Viromics Reveal a Number of Novel RNA Viruses in Swedish Mosquitoes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mosquito Collection, Species Separation and Pool Design
2.2. Homogenisation, Nucleic acid Extraction, Pre-Sequencing Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. Metagenomics Data Analysis
2.4. PCR Gap Closure of Viral Genome
2.5. Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Mosquito Collection
3.2. The Mosquito Viromes
3.3. Diverse Distribution of Viral Reads
3.4. Positive-Sense RNA Viruses
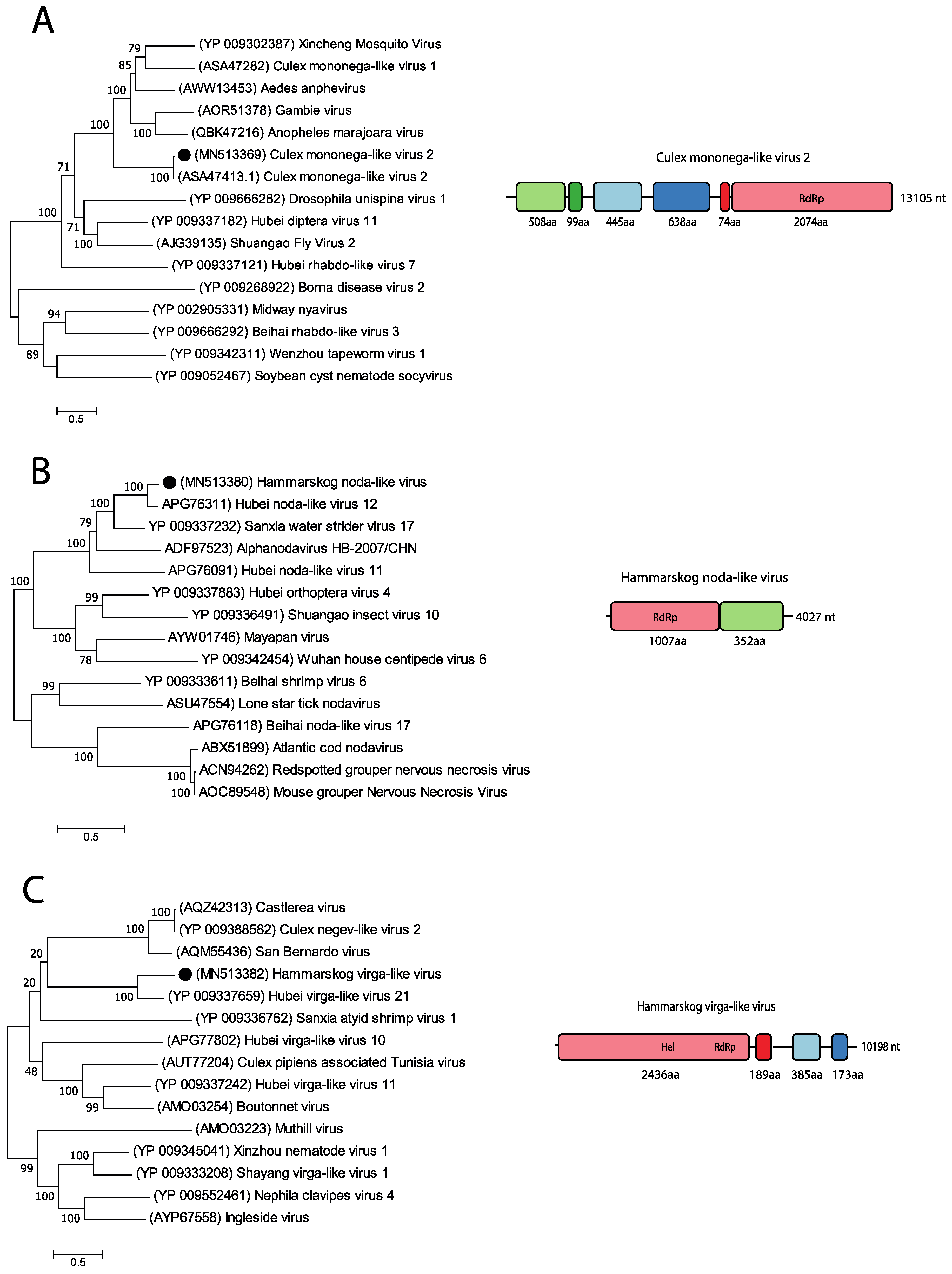
3.5. Negative-Sense RNA Viruses
3.6. Unclassified Viruses
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizzoli, A.; Jimenez-Clavero, M.A.; Barzon, L.; Cordioli, P.; Figuerola, J.; Koraka, P.; Martina, B.; Moreno, A.; Nowotny, N.; Pardigon, N.; et al. The challenge of West Nile virus in Europe: Knowledge gaps and research priorities. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauci, A.S.; Morens, D.M. Zika Virus in the Americas—Yet Another Arbovirus Threat. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.A.; Dermody, T.S. Chikungunya virus: Epidemiology, replication, disease mechanisms, and prospective intervention strategies. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, J.P.; Brady, O.J.; Scott, T.W.; Zou, C.; Pigott, D.M.; Duda, K.A.; Bhatt, S.; Katzelnick, L.; Howes, R.E.; Battle, K.E.; et al. Global spread of dengue virus types: Mapping the 70 year history. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.X.; Qin, X.C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.P.; Eden, J.S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Altan, E.; Deng, X.; Barker, C.M.; Fang, Y.; Coffey, L.L.; Delwart, E. Virome of >12 thousand Culex mosquitoes from throughout California. Virology 2018, 523, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Kang, Y.J.; Chen, L.J.; Qin, X.C.; Xu, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, K.G.; Biser, T.; Hamilton, T.; Santos, C.J.; Pimentel, G.; Mokashi, V.P.; Bishop-Lilly, K.A. Bioinformatic Characterization of Mosquito Viromes within the Eastern United States and Puerto Rico: Discovery of Novel Viruses. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2016, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junglen, S.; Drosten, C. Virus discovery and recent insights into virus diversity in arthropods. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.L.; Longdon, B.; Lewis, S.H.; Obbard, D.J. Twenty-Five New Viruses Associated with the Drosophilidae (Diptera). Evol. Bioinform. Online 2016, 12, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolling, B.G.; Olea-Popelka, F.J.; Eisen, L.; Moore, C.G.; Blair, C.D. Transmission dynamics of an insect-specific flavivirus in a naturally infected Culex pipiens laboratory colony and effects of co-infection on vector competence for West Nile virus. Virology 2012, 427, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hobson-Peters, J.; Yam, A.W.; Lu, J.W.; Setoh, Y.X.; May, F.J.; Kurucz, N.; Walsh, S.; Prow, N.A.; Davis, S.S.; Weir, R.; et al. A new insect-specific flavivirus from northern Australia suppresses replication of West Nile virus and Murray Valley encephalitis virus in co-infected mosquito cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney, J.L.; Solberg, O.D.; Langevin, S.A.; Brault, A.C. Characterization of a novel insect-specific flavivirus from Brazil: Potential for inhibition of infection of arthropod cells with medically important flaviviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2796–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goenaga, S.; Kenney, J.L.; Duggal, N.K.; Delorey, M.; Ebel, G.D.; Zhang, B.; Levis, S.C.; Enria, D.A.; Brault, A.C. Potential for Co-Infection of a Mosquito-Specific Flavivirus, Nhumirim Virus, to Block West Nile Virus Transmission in Mosquitoes. Viruses 2015, 7, 5801–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasar, F.; Erasmus, J.H.; Haddow, A.D.; Tesh, R.B.; Weaver, S.C. Eilat virus induces both homologous and heterologous interference. Virology 2015, 484, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall-Mendelin, S.; McLean, B.J.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Hall, R.A.; van den Hurk, A.F. The insect-specific Palm Creek virus modulates West Nile virus infection in and transmission by Australian mosquitoes. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklewitz, M.; Zirkel, F.; Kurth, A.; Drosten, C.; Junglen, S. Evolutionary and phenotypic analysis of live virus isolates suggests arthropod origin of a pathogenic RNA virus family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7536–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crochu, S.; Cook, S.; Attoui, H.; Charrel, R.N.; De Chesse, R.; Belhouchet, M.; Lemasson, J.J.; de Micco, P.; de Lamballerie, X. Sequences of flavivirus-related RNA viruses persist in DNA form integrated in the genome of Aedes spp. mosquitoes. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 1971–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholleti, H.; Hayer, J.; Abilio, A.P.; Mulandane, F.C.; Verner-Carlsson, J.; Falk, K.I.; Fafetine, J.M.; Berg, M.; Blomstrom, A.L. Discovery of Novel Viruses in Mosquitoes from the Zambezi Valley of Mozambique. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Neville, P.; Nicholson, J.; Eden, J.S.; Imrie, A.; Holmes, E.C. High-Resolution Metatranscriptomics Reveals the Ecological Dynamics of Mosquito-Associated RNA Viruses in Western Australia. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlm, C.; Eliasson, M.; Vapalahti, O.; Evander, M. Seroprevalence of Sindbis virus and associated risk factors in northern Sweden. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lwande, O.W.; Bucht, G.; Ahlm, C.; Ahlm, K.; Naslund, J.; Evander, M. Mosquito-borne Inkoo virus in northern Sweden-isolation and whole genome sequencing. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putkuri, N.; Kantele, A.; Levanov, L.; Kivisto, I.; Brummer-Korvenkontio, M.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Acute Human Inkoo and Chatanga Virus Infections, Finland. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lundstrom, J.O. Mosquito-borne viruses in western Europe: A review. J. Vector Ecol. 1999, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hubalek, Z. Mosquito-borne viruses in Europe. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103 (Suppl. 1), S29–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Petric, D.; Zgomba, M.; Boase, C.; Dahl, C.; Madon, M.; Kaiser, A. Mosquitoes and Their Control, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berling/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 1–577. [Google Scholar]
