Study of Preparation and Performance Porous Thermal Insulation Refractory Materials from Aluminum Ash and Red Mud
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
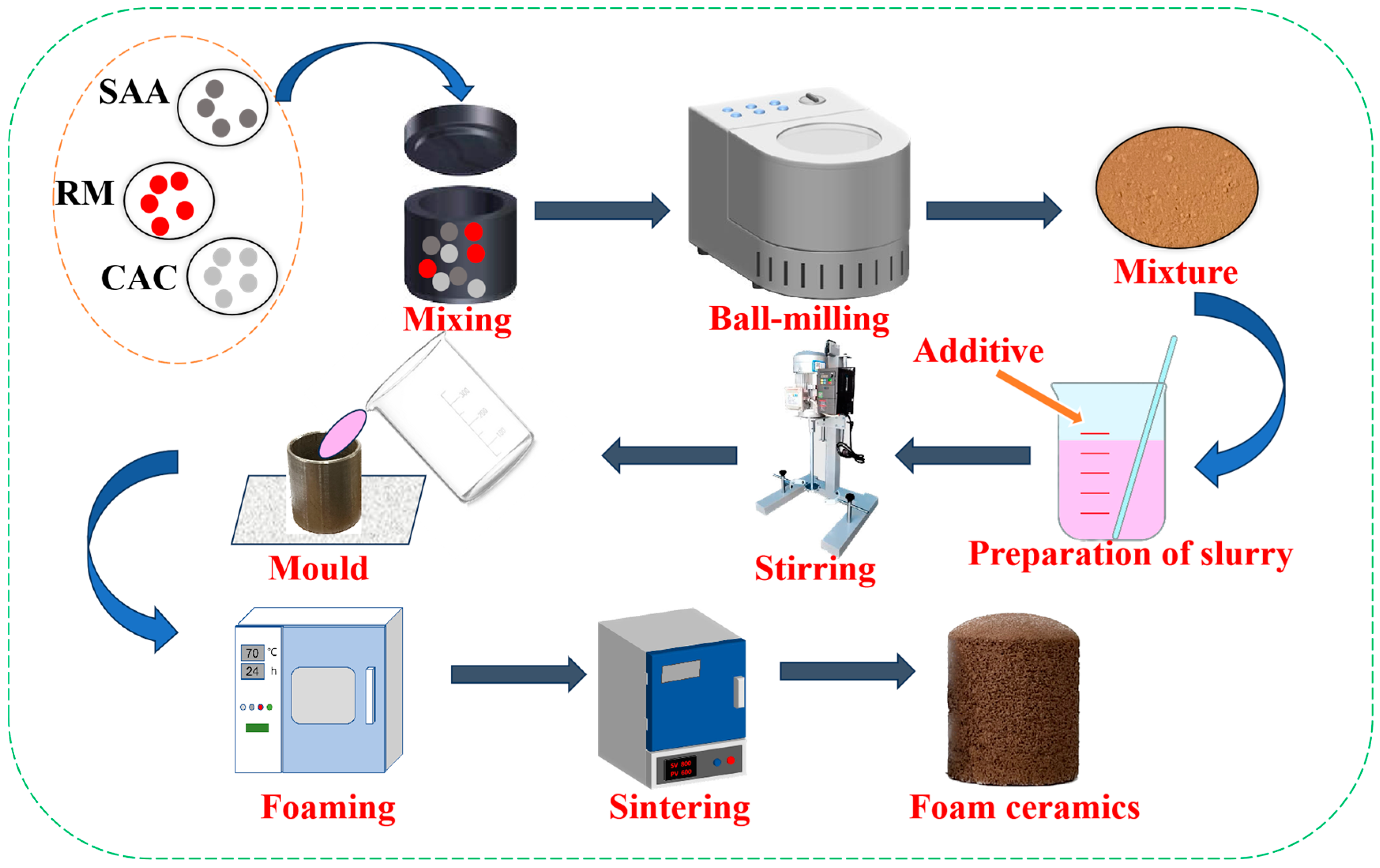
2.2. Preparation of Porous Ceramics
2.3. Preparation of Slurry
2.4. Methods
- (1)
- Rheological characterization
- (2)
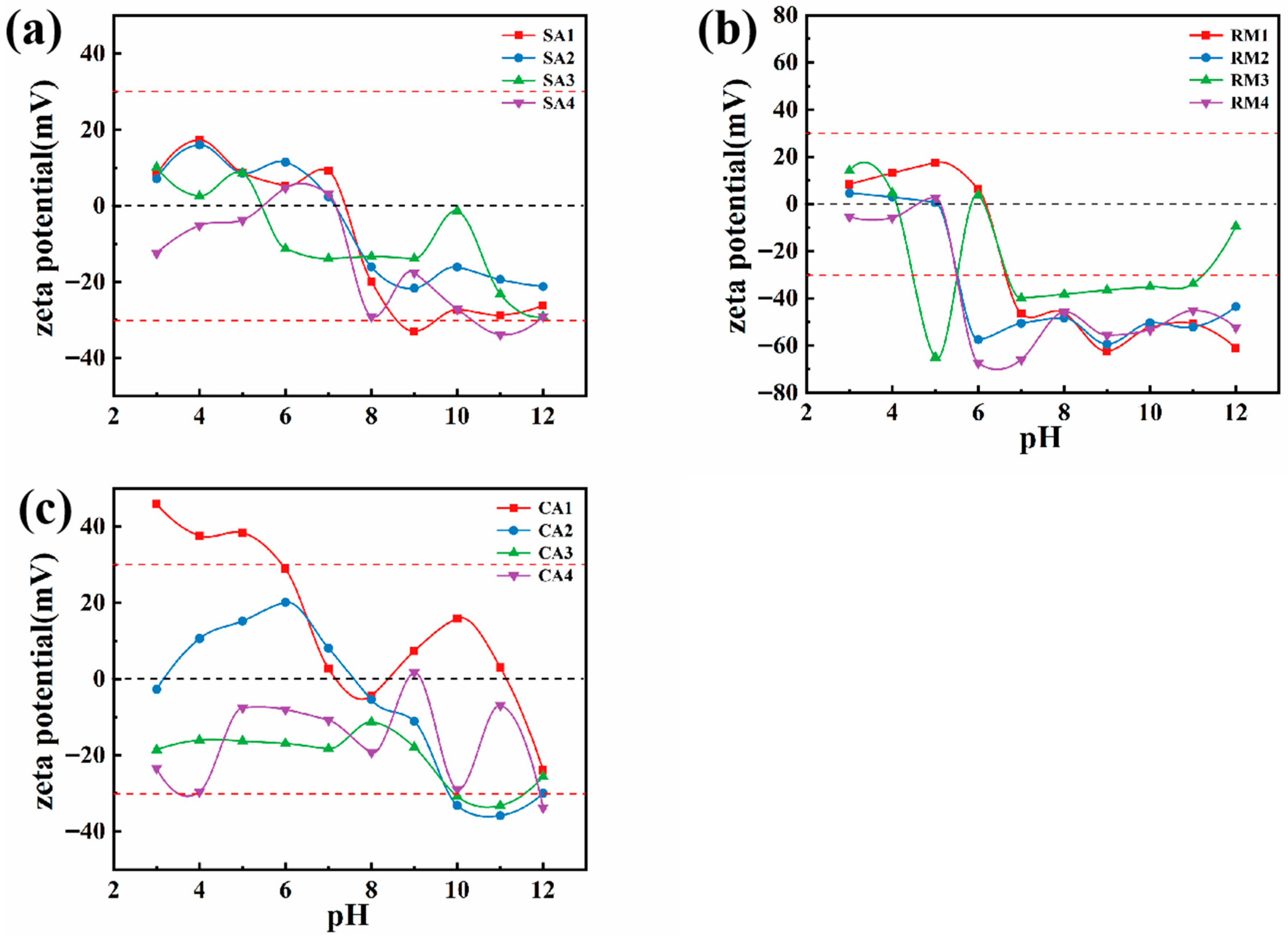
- The zeta potential
- (3)
- The compressive strength
- (4)
- The microstructure and pore-size distribution
- (5)
- The porosity
- (6)
- X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis
- (7)
- X-ray fluorescence (XRF)
- (8)
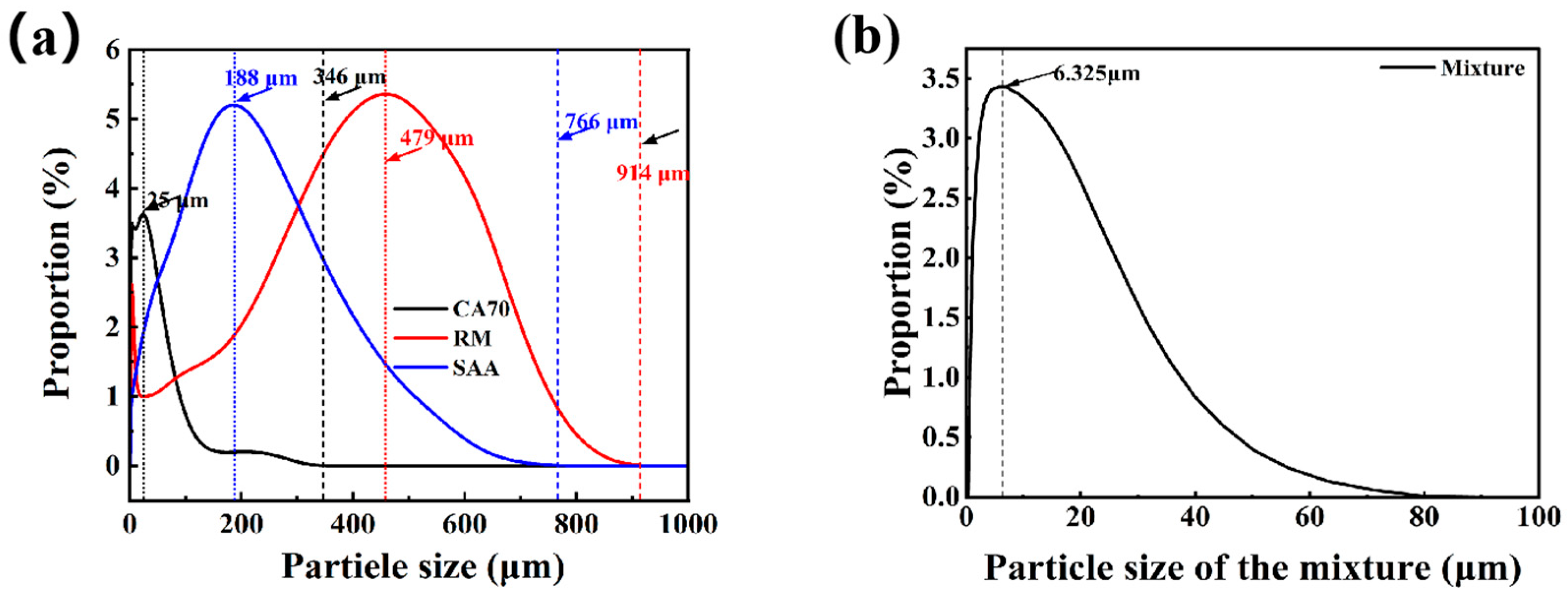
- Particle size distribution
- (9)
- The refractory properties
3. Results
3.1. Rheological Analysis
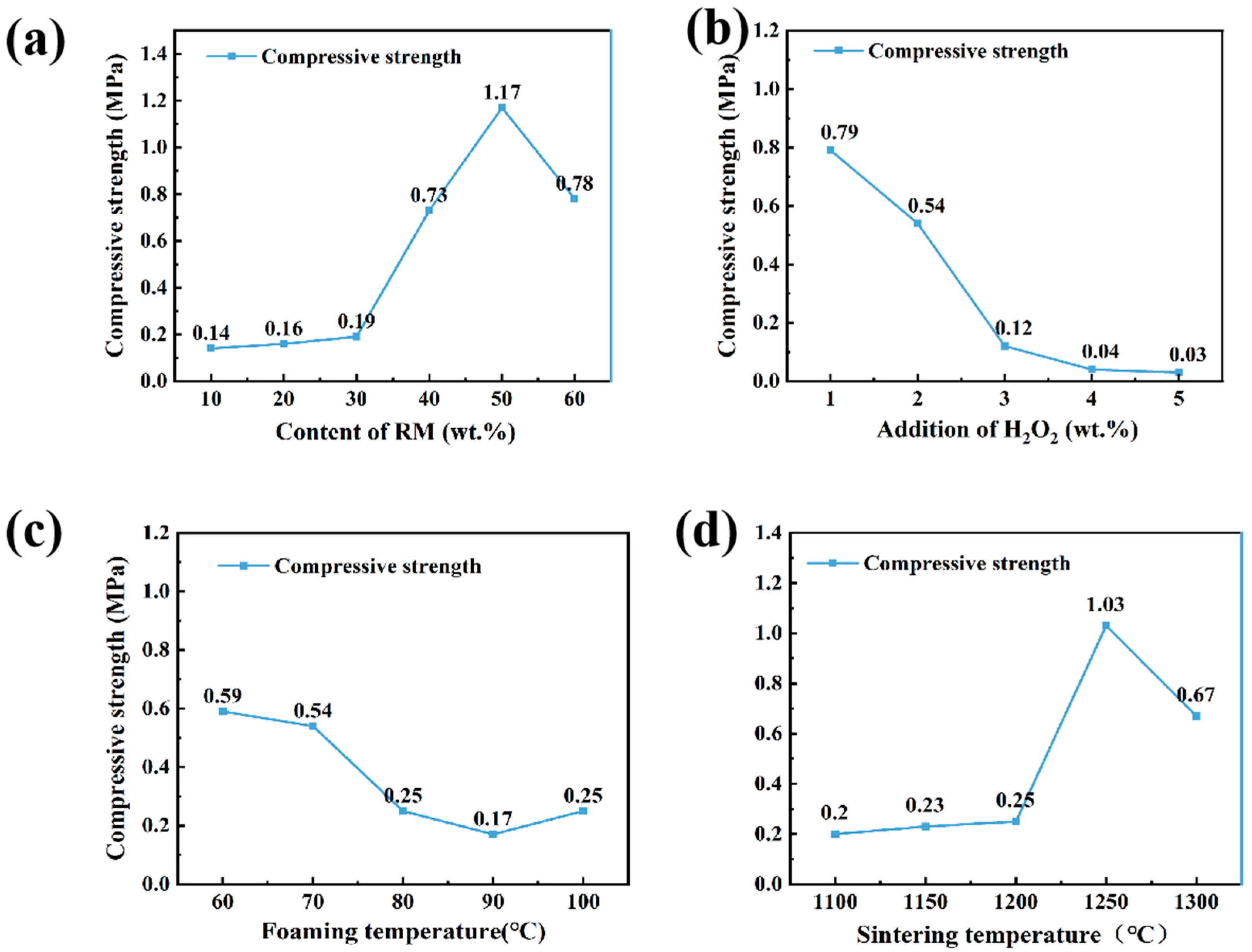
3.2. Compressive Strength Analysis
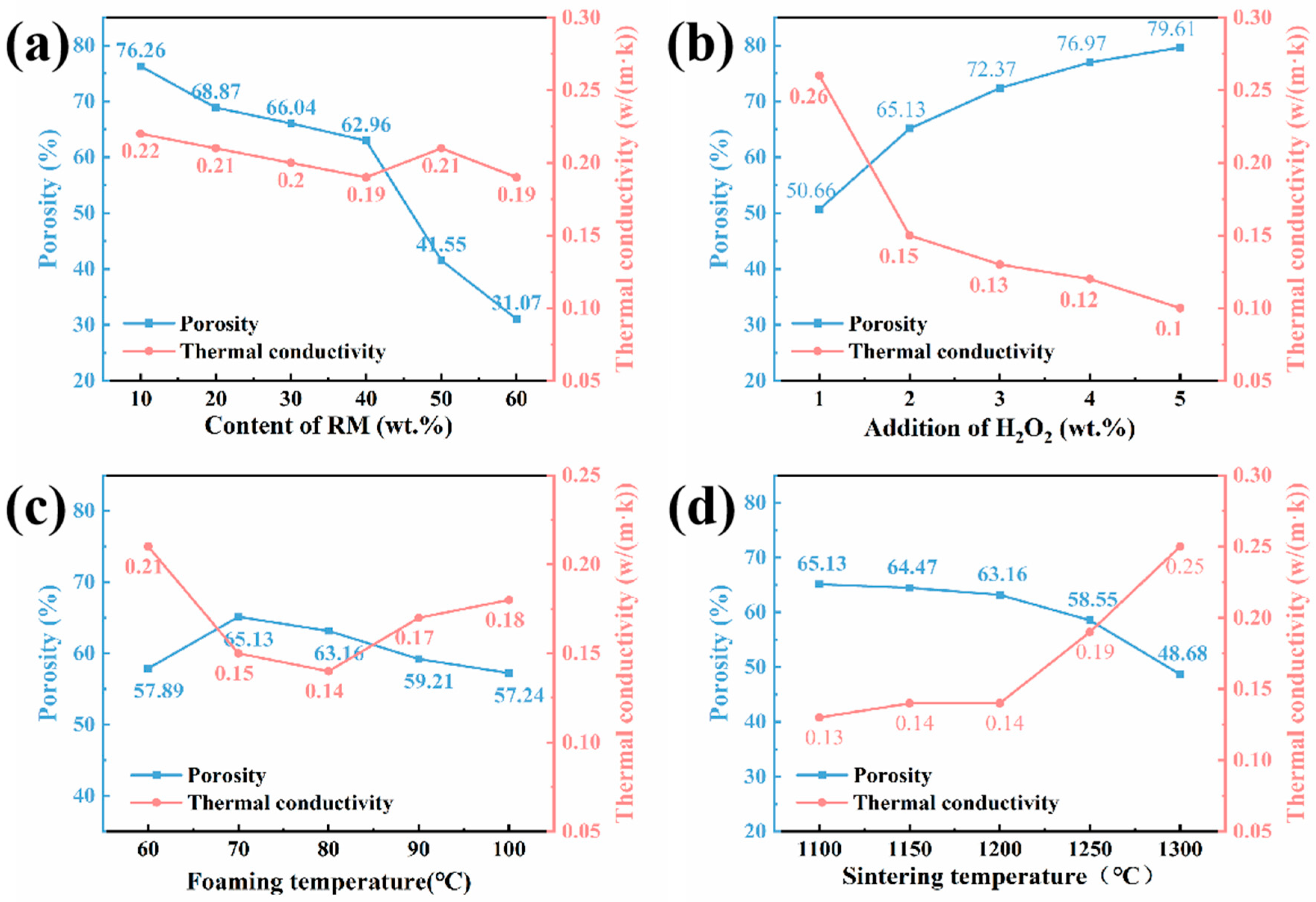
3.3. Porosity and Thermal Conductivity
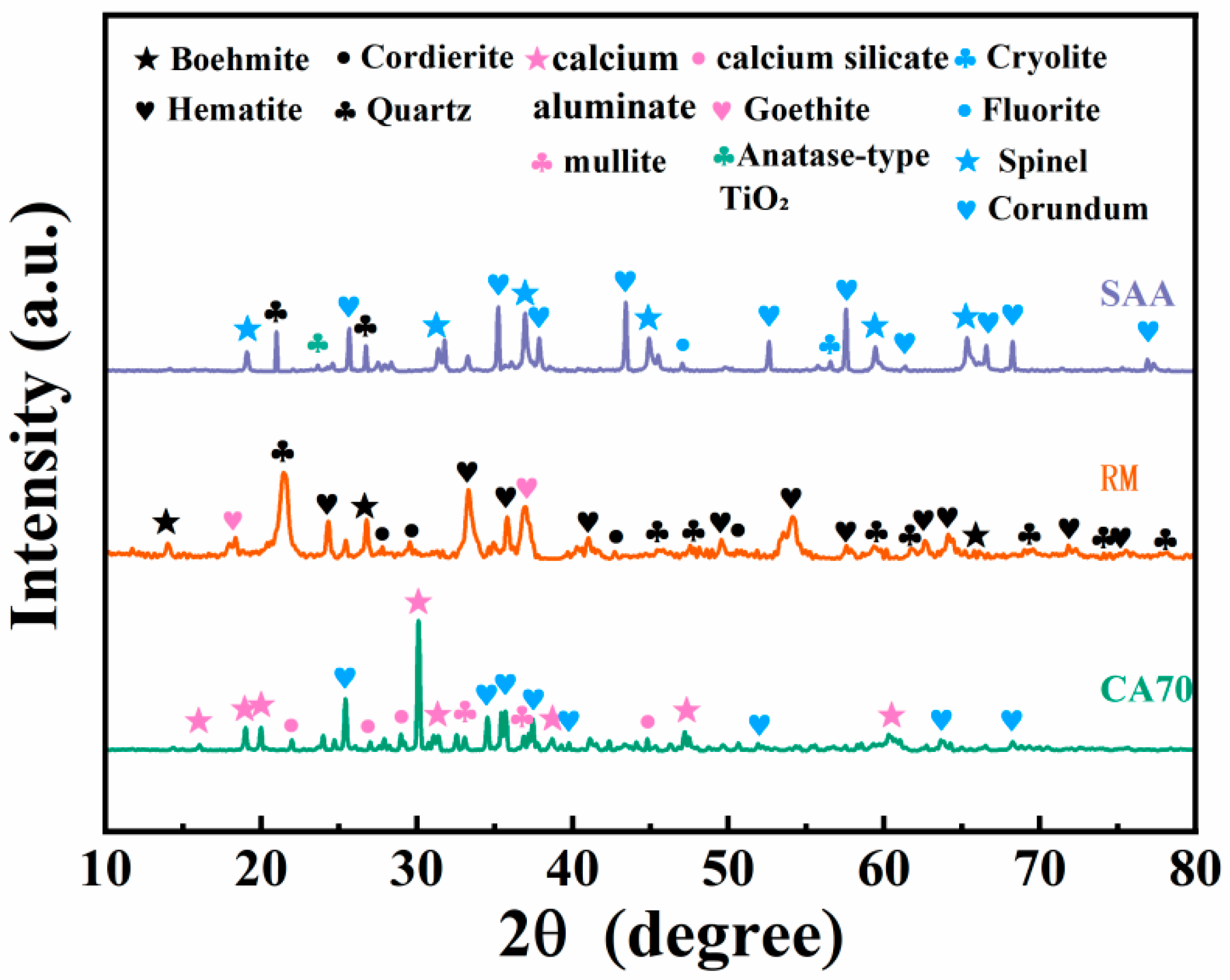
3.4. XRD Analysis
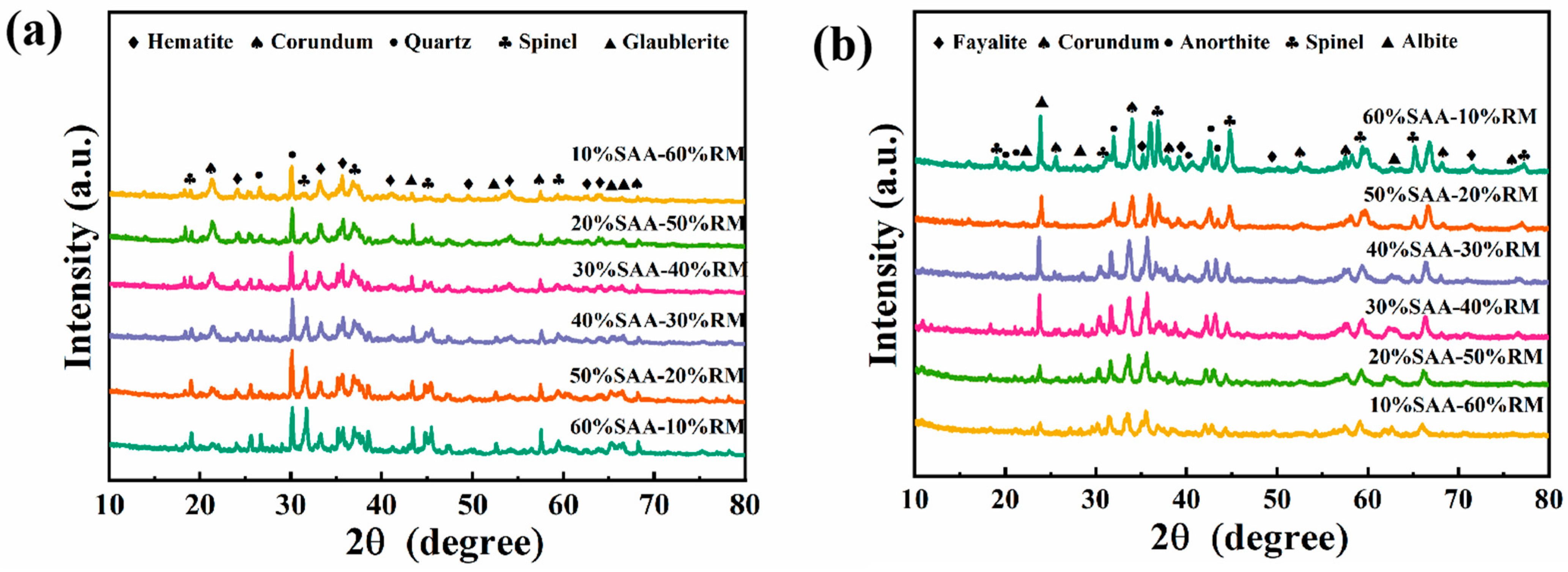
3.4.1. XRD Spectra of Porous Insulation Materials Prepared with Different Aluminum Ash/Red Mud Ratios
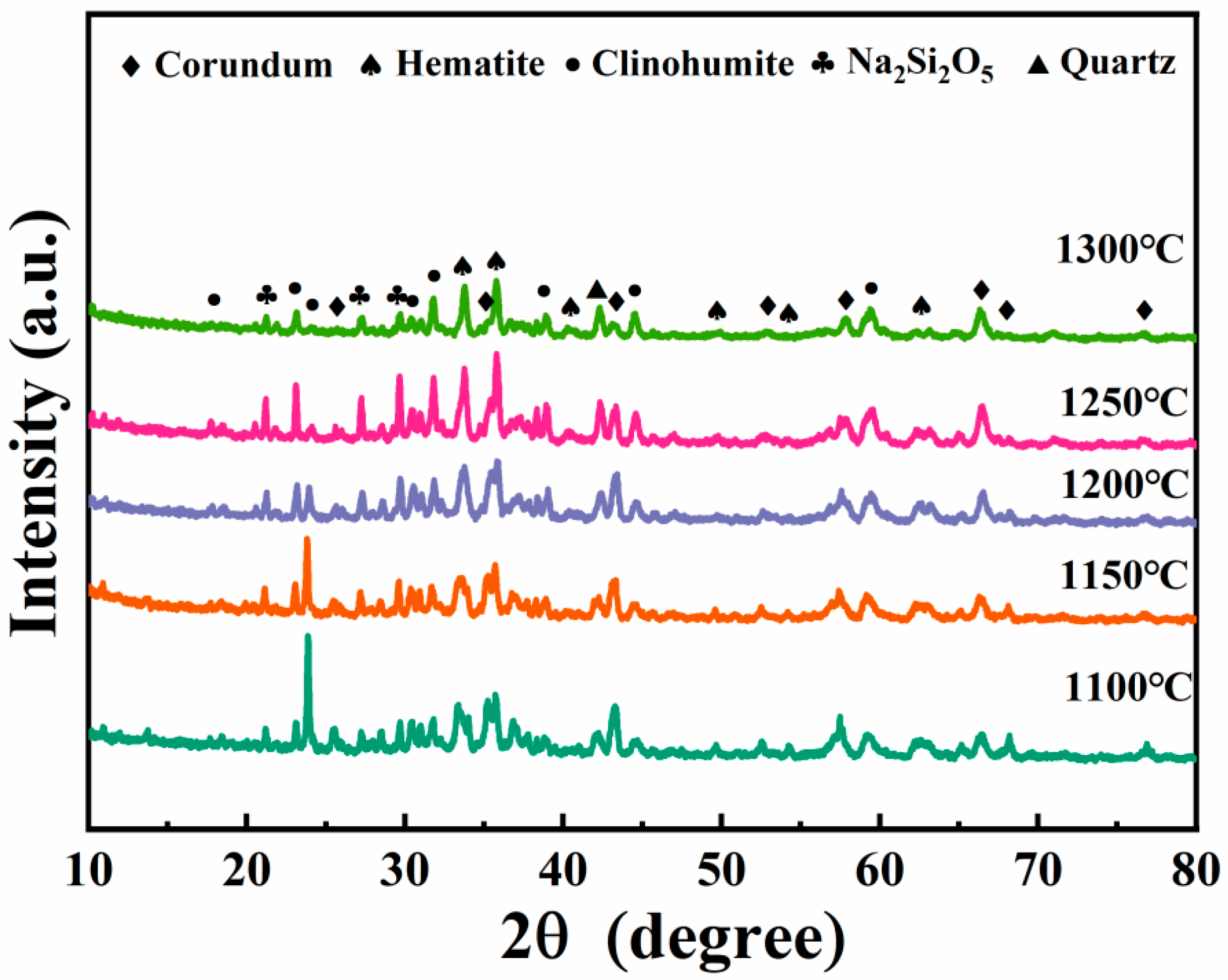
3.4.2. XRD Spectra of Porous Insulation Materials Prepared at Different Sintering Temperatures
3.5. SEM and EDS Analysis
3.5.1. SEM-EDS and Pore-Size Distribution of Porous Insulation Materials Prepared with Different Aluminum Ash/Red Mud Ratios
3.5.2. SEM and Pore-Size Distribution of Porous Insulation Materials Prepared with Different Amounts of H2O2 Addition
3.5.3. SEM and Pore-Size Distribution of Porous Insulation Materials Prepared at Different Foaming Temperatures
3.5.4. SEM and Pore-Size Distribution of Porous Insulation Materials Prepared at Different Sintering Temperatures
3.6. Fire Resistance Performance
3.6.1. Refractoriness
