Boosting Caloric Performances of Ni-Co-Mn-Ti Shape Memory Alloy for Multi-Scenario Refrigeration by Spark Plasma Sintering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
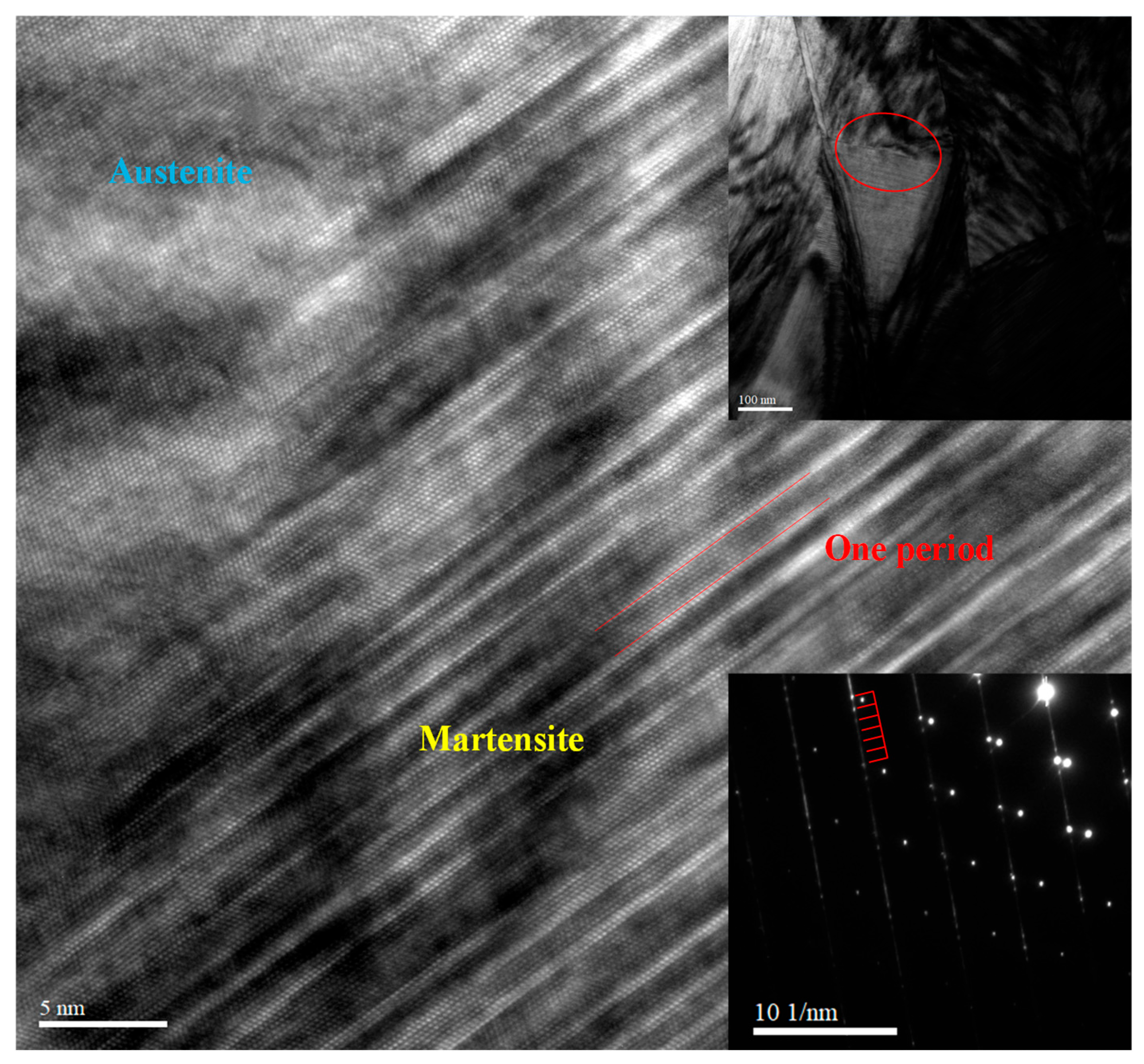
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z. Room-Temperature Colossal Elastocaloric effects in three-dimensional graphene architectures: An atomistic study. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2203866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchenko, E.Y.; Yanushonite, E.I.; Eftifeeva, A.S.; Tokhmetova, A.B.; Kurlevskaya, I.D.; Tagiltsev, A.I.; Surikov, N.S.; Timofeeva, E.E.; Chumlyakov, Y.I. Elastocaloric Effect in aged single crystals of Ni54Fe19Ga27 ferromagnetic shape memory alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Nie, Z.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Large elastocaloric effect in a polycrystalline Ni45.7Co4.2Mn37.3Sb12.8 alloy with low transformation strain. Scr. Mater. 2019, 162, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnot, E.; Romero, R.; Mañosa, L.; Vives, E.; Planes, A. Elastocaloric Effect Associated with the Martensitic Transition in Shape-Memory Alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 125901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Zuo, L. Effect of burst-type martensitic transformation on superelastic and elastocaloric properties in a <116> oriented Cu70.5Al17.5Mn12 single crystal. Scr. Mater. 2024, 246, 116092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bez, H.N.; Pathak, A.K.; Biswas, A.; Zarkevich, N.; Balema, V.; Mudryk, Y.; Johnson, D.D.; Pecharsky, V.K. Giant enhancement of the magnetocaloric response in Ni–Co–Mn–Ti by rapid solidification. Acta Mater. 2019, 173, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Cong, D.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Manipulation of thermal hysteresis and magnetocaloric effect in the Ni-Co-Mn-In alloys through lattice contraction: Effect of Ge substitution for In. Acta Mater. 2023, 246, 118694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, Y.; Goto, M.; Tan, Z.; Fujita, A.; Saito, T.; Kamiyama, T.; Chen, W.; Chuang, Y.; Sheu, H.; Kan, D.; et al. Colossal Barocaloric Effect by Large Latent Heat Produced by First-Order Intersite-Charge-Transfer Transition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischenko, A.S.; Zhang, Q.; Scott, J.F.; Whatmore, R.W.; Mathur, N.D. Giant electrocaloric effect in thin-film PbZr0.95Ti0.05O3. Science 2006, 311, 1270–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.; Luo, F.; Zhu, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Ma, G.; Chen, F.; et al. Enhanced elastocaloric effect and mechanical properties of Gd-doped Ni-Co-Mn-Ti-Gd metamagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.