- Hesson, J.C.; Lundstrom, J.O.; Halvarsson, P.; Erixon, P.; Collado, A. A sensitive and reliable restriction enzyme assay to distinguish between the mosquitoes Culex torrentium and Culex pipiens. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2010, 24, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Attwood, T.K.; Babbitt, P.C.; Blum, M.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Brown, S.D.; Chang, H.Y.; El-Gebali, S.; Fraser, M.I.; et al. InterPro in 2019: Improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D351–D360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kall, L.; Krogh, A.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Advantages of combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction—the Phobius web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W429–W432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, S.Q.; Gascuel, O. An improved general amino acid replacement matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanborn, M.A.; Klein, T.A.; Kim, H.C.; Fung, C.K.; Figueroa, K.L.; Yang, Y.; Asafo-Adjei, E.A.; Jarman, R.G.; Hang, J. Metagenomic Analysis Reveals Three Novel and Prevalent Mosquito Viruses from a Single Pool of Aedes vexans nipponii Collected in the Republic of Korea. Viruses 2019, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Wolf, Y.I.; Nagasaki, K.; Dolja, V.V. The Big Bang of picorna-like virus evolution antedates the radiation of eukaryotic supergroups. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Gutierrez, M.A.; Nunes, M.R.T.; Guzman, H.; Uribe, S.; Suaza Vasco, J.D.; Cardoso, J.F.; Popov, V.L.; Widen, S.G.; Wood, T.G.; Vasilakis, N.; et al. Sinu virus, a novel and divergent orthomyxovirus related to members of the genus Thogotovirus isolated from mosquitoes in Colombia. Virology 2017, 501, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, P.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Ayllon, M.A.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Blasdell, K.R.; Briese, T.; Brown, P.A.; Bukreyev, A.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; et al. Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: Second update 2018. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahul Hameed, A.S.; Ninawe, A.S.; Nakai, T.; Chi, S.C.; Johnson, K.L.; ICTV Report Consortium. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Nodaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.J.; Adkins, S.; Bragard, C.; Gilmer, D.; Li, D.; MacFarlane, S.A.; Wong, S.M.; Melcher, U.; Ratti, C.; Ryu, K.H.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Virgaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1999–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Mushegian, A.R.