The First Complete Genome Sequences of Hepatitis C Virus Subtype 2b from Latin America: Molecular Characterization and Phylogeographic Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Long Template RT-PCR and Genome Sequencing
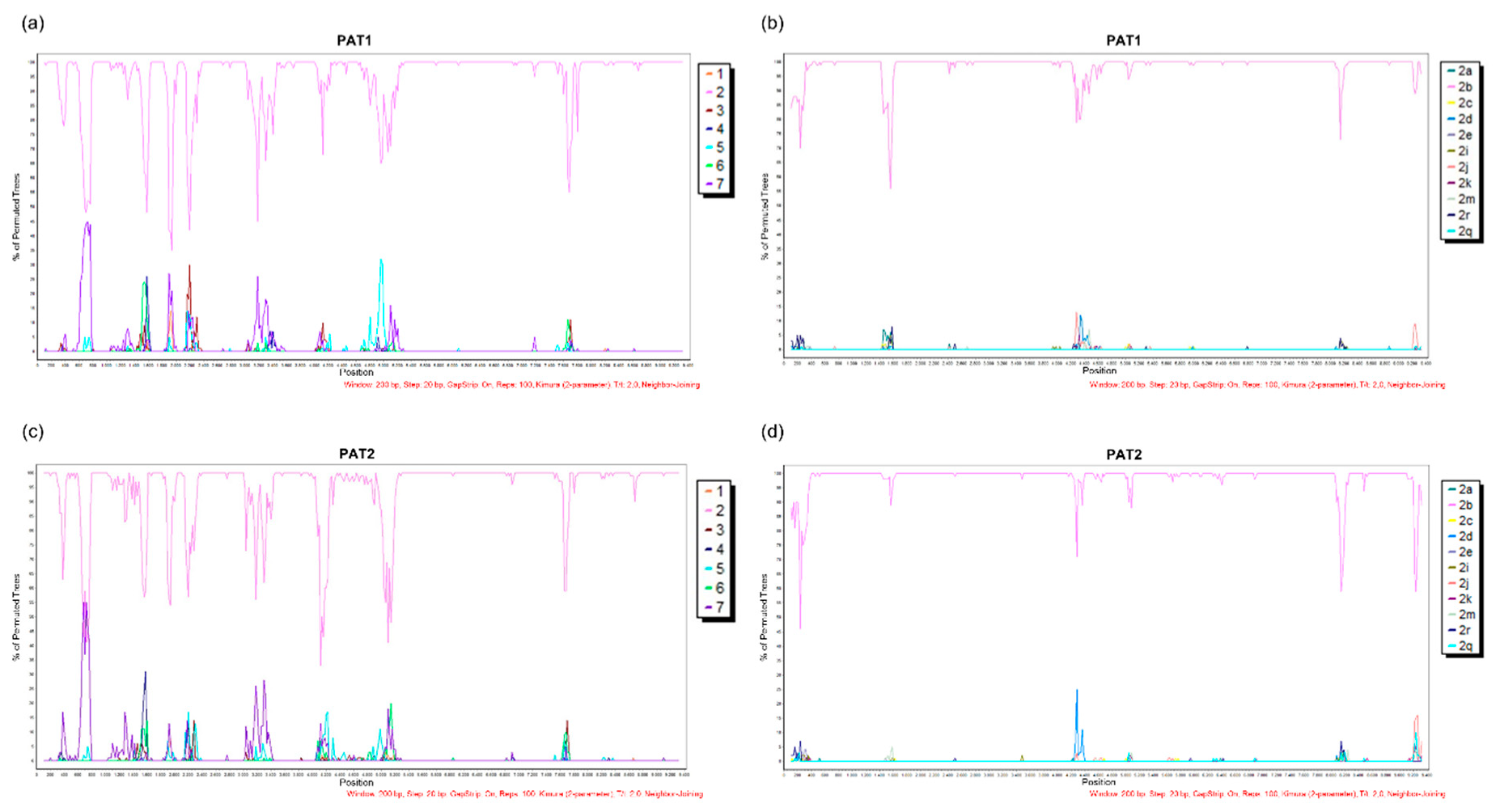
2.3. Phylogenetic and Genetic Analyses
2.4. HCV-2b Datasets
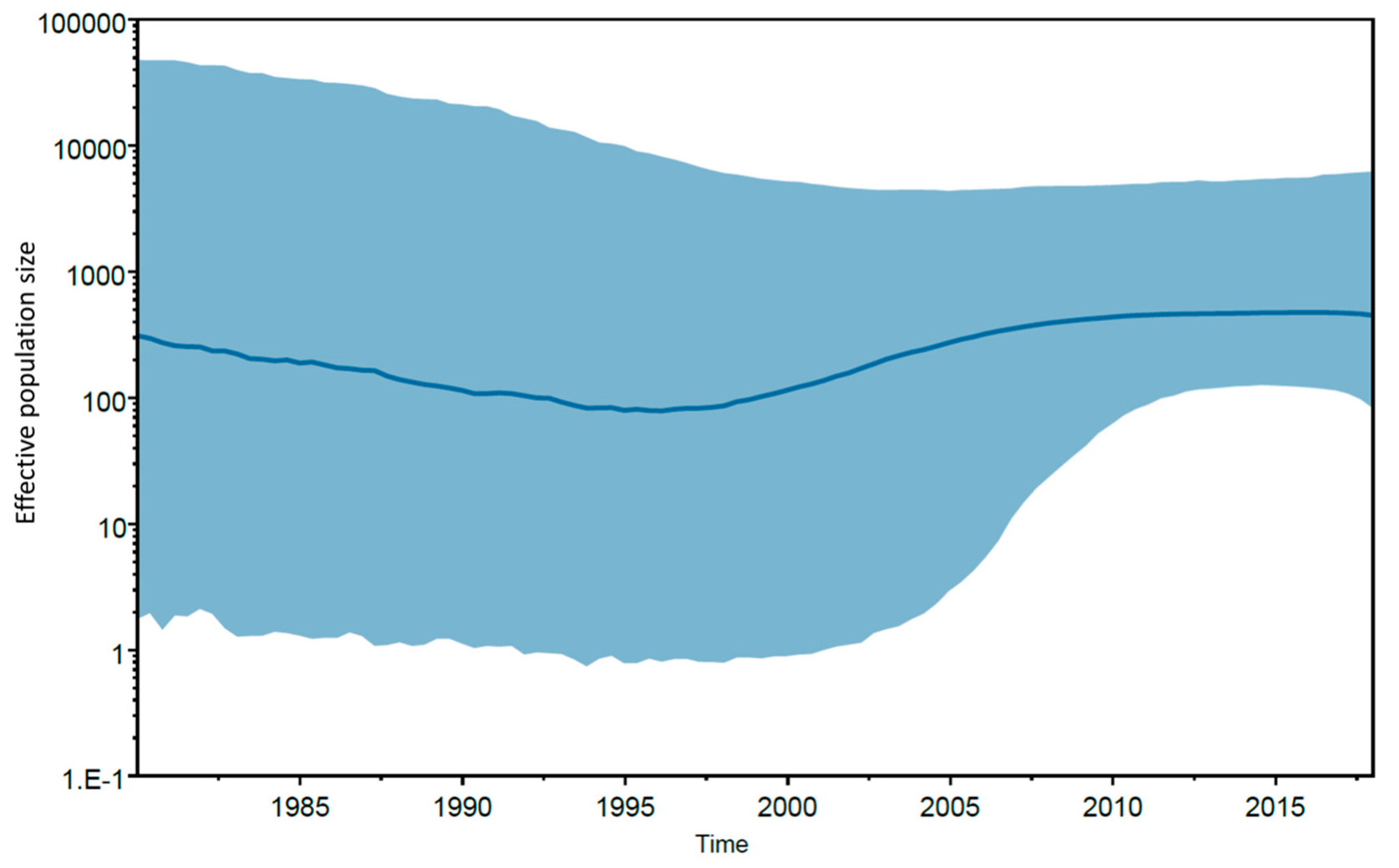
2.5. Molecular Clock Analysis
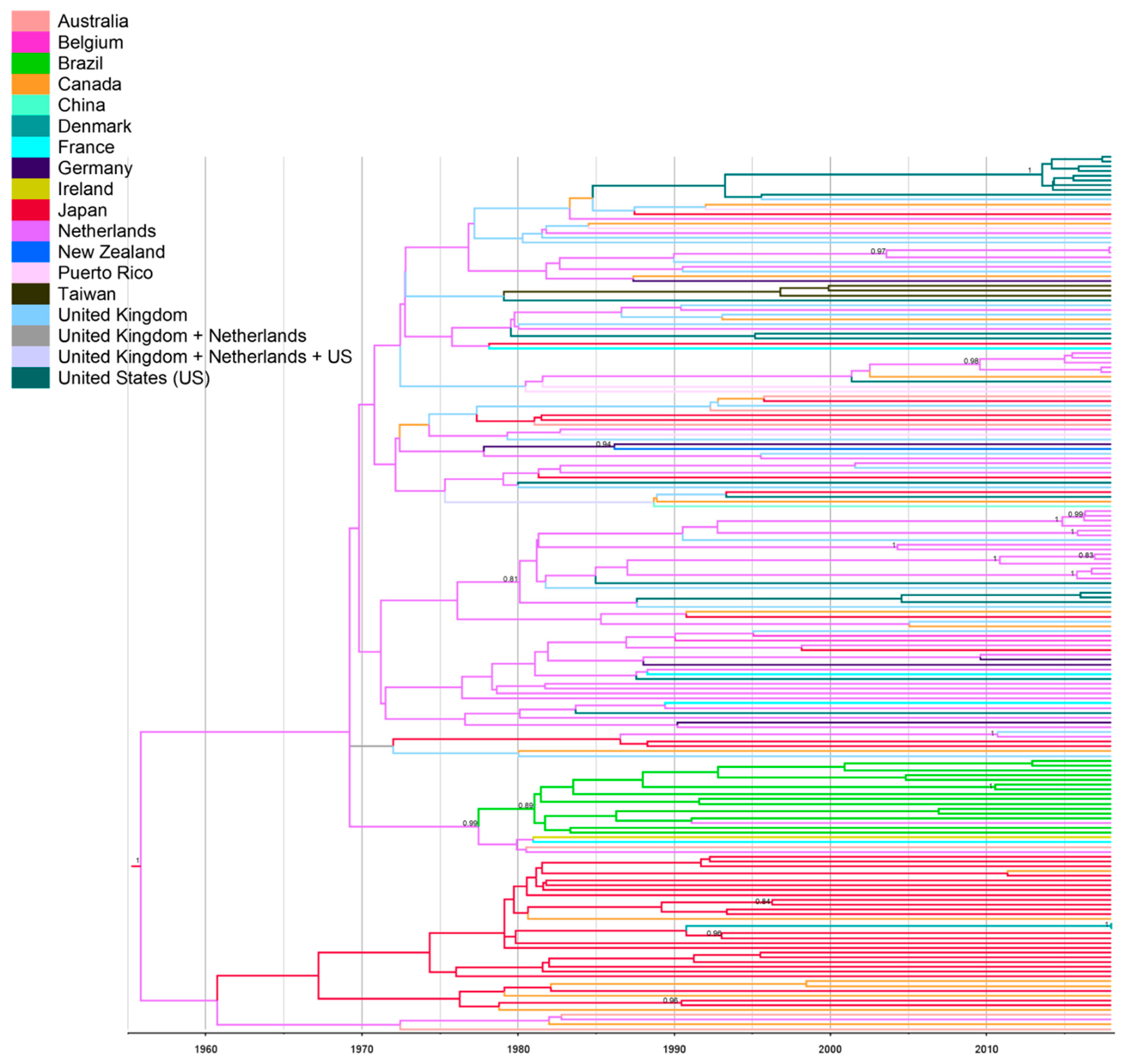
