Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus Triggers Ferroptosis in CPB Cells to Enhance Virus Replication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Virus, and Main Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Virus Infection
2.3. Integrated Multi-Omics Analysis of Ferroptosis During ISKNV Infection
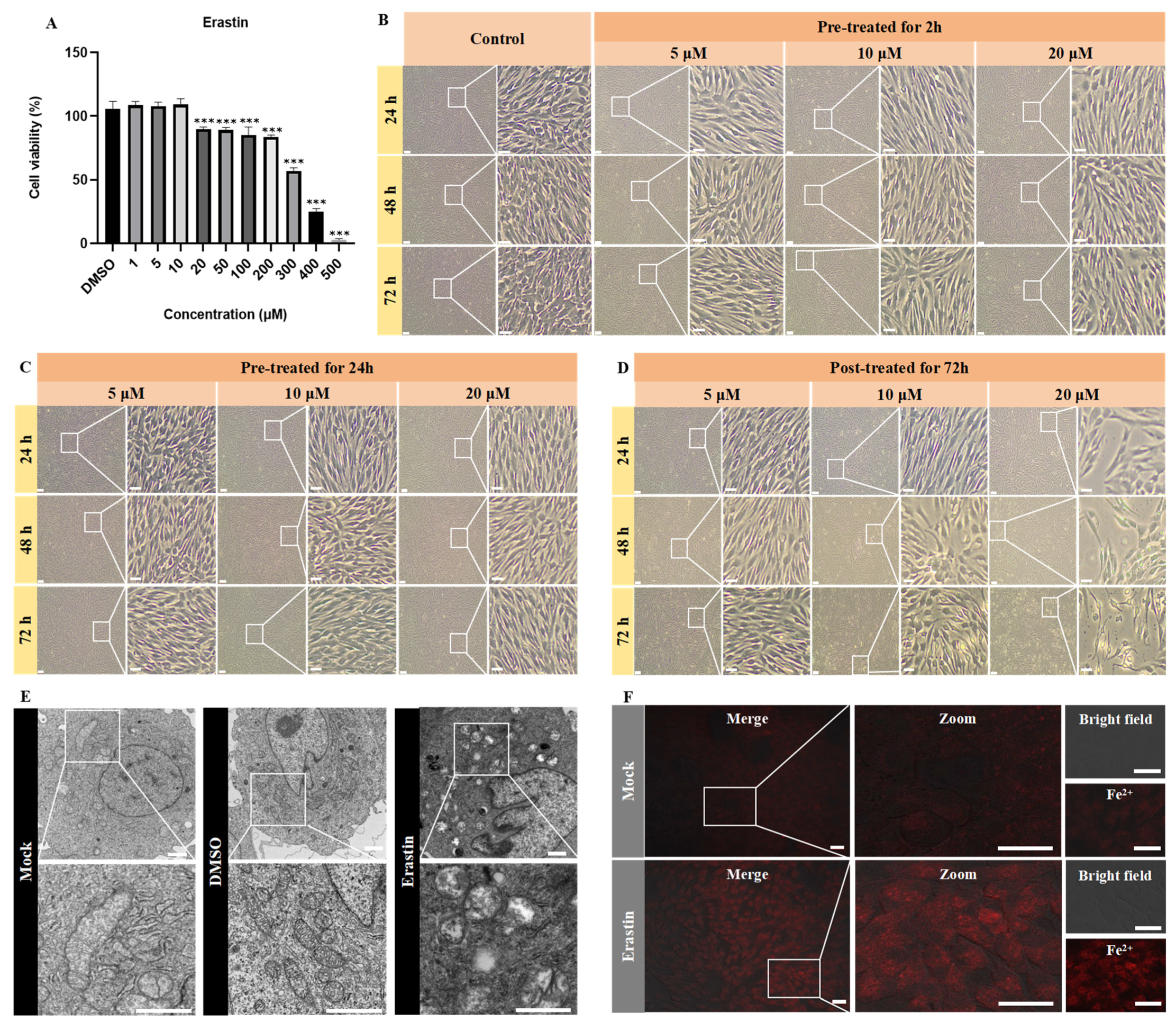
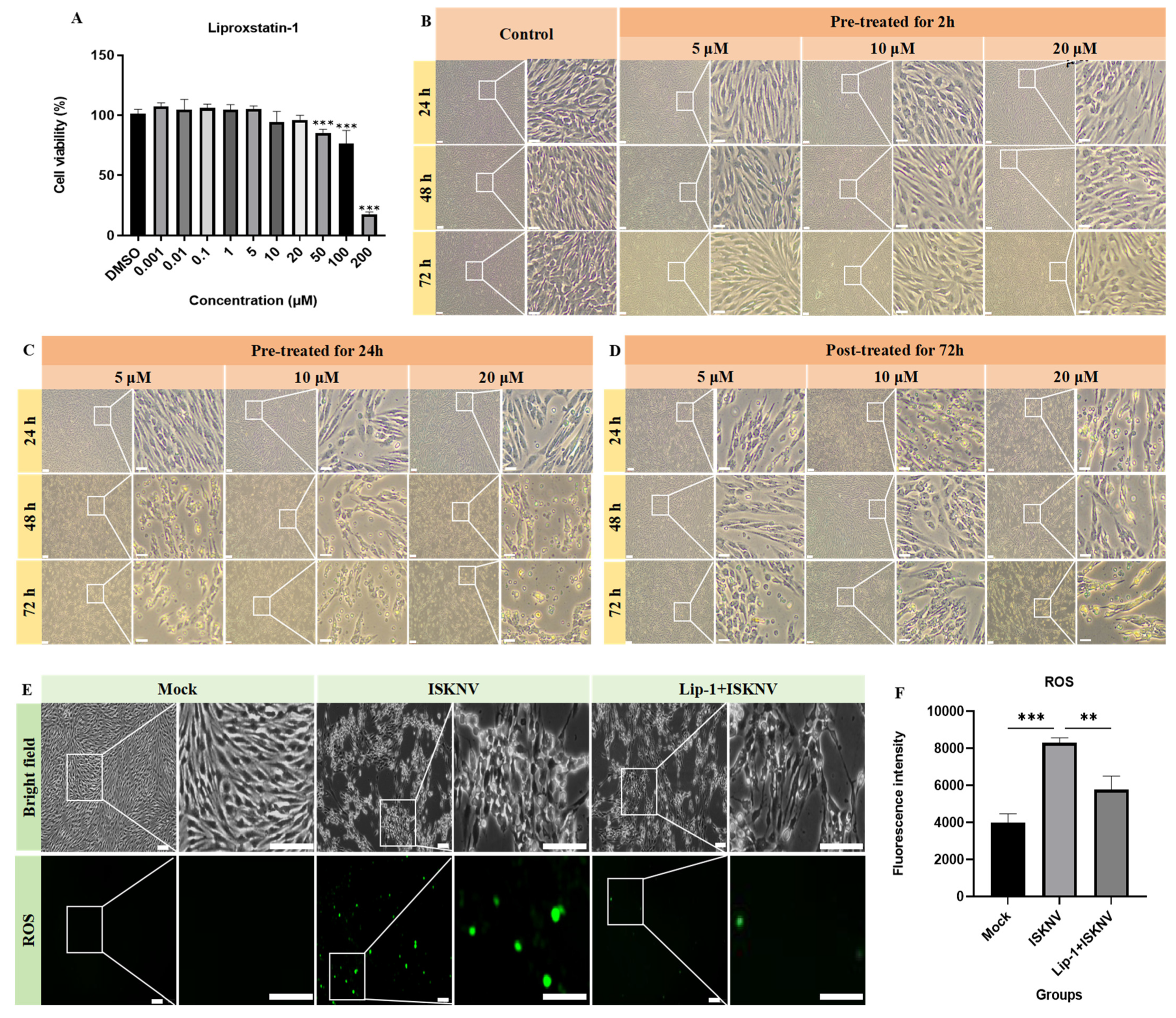
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assessment of Ferroptosis Modulators Using CCK-8 Assay
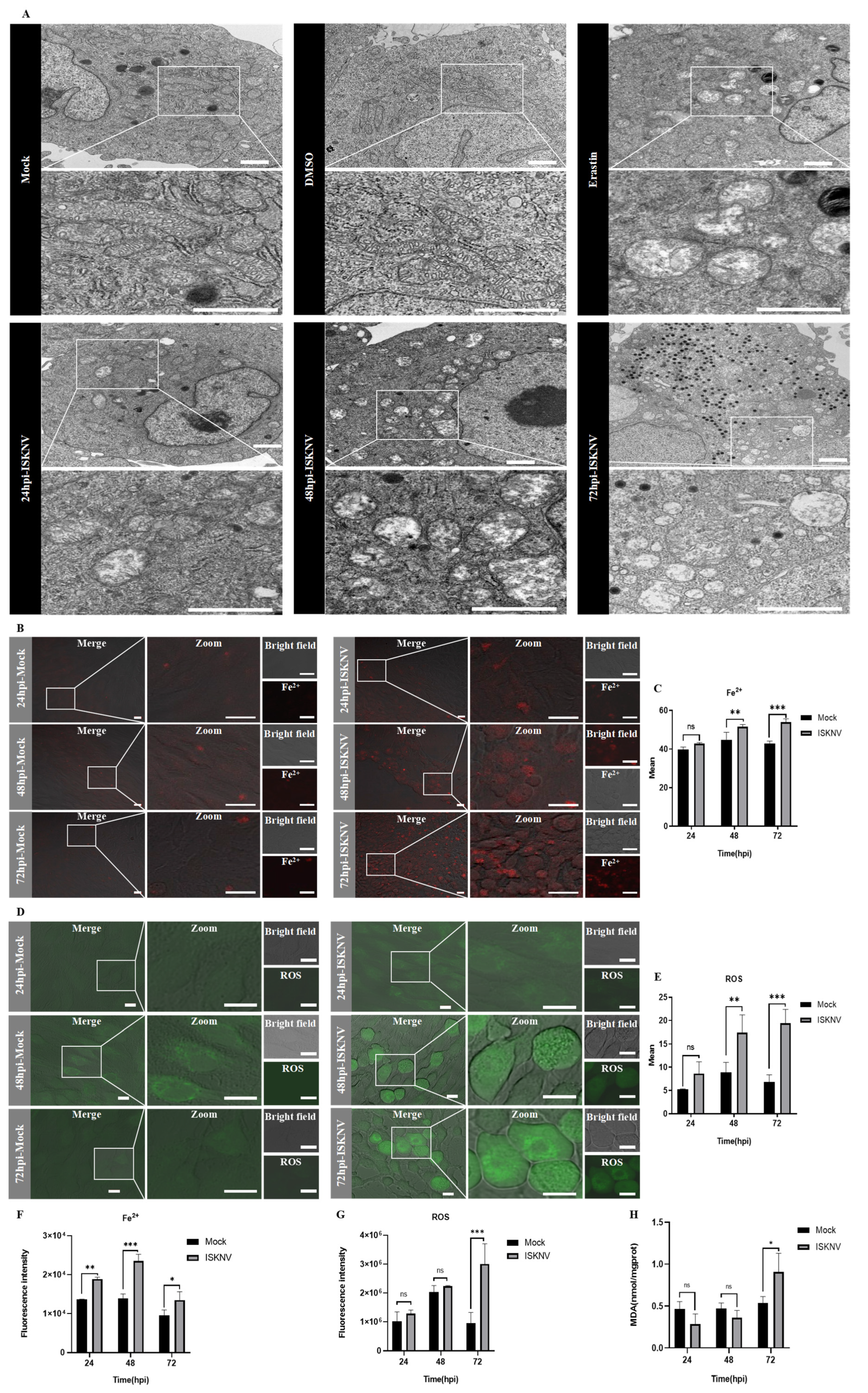
2.5. Ultrastructural Analysis by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6. Fe2+, ROS, and MDA Detection
2.7. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.8. DNA Extraction and qPCR
2.9. Western Blot
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
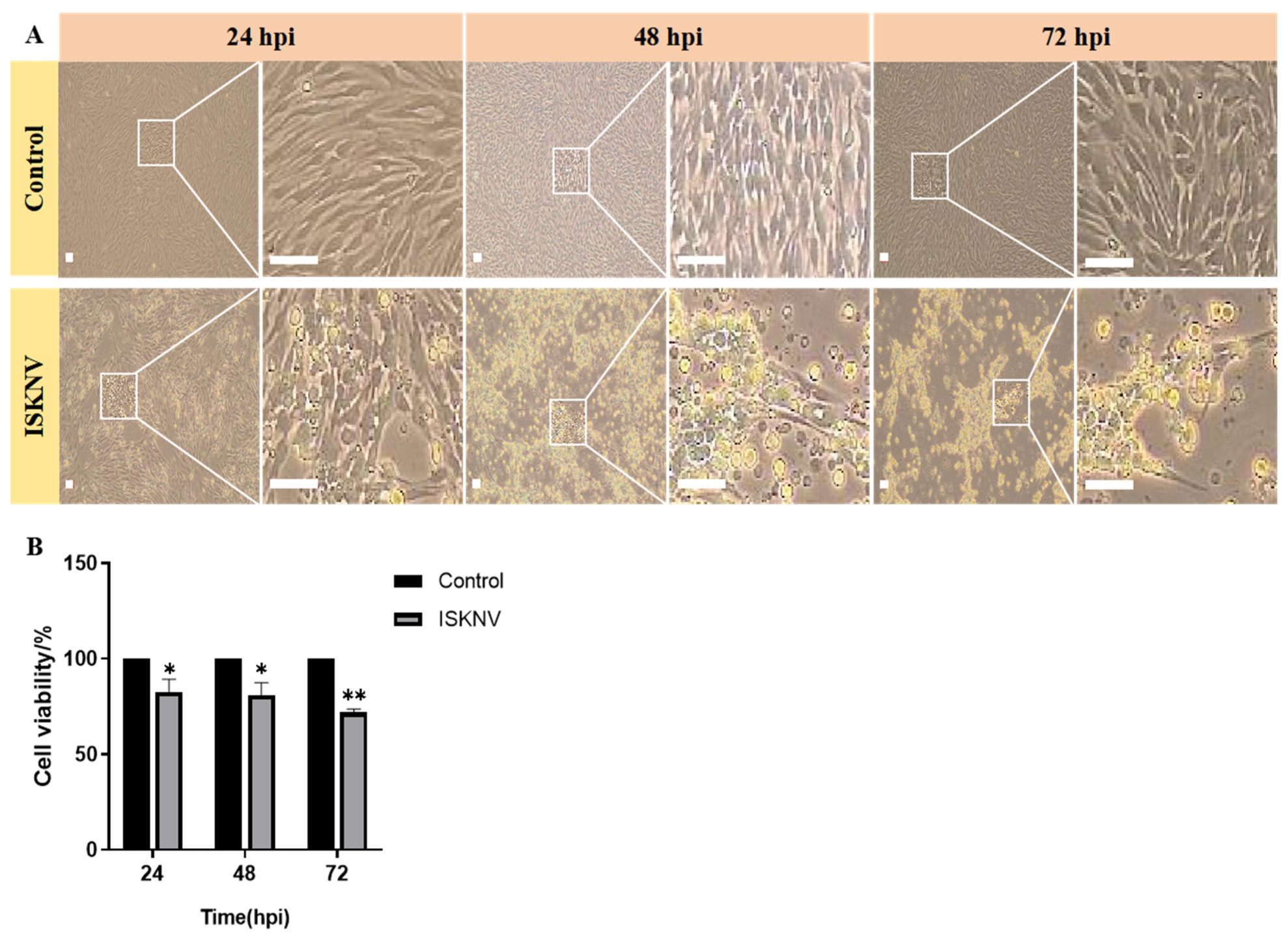
3.1. ISKNV Induces Ferroptosis Cell Death
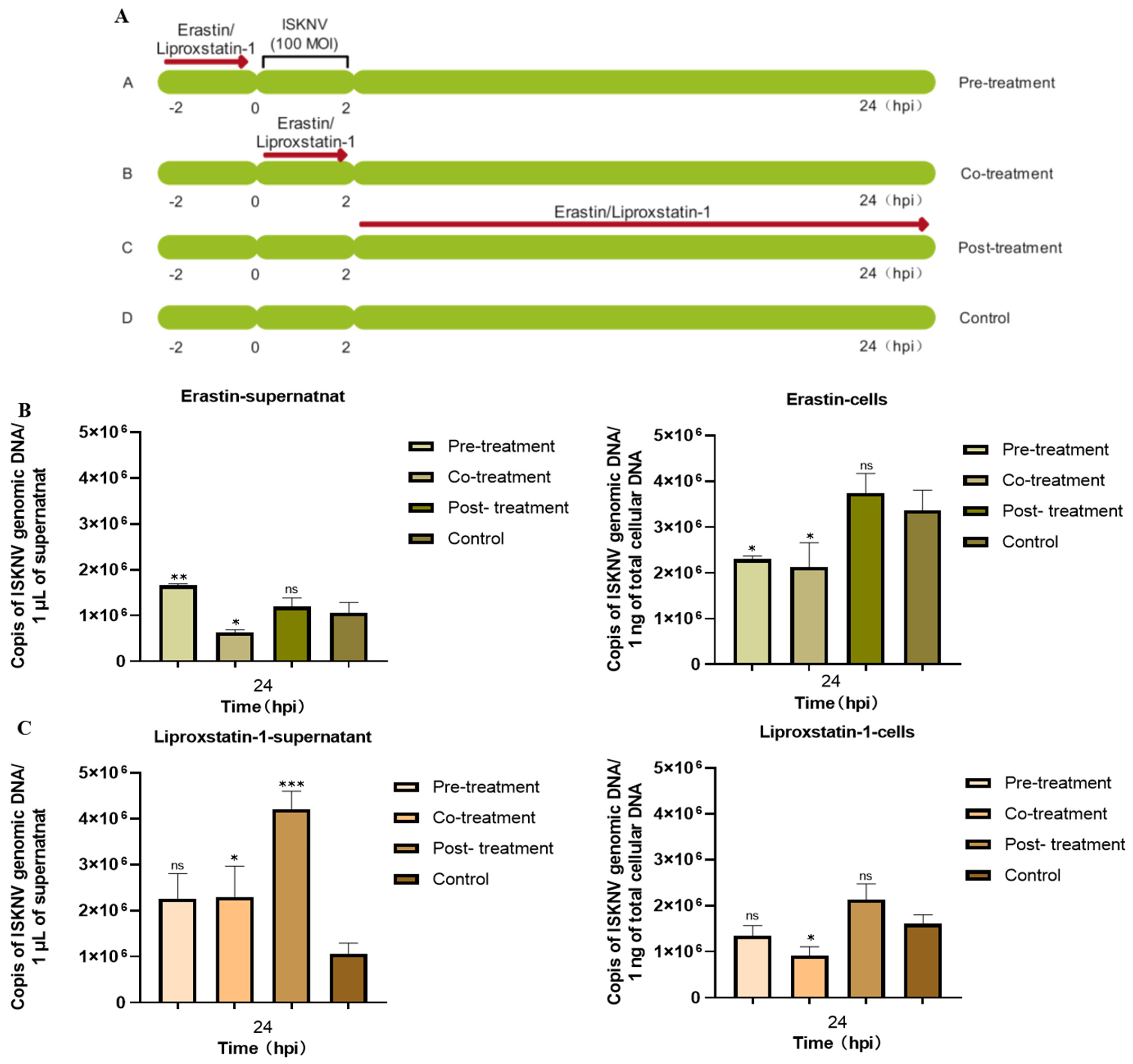
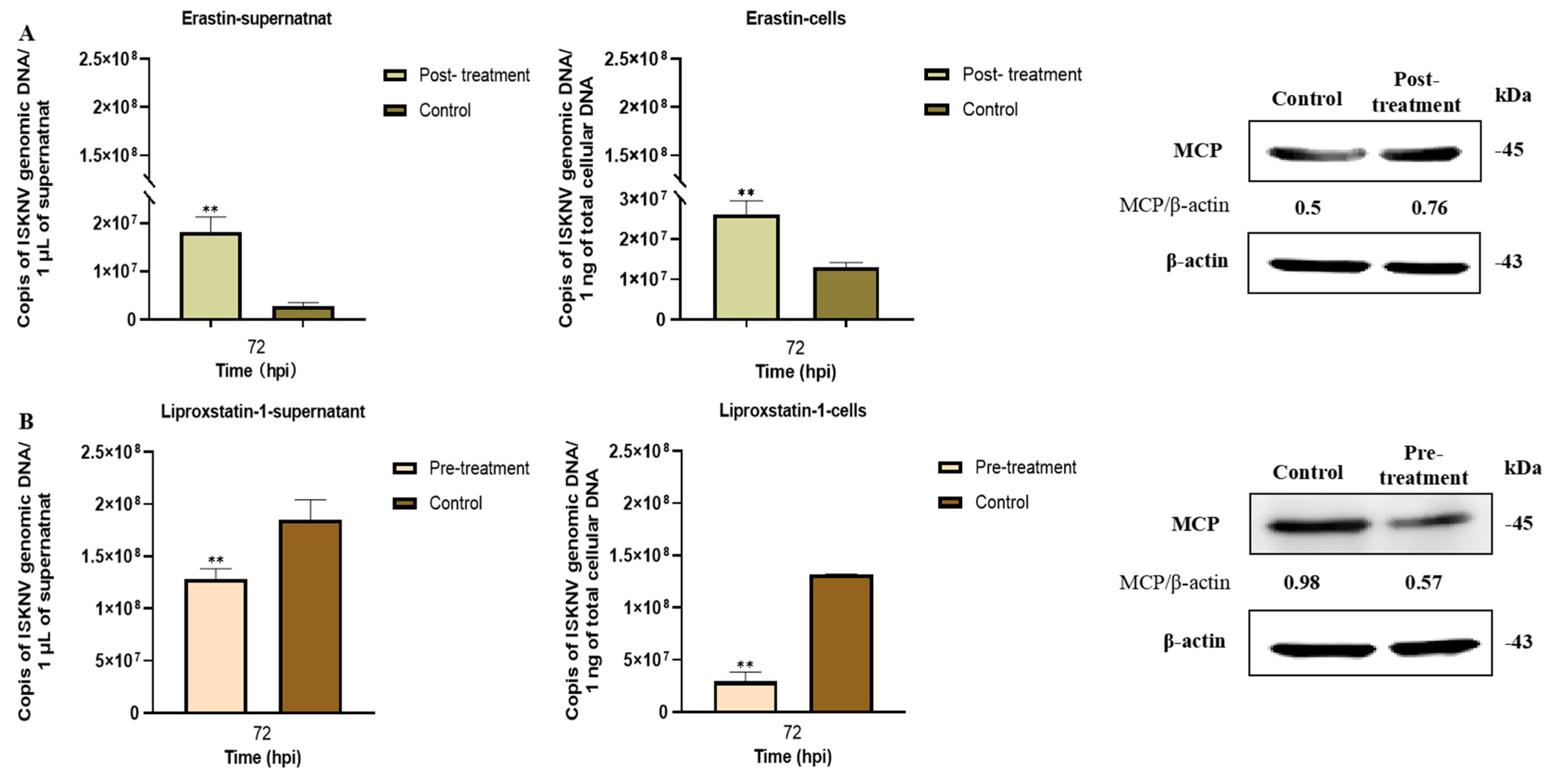
3.2. Ferroptosis Increases ISKNV Replication in CPB Cells
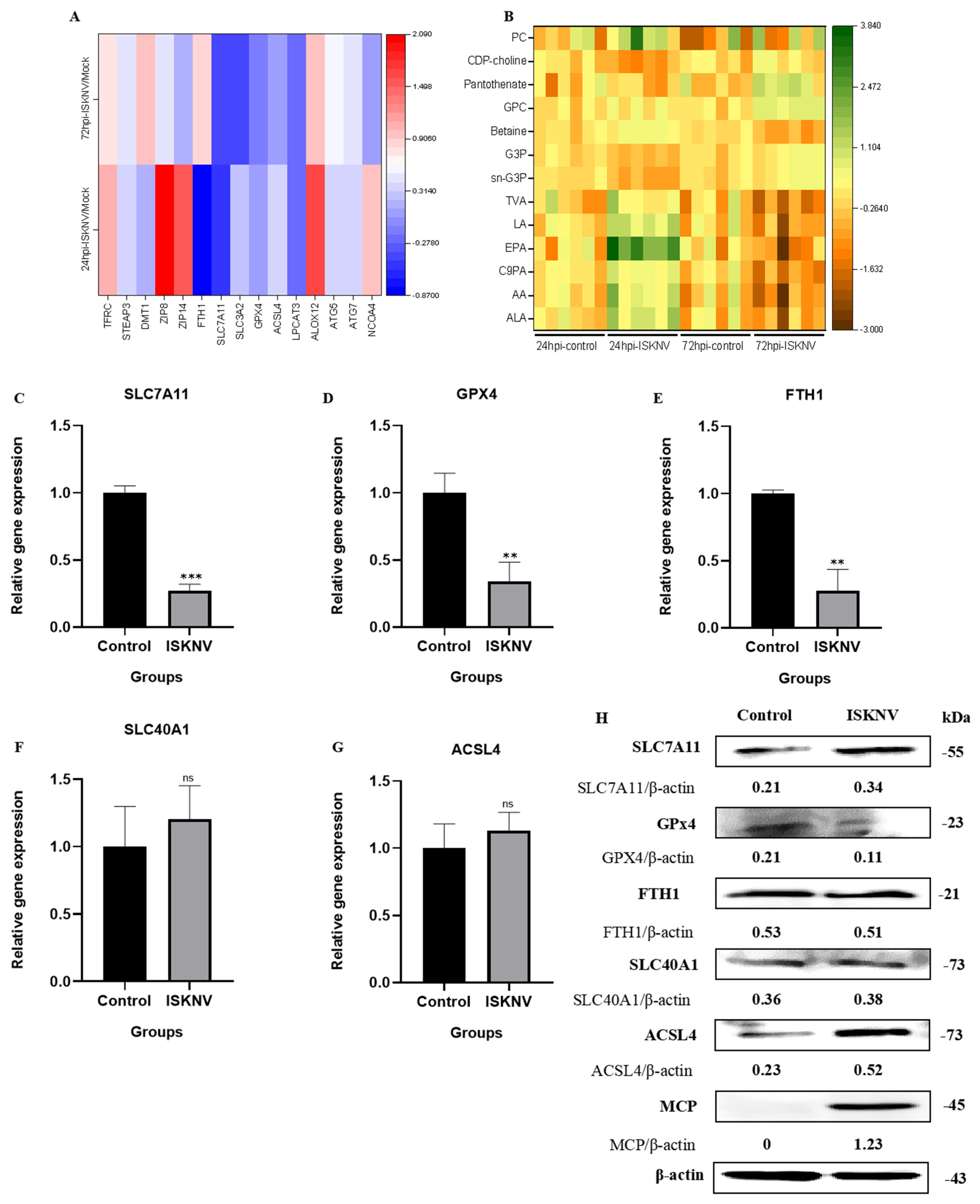
3.3. ISKNV Triggers Ferroptosis Through Suppressing GPx4 and Promoting ACSL4
