Indium-Doped ZnO Thin Films Obtained Using Spray Pyrolysis for Position-Sensitive Photodetection
Abstract
1. Introduction
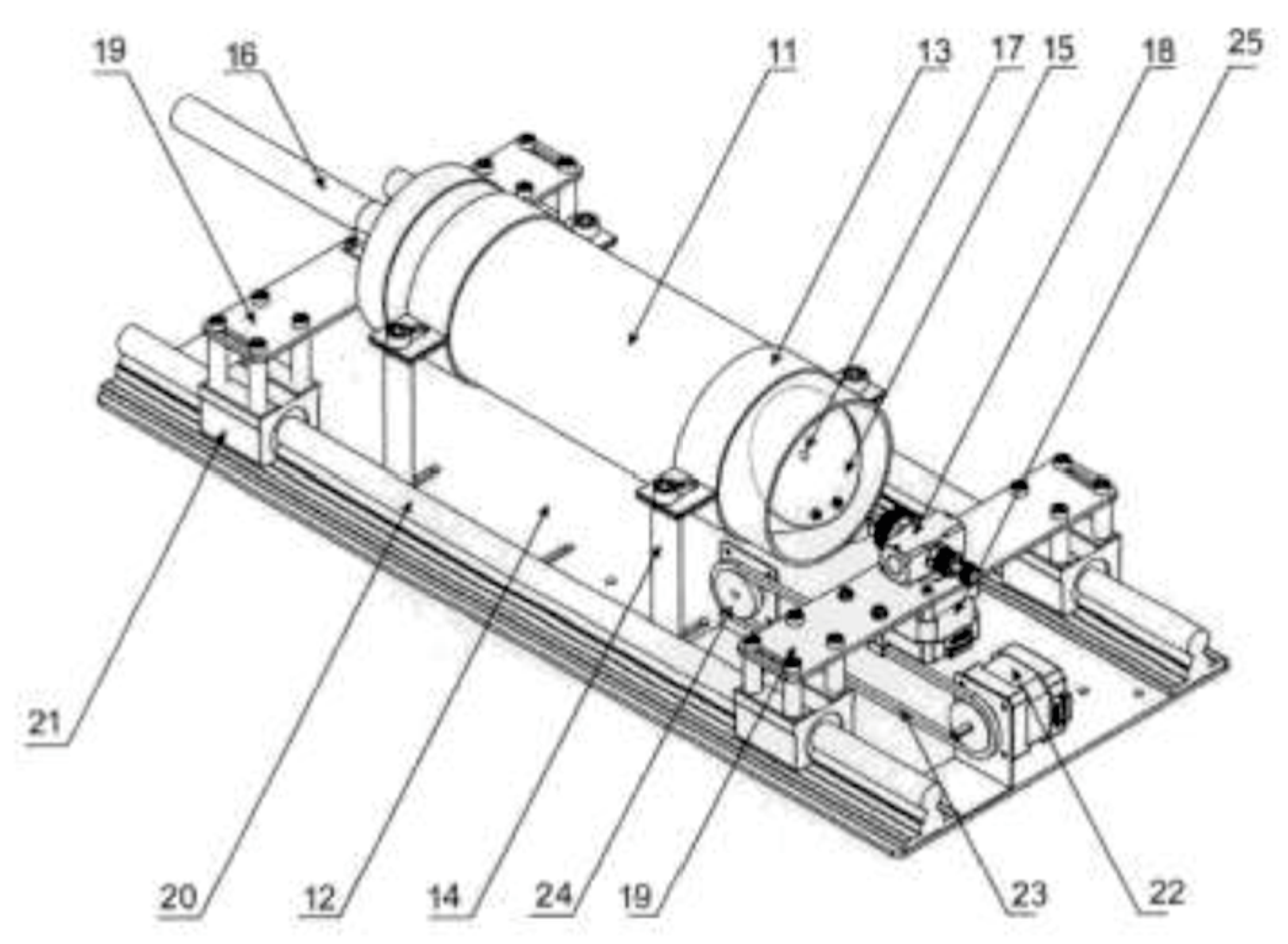
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Structural Studies
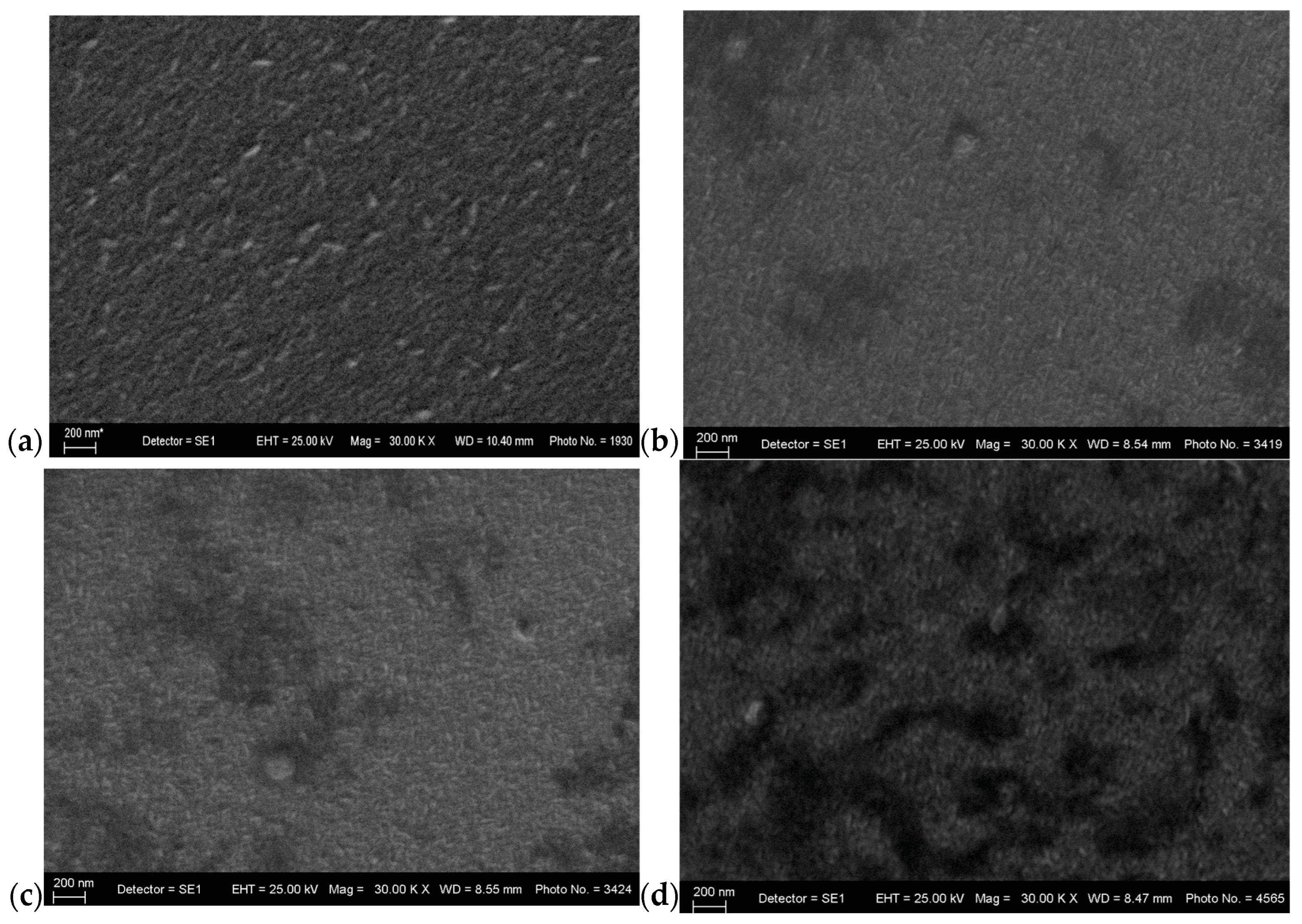
3.2. Morphological Studies
3.3. Optical Studies
3.3.1. Optical Transmittance
3.3.2. Films’ Thickness
3.3.3. Band Gap Analysis
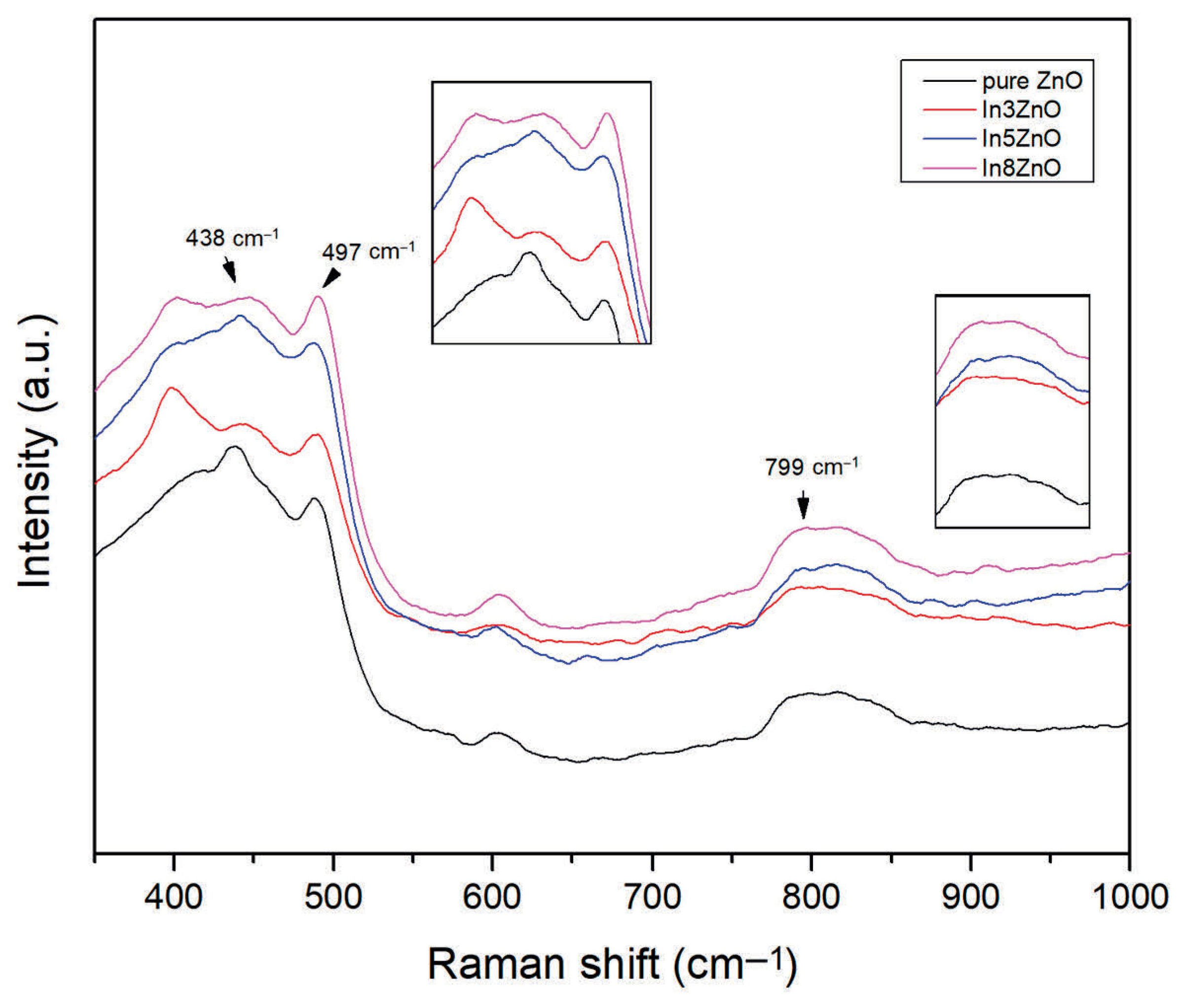
3.3.4. Raman Analysis
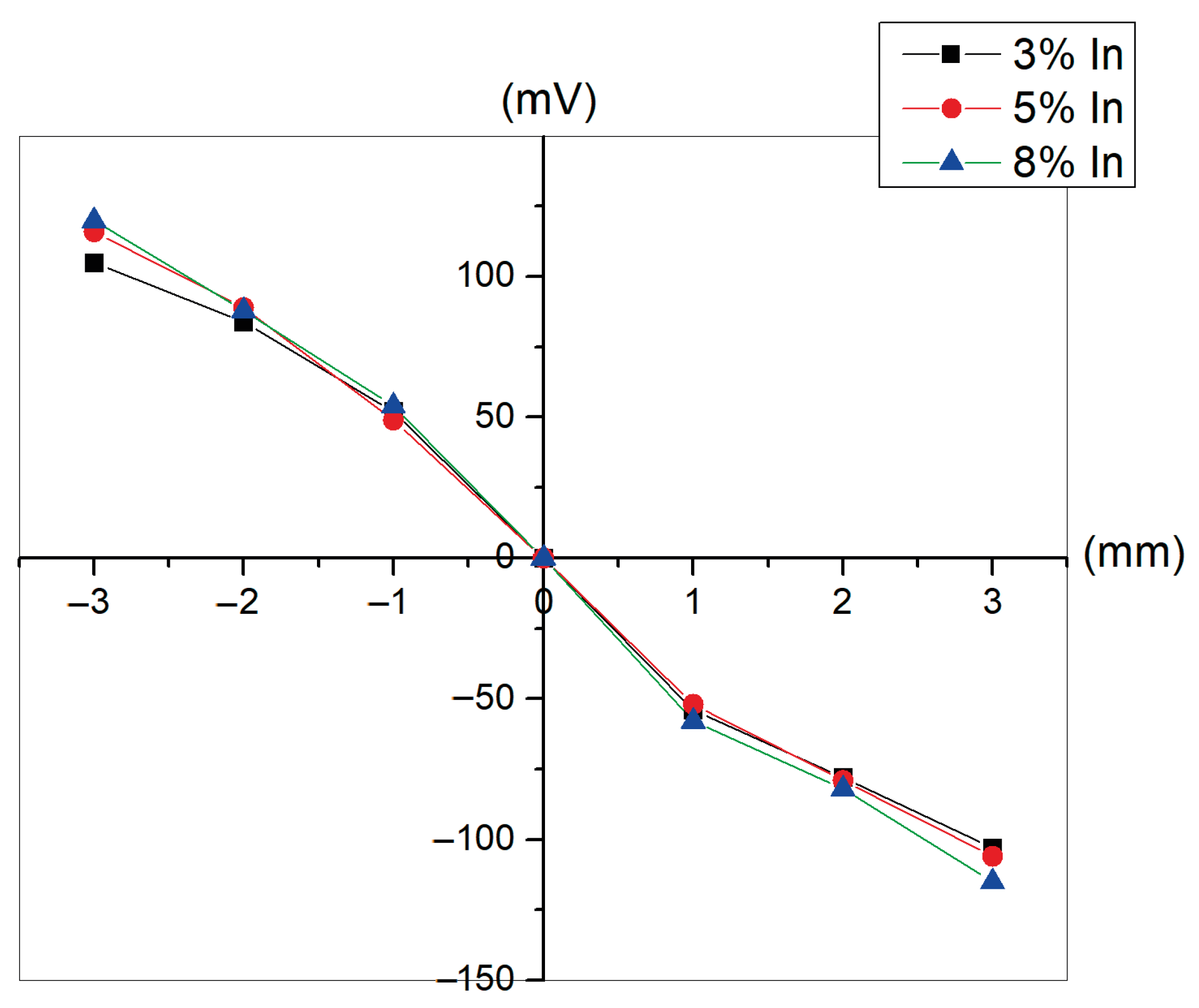
4. Electrical Properties and Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, L.P.; Fang, L.; Yang, X.F.; Li, Y.J.; Huang, Q.L.; Wu, F.; Kong, C.Y. Effect of annealing temperature on the structure and optical properties of In-doped ZnO thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 484, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swapna, R.; Kumar, M.C.S. The role of substrate temperature on the properties of nanocrystalline Mo doped ZnO thin films by spray pyrolysis. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 3875–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhi, H.F.; Rozati, S.M. Synthesis and investigating effect of tellurium-doping on physical propetryies of zinc oxide thin films by spray pyrolysis. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KaniAmuthan, B.; Vinoth, S.; Karthikeyan, V.; Roy, V.A.L.; Thilakan, P. Influence of nitrogen dopant source on the structural, photoluminescence and electrical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by pulsed spray pyrolysis. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 24324–24330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, V.; Anila, K.R.; Jayarama, A.; Bhat, S.; Rai, C.S.; Pinto, R. Spray pyrolysis deposited aluminium-indium zinc oxide thin films and study their electrical and photoluminescence properties. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 55, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Carraro, G.; Barreca, D.; Binions, R. Growth and electro-optical properties of Ga-doped ZnO films prepared by aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition. Thin Solid Film. 2015, 584, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettumperumal, R.; Kalyanaraman, S.; Thangavel, R. Effect on Er concentration on surface and optical properties of K doped ZnO sol-gel thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 2015, 83, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, A.R.; Salameh, B.; Alsmadi, A.M. Optical transmittance and photoluminescence of fluorine-doped zinc oxide thin films prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 19473–19480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, H.; Shimizu, H. Influence of crystallographic polarity on the opto-electrical properties of polycrystalline ZnO thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Bhatti, K.A.; Quindeel, R.; Alonizan, N.; Althobaiti, H.S. Characterizations of multilayer ZnO thin films deposited by sol-gel spin coating technique. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambedkar, A.K.; Singh, M.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, V.; Singh, B.P.; Kumar, A.; Gautam, Y.K. Structural, optical and thermoelectric properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 19, 100504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchuweni, E.; Sathiaraj, T.S.; Nyakotyo, H. Effect of gallium doping on the structural, optical and electrical properties of zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Ceram. Interfaces 2016, 42, 10066–10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, D.; Kumar, M.C.S. Synergetic effects of aluminium and indium dopants in the physical properties of ZnO thin films via spray pyrolysis. Superlattices Microstruct. 