Mounting Evidence for an Expanded Host Range of Influenza B Viruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Models of IBV Infection to Inform Transmission and Host Species Restriction
3. Evidence of IBV Infections in Animals
4. IBV-like Viruses from Fish and Amphibians
| HA | NA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor Specificity 1 | HA Activity 2 | Fusogenic Activity 3 | Protease Cleavage Profile | Enzymatic Activity 6 | Inhibitor Susceptibility | |
| IBV | α2,3-linked sialic acid α2,6 linked sialic acid | Yes | Fusogenic at a range of pH conditions (4.5–5.9) | Cleavable by various human TTSPs and KLKs 5 | Yes | Peramivir > Zanamivir > Oseltamivir |
| SILV | Unknown, did not interact with sialic acids | No | Not detected 4 | Not cleavable by human TTSPs and KLKs or trypsin | Not tested | Not tested |
| SAEILV | α2,3-linked sialic acid sialyated Lewis X | Yes | Fusogenic at a range of pH conditions (4.5–5.9) | Cleavable by TMPRSS4, TMPRSS13, KLK5, KLK14 | Yes | Zanamivir > Peramivir > Oseltamivir |
| CSILV | α2,3-linked sialic acid | Yes | Not detected 4 | Not cleavable by human TTSPs and KLKs or trypsin | Not tested | Not tested |
| WSEIV | monosialic ganglioside 2 (GM2) | No | Fusogenic at a range of pH conditions (4.5–5.9) | Not cleavable by human TTSPs and KLKs, cleavable by trypsin | Yes | Peramivir > Zanamivir > Oseltamivir |
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wille, M.; Holmes, E.C. The Ecology and Evolution of Influenza Viruses. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a038489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Smith, G.J.D.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Peiris, M.; Kedzierska, K.; Doherty, P.C.; Palese, P.; Shaw, M.L.; Treanor, J.; Webster, R.G.; et al. Influenza. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://ictv.global/report_9th/RNAneg/Orthomyxoviridae (accessed on 29 October 2025).
- Koutsakos, M.; Kedzierska, K.; Subbarao, K. Immune Responses to Avian Influenza Viruses. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Sandt, C.E.; Bodewes, R.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; de Vries, R.D. Influenza B Viruses: Not to Be Discounted. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1447–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsakos, M.; Nguyen, T.H.; Barclay, W.S.; Kedzierska, K. Knowns and Unknowns of Influenza B Viruses. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaraket, H.; Hurt, A.C.; Clinch, B.; Barr, I.; Lee, N. Burden of Influenza B Virus Infection and Considerations for Clinical Management. Antivir. Res. 2021, 185, 104970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsakos, M.; Kent, S.J. Influenza B viruses: Underestimated and overlooked. Microbiol. Aust. 2021, 42, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensen, L.; Kedzierska, K.; Koutsakos, M. Innate and Adaptive Immunity Toward Influenza B Viruses. Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsakos, M.; Wheatley, A.K.; Laurie, K.; Kent, S.J.; Rockman, S. Influenza Lineage Extinction During the COVID-19 Pandemic? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 741–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanasekaran, V.; Sullivan, S.; Edwards, K.M.; Xie, R.; Khvorov, A.; Valkenburg, S.A.; Cowling, B.J.; Barr, I.G. Human Seasonal Influenza under COVID-19 and the Potential Consequences of Influenza Lineage Elimination. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsakos, M.; Rockman, S.; Krammer, F. Is Eradication of Influenza B Viruses Possible? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, J.; Onta, T.; Kida, H.; Yanagawa, R. Distribution of Antibodies in Animals against Influenza B and C Viruses. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 1978, 26, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Z.; Shen, H.; Lang, Y.; Kolb, E.A.; Turan, N.; Zhu, L.; Ma, J.; Bawa, B.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; et al. Domestic Pigs Are Susceptible to Infection with Influenza B Viruses. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4818–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.P.; Tsai, H.J. Influenza B Viruses in Pigs, Taiwan. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2019, 13, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buitendijk, H.; Fagrouch, Z.; Niphuis, H.; Bogers, W.M.; Warren, K.S.; Verschoor, E.J. Retrospective Serology Study of Respiratory Virus Infections in Captive Great Apes. Viruses 2014, 6, 1442–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horimoto, T.; Gen, F.; Murakami, S.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Kato, K.; Akashi, H.; Hisasue, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Kawaoka, Y.; Maeda, K. Serological Evidence of Infection of Dogs with Human Influenza Viruses in Japan. Vet. Rec. 2014, 174, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.H.; Harris, P.A.; Alexander, D.J. Serological Studies of Influenza Viruses in Pigs in Great Britain 1991-2. Epidemiol. Infect. 