From Mechanochemically Driven Complexation and Multimodal Characterization to Stability and Toxicological Insight: A Study of Cinnarizine–β-Cyclodextrins Complexes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Cyclodextrin Complexes in the Solid-State
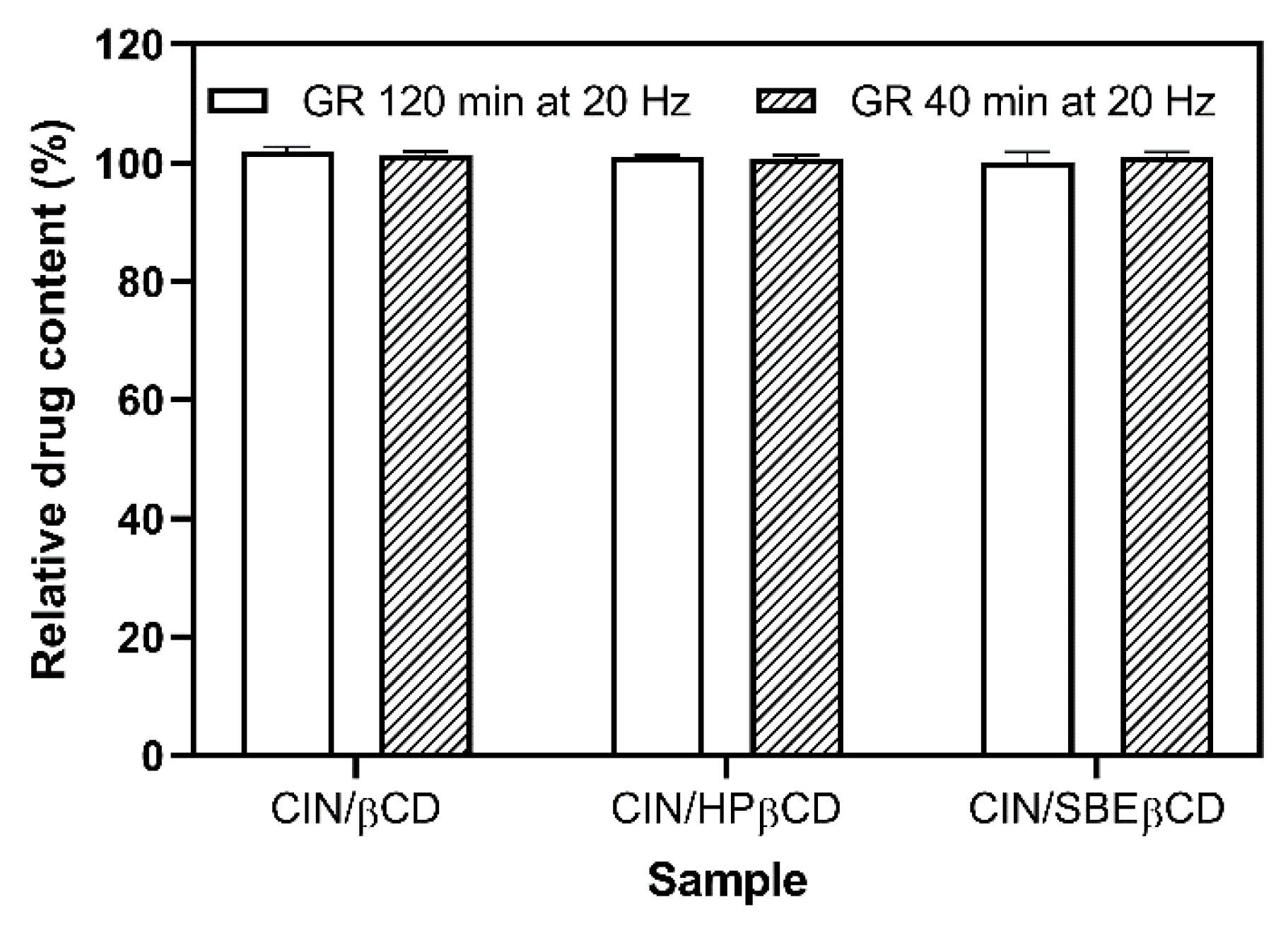
2.2. Stability of CIN During the Co-Grinding with CDs
2.3. In Vitro Dissolution Test
2.4. In Vitro Permeability Study
2.5. Stability Testing of Prepared CIN/CD Complexes
2.5.1. Forced Degradation Studies
2.5.2. Accelerated Stability Studies
2.6. UPLC-DAD and UPLC-HRMS(/MS) Measurements
2.7. Theoretical Toxicity Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
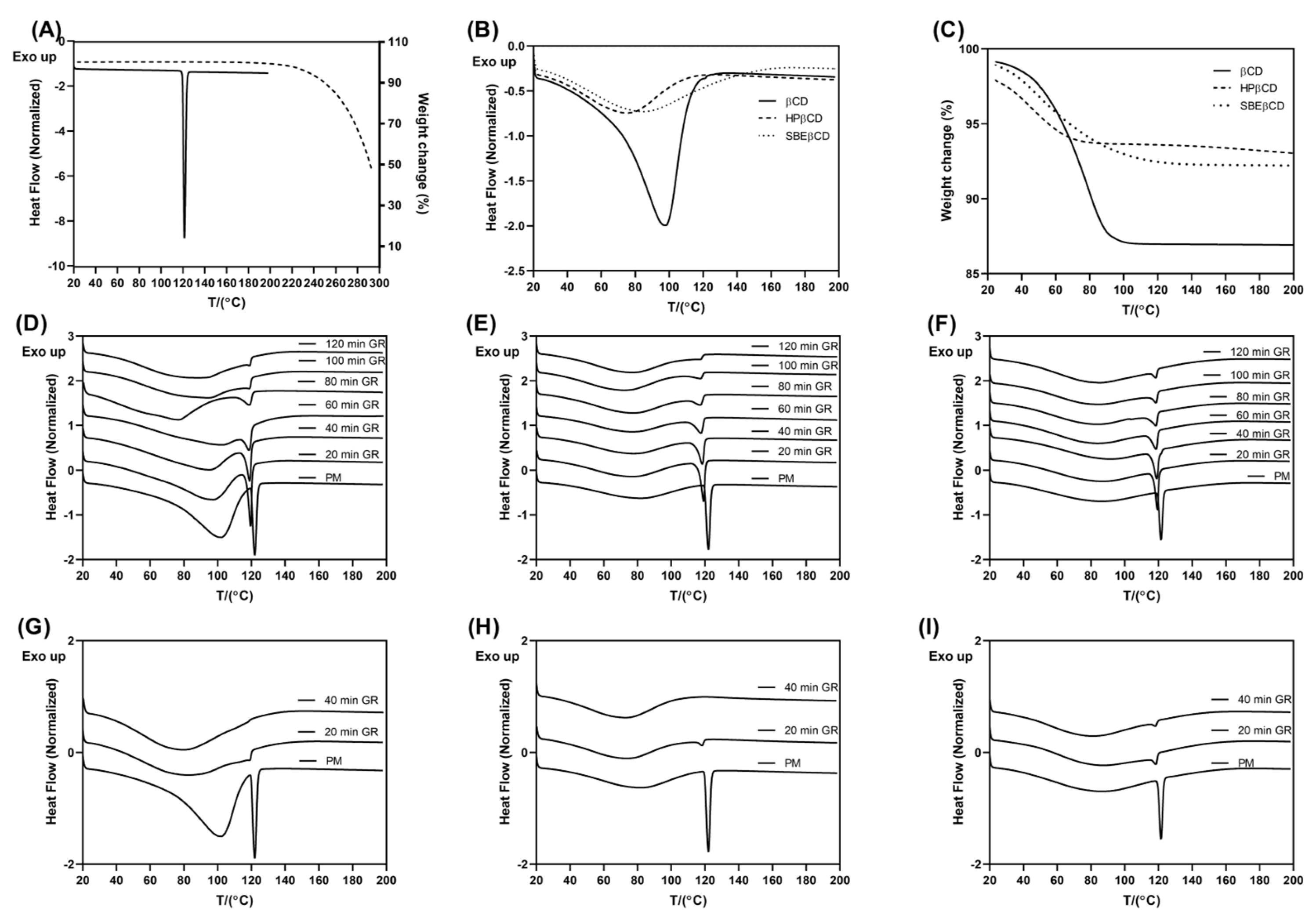
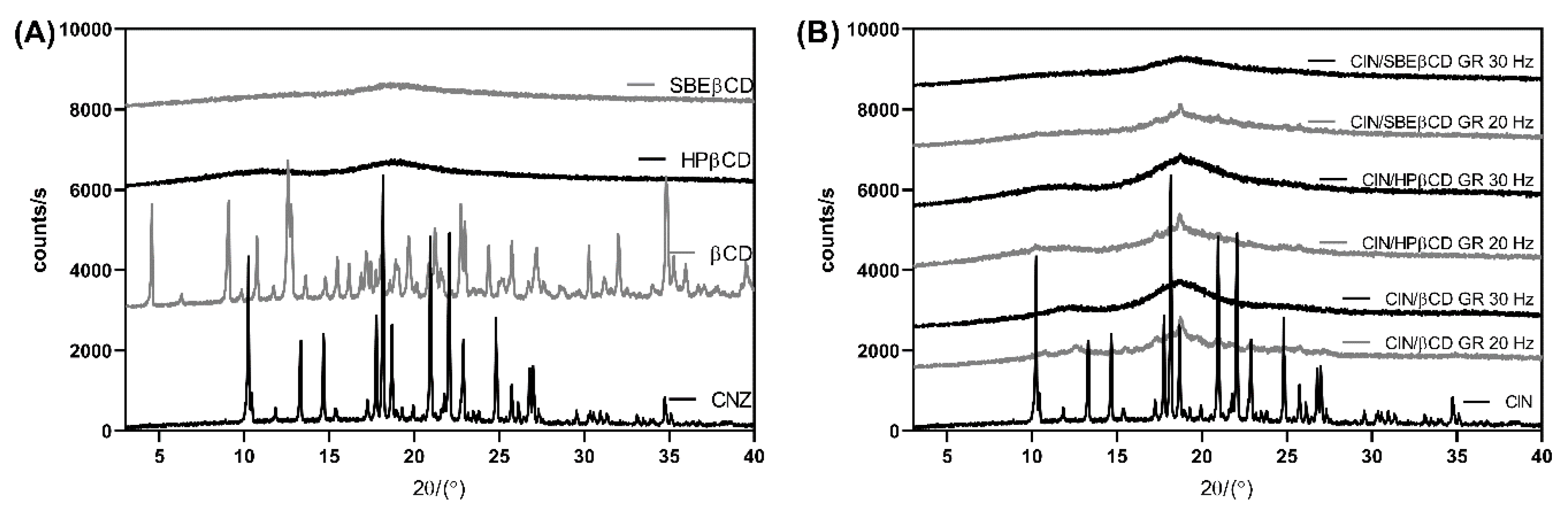
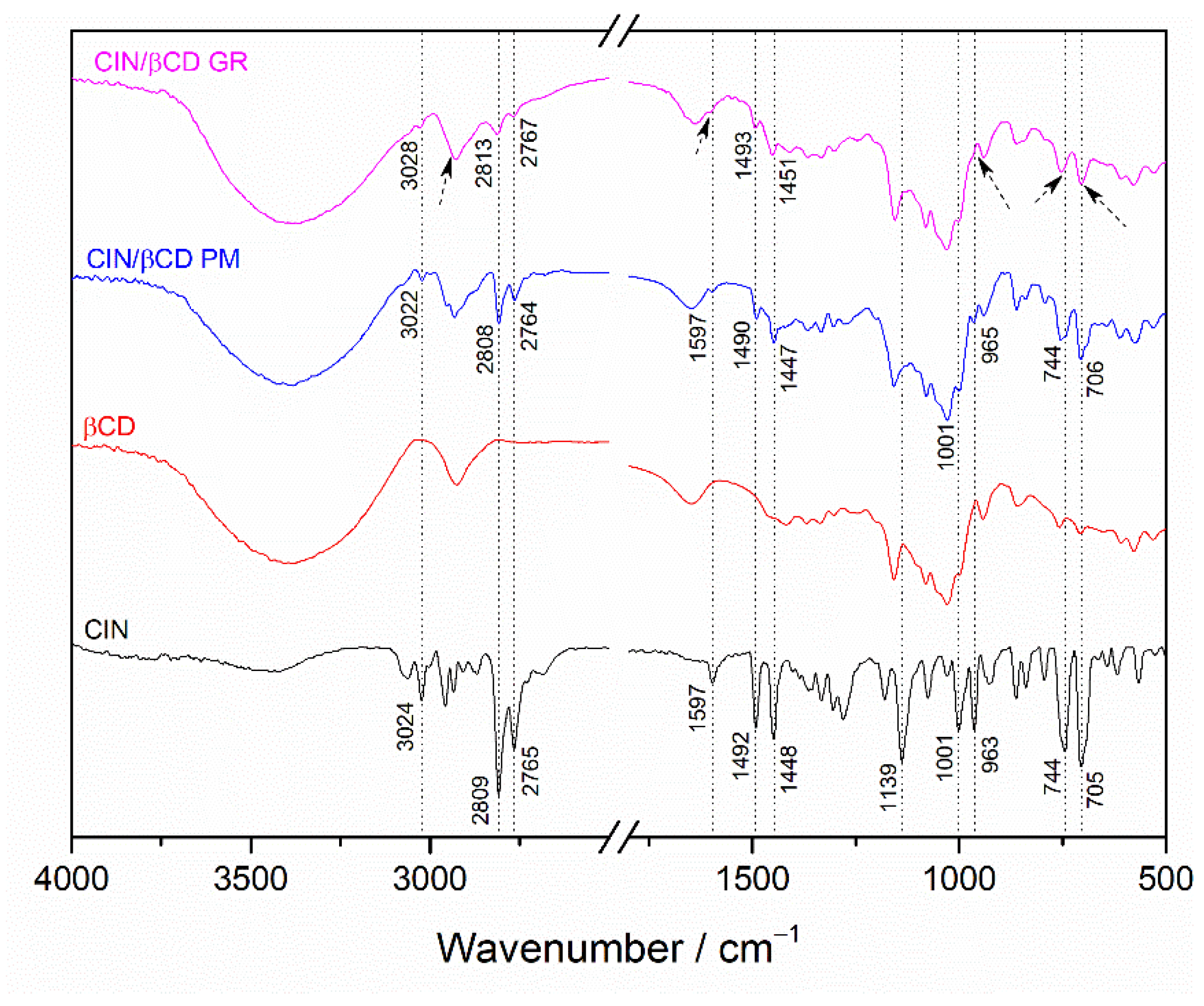
3.1. Preparation and Solid-State Characterization of Co-Ground CD Complexes
3.2. In Vitro Dissolution and In Vitro Permeability Properties of the Co-Ground Complexes
3.3. Effect of Cyclodextrins on CIN Stability
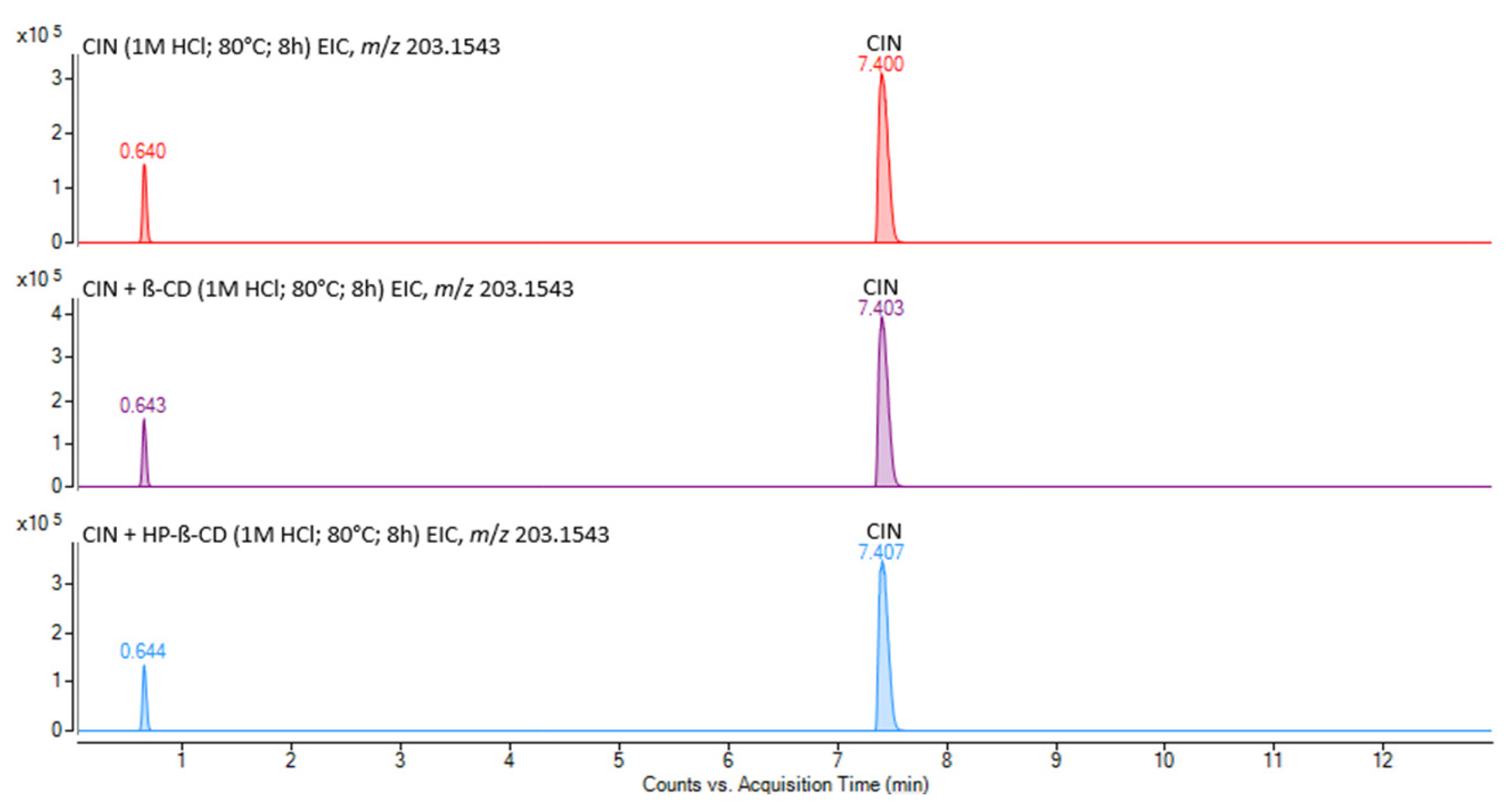
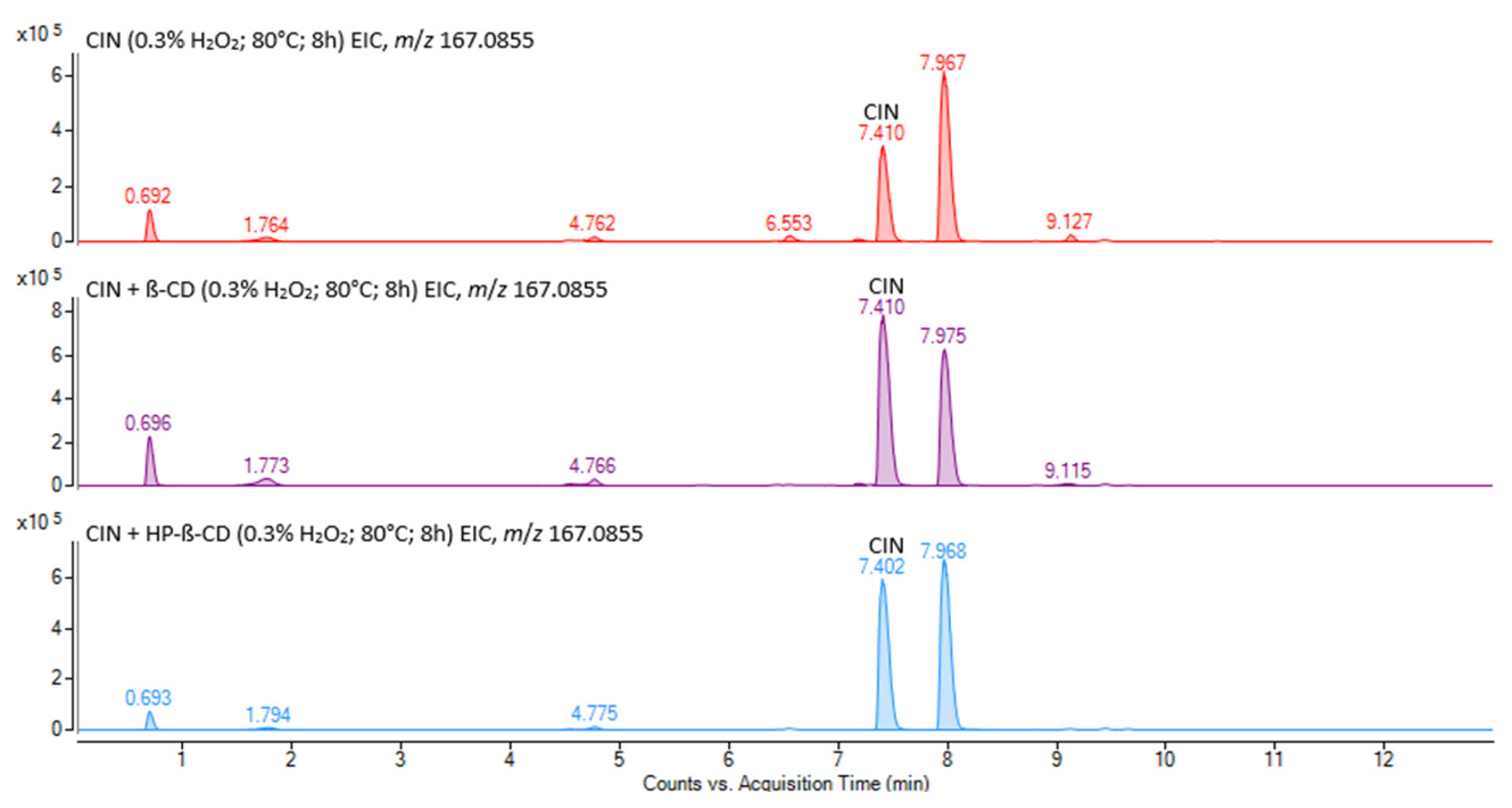
3.3.1. Forced Degradation Studies
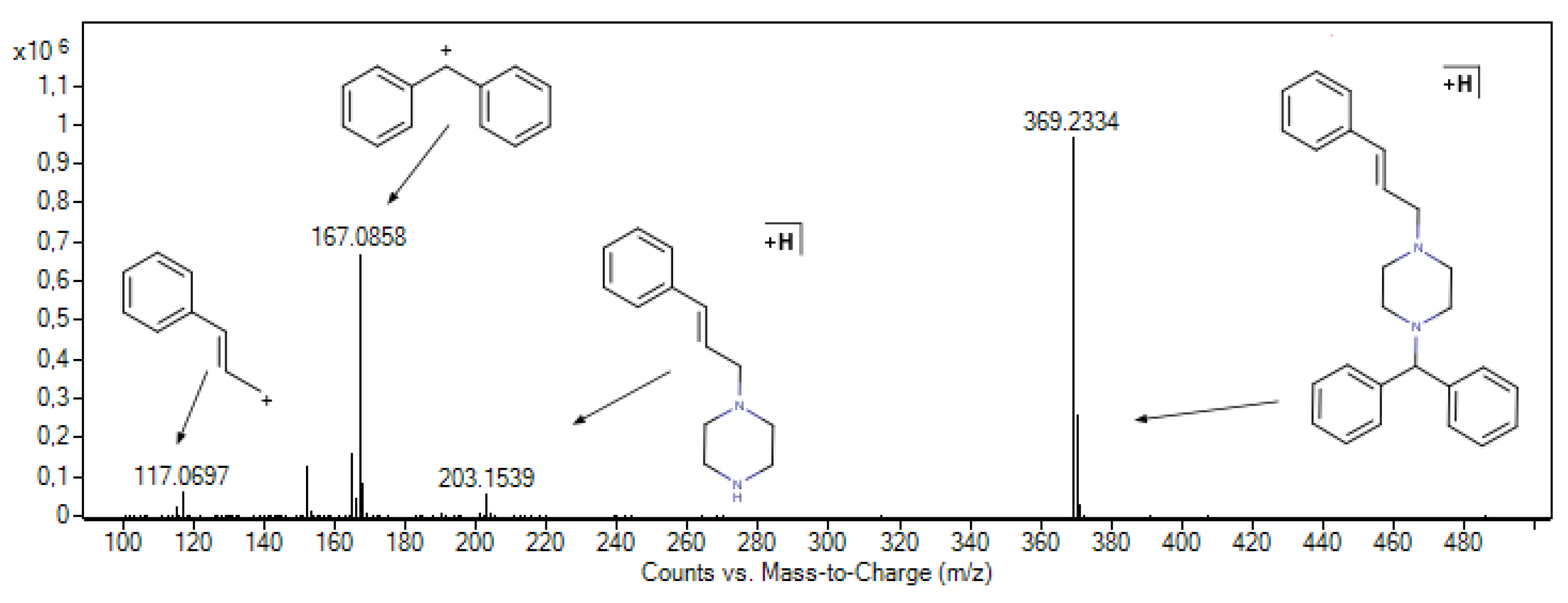
3.3.2. Identification of Cinnarizine Degradation Products
3.3.3. In Silico Toxicological Profiling of Cinnarizine Degradation Products
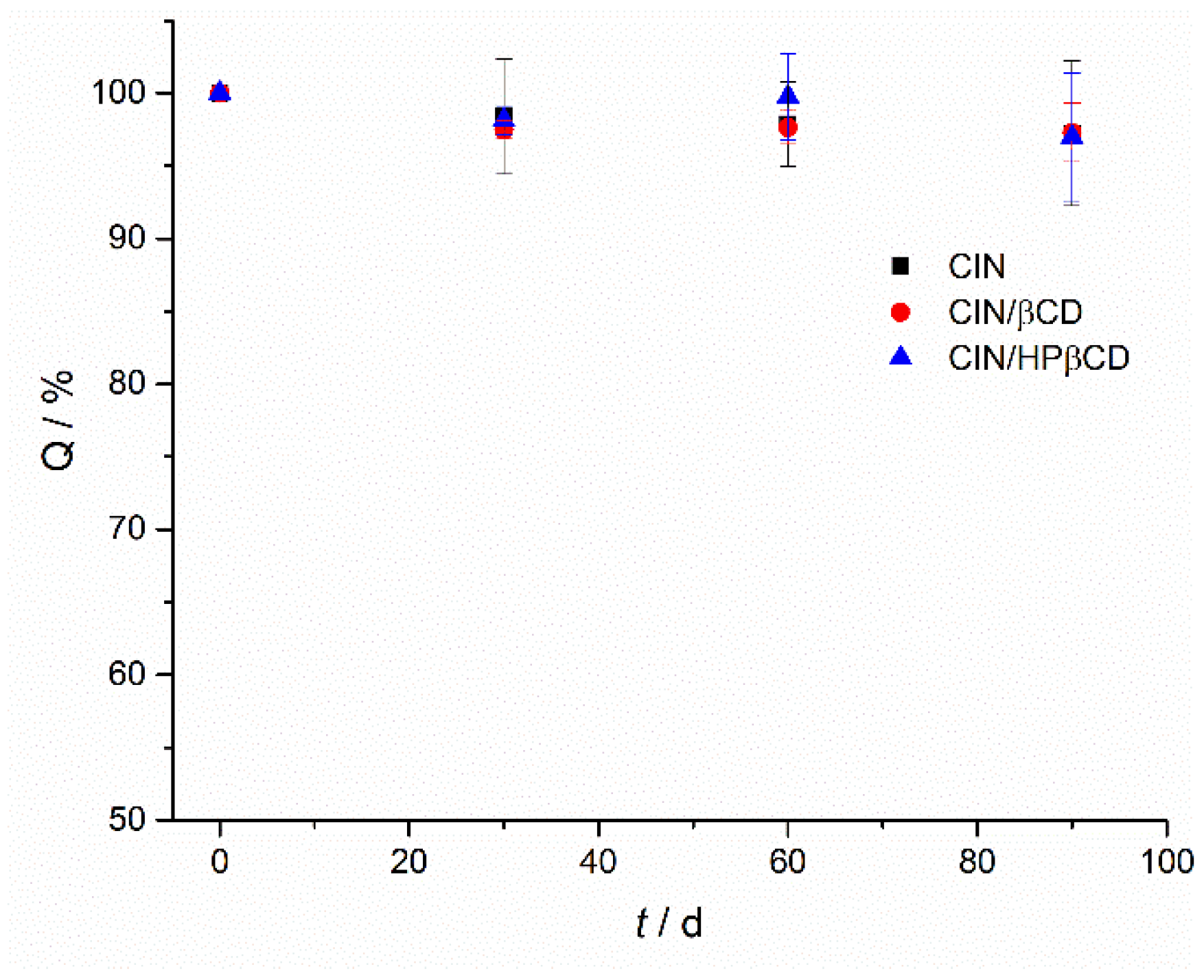
3.3.4. Accelerated Stability Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haress, N.G. Cinnarizine: Comprehensive Profile. In Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 40, pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Kumar, M.; Gupta, S.; Sekharan, T.R.; Tamilvanan, S. Influence of Hydrophilic Polymers Addition into Cinnarizine–β-Cyclodextrin Complexes on Drug Solubility, Drug Liberation Behaviour and Drug Permeability. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 2987–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafie’ei, M.; Kouhanjani, M.F.; Akbari, Z.; Sarvipour, N.; Shekouh, D.; Gholampour, M.; Ardestani, P.M.; Nemati, H. Application of Cinnarizine in Migraine Prevention: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain Pract. 2022, 22, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, M.; Przyklenk, K.-H.; Richtberg, A.; Baumann, W.; Dressman, J.B. Prediction of Oral Absorption of Cinnarizine—A Highly Supersaturating Poorly Soluble Weak Base with Borderline Permeability. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polkovnikova, Y.A.; Chistyakova, V.M. Physicochemical and Biopharmaceutical Studies of Solid Dispersions of Cinnarizine. Pharm. Chem. J. 2023, 57, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoodi, M.; Nokhodchi, A.; Oskuei, M.A.; Heidari, S. Formulation of Cinnarizine for Stabilization of Its Physiologically Generated Supersaturation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järvinen, T.; Järvinen, K.; Schwarting, N.; Stella, V.J. Β-Cyclodextrin Derivatives, SBE4-β-CD and HP–Β-CD, Increase the Oral Bioavailability of Cinnarizine in Beagle Dogs. J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 84, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okimoto, K.; Rajewski, R.A.; Uekama, K.; Jona, J.A.; Stella, V.J. The Interaction of Charged and Uncharged Drugs with Neutral (HP-β-CD) and Anionically Charged (SBE7-β-CD) Beta-Cyclodextrins. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumura, T.; Ueda, H.; Tsushima, Y.; Kasai, M.; Kayano, M.; Amada, I.; Machida, Y.; Nagai, T. Inclusion Complex of Cinnarizine with β-Cyclodextrin in Aqueous Solution and in Solid State. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 1984, 2, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vij, M.; Dand, N.; Kumar, L.; Choudhary, N.; Kumar, P.; Wadhwa, P.; Wani, S.U.D.; Shakeel, F.; Ali, M. Novel Microwave-Based Green Approach for the Synthesis of Dual-Loaded Cyclodextrin Nanosponges: Characterization, Pharmacodynamics, and Pharmacokinetics Evaluation. Green Process. Synth. 2024, 13, 20240187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, F.; Holm, R.; Stappaerts, J.; Bauer-Brandl, A. Absorption of Cinnarizine from Type II Lipid-Based Formulations: Impact of Lipid Chain Length, Supersaturation, Digestion, and Precipitation Inhibition. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 197, 106765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, F.; Bauer-Brandl, A.; Stappaerts, J.; Holm, R. Digestion Is a Critical Element for Absorption of Cinnarizine from Supersaturated Lipid-Based Type I Formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 192, 106634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahba, A.A.-W.; Alanazi, F.K.; Abdel-Rahman, S.I. Stabilization Benefits of Single and Multi-Layer Self-Nanoemulsifying Pellets: A Poorly-Water Soluble Model Drug with Hydrolytic Susceptibility. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, R.; Olesen, N.E.; Hartvig, R.A.; Jørgensen, E.B.; Larsen, D.B.; Westh, P. Effect of Cyclodextrin Concentration on the Oral Bioavailability of Danazol and Cinnarizine in Rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 101, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, T.; Nagy, P.; Panyi, G.; Szente, L.; Varga, Z.; Zakany, F. Cyclodextrins: Only Pharmaceutical Excipients or Full-Fledged Drug Candidates? Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiassa, V.; Garnero, C.; Zoppi, A.; Longhi, M.R. Cyclodextrins and Their Derivatives as Drug Stability Modifiers. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Wei, S.; Liu, J.; Tian, B. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Cyclodextrin-Based Oral Drug Delivery Formulations for Disease Therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 329, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klarić, D.; Kelrajter, M.; Čikoš, A.; Budimir, A.; Galić, N. Inclusion Complexes of Nabumetone with β-Cyclodextrins: Spectroscopic, Spectrometric and Calorimetric Studies in Solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 397, 124152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocrnić, M.; Hoelm, M.; Ignaczak, A.; Čikoš, A.; Budimir, A.; Tomišić, V.; Galić, N. Inclusion Complexes of Loratadine with β-Cyclodextrin and Its Derivatives in Solution. Integrated Spectroscopic, Thermodynamic and Computational Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 410, 125515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumura, T.; Tatsuishi, K.; Kayano, M.; Machida, Y.; Nagai, T. Effect of β-Cyclodextrin on the Degradation Rate of Cinnarizine in Aqueous Solution. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jug, M.; Mura, P.A. Grinding as Solvent-Free Green Chemistry Approach for Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex Preparation in the Solid State. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, P. Analytical Techniques for Characterization of Cyclodextrin Complexes in the Solid State: A Review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berben, P.; Bauer-Brandl, A.; Brandl, M.; Faller, B.; Flaten, G.E.; Jacobsen, A.-C.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P. Drug Permeability Profiling Using Cell-Free Permeation Tools: Overview and Applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 119, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, M.H.; Shakeel, F.; Foudah, A.I.; Aljarba, T.M.; Mahdi, W.A.; Bar, F.M.A.; Alshehri, S.; Alam, P. A Validated, Stability-Indicating, Eco-Friendly HPTLC Method for the Determination of Cinnarizine. Separations 2023, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Khan, S. Identification and Characterization of Two New Oxidation Degradation Impurities in Cinnarizine through LC-HRMS/MS and 1H NMR, along with in Silico Toxicity Predictions of Its Degradation Products. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2024, 38, e6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Pharmacopoeia. 5.17.1. Recommendations on Dissolution Testing; European Pharmacopeia: Strasbourg, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, N.H.; Bauer, M.; Boussac, N.; Khan-Malek, R.; Munden, P.; Sardaro, M. An Evaluation of Fit Factors and Dissolution Efficiency for the Comparison of in Vitro Dissolution Profiles. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1998, 17, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Quiñones, N.C.; López-Méndez, L.J.; Guadarrama, P. Inclusion and Non-Inclusion Complexes between Curcumin and β-Cyclodextrin with High-Curcumin Loading and Enhanced Aqueous Solubility Obtained by Mechanochemistry. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202303254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klarić, D.; Soldin, Ž.; Vincze, A.; Szolláth, R.; Balogh, G.T.; Jug, M.; Galić, N. Biopharmaceutical Characterization and Stability of Nabumetone–Cyclodextrins Complexes Prepared by Grinding. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassene, P.J.; Knopp, M.M.; Hesselkilde, J.Z.; Koradia, V.; Larsen, A.; Rades, T.; Müllertz, A. Precipitation of a Poorly Soluble Model Drug during In Vitro Lipolysis: Characterization and Dissolution of the Precipitate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4982–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.; Kakumanu, V.K.; Bansal, A.K. Analytical Techniques for Quantification of Amorphous/Crystalline Phases in Pharmaceutical Solids. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1641–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Loots, L.; Friščić, T. Towards Medicinal Mechanochemistry: Evolution of Milling from Pharmaceutical Solid Form Screening to the Synthesis of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 7760–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Rades, T.; Boyd, B.J. Lipid-Based Formulations Can Enable the Model Poorly Water-Soluble Weakly Basic Drug Cinnarizine To Precipitate in an Amorphous-Salt Form During In Vitro Digestion. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3783–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasoya, J.M.; Lee, H.L.; Lee, T.