Pathogenic Intronic Splice-Affecting Variants in MYBPC3 in Three Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment and Genetic Testing
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Human K562 Cell Culture
2.4. In Vitro Splicing Minigene Assay
2.5. Reverse-Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
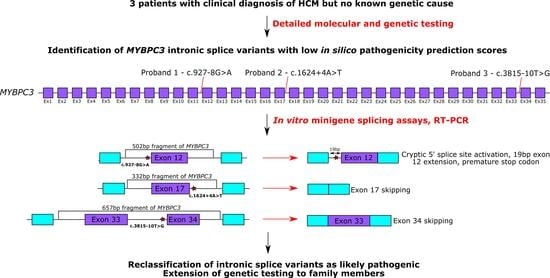
3. Results
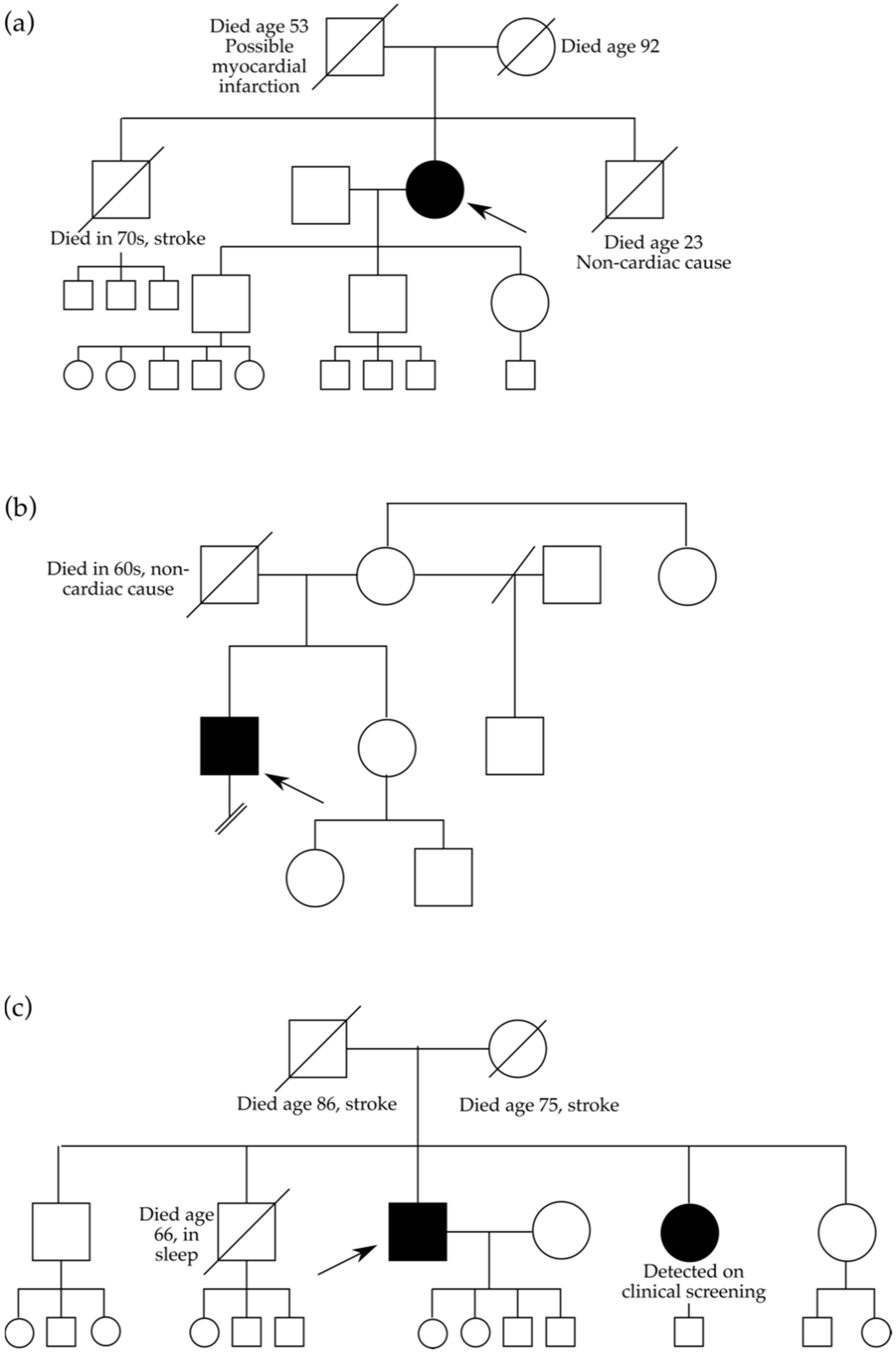
3.1. Clinical Characteristics Associated with Three Intronic MYBPC3 Variants
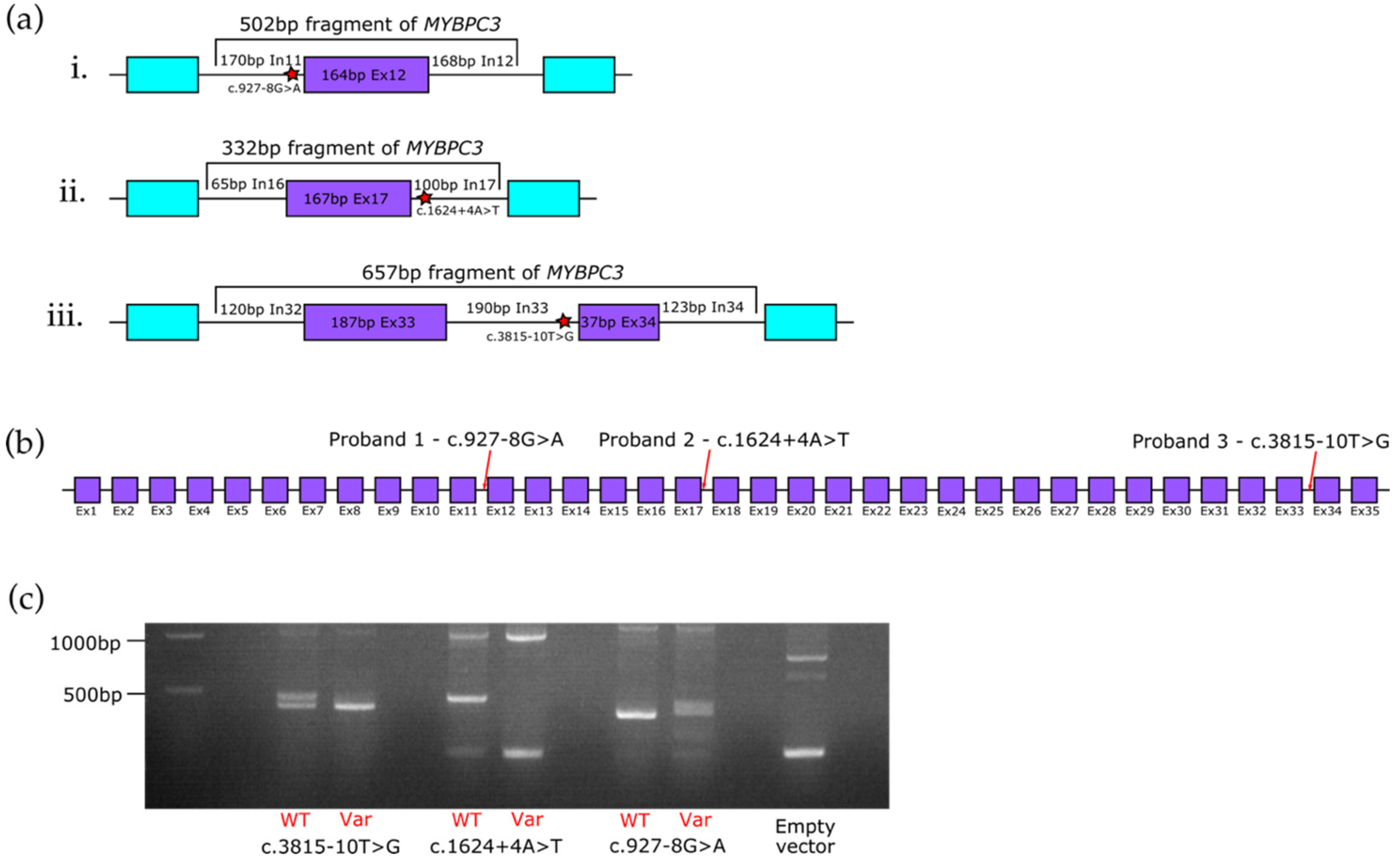
3.2. In Vitro Minigene Assays to Assess the Impact of Intronic MYBPC3 Splice-Affecting Variants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Towbin, J.A. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2009, 32, S23–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, N.; Dietrich, J.; Nyhan, D.; Mitter, N.; Yee, M.-S.; Brady, M. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Anesthesia Analg. 2015, 120, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, A.J.; Braunwald, E. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 749–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, P.M.; Poloniecki, J.; Dickie, S.; Sharma, S.; Monserrat, L.; Varnava, A.; Mahon, N.G.; McKenna, W.J. Sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Identification of high risk patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenneaux, M.P.; Counihan, P.J.; Caforio, A.L.; Chikamori, T.; McKenna, W.J. Abnormal blood pressure response during exercise in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation 1990, 82, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirito, P.; Bellone, P.; Harris, K.M.; Bernabò, P.; Bruzzi, P.; Maron, B.J. Magnitude of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Risk of Sudden Death in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, W.J.; Franklin, R.C.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.; Robinson, K.C.; Deanfield, J.E.; Dickie, S.; Krikler, S.J. Arrhythmia and prognosis in infants, children and adolescents with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1988, 11, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, S.C.; Roche, A.H.; Neutze, J.M.; Whitlock, R.M.; Veale, A.M. Inheritance of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A cross sectional and M mode echocardiographic study of 50 families. Heart 1987, 58, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branzi, A.; Romeo, G.; Specchia, S.; Lolli, C.; Binetti, G.; Devoto, M.; Bacchi, M.; Magnani, B. Genetic heterogeneity of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 1985, 7, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmannova, H.; Kubanek, M.; Sramko, M.; Piherova, L.; Noskova, L.; Hodanova, K.; Stranecky, V.; Pristoupilova, A.; Sovova, J.; Marek, T.; et al. Isolated X-Linked Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Caused by a Novel Mutation of the Four-and-a-Half LIM Domain 1 Gene. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marian, A.J. Modifier genes for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2002, 17, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, B. Next-generation sequencing identifies pathogenic and modifier mutations in a consanguineous Chinese family with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Medicine 2017, 96, e7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, F.; Munkhsaikhan, U.; Boyle, C.; Borcky, T.; Zhao, W.; Purevjav, E.; Towbin, J.A.; Liao, F.; Williams, R.W.; et al. Identifying modifier genes for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 144, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millat, G.; Bouvagnet, P.; Chevalier, P.; Dauphin, C.; Jouk, P.S.; Da Costa, A.; Prieur, F.; Bresson, J.