The Viruses of Botrytis cinerea and Beyond: Molecular Characterization of RNA Viruses and Retroplasmids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Material
2.2. Total RNA Extraction, RNA Sequencing
2.3. Contig Assembly and Virus Identification
2.4. Virus Terminal Sequence Determination
2.5. Phylogenetic Tree Construction and Visualization
3. Results
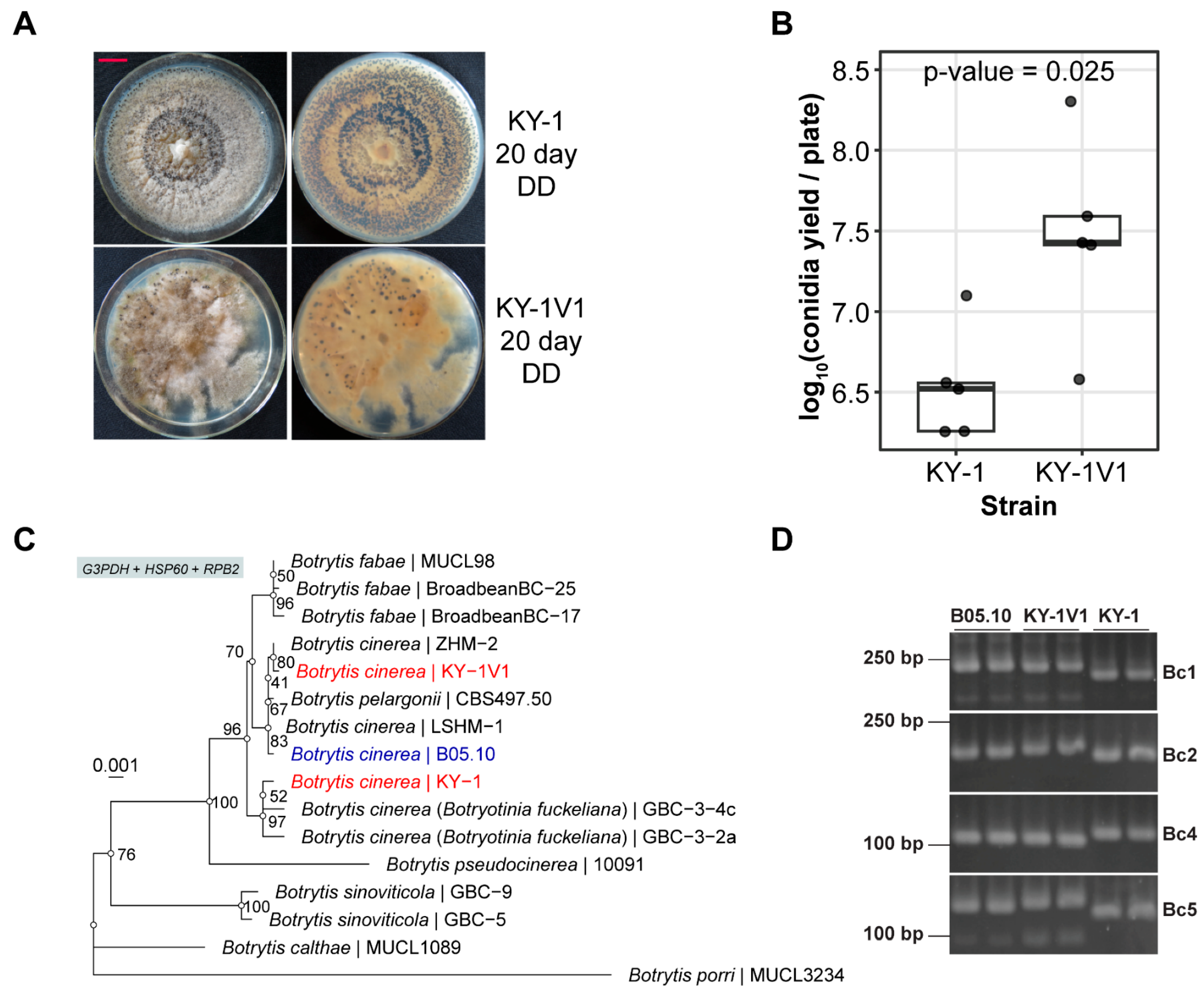
3.1. KY-1 and KY-1V1 Are Two Distinct Fungal Strains of B. cinerea
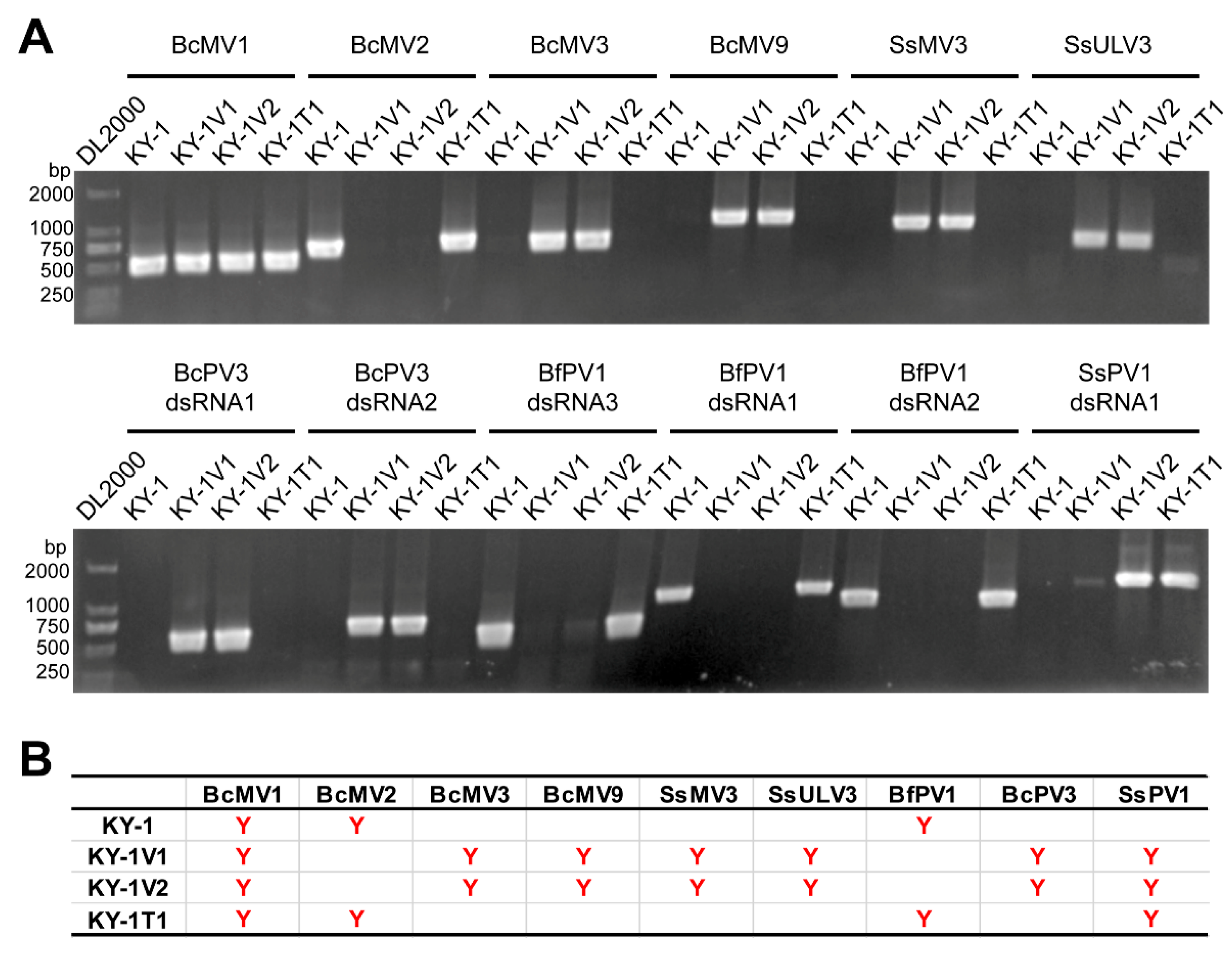
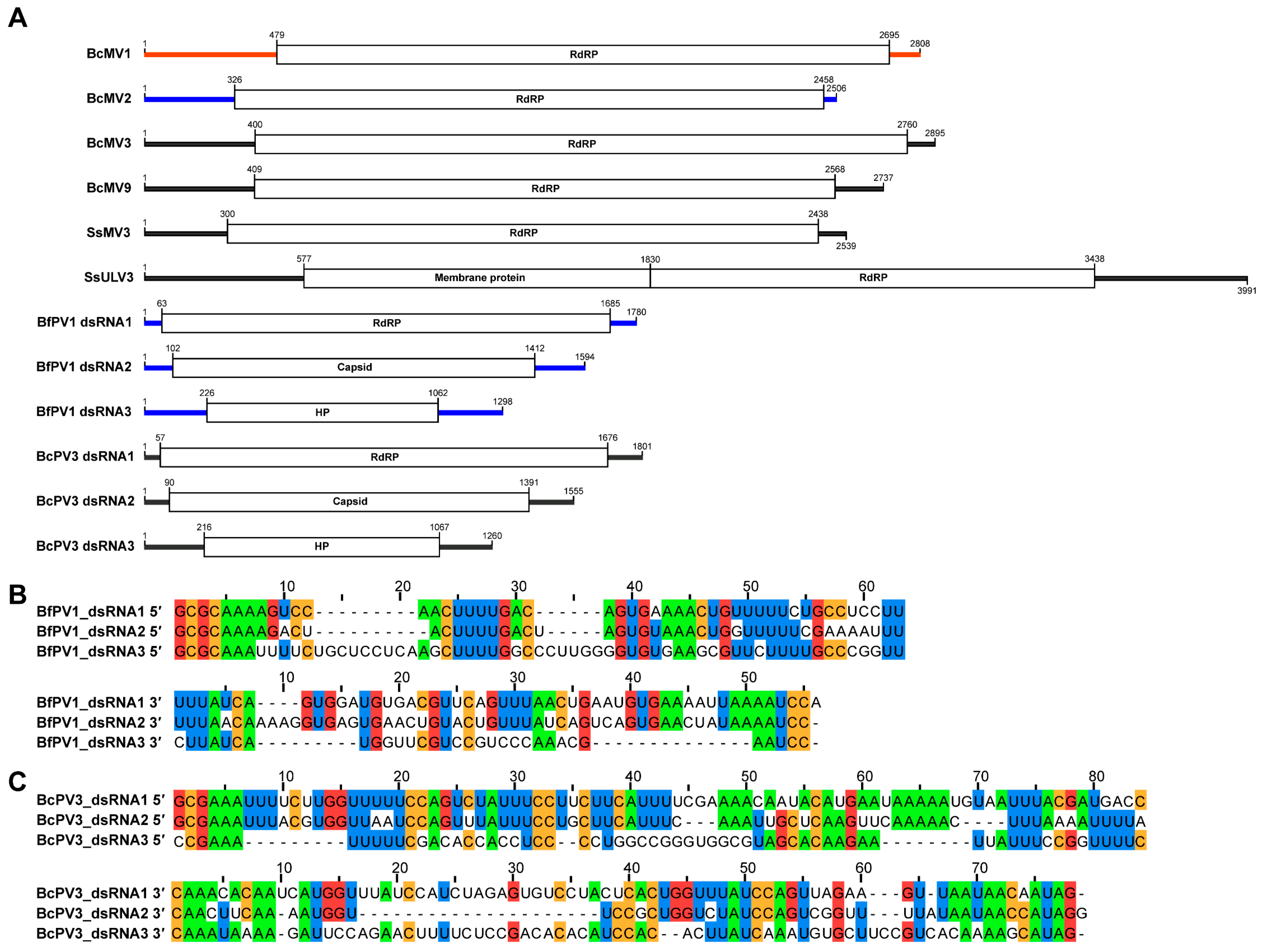
3.2. KY-1 and KY-1V1 Contain Different Virus Composition
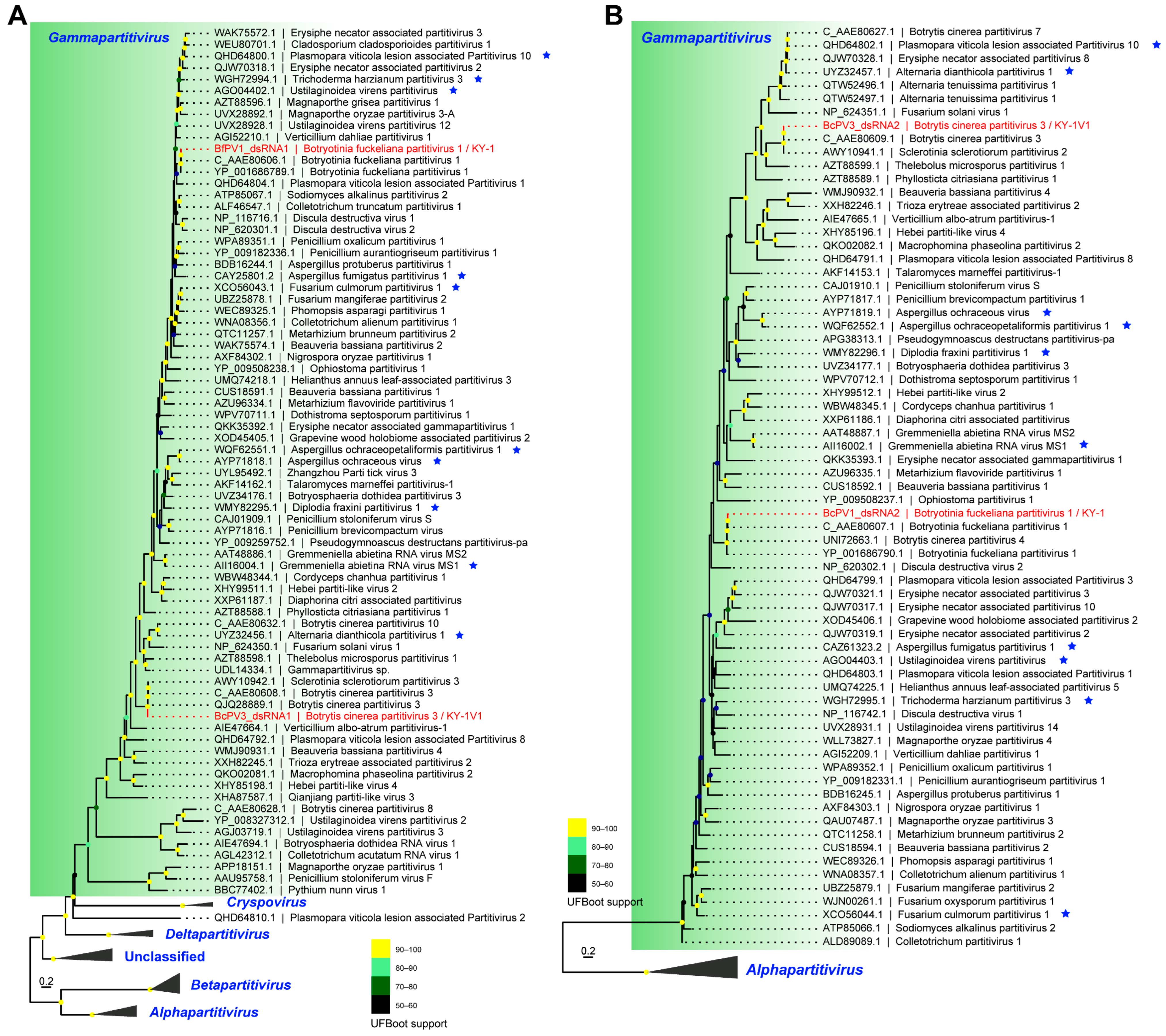
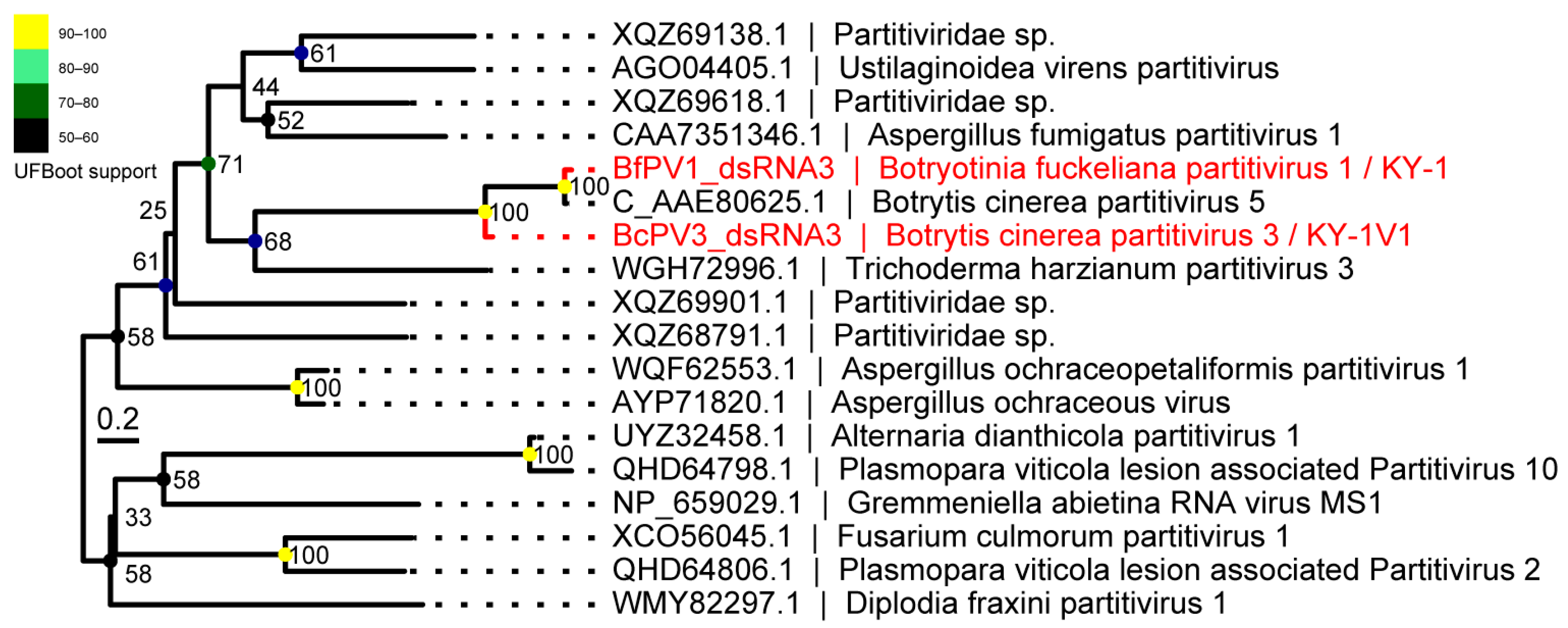
3.3. Phylogenetic Position of Identified RNA Viruses
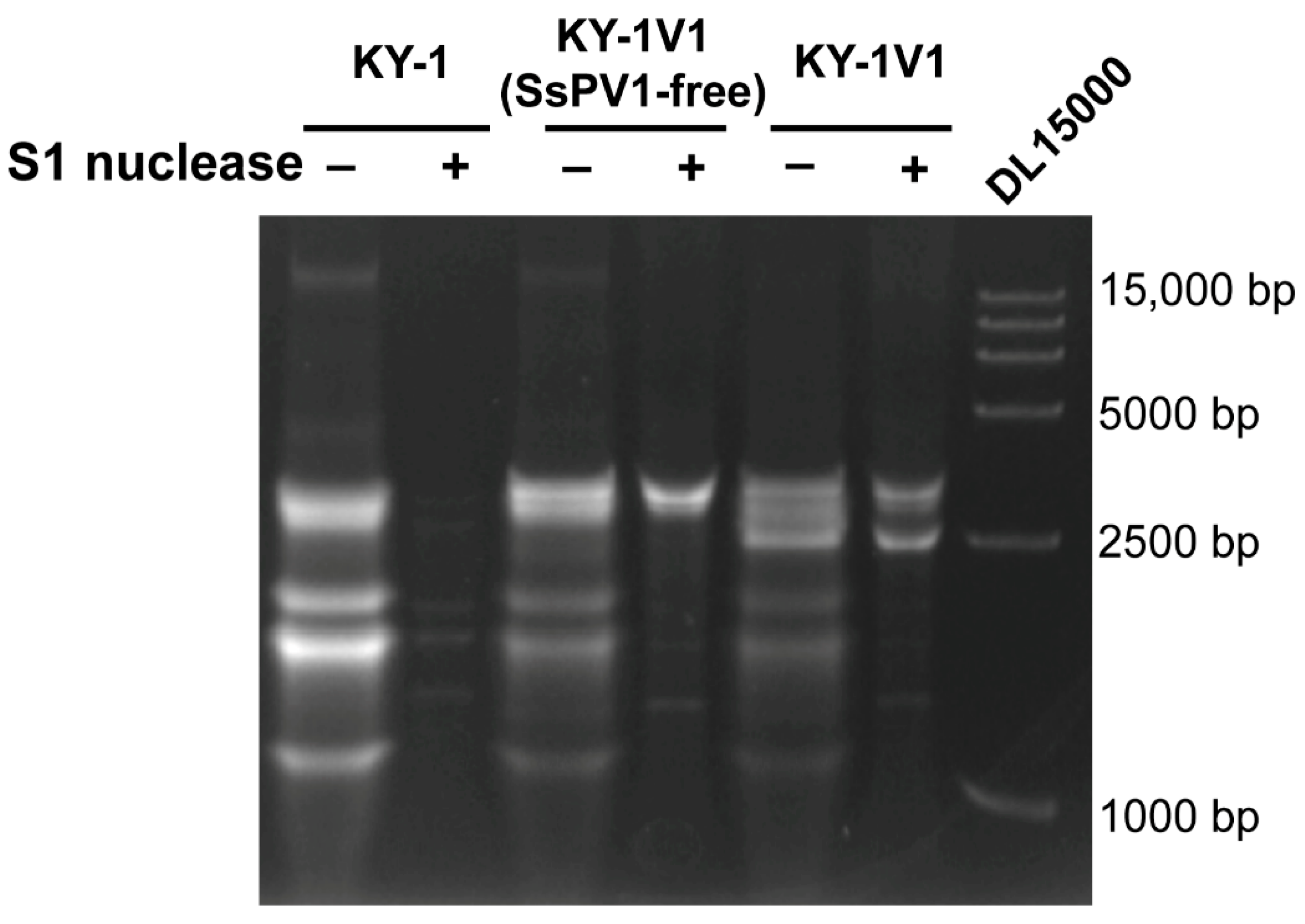
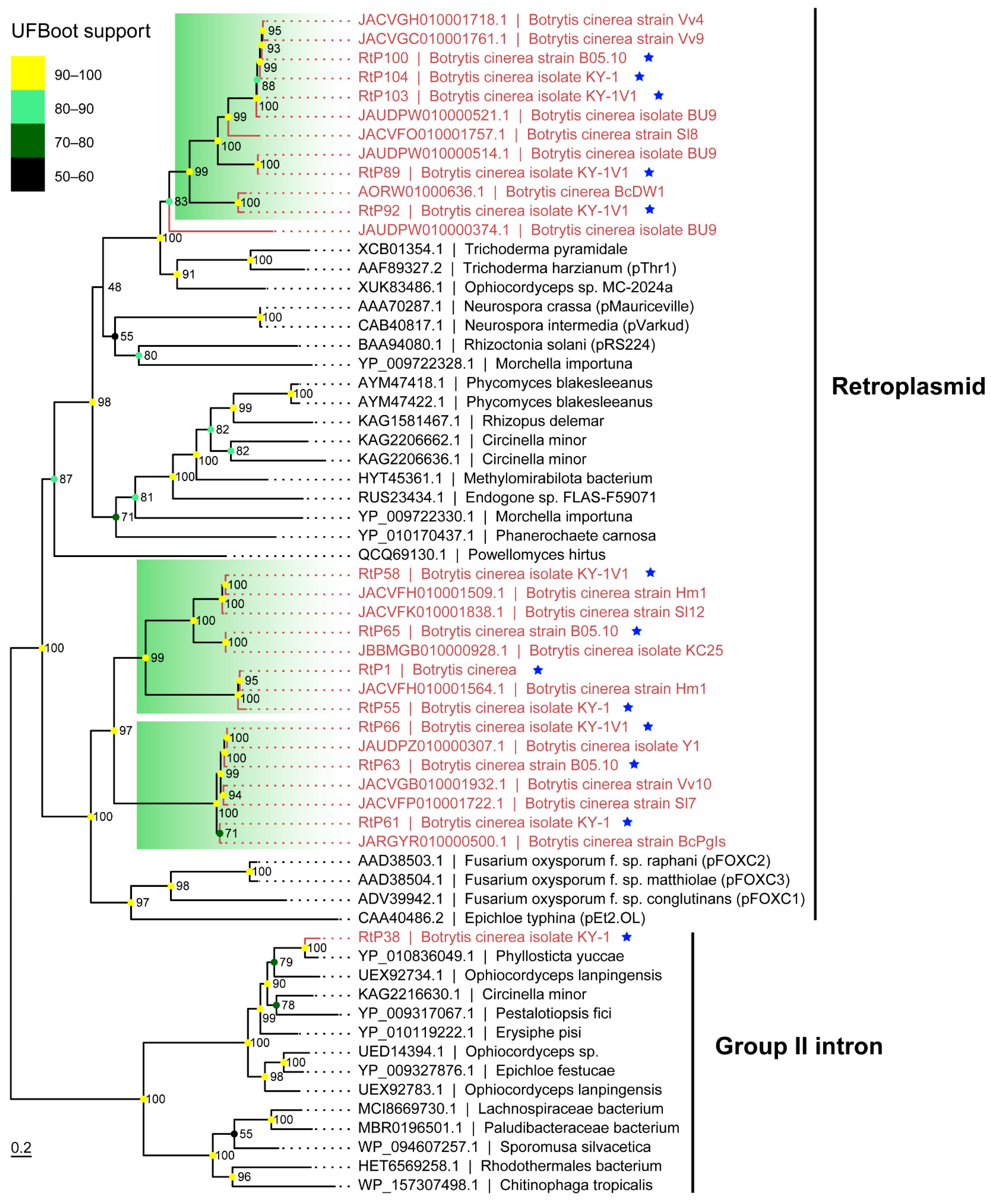
3.4. Discovery of Retroplasmids in B. cinerea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HP | Hypothetical protein |
| MGE | Mobile genetic element |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| RACE | Rapid amplification of cDNA ends |
| RdRP | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| RtP | Retroplasmid |
References
- Elad, Y.; Pertot, I.; Cotes Prado, A.M.; Stewart, A. Plant hosts of Botrytis spp. In Botrytis—The Fungus, the Pathogen and Its Management in Agricultural Systems; Fillinger, S., Elad, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 413–486. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Caseys, C.; Kliebenstein, D.J. Genetic and molecular landscapes of the generalist phytopathogen Botrytis cinerea. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 25, e13404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.; Van Kan, J.A.L.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Di Pietro, A.; Spanu, P.D.; Rudd, J.J.; Dickman, M.; Kahmann, R.; Ellis, J.; et al. The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiberg, A.; Wang, M.; Lin, F.-M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kaloshian, I.; Huang, H.-D.; Jin, H. Fungal small RNAs suppress plant immunity by hijacking host RNA interference pathways. Science 2013, 342, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, E.; Gladieux, P.; Giraud, T. The ‘Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde fungus’: Noble rot versus gray mold symptoms of Botrytis cinerea on grapes. Evol. Appl. 2013, 6, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, F.; Ji, Q.; Huo, L.; Qiao, C.; Pan, L. Characterization of the flavors and organoleptic attributes of Petit Manseng noble rot wines from the eastern foothills of Helan Mountain in Ningxia, China. Foods 2025, 14, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Jiang, D. Understanding the diversity, evolution, ecology, and applications of mycoviruses. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 78, 595–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Li, G. Mycoviruses and their ecological impacts on fungi. Virology 2025, 610, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitt, R.L.J.; Beever, R.E.; Pearson, M.N.; Forster, R.L.S. Presence of double-stranded RNA and virus-like particles in Botrytis cinerea. Mycol. Res. 1995, 99, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M.N.; Bailey, A.M. Chapter nine—viruses of Botrytis. In Advances in Virus Research; Ghabrial, S.