On Neighborhood Structures and Repair Techniques for Blocking Job Shop Scheduling Problems †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Problem Description and Benchmark Instances
4. Representations of a Schedule
4.1. Permutation-Based Encodings
- The operations belong to different jobs.
- The operations require different machines.
- The operations are not connected by a blocking constraint.
- None of the operations is involved in a swap.
| : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | … |
| : | … |
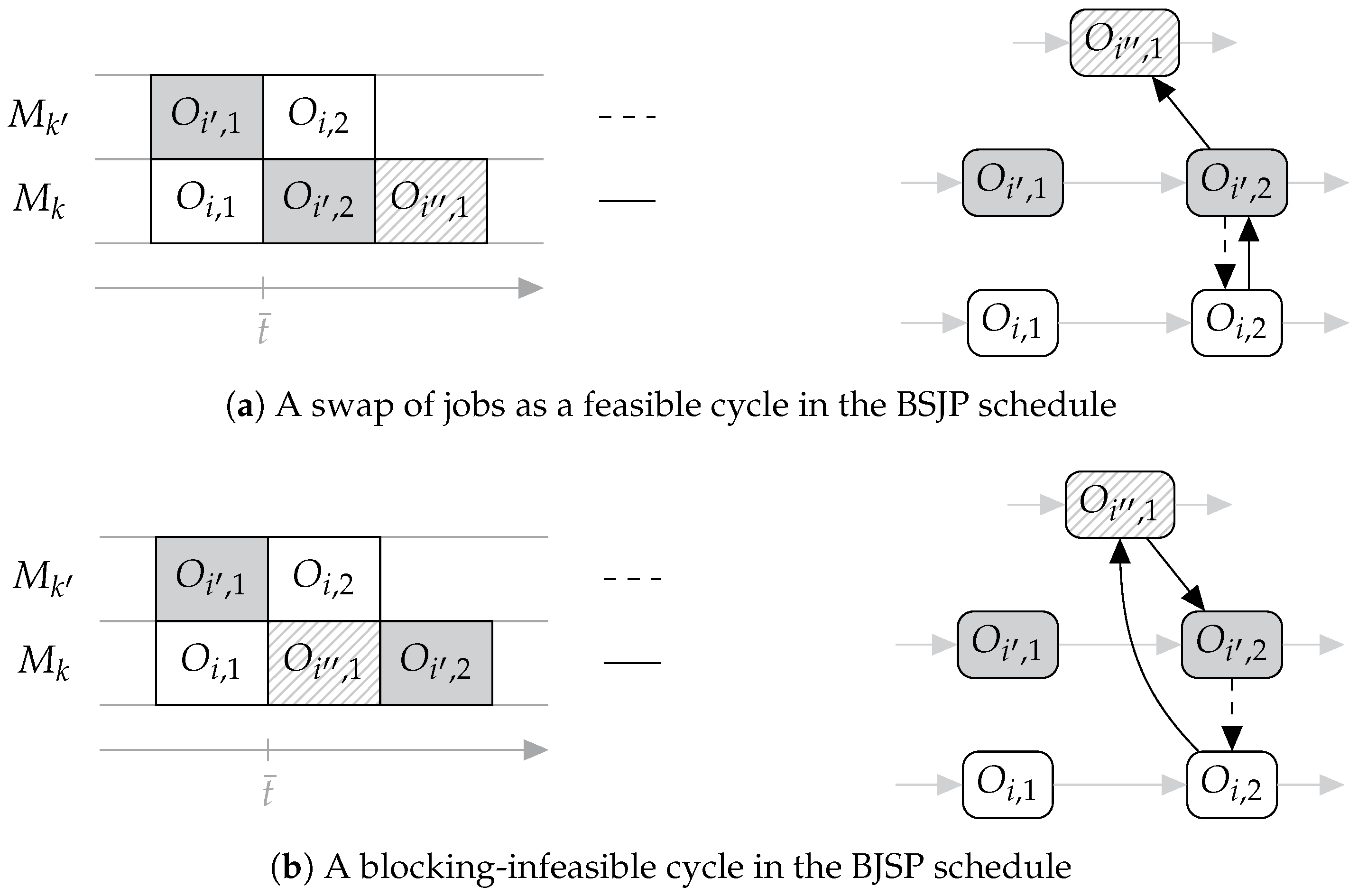
4.2. Involving Swaps