-Y.; Guo, Y.-X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Jia, N.; Yan, H.-L.; Zuo, L. Large low-stress elastocaloric effect in Ti-Zr-Cr-Sn. Scr. Mater. 2024, 244, 116002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jo, M.-G.; Park, J.-W.; Park, H.-K.; Han, H.N. Elastocaloric effect in polycrystalline Ni50Ti45.3V4.7 shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 2018, 144, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, B.; Wang, D.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; et al. Influence of austenite ferromagnetism on the elastocaloric effect in a Ni44.9Co4.9Mn36.9In13.3 metamagnetic shape memory alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 083903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Zuo, L. Formation of a-b twin induced by tension in Ni-Mn-Ga magnetic shape memory alloys. Mater. Charact. 2024, 209, 113710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Liu, E.K.; Chen, J.H.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.D.; Luo, H.Z.; Xi, X.K.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, W.H.; Wu, G.H. Realization of multifunctional shape-memory ferromagnets in all-d-metal Heusler phases. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 022406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Bai, J.; Sun, S.; Gu, J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Extraordinary mechanical properties and successive caloric effects with ultrahigh cyclic stability in directionally solidified Ni36.6Co12.8Mn34.7Ti15.9 alloy. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 29, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, A. Giant caloric effect of low-hysteresis metamagnetic shape memory alloys with exceptional cyclic functionality. Acta Mater. 2017, 133, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, H. Compressive response of a single crystalline CoNiAl shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 2004, 51, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Morley, N.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Ni-Co-Mn-Ti-B high performance multiferroic phase transformation material: Simultaneous modulation of mechanical properties and successive caloric effects by B doping. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 36, 101183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Zuo, L. Orientation dependence of elastocaloric effect in a Cu71.3Al17.5Mn11.2 single crystal. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 969, 172392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, S.; Yang, B.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, D. Enhancing the elastocaloric effect and thermal cycling stability in dendritic-like Ni50Mn31.6Ti18.4 single crystal. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 936, 168310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Colossal elastocaloric effect in a A oriented Ni49Mn33Ti18 polycrystalline alloy. Scr. Mater. 2023, 234, 115584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Ultrahigh cyclic stability and giant elastocaloric effect in directionally solidified (Ni50Mn28Fe2.5Ti19.5)99.4B0.6 alloy. Scr. Mater. 2023, 229, 115353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; et al. Achieving a broad refrigeration temperature region through the combination of successive caloric effects in a multiferroic Ni50Mn35In15 alloy. Acta Mater. 2020, 192, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, W.; Wen, H.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lavernia, E.J. Microstructure and strengthening mechanisms in an FCC structured single-phase nanocrystalline Co25Ni25Fe25Al7.5Cu17.5 high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 107, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Sui, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Cai, W. Grain size effect on martensitic transformation, mechanical and magnetic properties of Ni–Mn–Ga alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 514, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Ai, Z.; Yang, B.; Hao, X.; Li, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Simultaneously achieved good mechanical properties and large magnetocaloric effect in spark plasma sintered Ni-Mn-In alloys. Intermetallics 2020, 124, 106868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guan, Z.; Tang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zuo, L. Excellent mechanical properties and giant room-temperature elastocaloric effect in spark plasma sintered Ni-Co-Mn-Ti shape memory alloy. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2025, 696, 416611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Wu, H.; Jiang, C.; Xu, H. Microstructure and the correlated martensitic transformation of melt spinning Ni50Mn29Ga21−xTbx (x = 0–1) ribbons. Acta Mater. 2016, 104, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, P. Enhanced elastocaloric effect and cycle stability in B and Cu co-doping Ni-Mn-In polycrystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 033901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.-L.; Wang, L.-D.; Liu, H.-X.; Huang, X.-M.; Jia, N.; Li, Z.-B.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; et al. Giant elastocaloric effect and exceptional mechanical properties in an all-d-metal Ni–Mn–Ti alloy: Experimental and ab-initio studies. Mater. Des. 2019, 184, 108180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Lu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zuo, L. Enhanced elastocaloric effect and refrigeration properties in a Si-doped Ni-Mn-In shape memory alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 117, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, D.