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 86, pp. 249–272. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Li, G. RNA mycoviruses and their role in Botrytis biology. In Botrytis—The Fungus, the Pathogen and Its Management in Agricultural Systems; Fillinger, S., Elad, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 71–90. [Google Scholar]
- Howitt, R.L.J.; Beever, R.E.; Pearson, M.N.; Forster, R.L.S. Genome characterization of Botrytis virus F, a flexuous rod-shaped mycovirus resembling plant ‘potex-like’ viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitt, R.L.J.; Beever, R.E.; Pearson, M.N.; Forster, R.L.S. Genome characterization of a flexuous rod-shaped mycovirus, Botrytis virus X, reveals high amino acid identity to genes from plant ‘potex-like’ viruses. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaire, L.; Pagán, I.; Ayllón, M.A. Characterization of Botrytis cinerea negative-stranded RNA virus 1, a new mycovirus related to plant viruses, and a reconstruction of host pattern evolution in negative-sense ssRNA viruses. Virology 2016, 499, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaire, L.; Rozas, J.; Ayllón, M.A. Molecular characterization of Botrytis ourmia-like virus, a mycovirus close to the plant pathogenic genus Ourmiavirus. Virology 2016, 489, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaire, L.; Ayllón, M.A. Deep sequencing of mycovirus-derived small RNAs from Botrytis species. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Padilla, A.; Rodríguez-Romero, J.; Gómez-Cid, I.; Pacifico, D.; Ayllón, M.A. Novel mycoviruses discovered in the mycovirome of a necrotrophic fungus. mBio 2021, 12, e03705-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Suárez, H.; Ruiz-Padilla, A.; Donaire, L.; Benito, E.P.; Ayllón, M.A. Reexamining the mycovirome of Botrytis spp. Viruses 2024, 16, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, S.C.; Poursalavati, A.; Lemoyne, P.; Xu, D.; Moffett, P.; Carisse, O.; van der Heyden, H.; Fall, M.L. Exploring the mycovirome: Novel and diverse mycoviruses in Botrytis cinerea. bioRxiv 2025, 2025.2003.2028.645015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yao, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, A.; Kong, X.; Lin, Y.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. The rules in co-infection of multiple viruses across diverse lineages in a fungal host. mBio 2025, 16, e0026225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, M.E.; Ayllón, M.A.; Rodriguez Coy, L.; Plummer, K.M.; Gendall, A.R.; Chooi, K.M.; van Kan, J.A.L.; MacDiarmid, R.M. Mycologists and virologists align: Proposing Botrytis cinerea for global mycovirus studies. Viruses 2024, 16, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.; Wu, M.; Li, G. Characterization of a novel genomovirus in the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea. Virology 2021, 553, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.E.; MacDiarmid, R.M. A mechanically transmitted DNA mycovirus is targeted by the defence machinery of its host, Botrytis cinerea. Viruses 2021, 13, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Padilla, A.; Turina, M.; Ayllón, M.A. Molecular characterization of a tetra segmented ssDNA virus infecting Botrytis cinerea worldwide. Virol. J. 2023, 20, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.D.