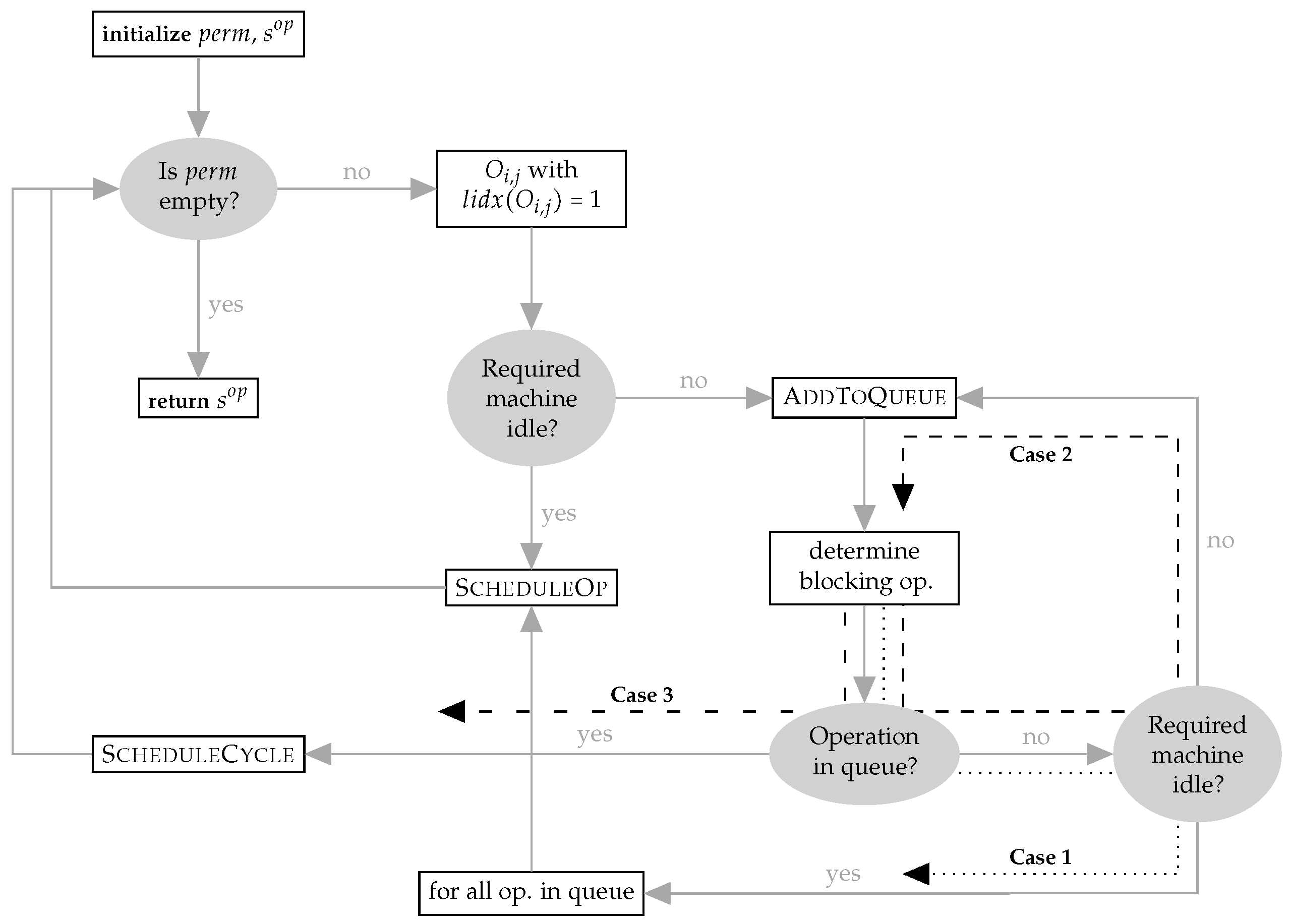
4.3. Feasibility Guarantee
- determines and stores the earliest possible starting time of the considered operation,
- removes the operation from ,
- adds the operation to the next idle list index in , and
- sets the status of to blocked provided that a job successor exists.
- (1)
- the resulting permutation is feasible with regard to the processing sequences of all jobs ,
- (2)
- the resulting permutation is feasible with regard to blocking constraints and
- (3)
- every operation is assigned to a position in the feasible permutation exactly once.
