil through chemicals and dirty water use) (n = 1) | Guenat et al. 2019 [41]. |
| Preferences for Design | Authors |
|---|---|
| Tree or flower abundance, biodiversity (n = 10) | Koo et al. 2013 [60]; Zhang et al. 2013 [61]; Baur et al. 2016 [62]; Arnberger et al. 2017 [63]; Derkzen et al. 2017 [64]; Pietrzyk-Kuszynska et al. 2017 [65]; Ayala-Azcárraga et al. 2019 [66]; Hwang et al. 2019 [67]; Rahnema et al. [58]; Ramer et al. 2019 [68]. |
| Increase in fauna (n = 5) | Caula 2009 [69]; Koo et al. 2013 [60]; Ayala-Azcárraga et al. 2019 [66]; Hwang et al. 2019 [67]; Ramer et al. 2019 [68]. |
| Water, streams, and fountains (n = 4) | Arnberger et al. 2017 [63]; Karanikola et al. 2017 [70]; Menconi and Grohmann 2018 [71]; Rahnema et al. 2019 [58]. |
| Walkways, stepping stone corridors (n = 5) | Zhang et al. 2013 [61]; Karanikola et al. 2017 [70]; Ayala-Azcárraga et al. 2019 [66]; Hwang et al. 2019 [67]; Shams and Barker 2019 [72]. |
| Security (n = 3) | Zhang et al. 2013 [61]; Baur et al. 2016 [62]; Shams and Barker 2019 [72]. |
| Cleanliness and proper maintenance (n = 3) | Baur et al. 2016 [62]; Pietrzyk-Kaszyńska et al. 2017 [65]; Shams and Barker 2019 [72]. |
| Naturalness and wilderness areas (n = 5) | Zhang et al. 2013 [61]; Baur et al. 2016 [62]; Hwang et al. 2019 [67]; Rahnema et al. 2019 [58]; Shams and Barker 2019 [72]. |
| Accessibility, distance to home or to city center (n = 6) | Zhang et al. 2013 [61]; Arnberger et al. 2017 [63]; Derkzen et al. 2017 [64]; Pietrzyk-Kuszynska et al. 2017 [64]; Ayala-Azcárraga et al. 2019 [66]; Shams and Barker 2019 [72]. |
| Information signs and environmental education (n = 5) | Caula 2009 [69]; Koo et al. 2013 [60]; Karanikola et al. 2017 [70]; Pietrzyk-Kuszynska et al. 2017 [65]; Shams and Barker 2019 [72]. |
| Facilitate social interactions (Seats, tables, picnic or barbecue areas, shelters) (n = 5) | Zhang et al. 2013 [61]; Karanikola et al. 2017 [70]; Menconi and Grohmann 2018 [71]; Ayala-Azcárraga et al. 2019 [66]; Shams and Barker 2019 [72]. |
| Kids playground (n = 3) | Zhang et al. 2013 [61]; Menconi and Grohmananan 2018 [71]; Ayala-Azcárraga et al. 2019 [66]. |
| Sports and recreational facilities (n = 3) | Karanikola et al. 2017 [70]; Menconi and Grohmann 2018 [71]; Shams and Barker 2019 [72]. |
| Connectivity to places of interest (e.g., parks, restaurants, shops, monuments) (n = 2) | Pietrzyk-Kuszynska et al. 2017 [65]; Shams and Barker 2019 [72]. |
| Green space into buildings (n = 2) | Tsantopoulos et al. 2018 [59]; Xue et al. 2019 [3]. |
| NBS challenges | Authors |
|---|---|
| Lack of knowledge and awareness about the environmental problems and their possible solutions and impacts (n = 8) | Lamichhane and Thapa 2012 [73]; Keeley et al. 2013 [74]; Hoyle et al. 2017 [75]; Furlong et al. 2018 [76]; Khoshkar et al. 2018 [77]; Onori et al. 2018 [78]; Girma 2019 [79]; Molla and Mekonnen 2019 [80]. |
| Lack of evidence of the success and efficacy of the solutions (n = 1) | Kabisch et al. 2016 [14]. |
| Lack of political support/guidance (n = 8) | Lamichhane and Thapa 2012 [73]; Keeley et al. 2013 [74]; Zivojinovic and Wolfslehner 2015 [81]; Furlong et al. 2018 [76]; Khoshkar et al. 2018 [77]; Girma 2019 [79]; Lähde and Marino 2019 [82]; Molla and Mekonnen 2019 [80]. |
| Financial constraints and lack of funding (n = 8) | Lamichhane and Thapa 2012 [73]; Keeley et al. 2013 [74]; Rall et al. 2015 [83]; Zivojinovic and Wolfslehner 2015 [81]; Furlong et al. 2018 [76]; Khoshkar et al. 2018 [77]; Di Marino et al. 2019 [84]; Girma 2019 [79]. |
| Lack of engagement due low social cohesion (n = 7) | Lamichhane and Thapa 2012 [73]; Rall et al. 2015 [83]; Zivojinovic and Wolfslehner 2015 [81]; Kabisch et al. 2016 [14]; Hoyle et al. 2017 [75]; Bissonnette et al. 2018 [85]; Girma 2019 [79]. |
