The First Detection of Equine Coronavirus in Adult Horses and Foals in Ireland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
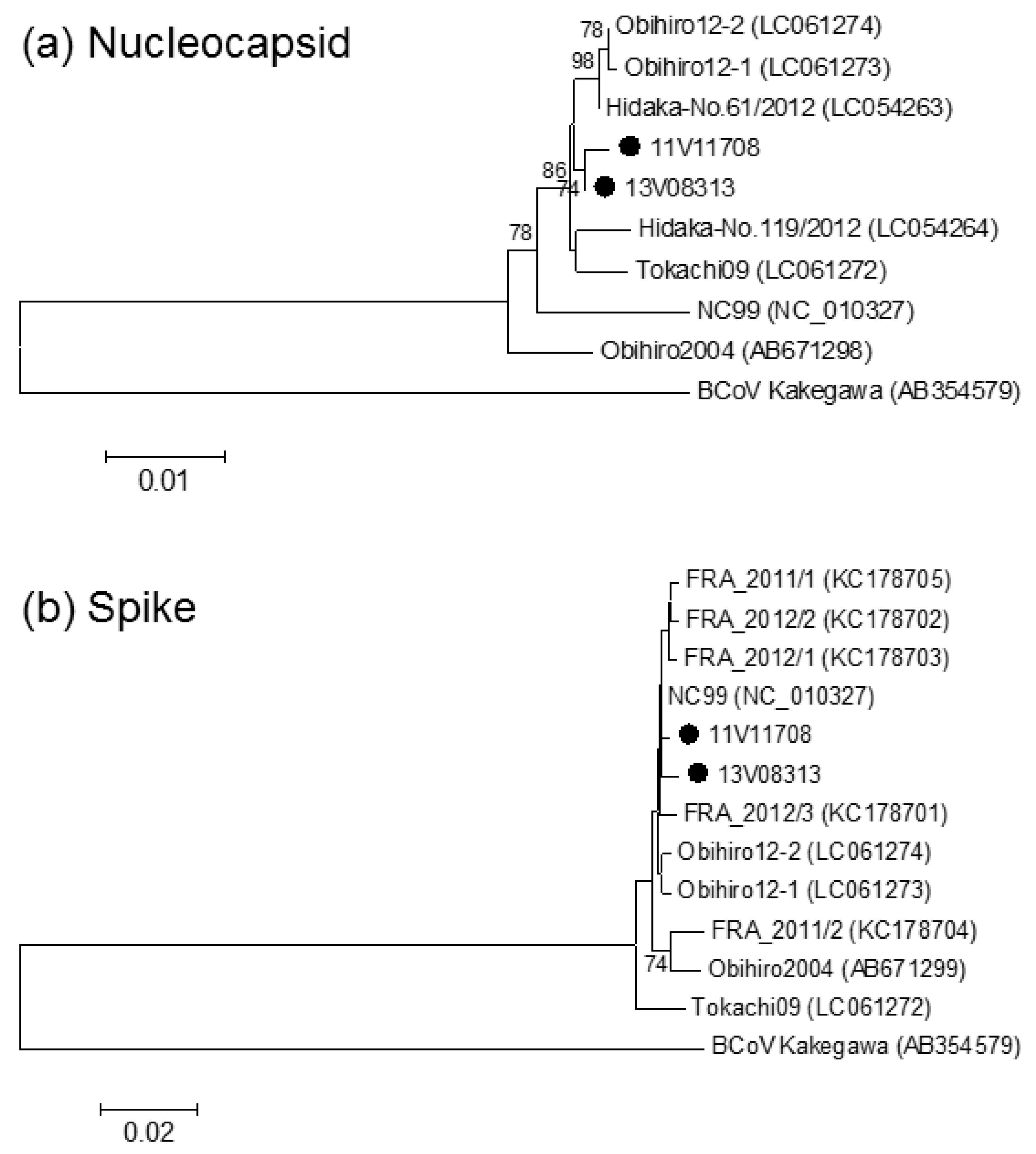
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nemoto, M.; Oue, Y.; Murakami, S.; Kanno, T.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Kondo, T. Complete genome analysis of equine coronavirus isolated in Japan. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 2903–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guy, J.S.; Snijder, E.J.; Denniston, D.A.; Timoney, P.J.; Balasuriya, U.B. Genomic characterization of equine coronavirus. Virology 2007, 369, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusterla, N.; Mapes, S.; Wademan, C.; White, A.; Ball, R.; Sapp, K.; Burns, P.; Ormond, C.; Butterworth, K.; Bartol, J.; et al. Emerging outbreaks associated with equine coronavirus in adult horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oue, Y.; Ishihara, R.; Edamatsu, H.; Morita, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Yoshima, M.; Hatama, S.; Murakami, K.; Kanno, T. Isolation of an equine coronavirus from adult horses with pyrogenic and enteric disease and its antigenic and genomic characterization in comparison with the NC99 strain. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 150, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oue, Y.; Morita, Y.; Kondo, T.; Nemoto, M. Epidemic of equine coronavirus at Obihiro Racecourse, Hokkaido, Japan in 2012. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, M.; Nobumoto, K.; Takeda, H.; Moriyama, T.; Morita, Y.; Nakaoka, Y. Prevalence of disease with inference of equine coronavirus infection among horses stabled in a draft-horse racecourse. J. Jpn. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2011, 64, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nemoto, M.; Oue, Y.; Morita, Y.; Kanno, T.; Kinoshita, Y.; Niwa, H.; Ueno, T.; Katayama, Y.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; et al. Experimental inoculation of equine coronavirus into Japanese draft horses. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 3329–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusterla, N.; Holzenkaempfer, N.; Mapes, S.; Kass, P. Prevalence of equine coronavirus in nasal secretions from horses with fever and upper respiratory tract infection. Vet. Rec. 2015, 177, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miszczak, F.; Tesson, V.; Kin, N.; Dina, J.; Balasuriya, U.B.; Pronost, S.; Vabret, A. First detection of equine coronavirus (ECoV) in Europe. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusterla, N.; Vin, R.