Abstract
In this research, a nanoscale magnetic biosorbent was synthesized by incorporating magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) into a natural carbon framework derived from black cumin (BC) seeds. The prepared Fe3O4/BC was utilized as a low-cost, eco-friendly, and reusable nanobiosorbent for the removal of organic (e.g., methylene blue (MB) dye) pollutants from synthetic solutions. The results indicated that Fe3O4/BC had extensive surface oxygenous functional groups with a high affinity for MB dye capture at different concentrations such as 10–60 mg L−1. The optimization results suggested the removal of ~99% of methylene blue from its initial concentration (i.e., 10 mg L−1) using 2.0 g L−1 of Fe3O4/BC at pH = 7, temperature = 27 °C, and contact time = 120 min, with equilibrium adsorption capacity = 5.0 mg g−1 and partition coefficient = ~57.0 L g−1. The equilibrium adsorption efficacy at the highest initial concentration (i.e., 60.0 mg L−1) was found to be 29.0 mg g−1. The adsorption isotherm was well explained by the Freundlich model for MB. The renderability of this magnetic bioadsorbent by acid treatments showed a ~66% decline in removal efficiency (%) (~99% to ~33%; ~5.0 to ~1.7 mg g−1) for MB after six repetitive cycles of adsorption and desorption. The current Fe3O4/BC gives a better partition coefficient than previously reported acid-washed BC seeds and other BC-seed-based nanobioadsorbents, Hence, a synthesized Fe3O4/BC nanobiosorbent demonstrates potential for use in treating water contaminated with organic pollutants.
1. Introduction
Nanomaterials (NMs) have been intensively implemented to help eliminate chemicals in various environmental media via the adsorption treatment process [1,2]. Currently, a magnetic sorbent is one of the preferable techniques in the existing advanced research on adsorption-based nanotechnology for the enhanced recovery of powdered nanosorbents from aqueous solutions under the impacts of an external magnetic field [3,4]. Specifically, many magnetite (Fe3O4)-based nanocomposites have been explored for their effectiveness in selectively removing a variety of dyes such as methylene blue (MB) and Congo red from aqueous solutions [5]. Their effectiveness is attributed to their cost-effective production and non-toxic nature [6,7,8].
Nonetheless, producing most of these magnetic nanocomposite sorbents involves the utilization of activated carbon and/or biochar supports for loading magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) [8,9]. Notably, synthesizing activated carbon/biochar from biowaste products involves chemical treatments and consumes a significant amount of energy, which increases the costs of production and poses the risk of secondary pollution throughout the synthesis process [10,11]. Additionally, it has been observed that most NPs non-covalently adhere to activated carbon/biochar nanocomposites (since their surfaces do not have functional groups). This leads to the rapid leaching of NPs into water throughout the adsorption process [12]. Continuously aggregating these discharged NPs poses significant risks to marine life as well as human health [12].
The aforementioned limitations might be mitigated via searching for a new carbon support and enhancing the interaction between magnetic NPs and the carbon support. In this respect, natural plant materials with enormous oxygen/amine functionalities were used effectively for the synthesis of nanobiocomposites, such as magnetic Azolla and fig leaves [13], Fe3O4-GLP@ CAB [14], magnetic date seeds [15], and magnetic Forsythia suspensa leaves [16].
In this respect, the seeds of cultivated BC are natural and versatile carbon frameworks with a number of hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxylic (-COOH) groups at the surface. The possible significance of BC particles as biosorbents has already been demonstrated in several prior studies [17,18]. For example, an oxygenated functionalized BC seed surface (e.g., -OH and -COOH) could accelerate the adsorption of cationic pollutants such as cationic dyes and heavy metals in wastewater solutions [17,18]. These oxygenated functional groups could serve as scaffolds for the synthesis and development of metal/oxide NPs by the accommodation of metal (Mn+) ions [19,20]. Given this potential, a great deal of work has gone into creating hybrid nanosorbent BC particles that interact with various NMs, e.g., reduced graphene oxide/zirconium oxide/BC-based hybrid composites (rGO-BC@ZrO2) [19], BC with Fe2O3-ZrO2 particles (Fe2O3-ZrO2/BC) [20], and BC with Fe2O3-SnO2 particles (Fe2O3-SnO2/BC) [21]. However, to our knowledge, all these reported BC-based nanocomposite sorbents lack magnetic behavior for easy recovery and separation from aqueous solutions. Hence, in this work, we propose hybridization between BC and iron oxide NPs (e.g., Fe3O4 NPs with magnetic features [14]) to design nanobiomagnetic Fe3O4/BC nanocomposite sorbents for wastewater treatment.
Recently, a group of researchers [22] magnetized BC seeds and investigated their antifungal activity; however, no studies can be found that use magnetized BC for water treatment. Based on the expected advantages, the objective of this research work was to design a smart Fe3O4/BC nanobiosorbent for methylene blue (MB) removal in water solutions. To the best of our knowledge, the use of Fe3O4/BC as a magnetic nanobiosorbent for organic pollutant removal is reported in this work for the first time.
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Reagents and Materials
Anhydrous ferric chloride (FeCl3; purity 96.0%) and ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4.7H2O; purity 99.0%) were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany). Sodium hydroxide (NaOH; purity 97.0%), hydrochloric acid (HCl; assay purity 37%), sulfuric acid (H2SO4; MW 98.08; purity 98.0%), and methylene blue (MB; purity 97.0% and λmax at 660 nm) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany). Potassium nitrate (KNO3; purity 99.0%) was procured from Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany). The BC was collected from New Delhi, India.
2.2. Preparation of Fe3O4/BC
The preparation of nanoscale magnetic Fe3O4/BC bioadsorbent was carried out, following the simple co-precipitation method given in the literature [22]. In detail, the BC was rinsed with double distilled water, followed by drying overnight at 80–90 °C, ground to powder, and finally sieved through 60–200 mesh. One gram of sieved BC was suspended in 100 mL distilled water under ultrasonication (20 kHz) for 5 min at 27 ± 1 °C. Afterwards, 50 mL solutions containing 0.1M FeCl3 and 0.05M FeSO4 were introduced to BC suspension. The residual solutions were stirred at 950 rpm and 60 ± 5 °C for 30 min. After 30 min, the pH of the solution was maintained at pH 10.5 ± 1 by adding 8.0 M NaOH solution dropwise in atmospheric conditions and followed by further stirring for 15 min under the same conditions. Finally, the solution was cooled down to room temperature and the resulting precipitate-like particles settled. The resulting precipitate was filtered and this was followed by multiple washings with distilled water. The washed Fe3O4/BC composite was obtained by utilizing an exterior magnetic field at 60 °C for 48 h in a vacuum oven.
In the current research, the BC functionalized with a cellulosic surface enriched with numerous functional groups such as -COOH and -OH served as a carbon framework to embed Fe2+/Fe3+ ions into the BC surface. The Fe2+/Fe3+ ions undergo oxidation via co-precipitation to produce Fe3O4 NPs under the BC carbon framework upon the addition of NaOH. Note that all materials utilized in the current study were of analytical grade, as presented in Section 2.1. The prepared Fe3O4/BC was also characterized by various techniques (given in Section 2.3) to understand its surface chemistry, crystallinity, morphology, magnetism, and texture properties.
2.3. Instrumentation
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra were collected with a Nicolet 6700 FTIR spectrometer, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA after the formation of pallets in KBr with the resolution range of 4000–400 cm−1. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern was demonstrated (PW-3710 diffractometer, Philips, Cambridge, MA, USA) using Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.54 Å) and a Cu filter, 35 kV, 30 mA. A scanning electron microscope (SEM; Zeiss EVO 18 SEM, Jena, Germany) equipped with EDAX and a transmission electron microscopy (TEM) using a Technai G2 20, Hillsboro, Oregon, USA were used to analyze the structure and morphology of the constructed products. The magnetic behavior of Fe3O4/BC was confirmed by monitoring at 27 °C in a magnetic field (between 1.5 and −1.5 Tesla) by employing an MPMS-XL-7 magnetometer (MPMS-XL-7 magnetometer, Quantum Design, San Diego, CA, USA). The degree of carbon framework degradation and heat stability were determined using these profiles.
2.4. Zero-Point Charge (pHzpc) of the Fe3O4/BC
The Fe3O4/BC pHzpc was demonstrated using the salt addition method [23]. Briefly, a series of 100 mL Erlenmeyer flasks were filled with 0.2 g of Fe3O4/BC that had been dispersed in 50 mL of 0.01M potassium nitrate (KNO3) solutions with a starting pH value of 2–10. The pH of solutions was adjusted by using 0.1M HCl and NaOH solutions. Afterwards, all flasks were subjected to vigorous agitation in an incubator at 215 rpm and 27 ± 1 °C for 2 h, then left for 24 h of equilibration under static conditions. Finally, the pHzpc value of Fe3O4/BC was determined from the plot between initial pH and its change (∆pH = initial − final pH) after 24 h of equilibration.
2.5. Preparation of Adsorbate (MB) Solutions
One gram of MB was dissolved in one liter of double-distilled water to provide a stock aqueous solution with a concentration of 1000 mg L−1. During the adsorption experimental investigations, the generated stock solutions of MB dye were then diluted to the recommended quantities. The concentration of MB was measured at a λmax value of 660 nm using a spectrophotometer.
2.6. Adsorption Experiments
The adsorption capability of Fe3O4/BC nanobiosorbent for MB dye removal was tested with a batch adsorption technique. Herein, all adsorption experiments have been performed by the addition of 0.02 g of Fe3O4/BC and 10 mL MB solution in a sequence of 50 mL Erlenmeyer flasks, then agitated at 215 rpm and 27 ± 1 °C. Using the one variable at a time (OVAT) optimization method, the adsorption performance of Fe3O4/BC for target pollutants was investigated and optimized in relation to a list of key variables controlling the adsorption processes. The tested variables were as follows: the amount of Fe3O4/BC (1.0–5.0 g L−1), pollutant concentrations (MB (10–60 mg L−1)), temperatures (27, 35, and 45 °C), solution’s pH (2.0–10.0), and reaction contact time (15–120 min). After each adsorption experiment, the Fe3O4/BC nanocomposite was excluded from the prepared solution by utilizing an external magnet. Finally, the residual MB concentration present in the treated solutions was determined at the λmax value of 660 nm, utilizing a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (T80-UV/VIS, PG instruments Ltd., Leicestershire, UK).
The adsorption capacity (Qe (mg g−1), Equation (1)) of Fe3O4/BC nanocomposite for MB and the removal percentage (Equation (2)) were computed using the following formulas [18].
where Qe (mg g−1) is expressed as equilibrium adsorption capacity. The starting and equilibrium MB concentrations (mg L−1) are Co and Ce, respectively. The Fe3O4/BC nanocomposite mass is m (g) and the solution volume is V (L).
2.7. Thermodynamic Analyses for MB Adsorption
In terms of adsorption thermodynamics (27–45 °C), the change in entropy (ΔS°: kJ mol−1 K−1), enthalpy (ΔH°: kJ mol−1), and Gibbs free energy (ΔG°: kJ mol−1) for the transfers of MB molecules from liquid to solid adsorbent phases were computed as a function of their concentrations (see Section 2.2) at equilibrium contact time (120 min). The thermodynamic parameters were estimated using the following equation [24].
R expressed as the universal gas constant (8.314 J K−1 mol−1), Kd = Qe/Ce is the distribution coefficient, and T is the absolute temperature (K).
Once the ∆G° values have been computed, Formula (4) may be used to evaluate the ΔH° and ΔS°, respectively.
2.8. Isotherm Studies for MB Adsorption
The Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin isotherm models were used in this study to simulate the relationship between adsorbed and residual concentrations of MB molecules onto Fe3O4/BC nanocomposite at equilibrium [18]. The Langmuir model (Equation (5)) is useful to describe the monolayer adsorption [25].
where Qo (mg g−1) represents the adsorbent maximal monolayer capacity and b (L g−1) is the Langmuir constant. Based on the Langmuir constant, RL (the separation constant) is calculated (Equation (6)) to verify the adsorption nature [26].
The multilayer sorption onto the homogeneous/heterogeneous solid surface was explained by the Freundlich isotherm (Equation (7)) [27].
Freundlich constants denoted by kF ([mg g−1][L mg−1]1/n) and n signify adsorption capacity at unit concentration and intensity of adsorption, respectively.
The Temkin isotherm (Equation (8)) is applicable to examine the indirect solute–solid interaction during the adsorption process. It assumed that the surface sorbent coverage with solute molecules increases as heat of adsorption (bT) reduces [28].
where the constants for the maximal binding energy and heat adsorption are AT (L g−1) and bT (kJ mol−1), respectively.
2.9. Kinetic Studies for MB Adsorption
In optimum operation conditions, the kinetic studies have been performed to demonstrate the adsorption mechanism for MB on Fe3O4/BC nanobiosorbent and predict the rate-controlling adsorption process. In this respect, three kinetic models of pseudo-first-order (PFOM, Equation (9)), pseudo-second-order (PSOM, Equation (10)), and Elovich (Equation (11)) equations were used to examine the physicochemical interaction between MB and Fe3O4/BC surfaces [18,29]. In addition, a mechanistic kinetic diffusion model (e.g., intra-particle diffusion (IPD), Equation (12)) has been implemented to determine the rate-controlling adsorption method [18,29].
The k1 (min−1) is expressed as the PFOM kinetic rate constant, h is the starting rate constant (h = k2Qe2), and k2 (mg(1−n) Ln g−1) is PSOM’s overall kinetic rate constant. Qt (mg g−1) is solute removal capacity at time t (min). Additionally, Elovich constants α (mg g−1 min−1) and β (g mg−1 min−1) control the starting rates of adsorption and desorption, respectively. The β value also explains the degree of surface covering and chemical interaction activation energy [29].
The IPD (Equation (12)) model is expressed as follows.
2.10. Adsorption Activation Energy
In order to understand the mechanism of adsorption, whether it is physical adsorption or chemical adsorption, it is important to find out the activation energy. The activation energy can be determined by the Arrhenius equation (Equation (13)) [26].
Herein, K2 is the rate constant at various temperatures (27–45 °C), Ea is the activation energy (J mol−1), A is the Arrhenius frequency factor, R is the molar gas constant (8.314 J mol−1 K−1), and T is the absolute temperature (K).
By plotting a plot between lnK2 and 1/T, we can find the value of Ea.