| Lack of skilled personnel/technical and scientific knowledge (n = 3) | Keeley et al. 2013 [74]; Zivojinovic and Wolfslehner 2015 [81]; Girma 2019 [79]. |
| Maintenance and monitoring (n = 4) | Lamichhane and Thapa 2012 [73]; Rall et al. 2015 [83]; Keeley et al. 2017 [74]; Khoshkar et al. 2018 [77]. |
| Opportunities (n = 16) | Authors |
|---|---|
| Promote social cohesion (cooperative working, mutual learning, and experience-sharing) (n = 6) | Chou et al. 2017 [87]; Fors et al. 2018 [88]; Harper et al. 2018 [89]; Kosová et al. 2018 [90]; Ugolini et al. 2018 [91]; Rolf et al. 2019 [92]. |
| Add-value to urban natural and social capital (n = 2) | Dennis and James 2016 [93]; Dennis and James 2016 [94]. |
| Increase biodiversity (n = 3) | Mabelis and Maksymiuk 2009 [13]; Dennis and James 2016 [94]; Fischer et al. 2019 [95]. |
| Contextualize functions with ecosystem services (n = 1) | Dennis and James 2016 [93]. |
| Develop initiatives of environmental education (n = 3) | Moskell and Allred 2013 [96]; Chou et al. 2017 [87]; Fischer et al. 2019 [95]. |
| Intensify the public acceptability, confidence, consciousness and sense of belonging (n = 4) | Sipilä and Tyrväinen 2005 [12]; Fors et al. 2018 [88]; Gulsrud et al. 2018 [97]; Rolf et al. 2019 [92]. |
| Influence social learning and innovation (n = 6) | Travaline et al. 2015 [98]; Dennis et al. 2016 [99]; Chou et al. 2017 [87]; Gulsrud et al. 2018 [97]; Kosová et al. 2018 [90]; Ugolini et al. 2018 [91]. |
| Benefit from multifunctionality (n = 2) | Belmeziti et al. 2018 [100]; Rolf et al. 2019 [92]. |
| Connect people with nature (n = 3) | Chou et al. 2017 [87]; Gulsrud et al. 2018 [97]; Fors et al. 2018 [88]. |
| Establish long-term partnerships to attain funding (n = 1) | Ugolini et al. 2018 [91]. |
| Prevent conflicts (n = 2) | Sipilä and Tyrväinen 2005 [12]; Rolf et al. 2019 [92]. |
| Challenges (n = 10) | Authors |
|---|---|
| Deal with conflicting points of view and interests (n = 3) | Sipilä and Tyrväinen 2005 [12]; Cousins 2017 [102]; Ugolini et al. 2018 [91]. |
| Understand the hierarchies of institutions and bureaucracies (n = 5) | Mattijssen et al. 2017 [103]; Mensah et al. 2017 [104]; Gulsrud et al. 2018 [97]; Liu and Jensen 2018 [105]; Ugolini et al. 2018 [91]. |
| Overtake the lack of political support (n = 2) | Gulsrud et al. 2018 [97]; Liu and Jensen 2018 [105]. |
| Feel the involvement as being time consuming and expensive (n = 3) | Sipilä and Tyrväinen 2005 [12]; Mabelis and Maksymiuk 2009 [13]; Travaline et al. 2015 [98]. |
| Overcome the poor flow of information and social mobilization (n = 2) | Moskell and Allred 2013 [96]; Mensah et al. 2017 [104]. |
| Maintain continuity of the collaboration (n = 1) | Mattijssen et al. 2017 [103]. |
| Motivations/Drivers | Authors | |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental (n = 7) | Environment protection and contribution to sustainability (n = 5) | Asah and Blahna 2012 [107]; Shan 2012 [108]; Zare et al. 2015 [109]; Chelleri et al. 2016 [25]; Beery et al. 2018 [110]. |
| Characteristics of the physical environment (n = 2) | Fors 2019 [111]; Murphy 2019 [112]. | |
| Communal (n = 8) | Protect the community/improve collective health (n = 2) | Zare et al. 2015 [109]; Beery et al. 2018 [110]. |
| Promote social interactions (n = 2) | Asah and Blahna 2012 [107]; Zare et al. 2015 [109]. | |
| Bring neighbors to participate and be part of the experiences (n = 5) | Green et al. 2012 [113]; Lewis et al. 2018 [114]; Lieberherr and Green 2018 [115]; Lim 2018 [116]; Fors 2019 [111]. | |
| Personal (n = 8) | Possibility to learn from and experience environmentally friend solutions (n = 3) | Asah and Blahna 2012 [107]; Chelleri et al. 2016 [25]; Lewis et al. 2018 [114]. |
| Interest in gardening (n = 2) | Fors 2019 [111]; Petrovic et al. 2019 [117]. | |
| Sense of place and attachment (n = 3) | Murphy 2019 [112]; Petrovic et al. 2019 [117]; Romolini 2019 [118]. | |