3.6.2. Durability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freitas Dutra, L.; Freitas, M.E.; Grillet, A.-C.; Mendes, N.; Woloszyn, M. Microstructural Characterization of Porous Clay-Based Ceramic Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoara, A.I.; Alecu, A.E.; Balaceanu, G.-C.; Puscasu, E.M.; Vasile, B.S.; Trusca, R. Fabrication and Characterization of Porous Diopside/Akermanite Ceramics with Prospective Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials 2023, 16, 5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ban, X.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Ru, H.; Su, D. Fabrication of SiC Porous Ceramics by Foaming Method. Materials 2023, 16, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramovskis, V.; Drunka, R.; Csáki, Š.; Lukáč, F.; Veverka, J.; Illkova, K.; Gavrilovs, P.; Shishkin, A. Preparation and Characteristics of High-Performance, Low-Density Metallo–Ceramics Composite. Materials 2023, 16, 7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Guo, A.; Du, H.; Hou, F.; Liu, J. Lightweight Porous Silica Ceramics with Ultra-Low Thermal Conductivity and Enhanced Compressive Strength. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 9788–9796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, J.; Han, L.; Huang, Z.; Xu, K.; Cai, W.; Wu, S.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Foam Gel-Casting Preparation of SiC Bonded ZrB2 Porous Ceramics for High-Performance Thermal Insulation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, H.; Lei, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. Review of Lightweight, High-Temperature Thermal Insulation Materials for Aerospace. Materials 2025, 18, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Suh, D.-J. Recent Research Trends for Green Building Thermal Insulation Materials. Clean Technol. 2012, 18, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, A.; Kang, L.; Wang, C.; Cao, D. A Simple and Effective Model for Prediction of Effective Thermal Conductivity of Vacuum Insulation Panels. Future Cities Environ. 2015, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Le Ferrand, H. 3D Printed Gyroid Scaffolds Enabling Strong and Thermally Insulating Mycelium-Bound Composites for Greener Infrastructures. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.H.; Yu, W.H. Porous Refractory Material and Preparation Method Thereof. CN Patent 201610774829.6, 15 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlenko, A.M.; Koshlak, H.V. Thermal Insulation Materials with Porous Structure. Struct. Environ. 2018, 10, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Gu, H.; Huang, A.; Or, S.W.; Zou, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, M. Design, Fabrication and Properties of Lightweight Wear Lining Refractories: A Review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 744–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwajler, B.; Szołomicki, J.; Noszczyk, P.; Baryś, M. The Potential of 3D Printing in Thermal Insulating Composite Materials—Experimental Determination of the Impact of the Geometry on Thermal Resistance. Materials 2024, 17, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielce University of Technology; Koshlak, H.; Pavlenko, A. Thermophysical Properties of Porous Materials. J. New Technol. Environ. Sci. 2020, 7, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xiang, H.; Dai, F.-Z.; Liu, J.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y. High Porosity and Low Thermal Conductivity High Entropy (Zr0.2Hf0.2Ti0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1700–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, M.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Z. Current Status and Development Trend of Cold Sintering Process. J. Inorg. Mater. 2023, 38, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Shang, Y.; Li, H. Porous Thermal Insulation Polyurethane Foam Materials. Polymers 2023, 15, 3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Shen, H.; Wen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. Theoretical and Experimental on the Thermodynamic, Kinetic and Phase Evolution Characteristics of Secondary Aluminum Ash. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 3857–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhao, H.; Zuo, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, F. A Thermodynamic and Kinetic Study of Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Aluminum Nitride in Secondary Aluminum Dross. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 9735–9745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Wu, W.; Sun, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, S. Removal of Nitrides and Fluorides from Secondary Aluminum Dross by Catalytic Hydrolysis and Its Mechanism. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.; Konyukhov, Y.; Zinoveev, D.; Jayasankar, K.; Burmistrov, I.; Kravchenko, M.; Mukherjee, P.S. Red Mud as a Secondary Resource of Low-Grade Iron: A Global Perspective. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Pradhan, P.; Padole, A.; Agnihotri, A. Recovery of Metal Values from Bauxite Residue/Red Mud: A Review. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2025, 16, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sglavo, V.M.; Maurina, S.; Conci, A.; Salviati, A.; Carturan, G.; Cocco, G. Bauxite ‘Red Mud’ in the Ceramic Industry. Part 2: Production of Clay-Based Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 20, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakalova, T.V.; Sergeev, N.P.; Tolegenov, D.T.; Tolegenova, D.Z.; Mitina, N.A. Red Mud in High-Strength Ceramics Production. Vestn. Tomsk. Gos. Arkhitekturno-stroit. Univ. J. Constr. Archit. 2024, 26, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Luan, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, X.; Dong, C. Corrosion, Permeation and Mass Transfer Mechanisms of Alkali Metals in Corundum Refractories. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 33455–33463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, A.; Djonga, P.N.D.; Tsamo, C.; Valery, H.G.; Azangueu, J.; Noukelag, S.K. Structural Characterization of Bauxite Red Mud to Utilization in Ceramic Wall/Roofing Tile: Effect of Temperature on Mechanical Properties and Physic-Chemical Stability. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2022, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Shen, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. In-Situ Preparation of Porous Metal-Ceramic Composite from Secondary Aluminum Dross and Red Mud for Adsorption of Organic Pollutant. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 986, 174135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Lou, B.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S. In-Situ Preparation of Alumina-Based Cermet after Reduction of Iron Oxide in Red Mud with Aluminum Dross. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 21630–21637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.J.; Yu, C.L.; Lu, M.J.; Luo, Y.K.; Fang, H.; Huang, H.; Guo, X. Sintering Fabrication of Magnesia-Alumina Spinel by Secondary Aluminum Dross. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2021, 12, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Cui, S.; Pu, X. Performance Study of Foam Ceramics Prepared by Direct Foaming Method Using Red Mud and K-Feldspar Washed Waste. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 5197–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.B.; Chen, W.H.; Fan, Y.; Yang, T.L.; Liu, Z.B.; Cang, D.Q. Complementation in the Composition of Steel Slag and Red Mud for Preparation of Novel Ceramics. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2018, 25, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinek, D. DLVO Theory. In Encyclopedia of Applied Electrochemistry; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 343–346. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 5072-2023; Refractory Products—Determination of Cold Compressive Strength. Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2023.
- GB/T 2997-2015; Test Method for Bulk Density, Apparent Porosity and True Porosity of Dense Shaped Refractory Products. China National Technical Committee for Standardization of Refractory Materials: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GB/T 7322-2017; Refractory Products-Determination of Refractoriness. Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB/T 5988-2022; Test Method for Permanent Linear Change of Refractories Upon Heating. Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2022.
- Wu, C.-R.; Tang, W.; Zhan, B.-J.; Kou, S.-C. Feasibility Study on Using Red Mud as a Viscosity-Modifying Agent for Self-Compacting Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 445, 137871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltramo, P.J.; Gupta, M.; Alicke, A.; Liascukiene, I.; Gunes, D.Z.; Baroud, C.N.; Vermant, J. Arresting Dissolution by Interfacial Rheology Design. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10373–10378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Chen, B. Experimental Research on Magnesium Phosphate Cements Modified by Red Mud. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 231, 117131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Qiu, J.; Hou, C.; Guo, Z. Fluidity and Strength Behaviors of Cemented Foam Backfill: Effect of Particle Size Distribution and Foaming Agent Dosage. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 3177–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; An, L.; Zhao, J.; Shimai, S.; Mao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, S. High-Strength Porous Alumina Ceramics Prepared from Stable Wet Foams. J. Adv. Ceram. 2021, 10, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


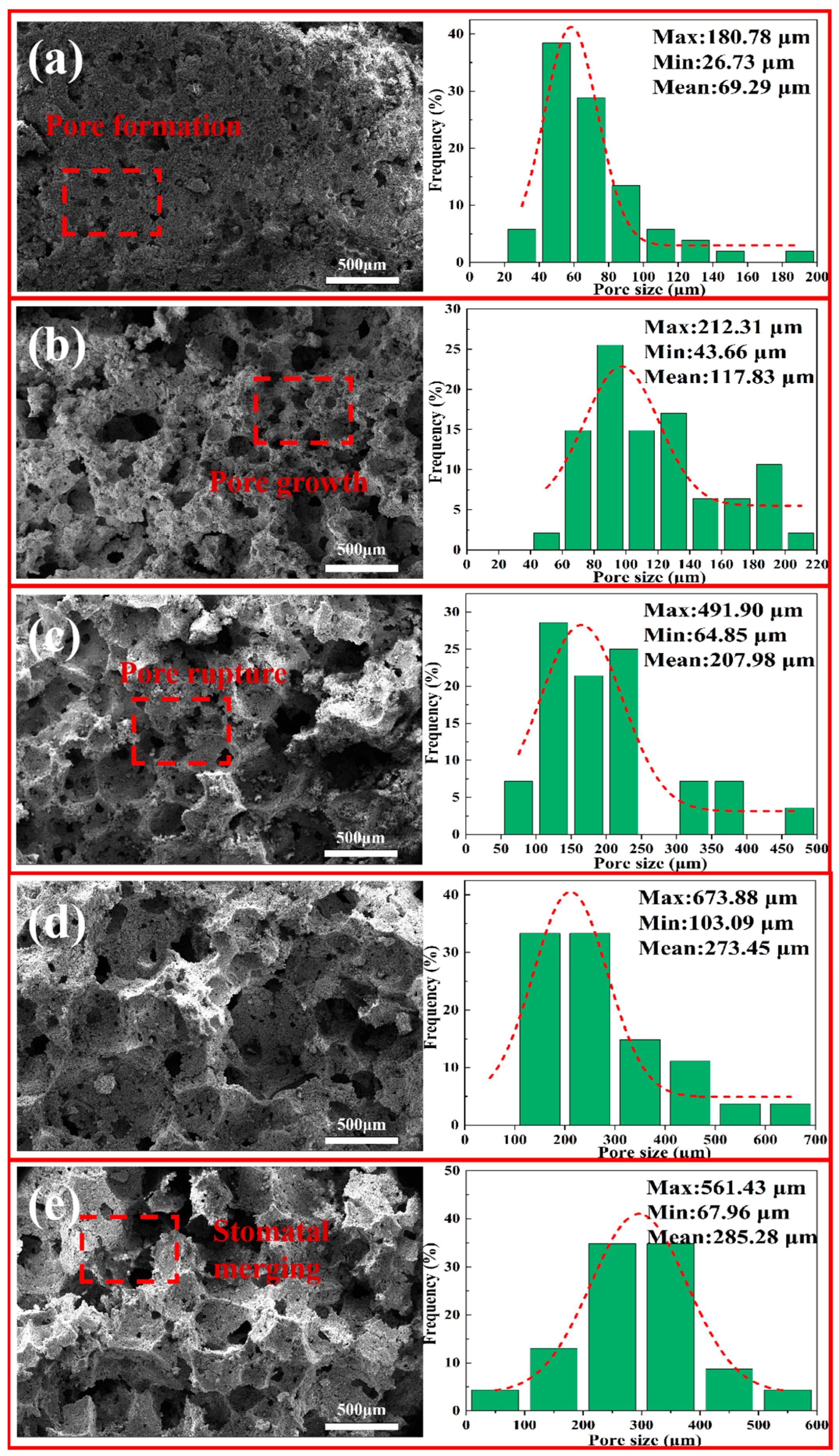
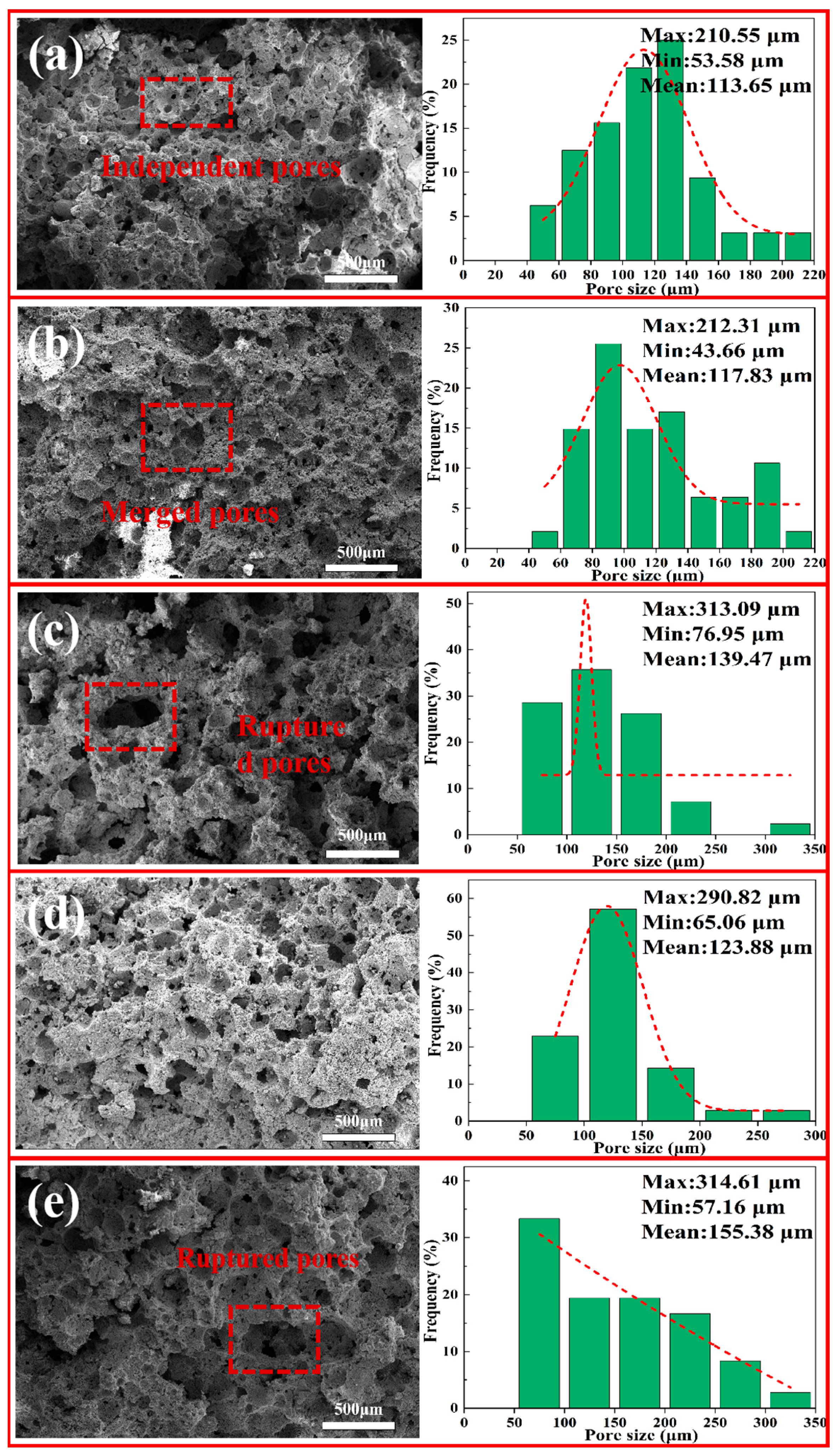

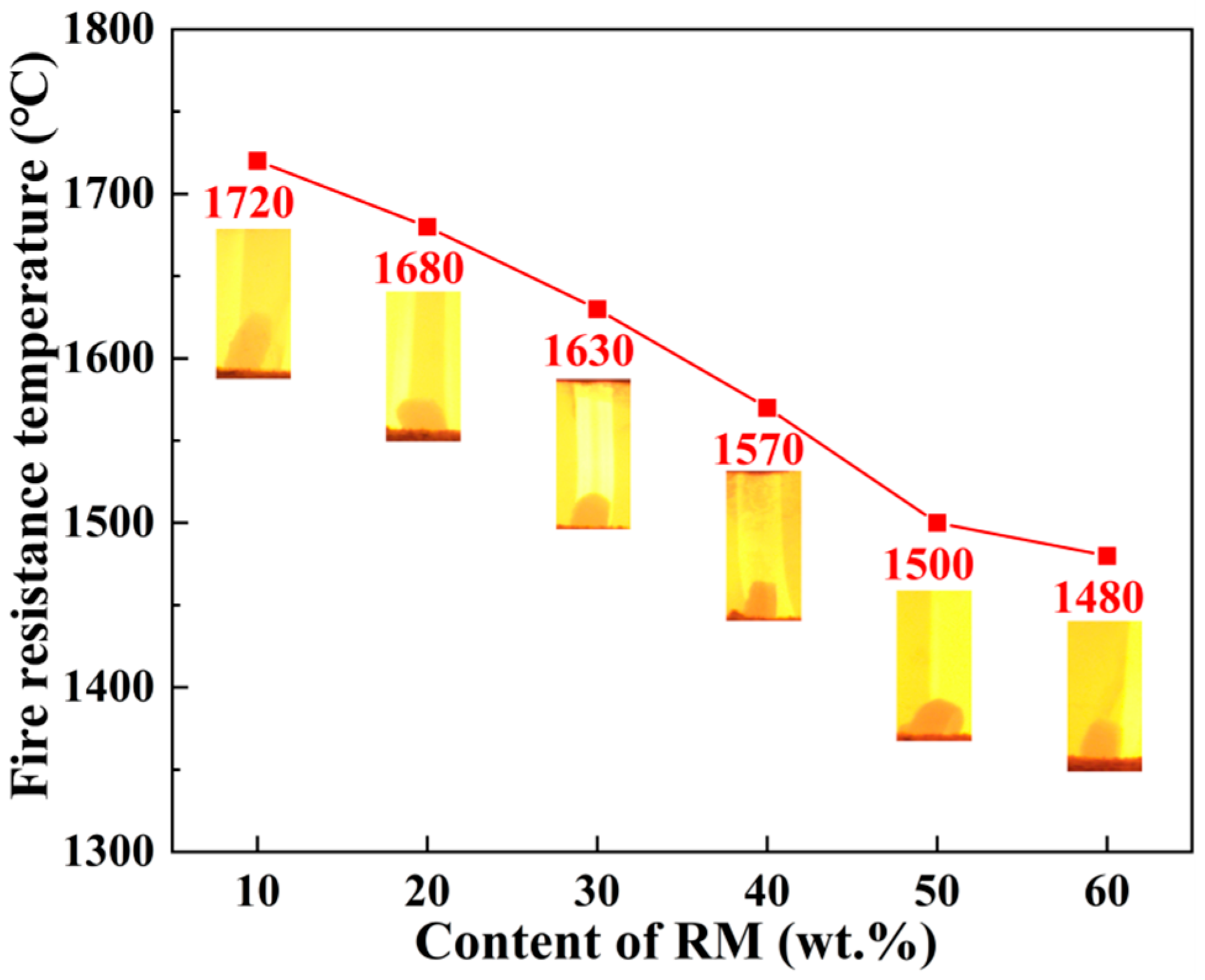

| Component | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | K2O | Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red mud | 16.50 | 1.71 | 0.28 | 7.09 | 12.00 | 48.00 | 0.18 | 0.06 |
| Aluminum ash | 63.6 | 0.828 | 9.23 | 8.78 | 2.64 | 0.446 | 2.31 | 6.62 |