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.Q.; Jiang, D.H.; Hou, M.S.; Huang, H.C. Hypovirulence and double-stranded RNA in Botrytis cinerea. Phytopathology 2007, 97, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Jiang, D.; Ghabrial, S.A. Genome characterization of a debilitation-associated mitovirus infecting the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea. Virology 2010, 406, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; De Wu, M.; Li, G.Q.; Jiang, D.H.; Huang, H.C. Effect of Mitovirus infection on formation of infection cushions and virulence of Botrytis cinerea. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 75, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Jin, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Jiang, D.; Li, G. Characterization of a novel bipartite double-stranded RNA mycovirus conferring hypovirulence in the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis porri. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Sang, W.; Wu, M.-D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.-J.; Chen, W.-D.; Li, G.-Q. Novel hypovirulence-associated RNA mycovirus in the plant-pathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea: Molecular and biological characterization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2299–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruzzaman, M.; He, G.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, G. A novel partitivirus in the hypovirulent isolate QT5-19 of the plant pathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea. Viruses 2019, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Khan, H.A.; Jamal, A.; Virk, N.; Bhatti, M.F. Characterization of two novel fusariviruses co-infecting a single isolate of phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea. Virus Genes 2024, 60, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Ding, T.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, G. Two novel hypovirulence-associated mycoviruses in the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea: Molecular characterization and suppression of infection cushion formation. Viruses 2018, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdoba, L.; Ruiz-Padilla, A.; Rodríguez-Romero, J.; Ayllón, M.A. Construction and characterization of a Botrytis virus F infectious clone. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottet, L.; Armijo-Godoy, G.; Castillo, A. Heterologous expression of the hypovirus CHV1-EP713 full-length cDNA in Botrytis cinerea: Transformation with Agrobacterium tumefaciens and evaluation of changes in the fungal phenotype. Biol. Res. 2025, 58, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V.; Krupovic, M.; Kuhn, J.H. Viruses defined by the position of the virosphere within the replicator space. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e0019320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galligan, J.T.; Kennell, J.C. Retroplasmids: Linear and circular plasmids that replicate via reverse transcription. In Microbial Linear Plasmids; Meinhardt, F., Klassen, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 163–185. [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush, T.H. Telomerase and retrotransposons: Which came first? Science 1997, 277, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, T.C.; Kennell, J.C. Linear mitochondrial plasmids of F. oxysporum are novel, telomere-like retroelements. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-C.; Kennell, J.C.; Leslie, W.A.; Lambowitz, A.M. A mitochondrial retroplasmid integrates into mitochondrial DNA by a novel mechanism involving the synthesis of a hybrid cDNA and homologous recombination. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 6419–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akins, R.A.; Kelley, R.L.; Lambowitz, A.M. Mitochondrial plasmids of Neurospora: Integration into mitochondrial DNA and evidence for reverse transcription in mitochondria. Cell 1986, 47, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, S.; Wanner, L.A.; Bertrand, H.; Lambowitz, A.M. Characterization of an unusual tRNA-like sequence found inserted in a Neurospora retroplasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahan, P.; Kennell, J.C. Identification and distribution of sequences having similarity to mitochondrial plasmids in mitochondrial genomes of filamentous fungi. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2005, 273, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idnurm, A. Mystique of Phycomyces blakesleeanus is a peculiar mitochondrial genetic element that is highly variable in DNA sequence while subjected to strong negative selection. J. Genet. 2018, 97, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Shu, F.; Ma, X.; Bian, Y. The mitochondrial genome of Morchella importuna (272.2 kb) is the largest among fungi and contains numerous introns, mitochondrial non-conserved open reading frames and repetitive sequences. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, A.; Wang, F.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, N. The 206 kbp mitochondrial genome of Phanerochaete carnosa reveals dynamics of introns, accumulation of repeat sequences and plasmid-derived genes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, M.; Groeneveld, J.; Aanen, D.K. Horizontal transfer of tRNA genes to mitochondrial plasmids facilitates gene loss from fungal mitochondrial DNA. Curr. Genet. 2023, 69, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.A.; Stohl, L.L.; Cole, M.D.; Lambowitz, A.M. Characterization of a novel plasmid DNA found in mitochondria of N. crassa. Cell 1981, 24, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nargang, F.E.; Bell, J.B.; Stohl, L.L.; Lambowitz, A.M. The DNA sequence and genetic organization of a Neurospora mitochondrial plasmid suggest a relationship to introns and mobile elements. Cell 1984, 38, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.G.; Finnegan, P.M. RNA plasmids. In International Review of Cytology; Bourne, G.H., Jeon, K.W., Friedlander, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989; Volume 117, pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chiba, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Ikeda, A.; Miyashita, S.; Hagiwara, D.; Urayama, S.