Abstract
In this work, Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass has been studied using spectroscopic methods. Based on absorption spectrum measurements, the oscillator strengths for Sm3+ ions were determined and compared to those calculated from the Judd–Ofelt theory. This procedure was applied to evaluate some radiative parameters (radiative transition rates, emission branching ratios, radiative lifetime) of Sm3+ ions in lead phosphate glass. Further luminescent studies indicate that lead phosphate glass doped with Sm3+ emits intense reddish-orange light due to 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H7/2 transition, for which several important spectroscopic parameters like emission linewidth and lifetime, quantum efficiency, peak stimulated emission cross-section, and figure of merit for laser gain were determined. The factors for Sm3+ ions in lead phosphate glass are as follows: η = 53%, FWHM = 10.5 nm, τexp = 1.925 ms, σem = 7.6 × 10−22 cm2, σem × τexp = 14.6 × 10−25 cm2s. The experimental and theoretical results suggest that samarium-doped lead phosphate glass can be successfully used as a reddish-orange-emitting component in photonic devices.
1. Introduction
Samarium-doped inorganic glasses, due to their enhanced luminescent transition 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H7/2 (Sm3+), are known as promising reddish-orange emitting materials useful in solid-state lighting (SSL) technology and photonic devices [1,2,3,4,5]. Emission properties have been examined for numerous glass systems doped with Sm3+ ions, i.e., silicate [6,7,8,9,10], germanate [11,12,13], tellurite [14,15,16], and multicomponent mixed network-former glasses [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Luminescence behavior of Sm3+ ions in non-oxide glasses (chalcogenide, fluoride) has also been explored [28,29,30,31]. A great attention has been paid to borate [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] and phosphate [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49] glasses containing Sm3+ ions. The impact of fluoride and oxide network modifiers on local structure and physicochemical properties (especially luminescence) of Sm3+-doped glasses has been analyzed in detail [50,51,52,53]. From numerous literature data, it is also well-known that trivalent samarium ions play an important role as an excellent acceptor in Dy3+/Sm3+ [54,55,56,57,58,59] and Tb3+/Sm3+ [60,61,62,63,64,65] co-doped glass systems through the excitation energy transfer processes.
Among inorganic glass systems, rare-earth-activated lead phosphate glasses represent a family of heavy metal glass (HMG) systems [66,67,68,69,70,71,72], and they are really attractive for optical applications. Recent studies concerned with rare-earth-activated lead phosphate-based glasses emitting visible light [73,74,75,76] and near-infrared radiation [76,77,78,79]. Owing to the hygroscopic nature of the main component P2O5, the procedure for glass synthesis should be strongly restrictive, i.e., glass samples should be synthesized in a glove-box in order to eliminate hydroxyl groups, which quench emission from excited states of rare earths [80]. Our previous investigations for rare-earth-activated lead phosphate glasses revealed that the intensities of the IR band assigned to the vibration of the hydroxyl groups were significantly lower for glasses fabricated in a glove box than in open air [81]. Thus, luminescence characteristics and spectroscopic parameters for rare earths are enhanced significantly, which is extremely important from the optical point of view.
In this work, lead phosphate glass based on PbO-P2O5-Ga2O3-Sm2O3 composition has been studied using optical spectroscopy. The introduction of the third component Ga2O3 to several glass host matrices increases their thermal stability [82]. It was also confirmed for lead phosphate glasses, for which the thermal stability increases with increasing Ga2O3 content [83]. The Sm3+ concentration was close to 0.5 mol%. From the luminescent studies published previously, low-concentrated (0.5 mol%) Sm3+ doped glasses [84,85,86,87,88,89] showed optical maximum emission intensity in the reddish-orange spectral region. Above 0.5 mol% of Sm3+, the activator concentration effects in glass samples are clearly observed due to cross-relaxation processes occurring between samarium ions [90,91,92]. Based on the optical experiments (absorption and emission spectra measurements) and calculations using the standard Judd–Ofelt theory [93,94], several spectroscopic and laser parameters of samarium ions in lead phosphate glass were determined. At this moment, it should be pointed out that the Judd–Ofelt calculation strategy was greatly developed, and some calculation routes were established in recent years. The Judd–Ofelt parameters of rare earths have been determined according to the excitation spectrum [95]. Luo et al. [96] have established a fluorescence decay route to calculate the Judd–Ofelt parameters of rare earth ions. In the current work, measured and calculated spectroscopic parameters were compared to the previous results published for similar Sm3+-doped glasses. The optical results indicate that Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass is promising for reddish-orange emission applications.
2. Materials and Methods
Lead phosphate glass with the following chemical formula given in mole percent (mol%) 45PbO-45P2O5-9.5Ga2O3-0.5Sm2O3 was prepared by mixing and melting amounts of P2O5 and appropriate metal oxides. Oxide components of high purity (99.99%, Aldrich Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) were used to prepare a glass sample in a glove box, where a homogeneous mixture was heated in a protective atmosphere of dried argon (99.99%). In our case, the argon is necessary, contrary to the cheaper, but strongly reducing atmosphere of nitrogen, which can effectively reduce Sm3+ to Sm2+ ions. Reagents were melted in a Pt crucible at T = 1100 °C for 0.5 h.
In order to characterize the prepared glass, the XRD pattern (X’Pert Pro diffractometer, Panalytical, Almelo, The Netherlands), the DSC curve (Perkin Elmer differential scanning calorimeter, Shelton, CT, USA), and the Raman spectrum (Thermo ScientificTM DXRTM2xi Raman imaging microscope, Waltham, MA, USA) were measured, whereas the Metricon 2010 prism coupler (Pennington, NJ, USA) using λ = 632.8 nm was used to estimate the refractive index. Absorption and emission spectra were measured using a UV-VIS-NIR spectrophotometer (Cary 5000, Agilent Technology, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and a PTI QM40 spectrofluorometer (Photon Technology International, Birmingham, NJ, USA). Details for the equipment of the spectrofluorometer are given in previous work [97]. Resolution for the absorption and emission spectra was ±0.1 nm. The decay emission curve was measured with an accuracy of ±1 μs. All measurements were carried out at room temperature.