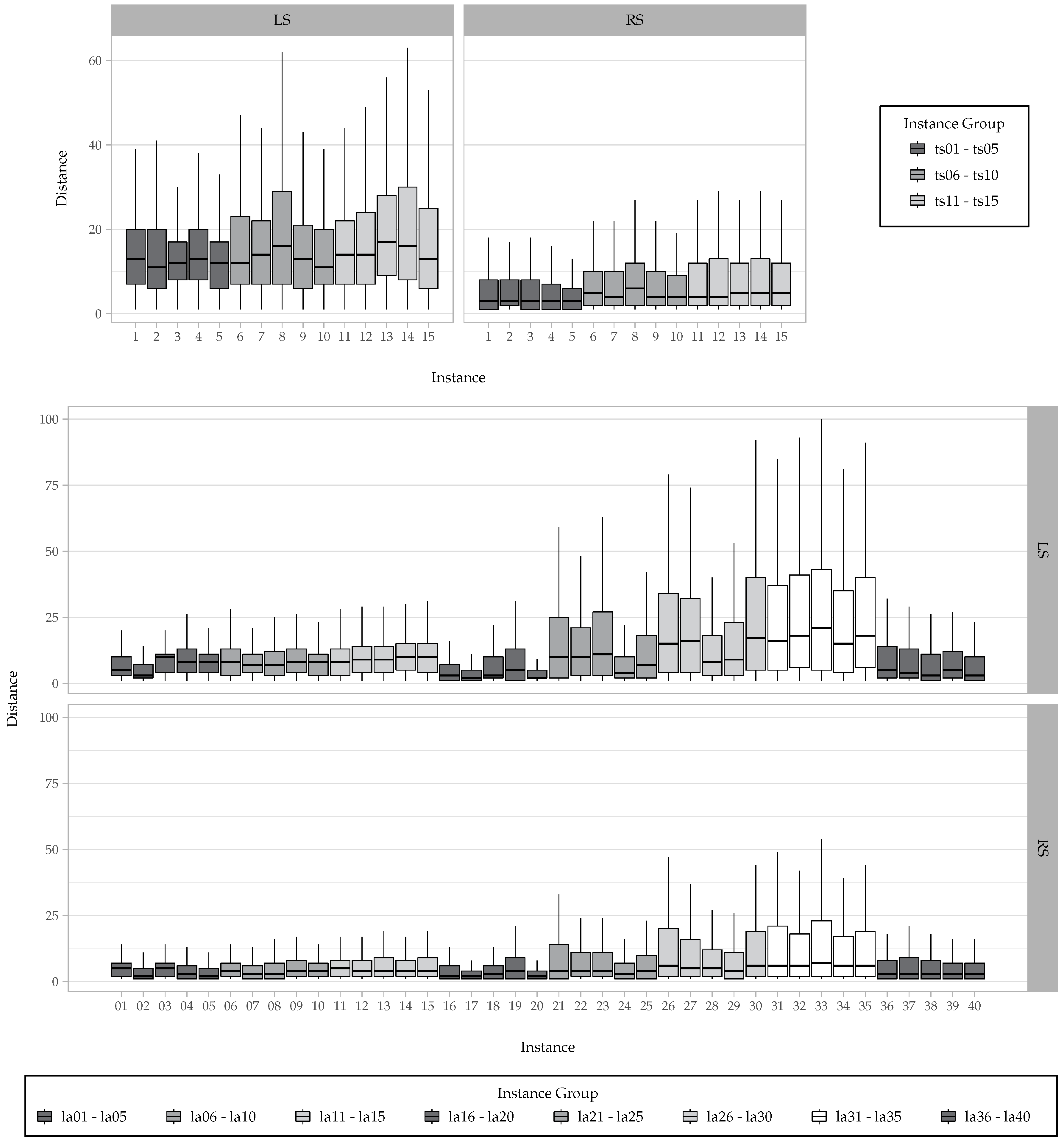
4.4. Distance of Schedules
5. Neighborhood Structures
5.1. Introducing Interchange- and Shift-Based Neighborhoods
5.1.1. Transition Schemes and Their Implementation
- the technological routes of the jobs and the corresponding processing sequences on other machines or
- the release date of the job of the succeeding operation.
