Multi-Scale Study on Ultrasonic Cutting of Nomex Honeycomb Composites of Disc Cutters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Multi-Scale Analysis
2.1. Microscopic Scale: Fiber Distribution and Matrix Interaction
2.2. Mesoscopic Scale: Deformation Features of Honeycomb Cells
2.3. Macroscopic Scale: Analysis of Cutting Mechanics
3. Materials and Methods
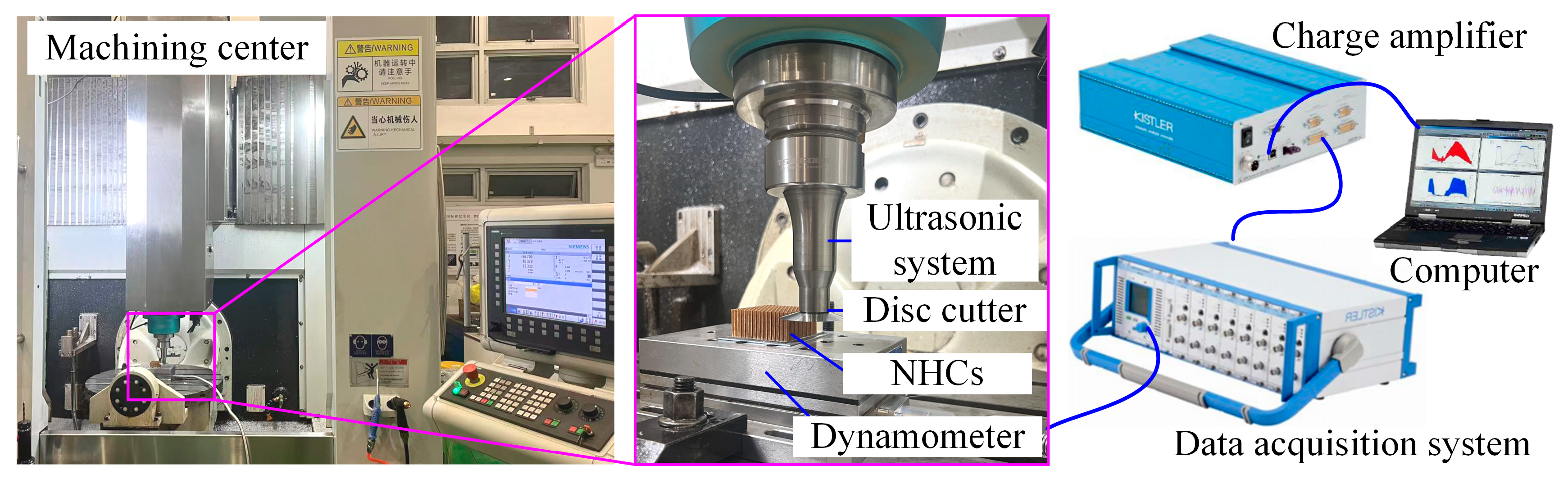
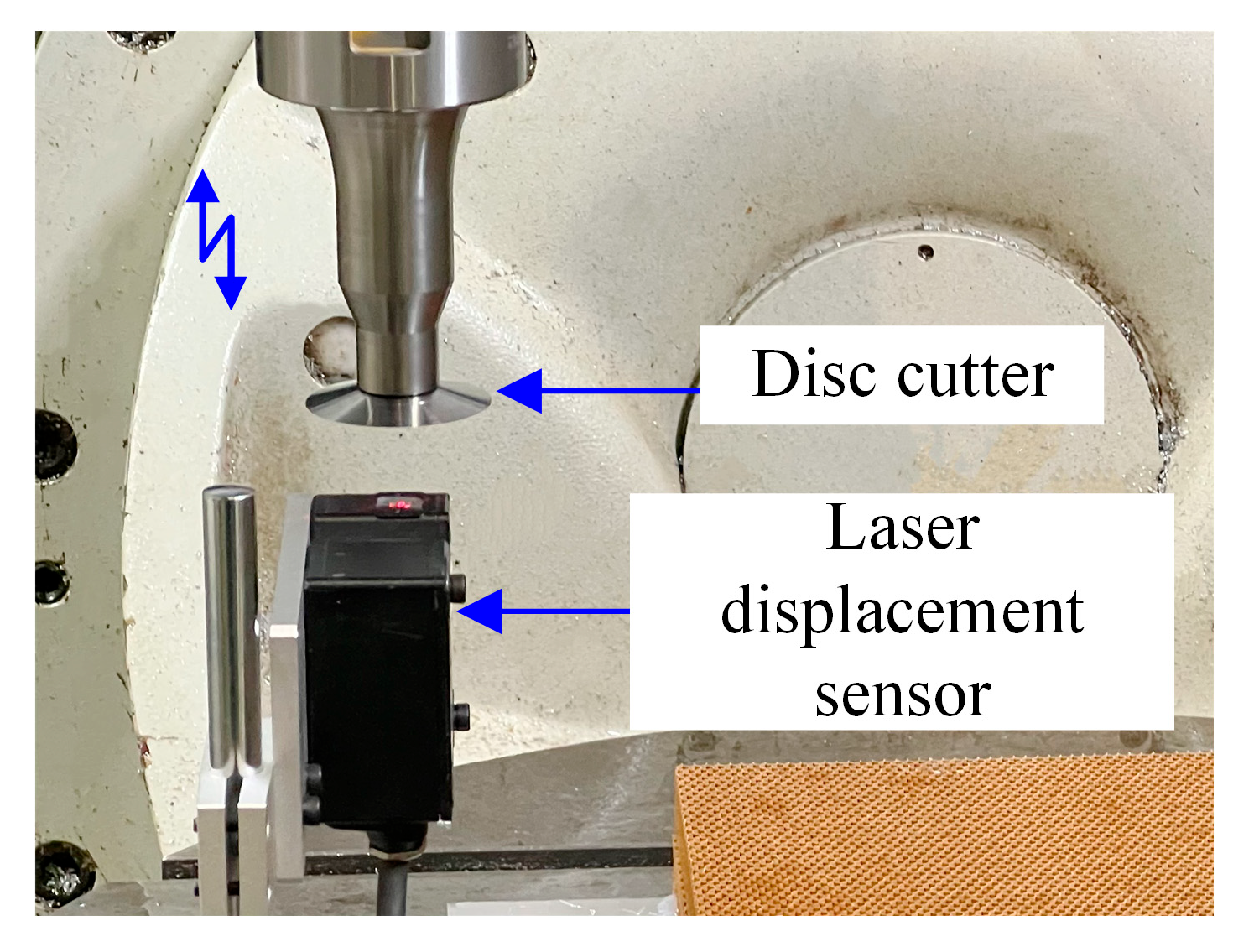
3.1. Experimental Platform
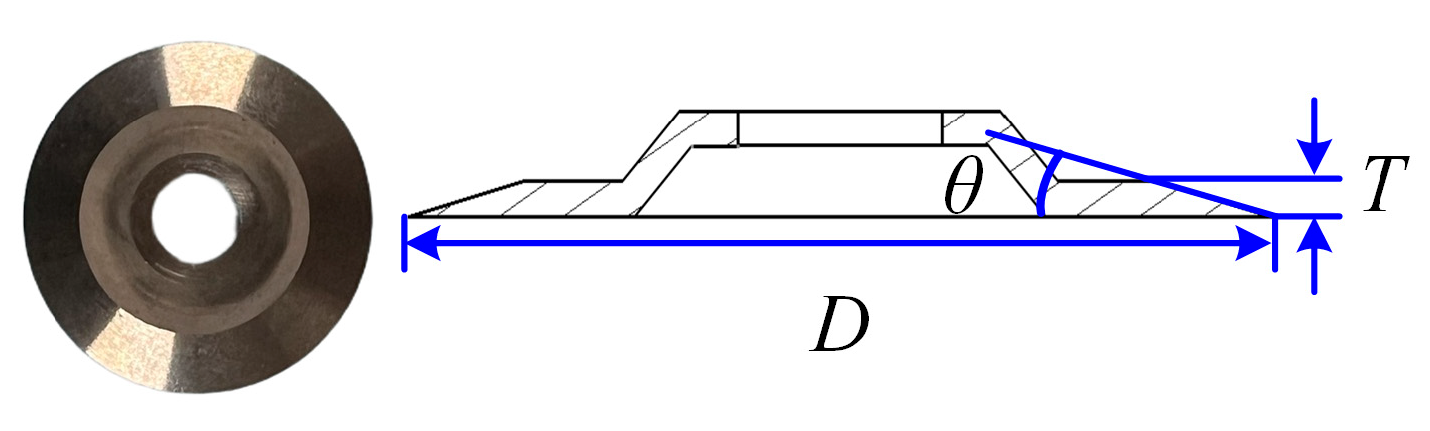
3.2. Experimental Methods