3. Results
Figure 1 presents the XRD pattern, DSC curve and Raman spectrum for Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass. The X-ray diffraction analysis indicated that the studied sample is fully amorphous without narrow diffraction lines characteristic of crystalline systems. However, we do not exclude the presence of several small crystalline particles inside the glass that cannot be detected due to the resolution limit. The DSC curve was registered for the glass sample up to 600 °C, because the operating temperature range of the calorimeter is limited. Based on the DSC curve measurement, the glass transition temperature Tg was estimated, and its value is equal to 435 °C. Owing to the lack of the exothermic peak in the temperature range between Tg and T = 600 °C, we suggest that Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass exhibits relatively good thermal stability (ΔT larger than 165 °C) against devitrification. The Raman spectrum shows that several vibration modes related to the characteristic phosphate groups are involved in the studied glass. The assignments of the unresolved bands for lead fluorophosphate glass were reported earlier by Kesavulu and Jayasankar [98]. The Raman bands centered at about 1050 cm−1 and 1107 cm−1 are due to symmetric stretching vibration of diphosphate and metaphosphate groups, whereas the shoulders near 900 cm−1 and 1250 cm−1 correspond to the symmetric (PO4 groups) and asymmetric (PO2 groups) stretching vibrations, respectively. Additionally, the broad Raman band located at about 750 cm−1 (not presented here) is assigned to P–O–P stretching vibration [98]. Phonon energy of the studied glass (mode with maximum energy) obtained from the Raman spectrum measurements is equal to nearly 1107 cm−1. For that reason, it was suggested that lead phosphate glass belongs rather to a medium-phonon system located between high-phonon borate-based glasses (hω = 1300 ÷ 1400 cm−1) and low-phonon tellurite or germanate glass matrices (700 ÷ 800 cm−1), respectively.
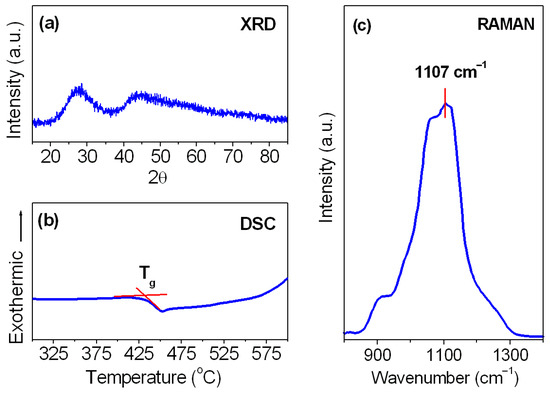
Figure 1.
(a) XRD pattern, (b) DSC curve and (c) the Raman spectrum for Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass.
The Raman results are well correlated with the following value 1117 cm−1, which was obtained for Eu3+-activated lead phosphate glass from the phonon sideband excitation spectrum measurements [99]. Selected physicochemical properties of Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Some physicochemical properties of Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass.
In the next step, the absorption spectrum of Sm3+-doped lead phosphate glass was measured in the UV-VIS and NIR spectral range. The cut-off wavelength is close to 304 nm (UV range). The spectrum consists of bands characteristic of the 4f5-4f5 electronic intraconfigurational transitions of samarium ions. Absorption bands are assigned to transitions originating from 6H5/2 ground state to the following excited states of Sm3+: 4D7/2, 4D3/2, 4D1/2 + 6P7/2, 6P3/2, 6P5/2, 4M17/2, 4M15/2 + 4IJ/2 (J = 9, 11, 13, 15), 4G7/2, 4F3/2, 4G5/2 (UV-VIS absorption range) and 6F11/2, 6F9/2, 6F7/2, 6F5/2, 6F3/2, 6H15/2 and 6F1/2 (NIR absorption range), respectively. The absorption spectrum for Sm3+-doped lead phosphate glass is presented in Figure 2. Then, the standard Judd–Ofelt framework [93,94] was used to calculate the theoretical oscillator strengths for each transition of Sm3+ ions in lead phosphate glass, which were compared to the measured oscillator strengths estimated by measuring the areas under the absorption bands (Figure 2). The absorption bands from the 6H5/2 ground state to the 6FJ excited states with the spin selection rule ΔS = 0 were taken into account in the Judd–Ofelt calculation, because these transitions are allowed and their intensities are relatively strong [20]. The absorption transitions in the UV-VIS region are overlapped, and the energy states are lying very close to each other, thus the Judd–Ofelt calculations become more complicated. The calculation procedure using the Judd–Ofelt theory has been successfully applied to numerous Sm3+-activated inorganic glass systems [100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107].
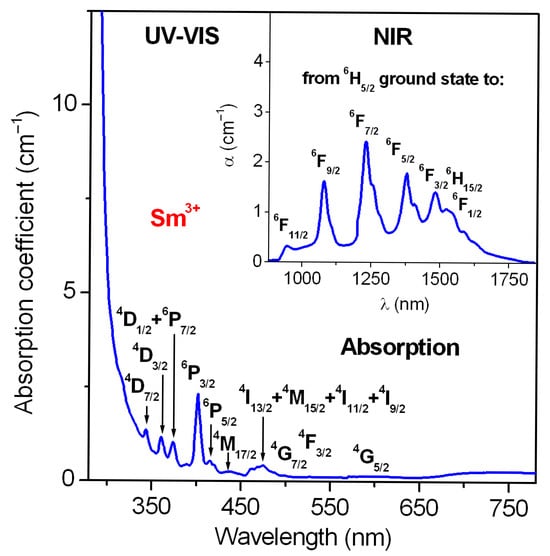
Figure 2.
UV-VIS absorption spectrum of Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass. Inset presents the absorption measured in the NIR spectral range.
The experimental and theoretical oscillator strengths of Sm3+ ions were determined using the following relations:
where ∫ε(ν)dv is the area under the absorption band and ε(ν) = A/c × l. In this relation, A, c and l denote the absorbance, the Sm3+ concentration and the optical path length.
where m, c, h and λ denote the electron mass, the light velocity, the Planck constant and the mean wavelength of each transition. Here, ║Ut║2 for samarium ions was adopted from Ref. [108]. The experimental and theoretical oscillator strengths for samarium ions in lead phosphate glass are given in Table 2. Small deviation of root mean square value (rms = ±0.34 × 10−6) between Pmeas and Pcalc suggests good fitting between them.

Table 2.
Measured and calculated oscillator strengths (P × 10−6) for lead phosphate glass with Sm3+.
Based on comparison of the experimental and theoretical oscillator strengths for Sm3+ ions, the Judd–Ofelt intensity parameters Ωt (where t = 2, 4, 6) were determined and compared to some glass systems [109,110,111,112]. The results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Judd–Ofelt parameters for Sm3+ in lead phosphate glass compared to some glass systems.
In the following step, the factors Ωt were applied to obtain the radiative transition rates and emission branching ratios using the following relation:
The radiative transition rates and emission branching ratios for samarium in lead phosphate glass are presented in Table 4. The total radiative transition rate, defined as the sum of the AJ values calculated for each transition from the 4G5/2 excited state to the lower lying states of Sm3+ ions, is equal to ATOTAL = 275.5 s−1, whereas the radiative lifetime τrad for the state 4G5/2 (Sm3+) as an inverse of ATOTAL is close to 3.63 ms. Details for the Judd–Ofelt analysis and calculations using relations (1)–(4) are given elsewhere [97].