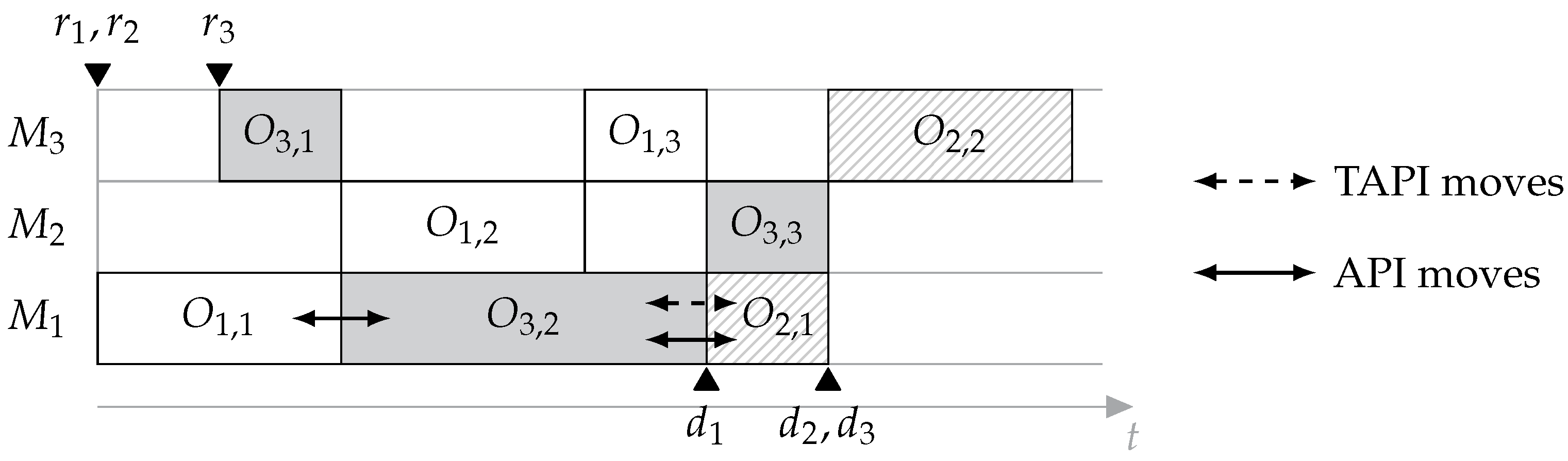
5.1.2. Generating Feasible API-Based Neighbors
- (1)
- an adaptation does not violate the processing sequences of the jobs,
- (2)
- an adaptation can never be reverted,
- (3)
- the number of possible adaptations is finite and
- (4)
- there exists a sequence of adaptations leading to a feasible schedule for the BJSP including the predefined pairwise sequence .
5.1.3. Definition of the Neighborhoods
5.2. Characteristics and Evaluation
5.2.1. Connectivity of the Neighborhoods
5.2.2. Observations on the Interchange-Based Transition Scheme
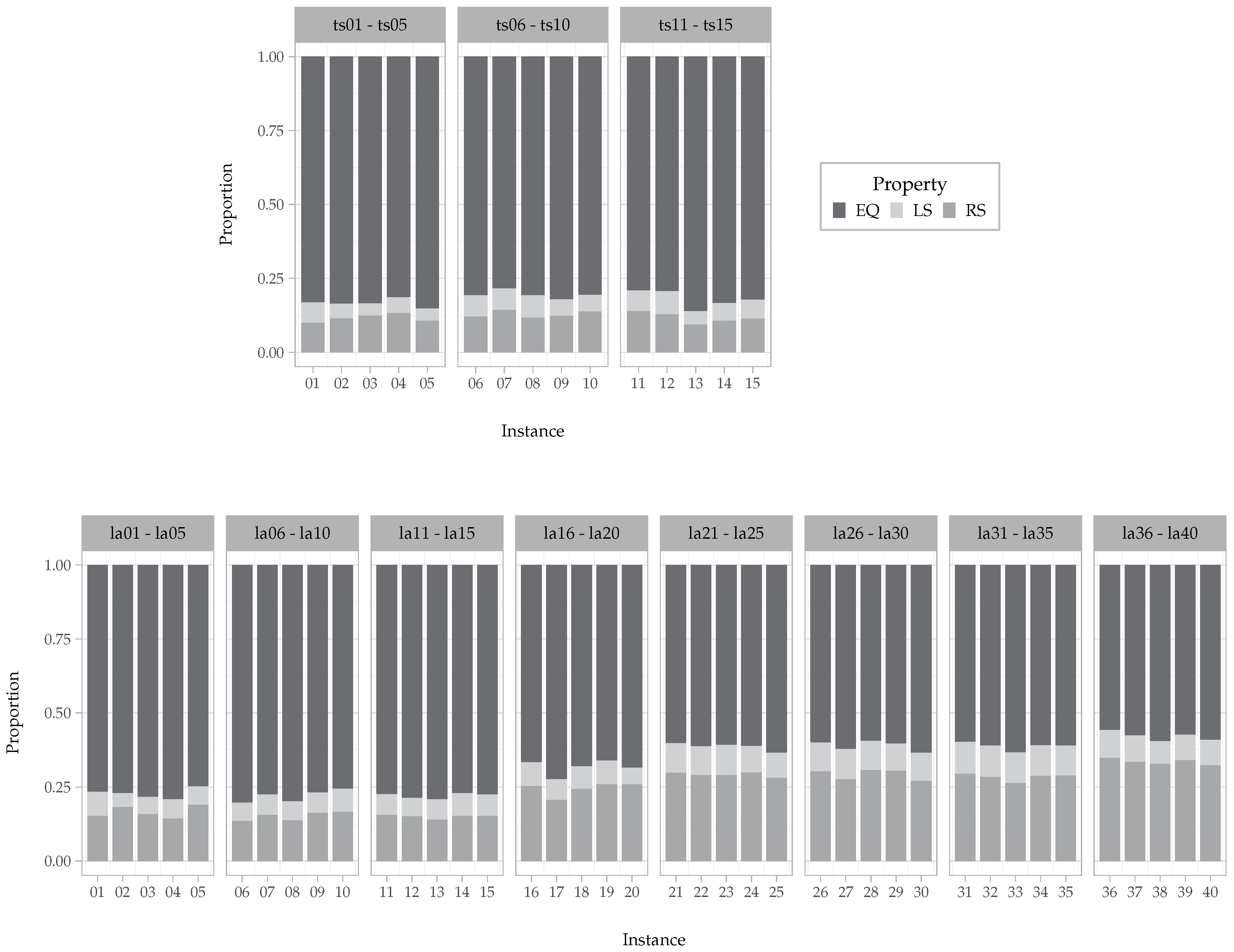
6. Computational Experiments and Results
6.1. A Simulated Annealing Algorithm
6.2. Numerical Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garey, M.R.; Johnson, D.S.; Sethi, R. The Complexity of Flowshop and Jobshop Scheduling. Math. Oper. Res. 1976, 1, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Laarhoven, P.J.; Aarts, E.H.; Lenstra, J.K. Job shop scheduling by simulated annealing. Oper. Res. 1992, 40, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.; Balas, E.; Zawack, D. The shifting bottleneck procedure for job shop scheduling. Manag. Sci. 1988, 34, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, E.; Smutnicki, C. A fast taboo search algorithm for the job shop problem. Manag. Sci. 1996, 42, 797–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgy, R.; Gröflin, H. The blocking job shop with rail-bound transportation. J. Comb. Optim. 2016, 31, 152–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ariano, A.; Pacciarelli, D.; Pranzo, M. A branch and bound algorithm for scheduling trains in a railway network. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 183, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Kozan, E. Scheduling trains as a blocking parallel-machine job shop scheduling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2009, 36, 2840–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mati, Y.; Rezg, N.; Xie, X. A taboo search approach for deadlock-free scheduling of automated manufacturing systems. J. Intell. Manuf. 2001, 12, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgy, R. A neighborhood for complex job shop scheduling problems with regular objectives. J. Sched. 2017, 20, 391–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, J.; Voss, T. Optimal Scheduling of AGVs in a Reentrant Blocking Job-shop. Procedia CIRP 2018, 67, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.; Werner, F. Approaches to modeling train scheduling problems as job-shop problems with blocking constraints. J. Sched. 2018, 21, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizuela, C.A.; Zhao, Y.; Sannomiya, N. No-wait and blocking job-shops: Challenging problems for GA’s. Int. Conf. Syst. Man Cybern. 2001, 4, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar]