4. Results and Discussion
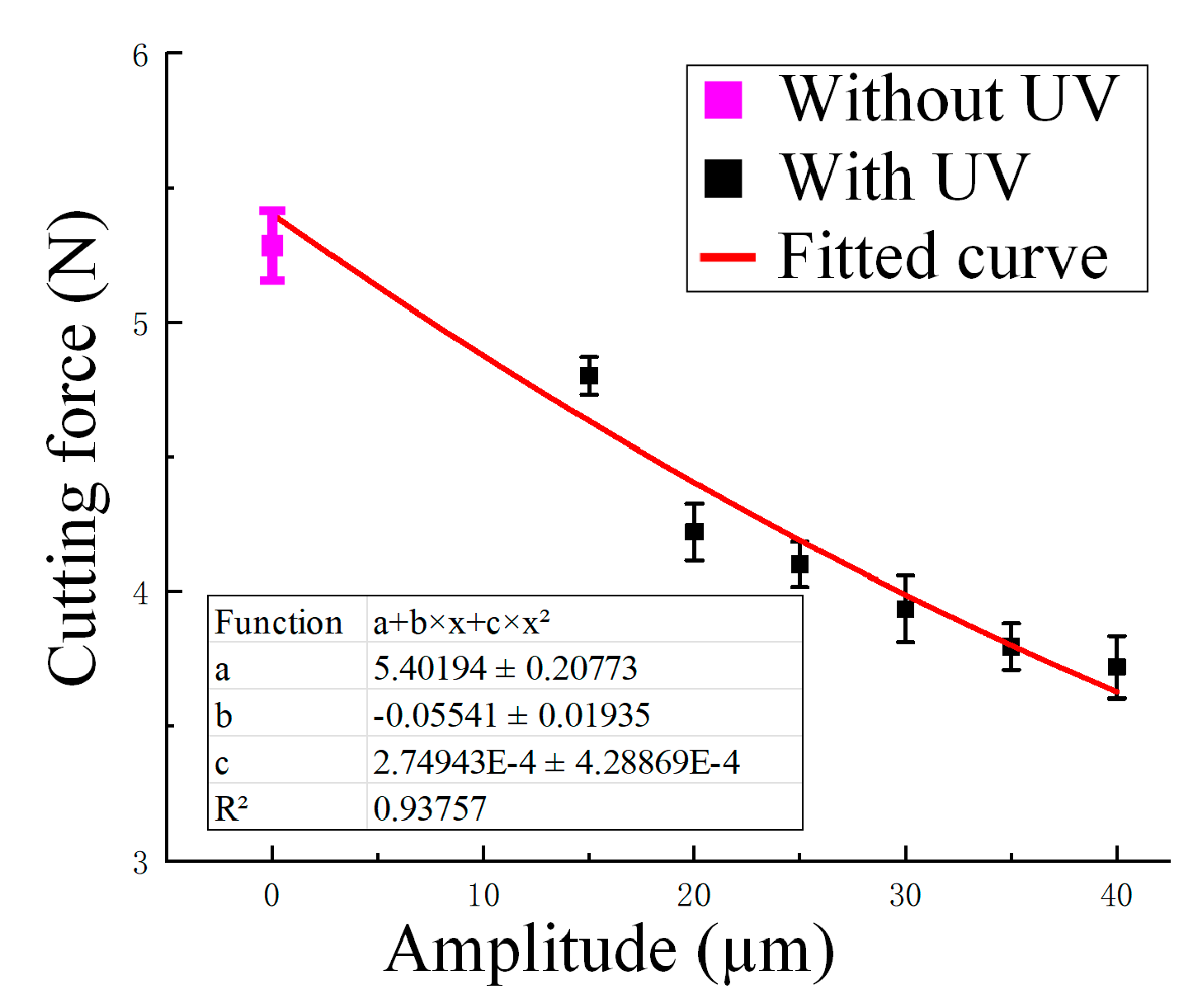
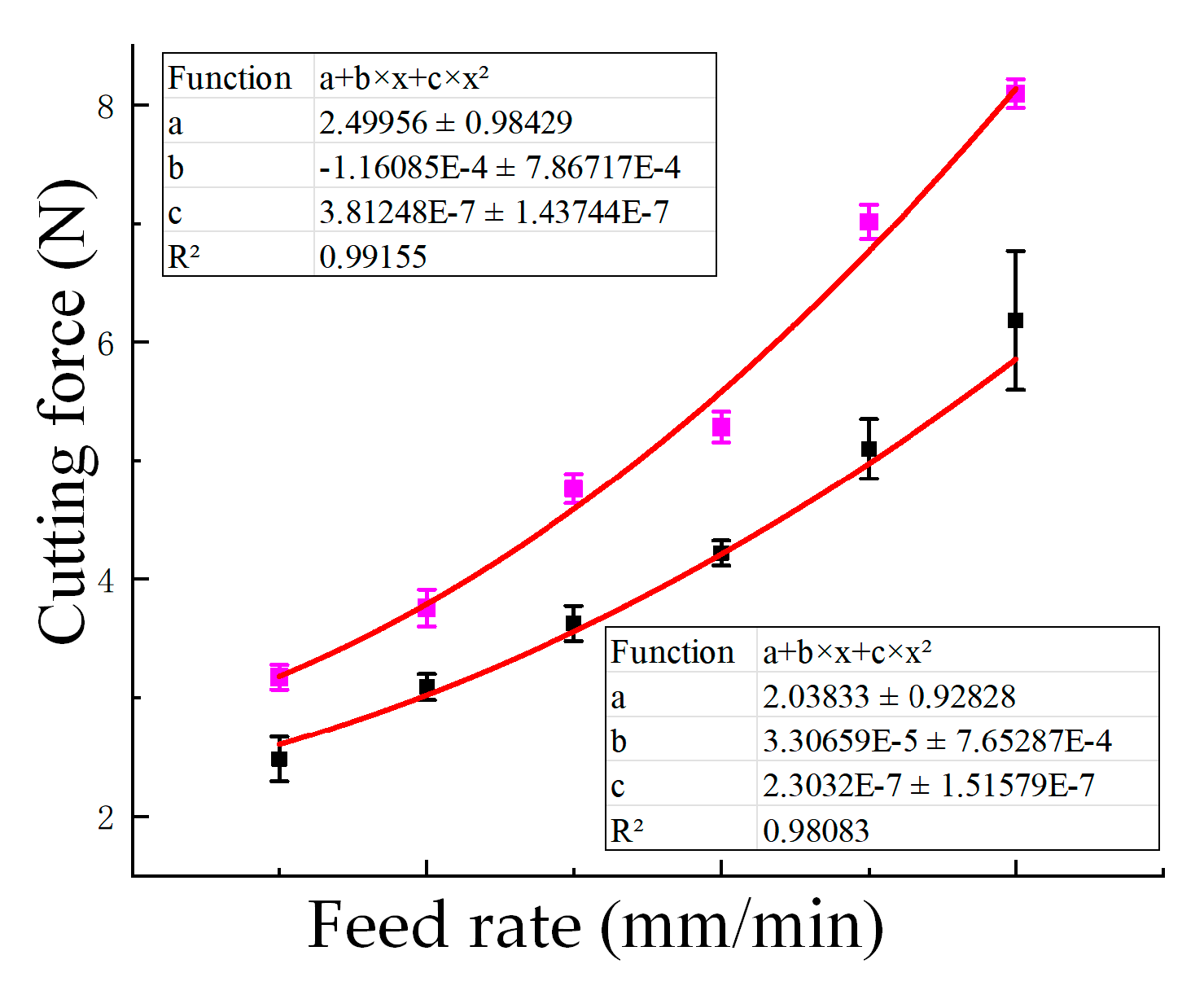
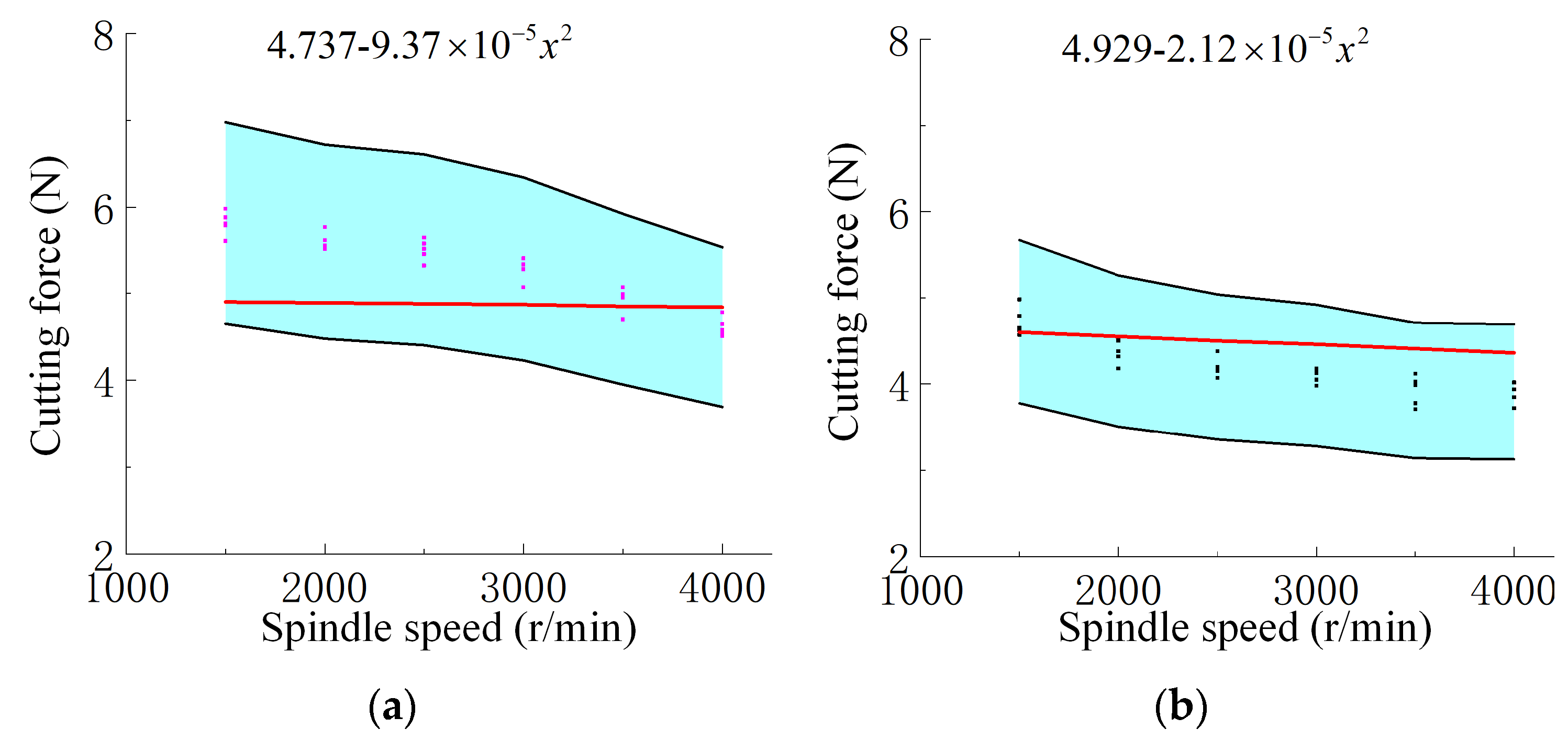
4.1. Macroscopic Scale Results and Discussion
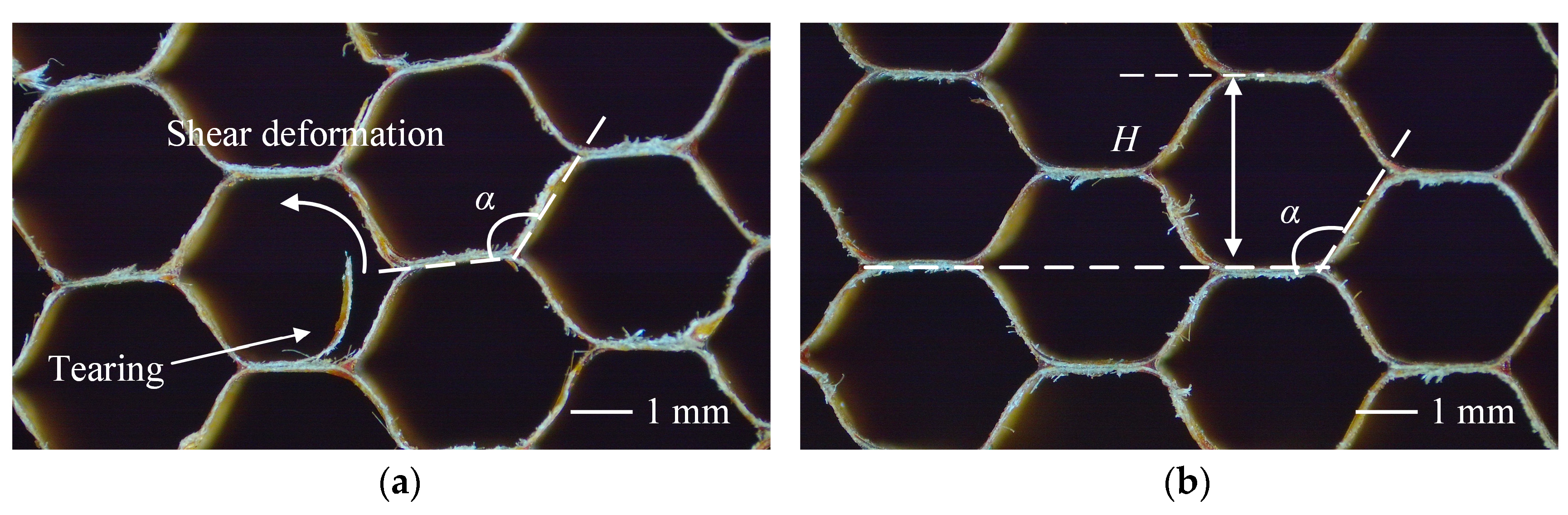
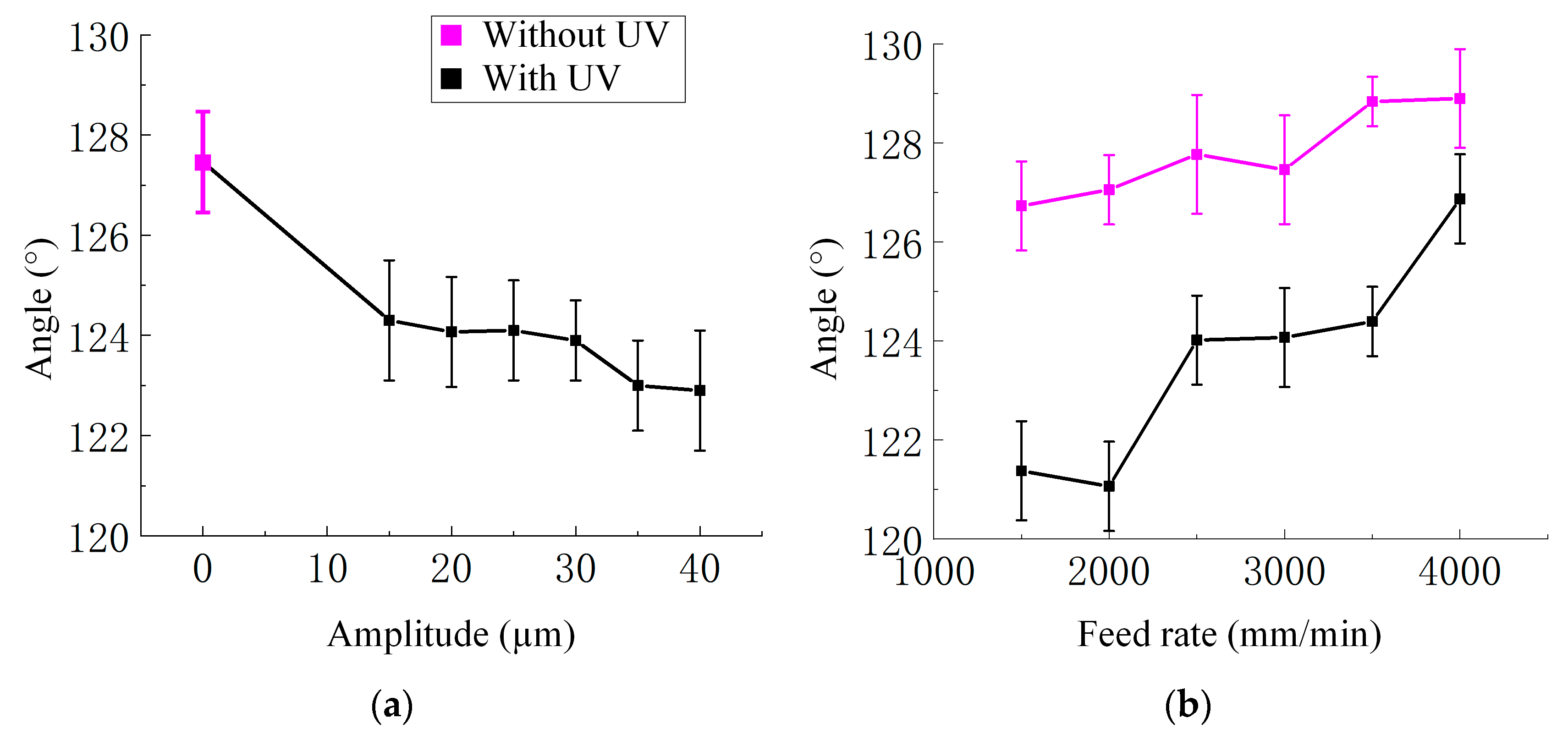