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; Harrach, B.; Harrison, R.L.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Junglen, S.; et al. Changes to virus taxonomy and the International Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2019). Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hang, J.; Klein, T.A.; Kim, H.C.; Yang, Y.; Jima, D.D.; Richardson, J.H.; Jarman, R.G. Genome Sequences of Five Arboviruses in Field-Captured Mosquitoes in a Unique Rural Environment of South Korea. Genome Announc. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.D. Tombusvirus-Host Interactions: Co-Opted Evolutionarily Conserved Host Factors Take Center Court. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 491–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
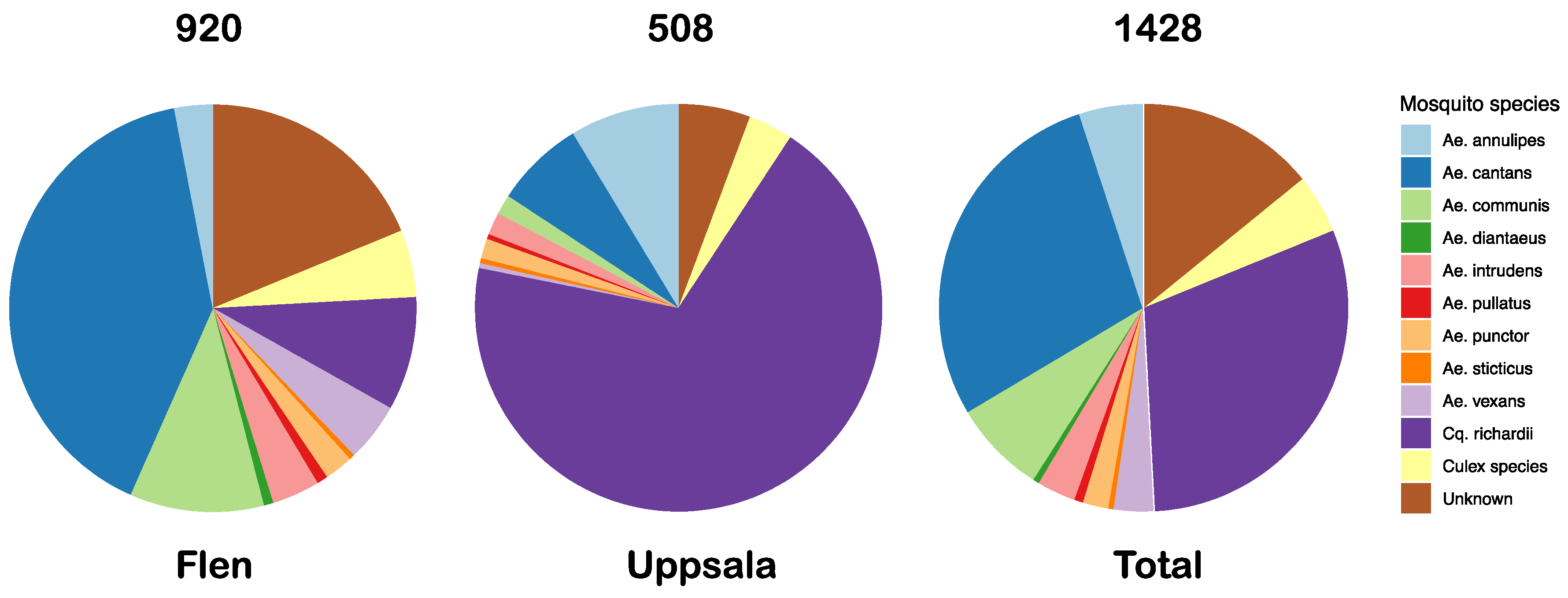
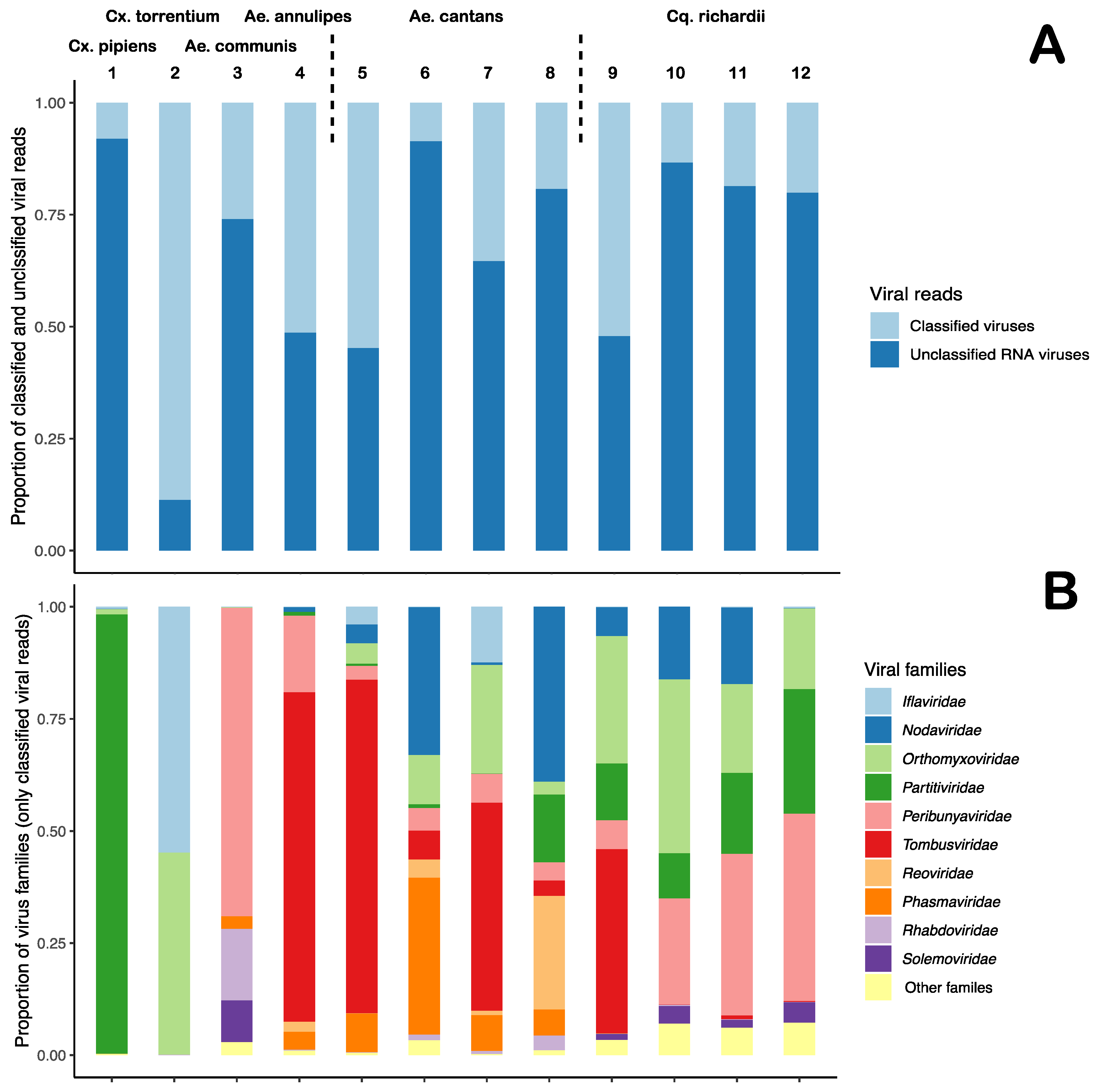
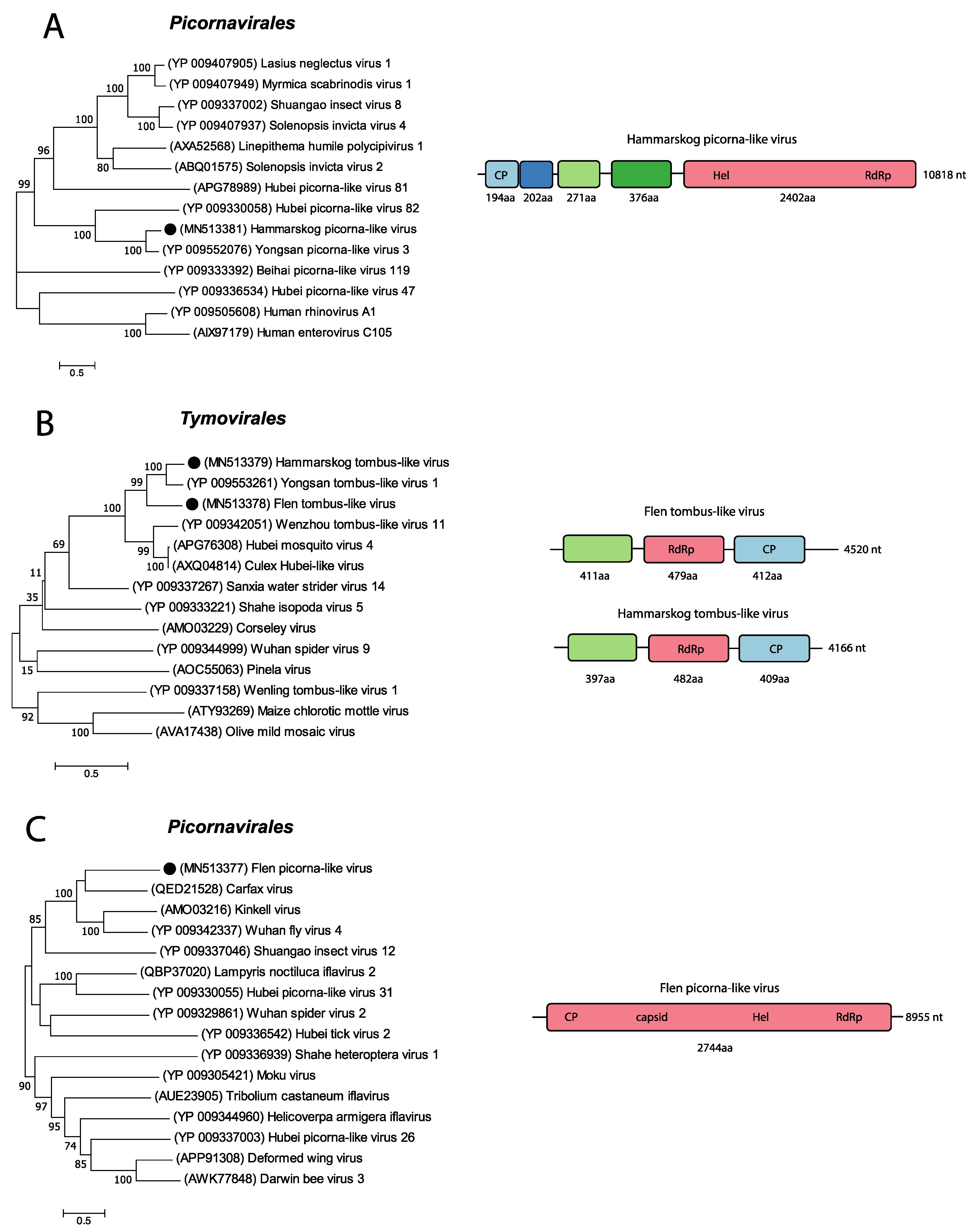
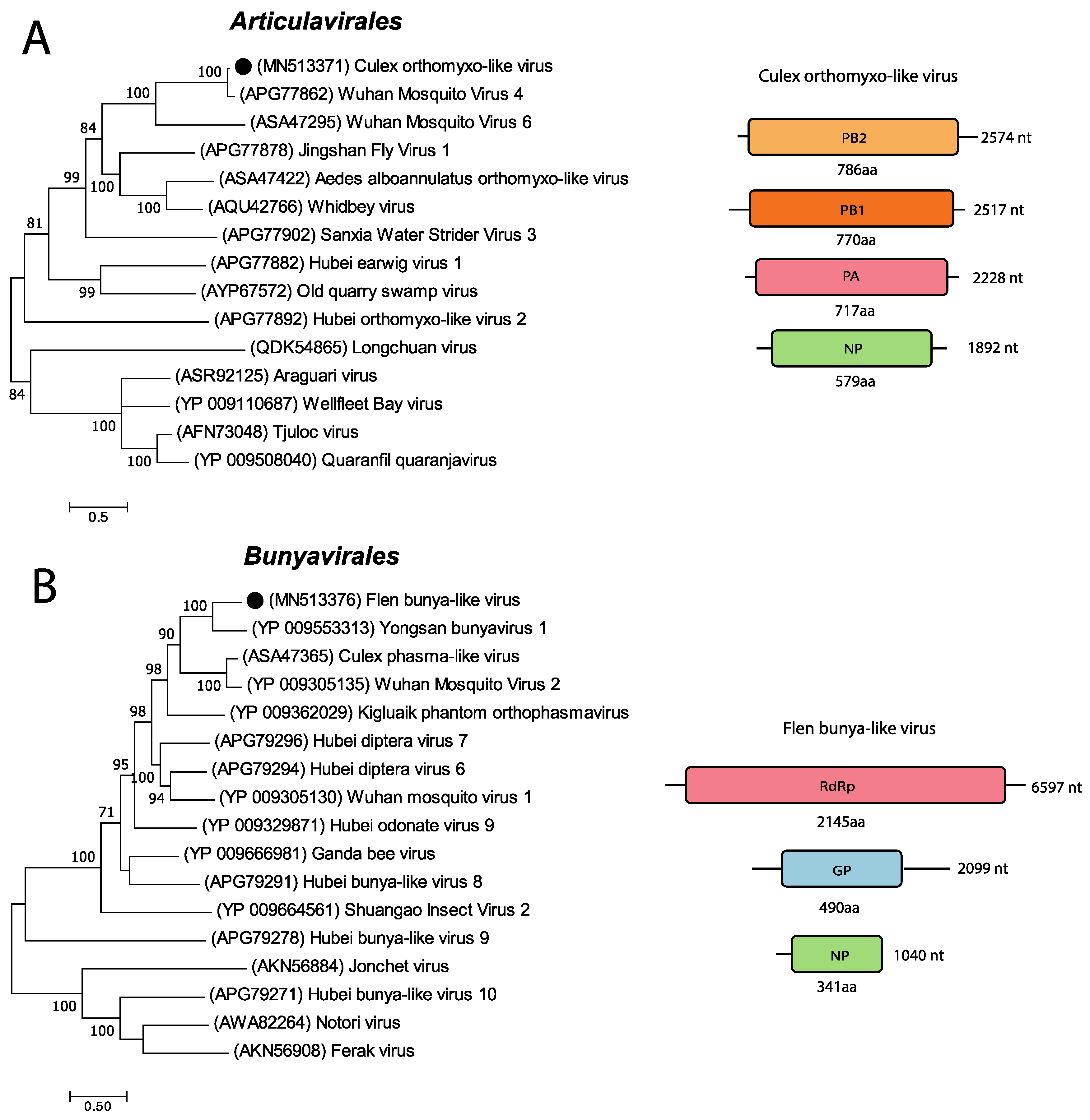
| Pool Name | Mosquito spp | Sample Location | Sample Time Point | Raw Reads | Diptera Reads (%) | Microbial Reads (%) | Viral Reads (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cx. pipiens | Mix | Mix | 2 985 629 | 7.6% | 27.55% | 8.76% |
| 2 | Cx. torrentium | Mix | Mix | 4 713 173 | 42.65% | 56.21% | 4.86% |
| 3 | Ae. commnus | Mix | Mix | 8 590 873 | 1.43% | 13.78% | 1.44% |
| 4 | Ae. annulipes | Mix | Mix | 1 842 681 | 5.42% | 27.65% | 12.47% |
| 5 | Ae. cantans | Flen | May and June | 1 427 446 | 5.35% | 24.75% | 11.00% |
| 6 | Ae. cantans | Flen | July | 5 877 722 | 3.3% | 13.23% | 5.43% |
| 7 | Ae. cantans | Flen | August | 2 269 961 | 5.11% | 19.73% | 8.48% |
| 8 | Ae. cantans | Uppsala | mix | 1 238 350 | 6.5% | 23.54% | 8.00% |
| 9 | Cq. richardii | Uppsala | June | 5 201 595 | 14.02% | 26.8% | 3.13% |
| 10 | Cq. richardii | Uppsala | July | 8 889 584 | 12.6% | 26.37% | 5.39% |
| 11 | Cq. richardii | Uppsala | August | 4 821 295 | 9.19% | 27.73% | 10.4% |
| 12 | Cq. richardii | Flen | Mix | 4 247 080 | 12.2% | 29.19% | 5.81% |
| Abundance of Viruses (% of Total Reads) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cx. Pipiens | Cx. Torrentium | Ae. Communis | Ae. Annulipes | Ae. Cantans | Cq. Richardii | |||||||
| Viruses | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Negative-sense ssRNA virus | ||||||||||||