1995, 114, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodewes, R.; Morick, D.; de Mutsert, G.; Osinga, N.; Bestebroer, T.; van der Vliet, S.; Smits, S.L.; Kuiken, T.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Recurring Influenza B Virus Infections in Seals. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Martina, B.E.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Fouchier, R.A. Influenza B Virus in Seals. Science 2000, 288, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Measures, L.N.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Antibodies against Influenza Virus Types a and B in Canadian Seals. J. Wildl. Dis. 2021, 57, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, K.; Ninomiya, A.; Kida, H.; Park, C.H.; Maruyama, T.; Arai, T.; Katsumata, E.; Tobayama, T.; Boltunov, A.N.; Khuraskin, L.S.; et al. Serological Evidence of Transmission of Human Influenza A and B Viruses to Caspian Seals (Phoca caspica). Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 46, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydyrmanov, A.; Karamendin, K.; Kassymbekov, Y.; Kumar, M.; Mazkirat, S.; Suleimenova, S.; Baimukanov, M.; Carr, I.M.; Goodman, S.J. Exposure of Wild Caspian Seals (Pusa caspica) to Parasites, Bacterial and Viral Pathogens, Evaluated Via Molecular and Serological Assays. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1087997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamendin, K.; Goodman, S.J.; Kasymbekov, Y.; Kumar, M.; Nuralibekov, S.; Kydyrmanov, A. Viral Metagenomic Survey of Caspian Seals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1461135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, R.; Wille, M.; Turnbull, O.M.H.; Geoghegan, J.L.; Holmes, E.C. Divergent Influenza-Like Viruses of Amphibians and Fish Support an Ancient Evolutionary Association. Viruses 2020, 12, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Chen, X.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Li, K.; Wang, W.; Eden, J.S.; Shen, J.J.; Liu, L.; et al. The Evolutionary History of Vertebrate RNA Viruses. Nature 2018, 556, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belser, J.A.; Eckert, A.M.; Huynh, T.; Gary, J.M.; Ritter, J.M.; Tumpey, T.M.; Maines, T.R. A Guide for the Use of the Ferret Model for Influenza Virus Infection. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.S.H.; Banner, D.; Paquette, S.G.; Leon, A.J.; Kelvin, A.A.; Kelvin, D.J. Pathogenic Influenza B Virus in the Ferret Model Establishes Lower Respiratory Tract Infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Park, S.J.; Kwon, H.I.