Future Perspective for ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with Initial Central Nervous System (CNS) Involvement: Could Next-Generation ALK Inhibitors Replace Brain Radiotherapy for the Prevention of Further CNS Relapse?
Abstract
1. Introduction
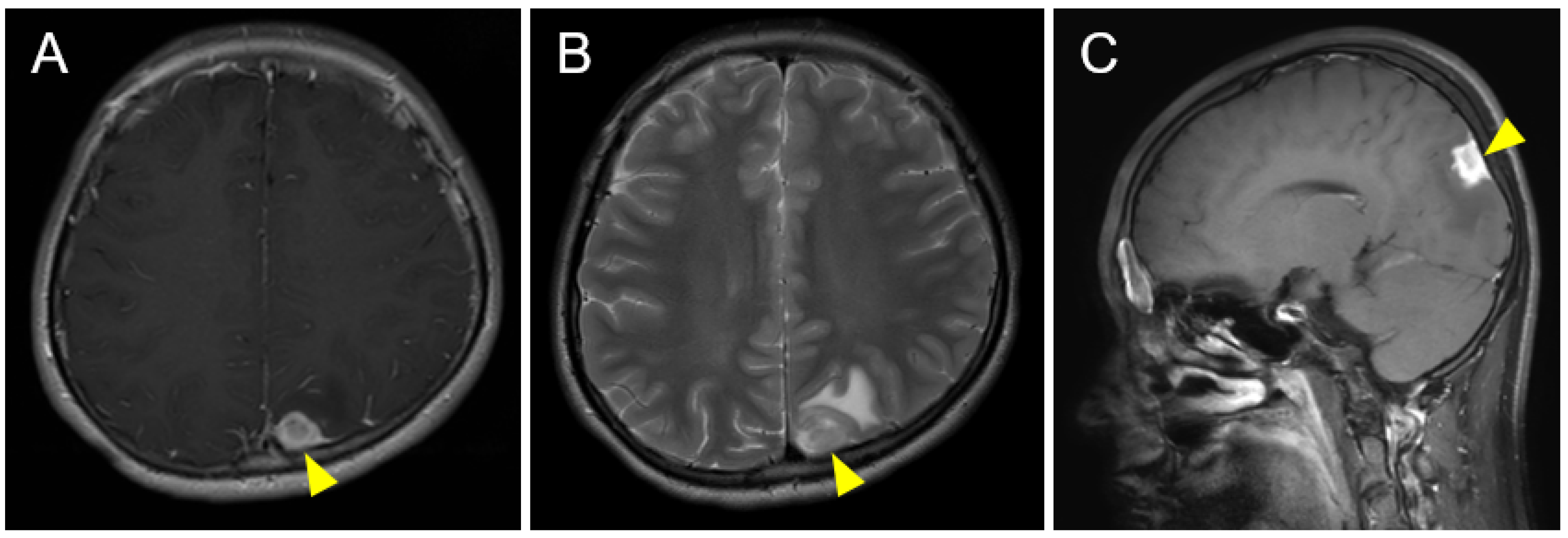
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Oschlies, I.; Niggli, F.; Mann, G.; Parwaresch, R.; Riehm, H.; Schrappe, M.; Reiter, A.; BFM Group. The impact of age and gender on biology, clinical features and treatment outcome of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in childhood and adolescence. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 131, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugieres, L.; Le Deley, M.C.; Rosolen, A.; Williams, D.; Horibe, K.; Wrobel, G.; Mann, G.; Zsiros, J.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Marky, I.; et al. Impact of the methotrexate administration dose on the need for intrathecal treatment in children and adolescents with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Results of a randomized trial of the EICNHL Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussolin, L.; Le Deley, M.C.; Carraro, E.; Damm-Welk, C.; Attarbaschi, A.; Williams, D.; Burke, A.; Horibe, K.; Nakazawa, A.; Wrobel, G.; et al. Prognostic Factors in Childhood Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Long Term Results of the International ALCL99 Trial. Cancers 2020, 12, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Deley, M.C.; Rosolen, A.; Williams, D.M.; Horibe, K.; Wrobel, G.; Attarbaschi, A.; Zsiros, J.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Marky, I.M.; Lamant, L.; et al. Vinblastine in children and adolescents with high-risk anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Results of the randomized ALCL99-vinblastine trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3987–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.; Mori, T.; Reiter, A.; Woessman, W.; Rosolen, A.; Wrobel, G.; Zsiros, J.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Marky, I.; Le Deley, M.C.; et al. Central nervous system involvement in anaplastic large cell lymphoma in childhood: Results from a multicentre European and Japanese study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, E118–E121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, A.; Schrappe, M.; Tiemann, M.; Parwaresch, R.; Zimmermann, M.; Yakisan, E.; Dopfer, R.; Bucsky, P.; Mann, G.; Gadner, H.; et al. Successful treatment strategy for Ki-1 anaplastic large-cell lymphoma of childhood: A prospective analysis of 62 patients enrolled in three consecutive Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster group studies. J. Clin. Oncol. 1994, 12, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidemann, K.; Tiemann, M.; Schrappe, M.; Yakisan, E.; Simonitsch, I.; Janka-Schaub, G.; Dorffel, W.; Zimmermann, M.; Mann, G.; Gadner, H.; et al. Short-pulse B-non-Hodgkin lymphoma-type chemotherapy is efficacious treatment for pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A report of the Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster Group Trial NHL-BFM 90. Blood 2001, 97, 3699–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Kiyokawa, N.; Shimada, H.; Miyauchi, J.; Fujimoto, J. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma in Japanese children: Retrospective analysis of 34 patients diagnosed at the National Research Institute for Child Health and Development. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 121, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, E.M.; Ullrich, N.J.; Seidel, K.; Leisenring, W.; Sklar, C.A.; Armstrong, G.T.; Diller, L.; King, A.; Krull, K.R.; Neglia, J.P.; et al. Longitudinal assessment of late-onset neurologic conditions in survivors of childhood central nervous system tumors: A Childhood Cancer Survivor Study report. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsby, R.E.; Liu, Q.; Nathan, P.C.; Bowers, D.C.; Yeaton-Massey, A.; Raber, S.H.; Hill, D.; Armstrong, G.T.; Yasui, Y.; Zeltzer, L.; et al. Late-occurring neurologic sequelae in adult survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, P.C.; Patel, S.K.; Dilley, K.; Goldsby, R.; Harvey, J.; Jacobsen, C.; Kadan-Lottick, N.; McKinley, K.; Millham, A.K.; Moore, I.; et al. Guidelines for identification of, advocacy for, and intervention in neurocognitive problems in survivors of childhood cancer: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2007, 161, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.R.; Chien, P.N.; Nam, S.Y.; Heo, C.Y. Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Molecular Pathogenesis and Treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Noe, J.; Nowicka, M.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Cheema, P.; Pavlakis, N.; de Marinis, F.; et al. Updated Efficacy and Safety Data and Impact of the EML4-ALK Fusion Variant on the Efficacy of Alectinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Global Phase III ALEX Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Hida, T.; Nokihara, H.; Morise, M.; Azuma, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Seto, T.; Takiguchi, Y.; Nishio, M.; Yoshioka, H.; et al. Final progression-free survival results from the J-ALEX study of alectinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 139, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, L.; Shohdy, K.S.; Lasheen, S.; Abdel-Rahman, O.; Ali, A.; Abdel-Malek, R.R. Safety issues with the ALK inhibitors in the treatment of NSCLC: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 134, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Sun, D.; Liu, K.; Jiang, M.; Liu, D.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, N.; Cong, J.; Zhang, X. The safety and serious adverse events of approved ALK inhibitors in malignancies: A meta-analysis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 4109–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, A.D.J.; Barry, E.; Mosse, Y.P.; Ligas, F.; Bird, N.; de Rojas, T.; Zimmerman, Z.F.; Wilner, K.; Woessmann, W.; Weiner, S.; et al. Second Paediatric Strategy Forum for anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibition in paediatric malignancies: ACCELERATE in collaboration with the European Medicines Agency with the participation of the Food and Drug Administration. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 157, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukano, R.; Mori, T.; Sekimizu, M.; Choi, I.; Kada, A.; Saito, A.M.; Asada, R.; Takeuchi, K.; Terauchi, T.; Tateishi, U.; et al. Alectinib for relapsed or refractory anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma: An open-label phase II trial. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 4540–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaud, C.; Abbou, S.; Ducassou, S.; Simonin, M.; Le Mouel, L.; Pereira, V.; Gourdon, S.; Lambilliotte, A.; Geoerger, B.; Minard-Colin, V.; et al. Profound and sustained response with next-generation ALK inhibitors in patients with relapsed or progressive ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma with central nervous system involvement. Haematologica 2022, 107, 2255–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Baldo, G.; Abbas, R.; Woessmann, W.; Horibe, K.; Pillon, M.; Burke, A.; Beishuizen, A.; Rigaud, C.; Le Deley, M.C.; Lamant, L.; et al. Neuro-meningeal relapse in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Incidence, risk factors and prognosis—A report from the European intergroup for childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessmann, W.; Zimmermann, M.; Lenhard, M.; Burkhardt, B.; Rossig, C.; Kremens, B.; Lang, P.; Attarbaschi, A.; Mann, G.; Oschlies, I.; et al. Relapsed or refractory anaplastic large-cell lymphoma in children and adolescents after Berlin-Frankfurt-Muenster (BFM)-type first-line therapy: A BFM-group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3065–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima-Yamashita, Y.; Mori, T.; Nakazawa, A.; Fukano, R.; Takimoto, T.; Tsurusawa, M.; Kobayashi, R.; Horibe, K. Prognostic impact of minimal disseminated disease and immune response to NPM-ALK in Japanese children with ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 107, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.; Fukano, R.; Saito, A.; Takimoto, T.; Sekimizu, M.; Nakazawa, A.; Tsurusawa, M.; Kobayashi, R.; Horibe, K.; Japanese Pediatric Leukemia/Lymphoma Study Group. Analysis of Japanese Registration from the Randomized International Trial for ChildhoodAnaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL99-R1). Rinsho Ketsueki 2014, 55, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thorer, H.; Zimmermann, M.; Makarova, O.; Oschlies, I.; Klapper, W.; Lang, P.; von Stackelberg, A.; Fleischhack, G.; Worch, J.; Juergens, H.; et al. Primary central nervous system lymphoma in children and adolescents: Low relapse rate after treatment according to Non-Hodgkin-Lymphoma Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster protocols for systemic lymphoma. Haematologica 2014, 99, e238–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A.; Khan, D.; Hall, G.W.; Collins, G.P. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma: Current and future perspectives in adult and paediatric disease. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 93, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, S.; Hebart, H.; Hjalgrim, L.L.; Kabickova, E.; Lang, P.; Steinbach, D.; Schwabe, G.C.; Woessmann, W. CNS progression during vinblastine or targeted therapies for high-risk relapsed ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A case series. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.L.; Pickering, D.; Lowe, E.J.; Zwick, D.; Abromowitch, M.; Davenport, G.; Cairo, M.S.; Sanger, W.G. Childhood anaplastic large cell lymphoma has a high incidence of ALK gene rearrangement as determined by immunohistochemical staining and fluorescent in situ hybridisation: A genetic and pathological correlation. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 131, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosse, Y.P.; Voss, S.D.; Lim, M.S.; Rolland, D.; Minard, C.G.; Fox, E.; Adamson, P.; Wilner, K.; Blaney, S.M.; Weigel, B.J. Targeting ALK With Crizotinib in Pediatric Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma and Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3215–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Gandhi, L.; Riely, G.J.; Chiappori, A.A.; West, H.L.; Azada, M.C.; Morcos, P.N.; Lee, R.M.; Garcia, L.; Yu, L.; et al. Safety and activity of alectinib against systemic disease and brain metastases in patients with crizotinib-resistant ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (AF-002JG): Results from the dose-finding portion of a phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.B.; Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.H.; Solomon, B.J.; Riely, G.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Zhou, C.; Shreeve, S.M.; Selaru, P.; Polli, A.; et al. Clinical Experience With Crizotinib in Patients With Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Perol, M.; Wrona, A.; Novello, S.