2.6. Bayesian Phylogeographic Analyses
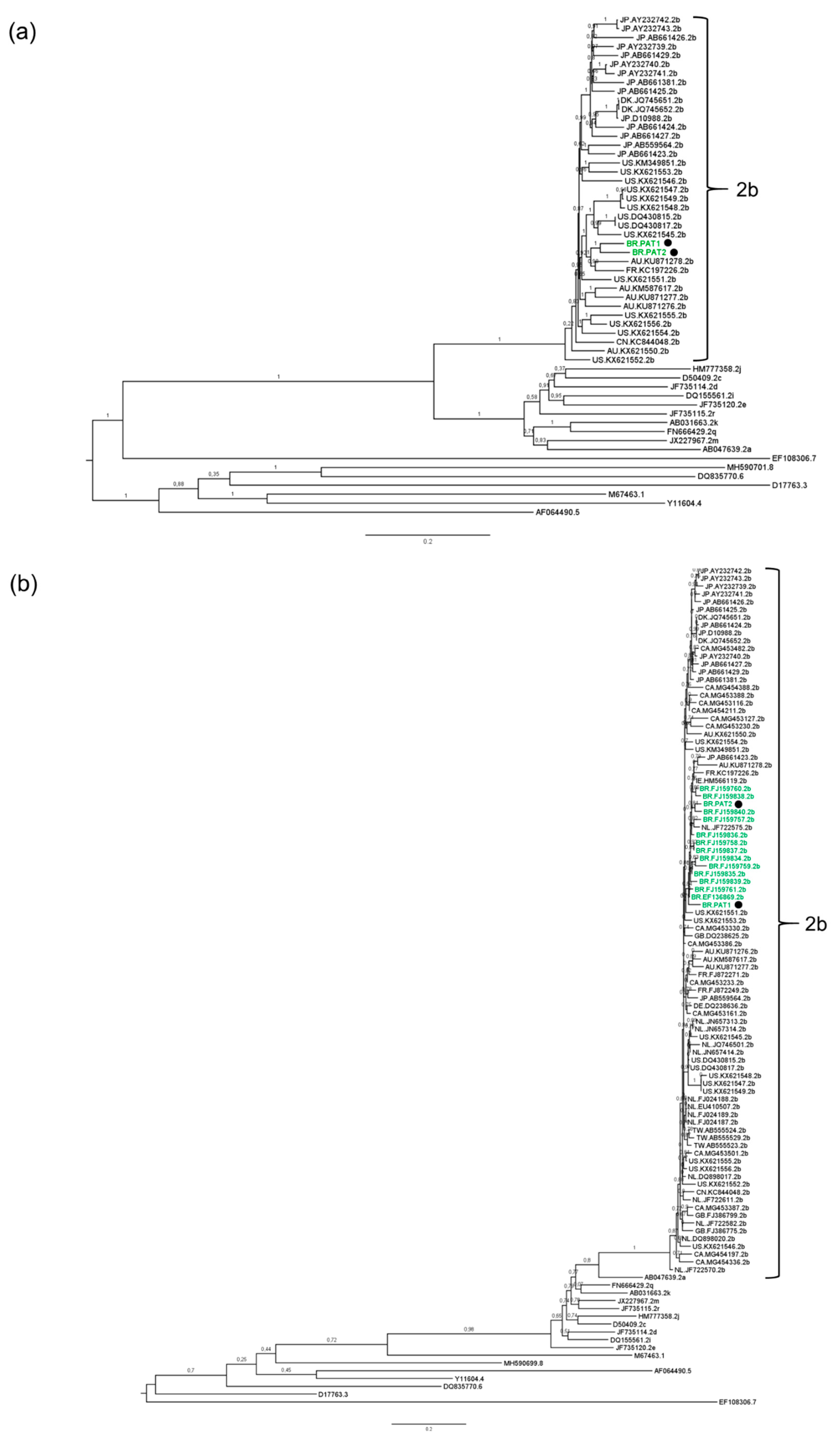
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Webster, D.P.; Klenerman, P.; Dusheiko, G.M. Hepatitis C. Lancet 2015, 385, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Hepatitis C; Key Facts; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland; Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c (accessed on 14 February 2019).