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, Y.I.; Song, M.S.; Choi, E.J.; Pascua, P.N.; Choi, Y.K. Mouse Adaptation of Influenza B Virus Increases Replication in the Upper Respiratory Tract and Results in Droplet Transmissibility in Ferrets. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrukee, R.; Zarebski, A.E.; McCaw, J.M.; Bloom, J.D.; Reading, P.C.; Hurt, A.C. Characterization of Influenza B Virus Variants with Reduced Neuraminidase Inhibitor Susceptibility. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascua, P.N.Q.; Jones, J.C.; Marathe, B.M.; Seiler, P.; Caufield, W.V.; Freeman, B.B., 3rd; Webby, R.J.; Govorkova, E.A. Baloxavir Treatment Delays Influenza B Virus Transmission in Ferrets and Results in Limited Generation of Drug-Resistant Variants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0113721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.C.; Pascua, P.N.Q.; Fabrizio, T.P.; Marathe, B.M.; Seiler, P.; Barman, S.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G.; Govorkova, E.A. Influenza A and B Viruses with Reduced Baloxavir Susceptibility Display Attenuated In Vitro Fitness but Retain Ferret Transmissibility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 8593–8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elderfield, R.A.; Koutsakos, M.; Frise, R.; Bradley, K.; Ashcroft, J.; Miah, S.; Lackenby, A.; Barclay, W.S. NB Protein Does Not Affect Influenza B Virus Replication In Vitro and Is Not Required for Replication in or Transmission between Ferrets. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schwab, L.S.U.; Do, T.H.T.; Pilapitiya, D.; Koutsakos, M. Dissemination of Influenza B Virus to the Lower Respiratory Tract of Mice Is Restricted by the Interferon Response. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0160423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Kim, H.M.; Kang, Y.M.; Ku, K.B.; Park, E.H.; Yum, J.; Kim, J.A.; Kang, Y.K.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Severe Pathogenesis of Influenza B Virus in Pregnant Mice. Virology 2014, 448, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pica, N.; Iyer, A.; Ramos, I.; Bouvier, N.M.; Fernandez-Sesma, A.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Lowen, A.C.; Palese, P.; Steel, J. The DBA.2 Mouse Is Susceptible to Disease Following Infection with a Broad, but Limited, Range of Influenza A and B Viruses. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12825–12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y.; Lee, I.; Kim, J.I.; Park, S.; Yoo, K.; Park, M.; Kim, G.; Park, M.