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Continuous Synthesis of Cinnarizine Salt with Malic Acid by Applying Green Chemistry Using Water-Assisted Twin Screw Extrusion. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 5160–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.K.; Olusanya, T.O.B.; Chaw, C.S.; Elkordy, A.A. Brief Effect of a Small Hydrophobic Drug (Cinnarizine) on the Physicochemical Characterisation of Niosomes Produced by Thin-Film Hydration and Microfluidic Methods. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Attia, A.K. Thermal Behavior and Decomposition Kinetics of Cinnarizine under Isothermal and Non-Isothermal Conditions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 127, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavà, C.; Crupi, V.; Ficarra, P.; Guardo, M.; Majolino, D.; Stancanelli, R.; Venuti, V. Physicochemical Characterization of Coumestrol/β-Cyclodextrins Inclusion Complexes by UV–Vis and FTIR-ATR Spectroscopies. Vib. Spectrosc. 2008, 48, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šagud, I.; Zanolla, D.; Zingone, G.; Perissutti, B.; Škorić, I. Impact of Mesoporous Silica on the Chemical Degradation of Praziquantel upon Grinding. C. R. Chim. 2021, 24, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šagud, I.; Zanolla, D.; Perissutti, B.; Passerini, N.; Škorić, I. Identification of Degradation Products of Praziquantel during the Mechanochemical Activation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 159, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissutti, B.; Passerini, N.; Trastullo, R.; Keiser, J.; Zanolla, D.; Zingone, G.; Voinovich, D.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; Trastullo, R.; et al. An Explorative Analysis of Process and Formulation Variables Affecting Comilling in a Vibrational Mill: The Case of Praziquantel. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lex, T.R.; Rodriguez, J.D.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, W.; Gao, Z. Development of In Vitro Dissolution Testing Methods to Simulate Fed Conditions for Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms. AAPS J. 2022, 24, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Dissolution Methods Database. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/dissolution-methods-database (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Grady, H.; Elder, D.; Webster, G.K.; Mao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Flanagan, T.; Mann, J.; Blanchard, A.; Cohen, M.J.; Lin, J.; et al. Industry’s View on Using Quality Control, Biorelevant, and Clinically Relevant Dissolution Tests for Pharmaceutical Development, Registration, and Commercialization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.; Patel, J.; Rajput, G.; Thakor, R. Formulation and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Tablets of Cinnarizine. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 72, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, S.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N. Different BCS Class II Drug-Gelucire Solid Dispersions Prepared by Spray Congealing: Evaluation of Solid State Properties and In Vitro Performances. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashish, A.Y.; Shahba, A.A.-W.; Alanazi, F.K.; Kazi, M. Adsorbent Precoating by Lyophilization: A Novel Green Solvent Technique to Enhance Cinnarizine Release from Solid Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (S-SNEDDS). Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pätzmann, N.; Beránek, J.; Griffin, B.T.; Kuentz, M.; O’Dwyer, P.J. Co-Milling of Glass Forming Ability Class III Drugs: Comparing the Impact of Low and High Glass Transition Temperatures. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 209, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kawakami, A.; Nanimatsu, A.; Horio, M.; Matsuoka, J.; Wada, T.; Kasaoka, S.; Yoshikawa, H. In Vivo Evaluation of Supersaturation/Precipitation/Re-Dissolution Behavior of Cinnarizine, a Lipophilic Weak Base, in the Gastrointestinal Tract: The Key Process of Oral Absorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, A.C.; Nielsen, S.; Brandl, M.; Bauer-Brandl, A. Drug Permeability Profiling Using the Novel Permeapad® 96-Well Plate. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popielec, A.; Fenyvesi, É.; Yannakopoulou, K.; Loftsson, T. Effect of Cyclodextrins on the Degradation Rate of Benzylpenicillin. Pharmazie 2016, 71, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špehar, T.K.; Pocrnić, M.; Klarić, D.; Bertoša, B.; Čikoš, A.; Jug, M.; Padovan, J.; Dragojević, S.; Galić, N. Investigation of Praziquantel/Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexation by NMR and LC-HRMS/MS: Mechanism, Solubility, Chemical Stability, and Degradation Products. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 4210–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanam, M.; Handa, T.; Sharma, P.; Jhajra, S.; Muthe, P.K.; Dappili, P.K.; Shah, R.P.; Singh, S. Critical Practical Aspects in the Application of Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometric Studies for the Characterization of Impurities and Degradation Products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 87, 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaro Bujak, I.; Klarić, D.; Lučić, B.; Bojanić, K.; Bujak, M.; Galić, N. Radiolytic Elimination of Nabumetone from Aqueous Solution: Degradation Efficiency, and Degradants’ Toxicity. Molecules 2024, 30, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Zhu, Q.-F.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Xiong, C.-F.; Hu, Y.-N.; Feng, Y.-Q. Integration of Chemical Derivatization and In-Source Fragmentation Mass Spectrometry for High-Coverage Profiling of Submetabolomes. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 11321–11328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakawa, D.; Mizuno, H.; Sugiyama, E.; Todoroki, K. In-Source Fragmentation of Phenethylamines by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry: Toward Highly Sensitive Quantitative Analysis of Monoamine Neurotransmitters. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 12033–12039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasito, H.; Causon, T.; Hann, S. Alternating In-Source Fragmentation with Single-Stage High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry with High Annotation Confidence in Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Talanta 2022, 236, 122828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitzer, P.M.; Searle, B.C. Incorporating In-Source Fragment Information Improves Metabolite Identification Accuracy in Untargeted LC–MS Data Sets. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Domingo-Almenara, X.; Guijas, C.; Palermo, A.; Rinschen, M.M.; Isbell, J.; Benton, H.P.; Siuzdak, G. Enhanced In-Source Fragmentation Annotation Enables Novel Data Independent Acquisition and Autonomous METLIN Molecular Identification. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 6051–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pereira, A.D.S.; Martin, J.W. Discovery of C5–C17 Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Water by In-Line SPE-HPLC-Orbitrap with In-Source Fragmentation Flagging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4260–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Elmosallamy, M.A.F.; Abbas, A.B. LC and TLC Determination of Cinnarizine in Pharmaceutical Preparations and Serum. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 28, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Chen, H.; Cui, Y.; Tang, X. Formulation, Stability and Degradation Kinetics of Intravenous Cinnarizine Lipid Emulsion. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 373, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaske, D.K.; Kumbhar, A.S. The New RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Cinnarizine, Its Five Specified Impurities, Two Degradation Products with Two Antioxidants and Confirmation of All by HPLC-ESI-MS in Different Pharmaceutical Drug Formulations. Anal. Chem. Lett. 2022, 12, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudijn, W.; van Wijngaarden, I. The Metabolism and Excretion of Cinnarizine by Rats. Life Sci. 1968, 7, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

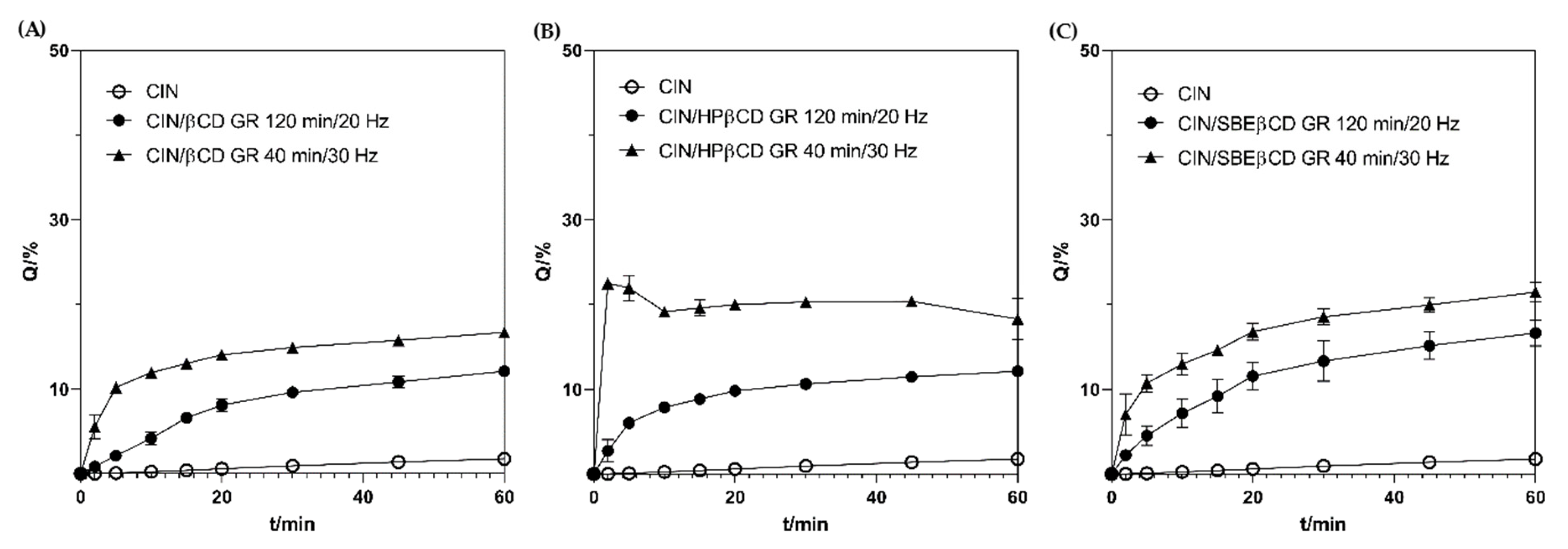

| Sample | Dissolution Efficiency/(%) | Enhancement Factor |
|---|---|---|
| CIN | 0.89 ± 0.04 | - |
| CIN/βCD GR 20 Hz | 8.32 ± 0.50 | 9.33 ± 0.56 |
| CIN/βCD GR 30 Hz | 13.88 ± 0.14 | 15.56 ± 0.16 |
| CIN/HPβCD GR 20 Hz | 9.73 ± 0.25 | 10.91 ± 0.29 |
| CIN/HPβCD GR 30 Hz | 19.74 ± 0.44 | 22.13 ± 0.50 |
| CIN/SBEβCD GR 20 Hz | 11.85 ± 0.70 | 13.28 ± 1.90 |
| CIN/SBEβCD GR 30 Hz | 16.95 ± 0,96 | 19.00 ± 1.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klarić, D.; Kutleša, L.; Jug, M.; Galić, N. From Mechanochemically Driven Complexation and Multimodal Characterization to Stability and Toxicological Insight: A Study of Cinnarizine–β-Cyclodextrins Complexes. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101338
Klarić D, Kutleša L, Jug M, Galić N. From Mechanochemically Driven Complexation and Multimodal Characterization to Stability and Toxicological Insight: A Study of Cinnarizine–β-Cyclodextrins Complexes. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101338
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlarić, David, Lucija Kutleša, Mario Jug, and Nives Galić. 2025. "From Mechanochemically Driven Complexation and Multimodal Characterization to Stability and Toxicological Insight: A Study of Cinnarizine–β-Cyclodextrins Complexes" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101338
APA StyleKlarić, D., Kutleša, L., Jug, M., & Galić, N. (2025). From Mechanochemically Driven Complexation and Multimodal Characterization to Stability and Toxicological Insight: A Study of Cinnarizine–β-Cyclodextrins Complexes. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101338