2.11. Recyclability of Fe3O4/BC
The regeneration method was performed using desorption of adsorbed MB on the Fe3O4/BC adsorbent surface using solutions of 0.1 M HCl. Herein, the exhausted Fe3O4/BC sorbent was dispersed in 100 mL of HCl solution, then agitated at 215 rpm and 27 ± 1 °C for 4 h. The regenerated Fe3O4/BC was thoroughly washed with distilled water until the solution of pH became neutral, followed by drying. The dried Fe3O4/BC was further used for the removal of MB pollutants using the adsorption method from water solutions in optimum conditions. This desorption/adsorption process was repeated over six cycles to assess the adsorption stability of Fe3O4/BC in the environmental field.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Data of Fe3O4/BC
Herein, Fe3O4/BC biocomposite (relative to the raw BC framework) was characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra, powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX), transition electron microscope (TEM), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) analytical techniques. Notably, all characteristic data confirmed the successful impregnation of spherical and/or quasi-spherical NPs of Fe3O4 in a BC carbon framework, with strong binding between Fe3O4 and BC functionalities, to develop nanocomposite binding with high chemical/thermal stability and magnetic properties, as discussed below.
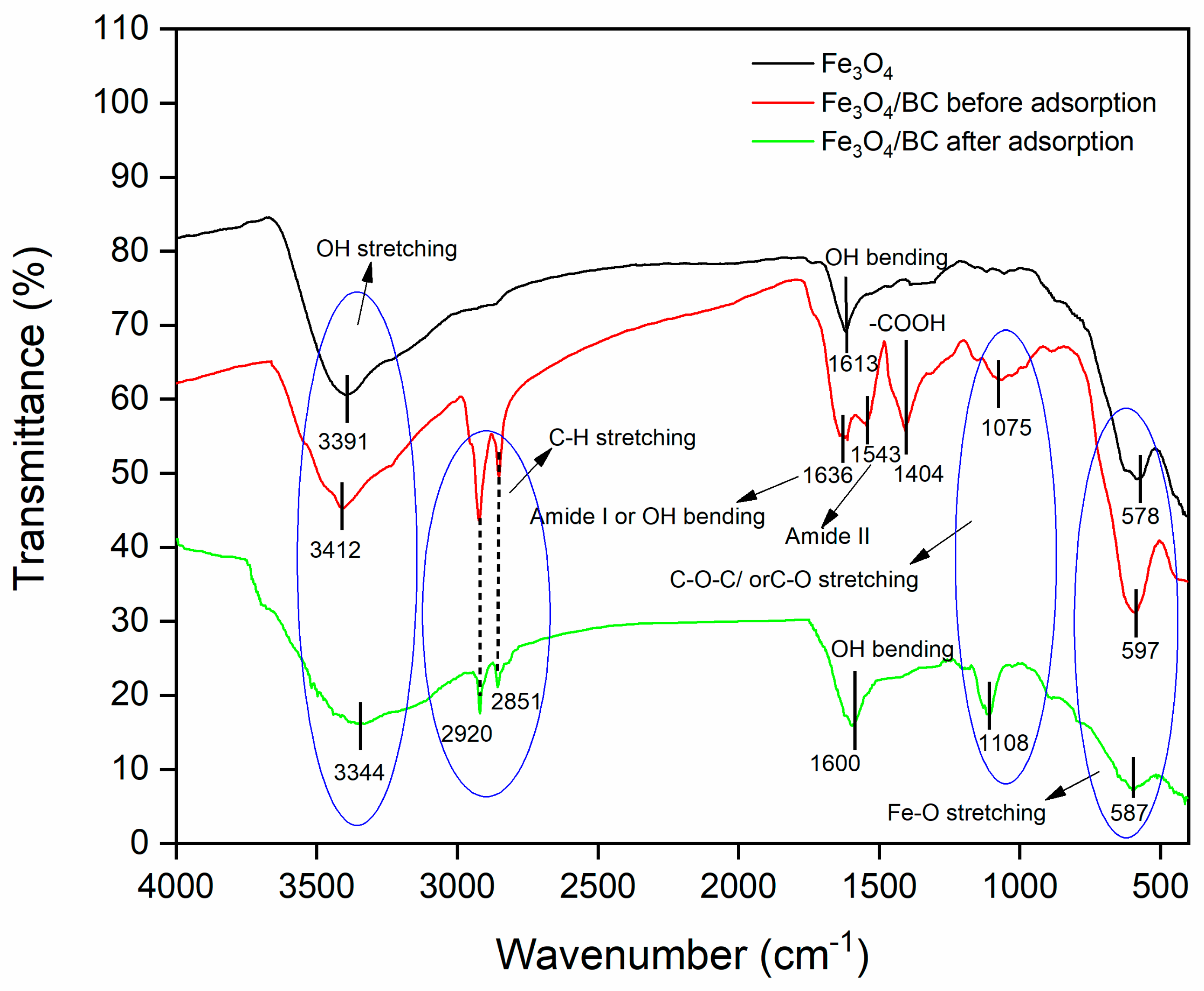
The FTIR spectrum of bare Fe3O4 NPs (prepared by a similar co-precipitation method) showed the vibration peaks of O-H (stretching at ~3391 cm−1 and bending at ~1613 cm−1; due to moisture absorbed) and metal–oxygen (Fe-O at ~578 cm−1) (Figure 1; black line). Compared to the FTIR spectrum of bare Fe3O4, the FTIR spectrum of Fe3O4/BC composite (Figure 1; red line) indicated the presence of various oxygen functionalities, which are related to the presence of the cellulosic framework of BC seed powder in the range of 600–4000 cm−1. In particular, the FTIR spectrum of Fe3O4/BC (Figure 1; red line) showed the following vibration peaks: O-H stretching (at ~3391 cm−1), stretching peaks (-C-H) of -CH3/-CH2 moieties (at ~2920 and 2851 cm−1) [30]), acidic carboxyl groups of cellulose (e.g., -COOH and C-O-C/C-O at ~1404 and ~1075 cm−1, respectively) [31,32,33], and amino acids of the protein–peptide bonds (e.g., N-H stretching amide II at ~1543 cm−1) [18,34]. The peak at ~1636 might be due to the peak of amide I and/or -OH bending [18,33,34]. All these peaks of functional groups observed in the FTIR spectrum of Fe3O4/BC showed strong agreement with the FTIR spectrum of BC seeds (with some shifting and disappearance) reported in our previous study (Figure S1). Furthermore, the newly observed stretching vibrational peak of Fe-BC (-O-Fe) at 597 cm−1 [35] indicates the successful impregnation of BC with Fe3O4 NPs and the presence of strong bonding among BC and Fe3O4. This is likely to suggest the bonding between the functional sites of BC (Figure S1) and Fe3+/Fe2+ during the in situ impregnation of Fe3O4 NPs. Similar FTIR results were observed for the previously reported magnetic Forsythia suspensa leaf [16] and quince seed mucilage nanocomposites [36].
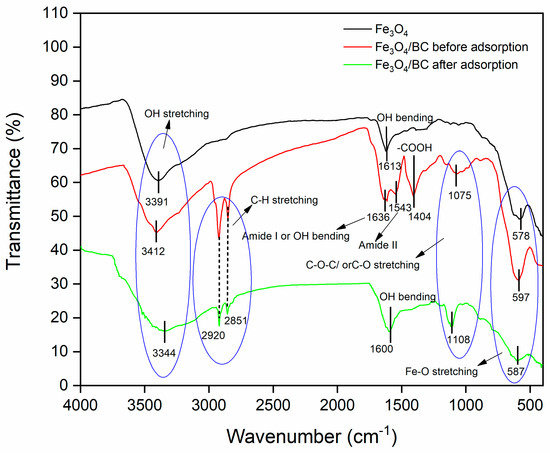
Figure 1.
FTIR spectrum of Fe3O4 (black line), Fe3O4/BC before adsorption (red line), and Fe3O4/BC after adsorption (green line).
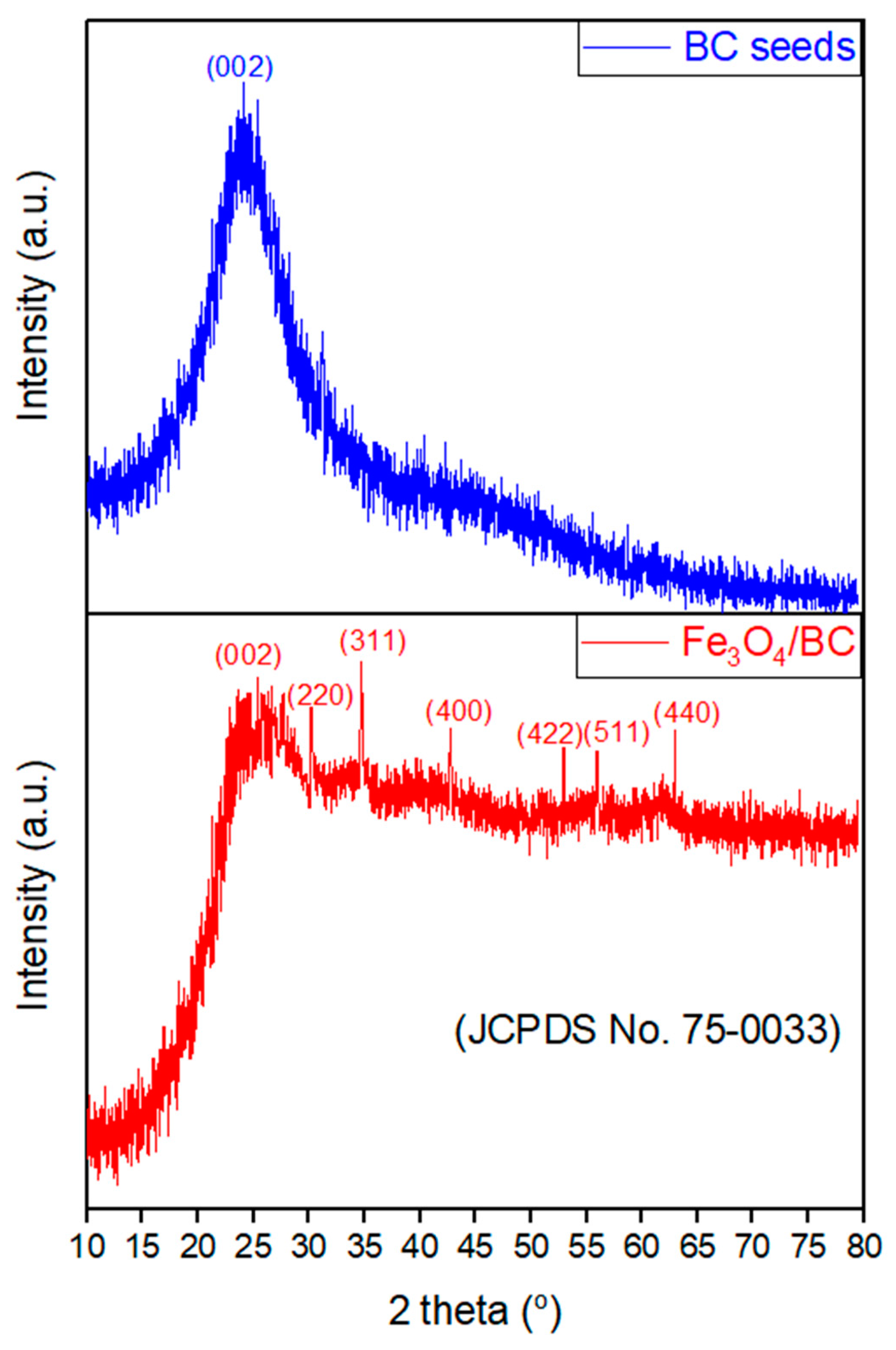
The XRD pattern of Fe3O4/BC (Figure 2; red line) showed characteristic patterns of Fe3O4 crystals at 2θ°of 30.1°, 34.9°, 42.8°, 53.0°, 56.0°, and 63.1°, belonging to [220], [311], [400], [422], [511], and [440], respectively [37]. These peaks are well-matched with JCPDS card no. 19-0629 of Fe3O4 crystals [38]. A broad peak corresponding to the [002] plane is also observed in the XRD spectrum of Fe3O4/BC at ~25.0°, which represents the carbon surface due to the BC seeds (see the comparative study with XRD of BC (Figure 2; blue line; since this study is an extension of our previous study [39], the XRD of BC was used with copyright permission from the publisher). This reflects the interaction between the crystalline Fe3O4 and amorphous BC [26,37,40].
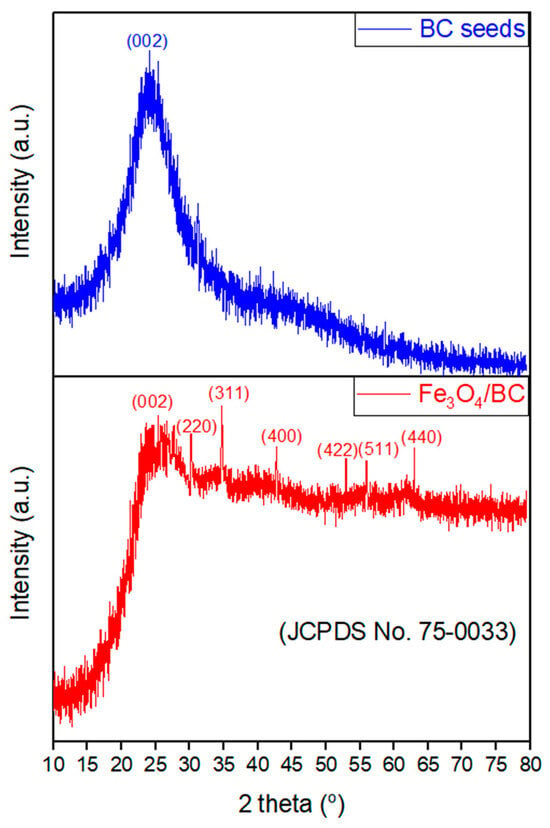
Figure 2.
XRD analysis of BC, reprinted from our previous study with permission from Siddiqui and Chaudhry [39], Copyright (2018) Elsevier (License No. 5990980697967), and Fe3O4/BC.
Nevertheless, it should be noticed that the color of the Fe3O4/BC sample changed from brownish-black to brown during the XRD study, which could have been caused by slight oxidation of Fe3O4 (magnetite) to the γ-Fe2O3 (maghemite) during preparation of composites through the investigated procedure [41]. This might suggest that the prepared Fe3O4/BC composite contains both Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3 phases. The Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3 showed exact XRD patterns so it is challenging to distinguish between these two phases [42]. Therefore, the predominate phase of the Fe3O4/BC composite might be determined using the XRD angular value as shown in Figure 2 (red line). In particular, the 2θ value of 35.35°, which belongs to the [311] plane, indicates the highest peak and confirms the presence of Fe3O4 (reported 2θ values for the [311] plane: 35.423° for Fe3O4 and 35.631° for γ-Fe2O3) [38]. Remarkably, the obtained 2θ value of the [311] plane of Fe3O4/BC is consistent (close) with the standard 2θ value for Fe3O4, confirming its dominant phase. Furthermore, the XRD peaks confirm that no other iron oxide is present in the prepared magnetic nanocomposite. Similar XRD results were observed for the previously reported quince seed mucilage magnetic nanocomposites [36].