Table 4.
Radiative transition rates and emission branching ratios for Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass.
In the next step, emission properties have been examined in detail. The emission spectrum of Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass is presented in Figure 3.
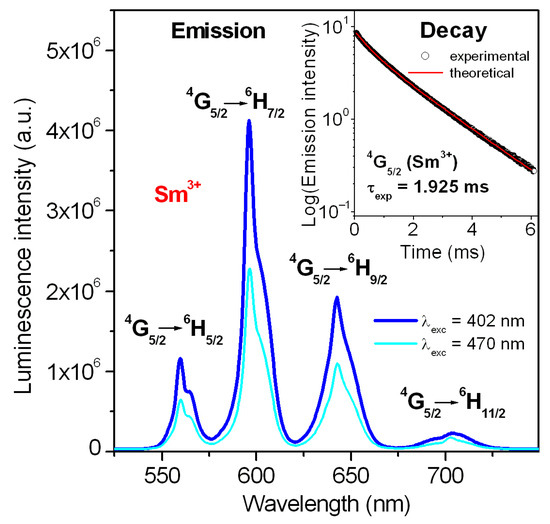
Figure 3.
Emission spectrum of Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass. Inset presents emission decay curve for the 4G5/2 excited state of Sm3+.
The results well demonstrated that the emission intensity is higher for the glass sample excited at 402 nm (6P3/2 state) than 470 nm (multiband due to 4M15/2 + 4IJ/2 (J = 9, 11, 13, 15) states), respectively. Four emission bands correspond to 4G5/2 ⟶ 6HJ/2 (where J = 5, 7 9, 11) transitions of samarium. Reddish-orange emission at 596 nm due to the 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H7/2 transition of samarium ions is the most intense. The inset shows a decay curve for the 4G5/2 state of samarium ions in lead phosphate glass. Luminescence lifetime was estimated based on the decay curve measurement. Its experimental value τexp for the excited state 4G5/2 (Sm3+) is close to 1.925 ms. Four emission lines are illustrated schematically on the energy level diagram of Sm3+ ions in Figure 4.
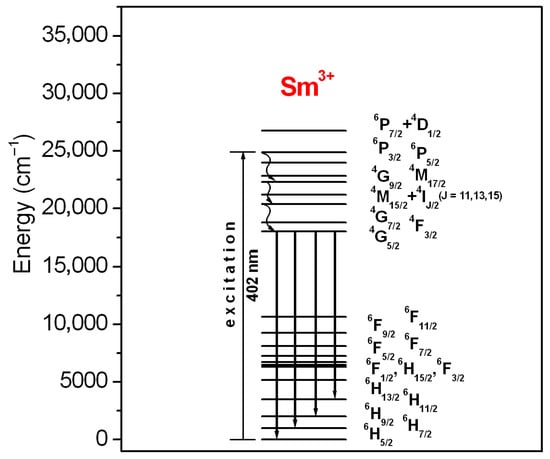
Figure 4.
Energetic diagram for samarium-activated lead phosphate glass. Luminescent transitions of Sm3+ ions are also indicated.
The experimental emission lifetime τexp as well as the radiative lifetime τrad and the radiative transition rate AJ from the Judd–Ofelt framework were used to calculate the quantum efficiency η and the peak stimulated emission cross-section σem. The appropriate relations (5) and (6) are given below:
In relation (6), n is the refractive index, and its value is close to 1.75 (Table 1), λp is the peak emission wavelength, whereas Δλ is the effective linewidth defined as full width at half maximum (FWHM).
Spectroscopic parameters for samarium ions in lead phosphate glass are given in Table 5. The results are compared to the previously published data for similar phosphate-based glass systems and heavy metal glasses containing lead [113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123].

Table 5.
Spectroscopic parameters for Sm3+ ions in lead phosphate glass and other glass systems.
4. Discussion
The physicochemical results obtained using XRD, DSC and Raman methods (Figure 1) confirmed that Sm3+-doped lead phosphate glass is fully amorphous, thermally stable and belongs to medium-phonon glass matrices (Table 1). Based on the absorption spectrum recorded in the UV-VIS and NIR ranges (Figure 2) and relations (1)–(4) from the Judd–Ofelt theory, several radiative parameters for samarium ions in lead phosphate glass were obtained. The measured and calculated oscillator strengths for transitions of Sm3+ ions were compared (Table 2), and the Judd–Ofelt parameters Ωt (t = 2, 4, 6) were achieved. The following trend Ω4 > Ω6 > Ω2 or Ω6 > Ω4 > Ω2 is usually observed for Sm3+ ions in inorganic glasses [124]. In our case, the Judd–Ofelt intensity parameters for Sm3+ ions are changed in direction Ω6 > Ω4 > Ω2, and this trend is similar to the results obtained earlier for other systems (Table 3). Moreover, the Judd–Ofelt intensity parameter Ω2, exhibiting the degree of bonding (covalent/ionic) between samarium ions and ligands is low. Its value is equal to 0.76 × 10−20 cm2. It suggests absolutely more ionic bonding in character between samarium ions and their nearest surroundings confirming previous Judd–Ofelt results obtained for phosphate-based glasses doped with Sm3+ [125,126,127].
The Judd–Ofelt parameters Ωt were used to obtain the radiative transition rates, emission branching ratios and radiative lifetime (Table 4). In particular, the luminescence properties of Sm3+-doped lead phosphate glass have been examined in detail. Luminescence spectrum (Figure 3) consists of four bands, which are associated with the following transitions: 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H5/2, 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H7/2, 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H9/2 and 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H11/2 centered at 560 nm, 596 nm, 648 nm and 710 nm, respectively. All transitions are indicated on the energetic diagram of samarium ions (Figure 4). Lead phosphate glass with Sm3+ emits reddish-orange light related to the most intense 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H7/2 transition at 596 nm. Based on emission spectrum and its decay from the 4G5/2 (Sm3+), and the appropriate relations (5) and (6), several spectroscopic parameters for trivalent samarium ions in lead phosphate glass were determined. The results are summarized in Table 5.