- Groeflin, H.; Klinkert, A. A new neighborhood and tabu search for the blocking job shop. Discret. Appl. Math. 2009, 157, 3643–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattfeld, D.C.; Bierwirth, C. An efficient genetic algorithm for job shop scheduling with tardiness objectives. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 155, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J. Solution Techniques for the Blocking Job Shop Scheduling Problem with Total Tardiness Minimization. Ph.D. Thesis, Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg, Magdeburg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.; Werner, F. A Permutation-Based Neighborhood for the Blocking Job-Shop Problem with Total Tardiness Minimization. In Operations Research Proceedings 2017; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 581–586. [Google Scholar]
- Mascis, A.; Pacciarelli, D. Job-shop scheduling with blocking and no-wait constraints. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 498–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.; Bürgy, R. Mixed-Integer Programming Heuristics for the Blocking Job Shop Scheduling Problem. In Proceedings of the 14th Workshop on Models and Algorithms for Planning and Scheduling Problems, MAPSP 2019, Renesse, The Netherlands, 3–7 June 2019; pp. 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki, E.; Smutnicki, C. An advanced tabu search algorithm for the job shop problem. J. Sched. 2005, 8, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, E.; Simonetti, N.; Vazacopoulos, A. Job shop scheduling with setup times, deadlines and precedence constraints. J. Sched. 2008, 11, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierwirth, C.; Kuhpfahl, J. Extended GRASP for the job shop scheduling problem with total weighted tardiness objective. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 261, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinedo, M.; Singer, M. A shifting bottleneck heuristic for minimizing the total weighted tardiness in a job shop. Nav. Res. Logist. (NRL) 1999, 46, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Wu, K.B. A revised simulated annealing algorithm for obtaining the minimum total tardiness in job shop scheduling problems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2000, 31, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bontridder, K.M.J. Minimizing total teighted tardiness in a generalized job shop. J. Sched. 2005, 8, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essafi, I.; Mati, Y.; Dauzère-Pérès, S. A genetic local search algorithm for minimizing total weighted tardiness in the job-shop scheduling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2008, 35, 2599–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülbül, K. A hybrid shifting bottleneck-tabu search heuristic for the job shop total weighted tardiness problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2011, 38, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mati, Y.; Dauzère-Pérès, S.; Lahlou, C. A general approach for optimizing regular criteria in the job-shop scheduling problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 212, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, C. A simulated annealing algorithm based on block properties for the job shop scheduling problem with total weighted tardiness objective. Comput. Oper. Res. 2011, 38, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.Á.; González-Rodríguez, I.; Vela, C.R.; Varela, R. An efficient hybrid evolutionary algorithm for scheduling with setup times and weighted tardiness minimization. Soft Comput. 