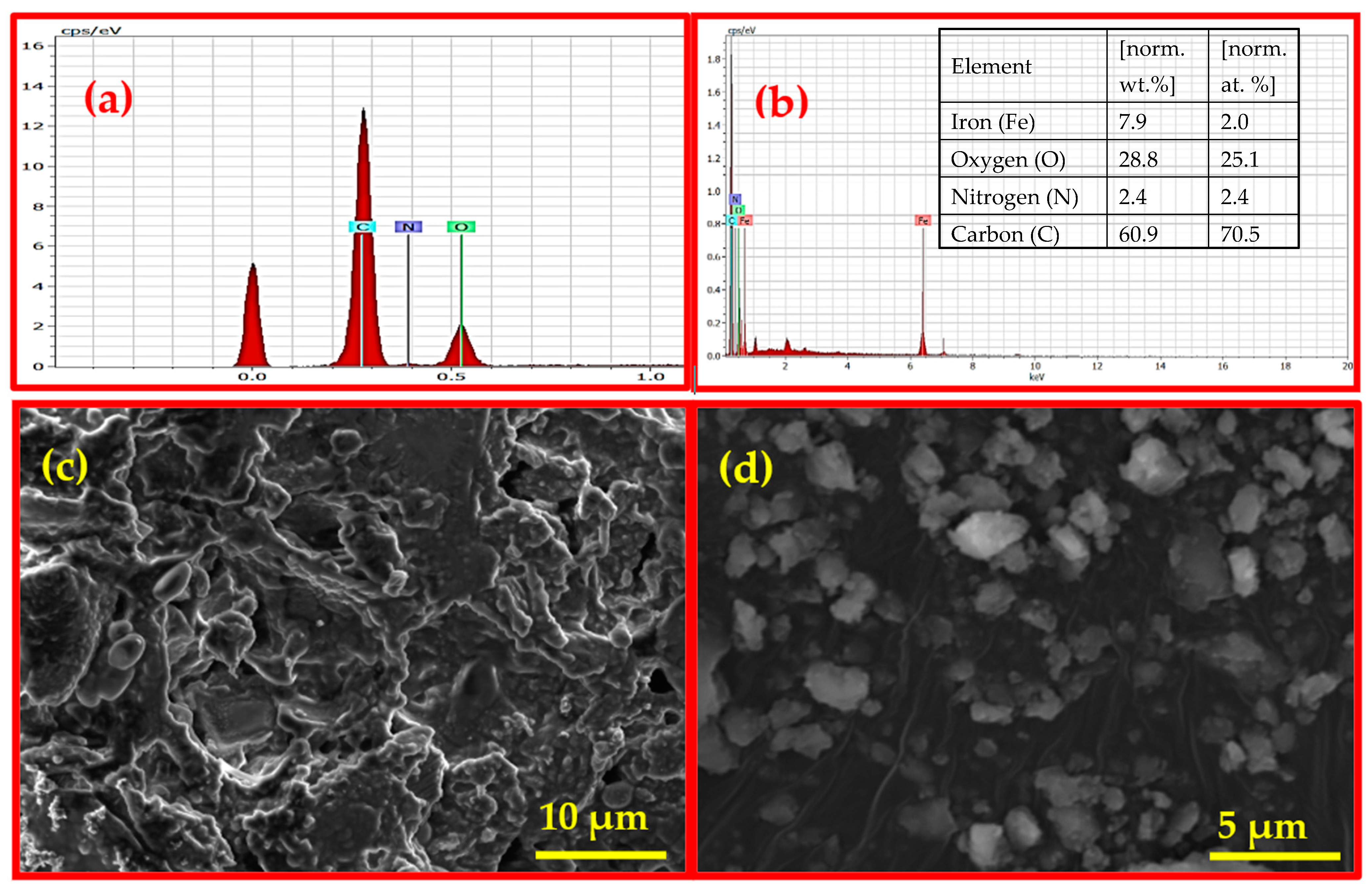
The structural appearance characteristic of Fe3O4/BC composite has been further demonstrated by using SEM, EDX, and TEM analysis, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. The SEM image of Fe3O4/BC (Figure 3d) showed high surface roughness incorporating quasi-spherical-shaped bright particles (relative to the smooth surface of BC in Figure 3c; since this study is an extension of our previous study [20], the SEM image of BC was used with copyright permission from the publisher) due to the amalgamation of Fe3O4 within the BC carbon framework.
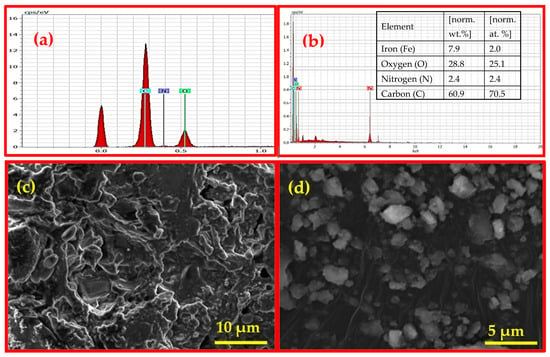
Figure 3.
EDX analysis of (a) BC (reprinted from our previous study with permission from Siddiqui and Chaudhry [39], Copyright (2018) Elsevier (License No. 5990980697967)) and (b) Fe3O4/BC (inset: elemental composition) and SEM images of (c) BC (reprinted from our previous study with permission from Siddiqui and Chaudhry [20], Copyright (2019) Elsevier (License No. 5990980217818)) and (d) Fe3O4/BC.
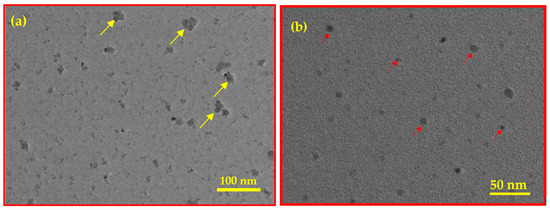
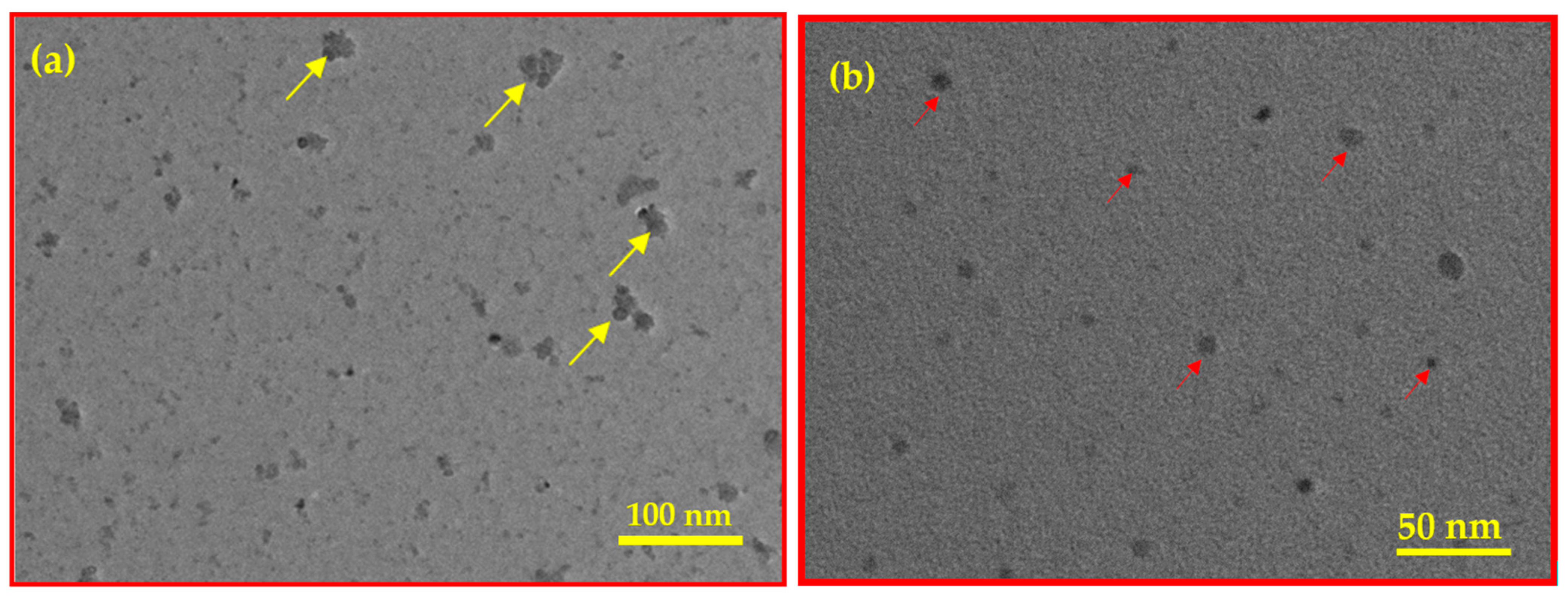
Figure 4.
TEM images of BC (a) and Fe3O4/BC (b).
The identification of Fe3O4/BC due to the presence of C, N, O, and Fe elements with weight percentages of 60.87, 2.45, 28.81, and 7.87, respectively, was further supported by EDX elemental techniques (Figure 3b). The presence of C, N, and O in nanobiocomposite (Fe3O4/BC) is due to the carbon framework of BC seeds (Figure 3a; since this study is an extension of our previous study [39], the EDX of BC was used with copyright permission from the publisher) while Fe is present due to the NPs.
The TEM image of BC (Figure 4a) shows small black round substances belonging to the vacuoles (indicated with a yellow arrow), suggesting mature and electron-dense granules due to the cellulosic structure of BC. These vacuoles are represented as active sites of Fe3O4 NPs, with diameters ranging from 20–100 nm within the BC (see Figure 4b for Fe3O4/BC composite). The van der Waals collisions as well as the magnetic nature of NPs caused the production of aggregated Fe3O4 NPs (red arrow, Figure 4b) on the BC as seen by TEM analysis. This results in low dispersibility and stress on Fe3O4 on the BC surface, leading to a rough, non-uniform distribution of Fe3O4/BC.
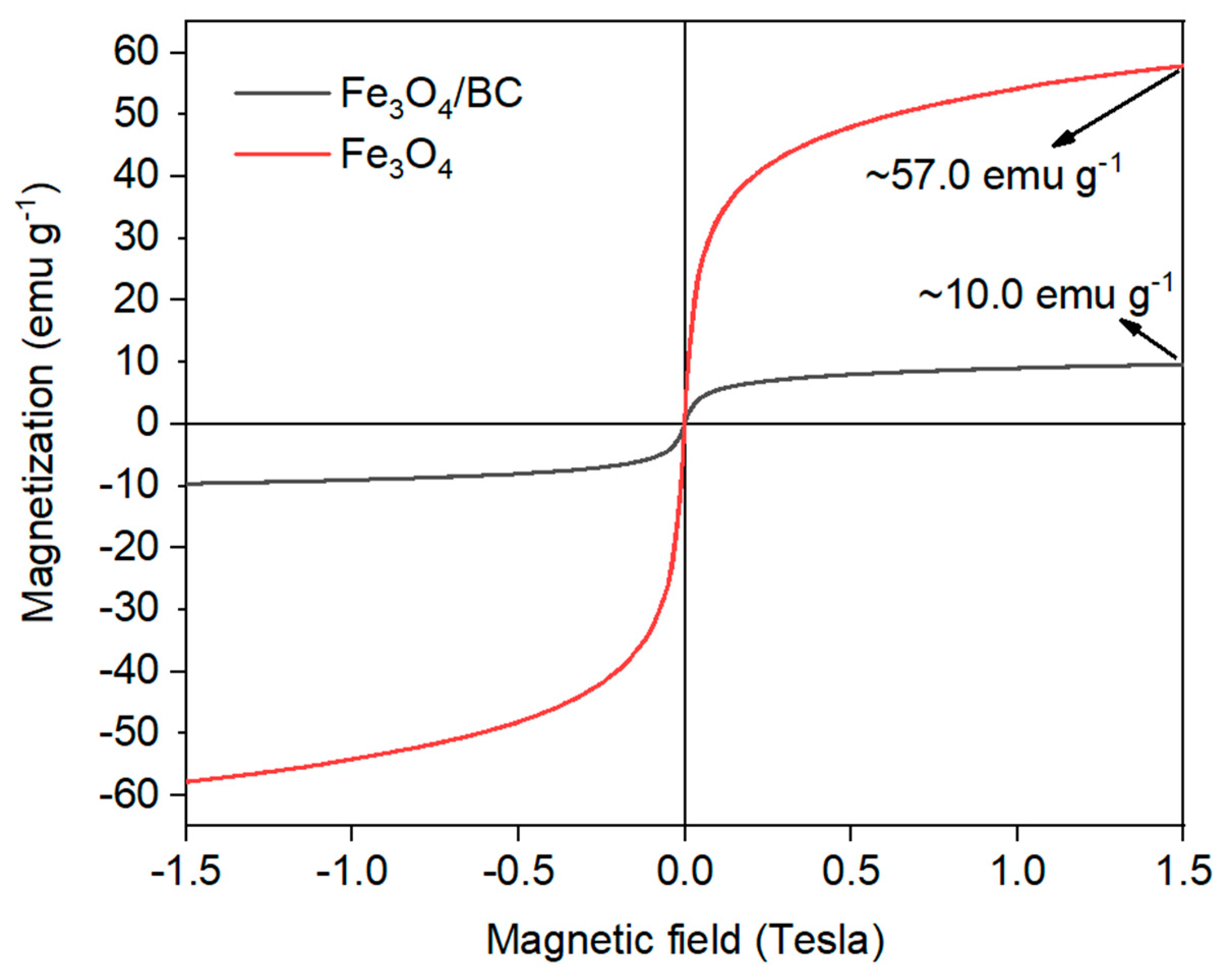
The magnetic behavior of Fe3O4/BC composite was also verified by VSM analysis at room temperature, as shown in Figure 5. As seen, the narrow hysteresis VSM loop of Fe3O4/BC with a very low coercive field and remanence value supported the magnetic significance of Fe3O4/BC at room temperature [40]. Nonetheless, the obtained saturation magnetism moment (Ms) of Fe3O4/BC composite was found to be approximately 10.0 emu g−1, that is reduced compared to bulk Fe3O4 (~90.0 emu g−1) listed in the previous works [43,44] as well as that prepared in this study as reference material (Figure 5; red line; ~57.0 emu g−1). This observation might be due to the partial oxidation of Fe3O4 to Fe2O3 and the presence of non-magnetic BC in the composite. Overall, the VSM results showed that Fe3O4/BC could be separated effectively after the adsorption process using a magnet.