2020, 142, 106511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, N.; Deepak, N.K. Enhancement of visible luminescence and photocatalytic activity of ZnO thin films via Cu doping. Optik 2018, 158, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sree, D.N.; Deborrah, S.P.M.; Gopinathan, C.; Inbanathan, S.S.R. Enhanced UV light induced photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by Fe doped spray pyrolysis deposited ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamodharan, P.; Chen, J.; Manoharan, C. Fabrication of In doped ZnO thin films by spray pyrolysis as photoanode in DSSCs. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 23, 100965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotchenkov, G.; Brinzari, V.; Ham, M.-H. In2O3-based thermoelectric materials: The stae of the art and the role of surface state in the improvement of the efficiency of thermoelectric conversion. Crystals 2018, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colder, H.; Guilmeau, E.; Harnois, C.; Marinel, S.; Retoux, R.; Savary, E. Preparation of Ni-doped ZnO ceramics for thermoelectric applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Seong, J.K.; Nahm, S. Improvement of thermoelectric properties with the addition of Sb to ZnO. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 455, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, A.; Majid, W.H.; Abrishami, M.; Yousefi, R.; Parvizi, R. Synthesis, magnetic properties and X-ray analysis of Zn0.97X0.03O nanoparyicles (X = Mn, Ni and Co) using Scherrer and size train plot methods. Solid State Sci. 2012, 14, 488–494. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmuganathan, G.; Banu, I.B.; Krishnan, S.; Ranganathan, B. Influence of K-doping on the optical properties of ZnO thin films grown by chemical bath deposition method. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 562, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.S.; Bhonsale, C.H.; Rajpure, K.Y. Photoelectrochemical properties of highly mobilized Li-doped ZnO thin films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 120, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, A.K.; Hashim, A.M.; Darroudi, M. Optical properties of ZnO/BaCO3 nanocomposites in UV and visible