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, C.; et al. A Single Amino Acid in the Polymerase Acidic Protein Determines the Pathogenicity of Influenza B Viruses. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pica, N.; Chou, Y.Y.; Bouvier, N.M.; Palese, P. Transmission of Influenza B Viruses in the Guinea Pig. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4279–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yang, C.; Xia, X.; Zanin, M.; Wong, S.S.; Yang, F.; Chang, J.; Mai, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The Tree Shrew Is a Promising Model for the Study of Influenza B Virus Infection. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottolini, M.G.; Blanco, J.C.G.; Eichelberger, M.C.; Porter, D.D.; Pletneva, L.; Richardson, J.Y.; Prince, G.A. The Cotton Rat Provides A Useful Small-Animal Model for the Study of Influenza Virus Pathogenesis. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2823–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Nakajima, N.; Ichiko, Y.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; Noda, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Kawaoka, Y. Syrian Hamster as an Animal Model for the Study of Human Influenza Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditchfield, J.; Macpherson, L.W. Zbitnew A: Upper Respiratory Disease in Thouroughbred Horses: Studies of Its Viral Etiology in the Toronto Area, 1960 to 1963. Can. J. Comp. Med. Vet. Sci. 1965, 29, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.P.; New, A.E.; Taylor, J.F.; Chiang, H.S. Influenza virus isolations from dogs during a human epidemic in Taiwan. Int. J. Zoonoses 1976, 3, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Leyva-Grado, V.H.; Mubareka, S.; Krammer, F.; Cardenas, W.B.; Palese, P. Influenza Virus Infection in Guinea Pigs Raised as Livestock, Ecuador. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.T.; Hou, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J.; He, H.; Si, W.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Xing, G.; et al. Virome Characterization of Game Animals in China Reveals a Spectrum of Emerging Pathogens. Cell 2022, 185, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.Y.; Yaqub, T.; Zhang, R.; Mukhtar, N.; Pervaiz, H.; Hussain Yawar, H.U.; Iqbal, M.; bin Aslam, H.; Aziz, M.W.; Akram, M.