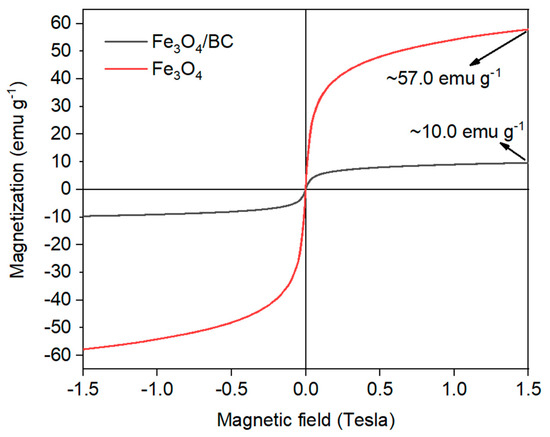
Figure 5.
VSM of bare Fe3O4 (red line) and Fe3O4/BC (black line).
3.2. Optimization of Fe3O4/BC Adsorption Behavior for MB Dye Pollutant
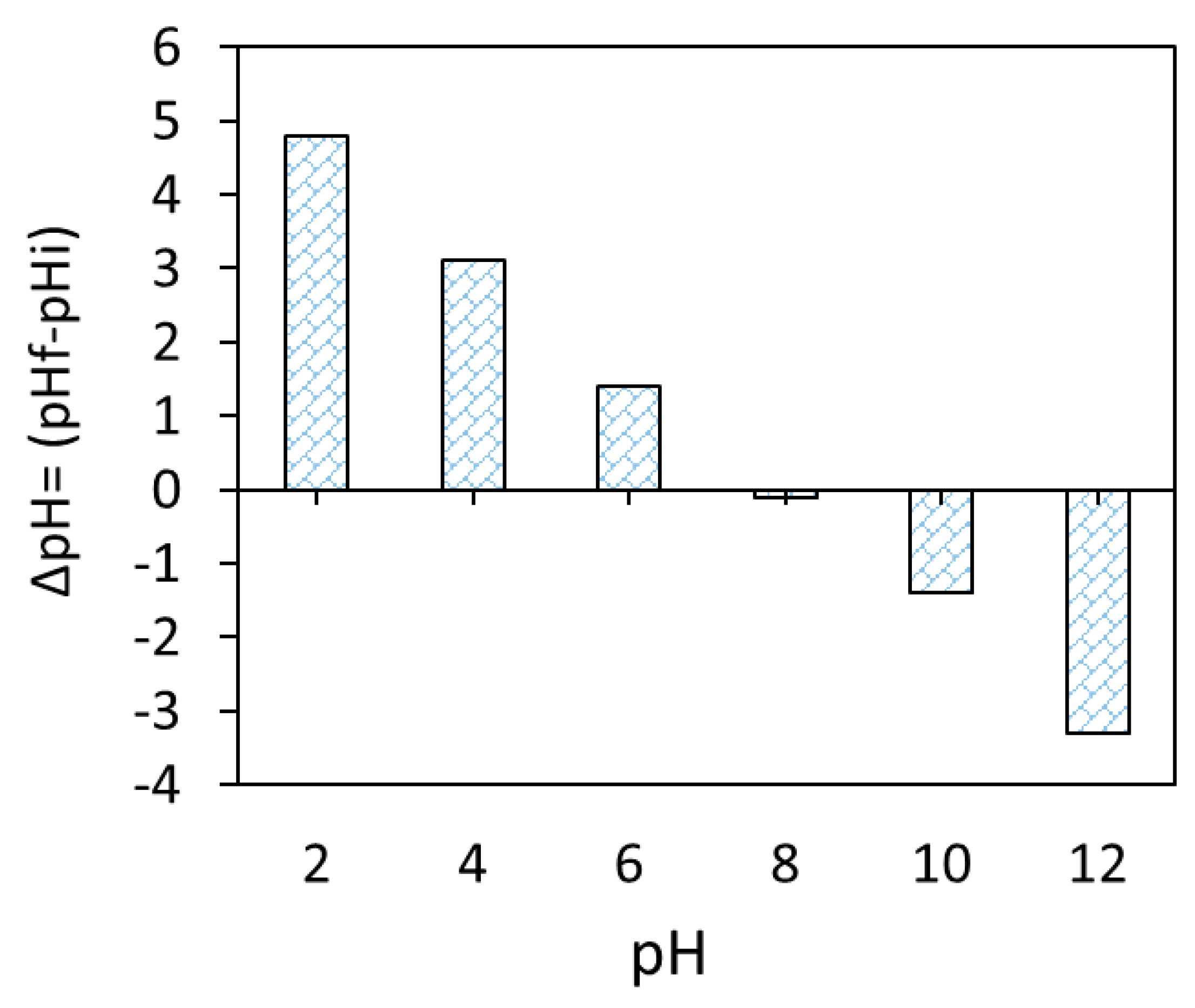
Based on the obtained FTIR and pHzpc (pHzpc ≈ 8.0, Figure 6) data of the Fe3O4/BC surface, the adsorption of MB dye onto Fe3O4/BC can be controlled by electrostatic/non-electrostatic (H bonding) interaction through suitably adjusting solution pH values. Hence, in this work, the amount of MB dye adsorbed onto Fe3O4/BC adsorbent was further investigated and optimized as a function of four key variables (e.g., adsorbent dose, contact time, initial pollutant concentrations, temperature, and solution pH).
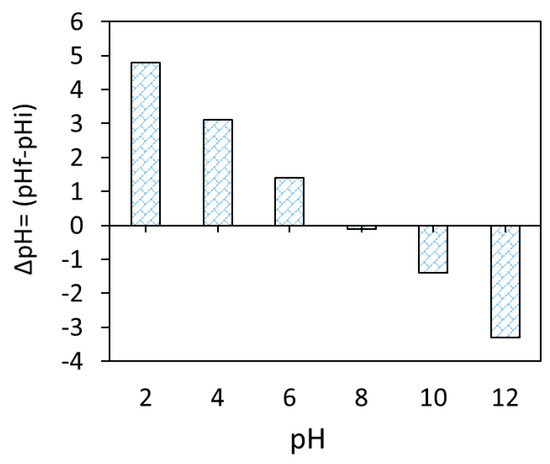
Figure 6.
Zero-point charge of magnetic Fe3O4/BC.
3.2.1. Effect of Fe3O4/BC Dosage
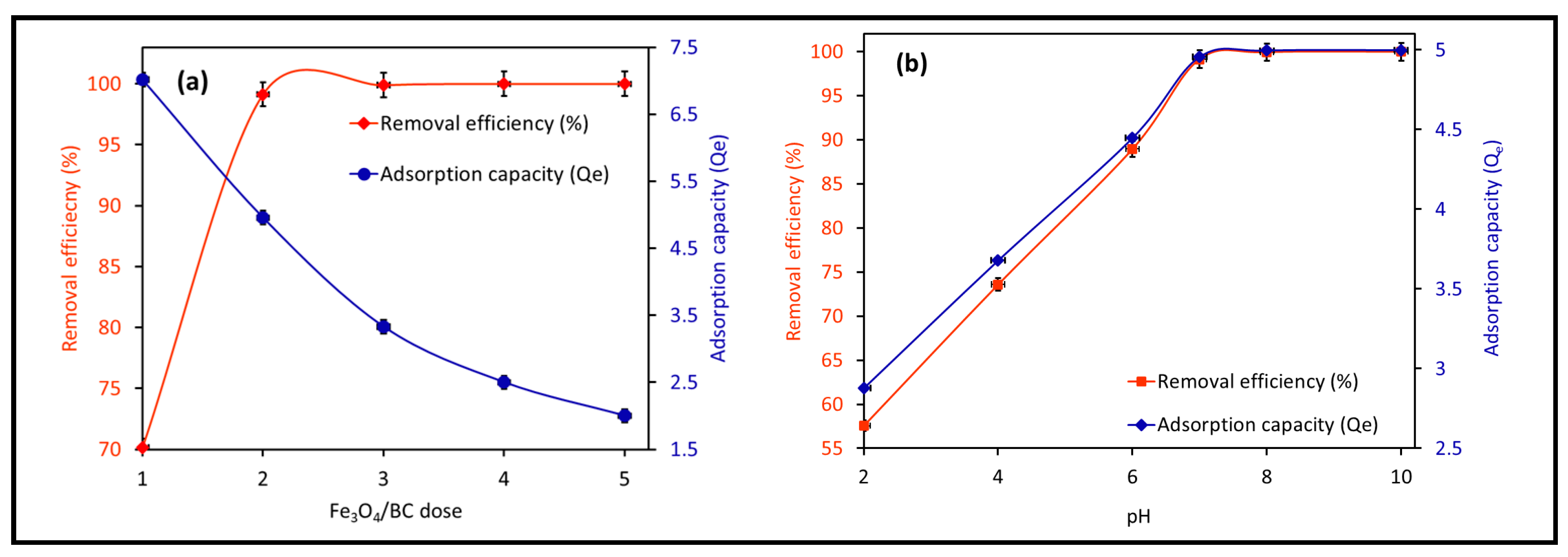
Figure 7a shows the effect of Fe3O4/BC dosage (1.0 to 5.0 g L−1) on the adsorption of 10 mg L−1 MB at fixed conditions of 120 min contact time, 27 ± 1 °C, and pH 7. The Fe3O4/BC adsorption capacity lowered from ~7.0 to 2.0 mg g−1 (for MB) by increasing nanobiosorbent dose from 1.0 to 5.0 g L−1 (Figure 7a). On the other hand, it was noted that approximately 99% of MB could be removed by increasing the Fe3O4/BC dose from 1.0 to 2.0 g L−1, followed by steady-state equilibrium curves (Figure 7a). The enhanced removal percentage with increasing Fe3O4/BC dose up to 2.0 g L−1 (as optimum value) may have been caused by the increased adsorption sites and stimulated collision between MB and Fe3O4/BC [20,29,45]. In contrast, the low adsorption capacity at a high adsorbent dosage (5 g L−1) could be a factor for three reasons: (i) the inversely proportional relationship of adsorption capacity to the adsorbent dose (see Equation (1)), (ii) the high capability of Fe3O4/BC for complete adsorption of M (≥99% removal) at a low dosage (2.0 g L−1); thus the increase in free available surface site numbers at a high dose could lead to their partial utilization (relative to lower Fe3O4/BC dosage (1.0 g L−1) with saturated adsorption sites), and/or (iii) the possible agglomeration of magnetic Fe3O4/BC composites at higher dosages may hinder the diffusion path of free MB adsorbate to the free active adsorption sites [46].
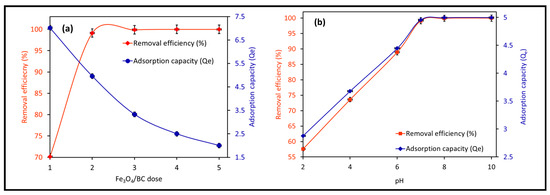
Figure 7.
Effect of operation conditions on the adsorption of MB on magnetic Fe3O4/BC adsorbent: (a) effect of adsorption dose (at pH = 7, MB initial concentration = 10 mg L−1, contact time = 120 min, and temperature 27 °C) and (b) effect of solution pH (at adsorption dose = 2.0 g L−1, MB initial concentration = 10 mg L−1, contact time = 120 min, and temperature 27 °C) on MB adsorption capacity/removal efficiency (%) of magnetic Fe3O4/BC.
3.2.2. Effect of Solution pH
The impact of pH changes from 2–10 on Fe3O4/BC adsorption efficacy for 10.0 mg L−1 MB in fixed conditions (27 ± 1°C and contact time of 120 min) is represented in Figure 7b at its optimum dose of 2.0-g L−1 Fe3O4/BC. The adsorption performance of Fe3O4/BC for both adsorbates is pH-dependent, with a maximum adsorption capacity at pH of 7.0–10.0 for MB. This pH–adsorption dependence can be explained based on the pHzpc value of Fe3O4/BC and the ionization/dissociation constant of MB vs. solution pH. At pH > pHzpc of 8, deprotonation of composite surface sites took place, leading negatively charged adsorbent surfaces (-O− and COO−). The opposite trend can be found at acidic pH (i.e., pH < pHzpc: positively charged surface -OH2+ and COOH2+ created by the hydration process).