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, S.Q.; Li, X.H.; Pan, H.J.; Huang, Z.B. Research on the Pathogen of the Outbreak-Ineective Disease of Siniperca Chuastsi. J. Fish. China 1997, 21, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.G.; Deng, M.; Weng, S.P.; Li, Z.; Zhou, S.Y.; Long, Q.X.; Wang, X.Z.; Chan, S.M. Complete Genome Analysis of the Mandarin Fish Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Iridovirus. Virology 2001, 291, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Lü, L.; Weng, S.P.; Huang, J.N.; Chan, S.M.; He, J.G. Molecular epidemiology and phylogenetic analysis of a marine fish infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus-like (ISKNV-like) virus. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, K.; He, J.G.; Weng, S.P.; Huang, Z.J. Transmission, Host Range, Temperature Sensibility of InfectiousSpleen and Kidney Necrosis(ISKN)Virus from Siniperca chuatsi. Virol. Sin. 1999, 14, 353–357. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.Z. Development of a Chinese Perch Cell Line Susceptible to ISKNV and Mechanism of Virus Repication Relying on Glutamine. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An Iron-Dependent Form of Nonapoptotic Cell Death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Patel, D.N.; Welsch, M.; Skouta, R.; Lee, E.D.; Hayano, M.; Thomas, A.G.; Gleason, C.E.; Tatonetti, N.P.; Slusher, B.S.