regions. Nanoscales Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafdallah, A.; Ynineb, F.; Aida, M.S.; Attaf, N. In doped thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 7267–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancheva-Koleva, P.; Zhelev, V.; Petkov, P.; Petkova, T. Molybdenum-doped ZnO thin films obtained by spray pyrolysis. Materials 2024, 17, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirk, J.; Rothmann, M.; Li, W.; Abou-Ras, D.; McKenna, K.P. Grain boundaries in polycrystalline materials for energy applications: First principles modeling and electron microscopy. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2024, 11, 011308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, A.; Chander, S.; Sharma, A.; Nehra, S.P.; Dhaka, M.S. Impact of low temperature annealing on structural, optical, electrical and morphological properties of ZnO thin films grown by RF sputtering for photovoltaic applications. Opt. Mater. 2015, 49, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.J.; Hung, F.Y.; Chang, S.J.; Hu, Z.S. Microstructures, optical and electrical properties of In-doped ZnO thin films prepared by sol-gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 6308–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.L.; Liu, Z.W.; Zeng, D.C.; Zhong, M.L.; Yu, H.Y.; Mikmekova, E. Nanostructured ZnO films with various morphologies prepared by ultrasonis spray pyrolysis and its growing process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Reddy, M.R.; Reddy, K. Structural, optical and electrical characteristics of nanostructured ZnO thin films with various thicknesses deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Res. J. Phys. Sci. 2013, 2320, 4796. [Google Scholar]
- Clabel, J.L.; Nazrin, S.N.; Lozano, G.; da Silva, M.P.; LI, M.S.; Marega, E., Jr. Activation energy and its fluctuations at grain boundaries of Er3+:BaTiO3 perovskite this films: Effect of doping concentration and annealing temperature. Vacuum 2021, 194, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.J.; Fang, T.H.; Hung, F.Y.; Ji, L.W.; Chang, S.J.; Young, S.J.; Hsiao, Y.J. The