The Influence of Reactive Ion Etching Chemistry on the Initial Resistance and Cycling Stability of Line-Type (Bridge) Phase-Change Memory Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
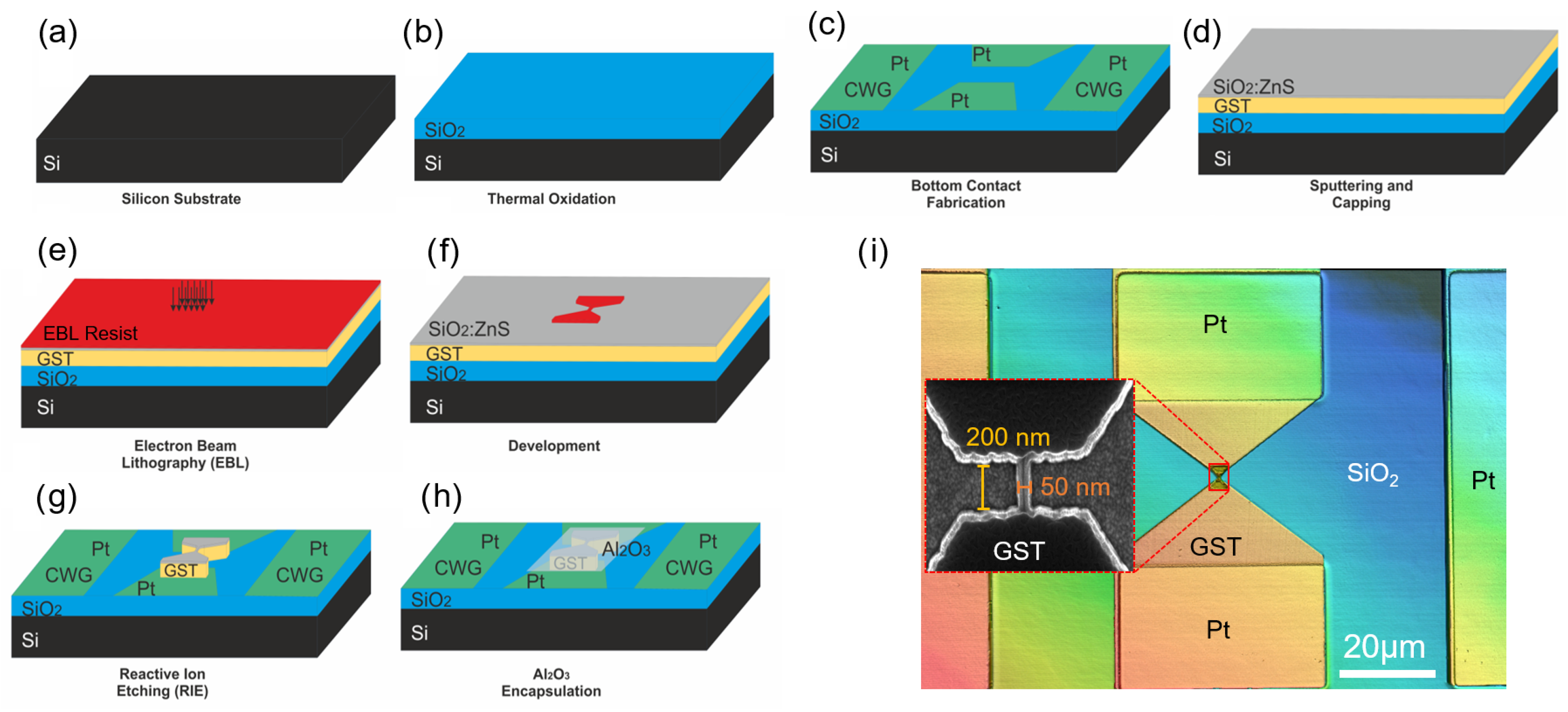
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. RIE Process
- CHF3:O2;
- H2:Ar;
- Ar.