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cystine–glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. eLife 2014, 3, e02523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; SriRamaratnam, R.; Welsch, M.E.; Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Cheah, J.H.; Clemons, P.A.; Shamji, A.F.; Clish, C.B.; et al. Regulation of Ferroptotic Cancer Cell Death by GPX4. Cell 2014, 156, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.T.; Guo, P.Y.; Xie, X.Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death, and its relationships with tumourous diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latunde-Dada, G.O. Ferroptosis: Role of lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology, and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.J.; Yin, Y.C.; Song, C.P.; Tan, L.; Qiu, X.S.; Liao, Y.; Liu, W.W.; Meng, S.S.; Sun, Y.J.; Ding, C. Newcastle-disease-virus-induced ferroptosis through nutrient deprivation and ferritinophagy in tumor cells. iScience 2021, 24, 102837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drakesmith, H.; Prentice, A. Viral infection and iron metabolism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.P.; Joshua, B.; Jin, N.Y.; Du, S.W.; Li, C. Ferroptosis in viral infection: The unexplored possibility. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Wei, J.H.; Ren, L.; Chen, S.Y.; Liu, E.M.; Zang, N. Ferroptosis of alveolar epithelial cells induced by HAdV-7 infection. J. Army Med. Univ. 2022, 44, 2146–2156. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Z. Pathogenicity of Novel Duck Orthoreovirus and Its Mechanism of Induction of Ferroptosis in Macrophages. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.Z.; Li, N.Q.; Lai, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.; Wu, S.; Su, J. A novel fish cell line derived from the brain of Chinese perch Siniperca chuatsi: Development and characterization. J. Fish. Biol. 2015, 86, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Z.; Li, N.Q.; Liu, L.H.; Lin, Q.; Wang, F.; Lai, Y.G.; Jiang, H.M.; Pan, H.J.; Shi, C.B.; Wu, S.Q. Genotype and host range analysis of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV). Virus Genes 2011, 42, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Z.; Li, N.Q.; Lin, Q.; Liu, L.H.; Wu, S.Q. Development and identification of monoclonal antibody against recombinant major capsid protein of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus from Sinipercachuatsi. J. Fish. China 2016, 40, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.Q.; Fu, X.Z.; Li, N.Q.; Dong, X.X.; Zhao, L.J.; Lan, J.F.; Ji, W.; Zhou, W.D.; Ai, T.S.; Wu, S.Q.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis of Mandarin fish brain cells infected with infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus with an emphasis on retinoic acid-inducible gene 1-like receptors and apoptosis pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Z.; Hu, X.Q.; Li, N.Q.; Zheng, F.F.; Dong, X.X.; Duan, J.; Lin, Q.; Tu, J.G.; Zhao, L.J.; Huang, Z.B.; et al. Glutamine and glutaminolysis are required for efficient replication of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus in Chinese perch brain cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 2400–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.F.; Li, F.Y.; Fu, X.Z.; Luo, X.; Lin, Q.; Liang, H.R.; Niu, Y.J.; Li, N.Q. Asparagine Availability Is a Critical Limiting Factor for Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus Replication. Viruses 2024, 16, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, P.; Bai, T.; Sun, Y. Mechanisms of Ferroptosis and Relations with Regulated Cell Death: A Review. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.Z.; Xu, X.W.; Tao, S.H.; Hou, Z.H. HBx facilitates ferroptosis in acute liver failure via EZH2 mediated SLC7A11 suppression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palamara, A.T.; Perno, C.F.; Ciriolo, M.R.; Dini, L.; Balestra, E.; D’Agostini, C.; Francesco, P.D.; Favalli, C.; Rotilio, G.; Garaci, E. Evidence for antiviral activity of glutathione: In vitro inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 replication. Antivir. Res. 1995, 27, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.M.; Tan, M.L.; Hu, M.M.; Yue, X.Y.; Tao, L.L.; Zhai, Y.R.; Li, Y.S. Important