Effectiveness of “Escape Room” Educational Technology in Nurses’ Education: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
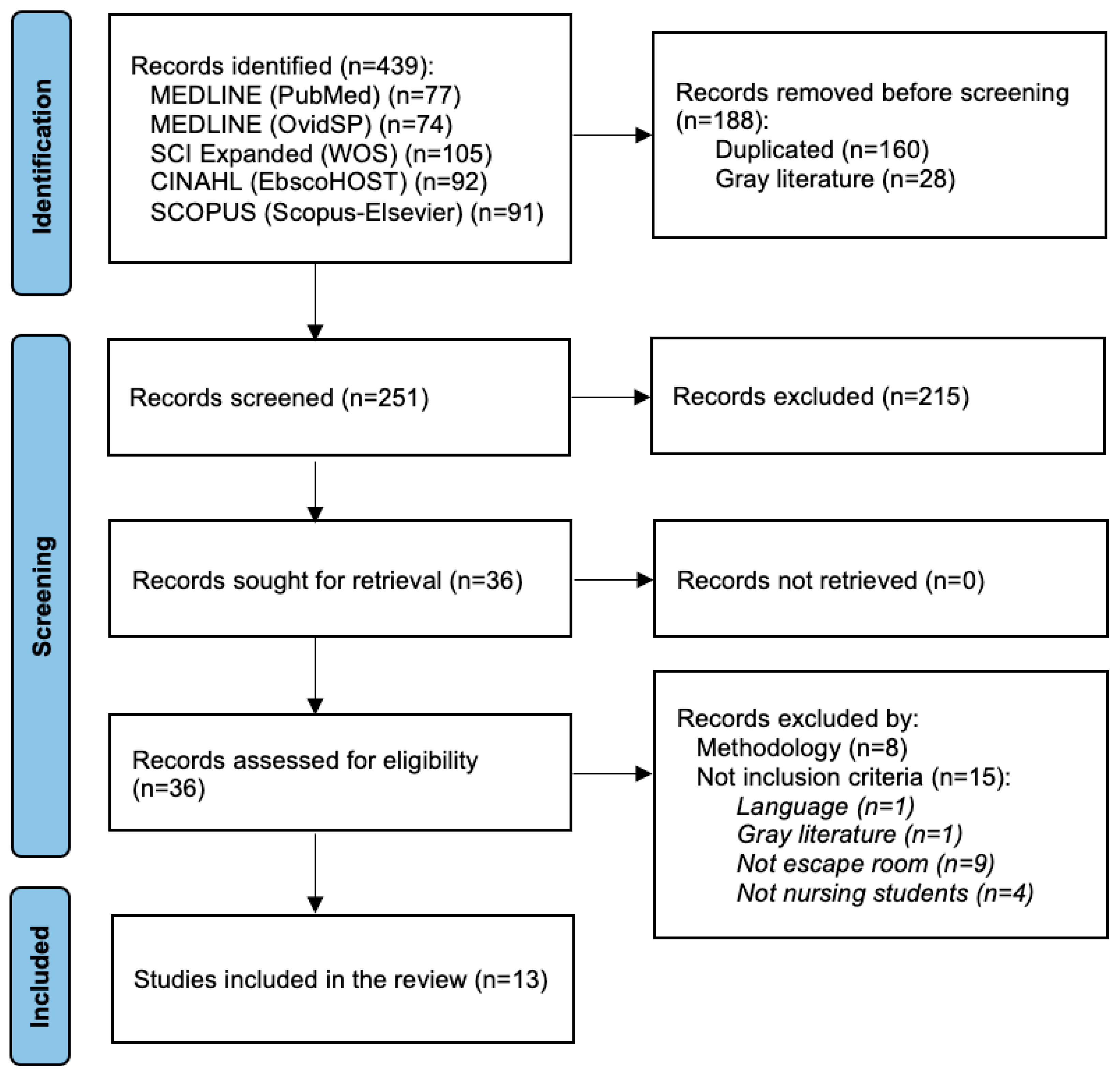
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Public Involvement Statement
Guidelines and Standards Statement
Use of Artificial Intelligence
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kowitlawakul, Y.; Tan, J.J.M.; Suebnukarn, S.; Nguyen, H.D.; Poo, D.C.C.; Chai, J.; Wang, W.; Devi, K. Utilizing educational technology in enhancing undergraduate nursing students’ engagement and motivation: A scoping review. J. Prof. Nurs. 2022, 42, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, M.M.; Dufrene, C. Educational competencies and technologies for disaster preparedness in undergraduate nursing education: An integrative review. Nurse Educ. Today 2014, 34, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahalan, F.; Alias, N.; Shaharom, M.S.N. Gamification and Game Based Learning for Vocational Education and Training: A Systematic Literature Review. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 29, 1279–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quek, L.H.; Tan, A.J.Q.; Sim, M.J.J.; Ignacio, J.; Harder, N.; Lamb, A.; Chua, W.L.; Lau, S.T.; Liaw, S.Y. Educational escape rooms for healthcare students: A systematic review. Nurse Educ. Today 2024, 132, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gaalen, A.E.J.; Brouwer, J.; Schönrock-Adema, J.; Bouwkamp-Timmer, T.; Jaarsma, A.D.C.; Georgiadis, J.R. Gamification of health professions education: A systematic review. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. Theory Pract. 2021, 26, 683–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yin, X.; Yin, W.; Dong, X.; Li, Q. Evaluation of gamification techniques in learning abilities for higher school students using FAHP and EDAS methods. Soft Comput. 2023, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbanev, I.; Agudelo-Londoño, S.; González, R.A.; Cortes, A.; Pomares, A.; Delgadillo, V.; Yepes, F.J.; Muñoz, Ó. A systematic review of serious games in medical education: Quality of evidence and pedagogical strategy. Med. Educ. Online 2018, 23, 1438718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eukel, H.; Morrell, B. Ensuring Educational Escape-Room Success: The Process of Designing, Piloting, Evaluating, Redesigning, and Re-Evaluating Educational Escape Rooms. Simul. Gaming 2021, 52, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antón-Solanas, I.; Rodríguez-Roca, B.; Urcola-Pardo, F.; Anguas-Gracia, A.; Satústegui-Dordá, P.J.; Echániz-Serrano, E.; Subirón-Valera, A.B. An evaluation of undergraduate student nurses’ gameful experience whilst playing a digital escape room as part of a FIRST year module: A cross-sectional study. Nurse Educ. Today 2022, 118, 105527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinkemeyer, E.A.; Chrisman, M.; Patel, S.E. Escape rooms in nursing education: An integrative review of their use, outcomes, and barriers to implementation. Nurse Educ. Today 2022, 119, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromataris, E.; Munn, Z. (Eds.) JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2020; Available online: https://synthesismanual.jbi.global (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.; Stern, C.; Aromataris, E.; Lockwood, C.; Jordan, Z. What kind of systematic review should I conduct? A proposed typology and guidance for systematic reviewers in the medical and health sciences. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kirtley, S.; Waffenschmidt, S.; Ayala, A.P.; Moher, D.; Page, M.J.; Koffel, J.B.; PRISMA-S Group. PRISMA-S: An extension to the PRISMA Statement for Reporting Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, F.; Zhu, C.; Tai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. The effect of an escape room game on college nursing students’ learning attitude and game flow experiences in teaching safe medication care for the elderly: An intervention educational study. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuhl, K.K.; Nagel, S.; Tamburro, R.; Jewell, T.M.; Gilbert, E.; Gonzalez, A.; Sullivan, D.L.; Sprague, J.E. Better together: Utilizing an interprofessional course and escape room to educate healthcare students about opioid use disorder. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Chang, C.Y.; Jen, H.J. Facilitating undergraduate students’ problem-solving and critical thinking competence via online escape room learning. Nurse Educ. Pract. 2023, 73, 103828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hursman, A.; Richter, L.M.; Frenzel, J.; Viets Nice, J.; Monson, E. An online escape room used to support the growth of teamwork in health professions students. J. Interprof. Educ. Pract. 2022, 29, 100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millsaps, E.R.; Swihart, A.K.; Lemar, H.B. Time is brain: Utilizing escape rooms as an alternative educational assignment in undergraduate nursing education. Teach. Learn. Nurs. 2022, 17, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Torres, G.; Cardona, D.; Requena, M.; Rodriguez-Arrastia, M.; Roman, P.; Ropero-Padilla, C. The impact of using an “anatomy escape room” on nursing students: A comparative study. Nurse Educ. Today 2022, 109, 105205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ferrer, J.M.; Manzano-León, A.; Cangas, A.J.; Aguilar-Parra, J.M. A Web-Based Escape Room to Raise Awareness About Severe Mental Illness Among University Students: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Serious Games 2022, 10, e34222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettergreen, S.A.; Stewart, M.P.; Huntsberry, A.M. Evaluation of an escape room approach to interprofessional education and the opioid crisis. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2022, 14, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, N.M.; Foltz-Ramos, K.; Ohtake, P.J. An Interprofessional Escape Room Experience to Improve Knowledge and Collaboration among Health Professions Students. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2022, 86, ajpe8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foltz-Ramos, K.; Fusco, N.M.; Paige, J.B. Saving patient x: A quasi-experimental study of teamwork and performance in simulation following an interprofessional escape room. J. Interprof. Care 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.; Campbell, N. Effectiveness of an escape room for undergraduate interprofessional learning: A mixed methods single group pre-post evaluation. BMC Med. Educ. 2021, 21, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Puertas, L.; Márquez-Hernández, V.V.; Román-López, P.; Rodríguez-Arrastia, M.J.; Ropero-Padilla, C.; Molina-Torres, G. Escape Rooms as a Clinical Evaluation Method for Nursing Students. Clin. Simul. Nurs. 2020, 49, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, B.L.M.; Eukel, H.N. Escape the Generational Gap: A Cardiovascular Escape Room for Nursing Education. J. Nurs. Educ. 2020, 59, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katonai, Z.; Gupta, R.; Heuss, S.; Fehr, T.; Ebneter, M.; Maier, T.; Meier, T.; Bux, D.; Thackaberry, J.; Schneeberger, A.R. Serious Games and Gamification: Health Care Workers’ Experience, Attitudes, and Knowledge. Acad. Psychiatry 2023, 47, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, S.V.; Gauthier, A.; L’Estrade Ehrstrom, B.; Wortley, D.; Lilienthal, A.; Tudor Car, L.; Dauwels-Okutsu, S.; Nikolaou, C.K.; Zary, N.; Campbell, J.; et al. Serious Gaming and Gamification Education in Health Professions: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, E.A.; Kairouz, V.F.; Sackett, K.M.; Erdley, W.S.; Mustafa, R.A.; Fiander, M.; Gabriel, C.; Schünemann, H. Educational games for health professionals. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 31, CD006411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintze, T.D.; Samuel, N.; Braaten, B. A Systematic Review of Escape Room Gaming in Pharmacy Education. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2023, 87, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicca, J.; Shellenbarger, T. Connecting with Generation Z: Approaches in nursing education. Teach. Learn. Nurs. 2018, 13, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eukel, H.; Frenzel, J.; Frazier, K.; Miller, M. Unlocking Student Engagement: Creation, Adaptation, and Application of an Educational Escape Room across Three Pharmacy Campuses. Simul. Gaming 2020, 51, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Urquiza, J.L.; Gómez-Salgado, J.; Albendín-García, L.; Correa-Rodríguez, M.; González-Jiménez, E.; Cañadas-De la Fuente, G.A. The impact on nursing students’ opinions and motivation of using a “nursing escape room” as a teaching game: A descriptive study. Nurse Educ. Today 2019, 72, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.S.; Pitt, M.; Norton, L. ESCAPE the Boring Lecture: Tips and Tricks on Building Puzzles for Medical Education Escape Rooms. J. Med. Educ. Curric. Dev. 2023, 10, 23821205231211200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, R.M.; Gaba, D.M. The role of debriefing in simulation-based learning. Simul. Healthc. 2007, 2, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppmann, R.; Bekk, M.; Klein, K. Gameful Experience in Gamification: Construction and Validation of a Gameful Experience Scale [GAMEX]. J. Interact. Mark. 2018, 43, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Puertas, L.; García-Viola, A.; Márquez-Hernández, V.V.; Garrido-Molina, J.M.; Granados-Gámez, G.; Aguilera-Manrique, G. Guess it (SVUAL): An app designed to help nursing students acquire and retain knowledge about basic and advanced life support techniques. Nurse Educ. Pract. 2021, 50, 102961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachaturoff, M.; Caboral-Stevens, M.; Gee, M.; Lan, V.M. Effects of peer-mentoring on stress and anxiety levels of undergraduate nursing students: An integrative review. J. Prof. Nurs. 2020, 36, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, R.H.; Lyman, B.; Miehl, N. Nursing students’ experiences with high-fidelity simulation. Int. J. Nurs. Educ. Scholarsh. 2015, 12, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, J.M.; Ferdig, R.E. Gaming and anxiety in the nursing simulation lab: A pilot study of an escape room. J. Prof. Nurs. 2021, 37, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, A.; Franklin, K.; Edwards, T.R.; Slivinski, A. Escaping the Silos: Utilization of a Pediatric Trauma Escape Room to Promote Interprofessional Education and Collaboration. J. Trauma Nurs. 2023, 30, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, N.M.; Foltz-Ramos, K.; Zhao, Y.; Ohtake, P.J. Virtual escape room paired with simulation improves health professions students’ readiness to function in interprofessional teams. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2023, 15, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abensur Vuillaume, L.; Laudren, G.; Bosio, A.; Thévenot, P.; Pelaccia, T.; Chauvin, A. A Didactic Escape Game for Emergency Medicine Aimed at Learning to Work as a Team and Making Diagnoses: Methodology for Game Development. JMIR Serious Games 2021, 9, e27291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckian, J.; Eveson, L.; May, H. The great escape? The rise of the escape room in medical education. Future Healthc. J. 2020, 7, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dams, V.; Burger, S.; Crawford, K.; Setter, R. Can You Escape? Creating an Escape Room to Facilitate Active Learning. J. Nurses Prof. Dev. 2018, 34, E1–E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, C.; Teaford, H.; Taubenheim, A.; Boland, P.; Sick, B. Escaping the professional silo: An escape room implemented in an interprofessional education curriculum. J. Interprof. Care 2019, 33, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldkamp, A.; van de Grint, L.; Knippels, M.