Metagenomic Insights into the Impact of Nutrition on Human Gut Microbiota and Associated Disease Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
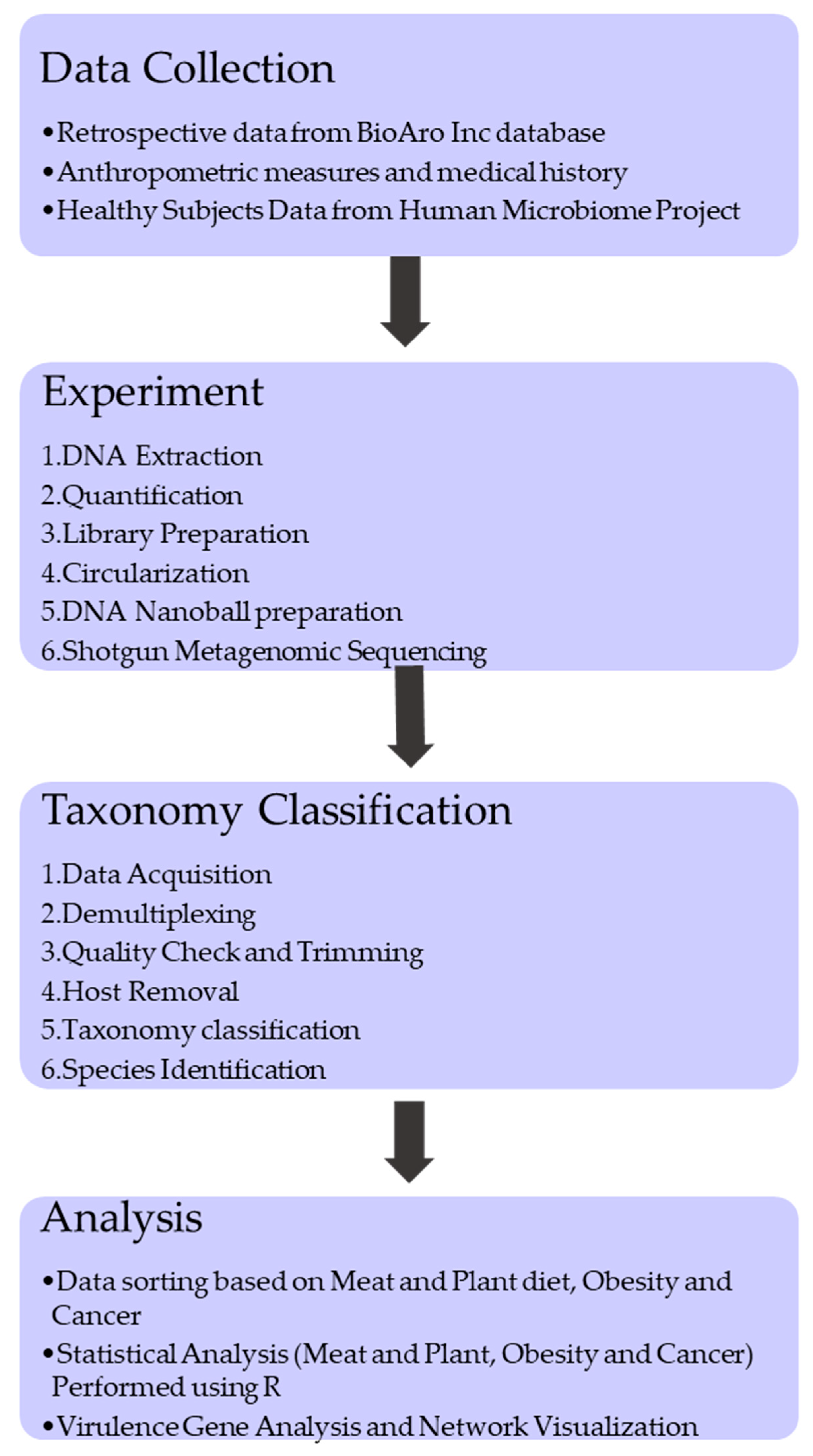
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Library Construction and Sequencing
2.3. Taxonomy Classification
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Virulence Gene Analysis
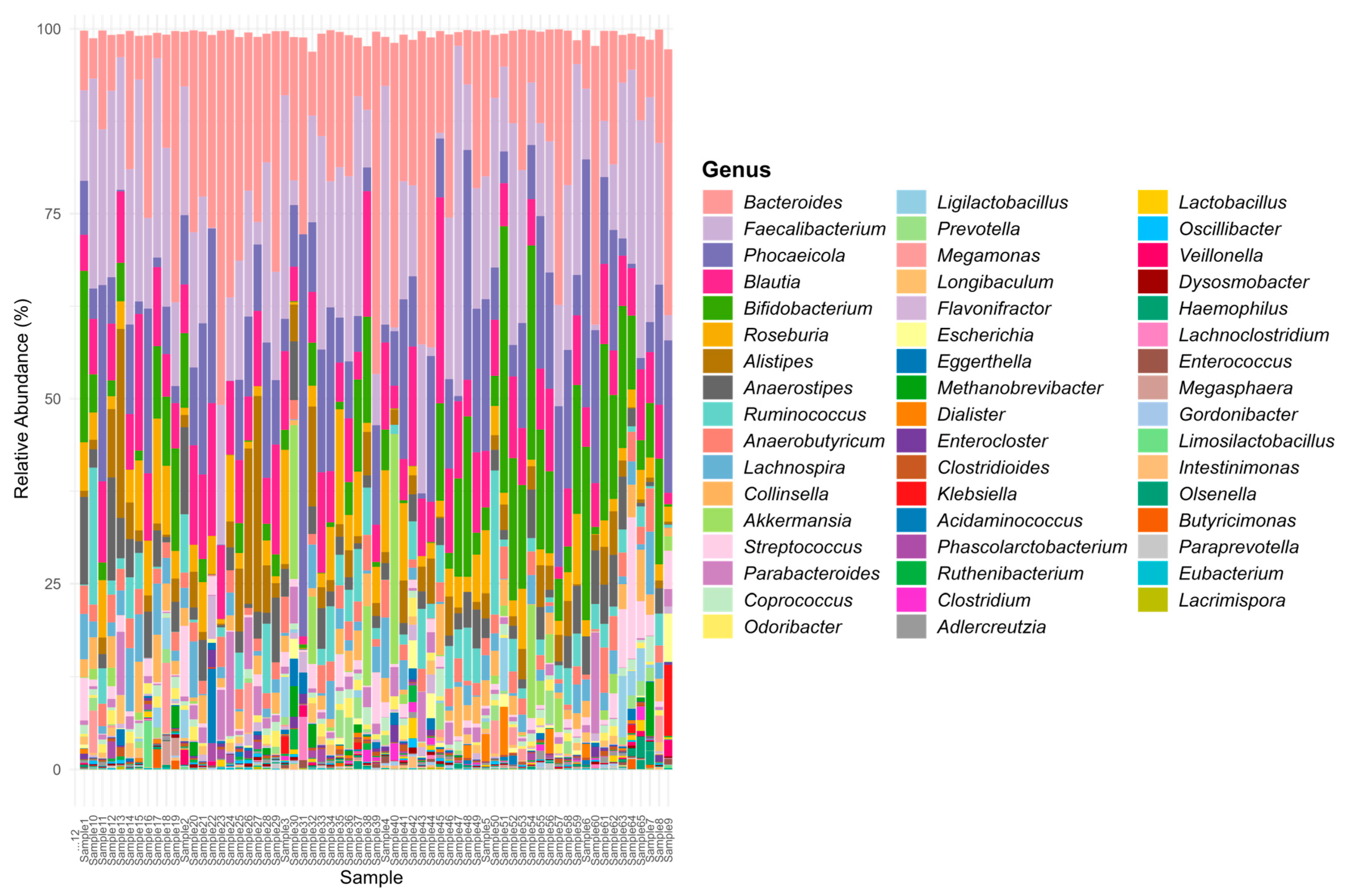
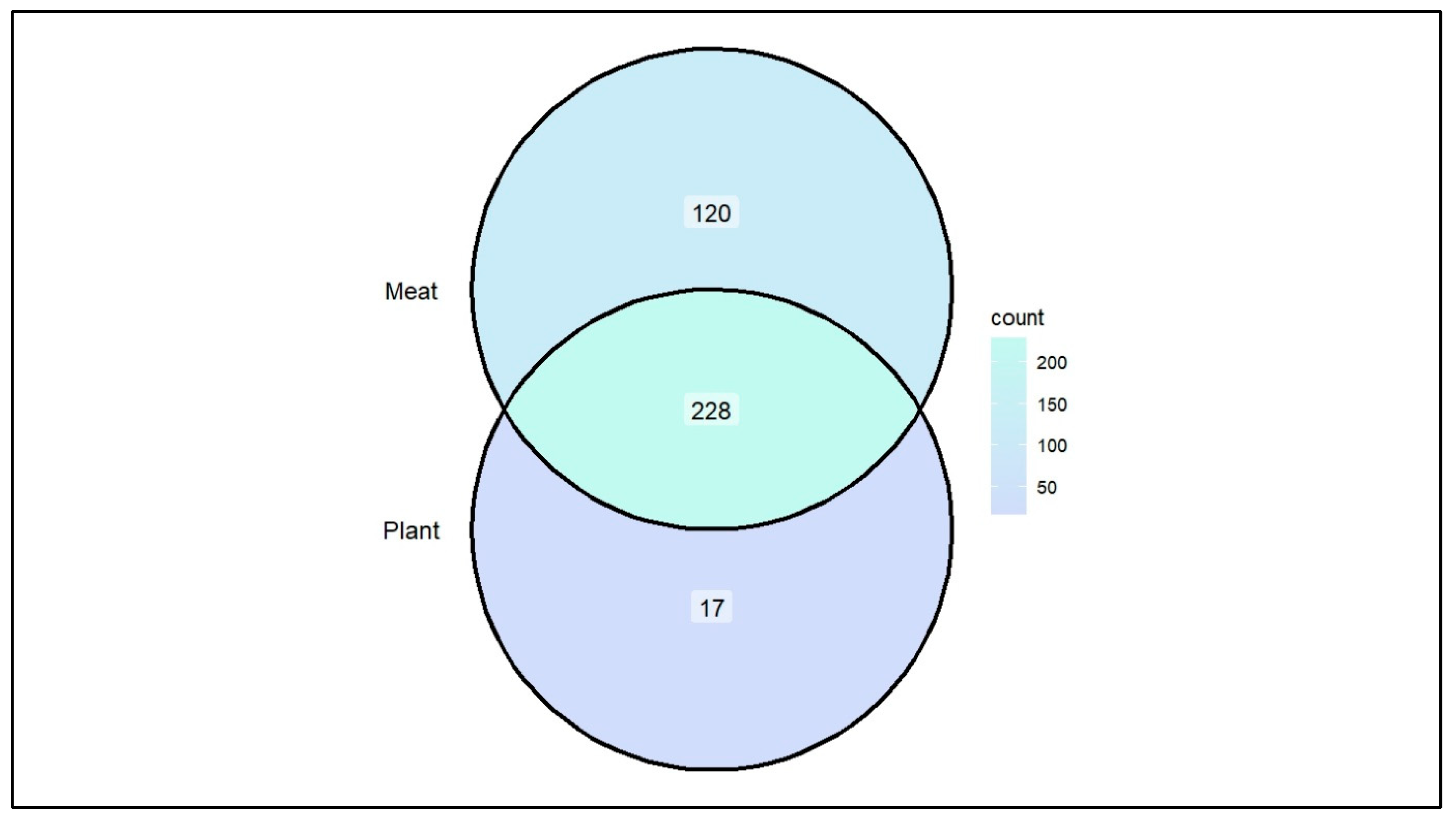
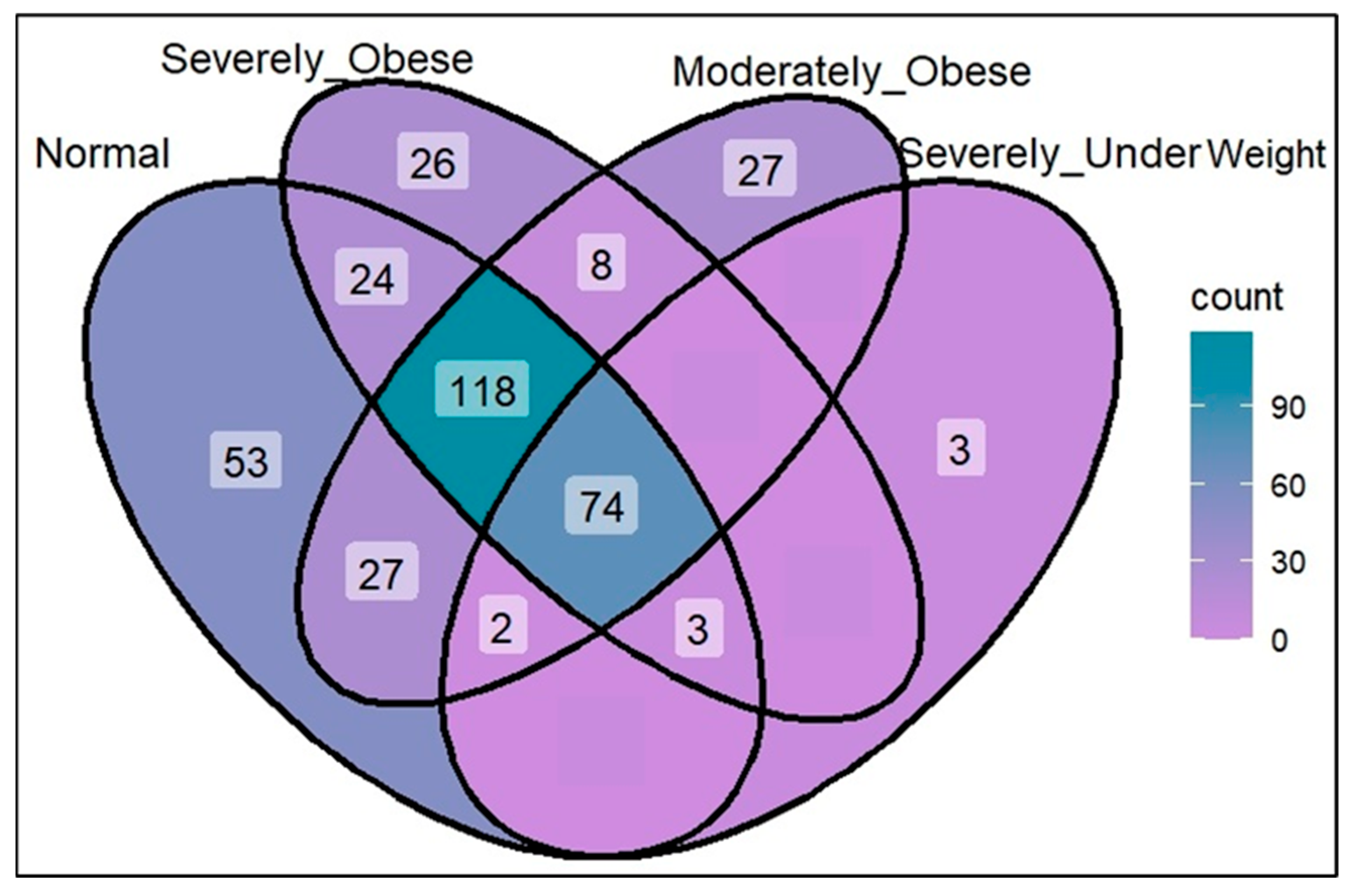
3. Results and Discussions
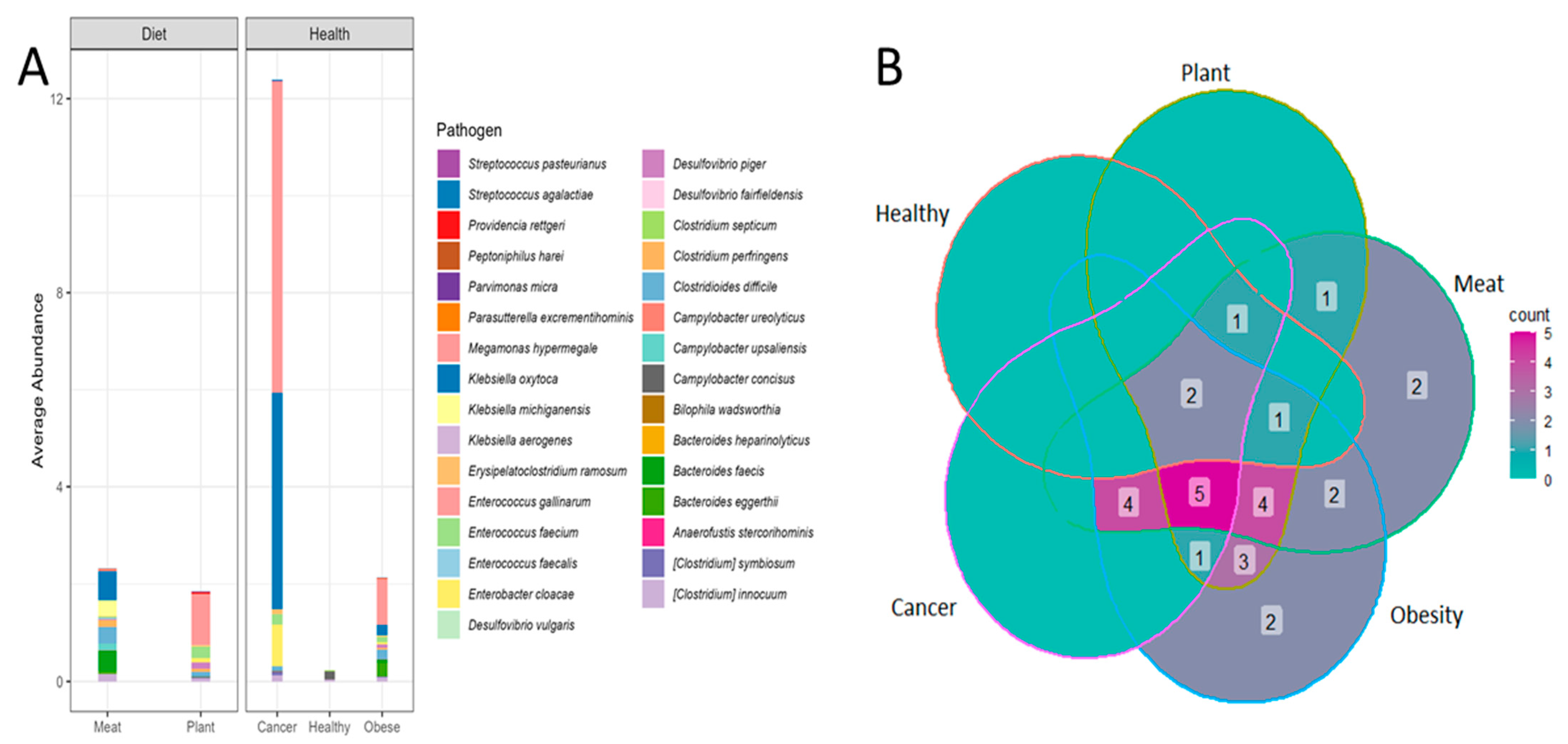
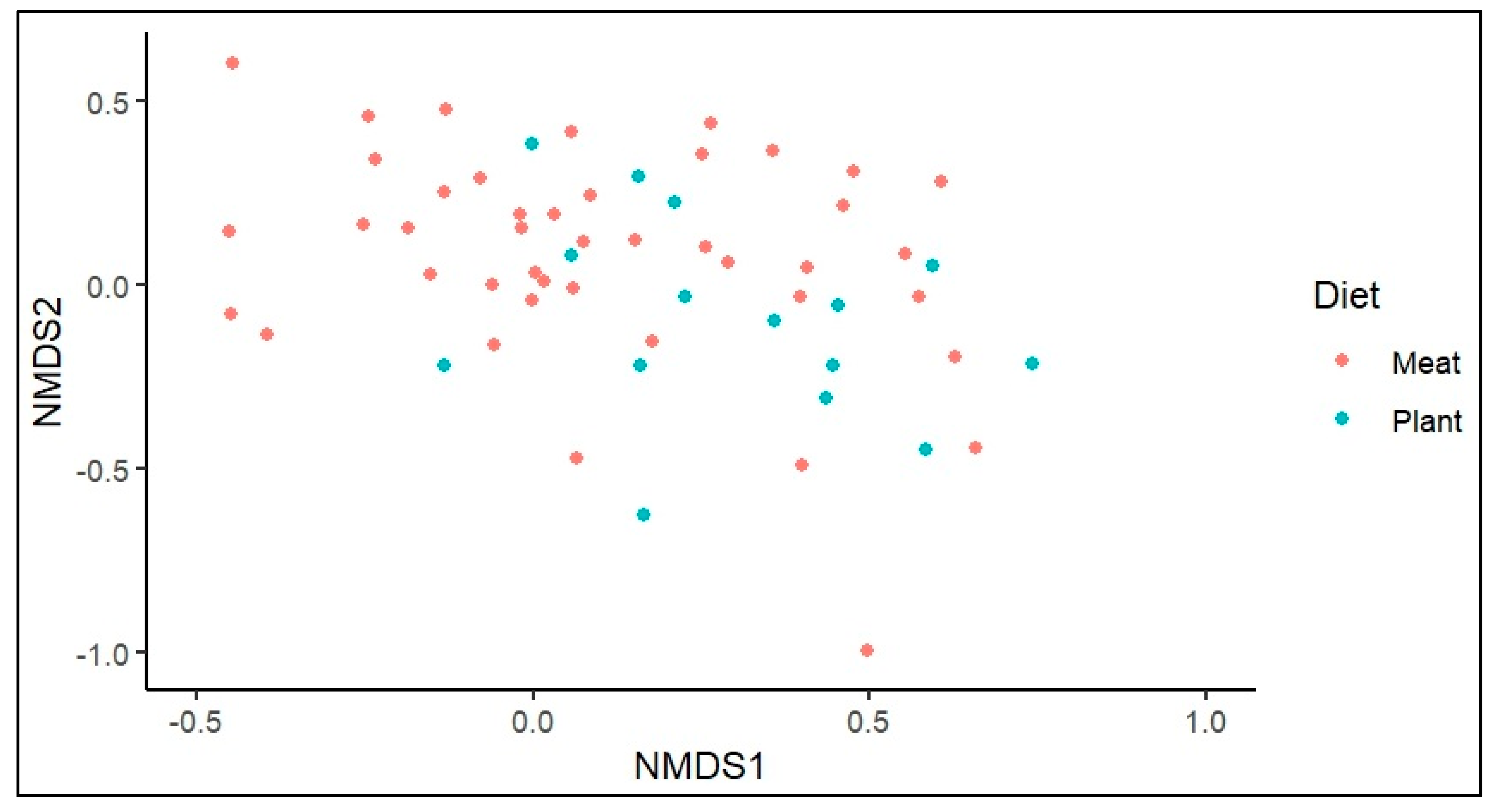
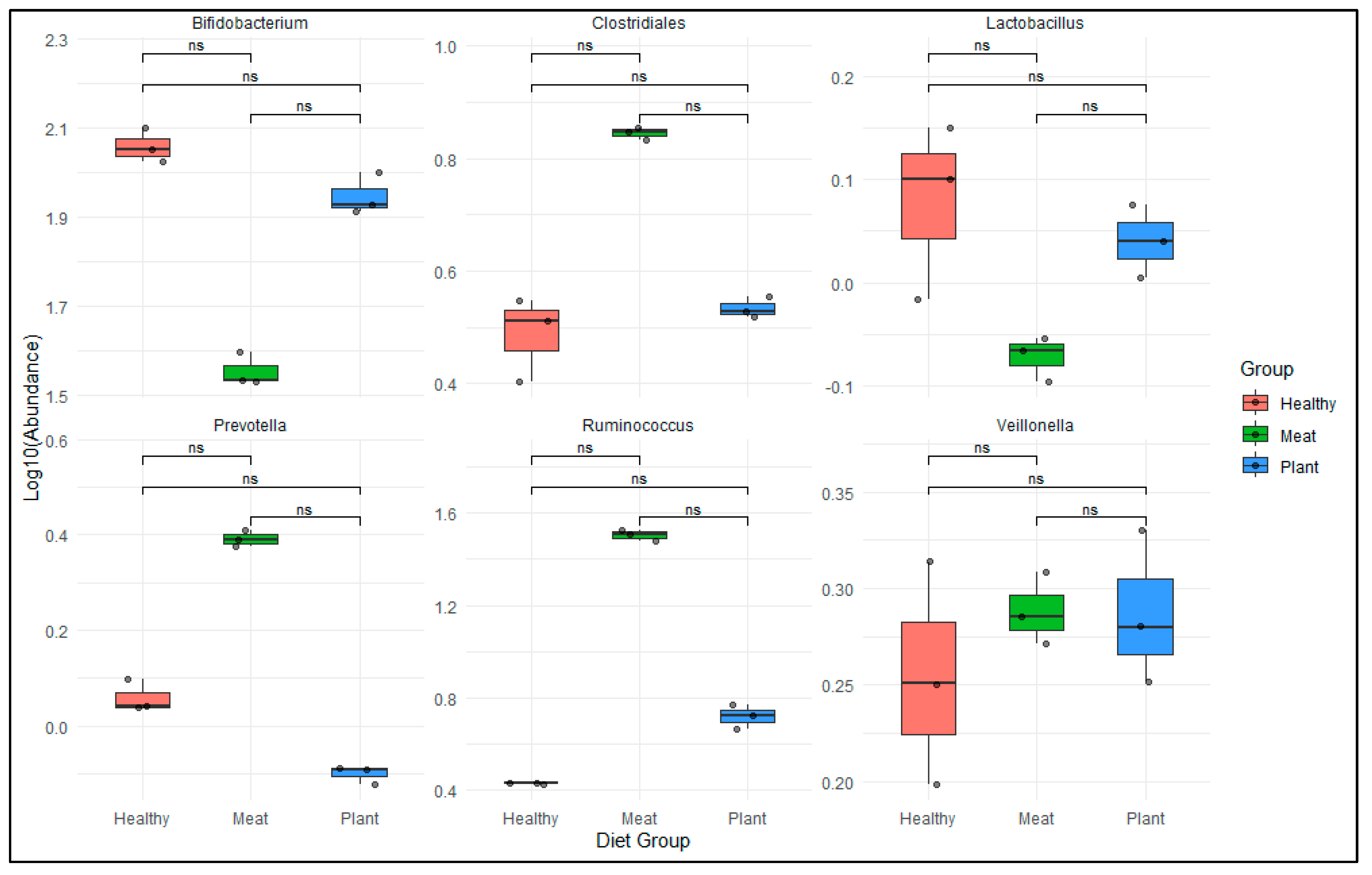
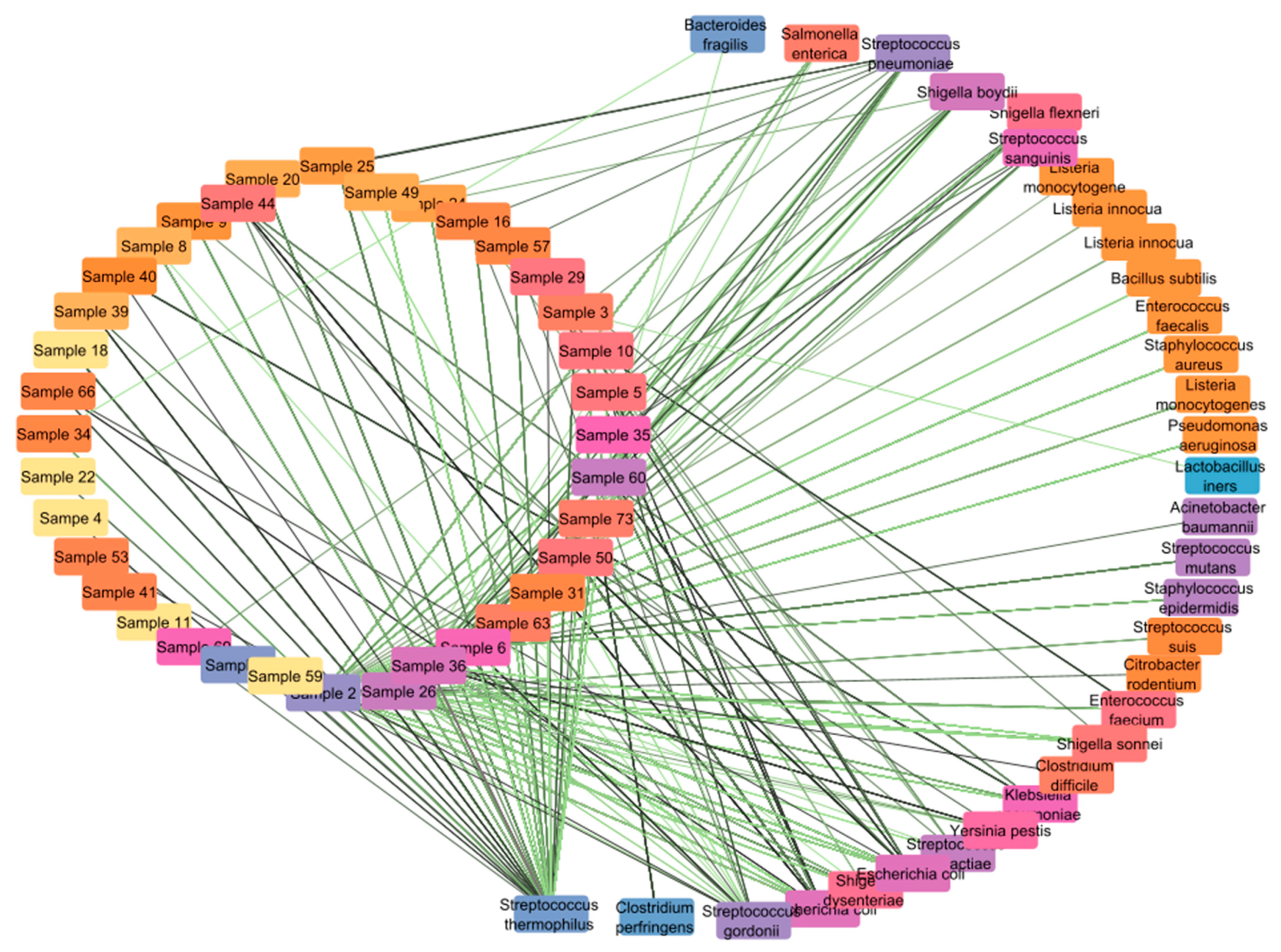
3.1. Opportunistic Pathogen Species and Disease Risk
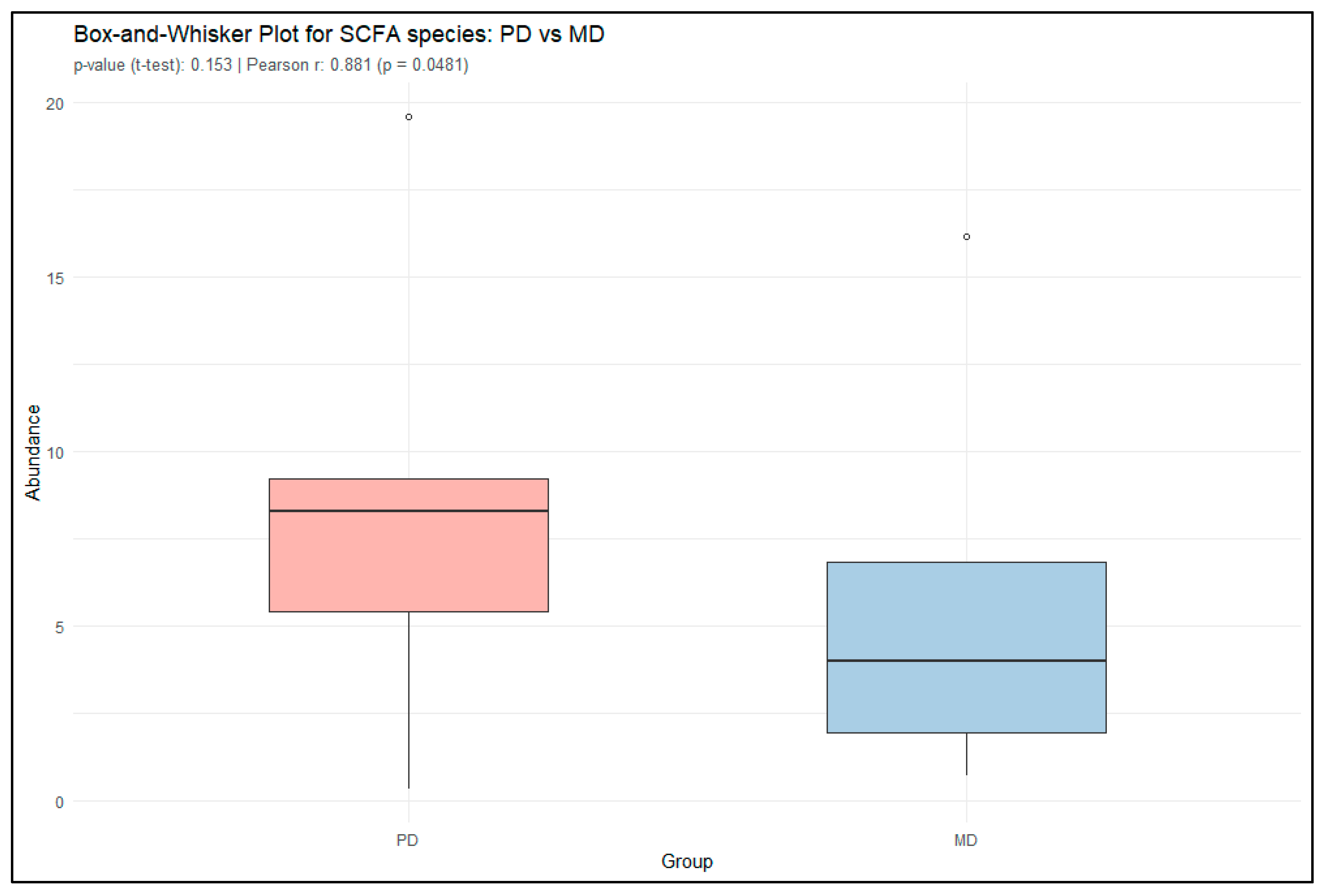
3.2. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production
3.3. Virulence Genes Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Knight, R.; Vrbanac, A.; Taylor, B.C.; Aksenov, A.; Callewaert, C.; Debelius, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Kosciolek, T.; McCall, L.I.; McDonald, D.; et al. Best practices for analysing microbiomes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheflin, A.M.; Melby, C.L.; Carbonero, F.; Weir, T.L. Linking Dietary Patterns with Gut Microbial Composition and Function. Gut Microbes 2016, 8, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adithya, K.K.; Rajeev, R.; Selvin, J.; Seghal Kiran, G. Dietary Influence on the Dynamics of the Human Gut Microbiome: Prospective Implications in Interventional Therapies. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 717–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Useros, N.; Nova, E.; González-Zancada, N.; Díaz, L.E.; Gómez-Martínez, S.; Marcos, A. Microbiota and Lifestyle: A Special Focus on Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Tohumcu, E.; Raoul, P.; Fiorani, M.; Cintoni, M.; Mele, M.C.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ianiro, G. The Role of Diet in Shaping Human Gut Microbiota. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 62–63, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet Rapidly and Reproducibly Alters the Human Gut Microbiome. Nature 2013, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Bäckhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-Induced Obesity Is Linked to Marked but Reversible Alterations in the Mouse Distal Gut Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noce, A.; Marrone, G.; Di Daniele, F.; Ottaviani, E.; Wilson Jones, G.; Bernini, R.; Romani, A.; Rovella, V. Impact of Gut Microbiota Composition on Onset and Progression of Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Balakrishnan, B.; Belobrajdic, D.; Feng, Q.-J.; Zhang, W. Role of Dietary Nutrients in the Modulation of Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, J.; Mayer, D.E.; Chen, S.; Mayer, E.A. Role of Diet and Its Effects on the Gut Microbiome in the Pathophysiology of Mental Disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, O.; Dai, C.L.; Kornilov, S.A.; Smith, B.; Price, N.D.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T. Health and Disease Markers Correlate with Gut Microbiome Composition across Thousands of People. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, S.J.D.; Li, J.V.; Lahti, L.; Ou, J.; Carbonero, F.; Mohammed, K.; Posma, J.M.; Kinross, J.; Wahl, E.; Ruder, E.; et al. Fat, Fibre and Cancer Risk in African Americans and Rural Africans. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Chang, H.-W.; Yan, D.; Lee, K.M.; Ucmak, D.; Wong, K.; Abrouk, M.; Farahnik, B.; Nakamura, M.; Zhu, T.H.; et al. Influence of Diet on the Gut Microbiome and Implications for Human Health. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. Influence of Foods and Nutrition on the Gut Microbiome and Implications for Intestinal Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Sonnenburg, E.D. Vulnerability of the Industrialized Microbiota. Science 2019, 366, eaaw9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Vannini, L.; Jeffery, I.B.; La Storia, A.; Laghi, L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Di Cagno, R.; Ferrocino, I.; Lazzi, C.; et al. High-Level Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet Beneficially Impacts the Gut Microbiota and Associated Metabolome. Gut 2015, 65, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Zhu, J.; Sun, C.