2012, 16, 2097–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhpfahl, J.; Bierwirth, C. A study on local search neighborhoods for the job shop scheduling problem with total weighted tardiness objective. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 66, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, C.; Pacciarelli, D.; Pranzo, M. A rollout metaheuristic for job shop scheduling problems. Ann. Oper. Res. 2004, 131, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddi, A.; Rasconi, R.; Cesta, A.; Smith, S.F. Iterative Improvement Algorithms for the Blocking Job Shop. In Proceedings of the ICAPS, Atibaia, Brazil, 25–29 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- AitZai, A.; Boudhar, M. Parallel branch-and-bound and parallel PSO algorithms for job shop scheduling problem with blocking. Int. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 16, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranzo, M.; Pacciarelli, D. An iterated greedy metaheuristic for the blocking job shop scheduling problem. J. Heuristics 2016, 22, 587–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabah, A.; Bendjoudi, A.; AitZai, A.; Taboudjemat, N.N. Efficient parallel tabu search for the blocking job shop scheduling problem. Soft Comput. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröflin, H.; Klinkert, A. Feasible insertions in job shop scheduling, short cycles and stable sets. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 177, 763–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.L.; Lawler, E.L.; Lenstra, J.K.; Rinnooy Kan, A. Optimization and approximation in deterministic sequencing and scheduling: A survey. In Annals of Discrete Mathematics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; Volume 5, pp. 287–326. [Google Scholar]
- Pinedo, M. Scheduling: Theory, Algorithms, and Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brucker, P.; Knust, S. Complex Scheduling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Błażewicz, J.; Ecker, K.H.; Pesch, E.; Schmidt, G.; Weglarz, J. Handbook on Scheduling: From Theory to Applications; International Handbook on Information Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S. Supplement to Resource Constrained Project Scheduling: An Experimental Investigation of Heuristic Scheduling Techniques; GSIA, Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Mascis, A.; Pacciarelli, D. Machine Scheduling via Alternative Graphs; Technical Report; Universita degli Studi Roma Tre, DIA: Rome, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bierwirth, C.; Mattfeld, D.C.; Watson, J.P. Landscape regularity and random walks for the job-shop scheduling problem. In European Conference on Evolutionary Computation in Combinatorial Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavinotto, T.; Stützle, T. A review of metrics on permutations for search landscape analysis. Comput. Oper. Res. 2007, 34, 3143–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, F. Some relations between neighbourhood graphs for a permutation problem. Optimization 1991, 22, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.J.; Glass, C.A.; Potts, C.N. Machine Scheduling. In Local Search in Combinatorial Optimization; Aarts, E.H.L., Lenstra, J.K., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1997; Chapter 11; pp. 361–414. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, J. A comparison of neighborhoods for the blocking job-shop problem with total tardiness minimization. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference of Project Management and Scheduling 208, Rome, Italy, 17–20 April 2018; pp. 132–135. [Google Scholar]