-i. Plasmid-like dynamics of persistent RNA viruses in the host fungal population. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e00582-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polashock, J.J.; Hillman, B.I. A small mitochondrial double-stranded (ds) RNA element associated with a hypovirulent strain of the chestnut blight fungus and ancestrally related to yeast cytoplasmic T and W dsRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8680–8684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Eickbush, T.H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 3353–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, C.; Soriano, B.; Krupovic, M.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Metaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 1131–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, C.; Soriano, B.; Krupovic, M.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Pseudoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Cheng, J.; Tang, J.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Baker Timothy, S.; Ghabrial Said, A.; Xie, J. A novel partitivirus that confers hypovirulence on plant pathogenic fungi. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10120–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amselem, J.; Cuomo, C.A.; van Kan, J.A.L.; Viaud, M.; Benito, E.P.; Couloux, A.; Coutinho, P.M.; de Vries, R.P.; Dyer, P.S.; Fillinger, S.; et al. Genomic analysis of the necrotrophic fungal pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes de novo assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Reuter, K.; Drost, H.-G. Sensitive protein alignments at tree-of-life scale using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabler, F.; Nam, S.-Z.; Till, S.; Mirdita, M.; Steinegger, M.; Söding, J.; Lupas, A.N.; Alva, V. Protein sequence analysis using the MPI bioinformatics toolkit. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 72, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, X.; Tang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, B.; et al. A group of segmented viruses contains genome segments sharing homology with multiple viral taxa. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0033225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Muscle5: High-accuracy alignment ensembles enable unbiased assessments of sequence homology and phylogeny. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenwyk, J.L.; Buida, T.J., III; Li, Y.; Shen, X.-X.; Rokas, A. ClipKIT: A multiple sequence alignment trimming software for accurate phylogenomic inference. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3001007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, L.; Luo, X.; Chen, M.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; Dai, Z.; Lam, T.T.; Guan, Y.; Yu, G. Ggtree: A serialized data object for visualization of a phylogenetic tree and annotation data. iMeta 2022, 1, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staats, M.; van Baarlen, P.; van Kan, J.A.L. Molecular phylogeny of the plant pathogenic genus Botrytis and the evolution of host specificity. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 22, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.D.; Nilsson, R.H.; Alias, S.A.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Blair, J.E.; Cai, L.; de Cock, A.W.A.M.; Dissanayake, A.J.; Glockling, S.L.; Goonasekara, I.D.; et al. One stop shop: Backbones trees for important phytopathogenic genera: I (2014). Fungal Divers. 2014, 67, 21–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, E.; Giraud, T.; Loiseau, A.; Vautrin, D.; Estoup, A.; Solignac, M.; Cornuet, J.M.; Brygoo, Y. Characterization of nine polymorphic microsatellite loci in the fungus Botrytis cinerea (Ascomycota). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2002, 2, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tian, L.; Tan, J.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; O’Neil, N.; Hirst, M.; Hieter, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Distribution of haploid chromosomes into separate nuclei in two pathogenic fungi. Science 2025, 388, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, F.; Xie, J.; Cheng, S.; You, M.P.; Barbetti, M.J.; Jia, J.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. Virome characterization of a collection of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum from Australia. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, G. Viral cross-class transmission results in disease of a phytopathogenic fungus. ISME J. 2022, 16, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; He, Y.; Fang, P.; Mei, S.-Q.; Xu, Z.; Wu, W.-C.; Tian, J.-H.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, Z.-Y.; Gou, Q.-Y.; et al. Using artificial intelligence to document the hidden RNA virosphere. Cell 2024, 187, 6929–6942.e6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Taylor, J.; Lin, V.; Altman, T.; Barbera, P.; Meleshko, D.; Lohr, D.; Novakovsky, G.; Buchfink, B.; Al-Shayeb, B.; et al. Petabase-scale sequence alignment catalyses viral discovery. Nature 2022, 602, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, B.; Steenkamp, E.; Wingfield, B.; Read, D. Fungal viruses unveiled: A comprehensive review of mycoviruses. Viruses 2023, 15, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Xu, C.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Jiang, J.; Lv, R.; Kong, L.; Li, S.; Hong, N.; Wang, G.; Coutts, R.H.A.; et al. Novel viroid-like RNAs naturally infect a filamentous fungus. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2204308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgia, M.; Navarro, B.; Daghino, S.; Cervera, A.; Gisel, A.; Perotto, S.; Aghayeva, D.N.; Akinyuwa, M.F.; Gobbi, E.; Zheludev, I.N.; et al. Hybrids of RNA viruses and viroid-like elements replicate in fungi. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dálya, L.B.; Hejna, O.; de la Peña, M.; Stanivuković, Z.; Kudláček, T.; Botella, L. Diversity of RNA viruses and circular viroid-like elements in Heterobasidion spp. in near-natural forests of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Viruses 2025, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.D.; Neri, U.; Roux, S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Camargo, A.P.; Krupovic, M.; Simmonds, P.; Kyrpides, N.; Gophna, U.; Dolja, V.V.; et al. Mining metatranscriptomes reveals a vast world of viroid-like circular RNAs. Cell 2023, 186, 646–661.e644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheludev, I.N.; Edgar, R.C.; Lopez-Galiano, M.J.; de la Peña, M.; Babaian, A.; Bhatt, A.S.; Fire, A.Z. Viroid-like colonists of human microbiomes. Cell 2024, 187, 6521–6536.e6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausner, G. Fungal mitochondrial genomes, plasmids and introns. In Applied Mycology and Biotechnology; Arora, D.K., Khachatourians, G.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 101–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hausner, G. Introns, mobile elements, and plasmids. In Organelle Genetics: Evolution of Organelle Genomes and Gene Expression; Bullerwell, C.E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 329–357. [Google Scholar]
- van der Gaag, M.; Debets, A.J.M.; Osiewacz, H.D.; Hoekstra, R.F. The dynamics of pAL2-1 homologous linear plasmids in Podospora anserina. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1998, 258, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, C.B.; Fox, A.N.; Kennell, J.C. Senescence associated with the over-replication of a mitochondrial retroplasmid in Neurospora crassa. Mol. Gen. Genet. 2000, 263, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.N.; Kennell, J.C. Association between variant plasmid formation and senescence in retroplasmid-containing strains of Neurospora spp. Curr. Genet. 2001, 39, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, A.D.; Sultana, S.; Maheshwari, R. Characterization and prevalence of a circular mitochondrial plasmid in senescence-prone isolates of Neurospora intermedia. Curr. Genet. 2005, 47, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, J.; Hausner, G. Organellar introns in fungi, algae, and plants. Cells 2021, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinget, B.; Bélanger, R.R. Discovery of new group I-D introns leads to creation of subtypes and link to an adaptive response of the mitochondrial genome in fungi. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorova, O.; Luo, M.; Jagdmann, G.E., Jr.; Van Zandt, M.C.; Sisto, L.; Pyle, A.M. Novel quinazoline derivatives inhibit splicing of fungal group II introns. ACS Chem. Biol. 2025, 20, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorova, O.; Jagdmann, G.E.; Adams, R.L.; Yuan, L.; Van Zandt, M.C.; Pyle, A.M. Small molecules that target group II introns are potent antifungal agents. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baidyaroy, D.; Hausner, G.; Hafez, M.; Michel, F.; Fulbright, D.W.; Bertrand, H. A 971-bp insertion in the rns gene is associated with mitochondrial hypovirulence in a strain of Cryphonectria parasitica isolated from nature. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Family | Query | Length (bp) | Hit Length | Hit Accession | Hit Title | Coverage (%) | Identity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitoviridae | BcMV1 | 2808 | 2788 | MT119677 | Botrytis cinerea mitovirus 1 isolate BCS1_DN4879 | 99 | 98 | |