-L.; Faivre, L.; Eicher, J.-C.; et al. Prevalence and spectrum of mutations in a cohort of 192 unrelated patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 53, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaski, J.P.; Syrris, P.; Esteban, M.T.T.; Jenkins, S.; Pantazis, A.; Deanfield, J.; McKenna, W.J.; Elliott, P.M. Prevalence of Sarcomere Protein Gene Mutations in Preadolescent Children with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, J.; Daehmlow, S.; Wischke, S.; Senyuva, M.; Werner, U.; Raible, J.; Tanis, N.; Dyachenko, S.; Hummel, M.; Hetzer, R.; et al. Mutation spectrum in a large cohort of unrelated consecutive patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Clin. Genet. 2003, 64, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, P.; Charron, P.; Carrier, L.; Ledeuil, C.; Cheav, T.; Pichereau, C.; Benaiche, A.; Isnard, R.; Dubourg, O.; Burban, M.; et al. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2003, 107, 2227–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigle, E.D.; Rakowski, H.; Kimball, B.P.; Williams, W.G. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 1995, 92, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, B.J.; Maron, M.S. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Lancet 2013, 381, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colegrave, M.; Peckham, M. Structural Implications of β-Cardiac Myosin Heavy Chain Mutations in Human Disease. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2014, 297, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Previs, M.J.; Previs, S.B.; Gulick, J.; Robbins, J.; Warshaw, D.M. Molecular Mechanics of Cardiac Myosin-Binding Protein C in Native Thick Filaments. Science 2012, 337, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previs, M.J.; Prosser, B.L.; Mun, J.Y.; Previs, S.B.; Gulick, J.; Lee, K.; Robbins, J.; Craig, R.; Lederer, W.J.; Warshaw, D.M. Myosin-binding protein C corrects an intrinsic inhomogeneity in cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, A.S.; Thompson, A.D.; Glazier, A.A.; Hafeez, N.; Kabani, S.; Rodriguez, J.; Yob, J.M.; Woolcock, H.; Mazzarotto, F.; Lakdawala, N.K.; et al. Spatial and Functional Distribution of MYBPC3 Pathogenic Variants and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2020, 13, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, S.; Copeland, O.; Jacques, A.; Livesey, K.; Tsang, V.; McKenna, W.J.; Jalilzadeh, S.; Carballo, S.; Redwood, C.; Watkins, H. Evidence from Human Myectomy Samples That MYBPC3 Mutations Cause Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Through Haploinsufficiency. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdmann, J.; Raible, J.; Maki-Abadi, J.; Hammann, J.; Wollnik, B.; Frantz, E.; Fleck, E.; Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Hummel, M.; Hetzer, R. Spectrum of clinical phenotypes and gene variants in cardiac myosin-binding protein C mutation carriers with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 38, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.P.; Kounas, S.; Syrris, P.; Christiansen, M.; Frank-Hansen, R.; Andersen, P.S.; Elliott, P.M.; McKenna, W.J. Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein-C Mutations in Families with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2012, 5, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.R.; Barbosa, P.; Torrado, M.; Quinn, E.; Merino, A.; Ochoa, J.P.; Jager, J.; Futema, M.; Carmo-Fonseca, M.; Monserrat, L.; et al. Cryptic Splice-Altering Variants in MYBPC3 Are a Prevalent Cause of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.; Arscott, P.; Concannon, M.; Saberi, S.; Day, S.M.; Yashar, B.M.; Helms, A.S. Genetic testing impacts the utility of prospective familial screening in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy through identification of a nonfamilial subgroup. Genet. Med. 2017, 20, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, A.J. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Anderson-Fabry Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelb, B.D.; Roberts, A.E.; Tartaglia, M. Cardiomyopathies in Noonan syndrome and the other RASopathies. Prog. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2015, 39, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, P.; Baker, R.; Pasquale, F.; Quarta, G.; Ebrahim, H.; Mehta, A.B.; Hughes, D.; on Behalf of the ACES Study Group. Prevalence of Anderson-Fabry disease in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: The European Anderson-Fabry Disease Survey. Heart 2011, 97, 1957–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Fleming, E.J.; Garratt, C.J. Mimics of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy—Diagnostic Clues to Aid Early Identification of Phenocopies. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. Rev. 2013, 2, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Patel, P.N.; Gorham, J.M.; McDonough, B.; DePalma, S.R.; Adler, E.E.; Lam, L.; MacRae, C.A.; Mohiuddin, S.M.; Fatkin, D.; et al. Identification of pathogenic gene mutations in LMNA and MYBPC3 that alter RNA splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7689–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnall, R.D.; Ingles, J.; Dinger, M.E.; Cowley, M.J.; Ross, S.B.; Minoche, A.E.; Lal, S.; Turner, C.; Colley, A.; Rajagopalan, S.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Improves Outcomes of Genetic Testing in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janin, A.; Chanavat, V.; Rollat-Farnier, P.; Bardel, C.; Nguyen, K.; Chevalier, P.; Eicher, J.; Faivre, L.; Piard, J.; Albert, E.; et al. Whole MYBPC3 NGS sequencing as a molecular strategy to improve the efficiency of molecular diagnosis of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 41, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank-Hansen, R.; Page, S.P.; Syrris, P.; McKenna, W.J.; Christiansen, M.; Andersen, P.S. Micro-exons of the cardiac myosin binding protein C gene: Flanking introns contain a disproportionately large number of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 16, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, E.S.; Ingles, J.; Semsarian, C.; Bagnall, R.D. Key Value of RNA Analysis of MYBPC3 Splice-Site Variants in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2019, 12, e002368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Orsborne, C.; Eden, J.; Wallace, A.; Church, H.J.; Tylee, K.; Deepak, S.; Cassidy, C.; Woolfson, P.; Miller, C.; et al. Mosaic Fabry Disease in a Male Presenting as Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiogenetics 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, K.; Panagiotopoulou, S.K.