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Ning, K.; He, L.; Zhao, X.-M.; Chen, W.-H. GMrepo V2: A Curated Human Gut Microbiome Database with Special Focus on Disease Markers and Cross-Dataset Comparison. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D777–D784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Shah, Y.A.; Hussain, M.; Rabail, R.; Socol, C.T.; Hassoun, A.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Rusu, A.V.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota in Health and Disease: Unveiling the Relationship. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 999001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, T.; Ng, S.C. The Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis and Therapeutics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, U.; Ranganathan, N. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics: Gut and Beyond. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.F.; Casarotti, S.N.; de Oliveira, G.L.V.; Penna, A.L.B. The Impact of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on the Biochemical, Clinical, and Immunological Markers, as Well as on the Gut Microbiota of Obese Hosts. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 61, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, J.P.; Cotter, P.D.; Endo, A.; Han, N.S.; Kort, R.; Liu, S.Q.; Bielke, L.R.; Kim, Y.S.; Patel, A.R.; Bintarti, A.F.; et al. Fermented foods in a global age: East meets West. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 184–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, J.D.; Ludlow, A.T.; LaRanger, R.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Comparison of DNA Quantification Methods for next Generation Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanaban, A.; Inche, A.; Gassmann, M.; Salowsky, R. High-Throughput DNA Sample QC Using the Agilent 2200 Tapestation System. J. Biomol. Tech. 2013, 24, S41. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. S1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quince, C.; Walker, A.W.; Simpson, J.T.; Loman, N.J.; Segata, N. Shotgun metagenomics, from sampling to analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved Metagenomic Analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Fan, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S.; Jia, S.; Lv, N.; Yuan, T.; Pan, Y.; Xue, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. An expanded database and analytical toolkit for identifying bacterial virulence factors and their associations with chronic diseases. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jia, H.; Cai, X.; Zhong, H.; Feng, Q.; Sunagawa, S.; Arumugam, M.; Kultima, J.R.; Prifti, E.; Nielsen, T.; et al. An integrated catalog of reference genes in the human gut microbiome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzosa, E.A.; McIver, L.J.; Rahnavard, G.; Thompson, L.R.; Schirmer, M.; Weingart, G.; Lipson, K.S.; Knight, R.; Caporaso, J.G.; Segata, N.; et al. Species-level functional profiling of metagenomes and metatranscriptomes. Nat. Methods 2015, 15, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crost, E.H.; Coletto, E.; Bell, A.; Juge, N. Ruminococcus Gnavus: Friend or Foe for Human Health. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuqwider, J.N.; Mauriello, G.; Altamimi, M. Akkermansia Muciniphila, a New Generation of Beneficial Microbiota in Modulating Obesity: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia Muciniphila in Overweight and Obese Human Volunteers: A Proof-of-Concept Exploratory Study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, E.; Corr, S.C. Lactobacillus Spp. For Gastrointestinal Health: Current and Future Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 840245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanifi, G.R.; Kafil, H.S.; Khosroshahi, H.T.; Shapouri, R.; Asgharzadeh, M. Bifidobacteriaceae Family Diversity in Gut Microbiota of Patients with Renal Failure. Arch. Razi. Inst. 2021, 76, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, O.; Lahti, L.; Kokkola, A.; Karla, T.; Tikkanen, M.; Ehsan, H.; Carpelan-Holmström, M.; Koskensalo, S.; Böhling, T.; Rautelin, H.; et al. Stool Microbiota Composition Differs in Patients with Stomach, Colon, and Rectal Neoplasms. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2950–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bistas, K.G.; Tabet, J.P. The Benefits of Prebiotics and Probiotics on Mental Health. Cureus 2023, 15, e43217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młynarska, E.; Gadzinowska, J.; Tokarek, J.; Forycka, J.; Szuman, A.; Franczyk, B.; Rysz, J. The Role of the Microbiome-Brain-Gut Axis in the Pathogenesis of Depressive Disorder. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Covián, D.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M.; De Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Salazar, N. Intestinal short chain fatty acids and their link with diet and human health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaar, E.P. The battle for iron between bacterial pathogens and their vertebrate hosts. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiles, T.J.; Mulvey, M.A. The RTX pore-forming toxin α-hemolysin of uropathogenic Escherichia coli: A potential therapeutic target. Microb. Pathog. 2013, 65, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Han, R.; Cao, Y.; Hua, W.; Zhao, L. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. ISME J. 2012, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balasundaram, P.; Dubli, K.; Chaudhari, R.; Vettrivelan, S.; Kaur, A.; Kapoor, R.; Singh, R.; Kapoor, A.; Borkar Tripathi, M. Metagenomic Insights into the Impact of Nutrition on Human Gut Microbiota and Associated Disease Risk. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16090197
Balasundaram P, Dubli K, Chaudhari R, Vettrivelan S, Kaur A, Kapoor R, Singh R, Kapoor A, Borkar Tripathi M. Metagenomic Insights into the Impact of Nutrition on Human Gut Microbiota and Associated Disease Risk. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(9):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16090197
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalasundaram, Preethi, Kirti Dubli, Rinku Chaudhari, Sarvesh Vettrivelan, Amrita Kaur, Raman Kapoor, Raja Singh, Anmol Kapoor, and Minal Borkar Tripathi. 2025. "Metagenomic Insights into the Impact of Nutrition on Human Gut Microbiota and Associated Disease Risk" Microbiology Research 16, no. 9: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16090197
APA StyleBalasundaram, P., Dubli, K., Chaudhari, R., Vettrivelan, S., Kaur, A., Kapoor, R., Singh, R., Kapoor, A., & Borkar Tripathi, M. (2025). Metagenomic Insights into the Impact of Nutrition on Human Gut Microbiota and Associated Disease Risk. Microbiology Research, 16(9), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16090197