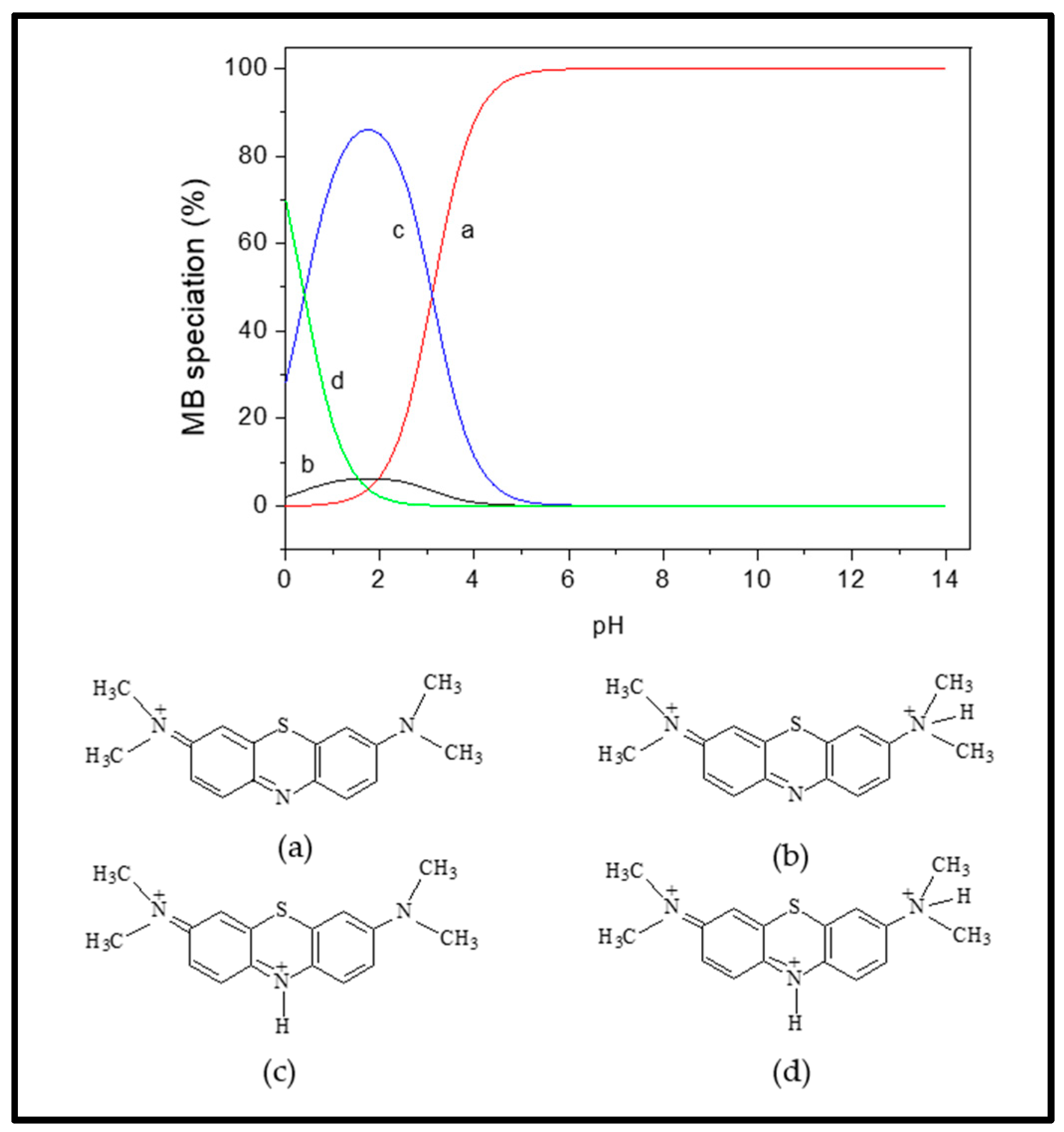
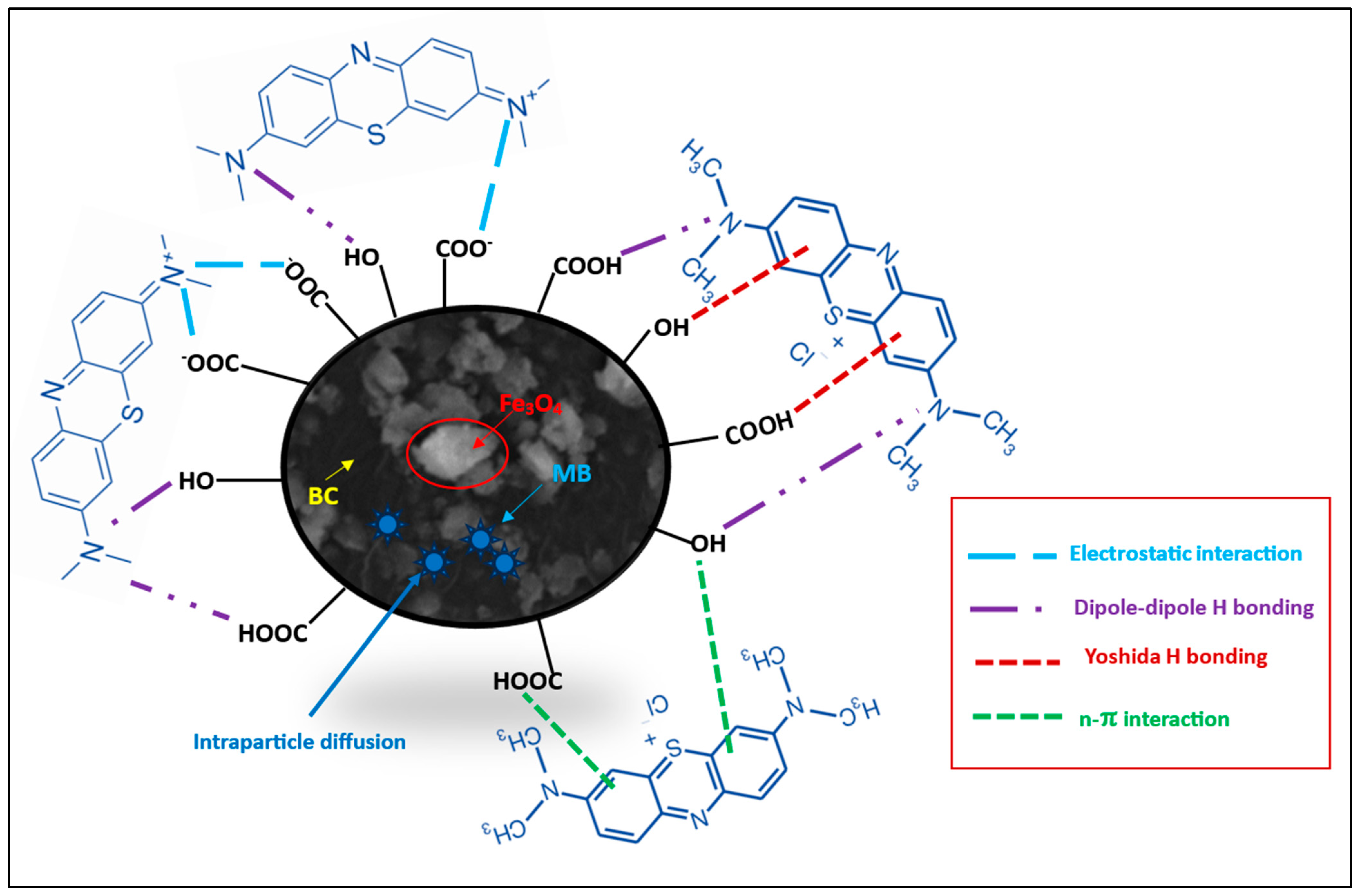
Considering the MB pKa value (i.e., 3.8), the predominant forms of MB in solutions should be the cationic species at 4.0 < pH < 4.0 (Figure 8; species a–d) [46]. At lower solution pH (2.0 to 7.0) < pHzpc, the cationic forms of MB+ molecules (Figure 8) can only be attracted to the protonated Fe3O4/BC surface through non-electrostatic interactions, such as van der Waals interactions, hydrophobic interactions, and/or ion exchange between -OH2+ and COOH2+ (on the Fe3O4/BC surface) and MB+ molecules (deprotonation effect). In the alkaline medium (pH ≥ pHzpc), the induced electrostatic interaction mechanism between the negatively charged Fe3O4/BC (Fe3O4/BC-O−) surfaces and cation MB+ molecules (cationic species ‘a’ in Figure 8) would accelerate the adsorption process to achieve the maximum capacity for MB dye at pHs of 7 to 10. Schematic representation for these interaction mechanisms between MB+ molecules and the Fe3O4/BC surface across varying solution pHs is visualized in Figure 9, as verified by FTIR analysis (before and after adsorption) in Section 3.1.
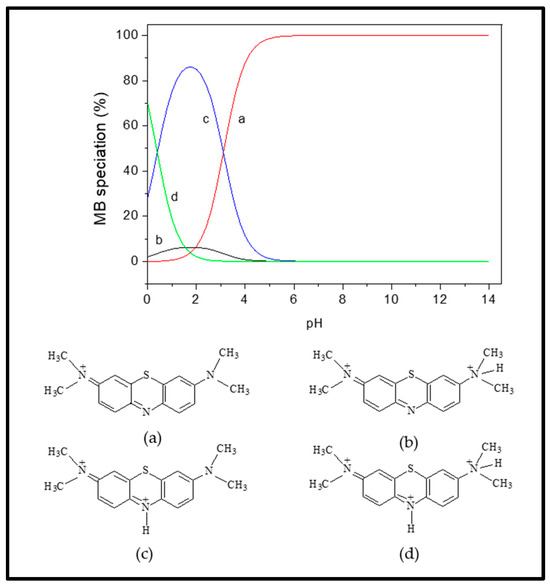
Figure 8.
Distribution of MB species (a–d) at different pHs. Adapted from the Sousa et al. [46], with copyright permission, Elsevier, 2019.
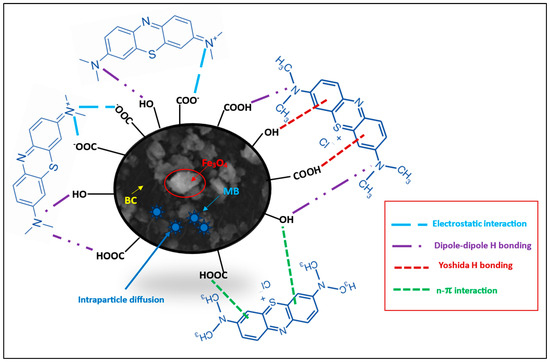
Figure 9.
Proposed mechanism of adsorption of MB onto Fe3O4/BC.
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorbate Concentrations and Temperature
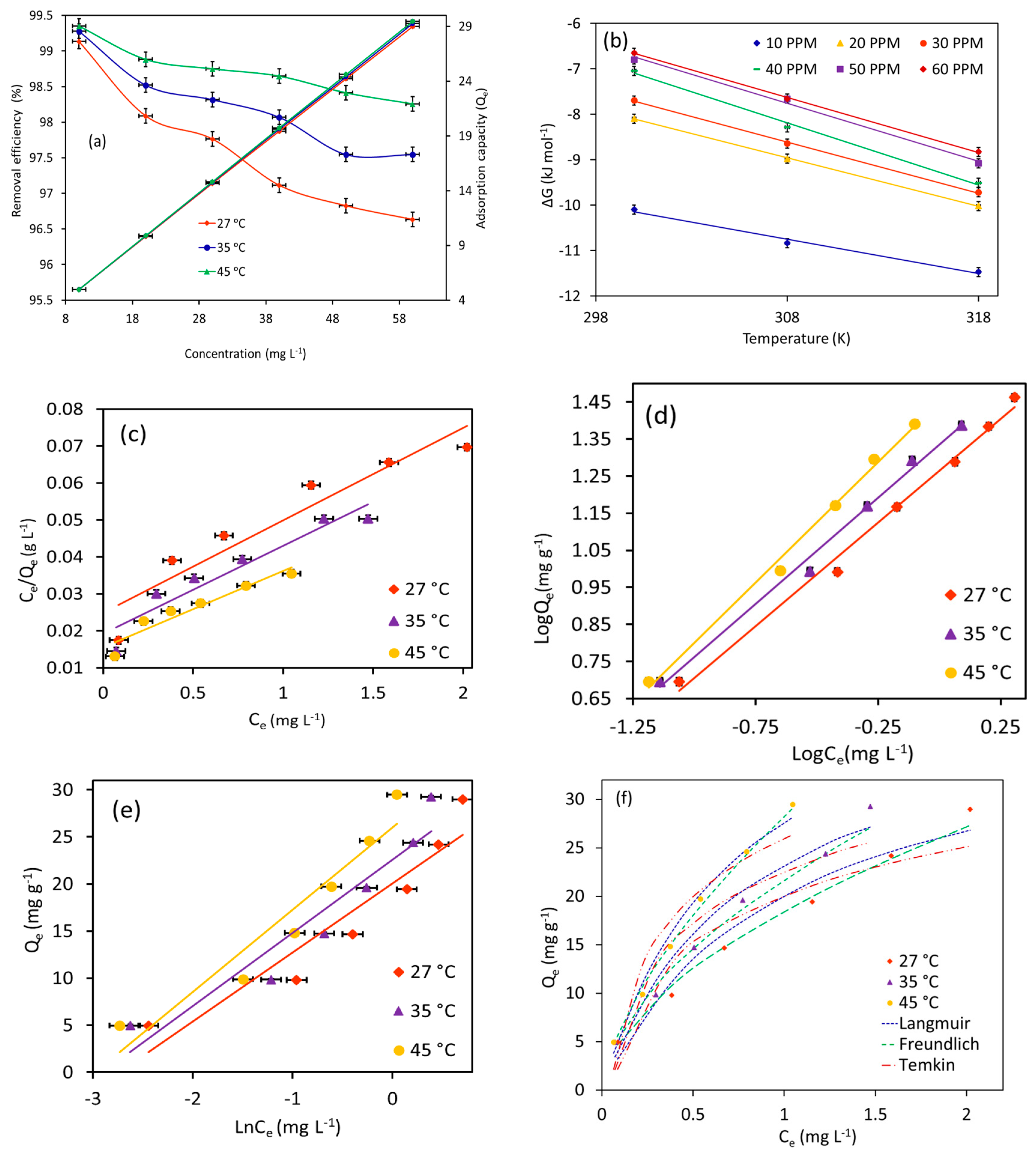
The combinatorial effects of MB starting concentrations ranging from 10–60 mg L−1 and temperature ranging from 27–45 °C on adsorption performance (equilibrium adsorption capacity and removal efficiency (%)) of Fe3O4/BC (2.0 g L−1) were also tested, as shown in Figure 10a (in fixed conditions of 120 min contact time and pH 7). In Figure 10a, the adsorption uptake of Fe3O4/BC for MB molecules increases from ~5.0 mg g−1 to ~29.0 mg g−1 by increasing the starting concentration from 10 to 60 mg L−1. On the other hand, it should be noted that the removal efficiency (%) was decreased with the increase in the initial MB concentration (Figure 10a). The improved adsorption uptake at higher initial concentrations could probably be attributed to the extent of the driving force of MB concentration gradients that promoted the interactions of MB molecules with available surface sites [29,47,48,49]. Nevertheless, it is important to note that the binding sites with a fixed amount of Fe3O4/BC may achieve a saturation point with an increase in initial loading level of adsorbate concentrations, leading to reducing the removal percentage of tested pollutants (Figure 10) as compared to the increased adsorption capacity.
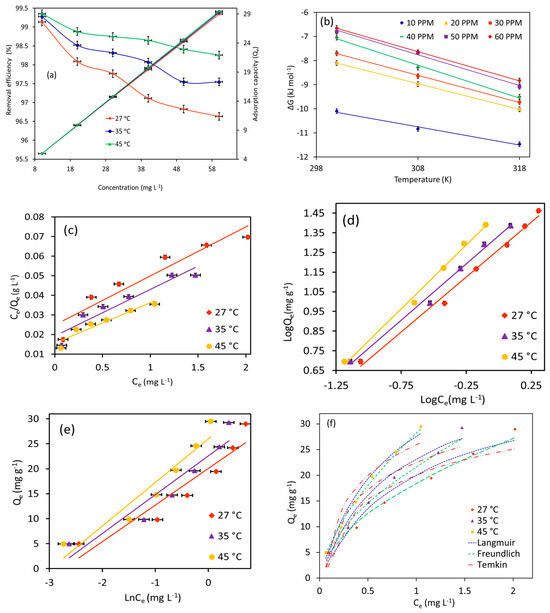
Figure 10.
Plots of (a) effect of temperatures and initial concentrations on MB adsorption, (b) thermodynamics, (c) Langmuir isotherm, (d) Freundlich isotherm, (e) Temkin isotherm, and (f) isotherm simulation at different temperatures for MB adsorption onto magnetic Fe3O4/BC (at pH = 7, adsorption dose = 2.0 g L−1, MB initial concentration = 10–60 mg L−1, and contact time = 120 min).
For the temperature effect, it was noted that increasing the temperature from 27 to 45 °C shows a slightly enhanced adsorption performance of Fe3O4/BC for MB uptake at all tested initial concentrations (Figure 10a). The favorable absorbent–adsorbate interaction with increased temperature indicates an endothermic and/or activated adsorption process [50]. With an increase in temperature, the kinetic energy and Brownian movement of adsorbate molecules in water solution could increase, leading to promoting the diffusion phenomenon of adsorbates to the Fe3O4/BC surfaces at higher temperatures [51]. Nonetheless, an increase in adsorbate kinetic energy at higher temperatures may lead to the breaking of physical interactions between MB adsorbate and Fe3O4/BC adsorbent surface (e.g., intermolecular H-bond, π–π interaction, and van der Waals bond), which play crucial roles in the adsorption process as discussed above [52]. This could slightly reduce the synergistic temperature effect on enhanced adsorption methods of Fe3O4/BC, especially at low starting concentrations of the pollutant (Figure 10a).