-C.P.J.; van Joolingen, W.R. Escape Education: A Systematic Review on Escape Rooms in Education. Educ. Res. Rev. 2020, 31, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Database | Date | Search Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Medline (PubMed) | 29 December 2023 | (“education, nursing”[MeSH Terms] OR “Nursing Education”[All Fields] OR (“education”[All Fields] AND “nursing”[All Fields]) OR “Nursing Education”[All Fields] OR (“educations”[All Fields] AND “nursing”[All Fields])) OR “Nursing Educations”[All Fields]) AND (“Gamification”[MeSH Terms] OR “escape room”[All Fields]) |
| Medline (Ovid) | 29 December 2023 | Gamification.mp. |
| “escape room”.m_titl. | ||
| 1 or 2 | ||
| Education, Nursing.mp. | ||
| 3 and 4 | ||
| CINHAL (EbscoHOST) | 29 December 2023 | S1 TX gamification |
| S2 TX “escape room” OR TX “scape room” OR TX “escape rooms | ||
| S3 TX “escape room” OR TX “scape room” OR TX “escape rooms”) AND (S1 OR S2) | ||
| S4 TX “nursing education” OR TX “education, nursing” | ||
| S5(TX “nursing education” OR TX “education, nursing”) AND (S3 AND S4) | ||
| Scopus (Scopus-Elsevier) | 29 December 2023 | (ALL (“escape room” OR “escape rooms” OR “scape room”) OR INDEXTERMS (gamification)) AND (INDEXTERMS (“education, nursing” OR “nursing education”)) |
| SCI Expanded (Web of Science) | 29 December 2023 | ((TS = (“gamification”)) OR TS = (“escape room” OR “scape room” OR “escape rooms”)) AND TS = (“education, nursing” OR “nursing education”) |
| Author (Year) Country | Design | Themes and Learning Topics | Aim and Main/Secondary Outcomes | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. (2023) China [15] | Quasi experimental pre-post with CG 1 | Gerontological Nursing (Safe Medication Care for the Elderly people) | To determine the effects of an intervention educational activity based on an ER 2 on nursing students’ learning attitude and the game flow experience after they had received nursing classroom teaching on safe medication use in older adults Main outcomes: learnings attitudes and experience of game | During the teaching process of the Gerontological Nursing course, an ER added at the end of classroom teaching can improve nursing students’ learning attitude and also help them to have a good game |
| Schmuhl et al. (2023) USA [16] | Quasi experimental pre-post | Interprofessional Collaboration and Opioid Use Disorder | To determine the impact of an innovative interprofessional educational activity on healthcare professional students’ learning. The educational activity targeted student knowledge of opioid use disorder and perceptions of working with an interprofessional team while caring for patients with opioid use disorder Main outcomes: attitudes about interprofessional collaboration Secondary outcomes: perceptions about opioid use disorder | An interprofessional educational experience including both an asynchronous course and virtual synchronous ER can increase participant knowledge around opioid use disorder and may improve student perceptions of working with an interprofessional team and caring for patients with opioid use disorder |
| Yang et al. (2023) Taiwan [17] | Quasi experimental with CG | Maternity care | To identify the efficiency of ER activities in terms of enhancing nursing students’ retention of maternity-related knowledge and their overall learning performance Main outcomes: knowledge about maternity care Secondary outcomes: students’ confidence and critical thinking | Maternity ER emerged as an online game-based approach that effectively stimulated nursing students and can serve as a practical resource for engaging in maternity care learning |