2.3. Measurement Setup
2.4. Measurement Algorithm
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. CHF3:O2 Etching Process
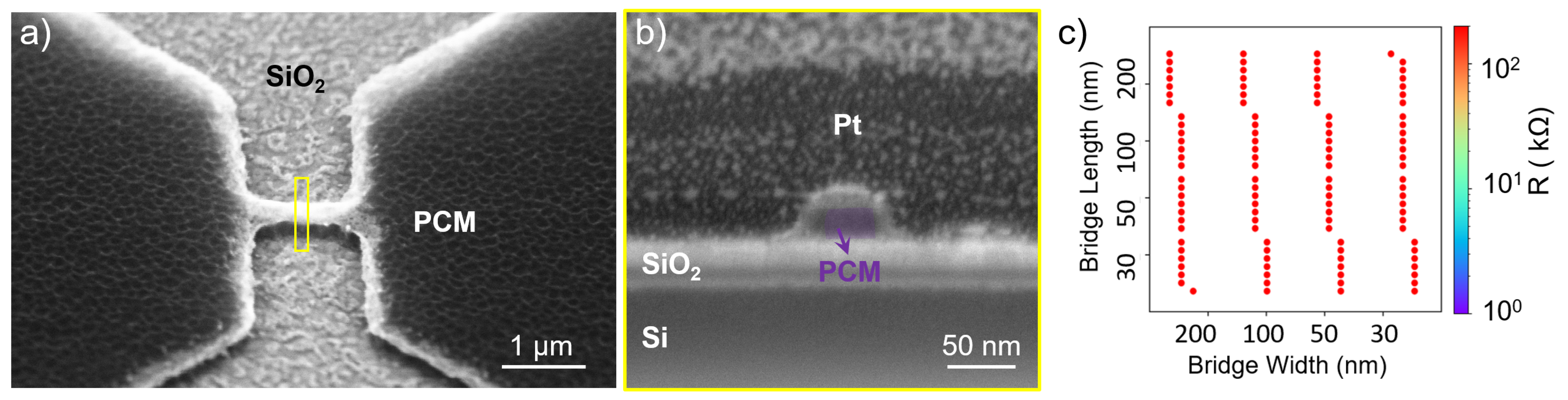
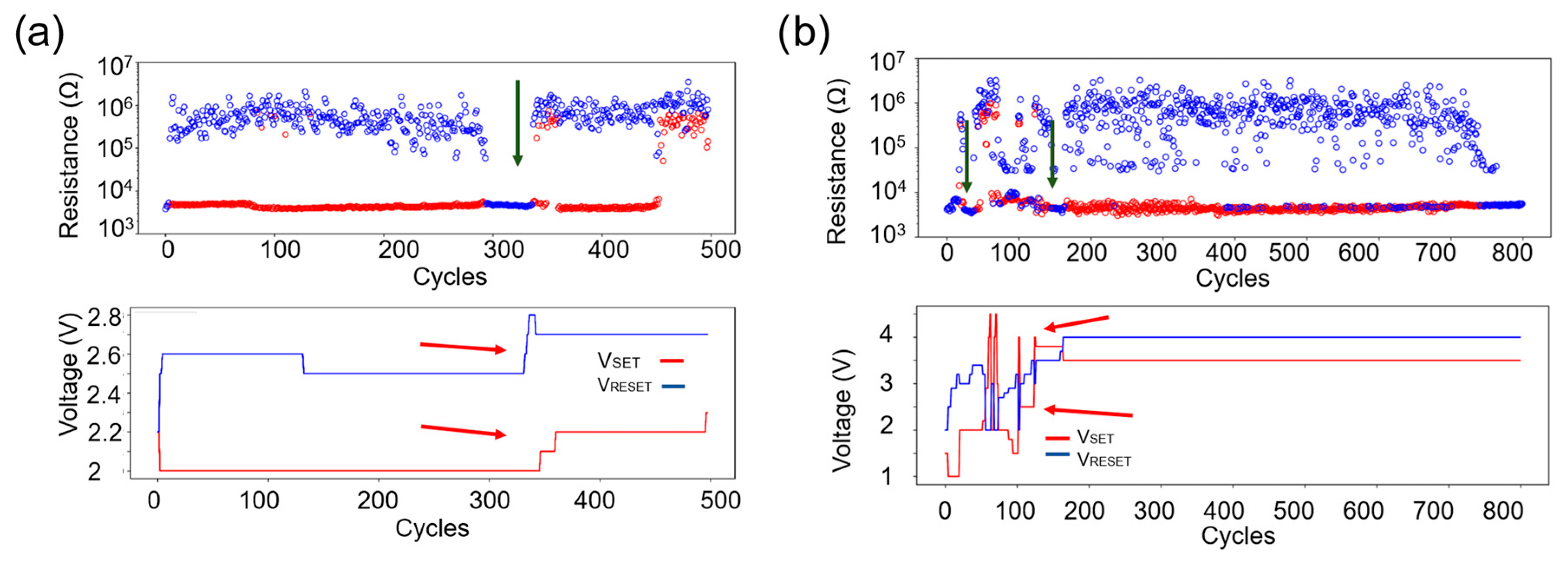
3.2. H2:Ar Etching Process
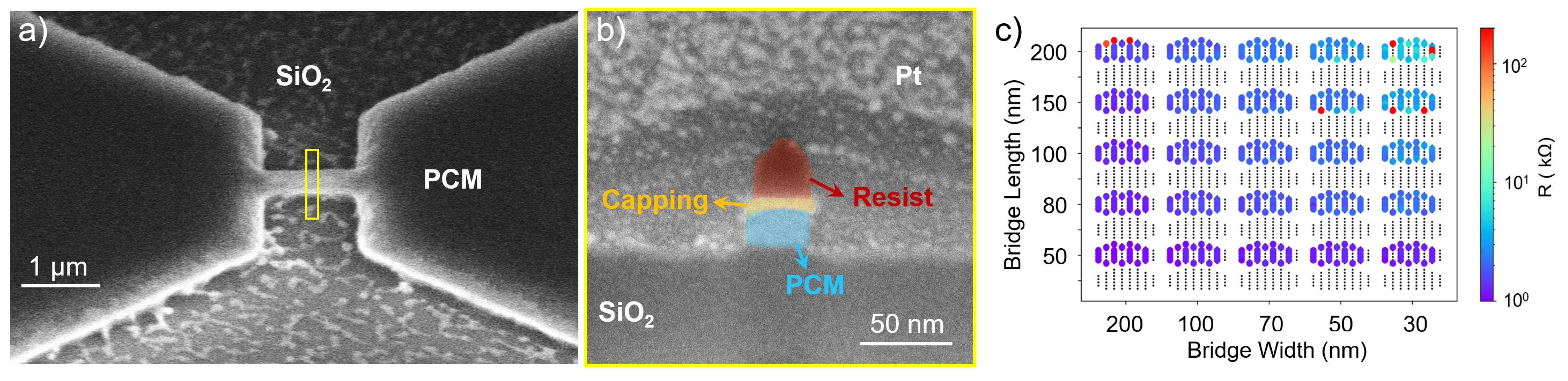

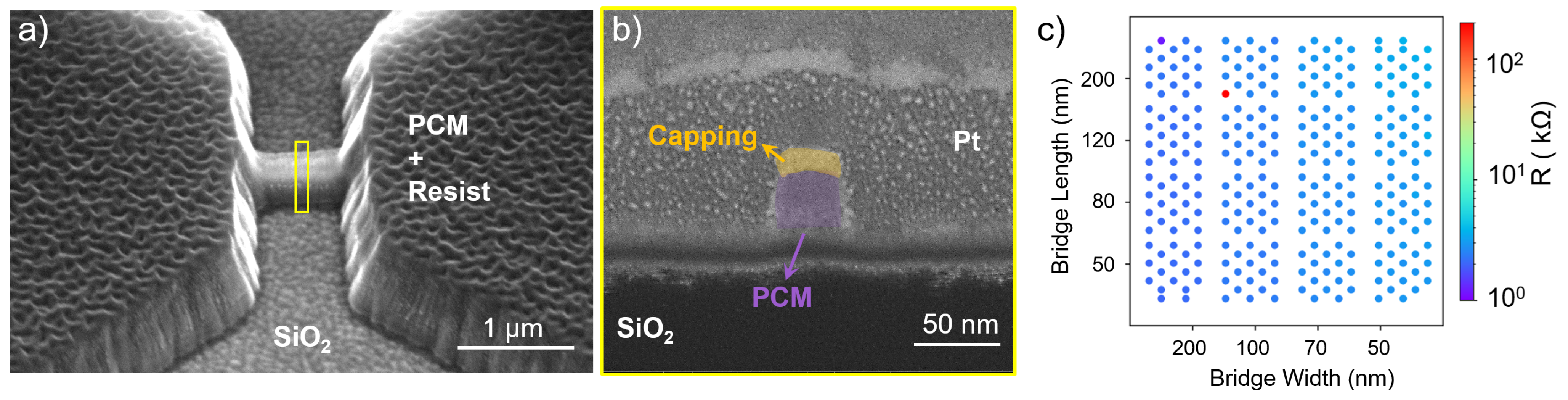
3.3. Ar Etching Process
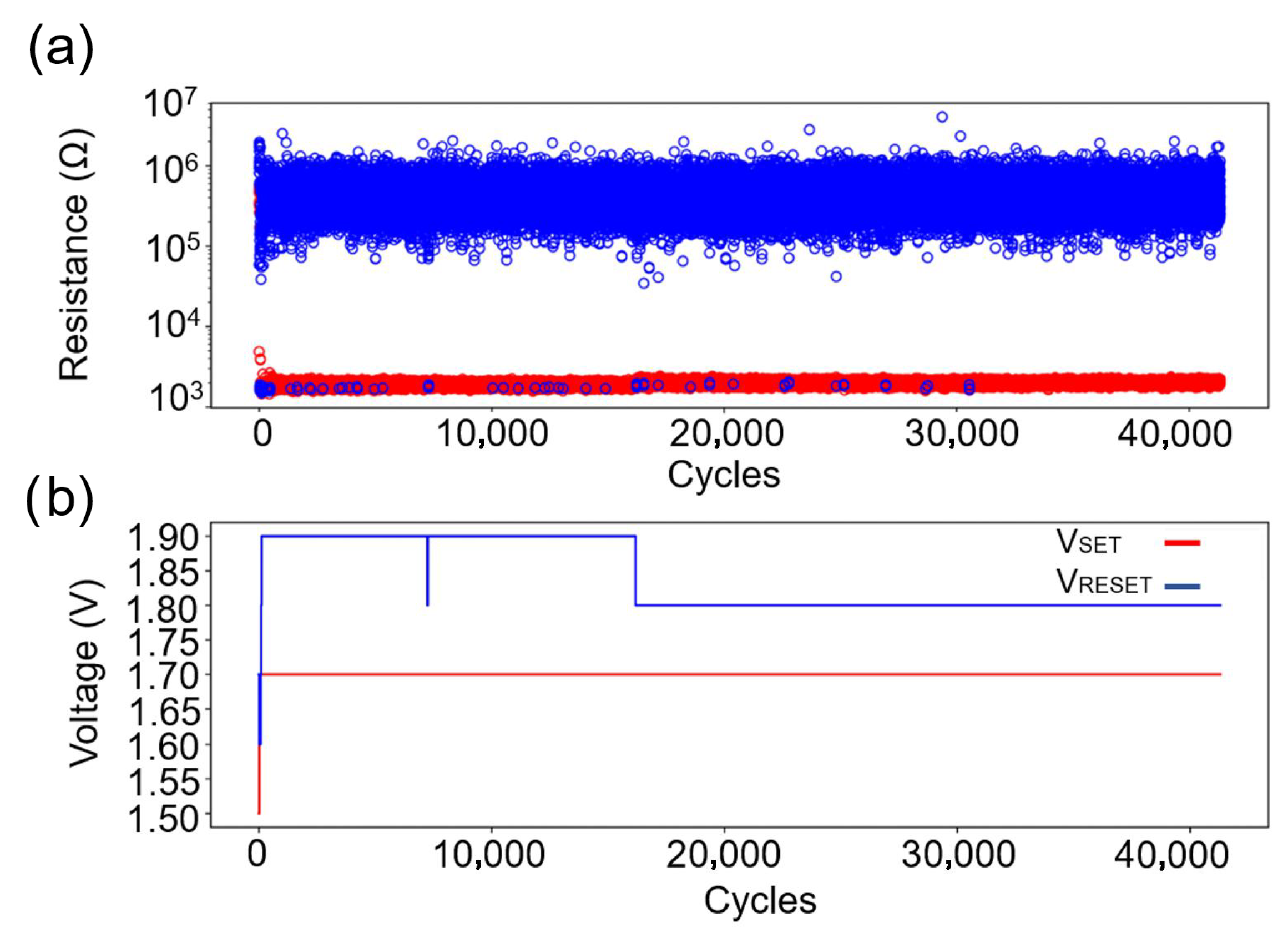
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCM | Phase-Change Memory |
| GST | GexSbyTez (Germanium–Antimony–Tellurium) |
| AIST | Ag4In3Sb67Te26 (Silver–Indium–Antimony–Tellurium) |
| RIE | Reactive Ion Etching |
| CPW | Coplanar Waveguide |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| ICP | Inductively Coupled Plasma |
| HRS | High-Resistance State |
| LRS | Low-Resistance State |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| sccm | Standard Cubic Centimeters per Minute |
| Pt | Platinum |
| Ti | Titanium |
| Al2O3 | Aluminum Oxide |
| ZnS:SiO2 | Zinc Sulfide–Silicon Dioxide Composite |
| SET | Operation that switches PCM to crystalline (low-resistance) state |
| RESET | Operation that switches PCM to amorphous (high-resistance) state |
| GS/s | Giga-Samples per Second |
| CMOS | Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor |
| CD | Critical Dimension |
| aixMATRIX | Automated Test System from aixACCT Systems |
| CASSINI | Python-Based Software Interface for Electrical Characterization |
References
- Ovshinsky, S.R. Reversible Electrical Switching Phenomena in Disordered Structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1968, 21, 1450–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobov, A.V.; Fons, P.; Frenkel, A.I.; Ankudinov, A.L.; Tominaga, J.; Uruga, T. Understanding the phase-change mechanism of rewritable optical media. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S. Current status of the phase change memory and its future. In Proceedings of the Technical Digest/IEDM, IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting 2003, Washington, DC, USA, 8–10 December 2003; pp. 10.1.1–10.1.