The main spectroscopic parameters for Sm3+ ions in PbO-P2O5-Ga2O3 glass system are as follows: the peak emission wavelength λp = 596 nm, the luminescence linewidth FWHM = 10.5 nm, the 4G5/2 theoretical radiative lifetime τrad = 3.63 ms, the experimental luminescence lifetime of 4G5/2 state τexp = 1.925 ms, the stimulated emission cross-section σem = 7.6 × 10−22 cm2 and the quantum efficiency 4G5/2 (Sm3+) η = 53%. The latter parameter, i.e., the quantum efficiency η is larger than 50% suggesting that Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass is also a potential laser material emitting in the reddish-orange region. Interestingly, the quantum efficiency for the 4G5/2 (Sm3+) state in lead phosphate glass is smaller than the η value (60.4%) obtained for Sm3+ ions in heavy metal oxide glass based on Li2O-PbO-Al2O3-B2O3 [113] but higher than η = 45.6% for Sm3+ in heavy metal oxyfluoride glass based on PbF2-TeO2-WO3 [114]. In fact, the quantum efficiency agrees with the results (54–58%) for multicomponent heavy metal oxide glass [115] and phosphate-based glasses with the presence [116] and absence [117,118] of lead. Contrary to η values, the peak stimulated emission cross-section σem for the main 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H7/2 reddish-orange transition of trivalent samarium ions in lead phosphate glass is higher compared to the values (σem = 5.8 ÷ 7.23 × 10−22 cm2) obtained for heavy metal glass systems as well as phosphate-based glasses [113,114,115,116,117,118]. At this moment, it should also be noted that both spectroscopic parameters seem to be smaller compared to the values η (77 ÷ 98%) and σem (9 ÷ 12.4 × 10−22 cm2) reported for some phosphate-based glasses with Sm3+ [119,120,121,122,123].
Finally, the figure of merit for laser gain defined as σem × τexp was determined for the 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H7/2 transition of Sm3+ ions in lead phosphate glass at 596 nm. Relatively large values of σem × τexp product are necessary to generate laser action in glass systems. In our case, the figure of merit for laser gain is close to 14.6 × 10−25 cm2s and its value is higher compared to the following results: 8.51 × 10−25 cm2s for PbF2-TeO2-WO3 [114], 10.4 × 10−25 cm2s for P2O5-K2O-MgO-Al2O3 [118], 11.7 × 10−25 cm2s for Li2O-PbO-Al2O3-B2O3 [113], as well as 12.8 × 10−25 cm2s for P2O5-PbO-Nb2O5 [116], respectively. The σem × τexp product for trivalent samarium ions in lead phosphate glass ranges between 13.54 × 10−25 cm2s for P2O5-K2O-Al2O3-Nb2O5 [122] and 16.1 × 10−25 cm2s for P2O5-K2O-Al2O3-PbF2-Na2O [119], even though these Sm3+-doped glass systems exhibit higher values of η and σem compared to our glass, as mentioned above. It suggests that the figure of merit for laser gain can be useful in comparison to reported laser phosphate glass systems with Sm3+ ions [119,120,121,122,123]. According to the previous results for PbO-P2O5-Ln2O3 (Ln = Sm, Gd) glass without Ga2O3, the lifetimes and the quantum efficiencies depend significantly on the Sm3+ content as well as on the heating time of glasses melted at high temperature [128]. On the other hand, thermal stability increases with increasing Ga2O3 concentration in lead phosphate glass, as mentioned in the Section 1 [83]. Therefore, we can conclude based on the spectroscopic results shown in Table 5 that the thermally stable samarium-doped lead phosphate glass modified by Ga2O3 is suitable for the applications of reddish-orange visible light. It can be successfully used as a glass component in photonic devices similar to other Sm3+-doped glass host matrices published recently, which seem to be excellent reddish-orange-emitting candidates for numerous luminescence applications [129]. For example, borosilicate glasses modified by alkaline/alkali (CaF2, NaF) fluorides [87] or mixed alkali (Li2O, Na2O) oxides [130] playing the role as the glass-network-modifiers are attractive for luminescence applications after Sm3+ ion doping. Based on the structural, thermal and optical studies, it was suggested that borosilicate-based glasses doped with Sm3+ ions are promising for radiation protection and photonic display devices [87] and luminescence applications in art and decoration [130].
5. Conclusions
Optical experiments and the Judd–Ofelt calculations have been successfully applied to Sm3+-doped lead phosphate glass, which emits intense reddish-orange light related to 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H7/2 transition at 596 nm. Several spectroscopic factors for trivalent Sm3+ were determined. The following spectroscopic parameters the for 4G5/2 ⟶ 6H7/2 transition of samarium in lead phosphate glass were achieved: the quantum efficiency η = 53%, the emission linewidth FWHM = 10.5 nm, the experimental emission lifetime τexp = 1.925 ms, the peak stimulated emission cross-section σem = 7.6 × 10−22 cm2 and the figure of merit for laser gain σem × τexp = 14.6 × 10−25 cm2s, respectively. The results compared to heavy metal glass systems and phosphate-based glasses published previously. The theoretical and experimental studies demonstrate that Sm3+-activated lead phosphate glass is a promising reddish-orange laser gain media operated at 596 nm.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.P. and W.A.P.; methodology, J.P. and W.A.P.; formal analysis, W.A.P.; investigation, J.P. and W.A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, J.P.; writing—review and editing, J.P.; supervision, W.A.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Karolina Dej for the absorption spectrum measurement. The research activities were co-financed by the funds granted under the Research Excellence Initiative of the University of Silesia in Katowice.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jayasankar, C.K.; Rukmini, E. Optical properties of Sm3+ ions in zinc and alkali zinc borosulphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 1997, 8, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jlassi, I.; Mnasri, S.; Elhouichet, H. Concentration dependent spectroscopic behavior of Sm3+-doped sodium fluoro-phosphates glasses for orange and reddish-orange light emitting applications. J. Lumin. 2018, 199, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolavekar, S.B.; Ayachit, N.H.; Rajaramakrishna, R.; Pramod, N.G.; Kaewkhao, J. Reddish-orange emission and Judd-Ofelt investigation of Sm3+ ions doped in zinc-bismuth-phospho-tellurite glasses for solid state lighting application. J. Lumin. 2020, 226, 117498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjeet; Kumar, A.; Anu; Lohan, R.; Deopa, N.; Kumar, A.; Chahal, R.P.; Dahiya, S.; Punia, R.; Rao, A.S. Impact of Sm3+ ions on structural, thermal, optical and photoluminescence properties of ZnO–Na2O–PbO–B2O3 glasses for optoelectronic device applications. Opt. Mater. 2023, 139, 113778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrabet, H.; Khattech, I.; Bouzidi, S.; Kechiche, L.; Jbeli, A.; Al Harbi, N.; Bouzidi, C.; Munoz, F.; Balda, R. Influence of barium substitution on the physical, thermal, optical and luminescence properties of Sm3+ doped metaphosphate glasses for reddish orange light applications. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, Y.K.; Surana, S.S.L.; Singh, R.K. Spectroscopic investigations and luminescence spectra of Sm3+ doped soda lime silicate glasses. J. Rare Earths 2009, 27, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Tewelde, M.; Kuhn, S.; Tiegel, M.; Rüssel, C. The effect of glass composition on the luminescence properties of Sm3+ doped alumino silicate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 502, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Zekri, M.; Maalej, R.; Rüssel, C. The Effect of Glass Structure on the Luminescence Spectra of Sm3+-Doped Aluminosilicate Glasses. Materials 2023, 16, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, I.R.M. Influence of Alkali Metal Ions on the Structural and Spectroscopic Properties of Sm3+-Doped Silicate Glasses. Ceramics 2023, 6, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Luo, X.; Lai, F.; Wang, W.; You, W.; Huang, J. Analysis of spectroscopic characteristics of Sm3+ ions doped gallium silicate glasses for orange-red LEDs. Opt. Mater. 2024, 157, 116085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.J.; Shen, L.F.; Pun, E.Y.B.; Lin, H. Sm3+-doped germanate glass channel waveguide as light source for minimally invasive photodynamic therapy surgery. Opt. Exp. 2012, 20, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Prakash, M.; Neelima, G.; Kummara, V.K.; Ravi, N.; Kiran, N.; Viswanath, C.S.D.; Rao, T.S.; Venkatramu, V. Optical and radiative properties of Sm3+ ions activated alkali-bismuth-germanate glasses. J. Lumin. 2019, 214, 116566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Guan, Z.; Wang, K.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, B. Luminescence and optical properties of sodium germanate glasses doped with Sm3+ ions. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 153, 111905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rai, D.K.; Rai, S.B. Optical properties of Sm3+ ions doped in tellurite glass. Spectrochim. Acta A 2003, 59, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, T.; Moorthy, L.R.; Babu, A.M. Optical and luminescent properties of Sm3+ doped tellurite glasses. Spectrochim. Acta A 2013, 104, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimesz, B.; Lisiecki, R.; Ryba-Romanowski, W. Sm3+-doped oxyfluorotellurite glasses—Spectroscopic, luminescence and temperature sensor properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 788, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.K.; Surana, S.S.L.; Dubedi, R.P.; Joshi, V. Spectroscopic and radiative properties of Sm3+ doped zinc fluoride borophosphate glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2005, 119, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshvaran, K.; Linganna, K.; Marimuthu, K. Composition dependent structural and optical properties of Sm3+ doped boro-tellurite glasses. J. Lumin. 2011, 131, 2746–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, K.; Marimuthu, K. Structural and spectroscopic studies on concentration dependent Sm3+ doped boro-tellurite glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 553, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.V.; Tuyen, V.P.; Quang, V.X.; Hung, L.X.; Thanh, L.D.; Ngoc, T.; Tam, N.V.; Huy, B.T. Investigation of spectroscopy and the dual energy transfer mechanisms of Sm3+-doped telluroborate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2016, 55, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.S.R.K.; Swapna, K.; Mahamuda, S.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Srinivas Prasad, M.V.V.K.; Rao, A.S.; Prakash, G.V. Structural, optical absorption and photoluminescence spectral studies of Sm3+ ions in Alkaline-Earth Boro Tellurite glasses. Opt. Mater. 2018, 79, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokce, M.; Kocyigit, D. Optical and luminescence characteristics of Sm3+ doped B2O3-GeO2-Gd2O3 glasses. Opt. Mater. 2018, 83, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantha Lakshmi, Y.; Swapna, K.; Mahamuda, S.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Rao, A.S. Photoluminescence properties of Sm3+ ions doped Bismuth Boro tellurite glasses. Solid State Sci. 2021, 116, 106609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Katyal, V.; Plakkot, V.; Deopa, N.; Prasad, A.; Rao, A.S. Radiative emission analysis of Sm3+ ions doped borosilicate glasses for visible orange photonic devices. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 572, 121106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, J.; Jana, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mahalingam, V. Optical and luminescence properties of Sm2O3 doped SrO–PbO–ZnO–P2O5–TeO2 glasses for visible laser applications. Solid State Sci. 2022, 129, 106910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalamin, S.N.F.; Zaid, M.H.M.; Matori, K.A.; Karim, M.K.A.; Yamin, N.A.M.; Ismail, N.A.N. Comprehensive study on optical and luminescence properties of Sm3+ doped magnesium borotellurite glasses. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 163, 110563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaran, S.A.R.; Padhi, R.K.; El Sayed, Y.; Marimuthu, K. Spectroscopic studies on Sm3+ ions doped modifiers incited calcium phospho-silicate glasses for photonic and optoelectronic applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2024, 623, 122692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.; Chen, Y. The fluorescence line narrowing of Sm3+ in ZBLAN fluoride glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1993, 161, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němec, P.; Jedelský, J.; Frumar, M. On the effect of composition on the Judd–Ofelt parameters of Sm3+-doped chalcogenide glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 326–327, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez, A.; Herrera, A.; Florez, M. Optical properties of Sm3+ ions and influence of odd third-order intensity parameters in fluoride glasses. Phys. Stat. Sol. C 2007, 4, 4156–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Xiong, H.; Chen, W.; Luo, L. The study of Sm3+-doped low-phonon-energy chalcohalide glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 2463–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.K.; Rai, D.K.; Rasi, S.B. Optical studies of Sm3+ doped oxyfluoroborate glass. Solid State Commun. 1998, 108, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasankar, C.K.; Babu, P. Optical properties of Sm3+ ions in lithium borate and lithium fluoroborate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 307, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuga Sundari, S.; Marimuthu, K.; Sivraman, M.; Babu, S.S. Composition dependent structural and optical properties of Sm3+-doped sodium borate and sodium fluoroborate glasses. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, D.; Balakrishna, A.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Luminescence, structural and dielectric properties of Sm3+ impurities in strontium lithium bismuth borate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2012, 35, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swapna, K.; Mahamuda, S.; Srinivasa Rao, A.; Sasikala, T.; Rama Moorthy, L. Visible luminescnence characteristics of Sm3+ doped zinc alumino bismuth borate glasses. J. Lumin. 2014, 146, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamuda, S.K.; Swapna, K.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Rao, A.S.; Shakya, S.; Prakash, G.V. Spectral characterisation of Sm3+ ions doped oxyfluoroborate glasses for visible orange luminescent applications. J. Lumin. 2014, 154, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deopa, N.; Rao, A.S.; Choudhary, A.; Saini, S.; Navhal, A.; Jayasimhadri, M.; Haranath, D.; Prakash, G.V. Photoluminescence investigations on Sm3+ ions doped borate glasses for tricolor w-LEDs and lasers. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 100, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, D.; Swapna, K.; Shanmukh Kumar, J.V.; Mahamuda, S.