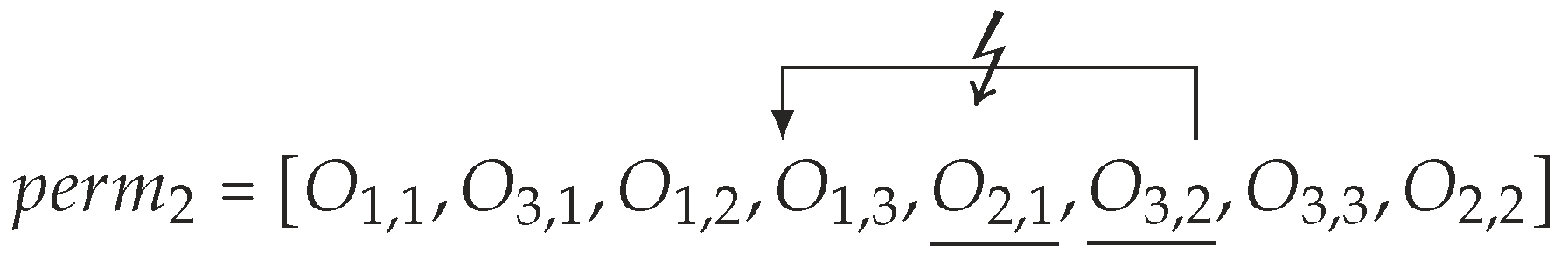


| Reference | Problem | Objective * | Max. Size | Solution Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nowicki and Smutnicki 2005 [19] | JSP | Tabu Search | ||
| Balas et al. 2008 [20] | JSP | Shifting Bottleneck Procedure | ||
| Singer and Pinedo 1999 [22] | JSP | Shifting Bottleneck Algorithm | ||
| Wang and Wu 2000 [23] | JSP | Simulated Annealing | ||
| Mattfeld and Bierwirth 2004 [14] | JSP | tardiness-based | Genetic Algorithm | |
| De Bontridder 2005 [24] | JSP | Tabu Search | ||
| Essafi et al. 2008 [25] | JSP | Hybrid Genetic Algorithm with Iterated Local Search | ||
| Bülbül 2011 [26] | JSP | Hybrid Shifting Bottleneck Procedure with Tabu Search | ||
| Mati et al. 2011 [27] | JSP | regular | Local Search Heuristic | |
| Zhang and Wu 2011 [28] | JSP | , | Simulated Annealing | |
| Gonzalez et al. 2012 [29] | JSP | Hybrid Genetic Algorithm with Tabu Search | ||
| Kuhpfahl and Bierwirth 2016 [30] | JSP | Local Descent Scheme, Simulated Annealing | ||
| Bierwirth and Kuhpfahl 2017 [21] | JSP | Greedy Randomized Adaptive Search Procedure | ||
| Brizuela et al. 2001 [12] | BJSP | Genetic Algorithm | ||
| Mati et al. 2001 [8] | BJSP | Tabu Search | ||
| Mascis and Pacciarelli 2002 [17] | BJSP | Greedy Heuristics | ||
| Meloni et al. 2004 [31] | BJSP | Rollout Metaheuristic | ||
| Gröflin and Klinkert 2009 [13] | BJSP | , | Tabu Search | |
| Oddi et al. 2012 [32] | BJSP | Iterative Improvement Scheme | ||
| AitZai and Boudhar 2013 [33] | BJSP | Particle Swarm Optimization | ||
| Pranzo and Pacciarelli 2016 [34] | BJSP | Iterative Greedy Algorithm | ||
| Bürgy 2017 [9] | BJSP | regular | , | Tabu Search |
| Dabah et al. 2019 [35] | BJSP | Parallel Tabu Search |
| Inst. | MIP | API | TAPI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ts01 | 138 * | 140.0 | 138 * | 142.6 | 138 * | |
| ts02 | 90 * | 95.0 | 91 | 96.6 | 90 * | |
| ts03 | 72 * | 78.8 | 72 * | 84.8 | 76 | |
| ts04 | 41 * | 41.4 | 41 * | 41.2 | 41 * | |
| ts05 | 71 * | 71.2 | 71 * | 71.6 | 71 * | |
| ts06 | 88 * | 125.0 | 108 | 119.4 | 109 | |
| ts07 | 172 * | 196.0 | 184 | 201.0 | 192 | |
| ts08 | 163 * | 185.6 | 163 * | 185.6 | 181 | |
| ts09 | 153 | 174.0 | 160 | 175.2 | 161 | |
| ts10 | 97 * | 116.6 | 107 | 112.6 | 108 | |
| ts11 | 366 | 409.4 | 387 | 411.8 | 392 | |
| ts12 | 419 | 429.2 | 412 | 442.4 | 419 | |
| ts13 | 452 | 492.2 | 472 | 478.2 | 445 | |
| ts14 | 459 | 500.6 | 473 | 508.8 | 492 | |
| ts15 | 418 | 433.2 | 413 | 428.2 | 387 | |
| Inst. | MIP | API | TAPI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ts01 | 138 * | 140.2 | 138 * | 140.0 | 138 * | |
| ts02 | 90 * | 94.6 | 91 | 95.2 | 91 | |
| ts03 | 72 * | 74.2 | 72 * | 74.4 | 72 * | |
| ts04 | 41 * | 41.8 | 41 * | 41.0 * | 41 * | |
| ts05 | 71 * | 71.4 | 71 * | 71.0 * | 71 * | |
| ts06 | 88 * | 121.6 | 107 | 119.8 | 111 | |
| ts07 | 172 * | 195.4 | 189 | 192.8 | 185 | |
| ts08 | 163 * | 184.2 | 179 | 185.0 | 181 | |
| ts09 | 153 | 178.8 | 168 | 177.4 | 174 | |