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5 Virus Exposure in goats and sheep. bioRxiv 2024. bioRxiv:2024.2008.2031.610397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, A.; Ruchansky, D.; Clara, M.; Achaval, F.; Le Bas, A.; Arbiza, J. Serologic Evidence of Influenza A and B Viruses in South American Fur Seals (Arctocephalus australis). J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epperson, S.; Jhung, M.; Richards, S.; Quinlisk, P.; Ball, L.; Moll, M.; Boulton, R.; Haddy, L.; Biggerstaff, M.; Brammer, L.; et al. Human Infections with Influenza A(H3N2) Variant Virus in the United States, 2011–2012. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57 (Suppl. S1), S4–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, A.; Bevins, S.; Chandler, J.; DeLiberto, T.J.; Ghai, R.; Lantz, K.; Lenoch, J.; Retchless, A.; Shriner, S.; Tang, C.Y.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Free-Ranging White-Tailed Deer in the United States. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oude Munnink, B.B.; Sikkema, R.S.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.F.; Molenaar, R.J.; Munger, E.; Molenkamp, R.; van der Spek, A.; Tolsma, P.; Rietveld, A.; Brouwer, M.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on Mink Farms between Humans and Mink and Back to Humans. Science 2021, 371, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.L.; Sit, T.H.C.; Brackman, C.J.; Chuk, S.S.Y.; Gu, H.; Tam, K.W.S.; Law, P.Y.T.; Leung, G.M.; Peiris, M.; Poon, L.L.M.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant (AY.127) from Pet Hamsters to Humans, Leading to Onward Human-to-Human Transmission: A case study. Lancet 2022, 399, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.Y.K.; Donato, C.; Deng, Y.M.; Teng, D.; Komadina, N.; Baas, C.; Modak, J.; O’Dea, M.; Smith, D.W.; Effler, P.V.; et al. Divergent Human-Origin Influenza Viruses Detected in Australian Swine Populations. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, A.M.; van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Isolation of a Novel Coronavirus from a Man with Pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; He, Y.; Fang, P.; Mei, S.Q.; Xu, Z.; Wu, W.C.; Tian, J.H.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Gou, Q.Y.; et al. Using Artificial Intelligence to Document the Hidden RNA Virosphere. Cell 2024, 187, 6929–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Shi, M.; Holmes, E.C. Using Metagenomics to Characterize an Expanding Virosphere. Cell 2018, 172, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Huang, J.; Bhavsar, D.; Vasilev, K.; Ferguson, J.A.; Boons, G.J.; Simon, V.; de Vries, R.P.; Han, J.; Ward, A.; et al. Characterization of the Glycoproteins of Fish and Amphibian Influenza B-Like Viruses. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eady8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunkumar, G.A.; Bhavsar, D.; Li, T.; Strohmeier, S.; Chromikova, V.; Amanat, F.; Bunyatov, M.; Wilson, P.C.; Ellebedy, A.H.; Boons, G.J.; et al. Functionality of the Putative Surface Glycoproteins of the Wuhan Spiny Eel Influenza Virus. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, M.; Stevaert, A.; Raeymaekers, V.; Boogaerts, T.; Nehlmeier, I.; Chiu, W.; Benkheil, M.; Vanaudenaerde, B.; Pohlmann, S.; Naesens, L. Hemagglutinin Cleavability, Acid Stability, and Temperature Dependence Optimize Influenza B Virus for Replication in Human Airways. J. Virol. 2019, 94, e01430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.H.T.; Wheatley, A.K.; Kent, S.J.; Koutsakos, M. Influenza B Virus Neuraminidase: A Potential Target for Next-Generation Vaccines? Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2024, 23, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chai, Y.; Peng, W.; Li, D.; Sun, L.; Gao, G.F.; Qi, J.; Xiao, H.; Liu, W.J.; von Itzstein, M.; et al. Structural and inhibitor Sensitivity Analysis of Influenza B-Like Viral Neuraminidases Derived from Asiatic Toad and Spiny Eel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2210724119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
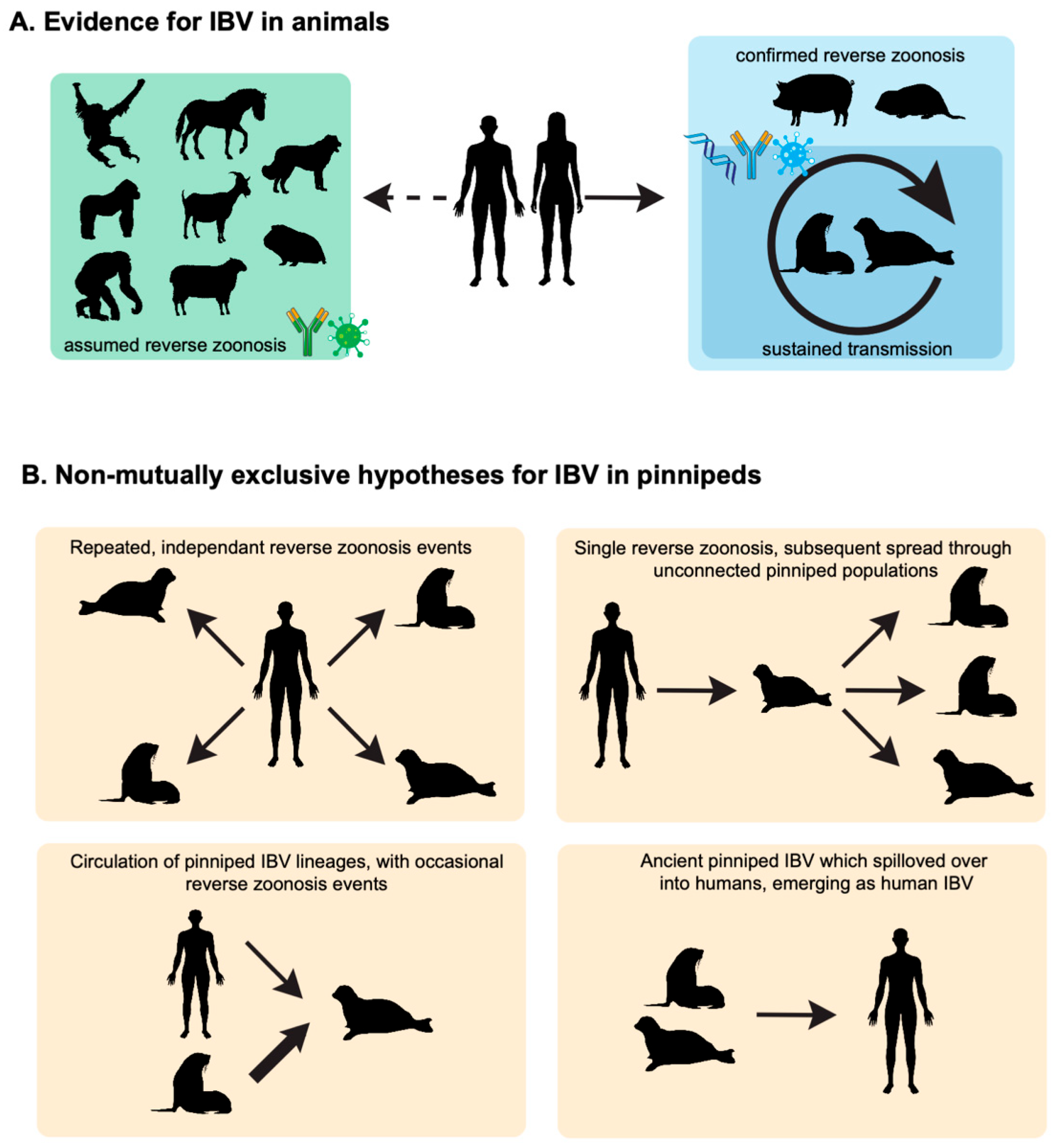
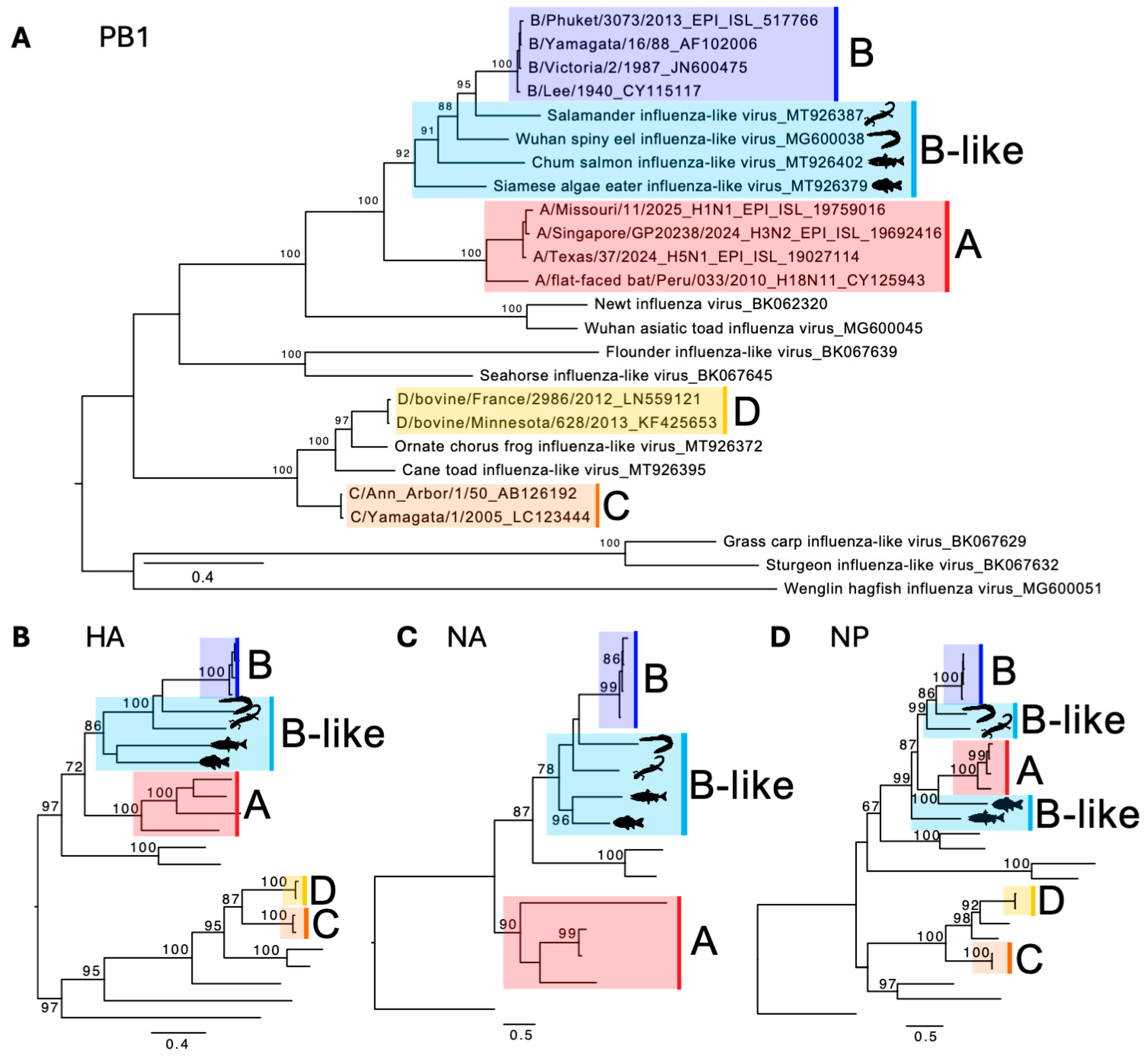
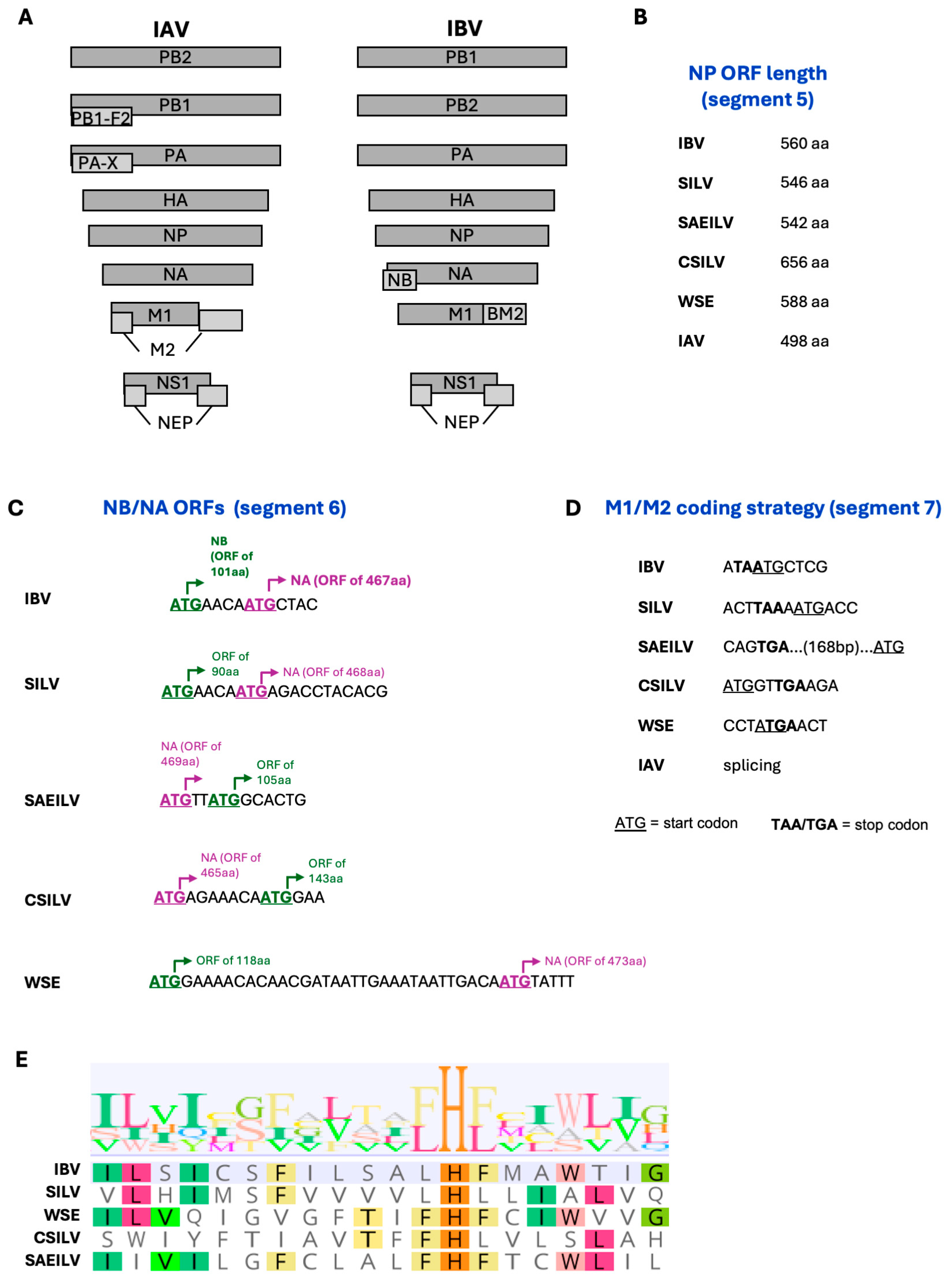
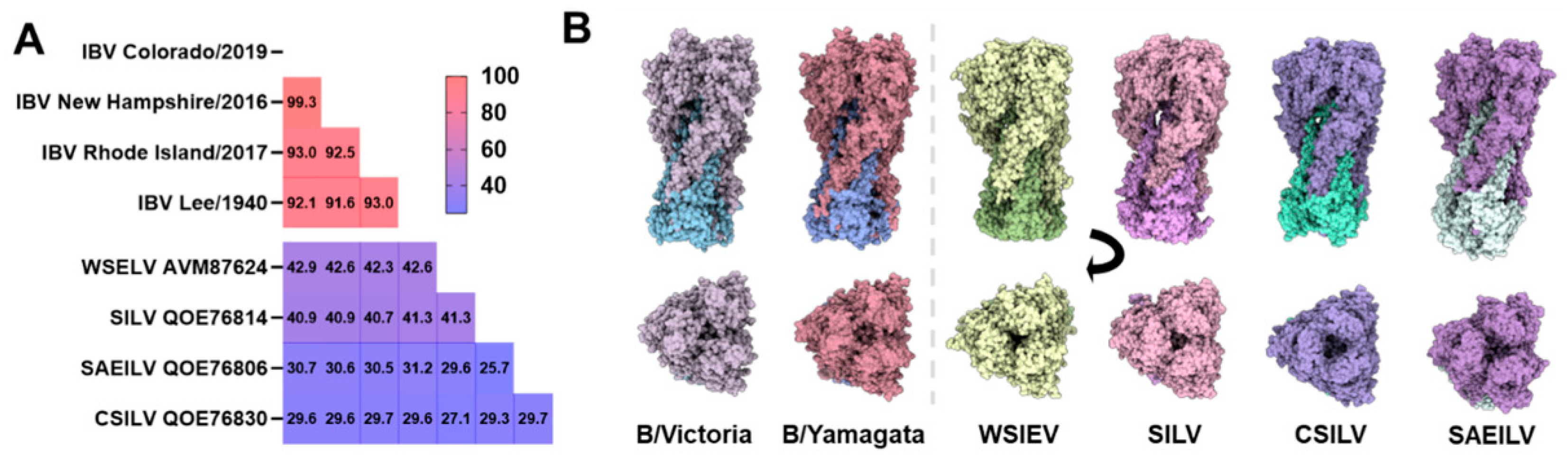
| Animal (Species Where Available) | Location, Year | Detection Methods | Frequency of Animals Positive | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animals in close contact with humans (pets, zoos, farms etc.) | ||||
| Horse | Japan, 1997 | HAI | 16/504 (3.2) | [13] |
| Horse | Canada, 1960–1963 | Complement fixation assay | Numbers not reported (30) | [42] |
| Pigs | Japan, 1997 | HAI | 1/1030 (0.1) | [13] |
| Pigs | USA, 2010–2012 | HAI, verified by NT | 41/560 (7.3), 3 RT-PCR+ nasal swabs | [14] |
| Pigs | Great Britain, October 1991–February 1992 | HAI, verified by NT and immunoblot | 8/2000 (0.4) | [18] |
| Pigs | Taiwan, 2007–2017 | HAI | 31/15,983 (0.2), 3 nasal swabs with culturable IBV | [15] |
| Goats | Pakistan, 2023 | Luminex assay to HA | 32/452 (7.1) | [46] |
| Sheep | Pakistan, 2023 | Luminex assay to HA | 15/329 (4.6) | [46] |
| Dogs | Taiwan, 1971 | Virus isolation from nasal swabs | 1/372 (0.3) | [43] |
| Dogs | Japan, 2009–2020 | NT, verified by immunoblot | 6/366 (1.6) | [17] |