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, F.O.; Hamroun, D.; Lalande, M.; Collod-Béroud, G.; Claustres, M.; Béroud, C. Human splicing finder: An online bioinformatics tool to predict splicing signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, L. Exploring human genomic diversity with gnomAD. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, S.; Khanna, A.; Stamm, S. Rapid generation of splicing reporters with pSpliceExpress. Gene 2008, 427, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.B.; Wood, K.A.; Buczek, W.A.; Gordon, C.T.; Pingault, V.; Attié-Bitach, T.; Hentges, K.E.; Varghese, V.C.; Amiel, J.; Newman, W.G.; et al. EFTUD2 missense variants disrupt protein function and splicing in mandibulofacial dysostosis Guion-Almeida type. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, M.I.; Monserrat, L.; Ortiz, M.; Fernández, X.; Cazón, L.; Núñez, L.; Barriales-Villa, R.; Maneiro, E.; Veira, E.; Castro-Beiras, A.; et al. Screening mutations in myosin binding protein C3 gene in a cohort of patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. BMC Med. Genet. 2010, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingford, J.M.; Thomas, H.B.; Rowlands, C.; Arno, G.; Beaman, G.; Gomes-Silva, B.; Campbell, C.; Gossan, N.; Hardcastle, C.; Webb, K.; et al. Functional and in-silico interrogation of rare genomic variants impacting RNA splicing for the diagnosis of genomic disorders. bioRxiv 2019, 781088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingles, J.; Doolan, A.; Chiu, C.; Seidman, J.; Seidman, C.; Semsarian, C. Compound and double mutations in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Implications for genetic testing and counselling. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, A.S.; Davis, F.M.; Coleman, D.; Bartolone, S.; Glazier, A.A.; Pagani, F.; Yob, J.M.; Sadayappan, S.; Pedersen, E.; Lyons, R.; et al. Sarcomere Mutation-Specific Expression Patterns in Human Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, L.; Bonne, G.; Bahrend, E.; Yu, B.; Richard, P.; Niel, F.; Hainque, B.; Cruaud, C.; Gary, F.; Labeit, S.; et al. Organization and Sequence of Human Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein C Gene (MYBPC3) and Identification of Mutations Predicted to Produce Truncated Proteins in Familial Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 1997, 80, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavigny, J.; Souchet, M.; Sébillon, P.; Berrebi-Bertrand, I.; Hainque, B.; Mallet, A.; Bril, A.; Schwartz, K.; Carrier, L. COOH-terminal truncated cardiac myosin-binding protein C mutants resulting from familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations exhibit altered expression and/or incorporation in fetal rat cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 294, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanavy, D.M.; McNulty, S.M.; Jairath, M.K.; Brnich, S.E.; Bizon, C.; Powell, B.C.; Berg, J.S. Comparative analysis of functional assay evidence use by ClinGen Variant Curation Expert Panels. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.L.; Fu, X.