| Wuhan Mosquito Virus 4 | 0.009 | 1.897 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.166 | 0.098 | 0.044 | 0.073 |
| Wuhan Mosquito Virus 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.031 | 0.01 | 0.119 | 0.006 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Xinzhou Mosquito Virus | 0 | 0 | 0.058 | 0.018 | 0.004 | 0 | 0.006 | 0 | 0.026 | 0.042 | 0.053 | 0.17 |
| Zhee Mosquito virus | 0 | 0 | 0.043 | 0.137 | 0.066 | 0.012 | 0.078 | 0.021 | 0.009 | 0.018 | 0.027 | 0.01 |
| Culex Bunya-like virus | 0 | 0 | 0.028 | 0.252 | 0.065 | 0.003 | 0.066 | 0 | 0.095 | 0.432 | 0.669 | 0.125 |
| Yongsan bunyavirus 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.016 | 2.844 | 0.852 | 0.169 | 0.177 | 2.235 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Xincheng anphevirus | 0 | 0 | 0.004 | 0.142 | 0.014 | 0.003 | 0 | 0.025 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Anopheles darlingi virus | 0 | 0 | 0.003 | 0.381 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0 | 0.009 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wuhan mosquito 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.003 | 0.043 | 0.215 | 0.099 | 0.122 | 0.022 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Whidbey virus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.042 | 0.009 | 0.102 | 0.007 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Positive-sense ssRNA virus | ||||||||||||
| Yongsan tombus-like virus 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.511 | 2.142 | 0.02 | 0.835 | 0.027 | 0.269 | 0 | 0.002 | 0 |
| Yongsan picorna-like virus 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.124 | 0.297 | 1.279 | 0.002 |
| Yongsan sobemo-like virus 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.015 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.021 |
| Culex Iflavi-like virus 3 | 0.003 | 2.298 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Kinkell virus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.087 | 0 | 0.109 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mosquito nodavirus MNV-1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0 | 0.003 | 0 | 0.042 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Alphanodavirus HB-2007/CHN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.025 | 0.026 | 0 |
| Unclassified RNA virus | ||||||||||||