molecular mechanisms in ferroptosis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2025, 480, 639–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.J.; Li, Q.; Yin, Y.; Chen, H.C.; Si, Y.H.; Zhu, B.B.; Cao, S.B.; Zhao, Z.K.; Ye, J. Ferroptosis contributes to JEV-induced neuronal damage and neuroinflammation. Virol. Sin. 2024, 39, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.D.; Zhai, J.B.; Hu, W.; Zheng, C.F. When ferroptosis meets pathogenic infections. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, Z.; You, F. Inhibiting ACSL1-Related Ferroptosis Restrains Murine Coronavirus Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Tao, J.; Li, B.; Shi, Y.; Liu, H.L. Swine influenza virus triggers ferroptosis in A549 cells to enhance virus replication. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Li, X.X.; Liu, L.B.; Yu, B.; Xue, Y.X.; Liu, Y.H. Erastin sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by restraining xCT and cystathionine-γ-lyase function. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Pozos, E.; Martínez-Lozada, Z.; Méndez-Flores, O.G.; Guillem, A.M.; Hernández-Kelly, L.C.; Castelán, F.; Olivares-Bañuelos, T.N.; Chi-Castañeda, D.; Najimi, M.; Ortega, A. Characterization of the cystine/glutamate antiporter in cultured Bergmann glia cells. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 108, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, J.P.F.; Schneider, M.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.A.; Hammond, V.J.; Herbach, N.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Eggenhofer, E.; et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Gan, B. Ferroptosis execution: Is it all about ACSL4? Cell Chem. Biol. 2022, 29, 1363–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, V.E.; Mao, G.; Qu, F.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Doll, S.; Croix, C.S.; Dar, H.; Liu, B.; Tyurin, V.A.; Ritov, V.B.; et al. Oxidized Arachidonic/Adrenic Phosphatidylethanolamines Navigate Cells to Ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18S-F | CATTCGTATTGTGCCGCTAGA | 120 | XR_006376550.1 |
| 18S-R | CAAATGCTTTCGCTTTGGTC | ||
| SLC7A11-F | GAGGAGGTAGATAACCCTGAACGG | 120 | XM_044205657.1 |
| SLC7A11-R | CTCCTCTGCTGACATCACAGTG | ||
| GPX4-F | CAACAGATGATCCCAGCGTGGT | 120 | XM_044218327.1 |
| GPX4-R | CACGCACACCAATACCCTGAAG | ||
| FTH1-F | CGCTGTGACGCTGATAATTATCC | 126 | XM_044194482.1 |
| FTH1-R | CTGCAGTTGATTGACAACTAGC | ||
| SLC40A1-F | CTAACCCACTCTGAGATTGTACGG | 125 | NC_058053.1 |
| SLC40A1-R | CTGGTACAGTTCATGTGGTGCTG | ||
| ACSL4-F | GCGTAAGCCTCAGCTATTCCAG | 132 | XM_044206073.1 |
| ACSL4-R | GGGAACAAACAGCGTTTCTTCAAC |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISKNV-F | CGAGGCCACATCCAACATC | 85 (bp) | Ma B. F. [24] |
| ISKNV-R | CGCCTTTAACGTGGGATATATTG | ||
| ISKNV-Probe | CACCAAACTGACCGCGGACTCGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Chang, O.; Lin, Q.; Liang, H.; Niu, Y.; Luo, X.; Ma, B.; Li, N.; Fu, X. Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus Triggers Ferroptosis in CPB Cells to Enhance Virus Replication. Viruses 2025, 17, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050713
Zhang Q, Chang O, Lin Q, Liang H, Niu Y, Luo X, Ma B, Li N, Fu X. Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus Triggers Ferroptosis in CPB Cells to Enhance Virus Replication. Viruses. 2025; 17(5):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050713
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qiushuang, Ouqin Chang, Qiang Lin, Hongru Liang, Yinjie Niu, Xia Luo, Baofu Ma, Ningqiu Li, and Xiaozhe Fu. 2025. "Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus Triggers Ferroptosis in CPB Cells to Enhance Virus Replication" Viruses 17, no. 5: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050713
APA StyleZhang, Q., Chang, O., Lin, Q., Liang, H., Niu, Y., Luo, X., Ma, B., Li, N., & Fu, X. (2025). Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus Triggers Ferroptosis in CPB Cells to Enhance Virus Replication. Viruses, 17(5), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050713