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Mittel, L.D.; Divers, T.J. Enteric coronavirus infection in adult horses. Vet. J. 2018, 231, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusterla, N.; Vin, R.; Leutenegger, C.; Mittel, L.; Divers, T. Equine coronavirus: An emerging enteric virus of adult horses. Equine Vet. Educ. 2016, 28, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovis, N.; Elam, J.; Estrada, M.; Leutenegger, C. Infectious agents associated with diarrhoea in neonatal foals in central Kentucky: A comprehensive molecular study. Equine Vet. J. 2014, 46, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, M.; Oue, Y.; Higuchi, T.; Kinoshita, Y.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Kondo, T. Low prevalence of equine coronavirus in foals in the largest Thoroughbred horse breeding region of Japan, 2012–2014. Acta Vet. Scand. 2015, 57, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, J.; Marr, C.M.; Mackenzie, C.J.; Mair, T.S.; Fletcher, A.; Cash, R.; Phillips, M.; Pusterla, N.; Mapes, S.; Foote, A.K. Detection of equine coronavirus in horses in the United Kingdom. Vet. Rec. 2019, 184, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemida, M.G.; Chu, D.K.W.; Perera, R.; Ko, R.L.W.; So, R.T.Y.; Ng, B.C.Y.; Chan, S.M.S.; Chu, S.; Alnaeem, A.A.; Alhammadi, M.A.; et al. Coronavirus infections in horses in Saudi Arabia and Oman. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, M.; Morita, Y.; Niwa, H.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Kondo, T. Rapid detection of equine coronavirus by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 215, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Met Eireann: The Irish Meteorological Service. Available online: http://www.met.ie/climate/irish-climate-monthly-summary.asp (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Economic Impact of Irish Breeding and Racing. 2017. Available online: https://www.hri.ie/uploadedFiles/HRI-Corporate/HRI_Corporate/Press_Office/Economic_Impact/HRI%20Report.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Kooijman, L.J.; James, K.; Mapes, S.M.; Theelen, M.J.; Pusterla, N. Seroprevalence and risk factors for infection with equine coronavirus in healthy horses in the USA. Vet. J. 2017, 220, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, M.M.; Bernard, W.V.; Riddle, T.W.; Latimer, C.R.; Fitzgerald, T.D.; Harrison, L.R. Review Paper: Mare Reproductive Loss Syndrome. Vet. Pathol. 2008, 45, 710–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer Name | Sequence 5′-3′ | Use | Target | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECoV-380-F | TGGGAACAGGCCCGC | PCR | Nucleocapsid | [3] |