3.3. Thermodynamics of MB Adsorption
The thermodynamic variables, such as ΔH° (kJ mol−1), ΔS° (kJ mol−1 K−1), and ΔG° (kJ mol−1), for adsorption of MB over the entire range of concentrations of MB (10 to 60 mg L−1) are listed in Table 1. Notably, the values of positive ΔH° represented favorable endothermic adsorption in nature for MB onto Fe3O4/BC [24]. The positive ΔS° revealed increased disorder at the solid–liquid interface due to the change in hydration conditions of the adsorbed dye and/or Fe3O4/BC throughout the adsorption method [24]. The positive ΔS° values also indicate the redistribution of energy (rotational and translational) and randomness between the analytes and the Fe3O4/BC surface sites during the process of adsorption. This indicates that the favorable endothermic adsorption process can be promoted by activating the desolvation process of the adsorbates in solution (breaking MB—H2O and Fe3O4/BC—H2O H-bonds) and displacing the water molecules from the adsorbent surface (e.g., causing randomness in the system) when increasing the temperature value [24,53]. Positive ΔS° values are also likely to account for different oxygenated functionalities (-OH and -C=O) on the Fe3O4/BC surface in water solutions. These functionalities participate in the interaction process with adsorbate molecules via either electrostatic (-COO—MB+/-C-O−—MB+) or H bond (-COOH—MB/-OH—MB) interactions (i.e., the randomness of the adsorption process at the solid–liquid interface). These interactions were explained by FTIR analysis of Fe3O4/BC after MB adsorption, as explained in Section 3.6.

Table 1.
Thermodynamic parameters for MB adsorption at various concentrations *.
Thermodynamically, the negative ∆G values (Table 1; Figure 10b) can also be used to judge the effectiveness of electrostatic interactions between MB and Fe3O4/BC. Herein, the negative ΔG° values were observed for MB adsorption at all tested concentrations, indicating the interaction of MB with Fe3O4/BC [24]. Also, the negative values of ΔG° were slightly increased with increased temperature at all tested concentrations of MB, while the ΔG° values greatly declined with increasing initial concentrations of MB adsorbate (Table 1). These findings indicate the low contribution of electrostatic interactions in the adsorption process (in particular at low concentrations) along with the favorability of adsorption at higher temperatures. At higher temperatures, the conversion of MB liquid to solid forms should be able to take place spontaneously through the interaction of MB with the protonated/deprotonated Fe3O4/BC adsorbent functionalities as follows.
ΔG° (adsorption) for MB = ΔG°Fe3O4/BC + ΔG°Fe3O4/BC-MB + ΔG°Fe3O4-MB + ΔG°BC-MB
3.4. Isotherm Studies of MB Adsorption
Herein, adsorption equilibrium data of MB on Fe3O4/BC at three temperature levels (27, 35, and 45 °C) were described using Langmuir (Figure 10c), Freundlich (Figure 10d), and Temkin (Figure 10e) models to understand adsorption mechanism.
From Table 2 and Figure 10c–f, it is evident that the Freundlich model presents a satisfactory fit for the MB equilibrium adsorption data onto Fe3O4/BC at all temperature ranges, with a high correlation factor (R2) of 0.99 (for linear plot; Figure 10d) and the lowest standard error (ARE; for simulation graph; Figure 10f). Notably, the Langmuir isotherm cannot be used to explain the adsorption data in this study due to the poor fitting with the experimental data of MB dye on Fe3O4/BC (Figure 10c,f). These findings indicated that the uptake mechanism of MB molecules appeared to follow multilayer adsorption on Fe3O4/BC surfaces that possess active surface sites with different energies (i.e., heterogeneous adsorption sites). This observation was supported by high theoretical adsorption intensity (n) values in a range of 1.8–1.5 for MB (Table 2), verifying the favorable adsorption onto heterogeneous adsorbent surfaces [20].

Table 2.
The isothermal parameters for the adsorption of MB onto Fe3O4/BC *.
Based on Temkin constants (Table 2), the adsorption process between the MB molecules and Fe3O4/BC surface (physical or chemical interactions) can be interpreted theoretically. As seen, the low values of the heat of adsorption parameter (bT, kJ mol−1: 0.34–0.30) indicate the dominant role of physisorption interactions between the MB and Fe3O4/BC surface sites [54].
From the Freundlich isotherm, the values of the kF constant were increased from 18.4 to 28.2 mg(1−n) Ln g−1 for MB as the temperature increased from 27 to 45 °C. This indicates that Fe3O4/BC has a good adsorption affinity for MB dye and that adsorption affinity may increase with temperature (i.e., improved interactions between the MB and Fe3O4/BC at higher temperatures). However, it should be noted that the estimated values of Temkin model parameters (AT (binding energy) and bT (heat of adsorption)) have been slightly affected by the alteration of adsorption temperature, suggesting the slight contribution of temperature to the MB adsorption on the Fe3O4/BC surface.
3.5. Kinetics Studies of MB Adsorption
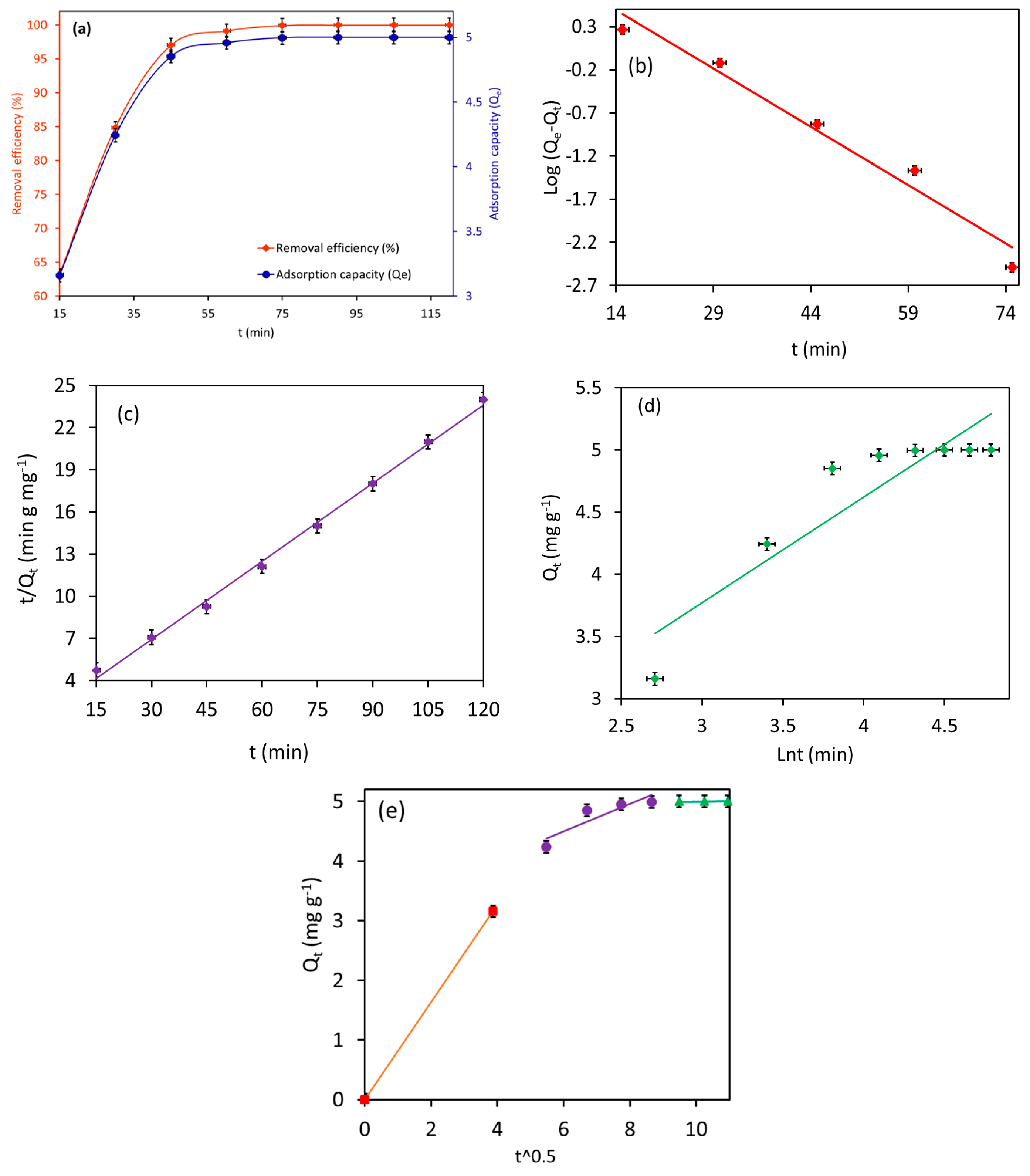
Figure 11a illustrates the adsorption rate of 10.0 mg L−1 MB by Fe3O4/BC (2.0 g L−1) as a function of contact time (15–120 min) in fixed conditions (temperature of 27 °C and pH 7).
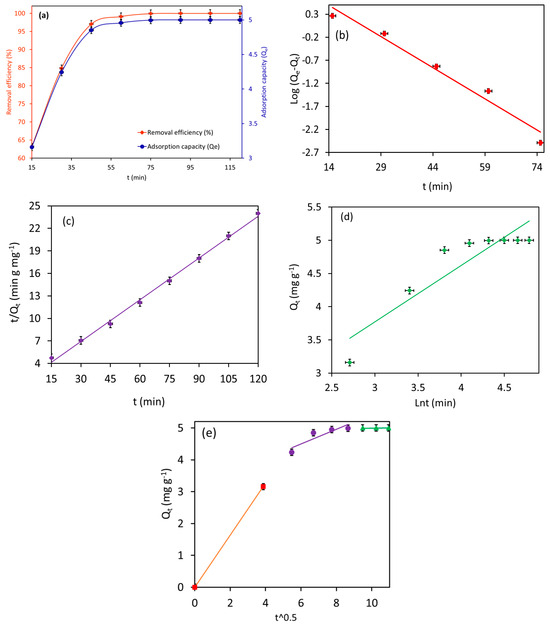
Figure 11.
Plots of (a) effect of contact time on MB adsorption, (b) PFO kinetic, (c) PSO kinetic, (d) Elovich kinetic, and (e) intraparticle diffusion model for MB adsorption onto the Fe3O4/BC (at pH = 7, adsorption dose = 2.0 g L−1, MB initial concentration = 10 mg L−1, and temperature 27 °C).
Notably, the Fe3O4/BC showed faster uptake for MB dye molecules (in 45 min, Figure 11a), confirming the high affinity of the developed sorbent for organic dye removal. The obtained time-dependent adsorption data of MB on Fe3O4/BC were also examined with the help of various kinetic models (PFO, PSO, Elovich, and IPD models) to understand the rate-controlling adsorption step. The kinetic plots of PFO, PSO, and Elovich models and their fitting to the experimental data are illustrated in Figure 11b–e, while the computed constants for these kinetic models are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
(a) Parameters of the PFO, PSO, and Elovich kinetic models for the adsorption of MB onto Fe3O4/BC *. (b) Parameters of the Weber–Morris model for adsorption of MB onto Fe3O4/BC *.
As shown in Table 3(a), the adsorption of MB onto Fe3O4/BC is better fitted to the PSO model (R2 of 0.99) than PFO (R2 of 0.97) and Elovich models (R2 of 0.83). The good agreement between the experimental and calculated adsorption capacity was shown by the PSOM (with ∆Q = 0.40) compared to PFOM (with ∆Q = 8.1). This finding suggests that the adsorption of MB onto Fe3O4/BC is likely to be controlled by chemisorption (electrostatic) interaction. It is also apparent that the prepared Fe3O4/BC adsorbent exhibited an uptake rate for MB (k2 = 0.025 g mg−1 min−1). Similar results were reported by Elkady et al. [29].
Notably, the Elovich plot has a low R2 (0.83) value which does not support the fact that the Fe3O4/BC adsorbed the MB pollutants through pure chemisorption (i.e., some form of physical absorption is also responsible for the current MB absorption). From Table 3(a), the higher value of α (3.6 mg g−1 min−1) than the value of β (1.2 mg g−1) suggested that the rate of MB adsorption onto Fe3O4/BC was much higher than the rate of their desorption at equilibrium [20]. Such results can be explained by the interactions of surface functionalities of Fe3O4/BC with adsorbate molecules via electrostatic (-COO—MB+/-C-O-—MB+) and non-electrostatic (e.g., H bond) interactions.
Referring to the IPD plots for MB adsorption (Figure 11e), it is quite clear that the adsorption of MB onto the Fe3O4/BC surface followed the three-step process at the given initial MB concentration. From the IPD plots (Figure 11e), the first, very steep stage (0–15 min for MB) reflected the instantaneous adsorption on the external adsorbent surface due to mass transfer. The second even steeper stage suggested MB adsorption due to boundary layer formation (film diffusion) [29]. The third gradual stage (linear portion) is attributed to the adsorption region in which the intraparticle diffusion is the rate-limiting step. It is evident from Figure 11e that the linear lines of IPD plots did not pass through the origin, suggesting that the rate-limiting adsorption mechanism was not only the intraparticle diffusion process [29]. In Table 3(b), the larger value of the intercept (boundary layer thickness, C2) and smaller value of the constant (Kd2) of IPD for the adsorption of MB on Fe3O4/BC indicate the high surface affinity (fast adsorption rate) for interaction with MB molecules (at the second stage) compared to that of their intraparticle diffusion (third stage) [29]. Based on these observations, intraparticle diffusion is the major rate-determining (slow) step for the adsorption of MB pollutants on the prepared Fe3O4/BC nanobioadsorbent [29].
These kinetic models may be evidence for the physicochemical adsorption process for MB adsorption onto the Fe3O4/BC along with the electrostatic/non-electrostatic interaction between the functional sites of Fe3O4/BC and MB (Figure 9) [15], which was further confirmed by comparative FTIR analysis before and after the adsorption process in Section 3.1.