-D.; Gribskov, M. Characteristics and regulatory elements defining constitutive splicing and different modes of alternative splicing in human and mouse. RNA 2005, 11, 1777–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, B.O.; Xu, Y.-M.; Huang, L.-F.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J.; Min, Q.-H.; Yang, W.-M.; Wang, X.-Z. Mechanism of alternative splicing and its regulation. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.; Thomson, K.L.; Ware, J.S.; Funke, B.H.; Woodley, J.; McGuire, K.J.; Mazzarotto, F.; Blair, E.; Seller, A.; Exome Aggregation Consortium; et al. Reassessment of Mendelian gene pathogenicity using 7,855 cardiomyopathy cases and 60,706 reference samples. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poetter, K.; Jiang, H.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Master, S.R.; Chang, A.; Dalakas, M.C.; Rayment, I.; Sellers, J.R.; Fananapazir, L.; Epstein, N.D. Mutations in either the essential or regulatory light chains of myosin are associated with a rare myopathy in human heart and skeletal muscle. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesna, D.; Ghosh, D.; Li, Q.; Gomes, A.V.; Guzman, G.; Arana, C.; Zhi, G.; Stull, J.T.; Potter, J.D. Familial Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Mutations in the Regulatory Light Chains of Myosin Affect Their Structure, Ca2+ Binding, and Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7086–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaźmierczak, K.; Muthu, P.; Huang, W.; Jones, M.; Wang, Y.; Szczesna-Cordary, D. Myosin regulatory light chain mutation found in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients increases isometric force production in transgenic mice. Biochem. J. 2012, 442, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farman, G.P.; Muthu, P.; Kazmierczak, K.; Szczesna-Cordary, D.; Moore, J.R. Impact of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy-linked mutations in the NH2 terminus of the RLC on β-myosin cross-bridge mechanics. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 117, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wood, K.A.; Ellingford, J.M.; Eden, J.; Thomas, H.B.; O’Keefe, R.T.; Hopton, C.; Newman, W.G. Pathogenic Intronic Splice-Affecting Variants in MYBPC3 in Three Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiogenetics 2021, 11, 73-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11020009
Wood KA, Ellingford JM, Eden J, Thomas HB, O’Keefe RT, Hopton C, Newman WG. Pathogenic Intronic Splice-Affecting Variants in MYBPC3 in Three Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiogenetics. 2021; 11(2):73-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleWood, Katherine A., Jamie M. Ellingford, James Eden, Huw B. Thomas, Raymond T. O’Keefe, Claire Hopton, and William G. Newman. 2021. "Pathogenic Intronic Splice-Affecting Variants in MYBPC3 in Three Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy" Cardiogenetics 11, no. 2: 73-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11020009
APA StyleWood, K. A., Ellingford, J. M., Eden, J., Thomas, H. B., O’Keefe, R. T., Hopton, C., & Newman, W. G. (2021). Pathogenic Intronic Splice-Affecting Variants in MYBPC3 in Three Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiogenetics, 11(2), 73-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11020009