Unraveling the Excellent High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of FeNiCuAl-Based Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Isothermal Oxidation Testing
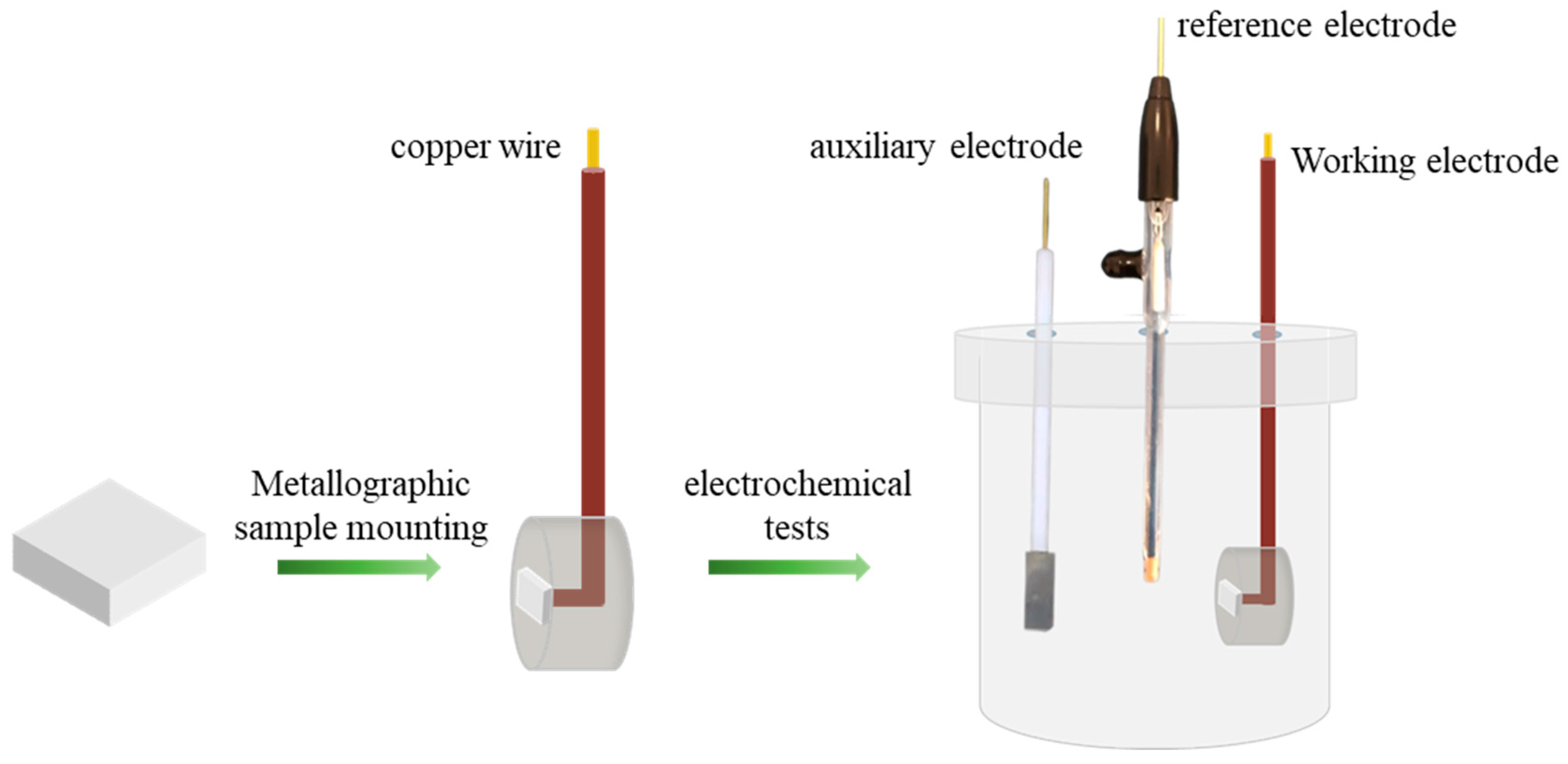
2.3. Corrosion Behavior in 3.5% NaCl Solution