| Hubei noda-like virus 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.035 | 0.034 | 0 | 0.042 | 0 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0 |
| Hubei virga-like virus 21 | 4.916 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hubei noda-like virus 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.023 | 1.197 | 4.219 | 0.045 |
| Hubei partiti-like virus 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.112 | 0 | 2.501 | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hubei diptera virus 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 | 0.054 | 0.028 | 0.025 | 0.076 |
| Hubei diptera virus 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.025 | 0.022 | 0.013 | 0.074 |
| Hubei sobemo-like virus 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.047 | 0.02 | 0.064 |
| Hubei sobemo-like virus 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.034 | 0.041 | 0.022 | 0.069 |
| Hubei mosquito virus 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.075 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hubei tetragnatha maxillosa virus 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.015 | 0.054 | 0.054 | 0.48 |
| Wuhan insect virus 13 | 0 | 0.29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wuhan fly virus 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.612 | 0 | 1.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| Wenzhou sobemo-like virus 4 | 0 | 0 | 0.034 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sanxia water strider virus 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.035 | 0.052 | 0 |
| Shuangao insect virus 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.024 | 0 | 0.166 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Renna virus | 0 | 0 | 0.038 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Culex mononega-like virus 2 | 0 | 0.216 | 0.112 | 0.721 | 0.091 | 0.017 | 0 | 0.189 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.002 |
| Culex mononega-like virus 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.006 | 0.112 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0 | 0.018 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ae camptorhynchus negev-like virus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.359 | 0.11 | 0.654 | 1.902 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ae alboannulatus orthomyxo-like virus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.183 | 0.038 | 0.323 | 0.015 | 0 | 0 | 0.002 | 0 |