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Enhanced cyclability of elastocaloric effect in a directionally solidified Ni55Mn18Ga26Ti1 alloy with low hysteresis. Scr. Mater. 2020, 189, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Zou, N.; Yan, H.; Yang, B.; Zuo, L. Crystallography of stress-induced martensitic transformation and giant elastocaloric effect in a A textured Ni27Cu21Mn46Sn6 shape memory alloy. Acta Mater. 2024, 263, 119546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Cong, D.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Highly sensitive elastocaloric response in a directionally solidified Ni50Mn33In15.5Cu1.5 alloy with strong A preferred orientation. Intermetallics 2022, 140, 107379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-M.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, H.-L.; Jia, N.; Tang, S.; Bai, J.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; et al. A multielement alloying strategy to improve elastocaloric and mechanical properties in Ni–Mn-based alloys via copper and boron. Scr. Mater. 2020, 185, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Zuo, L. Giant elastocaloric effect and improved cyclic stability in a directionally solidified (Ni50Mn31Ti19)99B1 alloy. Materials 2024, 17, 4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zuo, L.; Esling, C. Martensitic and magnetic transformation in Ni–Mn–Ga–Co ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 473, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Sun, W.; Zhao, D.; Liu, J. Influence of Cr on microstructure and elastocaloric effect in Ni–Mn–In–Co–Cr polycrystalline alloys. Phys. Lett. A 2018, 382, 2876–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Tai, Z.; Zhang, K.; Tian, X.; Cai, W. Simultaneous enhancement of magnetic and mechanical properties in Ni-Mn-Sn alloy by Fe doping. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep43387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhang, K.; Tan, C.; Guo, E. Influence of Doping Tb on the Mechanical Properties and Martensitic Transformation of Ni-Mn-Sn Magnetic Shape Memory Alloys. Crystals 2018, 8, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Zuo, L. Quasi-linear superelasticity and associated elastocaloric effect in boron-doped polycrystalline Ni-Mn-Ti alloys. Acta Mater. 2024, 281, 120411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Sun, W.; Shen, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, E.K.; Liu, J. Elastocaloric effect of all-d-metal Heusler NiMnTi(Co) magnetic shape memory alloys by digital image correlation and infrared thermography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 101903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Bi, X.; Xing, L.; Zhang, Q. Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Spark Plasma Sintering of Tantalum-Tungsten Alloy. Metals 2023, 13, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Liu, D.; Gu, J.; Jiang, X.; Liang, X.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Excellent mechanical properties and large magnetocaloric effect of spark plasma sintered Ni-Mn-In-Co alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 74, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Liu, Z.-X.; Tian, B.; Tong, Y.-X.; Chen, F.; Li, L. Microstructure, phase transformation and mechanical properties of NiMnGa particles/Cu composites fabricated by SPS. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 3291–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yuan, H.; Qiang, J. The Microstructure Evolution, Mechanical Properties and Densification Mechanism of TiAl-Based Alloys Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering. Metals 2017, 7, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Ren, D.C.; Tong, Y.X.; Chen, F.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F. Microstructure, phase transformation and mechanical property of Ni-Co-Mn-In alloy prepared by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Forum 2015, 815, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Sui, J.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Cai, W. Martensitic transformation, mechanical property and magnetic-field-induced strain of Ni–Mn–Ga alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 4081–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Nakai, M.; Niinomi, M.; Nakano, T. Influence of Sintering Temperature on Mechanical Properties of Ti-Nb-Zr-Fe Alloys Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 5719–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Cai, G. Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing Process Parameters on Properties and Fracture Behavior of Tungsten Alloy Powders and Sintered Bars. Materials 2022, 15, 8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.; Pickett, C.; Arrieta, E.; Murr, L.E.; Wicker, R.B.; Ahlfors, M.; Godfrey, D.; Medina, F. Effects of Postprocess Hot Isostatic Pressing Treatments on the Mechanical Performance of EBM Fabricated TI−6Al−2Sn−4Zr−2Mo. Materials 2020, 13, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Zuo, L. Giant elastocaloric effect covering a wide temperature region in a directionally solidified Ni50Mn30Ti20 alloy. Scr. Mater. 2023, 237, 115725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Wang, D.