2.4. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
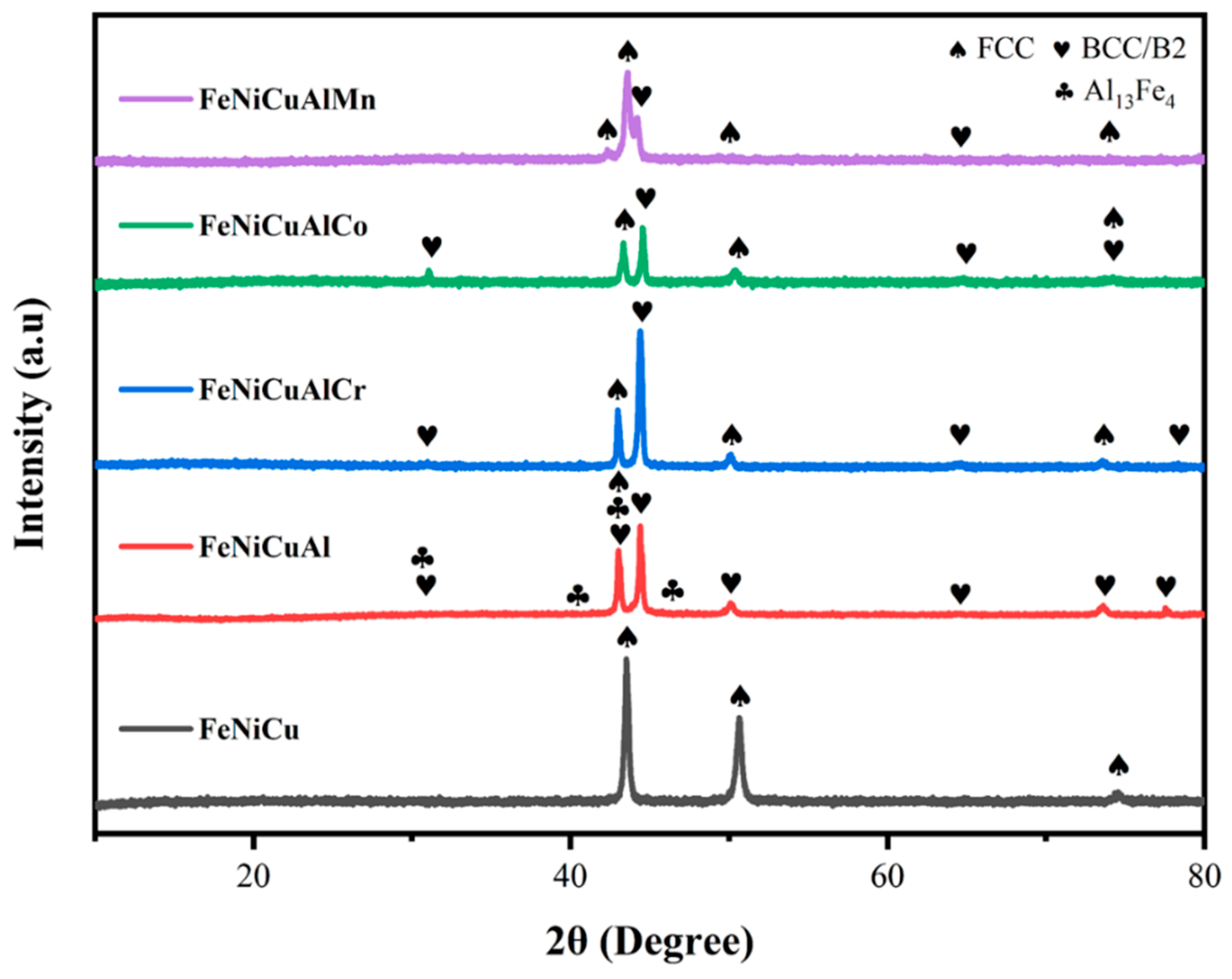
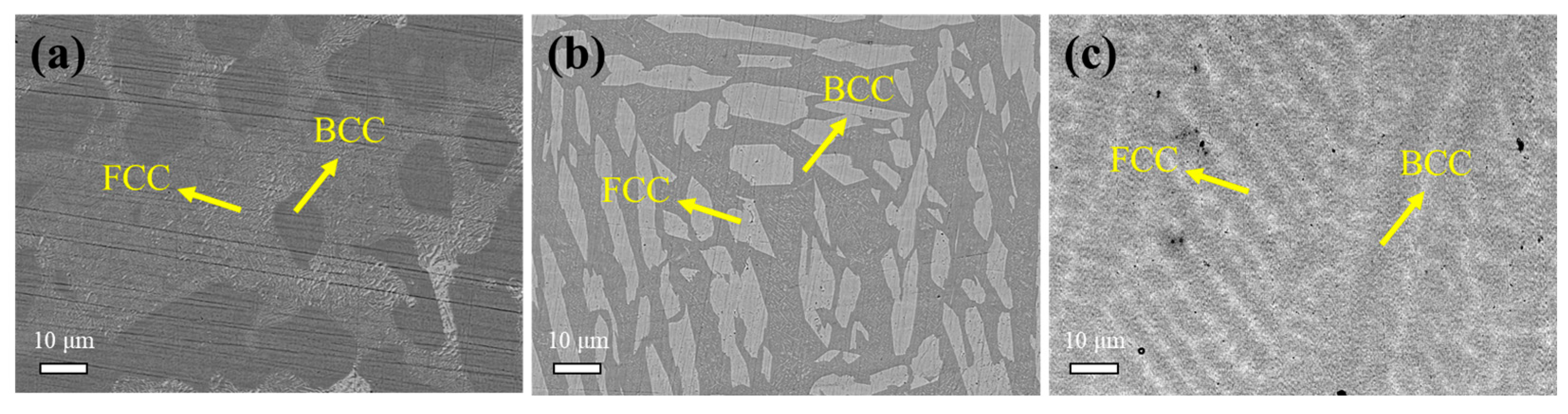
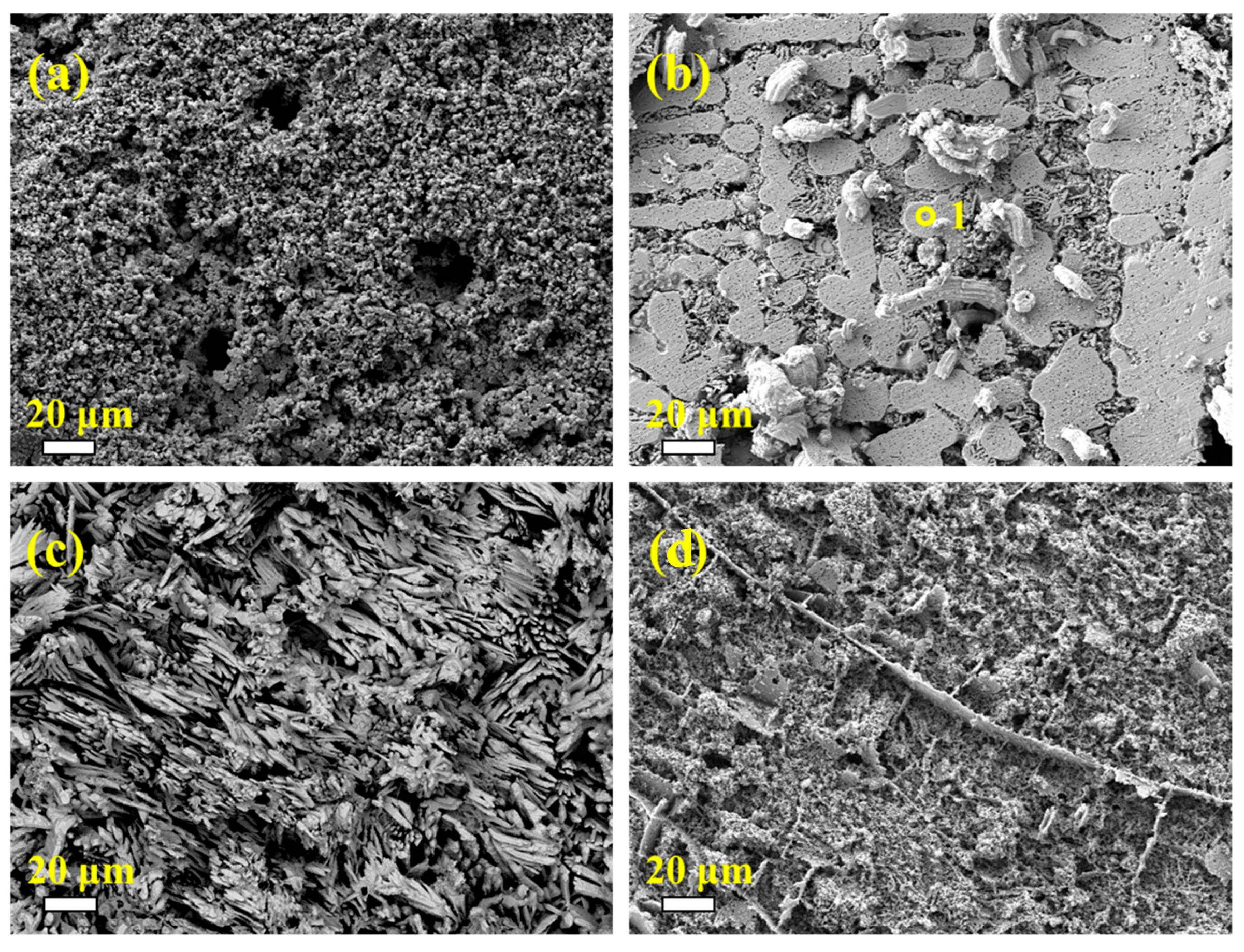
3.1. Substrate Analysis
3.2. Oxidation Kinetics
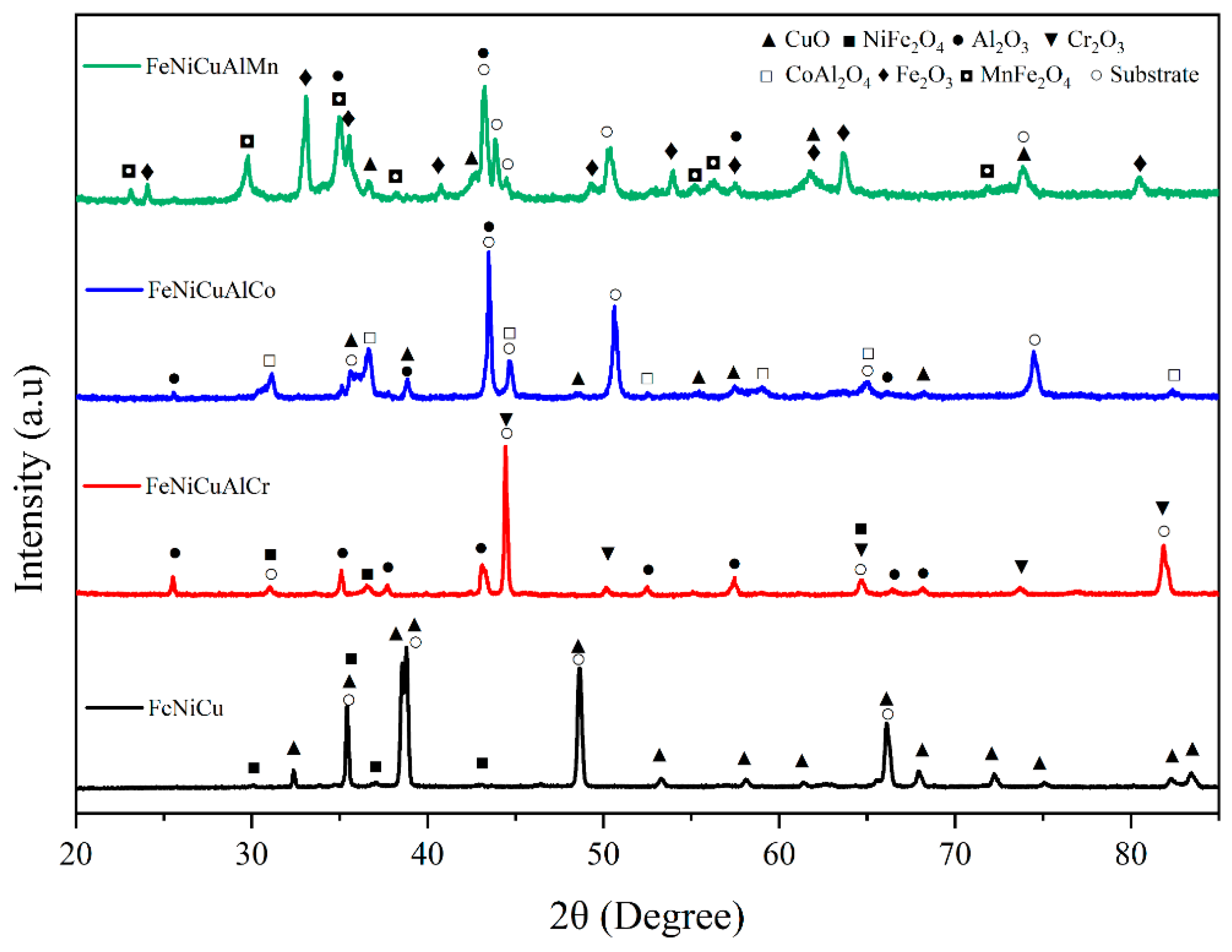