| Ae camptorhynchus reo-like virus | 0 | 0 | 0.046 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Salarivirus Mos8CM0 | 0 | 0 | 0.018 | 0.707 | 0.597 | 0.19 | 0.819 | 0.326 | 0.01 | 0.009 | 0.015 | 0.04 |
| Chaq virus-like 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.126 | 0.032 | 0.025 | 0.366 |
| uncultured virus | 0 | 0 | 0.021 | 0.032 | 0.128 | 0.015 | 0.071 | 0.021 | 0.251 | 0.347 | 0.434 | 0.485 |
| Caninovirus sp. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.068 | 0.082 | 0 | 0.096 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total reads in table (%) | 4.93 | 4.7 | 0.52 | 7.02 | 5.64 | 3.32 | 4.71 | 4.97 | 1.32 | 2.74 | 7 | 2.11 |
| Other viral reads (%) | 3.83 | 0.16 | 0.92 | 5.45 | 5.36 | 2.11 | 3.77 | 3.03 | 1.81 | 2.66 | 3.4 | 3.7 |
| Total viral reads (%) | 8.76 | 4.86 | 1.44 | 12.47 | 11 | 5.43 | 8.48 | 8 | 3.13 | 5.4 | 10.4 | 5.81 |
| ORFs | FTLV Protein | HTLV Protein | aa Identity between FTLV and HTLV | aa Identity to YPLV1 (FTLV) | aa Identity to YPLV1 (HTLV) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORF 1 | 411 aa | 379 aa | 46.88% | 43.98% | 70.59% | YP_009553260 |
| ORF 2 | 479 aa | 482 aa | 65.13% | 66.6% | 81.17% | YP_009553261 |
| ORF 3 | 412 aa | 409 aa | 62.77% | 64.63% | 87.5% | YP_009553263 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Öhlund, P.; Hayer, J.; Lundén, H.; Hesson, J.C.; Blomström, A.-L. Viromics Reveal a Number of Novel RNA Viruses in Swedish Mosquitoes. Viruses 2019, 11, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111027
Öhlund P, Hayer J, Lundén H, Hesson JC, Blomström A-L. Viromics Reveal a Number of Novel RNA Viruses in Swedish Mosquitoes. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111027
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖhlund, Pontus, Juliette Hayer, Hanna Lundén, Jenny C. Hesson, and Anne-Lie Blomström. 2019. "Viromics Reveal a Number of Novel RNA Viruses in Swedish Mosquitoes" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111027
APA StyleÖhlund, P., Hayer, J., Lundén, H., Hesson, J. C., & Blomström, A.-L. (2019). Viromics Reveal a Number of Novel RNA Viruses in Swedish Mosquitoes. Viruses, 11(11), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111027