3.6. Adsorption Activation Energy
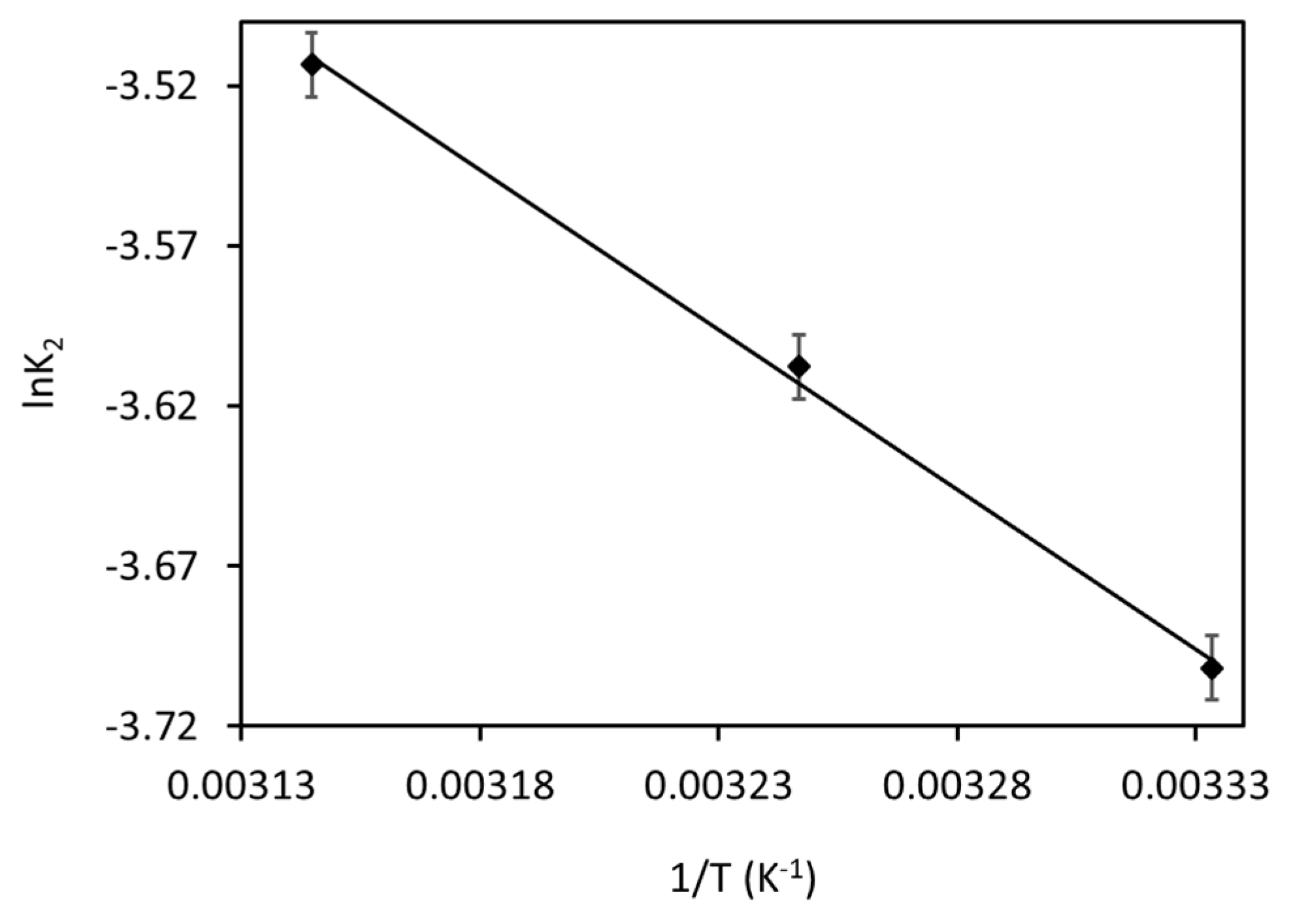
To find the Ea, a graph made between lnK2 and 1/T is shown in Figure 12. The Ea value for current MB adsorption was found to be 8.3 kJ mol−1, which confirms that the present MB adsorption is majorly governed by physisorption. This result can also be confirmed through previous studies [26].
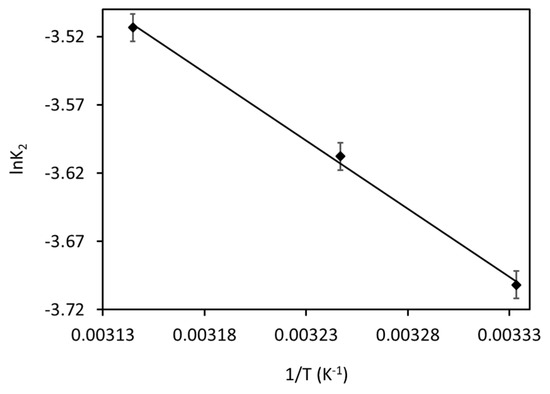
Figure 12.
Arrhenius plot for the MB adsorption onto Fe3O4/BC.
3.7. Adsorption Mechanism, Reusability Features, and Economic Efficiency
3.7.1. FTIR Analysis for MB-Loaded Fe3O4/BC: Adsorption Mechanism
The electrostatic/H-bonding interactions of MB dye with functional surface sites of Fe3O4/BC were confirmed by FTIR analyses before and after adsorption, as represented in Figure 1. The FTIR spectrum of Fe3O4/BC after MB adsorption in Figure 1 (green line) and the red-shift in the -OH stretching frequency from 3412 cm−1 (before adsorption) to 3344 cm−1 (after adsorption) may result from the H-bond formation between cationic MB and hydroxyl Fe3O4/BC. The carbonyl peak of amide I/OH bending and N-H stretching amide II bands also show a larger shift towards the lower wavenumber (for amide I/OH bending; 1636 cm−1 (before adsorption) to 1600 cm−1 (after adsorption)) and disappearance ((for amide II; 1543 cm−1 (before adsorption)), assuming a strong electrostatic interaction of MB with amide functional sites. Similarly, the disappearance in vibrational peaks (1404 cm−1 and 1075 cm−1) (Figure 1, red line) was obtained due to electrostatic interaction between MB and functional sites of Fe3O4/BC (Figure 1, green line). The existence of the C-S stretching bond of MB molecules was further demonstrated by characteristic peaks at 1108 cm−1 (after adsorption) that supported the idea that MB was adsorbed on Fe3O4/BC. These findings indicate that there was a specific electrostatic interaction between Fe3O4/BC and MB (Figure 9).
3.7.2. Comparative Performance Based on the Partition Coefficient Metric
The performance of Fe3O4/BC relative to the reported adsorbent in the literature for MB dye removal was evaluated through a comparative analysis based on maximum capacity (Qo mg g−1), removal efficiency (%), and partition coefficient (PC: L g−1). In this study, PC (L g−1) performance data have been considered a feasible key metric for comparative analysis because the operating conditions can alter the removal efficiency (%) and Qo values (e.g., initial concentration levels of the target compounds and mass of loaded adsorbent). In this regard, PC equations (Equation (15) or Equation (16)) were developed to provide a more reliable judgment on the performance by avoiding the variation in experimental conditions by considering the initial or residual pollutant concentrations and loaded mass of adsorbent in the capacity form [20].
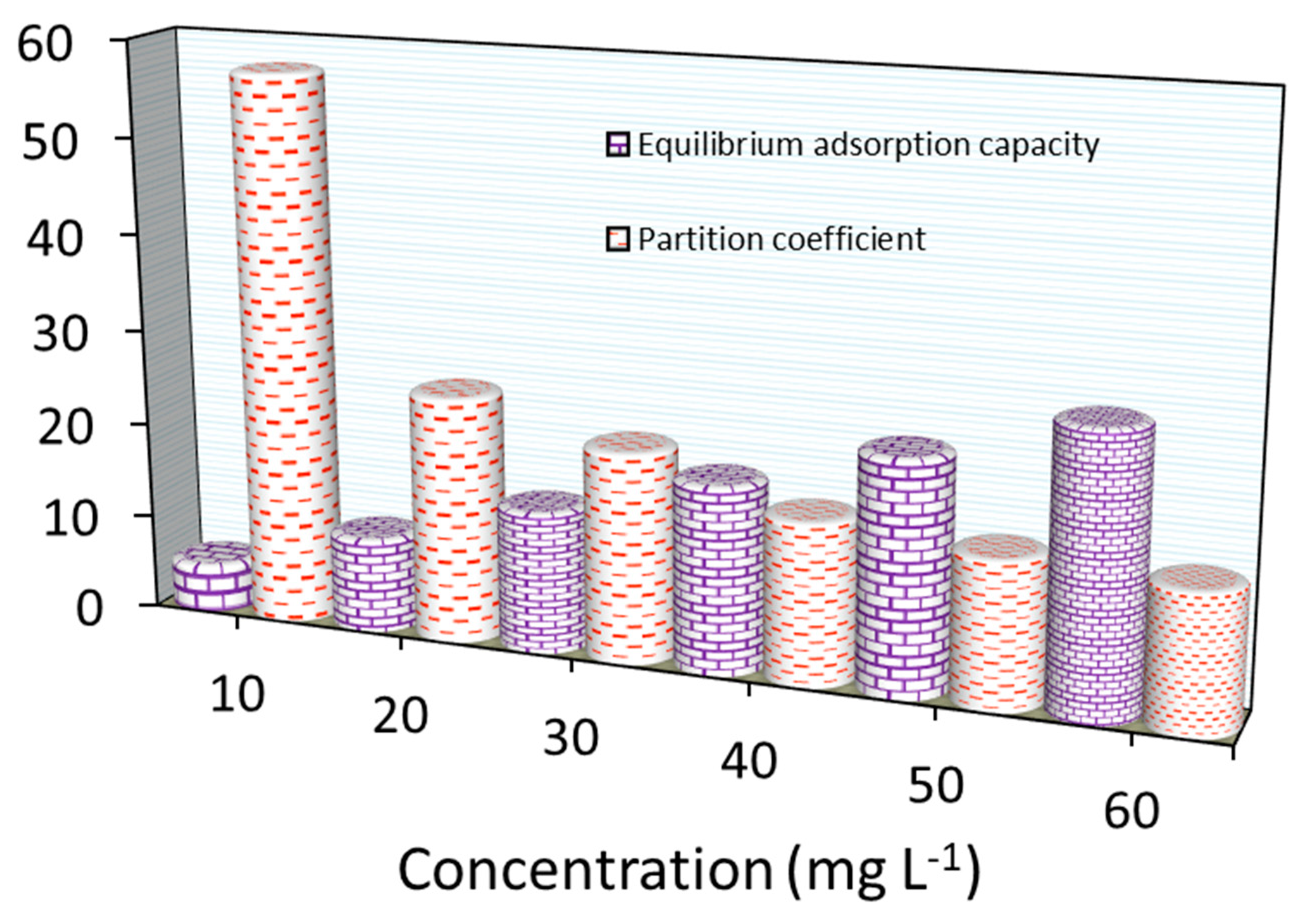
As summarized in Figure 13, the PC value (in g L−1) for MB adsorption decreased when increasing the initial loading concentrations. The PC values were ~57.0 to ~14.0 L g−1 for Fe3O4/BC as the MB concentration changed from 10.0–60.0 mg L−1. If these results are compared with those measured previously (for BC-based adsorbents) (as seen in Table 4), Fe3O4/BC has displayed the highest PC with noticeable Qo values. Based on PC values, Fe3O4/BC appears to be one of the most effective treatments for these contaminants. This feature may suggest the high efficiency of Fe3O4/BC for MB removal from groundwater reservoirs.
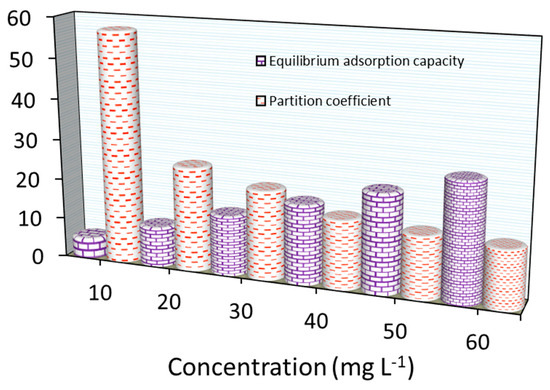
Figure 13.
Partition coefficient and equilibrium adsorption capacity for MB adsorption onto Fe3O4/BC at various concentrations.

Table 4.
Summary of experimental data obtained for performance evaluation of adsorbents used to remove MB from water and comparative Langmuir maximum adsorption capacity (Qo) values of adsorbents *.
3.7.3. Economic Efficiency, Reusability Features, and Implementation of Fe3O4/BC
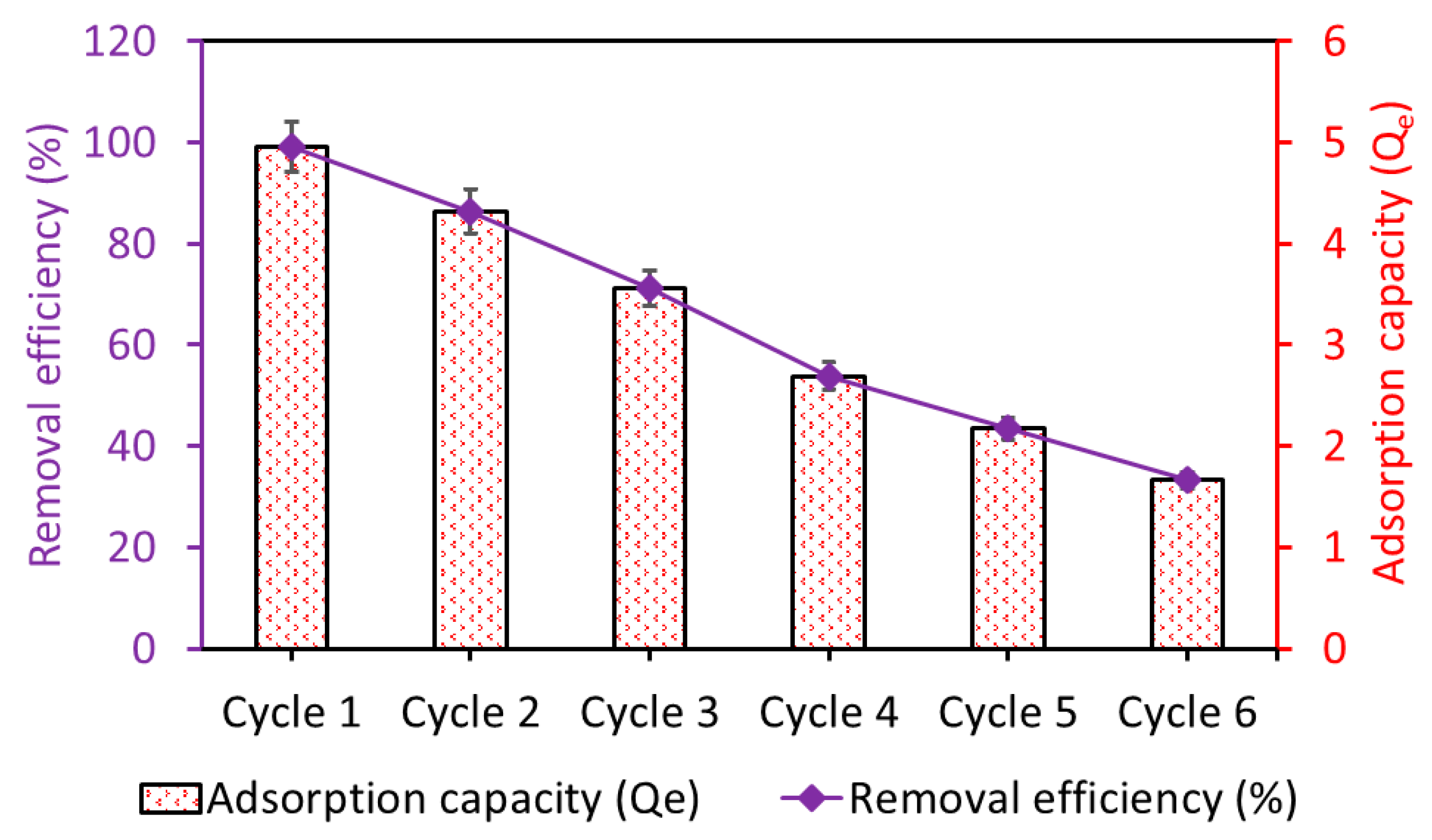
The reusability of Fe3O4/BC was investigated by running up to six cycles of adsorption–desorption, as shown in Figure 14. The prepared Fe3O4/BC bioadsorbent demonstrated excellent stability over the first two cycles, followed by a gradual decline in adsorption performance to achieve a total reduction in performance of 33% for MB after the sixth reusability cycle (Figure 14).