3.3. Oxide Phase Constituents
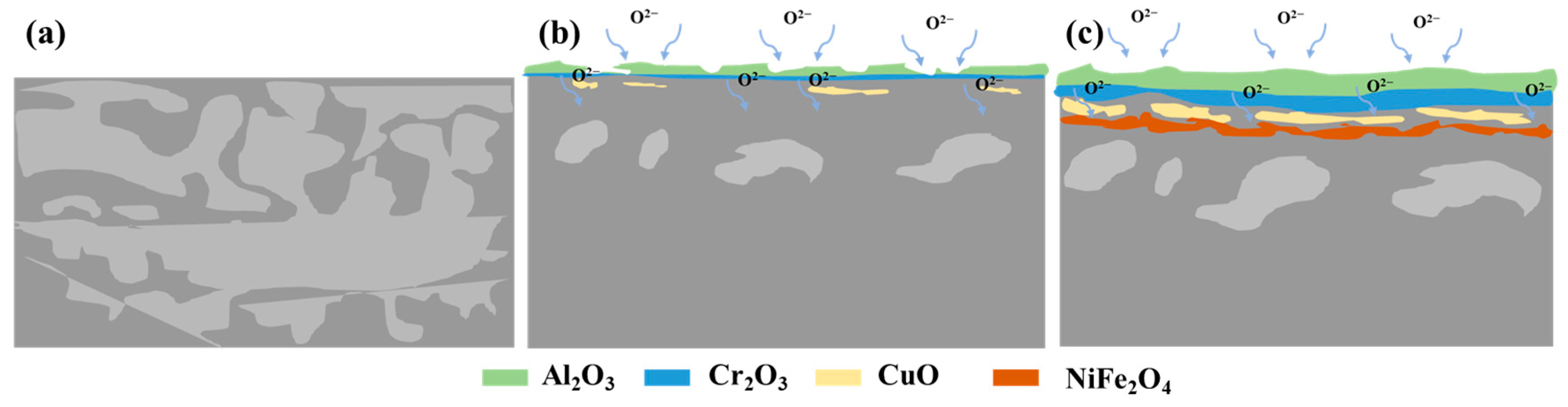
3.4. Microstructure and Chemical Composition of the Oxide Scale
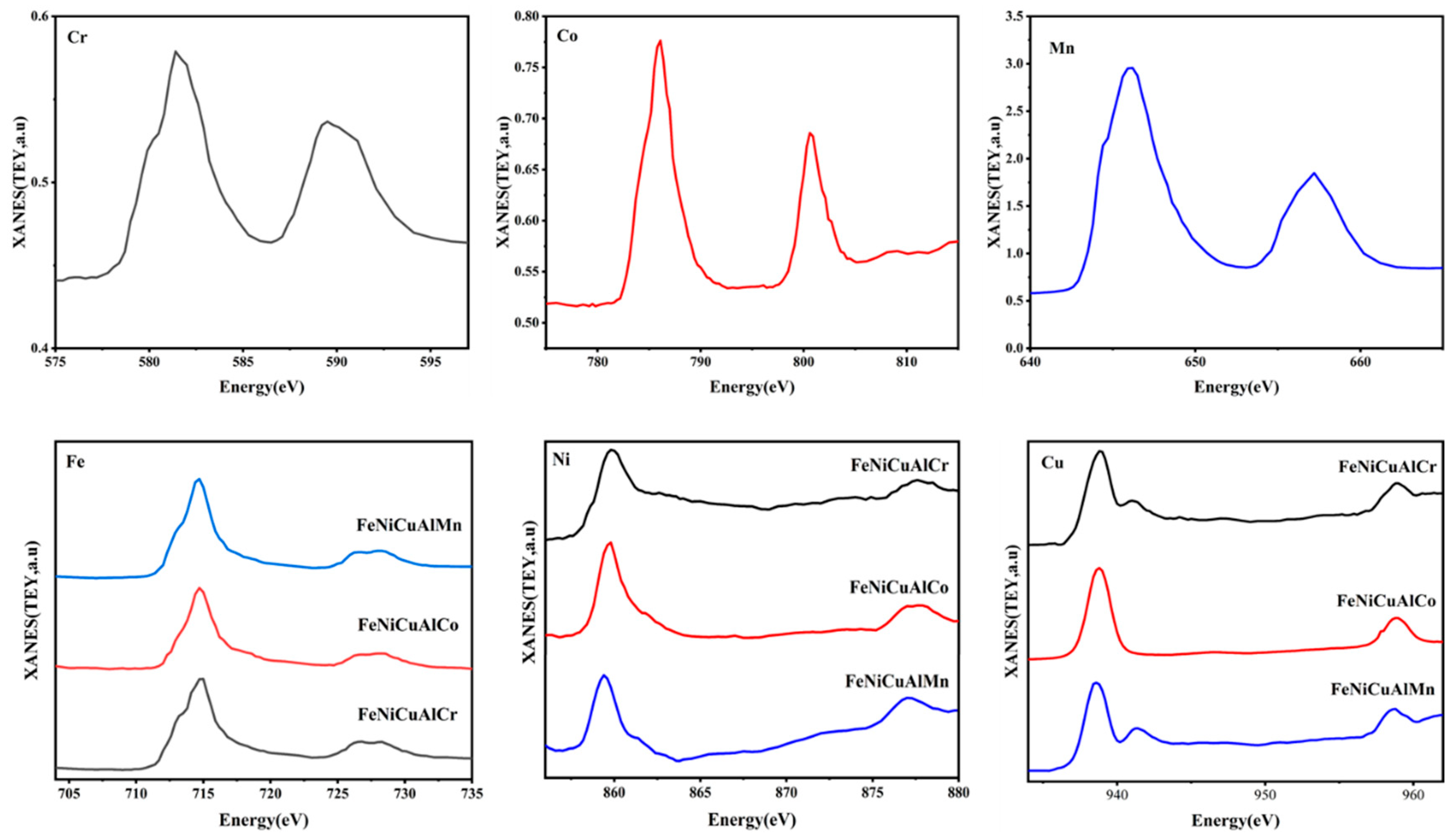
3.5. Soft X-Ray XANES
3.6. Crack Formation Mechanism of Oxide Scale