| Hursman et al. (2022) USA [18] | Quasi experimental pre-post | Interprofessional Colaboration | To enhance interprofessional students’ perceptions of their ability to communicate effectively and respectfully, work together to complete a task and to develop knowledge of the unique roles of members of the healthcare team Main outcomes: improvement in teamwork (effective communication) Secondary outcomes: perceptions and attitudes about gaming | This activity lays the groundwork for collaborative telehealth nursing that students will be exposed to in their future career. Results show the activity helped to build collaboration among team members, including those not in the same physical space. It also showed that virtual ER can be an effective activity to increase interprofessional teamwork perceptions in the online classroom environment and could prove to be useful in other online interprofessional settings |
| Millsaps et al. (2022) USA [19] | Quasi experimental pre-post | Neurological disorders with a focus on stroke | To promote engagement in undergraduate nursing coursework Main outcomes: knowledge about Stroke | ER experiences can be utilized in the preparation of associate degree nursing education to engage students while also ensuring that students meet key learning objectives |
| Molina-Torres et al. (2022) Spain [20] | Quasi experimental pre-post with CG | Anatomy | To evaluate the effectiveness of the ER for anatomy-related knowledge retention in nursing and the perceived value of the game Main outcomes: knowledge about Anatomy Secondary outcomes: satisfaction about gaming | According to the findings, the “Anatomy ER” is a game-based approach that motivates students and constitutes a down-to-earth resource for anatomy learning in healthcare students |
| Rodríguez-Ferrer et al. (2022) Spain [21] | RCT 3 | Stigma again Severe Mental Illness | To examine the effect of the Without Memories ER on nursing students’ stigma against Severe Mental Illness Main outcomes: modification of stigmatizing attitudes towards severe mental illness | The Without Memories ER can be used as an effective tool to educate and raise awareness about stigmatizing attitudes toward Severe Mental Illness in university students studying health care |
| Wettergreen et al. (2022) USA [22] | Quasi experimental pre-post | Interprofessional education and the opioid crisis | To evaluate the use of an interprofessional ER activity to increase clinical knowledge related to the opioid crisis. The secondary objective was to evaluate change in attitudes toward interprofessional collaboration Main outcomes: knowledge related to the opioid crisis Secondary outcomes: attitudes toward interprofessional collaboration | The use of an interprofessional ER as an educational method was effective in increasing some aspects of opioid crisis related knowledge and enhancing attitudes toward interprofessional collaboration. The educational model is applicable to various topics and inter-professional groups |
| Fusco et al. (2022) USA [23] | RCT | Interprofessional Collaboration Sepsis management and post-operative precautions (hip arthroplasty) | To extend our understanding of ER pedagogical design by investigating the impact of escape room puzzle content on changes in student immediate recall knowledge and demonstration of interprofessional skills during a subsequent interprofessional simulation Main outcomes: knowledge of interprofessional collaboration about sepsis Secondary outcomes: interprofessional collaborative skills during simulation | ER can be an innovative pedagogical tool that can positively impact immediate recall knowledge and interprofessional collaborative skills of health professions students |
| Foltz-Ramos et al. (2021) USA [24] | Quasi experimental pre-post with CG | Interprofessional Collaboration | To create and test the use of an interprofessional ER, as a method to improve teamwork, prior to interprofessional simulation Main outcomes: improvement of students’ performance in simulation Secondary outcomes: attitudes toward interprofessional collaboration | ER can, in a brief period of time, improve teamwork and consequently performance during simulation. Findings support the use of ER in interprofessional education curriculum as a method to promote teamwork |