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in treatment-naive anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive (ALK+) non-small-cell lung cancer: CNS efficacy results from the ALEX study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Tanaka, T.; Kuriki, H.; Zeaiter, A.; Tamura, T. Analysis of central nervous system efficacy in the J-ALEX study of alectinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 121, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Mussolin, L.; Brugieres, L. Abrupt Relapse of ALK-Positive Lymphoma after Discontinuation of Crizotinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, G.; Sharma, G.G.; Villa, M.; Mauri, M.; Crespiatico, I.; Fontana, D.; Manfroni, C.; Mastini, C.; Zappa, M.; Magistroni, V.; et al. Synergistic Drug Combinations Prevent Resistance in ALK+ Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugieres, L.; Afify, Z.; Lowe, E. ALK inhibitors for ALK-altered paediatric malignancies. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1646–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, E.J.; Reilly, A.F.; Lim, M.S.; Gross, T.G.; Saguilig, L.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Wu, R.; Alexander, S.; Bollard, C.M. Crizotinib in Combination With Chemotherapy for Pediatric Patients With ALK+ Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma: The Results of Children’s Oncology Group Trial ANHL12P1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2043–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Pei, K.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Su, X.; Gan, W.; Wang, P. Observation of Alectinib- and Crizotinib-included chemotherapy in children with ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A single institutional experience. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 7182–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, J.; Gu, W.Y.; Jin, L.; Duan, Y.L.; Huang, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.J.; et al. Central nervous system relapse in a pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma patient with CLTC/ALK translocation treated with alectinib: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, M.; Miura, H.; Ishimaru, S.; Furukawa, G.; Kawamura, Y.; Kozawa, K.; Yamada, S.; Ito, F.; Kudo, K.; Yoshikawa, T. Future Perspective for ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with Initial Central Nervous System (CNS) Involvement: Could Next-Generation ALK Inhibitors Replace Brain Radiotherapy for the Prevention of Further CNS Relapse? Pediatr. Rep. 2023, 15, 333-340. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15020029
Tanaka M, Miura H, Ishimaru S, Furukawa G, Kawamura Y, Kozawa K, Yamada S, Ito F, Kudo K, Yoshikawa T. Future Perspective for ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with Initial Central Nervous System (CNS) Involvement: Could Next-Generation ALK Inhibitors Replace Brain Radiotherapy for the Prevention of Further CNS Relapse? Pediatric Reports. 2023; 15(2):333-340. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Makito, Hiroki Miura, Soichiro Ishimaru, Gen Furukawa, Yoshiki Kawamura, Kei Kozawa, Seiji Yamada, Fumitaka Ito, Kazuko Kudo, and Tetsushi Yoshikawa. 2023. "Future Perspective for ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with Initial Central Nervous System (CNS) Involvement: Could Next-Generation ALK Inhibitors Replace Brain Radiotherapy for the Prevention of Further CNS Relapse?" Pediatric Reports 15, no. 2: 333-340. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15020029
APA StyleTanaka, M., Miura, H., Ishimaru, S., Furukawa, G., Kawamura, Y., Kozawa, K., Yamada, S., Ito, F., Kudo, K., & Yoshikawa, T. (2023). Future Perspective for ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with Initial Central Nervous System (CNS) Involvement: Could Next-Generation ALK Inhibitors Replace Brain Radiotherapy for the Prevention of Further CNS Relapse? Pediatric Reports, 15(2), 333-340. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15020029