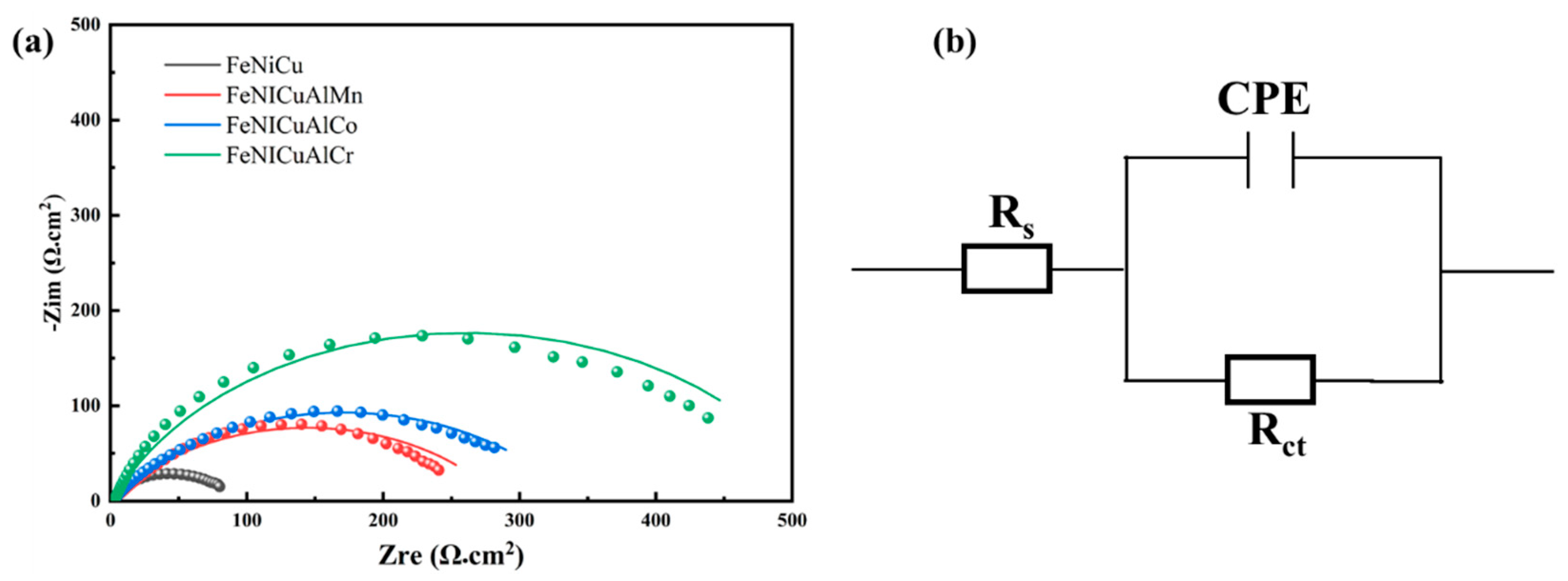
3.7. Corrosion Behavior
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The oxidation kinetics of the FeNiCuAlCr, FeNiCuAlCo, and FeNiCuAlMn HEAs in air at 900 °C follow a parabolic relationship. Among them, the FeNiCuAlCr HEA exhibited excellent oxidation resistance, with a low mass gain of 0.83 mg/cm2 after 108 h of exposure at 900 °C.
- (2)
- The outer oxidation layer of the FeNiCuAlCr HEA formed a dense and continuous Al2O3 and Cr2O3 layer, which provided effective protection for the substrate. In contrast, for the FeNiCuAlCo and FeNiCuAlMn HEAs, prolonged oxidation and increased high-temperature internal stress led to the partial peeling and wrinkling of the oxide scale at the interface between the scale and the alloy.