| Moore & Campbell (2021) Australia [25] | Quasi experimental pre-post | Interprofessional practice knowledge and competencies | To investigate the utility of an ER coupled with a debriefing workshop as an effective and engaging interprofessional learning activity. To evaluate the impact of the ER on participant knowledge about inter-professional practice and teamwork. To evaluate the impact of the ER through participant reflection on their personal contributions to the team Main outcomes: knowledge about interprofessional practice and teamwork and improvement in interprofessional learning activity | The ER intervention added value to the placement curriculum and proved flexible for a heterogeneous student cohort |
| Gutiérrez-Puertas et al. (2020) Spain [26] | Quasi experimental with CG | Gameful experience Clinical skills | To understand the gameful experience and satisfaction of nursing students in the evaluation of their clinical skills using an ER Main outcomes: satisfaction of clinical skills Secondary outcomes: experience of game | ER are a useful tool for the evaluation of nursing students compared with using the objective structured clinical evaluation |
| Morrel & Eukel (2020) USA [27] | Quasi experimental pre-post | Cardiovascular critical care | To evaluate the impact of a cardiovascular ER on student knowledge, as well as to understand student perceptions of the educational innovation Main outcomes: knowledge about cardiovascular critical care Secondary outcomes: perceptions about gaming | The cardiovascular ER increased student knowledge and was positively received by students. The educational innovation encouraged student engagement in learning, content application, peer communication, and nursing practice skills |
| Author (Year) | Instruments | Type of ER Game (Setting) and Time Session (in Minutes) | Size Team (Nursing for Team) | Study Population/Sample (IG 1/CG 2) | Lost Case (CG/IG) | Pre Mean (SD 3) (IG/CG) | Post Mean (SD) (IG/CG) | p-Value | Size Effect | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. (2023) [15] | - LAS 4: 23 items, four subscales: learning interest, learning experience, learning habit, and professional recognition. Total range 23–92. Higher scores indicate better learning attitude. - GFEQ 5: 19 items, 5 subscales: sense of control, telepresence, distorted sense of time, enjoyable feelings, and being unconscious of irrelevant surroundings. Total range 19–95. Higher scores indicate better game flow experience | Physical ER 6 (Geriatric nursing training room) (40) | 6–8 (6–8) | 84 Nursing students IG = 41 (6 group) CG = 33 | None | - LAS: IG = 60.93 (2.33) CG = 61.51(2.32) - CFEQ: IG = 63.27 (2.48) | - LAS: IG = 73.17 (1.67) CG = 61.63 (2.66) - CFEQ: IG = 81.29 (2.49) | - LAS: p < 0.001 t-test - GFEQ: p < 0.001 t-test | - LAS: Cohen’s d 5.196 (post-test score) - GFEQ: Cohen’s d 5.253 | - LAS (total score 45) for the ER 43.83 (4.49) |
| Schmuhl et al. (2023) [16] | - ATHCT 7 (14 item). Likert (1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = agree, 4 = strongly agree) - Survey to assess perceptions towards caring for patients with Opioid Use Disorder (11 item) Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = agree, 4 = strongly agree) | Synchronous virtual ER hosted via zoom breakout rooms (30) Physical ER (simulated emergency room) (90) | Not reported (Team inter professional) | 402 health professional students (216 Nursing students) No CG | None | - ATHCT: Performed for 14 items but NP 8 for total score. - Opioid Use Disorder: Performed for 11 items but NP for total score | - ATHCT: Performed for 14 items but NP for total score. - Opioid Use Disorder: Performed for 11 items but NP for total score | - ATHCT: p < 0.05 t-test - Opioid Use Disorder: p < 0.05 (7 items) t-test | NC 9 | Following ER, students strongly agreed that their intentions were to change and work collaborative on interprofessional teams |