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Large elastocaloric effect driven by stress-induced two-step structural transformation in a directionally solidified Ni55Mn18Ga27 alloy. Scr. Mater. 2019, 163, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Yan, H.; Yang, B.; Zuo, L. Large elastocaloric effect covering a broad temperature window in a composition-graded Ni50Mn31.5Ti18.5 alloy prepared by magnetic field-assisted directional solidification. Acta Mater. 2024, 274, 120020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Lu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zuo, L. Enhanced elastocaloric effect and specific adiabatic temperature variation in Ni-Mn-In-Si-Cu shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 920, 165955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Bruno, N.; Chen, J.-H.; Karaman, I.; Ross, J.H.; Li, J. Giant elastocaloric effect in directionally solidified Ni–Mn–In magnetic shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 2015, 105, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Yang, B.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; et al. Giant elastocaloric effect in a Mn-rich Ni44Mn46Sn10 directionally solidified alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 023902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, D.; Xiong, W.; Planes, A.; Ren, Y.; Mañosa, L.; Cao, P.; Nie, Z.; Sun, X.; Yang, Z.; Hong, X.; et al. Colossal Elastocaloric Effect in Ferroelastic Ni-Mn-Ti Alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 255703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cong, D.; Sun, X.; Nie, Z.; Wang, Y. Enhanced cyclability of elastocaloric effect in boron-microalloyed Ni-Mn-In magnetic shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 127, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cong, D.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nie, Z.; Li, R.; Wang, Y. Ultrahigh cyclability of a large elastocaloric effect in multiferroic phase-transforming materials. Mater. Res. Lett. 2019, 7, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Du, Y. Combining magnetocaloric and elastocaloric effects to achieve a broad refrigeration temperature region in Ni43Mn41Co5Sn11 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 550, 169082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.J.; Xu, K.; Wei, S.X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, Z.; Jing, C. Barocaloric effect associated with magneto-structural transformation studied by an effectively indirect method for the Ni58.3Mn17.1Ga24.6 Heusler alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 2915–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wei, S.