| BcMV2/KY-1 | 2506 | 2486 | PV443060 | Botrytis cinerea mitovirus 2 isolate IBc-374 | 99 | 96 | ||
| BcMV3/KY-1V1 | 2895 | 2870 | ON738336 | Botrytis cinerea mitovirus 3 isolate VPS3 | 98 | 93 | ||
| BcMV9/KY-1V1 | 2737 | 2720 | MT089704 | Botrytis cinerea mitovirus 9 isolate BCS1_DN2958 | 99 | 96 | ||
| SsMV3/KY-1V1 | 2591 | 2588 | NC_076556 | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum mitovirus 3 | 100 | 93 | ||
| “Ambiguiviridae” | SsULV3/KY-1V1 | 4003 | 3981 | MT230952 | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum umbra-like virus 3 isolate BCS17_DN25 | 92 | 97 | |
| Partitiviridae | BcPV1/ KY-1 | dsRNA1 | 1795 | 1780 | MN954881 | Botryotinia fuckeliana partitivirus 1 isolate BCS3_DN4616 segment RNA1 | 99 | 99 |
| 1793 | AM491609 | Botryotinia fuckeliana partitivirus 1, complete segment 1 | 100 | 98 | ||||
| dsRNA2 | 1594 | 1597 | MN954882 | Botryotinia fuckeliana partitivirus 1 isolate BCI12_DN10399 segment RNA2 | 99 | 96 | ||
| 1566 | AM491610 | Botryotinia fuckeliana partitivirus 1, complete segment 2 | 98 | 91 | ||||
| dsRNA3 | 1298 | n.a. | n.a. | No significant hit. | n.a. | n.a. | ||
| BcPV3/ KY-1V1 | dsRNA1 | 1784 | 1769 | MF444214 | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum partitivirus 3 isolate SsPV3 RdRP gene | 99 | 95 | |
| 1762 | MN954884 | Botrytis cinerea partitivirus 3 isolate BCS4_DN10017 segment RNA1 | 99 | 96 | ||||
| dsRNA2 | 1555 | 1547 | MF444213 | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum partitivirus 2 isolate SsPV2 coat protein gene | 98 | 97 | ||
| 1537 | MN954883 | Botrytis cinerea partitivirus 3 isolate BCS4_DN5031 segment RNA2 | 99 | 89 | ||||
| dsRNA3 | 1260 | n.a. | n.a. | No significant hit. | n.a. | n.a. | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Cai, Q.; Lin, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, B.; Yu, X.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, D.; et al. The Viruses of Botrytis cinerea and Beyond: Molecular Characterization of RNA Viruses and Retroplasmids. Viruses 2025, 17, 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121527
Huang H, Cheng J, Fu Y, Cai Q, Lin Y, Chen T, Li B, Yu X, Xiao X, Jiang D, et al. The Viruses of Botrytis cinerea and Beyond: Molecular Characterization of RNA Viruses and Retroplasmids. Viruses. 2025; 17(12):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121527
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Huang, Jiasen Cheng, Yanping Fu, Qing Cai, Yang Lin, Tao Chen, Bo Li, Xiao Yu, Xueqiong Xiao, Daohong Jiang, and et al. 2025. "The Viruses of Botrytis cinerea and Beyond: Molecular Characterization of RNA Viruses and Retroplasmids" Viruses 17, no. 12: 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121527
APA StyleHuang, H., Cheng, J., Fu, Y., Cai, Q., Lin, Y., Chen, T., Li, B., Yu, X., Xiao, X., Jiang, D., & Xie, J. (2025). The Viruses of Botrytis cinerea and Beyond: Molecular Characterization of RNA Viruses and Retroplasmids. Viruses, 17(12), 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121527