| CA cement | 68.7 | 29.2 | 0.173 | 0.32 | 1.12 | 0.276 | 0.0254 | 0.0078 |
| Bentonite | 12.67 | 7.77 | 1.72 | 0.24 | 73.98 | 1.25 | 2.02 | 0.02 |
| Sample | SAA | RM | CAC | SDS | Be | SP | H2O2 | Foaming Temperature | Sintering Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 60 | 10 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 70 | 1200 |
| A2 | 50 | 20 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 70 | 1200 |
| A3 | 40 | 30 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 70 | 1200 |
| A4 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 70 | 1200 |
| A5 | 20 | 50 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 70 | 1200 |
| A6 | 10 | 60 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 70 | 1200 |
| B1 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 1 | 70 | 1200 |
| B2 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 70 | 1200 |
| B3 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 3 | 70 | 1200 |
| B4 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 4 | 70 | 1200 |
| B5 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 5 | 70 | 1200 |
| C1 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 60 | 1200 |
| C2 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 70 | 1200 |
| C3 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 80 | 1200 |
| C4 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 90 | 1200 |
| C5 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 100 | 1200 |
| D1 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 80 | 1100 |
| D2 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 80 | 1150 |
| D3 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 80 | 1200 |
| D4 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 80 | 1250 |
| D5 | 30 | 40 | 30 | +2 | +8 | +4 | 2 | 80 | 1300 |
| SAA | RM | CA | H2O | SDS | SP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA1 | √ | - | - | - | - | - |
| SA2 | √ | - | - | √ | - | - |