crystallization and physical properties of Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 5791–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, M.; Kozuka, H.; Yoko, T. Sol-Gel Preparation of Transparent and Conductive Aluminum-Doped Zinc Oxide Films with Highly Preferential Crystal Orientation. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1998, 81, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D. The Elements of X-Ray Diffraction; Addison-Wesley, Reading: Boston, MA, USA, 1978; p. 102. [Google Scholar]
- Luna-Arredondo, E.J.; Maldonado, A.; Asomoza, R.; Acosta, D.R.; Melendez-Lira, M.A.; Olvera, M.d.l.L. Indium-doped ZnO thin films deposited by sol-gel technique. Solid Film. 2005, 490, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.P.; Santhoshkumar, M.C. Highly oriented (100) ZnO thin films by spray pyrolysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 7212–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiles, D. Introduction to the Electronic Properties of Materials; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. 180. [Google Scholar]
- Burstein, E. Anomalous optical absorption limit in InSb. Phys. Rev. 1954, 93, 632–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Ghosh, K.; Patel, R.; Mishra, S.R.; Kahol, P.K. Band gap engineering of ZnO thin films by In2O3 incorporation. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 3019–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribut, S.; Abdullah, C.A.C.; Yusoff, M.Z.M. Investigations of structural and optical properties of zinc oxide thin films growth on various substrates. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelev, V.; Petkov, P.; Shindov, P.; Bineva, I.; Ilcheva, V.; Petkova, T. As-doped SnO2 thin films for use as large area position sensitive photodetector. Thin Solid Film. 2018, 653, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelev, V.; Petkov, P.; Avdeev, G.; Lilova, V.; Petkova, T. Study of In2O3 thin films doped with As