| Proximity to disturbance and effects on residential properties (n = 2) | Hunter et al. 2011 [119]; Fors 2019 [111]. | |
| Participation Methods/Tools | Authors | |
|---|---|---|
| Social media (n = 3) | Afzalan and Muller 2014 [120]; Guerrero et al. 2016 [121]; Yamaki 2016 [106]. | |
| E-Tools/virtual tool (n = 2) | Shwartz et al. 2013 [122]; Møller et al. 2019 [123]. | |
| GIS-based tools (n = 8) | PPGIS | Janse and Konijnendijk 2007 [124]; Hawthorne et al. 2015 [125]; Raymond et al. 2016 [126]; Rall et al. 2019 [127]. |
| SolVES | Sun et al. 2019 [128]. | |
| VGI | Guerrero et al. 2016 [121]; Møller et al. 2019 [123]. | |
| 3D visualization | Neuenschwander et al. 2014 [129]. | |
| Focus Group (n = 3) | Nilsson et al. 2007 [130]; Kangas et al. 2014 [131]; Sturiable et al. 2018 [132]. | |
| Workshop (n = 4) | Janse and Konijnendijk 2007 [124]; Bellamy et al. 2017 [133]; Assmuth et al. 2017 [134]; van der Jagt et al. 2019 [135]. | |
| Questionnaire/Survey/Q methodology (n = 10) | Janse and Konijnendijk 2007 [124]; Kangas et al. 2014 [131]; Hawthorne et al. 2015 [125]; Lindemann and Briege 2016 [136]; Raymond et al. 2016 [126]; Sun and Hall 2016 [137]; Jayasooriya et al. 2019 [138]; Lafortezza and Giannico 2019 [139]; Møller et al. 2019 [123]; Rall et al. 2019 [127]. | |
| Interviews (n = 4) | Nordström et al. 2010 [140]; Kangas et al. 2014 [131]; Beumer and Martens 2015 [141]; Sturiable and Scuderi 2018 [132]. | |
| Meetings (n = 5) | Nordström et al. 2010 [140]; Afzalan and Muller 2014 [120]; O’Donnell et al. 2018 [142]; Sturiable and Scuderi 2018 [132]; Lafortezza and Giannico 2019 [139]. | |
| Visual methods (n = 4) | Qiu et al. 2013 [143]; Lindemann and Briege 2016 [136]; Rink and Arndt 2016 [31]; Sun et al. 2019 [128]. | |
| Learning Alliances (n = 2) | O’Donnell et al. 2018 [142]; van der Jagt et al. 2019 [135] | |
| Living Labs (n = 3) | Bellamy et al. 2017 [133]; Lafortezza and Giannico 2019 [139]; van der Jagt et al. 2019 [135] | |
| Collaborative Governance | Authors |
|---|---|
| Top-down approach and a central-government decision process (n = 6) | Rosol 2010 [144]; Faehnle et al. 2014 [145]; Skandrani et al. 2015 [146]; Gasperi et al. 2016 [147]; Kronenberg et al. 2016 [148]; Shifflet et al. 2019 [149]. |
| Bottom-up and citizen-led approaches (n = 6) | Rosol 2010 [144]; Cvejić et al. 2015 [150]; Skandrani et al. 2015 [146]; Gasperi et al. 2016 [147]; Jerome 2017 [151]; van der Jagt et al. 2017 [152]. |
| Public-private interactions (n = 5) | Young 2011 [86]; Milanovič and Foški 2015 [153]; Brink and Wamsler 2016 [31]; Simić et al. 2017 [154]; Buijs et al. 2019 [155]. |
| Cross-sectoral partnerships (n = 4) | Ugolini et al. 2015 [156]; Schifman et al. 2017 [157]; van der Jagt 2017 [152]; Frantzeskaki 2019 [158]. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, V.; Barreira, A.P.; Loures, L.; Antunes, D.; Panagopoulos, T. Stakeholders’ Engagement on Nature-Based Solutions: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020640
Ferreira V, Barreira AP, Loures L, Antunes D, Panagopoulos T. Stakeholders’ Engagement on Nature-Based Solutions: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability. 2020; 12(2):640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020640
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Vera, Ana Paula Barreira, Luís Loures, Dulce Antunes, and Thomas Panagopoulos. 2020. "Stakeholders’ Engagement on Nature-Based Solutions: A Systematic Literature Review" Sustainability 12, no. 2: 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020640
APA StyleFerreira, V., Barreira, A. P., Loures, L., Antunes, D., & Panagopoulos, T. (2020). Stakeholders’ Engagement on Nature-Based Solutions: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability, 12(2), 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020640