- (3)
- The electrochemical analysis revealed that the FeNiCuAlCr HEA possesses a high corrosion potential (Ecorr = −0.21 V) and a low corrosion current density (Icorr = 45.7 μA/cm2). The EIS results further confirmed the superior performance of the passive film, with a high polarization resistance (Rct = 519.2 Ω cm2), indicating excellent stability and protective efficacy.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hummel, R.E. Understanding Materials Science, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T.; Yang, Y. High-entropy alloy: Challenges and prospects. Mater. Today 2016, 20, 100638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Raabe, D.; Ritchie, R.O. High-entropy alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Mirostruct. Process. 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Juan, C.C.; Sheu, T.S.; Chen, S.K.; Yeh, J.W. Effect of Aluminum Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AlxCoCrFeMo0.5Ni High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 2013, 65, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Ma, H.; Spolenak, R. Ultrastrong ductile and stable high-entropy alloys at small scales. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Wang, W.R.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W. Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6308–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, H.N.; Lu, J.; Li, Y. High-Strength, and high-ductility nanostructured and amorphous metallic materials. Adv. Mater 2016, 26, 5518–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.Y.; Tao, Q.; Zhang, P. Microstructure and mechanical properties of undercooled Fe80C5Si10B5 eutectic alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 747, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ren, Y.; Du, Y.; Han, W.; Hua, D.; Zhai, H.; Huang, P.; Wang, F.; Wang, H. Identifying the significance of Sn addition on the tribological performance of Ti-based bulk metallic glass composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 780, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Xiao, P. Y-Hf co-doped AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coating with superior oxidation and spallation resistance at 1100 °C. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.M.; Alfano, J.P.; Martens, R.L.; Weaver, M.L. High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Al-Co-Cr-Ni-(Fe or Si) Multicom-ponent High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 2015, 67, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofstad, P. High-temperature oxidation of titanium. J. Less Common Met. 1967, 12, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-X.; Cheng, C.-Q.; Shang, J.-L.; Wang, R.; Li, P.; Zhao, J. Oxidation behavior of high-entropy alloys AlxCoCrFeNi (x=0.15, 0.4) in supercritical water and comparison with HR3C steel. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Venkataraman, M.B. High Temperature Corrosion and Oxidation of Metals. Metals 2019, 9, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselkov, S.; Samoilova, O.; Shaburova, N.; Trofimov, E. High-Temperature Oxidation of High-Entropic Alloys: A Review. Material 2021, 14, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-J.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; He, L.-Q.; Zhou, K.-C. A self-repairing cermet anode: Preparation and corrosion behavior of (Cu–Ni–Fe)/NiFe2O4 cermet with synergistic action. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, H.F.; Fan, J. Effect of NiO addition on the high-temperature oxidation and corrosion behaviors of Fe–Ni alloy as inert anode material for aluminum electrolysis. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 4065–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teslia, S.; Teslia, M.; Sun, Q.; Stepanchuk, A. Investigation of microstructural evolution and mechanical properties Al13Fe4 produced by casting and spark-plasma sintering. Vacuum 2023, 218, 112590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W. Fundamentals of solidification. Trans. Tech. Publ. Switz. 1998, 6, 71–92. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, B.; Mark, W. Influence of Annealing on the Microstructures and Oxidation Behaviors of Al8(CoCrFeNi)92, Al15(CoCrFeNi)85, and Al30(CoCrFeNi)70 High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2016, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzini, J.P.; Dirras, G.; Perri, L.; Chauveau, T.; Leroy, E.; Champion, Y.; Guillot, I. Microstructure of a near-equimolar refractory high-entropy alloy. Mater. Lett. 2014, 126, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, N.; Meier, G.H. Introduction to High-Temperature Oxidation of Metals; Edward Arnold Ltd.: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- West, J.M. Basic Corrosion and Oxidation; Ellis Horwood Limited: Chichester, UK, 1980; p. 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, H.L. A model for the oxide growth stress and its effect on the creep of metals. Metall. Trans. A 1991, 18, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplanche, G.; Volkert, U.F.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Oxidation Behavior of the CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy. Oxid. Met. 2016, 85, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sui, Y.; Qi, J.; He, Y.; Wei, F.; Meng, Q.; Sun, Z. Microstructure of Al1.3CrFeNi eutectic high entropy alloy and oxidation behavior at 1000 °C. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Xiao, P. Oxidation behavior of gas-atomized AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy powder at 900–1100 °C. Corros. Sci. 2021, 181, 109257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Shen, B. Oxidation behavior of AlCoCrFeNiSix high-entropy alloys at 1100 °C. Corros. Sci. 2021, 190, 109633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; An, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Mao, S.; Han, X. Effect of Al content on the thermal oxidation behaviour of AlHfMoNbTi high-entropy alloys analysed by in situ environmental TEM. Corros. Sci. 2021, 191, 109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Shi, R. Solute Segregation-induced High-temperature Oxidation Behavior of Cu-Ni-Sn Alloy Via Experimental and Thermodynamic Investigations. Corros. Sci. 2023, 216, 111071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Chang, Q.; Feng, J. Enhancement of high-temperature oxidation resistance of the AgCu-based alloy by in-situ fabricating three-dimensional TiC nanosheet reinforcement. Corros. Sci. 2022, 198, 110094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Han, T.; Zhou, F.; Qu, N.; Liao, M.; Lai, Z.; Zhu, J. High thermal stability and oxidation behavior of FeCrNiAl-based medium-entropy alloys prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 918, 165562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilling, N.; Bedworth, R. The Oxidation of Metals at High Temperatures. J. Inst. Met. 1923, 29, 529–582. [Google Scholar]
- Dąbrowa, J.; Cieślak, G.; Stygar, M.; Mroczka, K.; Berent, K.; Kulik, T.; Danielewski, M. Influence of Cu content on high temperature oxidation behavior of AlCoCrCuxFeNi high entropy alloys (x=0; 0.5; 1). Intermetallics 2017, 84, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palcut, M.; Drienovský, M.; Priputen, P.; Šulhánek, P.; Stacho, P.; Gerhátová, Ž.; Gogola, P.; Krajčovič, J.; Bónová, L.; Kusý, M. Oxidation resistance of AlCoFeNiCux high entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 1974–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorqasemi, E.; Abootalebi, O.; Peikari, M.; Haqdar, F. Investigating accuracy of the Tafel extrapolation method in HCl solutions. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.F.; Lee, T.D.; Chen, S.K.; Cang, Y.S. Electrochemical passive properties of AlxCoCrFeNi (x=0, 0.25, 0.50, 1.00) alloys in sulfuric acids. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Feng, K.; Li, Z.; Lu, F.; Li, R.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y. Microstructure and corrosion properties of CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396 Pt 2, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.-W. Microstructure and properties of AlCrFeNiCoCu high entropy alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 555, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, W.R.; Cremasco, A.; Andrade, P.N.; Garcia, A.; Caram, R. Electrochemical behavior of centrifuged cast and heat treated Ti–Cu alloys for medical applications. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 55, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocijan, A.; Merl, D.K.; Jenko, M. The corrosion behaviour of austenitic and duplex stainless steels in artificial saliva with the addition of fluoride. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Guo, H.; Yang, W.; Pang, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, T. Al0.3CrxFeCoNi high-entropy alloys with high corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. Interdiscip. J. Mater. Sci. Solid-State Chem. Phys. 2021, 860, 158436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| HEAs | Kp (mg2·cm4/s) | n |
|---|---|---|
| FeNiCu | 1.60 × 10−3 | 0.59 |
| FeNiCuAlCr | 1.72 × 10−6 | 0.40 |
| FeNiCuAlCo | 3.29 × 10−6 | 0.52 |
| FeNiCuAlMn | 1.71 × 10−5 | 0.45 |
| Al15CoCrFeNi [27] | 4.7 × 10−5 | |
| FeMnCrCoNi [28] | 4.1 × 10−5 |
| Region | Fe | Ni | Cu | Al | Cr | Co | Mn | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.27 | - | - | 24.95 | 13.49 | - | - | 61.29 |
| 2 | 6.80 | 2.94 | 1.22 | 20.81 | 9.32 | - | - | 58.91 |
| 3 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 41.24 | - | 0.11 | - | 58.16 |
| 4 | 0.13 | 0.72 | 4.42 | 36.33 | - | 1.41 | 56.99 | |
| 5 | 1.12 | 0.62 | 2.70 | 33.42 | - | 7.32 | 54.82 | |
| 6 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 33.96 | - | - | 0.37 | 65.54 |
| 7 | 16.35 | 9.11 | 10.32 | 7.11 | - | - | 13.07 | 44.04 |
| 8 | 19.45 | 13.00 | 13.09 | 10.11 | - | - | 18.22 | 26.13 |
| CuO | Al2O3 | Cr2O3 | Fe2O3 | NiFe2O4 | CoAl2O4 | MnFe2O4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeNiCuAlCr | 1.89 | 2.17 | 2.16 | - | 2.16 | - | - |
| FeNiCuAlCo | 1.96 | 2.16 | - | - | - | 2.09 | - |
| FeNiCuAlMn | 1.89 | 2.16 | - | 2.20 | - | - | 2.28 |
| Region | Fe | Ni | Cu | Al | Cr | Na | Cl | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 31.10 | 11.11 | 4.25 | 8.23 | 30.51 | 0.09 | 3.70 | 11.01 |
| Alloy | Ecorr (V) | Icorr (μA/cm2) | Rs (Ω cm2) | α | Rct (Ω cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeNiCu | −0.57 | 240 | 0.82 | 0.72 | 89.61 |
| FeNiCuAlCr | −0.21 | 45.7 | 1.53 | 0.76 | 519.2 |
| FeNiCuAlCo | −0.34 | 81.3 | 1.56 | 0.64 | 338.7 |
| FeNiCuAlMn | −0.56 | 85.1 | 1.39 | 0.63 | 286.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.; Li, G.; Wei, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Hua, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, W. Unraveling the Excellent High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of FeNiCuAl-Based Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153679
Wu G, Li G, Wei L, Chen H, Wang Y, Qiao Y, Hua Y, Shi C, Huang Y, Yang W. Unraveling the Excellent High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of FeNiCuAl-Based Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153679
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guangxin, Gaosheng Li, Lijun Wei, Hao Chen, Yujie Wang, Yunze Qiao, Yu Hua, Chenyang Shi, Yingde Huang, and Wenjie Yang. 2025. "Unraveling the Excellent High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of FeNiCuAl-Based Alloy" Materials 18, no. 15: 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153679
APA StyleWu, G., Li, G., Wei, L., Chen, H., Wang, Y., Qiao, Y., Hua, Y., Shi, C., Huang, Y., & Yang, W. (2025). Unraveling the Excellent High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of FeNiCuAl-Based Alloy. Materials, 18(15), 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153679