| SA3 | √ | - | - | √ | √ | - |
| SA4 | √ | - | - | √ | √ | √ |
| RM1 | - | √ | - | - | - | - |
| RM2 | - | √ | - | √ | - | - |
| RM3 | - | √ | - | √ | √ | - |
| RM4 | - | √ | - | √ | √ | √ |
| CA1 | - | - | √ | - | - | - |
| CA2 | - | - | √ | √ | - | - |
| CA3 | - | - | √ | √ | √ | - |
| CA4 | - | - | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Items | Sintering Temperature (°C) | Early Stage | Later Stage | Loss Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 1000 | 1.038 | 1.037 | 0.096 |
| 1100 | 1.036 | 1.034 | 0.193 | |
| Diameter (mm) | 1000 | 44.35 | 44.32 | 0.068 |
| 1100 | 43.91 | 43.83 | 0.182 | |
| Height (mm) | 1000 | 36.83 | 36.79 | 0.109 |
| 1100 | 36.25 | 36.18 | 0.193 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, J.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Yue, H.; Ma, L.; Zhao, H.; Jiao, W.; Wang, Y.; Chang, Z. Study of Preparation and Performance Porous Thermal Insulation Refractory Materials from Aluminum Ash and Red Mud. Materials 2025, 18, 5253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225253
Zhong J, Li Z, Li W, Yue H, Ma L, Zhao H, Jiao W, Wang Y, Chang Z. Study of Preparation and Performance Porous Thermal Insulation Refractory Materials from Aluminum Ash and Red Mud. Materials. 2025; 18(22):5253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225253
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Jiayi, Zichao Li, Weiyuan Li, Hongzhi Yue, Laijun Ma, Haoyu Zhao, Wenjuan Jiao, Yan Wang, and Zhiyang Chang. 2025. "Study of Preparation and Performance Porous Thermal Insulation Refractory Materials from Aluminum Ash and Red Mud" Materials 18, no. 22: 5253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225253
APA StyleZhong, J., Li, Z., Li, W., Yue, H., Ma, L., Zhao, H., Jiao, W., Wang, Y., & Chang, Z. (2025). Study of Preparation and Performance Porous Thermal Insulation Refractory Materials from Aluminum Ash and Red Mud. Materials, 18(22), 5253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225253