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, Z.; Jing, C. Enhanced barocaloric effect produced by hydrostatic pressure-induced martensitic transformation for Ni44.6Co5.5Mn35.5In14.4 Heusler alloy. Scr. Mater. 2018, 145, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Qi, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, B.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; et al. Low-pressure-induced large reversible barocaloric effect near room temperature in (MnNiGe)-(FeCoGe) alloys. Scr. Mater. 2021, 200, 113908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Hao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; et al. Barocaloric and magnetocaloric effects in isostructurally alloyed (MnCoGe)-(CuCoSn) systems. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 543, 168639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Bai, J.; Gu, J.; Guo, K.; Morley, N.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Extraordinary mechanical properties and room-temperature magnetocaloric effects in spark plasma sintered all-d-metal Ni-Co-Mn-Ti alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 976, 173406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, B.; Taubel, A.; Gottschall, T.; Pfeuffer, L.; Koch, D.; Staab, F.; Bruder, E.; Scheibel, F.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O. Giant magnetocaloric effect of Ni-Co-Mn-Ti all-d Heusler alloys in high magnetic fields. Acta Mater. 2025, 282, 120460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, R.; Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, J. Martensite transformation, mechanical properties and shape memory effects of Ni-Mn-In-Mg shape memory alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2018, 28, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
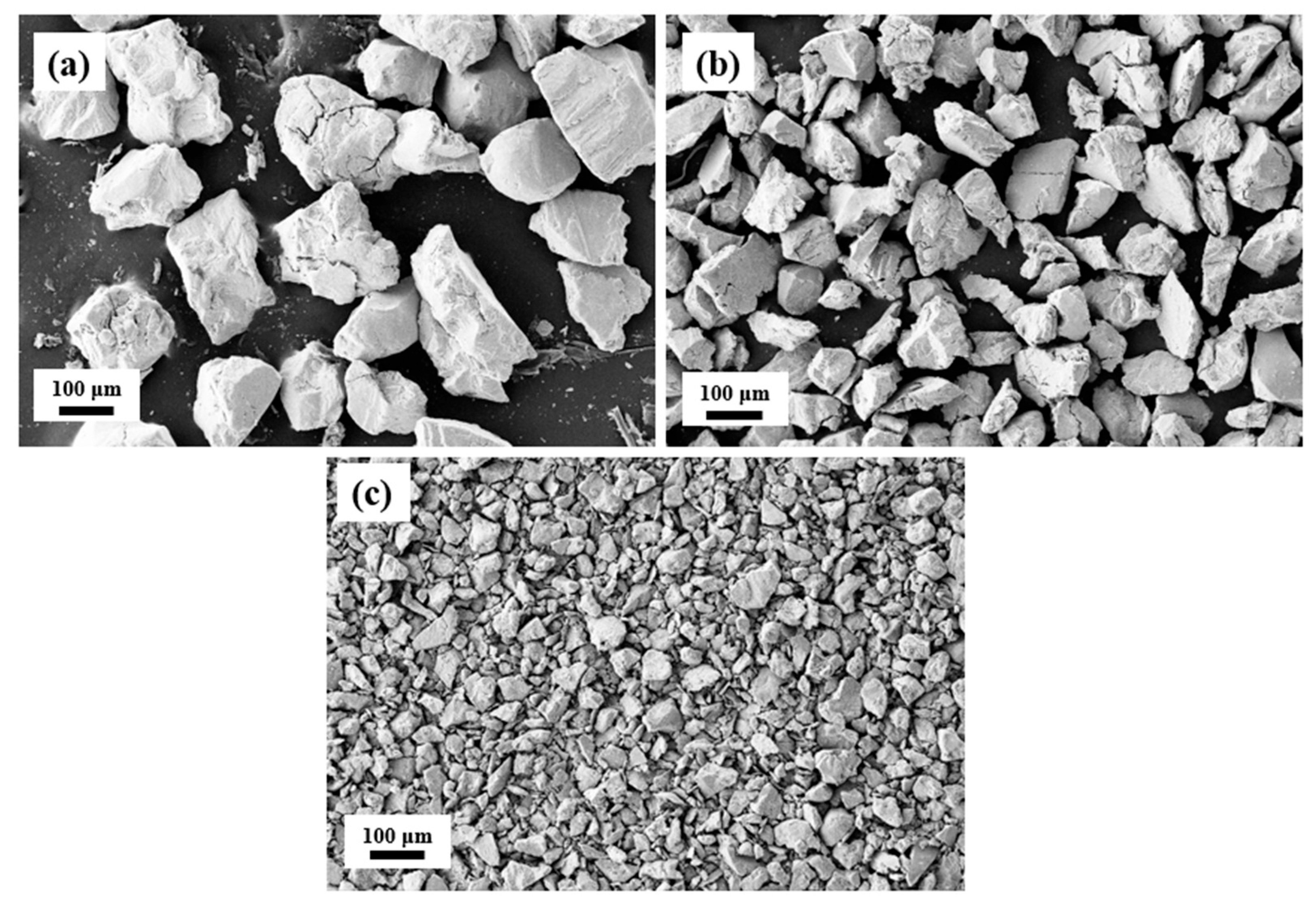
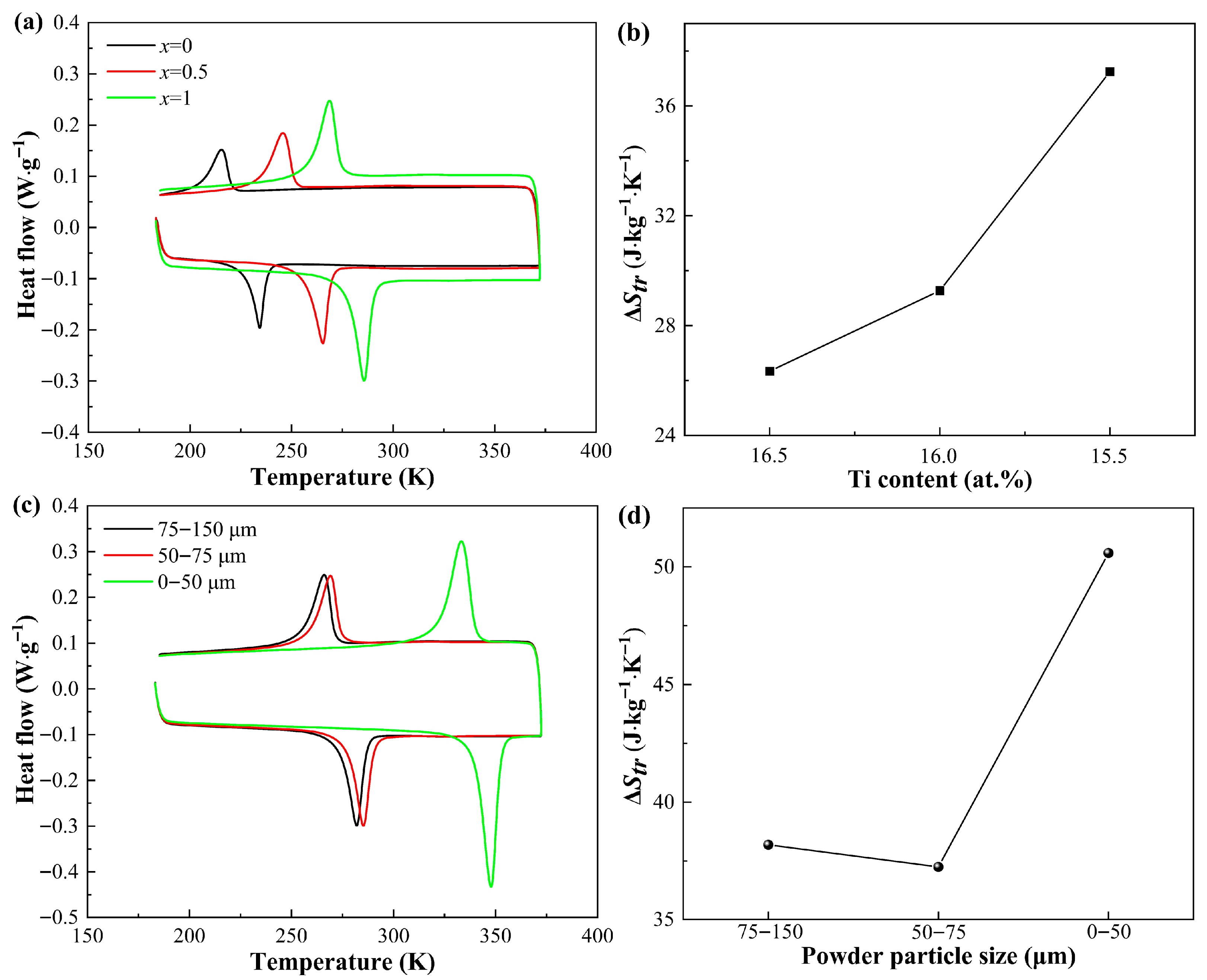



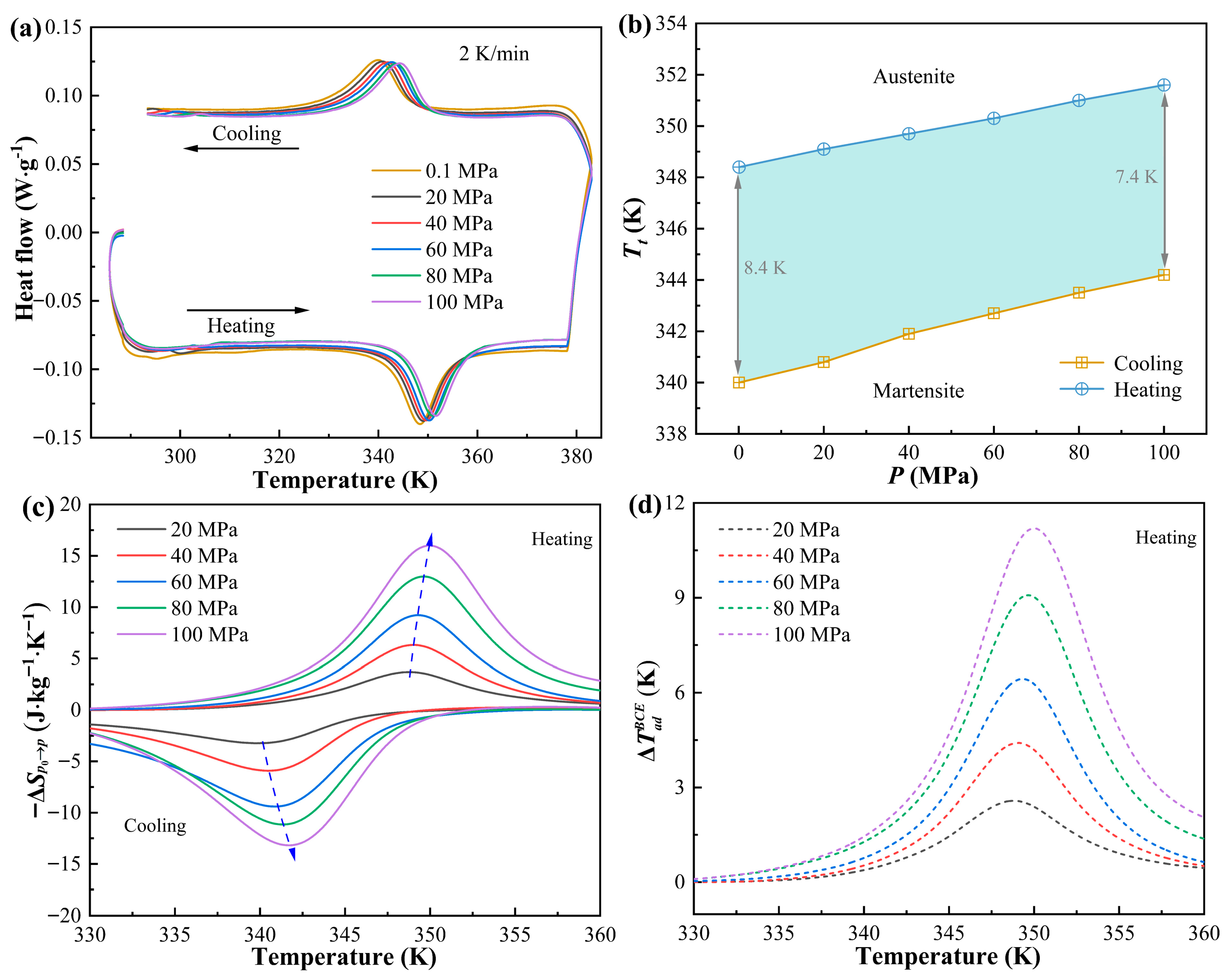
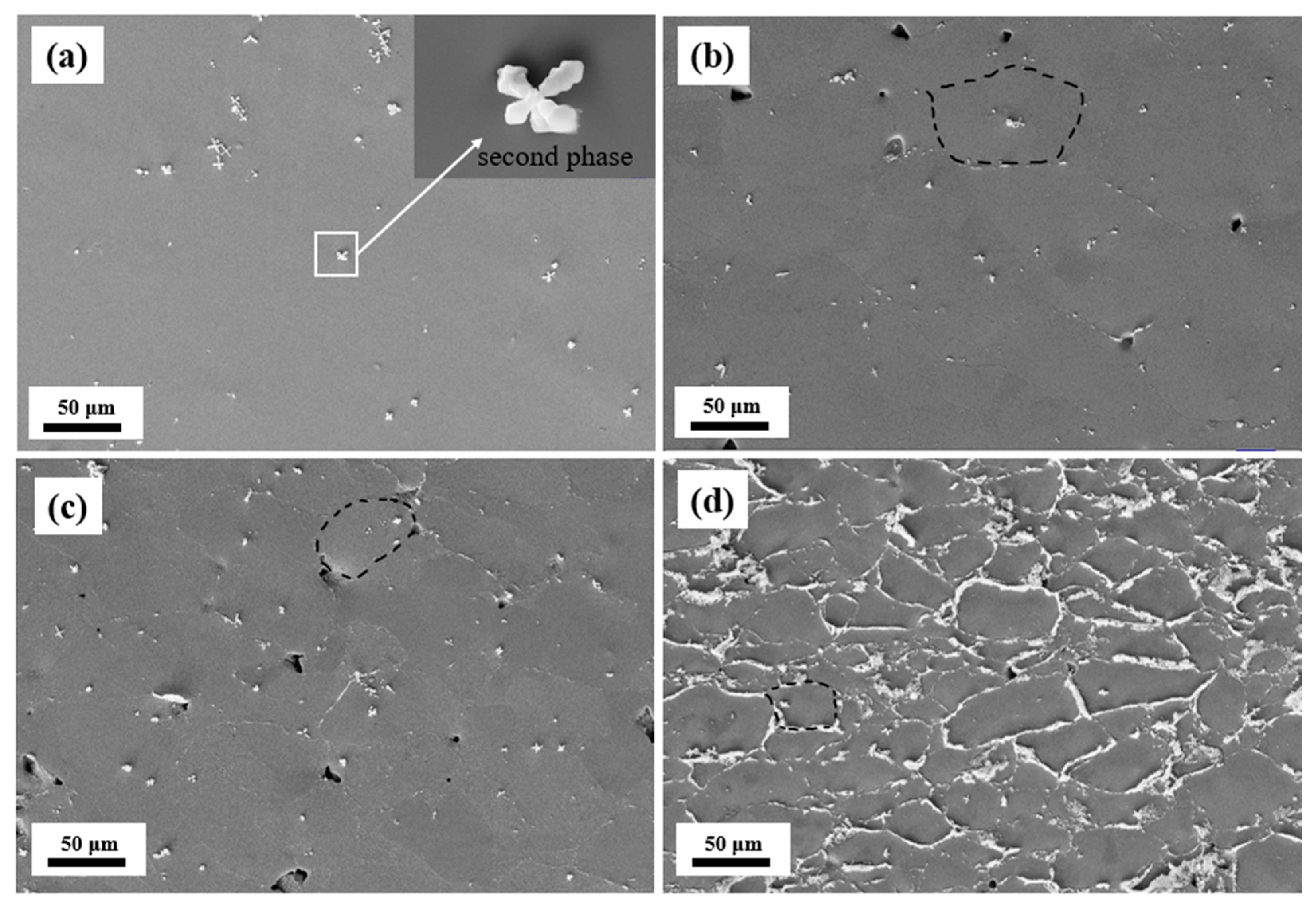
| Alloy | Sintering Method | Applied Pressure (MPa) | Sintering Time (Min) | Sintering Temperature (K) | Tensile/ Compressive Strength (MPa) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni37Co13Mn34.5Ti15.5 | SPS | 50 | 20 | 1223 | 2005 | This work |
| Ni50Mn34.7In15.3 | SPS | 50 | 15 | 1173 | 1800 | [27] |
| Ta–10 wt%W | SPS | 35 | 5 | 1873 | 693.41 | [44] |
| Ni43.75Mn37.5In12.5Co6.25 | SPS | 50 | 10 | 1073 | 1440 | [45] |
| 40% Ni49.8Mn28.5Ga21.7/Cu | SPS | 40 | 5 | 1073 | 865 | [46] |
| Ti-46.5Al-2.15Cr-1.90Nb | SPS | 50 | 7 | 1423 | 1820 | [47] |
| Ni45Co5Mn36.7In13.3 | SPS | 40 | 5 | 1073 | 1900 | [48] |
| Ni48.8Mn29.7Ga21.5 | SPS | 50 | 10 | 1173 | 1706 | [49] |
| Ti-15Nb-25Zr-8Fe | SPS | 50 | 10 | 1473 | 1920 | [50] |
| 93W-Ni-Fe | HIP | 140 | 240 | 1573 | 1582.8 | [51] |
| TI-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo | HIP | 103 | 120 | 1123 | 1048 | [52] |