| ts10 | 97 * | 114.8 | 97 * | 112.0 | 105 | |
| ts11 | 366 | 406.4 | 390 | 401.6 | 387 | |
| ts12 | 419 | 428.2 | 412 | 424.6 | 405 | |
| ts13 | 452 | 462.6 | 448 | 460.6 | 447 | |
| ts14 | 459 | 462.8 | 418 | 495.0 | 466 | |
| ts15 | 418 | 419.4 | 401 | 435.0 | 414 | |
| Inst. | MIP | API | TAPI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| la01 | 762 * | 787.4 | 773 | 783.8 | 773 | |
| la02 | 266 * | 283.4 | 266 * | 277.6 | 266 * | |
| la03 | 357 * | 357.0 * | 357 * | 357.0 * | 357 * | |
| la04 | 1165 * | 1217.2 | 1165 * | 1284.2 | 1165 * | |
| la05 | 557 * | 557.0 * | 557 * | 557.0 * | 557 * | |
| la06 | 2516 | 2790.0 | 2616 | 2912.4 | 2847 | |
| la07 | 1677 * | 1942.2 | 1869 | 1904.2 | 1677 * | |
| la08 | 1829 * | 2335.0 | 1905 | 2129.6 | 1829 * | |
| la09 | 2851 | 3275.2 | 3161 | 3226.6 | 3131 | |
| la10 | 1841 * | 2178.2 | 2069 | 2119.4 | 2046 | |
| la11 | 6534 | 6186.2 | 5704 | 5846.4 | 5253 | |
| la12 | 5286 | 5070.0 | 4859 | 4997.8 | 4809 | |
| la13 | 7737 | 7850.6 | 7614 | 7611.8 | 7342 | |
| la14 | 6038 | 6616.8 | 5714 | 6872.4 | 6459 | |
| la15 | 7082 | 7088.6 | 5626 | 7153.6 | 6330 | |
| la16 | 330 * | 395.8 | 335 | 360.8 | 335 | |
| la17 | 118 * | 144.2 | 120 | 118.8 | 118 * | |
| la18 | 159 * | 229.4 | 159 * | 264.0 | 235 | |
| la19 | 243 * | 306.6 | 243 * | 301.0 | 243 * | |
| la20 | 42 * | 55.6 | 42 * | 42.0 * | 42 * | |
| la21 | 1956 | 2847.2 | 2101 | 2961.8 | 2680 | |
| la22 | 1455 | 2052.8 | 1773 | 2123.0 | 1988 | |
| la23 | 3436 | 3692.6 | 3506 | 3746.8 | 3424 | |
| la24 | 560 * | 966.8 | 761 | 724.0 | 644 | |
| la25 | 1002 | 1557.4 | 1289 | 1583.0 | 1390 | |
| la26 | 7961 | 9275.8 | 8475 | 8600.8 | 7858 | |
| la27 | 8915 | 7588.0 | 6596 | 7641.8 | 6457 | |
| la28 | 2226 | 3430.8 | 2876 | 3367.6 | 2849 | |
| la29 | 2018 | 2948.0 | 2432 | 3099.0 | 2626 | |
| la30 | 6655 | 7621.6 | 6775 | 7372.8 | 6395 | |
| la31 | 20,957 | 18,921.8 | 17,984 | 18,409.6 | 17,751 | |
| la32 | 23150 | 21,991.4 | 20,401 | 21,632.2 | 20,546 | |
| la33 | none | 22,494.2 | 19,750 | 22,913.2 | 20,553 | |
| la34 | none | 20,282.8 | 18,633 | 21,911.8 | 19,577 | |
| la35 | none | 21,895.0 | 18,778 | 21,384.4 | 20,537 | |
| la36 | 675 | 1856.0 | 1711 | 1839.0 | 1599 | |
| la37 | 1070 | 1774.2 | 1621 | 1835.8 | 1594 | |
| la38 | 489 * | 760.4 | 645 | 745.4 | 676 | |
| la39 | 754 | 1573.0 | 1391 | 1850.2 | 1551 | |
| la40 | 407 * | 1008.6 | 613 | 1187.6 | 912 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lange, J.; Werner, F. On Neighborhood Structures and Repair Techniques for Blocking Job Shop Scheduling Problems. Algorithms 2019, 12, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12110242
Lange J, Werner F. On Neighborhood Structures and Repair Techniques for Blocking Job Shop Scheduling Problems. Algorithms. 2019; 12(11):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12110242
Chicago/Turabian StyleLange, Julia, and Frank Werner. 2019. "On Neighborhood Structures and Repair Techniques for Blocking Job Shop Scheduling Problems" Algorithms 12, no. 11: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12110242
APA StyleLange, J., & Werner, F. (2019). On Neighborhood Structures and Repair Techniques for Blocking Job Shop Scheduling Problems. Algorithms, 12(11), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12110242