| Guinea pigs | Ecuador | ELISA with whole virus, recombinant HA and NP, verified by immunoblot | 28/40 (70) | [44] |
| Bamboo rats | China, 2020 | Metagenomics | 1 full genome recovered | [45] |
| Chimpanzees | Netherlands, 1986, 1992, 1998, 2000 | Magnetic bead-based assay, verified by immunoblot | 80/305 (26.2) | [16] |
| Gorillas | Not specified, reported in 2014 | Magnetic bead-based assay, verified by immunoblot | 45/77 (58.4) | [16] |
| Orangutans | Indonesia, 1994–1998 | Magnetic bead-based assay, verified by immunoblot | 135/179 (75.4) | [16] |
| Wild animals | ||||
| Harbour seals (Phoca viulina) and grey seals (Halichoreus grypus) | Netherlands, 1995–1999 | HAI and ELISA to HA, NA, and NP | 0/580 < 1995 8/391 (2) 1995–1999 1 RT-PCR+ throat swab in 1999 | [20] |
| Harbour seals (Phoca viulina) and grey seals (Halichoreus grypus) | Netherlands, 2002–2012 | HAI | 10/71 2010–2011 0/454 (0) all other years | [19] |
| Caspian seals (Phoca capsica) | Caspian Sea, 1997–2000 | ELISA with whole virus | 5/77 (6) | [22] |
| South American fur seals (Arctocephalus australis) | Uruguay, 2004 | HAI | 25/37 (67.6) | [47] |
| Caspian seals (Phoca capsica) | Caspian Sea, 2007–2017 | HAI | 14/70 (20) | [23] |
| Caspian seals (Phoca capsica) | Caspian Sea, 2020 | metagenomics, confirmed by RT-PCR | partial PB2 and NS2 gene segment detected in spleen of dead animal in 2020 | [24] |
| Hooded seal (Cystophora cristata) Grey seal (Halichoerus grypus) Harbour seal (Phoca vitulina) Harp seal (Pagophilus groenlandica) | Canada, 1994, 2005 | ELISA, followed up by HAI | 29/394 (7.4%) by ELISA all negative by HAI | [21] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koutsakos, M.; Parry, R.H.; Wille, M. Mounting Evidence for an Expanded Host Range of Influenza B Viruses. Viruses 2025, 17, 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121528
Koutsakos M, Parry RH, Wille M. Mounting Evidence for an Expanded Host Range of Influenza B Viruses. Viruses. 2025; 17(12):1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121528
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoutsakos, Marios, Rhys H. Parry, and Michelle Wille. 2025. "Mounting Evidence for an Expanded Host Range of Influenza B Viruses" Viruses 17, no. 12: 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121528
APA StyleKoutsakos, M., Parry, R. H., & Wille, M. (2025). Mounting Evidence for an Expanded Host Range of Influenza B Viruses. Viruses, 17(12), 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121528