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Sruthi, P.; Shanmukha Sai, D.; Rao, A.S. Influence of Sm3+ ion concentration on the photoluminescence behavior of antimony lead oxy fluoro borate glasses. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 146, 111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, V.R.L.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Swapna, K.; Mahamuda, S.; Rekha Rani, P.; Rao, A.S. Physical and spectroscopic studies of Sm3+ ions doped Alumino Tungsten Borate glasses for photonic applications. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 190, 109806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatramu, V.; Babu, P.; Jayasankar, C.K.; Tröster, T.; Sievers, W.; Wortmann, G. Optical spectroscopy of Sm3+ ions in phosphate and fluorophosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2007, 29, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, M.; Dong, G.; Qiu, J. Spectroscopic properties of Sm3+-doped phosphate glasses. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 2111–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaya, R.; Venkatramu, V.; Babu, P.; Jayasankar, C.K.; Rodríguez-Mendoza, U.R.; Lavín, V. Spectroscopic properties of Sm3+ ions in phosphate and fluorophosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2013, 365, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Rocha, A.N.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M.; Caldiño, U. Orange and reddish-orange light emitting phosphors: Sm3+ and Sm3+/Eu3+ doped zinc phosphate glasses. J. Lumin. 2015, 167, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, M.; Radha, M.; Rajesh, D.; Barbosa, L.C.; Cordeiro, C.M.B.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Effect of ZnO on spectroscopic properties of Sm3+ doped zinc phosphate glasses. Phys. B 2015, 459, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Rooh, G.; Rajaramakrishna, R.; Chanthima, N.; Kiwsakunkran, N.; Kim, H.J.; Kaewkhao, J.; Tuscharoen, S. Comparative study of Sm3+ ions doped phosphate based oxide and oxy-fluoride glasses for solid state lighting applications. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Rooh, G.; Rajaramakrishna, R.; Chanthima, N.; Kim, H.J.; Tuscharoen, S.; Kaewkhao, J. Physical and luminescence properties of samarium doped oxide and oxyfluoride phosphate glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 229, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelima, G.; Kummar, V.K.; Ravi, N.; Suresh, K.; Rasool, S.K.N.; Tyagarajan, K.; Prasad, T.J. Investigation of spectroscopic properties of Sm3+-doped oxyfluorophosphate glasses for laser and display applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 110, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudeif, Y.M.; Moteb Alqahtani, M.; Emara, A.M.; Reben, M.; Yousef, E.-S. Luminescence of Phosphate Glasses: P2O5-ZnO-BaF2-K2TeO3-Al2O3-Nb2O5 doped with Sm3+ ions for display and laser materials. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 4144–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnakaram, Y.C.; Balakrishna, A.; Rajesh, D.; Seshadri, M. Influence of modifier oxides on spectroscopic properties of Sm3+ doped lithium fluoroborate glass. J. Mol. Struct. 2012, 1028, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indhrapriyadarshini, A.; Naseer, K.A.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Komal Poojha, M.K.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Marimuthu, K. Impact of Fluoride modifiers on Sm3+ ions doped Phospho-Borate glasses for radiation shielding applications. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2025, 237, 113057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Lin, Z.; Yue, H.; Luo, X.; Hou, H.; Lai, F.; Wang, W.; You, W.; Huang, J. Effect of network modifiers on spectroscopic properties of Sm3+ ions doped gallium silicate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2024, 152, 115445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josuva D’Silva, A.; Maheshvaran, K.; Arul Rayappan, I. Influence of alkali and alkaline-earth metal oxides on Sm3+ ions-doped borate glasses: Synthesis, structural, and optical investigations for reddish-orange solid-state-lighting applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaraiah, S.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Energy transfer studies and neutral to warm white light generation in Dy3+- Sm3+ co-doped bismuth phosphate glasses for lighting applications. J. Lumin. 2019, 207, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, A.; Krishnapriya, T.; Jose, T.A.; Joseph, C.; Unnikrishnan, N.V.; Biju, P.R. Color tunable luminescence characteristics and energy transfer analysis of Dy3+/Sm3+ co-doped multicomponent borosilicate glasses. Scr. Mater. 2021, 203, 114088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, V.; Jayasimhadri, M.; Haranath, D. Colour-tunable and warm white light emitting thermally stable Dy3+/Sm3+ co-activated tungstate-tellurite glasses for photonic applications. J. Lumin. 2024, 266, 120276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, J.; Jana, S.; Ghosh, S. Temperature dependent luminescence exploration in CIELab of Dy3+/Sm3+ ions co-imbued in phospho-tellurite glasses for eco-friendly light generation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2024, 630, 122890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Ge, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Cai, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y. Optical and spectroscopic spectral studies: Sm3+ and Dy3+ co-doped multi-component boro-silicate glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2024, 309, 117615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, A.S.; Bulus, I.; Yusoff, N.M. Exploring the luminescence potentials in Dy3+/Sm3+ co-doped zinc telluro-phospho-borate glasses for photonic devices. J. Lumin. 2025, 281, 121151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yuan, S.; Chen, G.; Pring, A.; Xia, F. Luminescence properties of Tb3+–Sm3+ codoped glasses for white light emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 091104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Rocha, A.N.; Munoz, H.G.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M.; Caldińo, U. Neutral and warm white light emission in Tb3+/Sm3+ zinc phosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2015, 47, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil Kumar, K.; Babu, S.; Reddy Prasad, V.; Damodaraiah, S.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Optical response and luminescence characteristics of Sm3+ and Tb3+/Sm3+ co- doped potassium-fluoro-phosphate glasses for reddish-orange lighting applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 90, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.-B.F.A.; Lakshminarayana, G.; Baki, S.O.; Bashar, K.A.; Kityk, I.V.; Mahdi, M.A. Optical and dielectric studies for Tb3+/Sm3+ co-doped borate glasses for solid-state lighting applications. Opt. Mater. 2018, 86, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarska, J.; Kos, A.; Sołtys, M.; Górny, A.; Pietrasik, E.; Pisarski, W.A. Spectroscopy and energy transfer in Tb3+/Sm3+ co-doped lead borate glasses. J. Lumin. 2018, 195, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Romero, O.; Huerta, E.F.; Meza-Rocha, A.N.; Caldiño, U. Orange and yellow emissions through Sm3+ and Tb3+/Sm3+ doped potassium-zinc phosphate glasses for WLED applications. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 36353–36359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumbaugh, W.H.; Lapp, J.C. Heavy-Metal Oxide Glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1992, 75, 2315–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezal, D.; Pedlikova, J.; Kostka, P.; Bludska, J.; Poulain, M.; Zavadil, J. Heavy metal oxide glasses: Preparation and physical properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 284, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarska, J.; Żur, L.; Pisarski, W.A. Visible luminescence of dysprosium ions in oxyhalide lead borate glasses. Spectrochim. Acta A 2011, 79, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisarski, W.A.; Pisarska, J.; Żur, L.; Goryczka, T. Structural and optical aspects for Eu3+ and Dy3+ ions in heavy metal glasses based on PbO-Ga2O3-XO2 (X = Te, Ge, Si). Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersundu, A.E.; Çelikbilek, M.; Baazouzi, M.; Soltani, M.T.; Troles, J.; Aydin, S. Characterization of new Sb2O3-based multicomponent heavy metal oxide glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.A.; Fayad, A.M. Heavy metal oxide glass responses for white light emission. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 14502–14511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, H.O.; Susoy, G.; Issa, S.A.M.; Ene, A.; Almisned, G.; Rammah, Y.S.; Ali, F.T.; Algethami, M.; Zakaly, H.M.H. Heavy metal oxide (HMO) glasses as an effective member of glass shield family: A comprehensive characterization on gamma ray shielding properties of various structures. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarski, W.A.; Żur, L.; Pisarska, J. Optical transitions of Eu3+ and Dy3+ ions in lead phosphate glasses. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa Rao, C.; Upendra Kumar, K.; Babu, P.; Jayasankar, C.K. Optical properties of Ho3+ ions in lead phosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2012, 35, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavapoornima, C.; Kesavulu, C.R.; Maheswari, T.; Pecharapa, W.; Depuru, S.R.; Jayasankar, C.K. Spectral characteristics of Pr3+-doped lead based phosphate glasses for optical display device applications. J. Lumin. 2020, 228, 117585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sołtys, M.; Pisarska, J.; Leśniak, M.; Sitarz, M.; Pisarski, W.A. Structural and spectroscopic properties of lead phosphate glasses doubly doped with Tb3+ and Eu3+ ions. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1163, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkata Krishnaiah, K.; Rajeswari, R.; Upendra Kumar, K.; Surendra Babu, S.; Martín, I.R.; Jayasankar, C.K. Spectroscopy and radiation trapping of Yb3+ ions in lead phosphate glasses. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 140, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarska, J.; Pisarski, W.A.; Goryczka, T.; Lisiecki, R.; Ryba-Romanowski, W. Thermal analysis and near-infrared luminescence of Er3+-doped lead phosphate glasses modified by PbF2. J. Lumin. 2015, 160, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Mitra, S. Compositional dependence of the luminescence properties of Nd3+ ions in lead phosphate glasses: The efficient laser active materials. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 141, 107123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Faber, A.J.; de Waal, H. Luminescence quenching by OH groups in highly Er-doped phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1995, 181, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarski, W.A.; Żur, L.; Goryczka, T.; Sołtys, M.; Pisarska, J. Structure and spectroscopy of rare earth—Doped lead phosphate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 587, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.-X.; Dai, S.-X.; Xu, T.-F.; Nie, Q.-H.; Shen, X. Effect of Ga2O3 on the spectroscopic properties of erbium-doped boro-bismuth glasses. Spectrochim. Acta A 2007, 68, 548–553. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, J.; Vosejková, K. Thermal properties of Ga2O3-PbO-P2O5 glass system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 104, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj Kumar, G.; Shivakiran Bhaktha, B.N.; Narayana Rao, D. Self-quenching of spontaneous emission in Sm3+ doped lead-borate glass. Opt. Mater. 2006, 28, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żmojda, J.; Kochanowicz, M.; Miluski, P.; Leśniak, M.; Sitarz, M.; Pisarski, W.; Pisarska, J.; Dorosz, D. Effect of GeO2 content on structural and spectroscopic properties of antimony glasses doped with Sm3+ ions. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1126, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Rooh, G.; Rajaramakrishna, R.; Srisittipokakun, N.; Kim, H.J.; Kothan, S.; Kaewkhao, J.; Kirdsiri, K. Comparative study of optical and luminescence properties of Sm3+-ions doped Li2O–Gd2O3–PbO–SiO2 and Li2O-GdF3-PbO–SiO2 glasses for orange emission solid state device application. J. Lumin. 2020, 222, 117136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Kavaz, E.; Raju, B.D.P. Photoluminescence, radiative shielding properties of Sm3+ ions doped fluoroborosilicate glasses for visible (reddish-orange) display and radiation shielding applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2021, 142, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopa; Eraiah, B. Impact of samarium ion concentration on the physical, structural and optical properties of multi-component borate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 596, 121866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayari, O.; Bouzidi, C.; Khlissa, F.; Garbout, A.; Hraiech, S. Investigation of spectroscopic properties of Sm3+ doped phosphate glasses for reddish orange light applications. Displays 2022, 74, 102266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, S.; Marimuthu, K. Concentration effect of Sm3+ ions in B2O3–PbO–PbF2–Bi2O3–ZnO glasses—Structural and luminescence investigations. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 565, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, M.; Marimuthu, K.; Sudarsan, V. Concentration dependent spectroscopic behavior of Sm3+ doped lead fluoro-borophosphate glasses for laser and LED applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, S.; Marimuthu, K.; Muralidharan, G. Structural and luminescence behavior of Sm3+ ions doped lead boro-telluro-phosphate glasses. J. Lumin. 2015, 159, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, B.R. Optical absorption intensities of rare-earth ions. Phys. Rev. 1962, 127, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofelt, G.S. Intensities of crystal spectra of rare-earth ions. J. Chem. Phys. 1962, 37, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Liao, J.; Li, R.; Chen, X. Determination of Judd–Ofelt intensity parameters from the excitation spectra for rare-earth doped luminescent materials. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 3276–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Fluorescence decay route of optical transition calculation for trivalent rare earth ions and its application for Er3+-doped NaYF4 phosphor. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 25177–25183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisarski, W.A. Judd–Ofelt Analysis and Emission Properties of Dy3+ Ions in Borogermanate Glasses. Materials 2022, 15, 9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavulu, C.R.; Jayasankar, C.K. White light emission in Dy3+-doped lead fluorophosphate glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarska, J.; Sołtys, M.; Żur, L.; Pisarski, W.A.; Jayasankar, C.K. Excitation and luminescence of rare earth-doped lead phosphate glasses. Appl. Phys. B 2014, 116, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, H.; Wollenhaupt, M.; Fröbel, P.; Lin, J.; Bärner, K.; Sun, G.S.; Braunstein, R. Determination of the Judd-Ofelt parameters of the optical transitions of Sm3+ in lithiumborate tungstate glasses. J. Lumin. 