- Neumann, A.U.; Lam, N.P.; Dahari, H.; Gretch, D.R.; Wiley, T.E.; Layden, T.J.; Perelson, A.S. Hepatitis C viral dynamics in vivo and the antiviral efficacy of interferon-alpha therapy. Science 1998, 282, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardin, F.; Stramer, S.L.; Rehermann, B.; Page-Shafer, K.; Cooper, S.; Bangsberg, D.R.; Hahn, J.; Tobler, L.; Busch, M.; Delwart, E. High levels of subgenomic HCV plasma RNA in immunosilent infections. Virology 2007, 365, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheroni, C.; Donnici, L.; Aghemo, A.; Balistreri, F.; Bianco, A.; Zanoni, V.; Pagani, M.; Soffredini, R.; D’Ambrosio, R.; Rumi, M.G.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Deletion Mutants Are Found in Individuals Chronically Infected with Genotype 1 Hepatitis C Virus in Association with Age, High Viral Load and Liver Inflammatory Activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamichali, E.; Chihab, H.; Kakkanas, A.; Marchio, A.; Karamitros, T.; Pogka, V.; Varaklioti, A.; Kalliaropoulos, A.; Martinez-Gonzales, B.; Foka, P.; et al. HCV Defective Genomes Promote Persistent Infection by Modulating the Viral Life Cycle. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Niu, J.; Zhong, J. Genetic Analysis of Serum-Derived Defective Hepatitis C Virus Genomes Revealed Novel Viral cis Elements for Virus Replication and Assembly. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noppornpanth, S.; Smits, S.L.; Lien, T.X.; Poovorawan, Y.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Haagmans, B.L. Characterization of hepatitis C virus deletion mutants circulating in chronically infected patients. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12496–12503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, S.; Mori, K.; Tanaka, E.; Matsumoto, A.; Sunaga, F.; Kiyosawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K. Identification of novel HCV subgenome replicating persistently in chronic active hepatitis C patients. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 77, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgia, S.M.; Hedskog, C.; Parhy, B.; Hyland, R.H.; Stamm, L.M.; Brainard, D.M.; Subramanian, M.G.; McHutchison, J.G.; Mo, H.; Svarovskaia, E.; et al. Identification of a Novel Hepatitis C Virus Genotype From Punjab, India: Expanding Classification of Hepatitis C Virus Into 8 Genotypes. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.B.; Bukh, J.; Kuiken, C.; Muerhoff, A.S.; Rice, C.M.; Stapleton, J.T.; Simmonds, P. Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: Updated criteria and genotype assignment web resource. Hepatology 2014, 59, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P.; Bukh, J.; Combet, C.; Deleage, G.; Enomoto, N.; Feinstone, S.; Halfon, P.; Inchauspe, G.; Kuiken, C.; Maertens, G.; et al. Consensus proposals for a unified system of nomenclature of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology 2005, 42, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C 2018. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 461–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gotte, M.; Feld, J.J. Direct-acting antiviral agents for hepatitis C: Structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacka, B.; Lamoury, F.; Simmonds, P.; Dore, G.J.; Grebely, J.; Applegate, T. Sequencing of the Hepatitis C Virus: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poljak, M. Next-Generation Sequencing: A Diagnostic One-Stop Shop for Hepatitis C? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2427–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremeaux, P.; Caporossi, A.; Thelu, M.A.; Blum, M.; Leroy, V.; Morand, P.; Larrat, S. Hepatitis C virus whole genome sequencing: Current methods/issues and future challenges. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 53, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, J.P.; Humphreys, I.; Flaxman, A.; Brown, A.; Cooke, G.S.; Pybus, O.G.; Barnes, E. Global distribution and prevalence of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology 2015, 61, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Pathirana, S.; Davidson, F.; Lawlor, E.; Power, J.; Yap, P.L.; Simmonds, P. The origin of hepatitis C virus genotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78 Pt 2, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, J. Genetic diversity and evolution of hepatitis C virus in the Latin American region. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 34 (Suppl. S2), S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershenobich, D.; Razavi, H.A.; Sanchez-Avila, J.F.; Bessone, F.; Coelho, H.S.; Dagher, L.; Goncales, F.L.; Quiroz, J.F.; Rodriguez-Perez, F.; Rosado, B.; et al. Trends and projections of hepatitis C virus epidemiology in Latin America. Liver Int. 2011, 31 (Suppl. S2), 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefort, V.; Longueville, J.E.; Gascuel, O. SMS: Smart Model Selection in PhyML. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2422–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anisimova, M.; Gascuel, O. Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: A fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lole, K.S.; Bollinger, R.C.; Paranjape, R.S.; Gadkari, D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Novak, N.G.; Ingersoll, R.; Sheppard, H.W.; Ray, S.C. Full-length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes from subtype C-infected seroconverters in India, with evidence of intersubtype recombination. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 152–160. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaghatgi, P.; Sikorski, A.M.; Knops, E.; Rupp, D.; Sierra, S.; Heger, E.; Neumann-Fraune, M.; Beggel, B.; Walker, A.; Timm, J.; et al. Geno2pheno[HCV]-A Web-based Interpretation System to Support Hepatitis C Treatment Decisions in the Era of Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, M.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U.; Bukh, J. Hepatitis C virus: An infectious molecular clone of a second major genotype (2a) and lack of viability of intertypic 1a and 2a chimeras. Virology 1999, 262, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Xie, Z.; Salemi, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. An index of substitution saturation and its application. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. DAMBE7: New and Improved Tools for Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G.; Ayres, D.L.; Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A. Many-core algorithms for statistical phylogenetics. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Max Carvalho, L.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A.; Shapiro, B.; Pybus, O.G. Bayesian coalescent inference of past population dynamics from molecular sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemey, P.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A. Bayesian phylogeography finds its roots. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pybus, O.G.; Charleston, M.A.; Gupta, S.; Rambaut, A.; Holmes, E.C.; Harvey, P.H. The epidemic behavior of the hepatitis C virus. Science 2001, 292, 2323–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P. Genetic diversity and evolution of hepatitis C virus-15 years on. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3173–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorkinis, G.; Magiorkinis, E.; Paraskevis, D.; Ho, S.Y.; Shapiro, B.; Pybus, O.G.; Allain, J.P.; Hatzakis, A. The global spread of hepatitis C virus 1a and 1b: A phylodynamic and phylogeographic analysis. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Laar, T.J.; Koppelman, M.H.; van der Bij, A.K.; Zaaijer, H.L.; Cuijpers, H.T.; van der Poel, C.L.; Coutinho, R.A.; Bruisten, S.M. Diversity and origin of hepatitis C virus infection among unpaid blood donors in the Netherlands. Transfusion 2006, 46, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, P.V.; van de Laar, T.J.; Thomas, X.V.; Aronson, S.J.; Weegink, C.J.; van den Berk, G.E.; Prins, M.; Pybus, O.G.; Schinkel, J. Colonial history and contemporary transmission shape the genetic diversity of hepatitis C virus genotype 2 in Amsterdam. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7677–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampe, E.; Espirito-Santo, M.P.; Martins, R.M.; Bello, G. Epidemic history of Hepatitis C virus in Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampe, E.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.; Espirito-Santo, M.P.; Delvaux, N.M.; Pereira, S.A.; Peres-da-Silva, A.; Martins, R.M.; Soares, M.A.; Santos, A.F.; Vidal, L.L.; et al. Genetic diversity of HCV in Brazil. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