| Materials | Maximum ΔTad | Conditions | Strain Rate | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni37Co13Mn34.5Ti15.5 | 34.2 K | loading | 2.8 × 10−1 | This work |
| DS-Ni45.7Co4.2Mn37.3Sb12.8 | 9.4 K | loading | 1.8 × 10−2 | [3] |
| DS-Ni49Mn33Ti18 | 33.6 K | loading | 1.7 | [22] |
| DS-Ni55Mn18Ga26Ti1 | 6.2 K | unloading | 4 × 10−2 | [33] |
| DS-(Ni50Mn31Ti19)99B1 | 17.8 K | loading | 2.2 × 10−2 | [37] |
| DS-Ni50Mn30Ti20 | 31.3 K | unloading | 2.8 | [53] |
| DS-Ni55Mn18Ga27 | 10.7 K | unloading | 2.0 × 10−1 | [54] |
| DS-Ni50Mn31.5Ti18.5 | 13.1 K | unloading | 1.7 | [55] |
| DS-Ni50Mn33In14Si1Cu2 | 18.2 K | unloading | 1.0 | [56] |
| DS-Ni48.4Mn34.8In16.8 | 4 K | unloading | 1.7 × 10−3 | [57] |
| DS-Ni44Mn46Sn10 | 18 K | unloading | 2.8 × 10−1 | [58] |
| C-Ni35.5Co13.5Mn35Ti14.9Gd0.1 | 13.5 K | loading | 2.8 × 10−2 | [10] |
| C-(Ni50Mn31.5Ti18.5)99.8B0.2 | 31.5 K | loading | 5.33 | [59] |
| C-(Ni51.5Mn33In15.5)99.7B0.3 | 6.6 K | loading | 4.2 × 10−2 | [60] |
| C-(Ni51Mn33In14Fe2)99.4B0.6 | 5.8 K | loading | 2.8 × 10−2 | [61] |
| C-Ni43Mn41Co5Sn11 | 9 K | unloading | 3.4 × 10−1 | [62] |
| Preparation Methods | Phase | Ni | Co | Mn | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arc-melted | Matrix | 37.2 | 13.2 | 34.1 | 15.5 |
| SPS (75–150 μm) | Second phase (on the grain boundary) | 25.2 | 9.0 | 25.6 | 40.2 |
| SPS (50–75 μm) | Second phase (on the grain boundary) | 25.0 | 8.8 | 24.2 | 42.0 |
| SPS (0–50 μm) | Second phase (on the grain boundary) | 27.2 | 9.1 | 25.7 | 38.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Guan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Lu, X. Boosting Caloric Performances of Ni-Co-Mn-Ti Shape Memory Alloy for Multi-Scenario Refrigeration by Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials 2025, 18, 4691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204691
Tang H, Guan Z, Wu Y, Li Z, Liu J, Lu X. Boosting Caloric Performances of Ni-Co-Mn-Ti Shape Memory Alloy for Multi-Scenario Refrigeration by Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials. 2025; 18(20):4691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204691
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Hongyuan, Ziqi Guan, Yanze Wu, Zhenzhuang Li, Jiaqi Liu, and Xing Lu. 2025. "Boosting Caloric Performances of Ni-Co-Mn-Ti Shape Memory Alloy for Multi-Scenario Refrigeration by Spark Plasma Sintering" Materials 18, no. 20: 4691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204691
APA StyleTang, H., Guan, Z., Wu, Y., Li, Z., Liu, J., & Lu, X. (2025). Boosting Caloric Performances of Ni-Co-Mn-Ti Shape Memory Alloy for Multi-Scenario Refrigeration by Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials, 18(20), 4691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204691