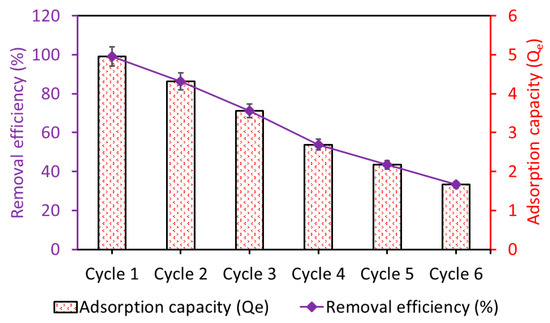
Figure 14.
Adsorption stability of the regenerated Fe3O4/BC bioadsorbent for MB pollutant.
Being a multifunctional material, the easily prepared Fe3O4/BC can be a useful nanobiosorbent for wastewater treatment because of its low production cost (around 0.07 USD/g) (computed manually), which is comparatively lower than that of those reported previously such as Fe2O3 (1.2 USD/g), Fe3O4 (0.44 USD/g), TiO2 (0.18 USD/g), ZVNI (0.14 USD/g), Fe2O3-ZrO2/BC (0.10 USD/g), Fe2O3-SnO2/BC (0.07 USD/g), and various other adsorbents [21]. The low application cost of magnetic Fe3O4/BC is mainly attributed to the high mass yield production from cheap and readily available resources of carbon frameworks (BC seeds), good performance stability over six reusable cycles, and the ease of recovery of exhausted sorbent from solution using an external magnetic field (low consumption of energy for recovery). The findings from this study indicate that Fe3O4/BC is an environmentally friendly and cost-effective adsorbent with significant adsorption capabilities for both inorganic and organic pollutants in wastewater treatment.
4. Conclusions
The magnetic nanobiomaterial Fe3O4/BC was synthesized for environmental applications via the incorporation of iron oxide in a carbon framework derived from cumin seeds through the co-precipitation method. The reported nanobiomaterial is eco-friendly, cost-effective, magnetic, and highly functionalized. This nanobiomaterial exhibited remarkable efficacy in extracting MB from water. Adsorption isotherms were also found to obey Freundlich models, indicating possible multilayer adsorption onto heterogeneous active adsorption sites. The current nanobiomaterial demonstrated superior efficiency such as maximal adsorption efficacy and partition coefficient compared to existing materials. Here, 2.0 g L−1 of Fe3O4/BC removed ~99% of MB with a 10 mg L−1 concentration at pH = 7, temperature = 27 °C, and contact time = 60 min. In contrast, its maximum equilibrium adsorption capacity (5.0 mg g−1) and maximum partition coefficient (57.0 L g−1) were observed at the starting concentration (10.0 mg L−1, 31.0 μM). Fe3O4/BC showed a better partition coefficient than previously reported BC seeds (acid-washed) and other BC-based adsorbents. The enhanced adsorption efficiency of the present nanobiomaterial is attributed to the excessive functional groups on its surface, as confirmed by the FTIR study. The utilized adsorbent also showed a high regeneration ability and could be reutilized over multiple adsorption–desorption cycles without a large reduction in adsorption capacity. Given the potential for the future, additional research including a range of contaminants will likely be required to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of these materials for a variety of water treatment applications. In the future, the antibacterial activities of these materials should also be addressed to assess the antibiofilm nature of adsorbents.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ma18092049/s1, Figure S1: FTIR spectrum of BC. Reprinted from our previous study with permission from Siddiqui and Chaudhry [39], Copyright (2018) Elsevier (License No. 5990980697967).
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. S.A.C. provided reagents, materials, and other resources. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by S.I.S., S.H. and S.A.C. The first draft of the manuscript was written by S.I.S. and S.H. R.H.A. and E.A.A. interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. S.O., N.M.A. and A.A.A.-G. commented on previous versions of the manuscript. S.O. supervised the work and provided the funding. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported (to Seungdae Oh) by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning) (No. RS-2024-00350751).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article and Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Hemavathy, R.V.; Jeevanantham, S.; Jawahar, M.J.; Neshaanthini, J.P.; Saravanan, R. A review on synthesis methods and recent applications of nanomaterial in wastewater treatment: Challenges and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, P.; Inbaraj, M.P. Applications of nanomaterials in wastewater treatment. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 2877–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigbe, U.O.; Ukhurebor, K.E.; Onyancha, R.B.; Okundaye, B.; Aigbe, E.; Kusuma, H.S.; Noto, L.L.; Osibote, O.A.; Atagana, H.I. Applications of magnetic nanomaterials for wastewater treatment. In Magnetic Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 129–169. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, E.; Shahadat, M.; Ahtesham, A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M. Synthesis, characterization, and applications of ambi-functional PANI/GO/MOF-Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite for removing industrial dye and emerging contaminant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 351, 128052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Ismail, A.M. Fabrication of magnetic Fe3O4/Polypyrrole/carbon black nanocomposite for effective uptake of congo red and methylene blue dye: Adsorption investigation and mechanism. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 976–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xiong, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, P.; Ye, F. Facile synthesis of low-cost biomass-based γ-Fe2O3/C for efficient adsorption and catalytic degradation of methylene blue in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; O’Connor, D.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xia, T.; Wang, L.; Tsang, D.C.; Ok, Y.S.; Hou, D. A green biochar/iron oxide composite for methylene blue removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Peighambardoust, S.H.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Adsorption of crystal violet dye using activated carbon of lemon wood and activated carbon/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite from aqueous solutions: A kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Molecules 2021, 26, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, E.; Pillay, K.; Brink, H. Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic-biochar nanocomposite derived from avocado peel and its performance as an adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue from wastewater. Mater. Today Sustain. 2022, 18, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.; Reinoso, F.R. Activated Carbon; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R. Biochar production technology. In Biochar for Environmental Management; Routledge: London, UK, 2012; pp. 159–178. [Google Scholar]
- Bundschuh, M.; Filser, J.; Lüderwald, S.; McKee, M.S.; Metreveli, G.; Schaumann, G.E.; Schulz, R.; Wagner, S. Nanoparticles in the environment: Where do we come from, where do we go to? Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, N.; Shariati, S.; Besharati, N. Adsorption of crystal violet and methylene blue on azolla and fig leaves modified with magnetite iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2017, 11, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagapati, V.S.; Wen, H.Y.; Gollakota, A.R.; Wen, J.C.; Lin, K.Y.A.; Shu, C.M.; Zyryanov, G.V. Magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles loaded guava leaves powder impregnated into calcium alginate hydrogel beads (Fe3O4-GLP@ CAB) for efficient removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous environment: Synthesis, characterization, and its adsorption performance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 246, 125675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimharao, K.; Al-Thabaiti, S.; Rajor, H.K.; Mokhtar, M.; Alsheshri, A.; Alfaifi, S.Y.; Siddiqui, S.I.; Abdulla, N.K. Fe3O4@ date seeds powder: A sustainable nanocomposite material for wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 3581–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Chang, J. Synthesis of magnetic Forsythia suspensa leaf powders for removal of metal ions and dyes from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabede, P.M.; Shooto, N.D. Application of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) seeds for the removal of metal ions and methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Cogent Eng. 2022, 9, 2013419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooto, N.D.; Thabede, P.M.; Naidoo, E.B. Simultaneous adsorptive study of toxic metal ions in quaternary system from aqueous solution using low cost black cumin seeds (Nigella sativa) adsorbents. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 30, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tara, N.; Alzahrani, E.A.; Alsebaii, N.M.; Dwivedi, P.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Aldahiri, R.H.; Nguyen, H.T.; Oh, S.; Chaudhry, S.A. Novel Hybrid rGO-BC@ZrO2 Composite: A Material for Methylene Blue Adsorption. Water 2025, 17, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.I.; Chaudhry, S.A. Nanohybrid composite Fe2O3-ZrO2/BC for inhibiting the growth of bacteria and adsorptive removal of arsenic and dyes from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 849–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.I.; Zohra, F.; Chaudhry, S.A. Nigella sativa seed based nanohybrid composite-Fe2O3–SnO2/BC: A novel material for enhanced adsorptive removal of methylene blue from water. Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; AlHarbi, L.; Nabi, A.; Alzahrani, K.A.; Narasimharao, K.; Kamli, M.R. Facile Synthesis of Magnetic Nigella sativa Seeds: Advances on Nano-Formulation Approaches for Delivering Antioxidants and Their Antifungal Activity against CANDIDA albicans. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.T.H.S.; Hussain, S.T.; Waseem, M.; Naeem, A.; Hussain, J.; Tariq Jan, M. Surface charge properties of zirconium dioxide. Iran. J. Sci. 2012, 36, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, P.; Chowdhury, S. Insight into adsorption thermodynamics. Thermodynamics 2011, 16, 349–364. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharby, N.F.; Almutairi, R.S.; Mohamed, N.A. Adsorption Behavior of Methylene Blue Dye by Novel CrossLinked O-CM-Chitosan Hydrogel in Aqueous Solution: Kinetics, Isotherm and Thermodynamics. Polymers 2021, 13, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, M.I.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetic of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Physiochimica USSR 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Elkady, M.F.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Abd El-Latif, M.M. Assessment of the adsorption kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic for the potential removal of reactive red dye using eggshell biocomposite beads. Desalination 2011, 278, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.N.; Mancini, M.C.; De Oliveira, F.C.S.; Passos, T.M.; Quilty, B.; Da Silva Moreira Thiré, R.M.; McGuinness, G.B. FTIR analysis and quantification of phenols and flavonoids of five commercially available plants extracts used in wound healing. Matéria 2016, 21, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, P.; Isasi, J.; Caballero, A.C.; Marco, J.F.; Martín-Hernández, F. Magnetic and structural studies of Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized via coprecipitation and dispersed in different surfactants. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 10333–10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooto, N.D.; Nkutha, C.S.; Guilande, N.R.; Naidoo, E.B. Pristine and modified mucuna beans adsorptive studies of toxic lead ions and methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 31, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. Encycl. Anal. Chem. 2000, 12, 10815–10837. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R.; Purwar, R. Influence of metal oxide nanoparticles on morphological, structural, rheological and conductive properties of mulberry silk fibroin nanocomposite solutions. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, S.; Hou, P.; Yang, Y.; Weng, J.; Li, X.; Li, M. Synthesis and characterization of biocompatible Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 80, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Mohammadi, S. Quince seed mucilage magnetic nanocomposites as novel bioadsorbents for efficient removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Jin, C.; Sun, Q. Preparation of high mechanical performance nano-Fe3O4/wood fiber binderless composite boards for electromagnetic absorption via a facile and green method. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Yang, W.S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.M.; Ye, H. Preparation and characterization of carboxyl-group functionalized superparamagnetic nanoparticles and the potential for bio-applications. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2007, 18, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.I.; Chaudhry, S.A. Nigella sativa plant based nanocomposite-MnFe2O4/BC: An antibacterial material for water purification. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, N.; Meng, Z.; Sui, G. Processing cellulose@ Fe3O4 into mechanical, magnetic and biodegradable synapse-like material. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 177, 107432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chow, G.M. Carboxyl group (–CO2H) functionalized ferrimagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for potential bio-applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2781–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeminezhad, I.; Mosivand, S. Phase Transition of Electrooxidized Fe3O4 to γ and α-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles Using Sintering Treatment. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2014, 125, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzian Baghani, A.; Mahvi, A.H.; Gholami, M.; Rastkari, N.; Delikhoon, M. One-Pot synthesis, characterization and adsorption studies of amine-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles for removal of Cr (VI) and Ni (II) ions from aqueous solution: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2016, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, H.; Tamjidi, S. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of natural clay/Fe3O4/graphene oxide for enhance removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous media. Environ. Sci. Pol. Res. 2020, 27, 31652–31664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.S.K.; Jiang, S.J. Chitosan-functionalized graphene oxide: A novel adsorbent an efficient adsorption of arsenic from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1698–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, H.R.; Silva, L.S.; Sousa, P.A.A.; Sousa, R.R.M.; Fonseca, M.G.; Osajima, J.A.; Silva-Filho, E.C. Evaluation of methylene blue removal by plasma activated palygorskites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5432–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.K.; Jiang, S.J. Synthesis of magnetically separable and recyclable magnetic nanoparticles decorated with β-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene oxide an excellent adsorption of As (V)/(III). J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 237, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Mondal, N.K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Das, B.; Das, K. Removal of arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) on chemically modified low-cost adsorbent: Batch and column operations. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lin, L.; Papelis, C.; Myint, M.; Cath, T.Y.; Xu, P. Use of drinking water treatment solids for arsenate removal from desalination concentrate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 445, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chingombe, P.; Saha, B.; Wakeman, R.J. Effect of surface modification of an engineered activated carbon on the sorption of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid and benazolin from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 297, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Adsorption characteristics for the removal of a toxic dye, tartrazine from aqueous solutions by a low cost agricultural by-product. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1629–S1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljeboree, A.M.; Alshirifi, A.N.; Alkaim, A.F. Kinetics and equilibrium study for the adsorption of textile dyes on coconut shell activated carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3381–S3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, V.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C. Insight into adsorbate–adsorbent interactions between aromatic pharmaceutical compounds and activated carbon: Equilibrium isotherms and thermodynamic analysis. Adsorption 2020, 26, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Gao, X.; Shi, W.; Tay, J.H. Adsorption mechanisms of crude oil onto polytetrafluoroethylene membrane: Kinetics and isotherm, and strategies for adsorption fouling control. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.I.; Rathi, G.; Chaudhry, S.A. Acid washed black cumin seed powder preparation for adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution: Thermodynamic, kinetic and isotherm studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 264, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).