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, T.N.; Wong, H.S.P. The End of Moore’s Law: A New Beginning for Information Technology. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2017, 19, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.S. What’s Next? [The end of Moore’s law]. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2017, 19, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwa, R.; Karthikeyan, R.; Rohith, R.; Sabaresh, A. Current Research and Future Prospects of Neuromorphic Computing in Artificial Intelligence. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 912, 062029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.; Xiao, S.; Zhu, C.; Han, W.; Zhang, Q. An overview of brain-like computing: Architecture, applications, and future trends. Front. Neurorobot. 2022, 16, 1041108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, D.; Wong, H.S.P. In-memory computing with resistive switching devices. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ambrosi, E.; Bricalli, A.; Ielmini, D. Logic Computing with Stateful Neural Networks of Resistive Switches. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1802554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankhorst, M.H.R.; Ketelaars, B.W.S.M.M.; Wolters, R.A.M. Low-cost and nanoscale non-volatile memory concept for future silicon chips. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gallo, M.; Sebastian, A. An overview of phase-change memory device physics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 213002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Sarangan, A.; Agha, I. A Review of Germanium-Antimony-Telluride Phase Change Materials for Non-Volatile Memories and Optical Modulators. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, H.; Harigaya, M.; Nonoyama, O.; Kageyama, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Yamada, K.; Hiroshi Deguchi, H.D.; Yukio Ide, Y.I. Completely Erasable Phase Change Optical Disc II: Application of Ag-In-Sb-Te Mixed-Phase System for Rewritable Compact Disc Compatible with CD-Velocity and Double CD-Velocity. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 32, 5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoux, S.; Wuttig, M. Phase Change Materials: Science and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, A.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, G.; Grethe, T. Recent developments in phase-change memory. Appl. Res. 2022, 1, e202200024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.S.; Shi, L.P.; Zhao, R.; Tan, P.K.; Lim, K.G.; Li, J.M.; Chong, T.C. Temperature Dependence of Phase Change Random Access Memory Cell. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wu, L.; Rao, F.; Song, Z.; Ren, K.; Ji, X.; Song, S.; Yao, D.; Feng, S. Uniform Ti-doped Sb2Te3 materials for high-speed phase change memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 053119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Xiao, Y.; Guo, X. Artificial Neural Networks Based on Memristive Devices: From Device to System. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padberg, H.; Espiari, A.; Schnieders, K.; Kiehn, A.; Jalil, A.R.; Waser, R.; Menzel, S.; Wiefels, S. Automated Endurance Characterization of Phase Change Memory. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 71214–71222, Early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoux, S.; Burr, G.W.; Breitwisch, M.J.; Rettner, C.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Shelby, R.M.; Salinga, M.; Krebs, D.; Chen, S.H.; Lung, H.L.; et al. Phase-change random access memory: A scalable technology. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2008, 52, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, G.W.; Breitwisch, M.J.; Franceschini, M.; Garetto, D.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Jackson, B.; Kurdi, B.; Lam, C.; Lastras, L.A.; Padilla, A.; et al. Phase change memory technology. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Nanotechnol. Microelectron. Mater. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2010, 28, 223–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Rettner, C.T.; Raoux, S.; Burr, G.W.; Chen, S.H.; Shelby, R.M.; Salinga, M.; Risk, W.P.; Happ, T.D.; McClelland, G.M.; et al. Ultra-Thin Phase-Change Bridge Memory Device Using GeSb. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–13 December 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, B.; Song, Z.; Feng, S.; Chen, B. Reactive-ion etching of Sn-doped Ge2Sb2Te5 in CHF3/O2 plasma for non-volatile phase-change memory device. Thin Solid Film. 2008, 516, 7871–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q.; Yao, D.; Gao, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Song, S.; Guo, X.; Zheng, H.; et al. CHF3/O2-Based Plasma Reactive Ion Etching of GeTe for Nonvolatile Phase Change Memory. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2016, 29, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Z.; Zhi-Tang, S.; Bo, L.; Song-Lin, F.; Bomy, C. Reactive Ion Etching as Cleaning Method Post Chemical Mechanical Polishing for Phase Change Memory Device. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2008, 25, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; Song, S.; Yin, W.; Yao, D.; et al. Etching characteristics of phase change material GeTe in inductively coupled BCl3/Ar plasma for phase change memory. Microelectron. Eng. 2016, 161, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.R.; Chang, S.J.; Su, Y.K.; Lan, W.H.; Lin, A.C.H.; Chang, H. Reactive Ion Etching of ZnSe, ZnSSe, ZnCdSe and ZnMgSSe by H2/Ar and CH4/H2/Ar. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 39, 3308–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politano, G.G.; Cazzanelli, E.; Versace, C.; Vena, C.; De Santo, M.P.; Castriota, M.; Ciuchi, F.; Bartolino, R. Graphene oxide on magnetron sputtered silver thin films for SERS and metamaterial applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiefels, S.; Liu, X.; Schnieders, K.; Schumacher, M.; Waser, R.; Nielen, L. Advanced Electrical Characterization of Memristive Arrays for Neuromorphic Applications. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Metrology for eXtended Reality, Artificial Intelligence and Neural Engineering (MetroXRAINE), Milano, Italy, 25–27 October 2023; pp. 