- Case Report
Critical Intestinal Perforations in Pediatric Immunocompromised Patients: A Case-Based Review
- William Hunt Stafford,
- Jennifer McArthur and
- Saad Ghafoor
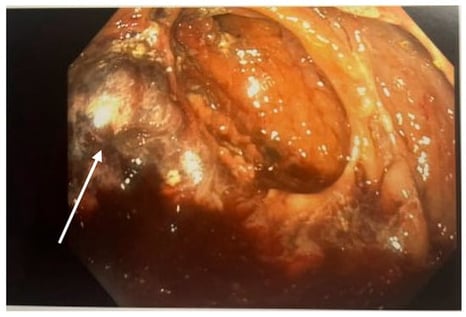
As survival rates for children with cancer and immune disorders have improved, clinical focus has shifted toward managing serious treatment-related complications. Intestinal perforation remains life-threatening and is typically diagnosed by signs of peritonitis and inflammation. This report presents three high-risk pediatric patients who developed severe intestinal perforation without the usual clinical symptoms. Each patient was receiving high-dose corticosteroids and/or targeted biologic immunomodulators (ruxolitinib, anakinra, tocilizumab, eculizumab). Classic indicators such as fever, leukocytosis, hemodynamic instability, and abdominal pain were absent, despite surgical findings of fecal contamination and bowel necrosis. All three patients survived to hospital discharge. These cases demonstrate that potent immunomodulatory therapies can mask the physiological response to perforation. Relying solely on traditional clinical signs may delay diagnosis. In this population, subtle findings such as persistent gastrointestinal bleeding, feeding intolerance, or minor imaging abnormalities should prompt consideration of perforation. Early imaging and multidisciplinary review are essential for timely intervention and improved outcomes.
14 February 2026