| Yang et al. (2023) [17] | - Knowledge test of maternity care: 10 items (maximum score 100 points) - Problem-solving scale: 5 items 5-points Likert scale - Critical thinking questionnaire: 6 items to assess students’ critical thinking abilities, knowledge and confidence | Online game-based ER (50) | 6–7 (6–7) | 42 Nursing students IG = 21 (Online game-based ER) CG = 21 (online learning without ER) | None | NP | - Knowledge: IG = 30.36 CG = 12.64 - Problem-solving: IG = 28.33 CG = 14.67 - Critical thinking: IG = 31.76 CG = 11.24 | - Knowledge: p < 0.001 (Mann Whitney U) - Problem-solving: p < 0.001 (Mann Whitney U) - Critical thinking: p < 0.001 (Mann Whitney U) | NC | |
| Hursman et al. (2022) [18] | Questionnaire Pre-Post: - Pre-survey 8-item of core competencies for interprofessional collaborative practice - Post-survey 26-item same items more 17 items to evaluate the effectiveness, usefulness of the activity and attitudes toward gaming | Online ER (60) | 5–7 (1–2) | 176 heath science students (95 Nursing students) No CG | None | NP for 6 items | NP for 6 items | 6 items (p ˂ 0.001) | NC | |
| Millsaps et al. (2022) [19] | - 5 questions of knowledge about Stroke | Prequiz (10) Pre-briefing (25) Physical ER (30) Debriefing (25) | 4 (4) | Under-graduate ASN 10 students (24 students) (12 morning session, and 12 afternoon session) No CG | None | Knowledge: 2.9 (1.06) Median: 3 | Knowledge: 3.8 (0.66) Median: 4 | p = 0.001 for median (Wilconxon) | NC | Not indicated punctuation system |
| Molina-Torres et al. (2022) [20] | - 10 questions of Knowledge about Anatomy (0–10 points) | Physical ER (University classroom) (15) | 4 (4) | 248 Nursing students IG = 128 CG = 120 | None | NP | Knowledge: IG = 8.94 (0.96) CG = 7.70 (1.25) | Post p = 0.001 (Student’s t) | NC | Also measured IG satisfaction using Satisfaction Questionnaire 11 (26 questions 1 to 5; higher score higher satisfaction) |
| Rodríguez-Ferrer et al. (2022) [21] | - Attributional Questionnaire (14-point Likert 1–9; higher score greater number of stigmatizing attitudes toward people with severe mental illness) - Motivation Questionnaire for Cooperative Playful Learning Strategies (Likert scale 1–7) | Web-based ER (60) | 4 (4) | 316 nursing students randomized IG = 204 (ER no memories) CG = 112 (ER locked In) | IG = 7 CG = 3 Final sample n = 306 IG = 197 CG = 109 | Higher scores greater stigma: IG = 47.57 (16.7) CG = 49.56 (16.03) | Higher scores greater stigma expressed: IG = 30.83 (14.79) CG = 49.55 (16.02) | Post p ˂ 0.001 (ANOVA) | 0.258 | |
| Wettergreen et al. (2022) [22] | - SPICE-R 12 Instrument (multiple response and true/false). Likert scale 1–5 points (higher score greater agreement with the statement) | Pre-brief (10) Virtual and Physical ER (60) Debrief (20) | 5 (not reported) | 80 Heath science students (7 Nursing students) No CG | 10 lost | SPICE-R Higher score greater agreement Mean: 4.48 | SPICE-R Higher score greater agreement Mean: 4.64 | Knowledge: post (p ˂ 0.05) (McNemar’s Exact Test) | NC | Pre Knowledge: 13 62.92% Post Knowledge: 74.30% |
| Fusco et al. (2022) [23] | - ISVS-21 14 - OIPC 15 tool: First 10 items: Adequacy of team to a common vision of the situation. Remaining 10 items: Team’s ability to develop a common action plan. For each item, rated a 3-point Likert (1 = inadequate, 2 = more-less adequate, 3 = adequate) | Physical ER (School of Nursing Simulation Center) (30) | 4 (2) | 233 Nursing and pharmacy students (118 Nursing students) IG = 120 (Simulation) CG = 113 (ER+ simulation) | None | - ISVS-21: IG = 5.3 (0.92) CG = 5.2 (1.0) - OIPC: NP | - ISVS-21: IG = 6.0 (0.72) CG = 5.9 (0.8) - OIPC: Median (IQR 16) IG: Items 1–10: 27 (26–28) IG: Items 11–20: 27 (26–28) Total 55 (53–56) CG: Items 1–10: 26 (24–28) CG: Item 11–20: 27 (25–28) Total 53 (49–56) | - ISVS-21: Mean (SD) * IG = 0.72 (0.81) CG = 0.64 (1.0) - OIPC: Items 1–10 p < 0.001 Item 11–20 p < 0.001 Total p < 0.001 | Cohen’s d: IG = 0.89 CG = 0.61 | |