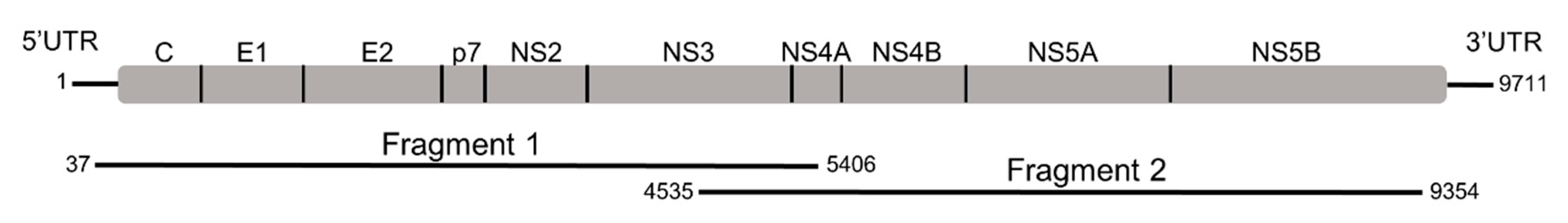

| Primer | Primer Sequence 5′–3′ | Sense | Position a |
|---|---|---|---|
| RT-nested-PCR primers | |||
| HCV17S | GGCGACACTCCGCCATGAATCACT | forward | 17–40 |
| HCV37S | CACTCCCCTGTGAGGAACTACTGTCTTCACG | forward | 37–67 |
| 2bDel1 | CTCSAACARCAGCATYACYTGGC | forward | 961–983 |
| HCV3007R | CACHAGGCGTGGGTGBAGAATG | reverse | 3007–2986 |
| HCV4328S | ATCCTTGGCATTGGAACRGTCCTYGACC | forward | 4328–4355 |
| HCV4535S | CATTCAAAGAAGAAGTGCGAYGAGCT | forward | 4535–4560 |
| HCV5406R | CGGCCDATGATGGAAAYGCAGCC | reverse | 5406–5384 |
| HCV5423R | GATCATTCAGGTGTADGCGGCC | reverse | 5423–5402 |
| HCV9354R | CTGTGAWADATGTCGCCCCCG | reverse | 9354–9334 |
| HCV9373R | GGGTCGGGCATGCGACACGCTGTGAWADATGTC | reverse | 9373–9341 |
| Sequencing primers | |||
| HCV37S | CACTCCCCTGTGAGGAACTACTGTCTTCACG | forward | 37–67 |
| S7 | AGACCGTGCACCATGAGCAC | forward | 329–348 |
| A5 | TACGCCGGGGGTCAKTRGGGCCCCA | reverse | 683–659 |
| HCV944S | TACGCCACYAATGATTGCTC | forward | 944–963 |
| Del1597 | CTGGCACATAAATCGGACCG | forward | 1597–1616 |
| HCV3007S | CATTCTVCACCCACGCCTDGTG | forward | 3007–2986 |
| HCV3920S | GCCAARTCYATTGACTTCATCCC | forward | 3920–3942 |
| HCV4356R | TGGTCRAGGACYGTTCCRATGCC | reverse | 4356–4334 |
| HCV4535 | CATTCAAAGAAGAAGTGCGAYGAGCT | forward | 4535–4560 |
| HCV5285S | ATCGCCACGTGCATGCARGCT | forward | 5285–5305 |
| HCV5406R | CGGCCDATGATGGAAAYGCAGCC | reverse | 5406–5384 |
| HCV6339R | GACAGCCAGTTYTTRAAGTCTG | reverse | 6339–6318 |
| HCV6984S | TGAAGGCYACCTGYACCACYCA | forward | 6984–7005 |
| HCV7059R | TCRCCYCCCATGAAVAGRTT | reverse | 7059–7040 |
| PR4 | GCNGARTAYCTVGTCATAGCCTC | reverse | 8709–8687 |
| HCV9354R | CTGTGAWADATGTCGCCCCCG | reverse | 9354–9334 |
| HCV9140S | CTTGGAGCGCCTCCCCTYAG | forward | 9140–9159 |
| Brazil | France | USA | Japan | Australia | China | Denmark | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| France | 0.090 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.004 | |
| USA | 0.100 | 0.097 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | |
| Japan | 0.106 | 0.102 | 0.098 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | |
| Australia | 0.103 | 0.101 | 0.099 | 0.101 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| China | 0.105 | 0.102 | 0.101 | 0.098 | 0.101 | 0.004 | |
| Denmark | 0.107 | 0.101 | 0.095 | 0.079 | 0.100 | 0.097 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spitz, N.; Barros, J.J.; do Ó, K.M.; Brandão-Mello, C.E.; Araujo, N.M. The First Complete Genome Sequences of Hepatitis C Virus Subtype 2b from Latin America: Molecular Characterization and Phylogeographic Analysis. Viruses 2019, 11, 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111000
Spitz N, Barros JJ, do Ó KM, Brandão-Mello CE, Araujo NM. The First Complete Genome Sequences of Hepatitis C Virus Subtype 2b from Latin America: Molecular Characterization and Phylogeographic Analysis. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111000
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpitz, Natália, José J. Barros, Kycia M. do Ó, Carlos E. Brandão-Mello, and Natalia M. Araujo. 2019. "The First Complete Genome Sequences of Hepatitis C Virus Subtype 2b from Latin America: Molecular Characterization and Phylogeographic Analysis" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111000
APA StyleSpitz, N., Barros, J. J., do Ó, K. M., Brandão-Mello, C. E., & Araujo, N. M. (2019). The First Complete Genome Sequences of Hepatitis C Virus Subtype 2b from Latin America: Molecular Characterization and Phylogeographic Analysis. Viruses, 11(11), 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111000