| ECoV-522-R | CCTAGTCGGAATAGCCTCATCAC | |||
| ECoV-436-probe | TGGGTCGCTAACAAG | |||
| ECoV-N-F | TCAGGCATGGACACCGCATTGTT | Sequencing | Nucleocapsid | [4] |
| ECoV-N-R | CCAGGTGCCGACATAAGGTTCAT | |||
| ECoV-S1-F | CAATGCCTTTATGGCTTGGT | Sequencing | Spike Gene | [9] |
| ECoVS1-R | AAACTCGGAAGGGATCTGAA | |||
| ECoV-p4.7-F | TAATCGGCCTTGCTGGTGTAGC | Sequencing | p4.7 to p12.7 genes | Oue (personal communication) |
| ECoV-p4.7-R | GCTTCATCAGCAGTCCAGGTA |
| Nucleotide Identities (%) of Nucleocapsid Gene to: | ||||||
| Name | 11V11708/IRL | 13V08313/IRL | NC99 | Obihiro2004 | Tokachi09 | |
| Accession No. | LC149485 | LC149486 | EF446615 | AB671298 | LC061272 | |
| 11V11708/IRL | - | 99.8 | 98.1 | 98.6 | 99.2 | |
| 13V08313/IRL | 99.8 | - | 98.3 | 98.7 | 99.4 | |
| Name | Obihiro12-1 | Obihiro12-2 | Hidaka-No.61/2012 | Hidaka-No.119/2012 | ||
| Accession No. | LC061273 | LC061274 | LC054263 | LC054264 | ||
| 11V11708/IRL | 99.3 | 99.4 | 99.5 | 99.2 | ||
| 13V08313/IRL | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.4 | ||
| Nucleotide Identities (%) of Spike Gene to: | ||||||
| Name | 11V11708/IRL | 13V08313/IRL | NC99 | Obihiro2004 | Tokachi09 | Obihiro12-1 |
| Accession No. | LC149487 | LC149488 | EF446615 | AB671299 | LC061272 | LC061273 |
| 11V11708/IRL | - | 99.5 | 99.7 | 98.9 | 98.6 | 99.4 |
| 13V08313/IRL | 99.5 | - | 99.5 | 98.8 | 98.5 | 99.2 |
| Name | Obihiro12-2 | FRA_2011/1 | FRA_2011/2 | FRA_2012/1 | FRA_2012/2 | FRA_2012/3 |
| Accession No. | LC061274 | KC178705 | KC178704 | KC178703 | KC178702 | KC178701 |
| 11V11708/IRL | 99.5 | 99.5 | 98.6 | 99.4 | 99.5 | 99.5 |
| 13V08313/IRL | 99.4 | 99.3 | 98.4 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nemoto, M.; Schofield, W.; Cullinane, A. The First Detection of Equine Coronavirus in Adult Horses and Foals in Ireland. Viruses 2019, 11, 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100946
Nemoto M, Schofield W, Cullinane A. The First Detection of Equine Coronavirus in Adult Horses and Foals in Ireland. Viruses. 2019; 11(10):946. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100946
Chicago/Turabian StyleNemoto, Manabu, Warren Schofield, and Ann Cullinane. 2019. "The First Detection of Equine Coronavirus in Adult Horses and Foals in Ireland" Viruses 11, no. 10: 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100946
APA StyleNemoto, M., Schofield, W., & Cullinane, A. (2019). The First Detection of Equine Coronavirus in Adult Horses and Foals in Ireland. Viruses, 11(10), 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100946