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, A.; Burr, G.W.; Rettner, C.T.; Topuria, T.; Rice, P.M.; Jackson, B.; Virwani, K.; Kellock, A.J.; Dupouy, D.; Debunne, A.; et al. Voltage polarity effects in Ge2Sb2Te5-based phase change memory devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 054501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttig, M.; Yamada, N. Phase-change materials for rewriteable data storage. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.L. Effects of Plasma Etching on GeSbTe Compositional Control. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espiari, A.; Padberg, H.; Kiehn, A.; Schnieders, K.; Zhang, J.; Mussler, G.; Wiefels, S.; Jalil, A.R.; Grützmacher, D. The Influence of Reactive Ion Etching Chemistry on the Initial Resistance and Cycling Stability of Line-Type (Bridge) Phase-Change Memory Devices. Materials 2025, 18, 4681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204681
Espiari A, Padberg H, Kiehn A, Schnieders K, Zhang J, Mussler G, Wiefels S, Jalil AR, Grützmacher D. The Influence of Reactive Ion Etching Chemistry on the Initial Resistance and Cycling Stability of Line-Type (Bridge) Phase-Change Memory Devices. Materials. 2025; 18(20):4681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204681
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspiari, Abbas, Henriette Padberg, Alexander Kiehn, Kristoffer Schnieders, Jiayuan Zhang, Gregor Mussler, Stefan Wiefels, Abdur Rehman Jalil, and Detlev Grützmacher. 2025. "The Influence of Reactive Ion Etching Chemistry on the Initial Resistance and Cycling Stability of Line-Type (Bridge) Phase-Change Memory Devices" Materials 18, no. 20: 4681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204681
APA StyleEspiari, A., Padberg, H., Kiehn, A., Schnieders, K., Zhang, J., Mussler, G., Wiefels, S., Jalil, A. R., & Grützmacher, D. (2025). The Influence of Reactive Ion Etching Chemistry on the Initial Resistance and Cycling Stability of Line-Type (Bridge) Phase-Change Memory Devices. Materials, 18(20), 4681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204681