as active layer in position sensitive structures. In Nanoscience and Nanotechnology in Security and Protection Against CBRN Threats; NATO Science for Peace and Security Series B: Physics and Biophysics; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| In, % | a, Å | c, Å | Size, nm | Strain, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICSD | 3.2530 | 5.2070 | - | - |
| 0 | 3.247 (2) | 5.216 (4) | 25 | 0.33 |
| 3 | 3.244 (4) | 5.197 (7) | 14 | 0.064 |
| 5 | 3.254 (5) | 5.211 (8) | 9 | 0.11 |
| 8 | 2.263 (9) | 5.22 (1) | 8 | 0.1 |
| Element | Mass (%) | at. % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | O | In | Zn | O | In | |
| In3ZnO | 3.57 | 7.17 | 0.09 | 1.32 | 10.84 | 0.02 |
| In5ZnO | 3.26 | 6.84 | 0.09 | 1.20 | 10.35 | 0.02 |
| In8ZnO | 2.78 | 6.03 | 0.10 | 1.01 | 8.98 | 0.02 |
| Measured Film Thickness, nm | Eg, eV | |
|---|---|---|
| pure ZnO | 350 | 3.341 |
| In3ZnO | 748 | 3.651 |
| In5ZnO | 760 | 3.656 |
| In8ZnO | 800 | 3.663 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bancheva-Koleva, P.; Zhelev, V.; Petkov, P.; Petkova, T. Indium-Doped ZnO Thin Films Obtained Using Spray Pyrolysis for Position-Sensitive Photodetection. Materials 2025, 18, 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163744
Bancheva-Koleva P, Zhelev V, Petkov P, Petkova T. Indium-Doped ZnO Thin Films Obtained Using Spray Pyrolysis for Position-Sensitive Photodetection. Materials. 2025; 18(16):3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163744
Chicago/Turabian StyleBancheva-Koleva, Pavlina, Veselin Zhelev, Plamen Petkov, and Tamara Petkova. 2025. "Indium-Doped ZnO Thin Films Obtained Using Spray Pyrolysis for Position-Sensitive Photodetection" Materials 18, no. 16: 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163744
APA StyleBancheva-Koleva, P., Zhelev, V., Petkov, P., & Petkova, T. (2025). Indium-Doped ZnO Thin Films Obtained Using Spray Pyrolysis for Position-Sensitive Photodetection. Materials, 18(16), 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163744