1999, 82, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasimhadri, M.; Cho, E.-J.; Jang, K.-W.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.I. Spectroscopic properties and Judd–Ofelt analysis of Sm3+ doped lead–germanate–tellurite glasses. J. Appl. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 175101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Shukla, R.; Sanghi, S.; Agarwal, A.; Pal, I. Spectroscopic properties of Sm3+ doped lead bismosilicate glasses using Judd–Ofelt theory. Spectrochim. Acta A 2014, 117, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, S.; Herrmann, A.; Rüssel, C. Judd–Ofelt analysis of Sm3+-doped lanthanum-aluminosilicate glasses. J. Lumin. 2015, 157, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawlud, S.Q.; Ameen, M.M.; Sahar, M.R.; Mahraz, Z.A.S.; Ahmed, K.F. Spectroscopic properties of Sm3+ doped sodium-tellurite glasses: Judd-Ofelt analysis. Opt. Mater. 2017, 69, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largot, H.; Aiadi, K.E.; Ferid, M.; Hraiech, S.; Bouzidi, C.; Charnay, C.; Horchani-Naifer, K. Spectroscopic investigations of Sm3+ doped phosphate glasses: Judd-Ofelt analysis. Phys. B 2019, 552, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravina; Naveen; Sheetal; Kumar, V.; Dahiya, S.; Deopa, N.; Punia, R.; Rao, A.S. Judd-Ofelt itemization and influence of energy transfer on Sm3+ ions activated B2O3–ZnF2–SrO–SiO2 glasses for orange-red emitting devices. J. Lumin. 2021, 229, 117651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, K.; Mishra, N.K.; Abdullahi, I.; Singh, P.J.; Tyagi, M.; Singh, S. Studies of luminescence traits and Judd-Ofelt analysis of Sm3+ activated oxyfluoride glasses. Opt. Mater. 2024, 147, 114579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnall, W.T.; Fields, P.R.; Rajnak, K. Electronic energy levels in the trivalent lanthanide aquo ions. I. Pr3+, Nd3+, Pm3+, Sm3+, Dy3+, Ho3+, Er3+, and Tm3+. J. Chem. Phys. 1968, 49, 4424–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Rai, S.B.; Rai, D.K. Optical properties of Sm3+ doped calibo glass with addition of lead oxide. Spectrochim. Acta A 2004, 60, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnakaram, Y.C.; Thirupathi Naidu, D.; Chakradhar, R.P.S. Spectral studies of Sm3+ and Dy3+ doped lithium cesium mixed alkali borate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 3914–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnakaram, Y.C.; Thirupathi Naidu, D.; Vijaya Kumar, A.; Gopal, N.O. Influence of mixed alkalies on absorption and emission properties of Sm3+ ions in borate glasses. Phys. B 2005, 358, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalaiah, B.C.; Vijaya Kumar, M.V.; Rama Gopal, K. Fluorescence properties and energy transfer mechanism of Sm3+ ion in lead telluroborate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2011, 33, 1643–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deopa, N.; Rao, A.S. Spectroscopic studies of Sm3+ ions activated lithium lead alumino borate glasses for visible luminescent device applications. Opt. Mater. 2017, 72, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan Babu, A.; Jamalaiah, B.C.; Sasikala, T.; Saleem, S.A.; Moorthy, L.R. Absorption and emission spectral studies of Sm3+-doped lead tungstate tellurite glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 4743–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.; Fernandes, R.G.; de Camargo, A.S.S.; Hernandes, A.C.; Buchner, S.; Jacinto, C.; Balzaretti, N.M. Visible–NIR emission and structural properties of Sm3+ doped heavy-metal oxide glass with composition B2O3–PbO–Bi2O3–GeO2. J. Lumin. 2016, 171, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena, R.; Venkatramu, V.; Babu, P.; Jayasankar, C.K. Fluorescence spectroscopy of Sm3+ ions in P2O5–PbO–Nb2O5 glasses. Phys. B 2008, 403, 3527–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhasini, T.; Suresh Kumar, J.; Sasikala, T.; Jang, K.; Lee, H.S.; Jayasimhadri, M.; Jeong, J.H.; Yi, S.S.; Moorthy, L.R. Absorption and fluorescence properties of Sm3+ ions in fluoride containing phosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2009, 31, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.S.; Jayasankar, C.K. Spectroscopic and radiative properties of Sm3+-doped K–Mg–Al phosphate glasses. Opt. Commum. 2013, 286, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Kesavulu, C.R.; Jayasankar, C.K. Spectroscopic properties of Sm3+ ions in lead fluorophosphate glasses. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 2802–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.-S.; Vijaya, N.; Kesavulu, C.R.; Jayasankar, C.K. Structural and luminescence properties of Sm3+ ions in zinc fluorophosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Basavapoornima, C.; Jayasankar, C.K. Spectroscopic and photoluminescence properties of Sm3+ ions in Pb–K–Al–Na phosphate glasses for efficient visible lasers. J. Lumin. 2014, 153, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srihari, T.; Jayasankar, C.K. Spectral investigations of Sm3+-doped niobium phosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2017, 66, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoudhi, D.; Bouzidi, C.; Matei, E.; Secu, M.; Galca, A.C. Optical characterization of Sm3+ doped phosphate glasses for potential orange laser applications. J. Lumin. 2024, 265, 120204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Sharma, Y.K.; Pal, S.; Bind, U.C.; Huang, S.-C.; Chung, S.-L. Structural, optical and physical analysis of B2O3–SiO2–Na2O–PbO–ZnO glass with Sm3+ ions for reddish–orange laser emission. J. Lumin. 2017, 192, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, M.; Rao, K.V.; Rao, J.L.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Spectroscopic and laser properties of Sm3+ doped different phosphate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 476, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaraiah, S.; Reddy Prasad, V.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Structural and luminescence properties of Sm3+-doped bismuth phosphate glass for orange-red photonic applications. Luminescence 2018, 33, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana, G.; Nageswara Rao, C.; Vasudeva Rao, P.; Al-Musawi, M.J.S.; Samatha, K.; Dhar, G.G. Luminescent properties of Sm3+ doped metal fluoro phosphate glasses. Optik 2020, 208, 163909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczyk, M.; Starynowicz, P.; Lisiecki, R.; Ryba-Romanowski, W. Synthesis, optical spectra and radiative properties of Sm2O3:PbO:P2O5 glass materials. Opt. Mater. 2008, 30, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indhrapriyadarshini, A.; Naseer, K.A.; Komal Poojha, M.K.; Kebaili, I.; Marimuthu, K. Spectroscopic assessments on Sm3+ ions doped phospho-borate glasses mixed with fluoride modifiers for the applications of reddish-orange visible light. Spectrochim. Acta A 2025, 324, 124963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poolprasroed, S.; Pengpat, K.; Srichumpong, T.; Deechob, S.; Eitssayeam, S.; Intatha, U.; Kamnoy, M.; Chattrapiban, N.; Kantarak, E. Low-cost samarium-doped mixed alkali borosilicate glasses: Structural, thermal, and optical characterization for luminescent applications in art and decoration. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1043, 184167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).