| Foltz-Ramos et al. (2021) [24] | - Knowledge Test (10 items multiple choice test) - ISVS-21: 21 items 7-point Likert scale. Items scores are added together and divided by 21 to calculate overall score | Physical ER (Simulation scenario in a Simulation center) (30) | 5 (2) | Senior nursing, third-year pharmacy, and second-year physical therapy students IG = 133 (Nursing: 54) ER acute management of sepsis CG = 129 (Nursing: 55) ER general acute care | None | - Knowledge #1: IG = 6.8 (1.9) CG = 6.7 (1.6) - ISVS-21: IG = 5.1 (0.92) CG = 5.2 (0.97) | - Knowledge #2: IG = 7.7 (1.6) CG = 7.3 (1.7) - ISVS-21: IG = 6.0 (0.77) CG = 6.0 (0.82) | - Knowledge #3: p = 0.06 - ISVS-21: p = 0.70 | NC | Three knowledge measures #1, #2, #3 |
| Moore and Campbell (2021) [25] | - Sharif and Nahas’ Questionnaire Adaptation - Knowledge questionnaire: 6 items about knowledge (1 = low–5 = excellent) | Welcome and formal consent (5) Physical ER (55) Comfort break and health care plan development, educational session and evaluation (90) | 6 (at least one nursing student) | 50 health science students (8 Nursing students) No CG | None | NP | NP | Knowledge difference of pre-post means for 6 questions values p ˂ 0.001 | NC | |
| Gutiérrez-Puertas et al. (2020) [26] | - GAMEX 17: 7 questions Likert scale (1 = never–5 = always) - Scale for level of satisfaction: scores between 13–52, higher scores indicate higher satisfaction - Practical examination of clinical skill: 10 questions (0, 0.25, 0.5, or 1 point) | Physical ER (30) | 5 (5) | 237 Nursing students IG = 117 (ER) CG = 120 (OSCE 18) | None | NP | Examination of clinical skills IG = 9.59 (0.36) CG = 7.46 (1.36) | p ˂ 0.05 (Mann Whitney U) | NC | Results of GAMEX 6 dimensions Mean (SD): - Enjoyment 27.60 (3.02) (range 6–30) - Absorption 22.74 (4.88) (range 6–30) - Creative thinking 15.55 (3.23) (range 4–20) - Activation 16.09 (2.98) (range 4–20) - Absence of negative effects 4.66 (2.32) (range 3–15) - Dominance 13.52 (3.12) (range 4–20) |
| Morrel and Eukel (2020) [27] | Knowledge questionnaire: - Pre: 10 questions - Post: Same question + perception scale (11 item) | Physical ER (60) | 4 (4) | 31 Nursing students No CG | 2 lost | NP | NP | p ˂ 0.05 | NC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-de la Torre, H.; Hernández-De Luis, M.-N.; Mies-Padilla, S.; Camacho-Bejarano, R.; Verdú-Soriano, J.; Rodríguez-Suárez, C.-A. Effectiveness of “Escape Room” Educational Technology in Nurses’ Education: A Systematic Review. Nurs. Rep. 2024, 14, 1193-1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep14020091
González-de la Torre H, Hernández-De Luis M-N, Mies-Padilla S, Camacho-Bejarano R, Verdú-Soriano J, Rodríguez-Suárez C-A. Effectiveness of “Escape Room” Educational Technology in Nurses’ Education: A Systematic Review. Nursing Reports. 2024; 14(2):1193-1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep14020091
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-de la Torre, Héctor, María-Naira Hernández-De Luis, Sergio Mies-Padilla, Rafaela Camacho-Bejarano, José Verdú-Soriano, and Claudio-Alberto Rodríguez-Suárez. 2024. "Effectiveness of “Escape Room” Educational Technology in Nurses’ Education: A Systematic Review" Nursing Reports 14, no. 2: 1193-1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep14020091
APA StyleGonzález-de la Torre, H., Hernández-De Luis, M.-N., Mies-Padilla, S., Camacho-Bejarano, R., Verdú-Soriano, J., & Rodríguez-Suárez, C.-A. (2024). Effectiveness of “Escape Room” Educational Technology in Nurses’ Education: A Systematic Review. Nursing Reports, 14(2), 1193-1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep14020091