4.2. Mesoscopic Scale Results and Discussion
4.3. Microscopic Scale Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- At the macroscopic scale, the prediction error for the average cutting force in the feed direction is 8.6%. The application of ultrasonic vibration led to a reduction in cutting force across different amplitudes, feed rates, and spindle speeds. This reduction results from the intermittent contact mechanism introduced by the vibration, which lowers cutting resistance. Notably, the maximum reduction in cutting force reached approximately 29.7% at an amplitude of 40 μm.
- (2)
- At the mesoscopic scale, the prediction error for the structural deformation analytical model for the damage area is less than 10.5%. The degree of deformation in honeycomb cells was assessed by analyzing the variation in cell angle α. Experimental results showed that ultrasonic vibration reduced the deformation from the regular hexagonal structure, reflecting a mitigating effect on structural damage.
- (3)
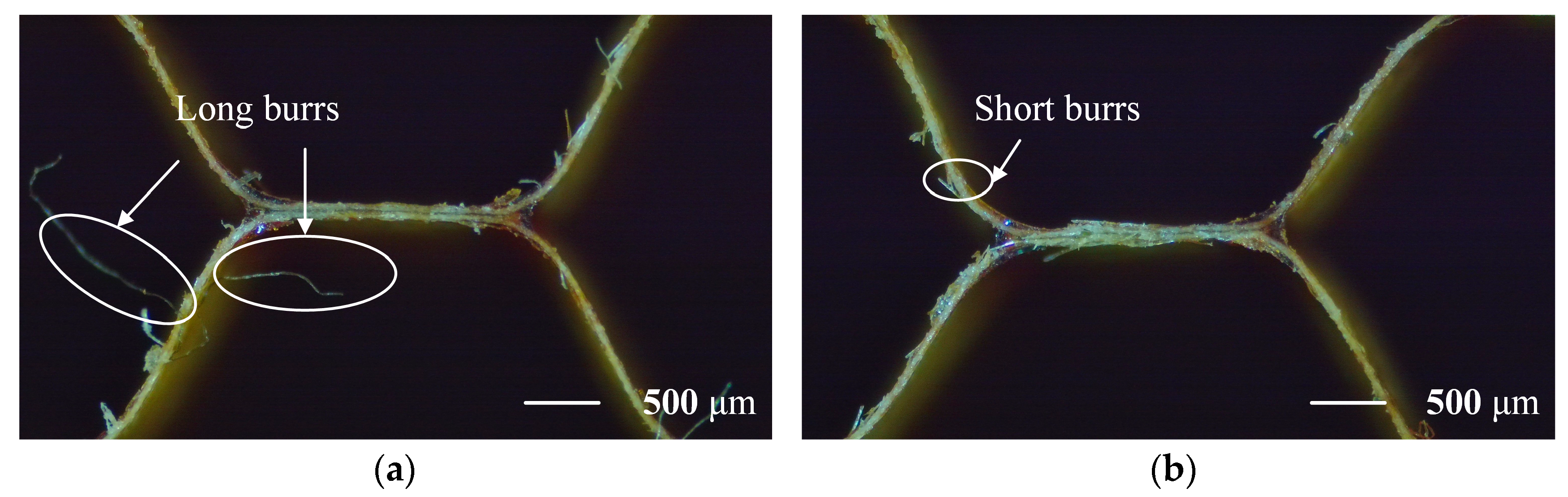
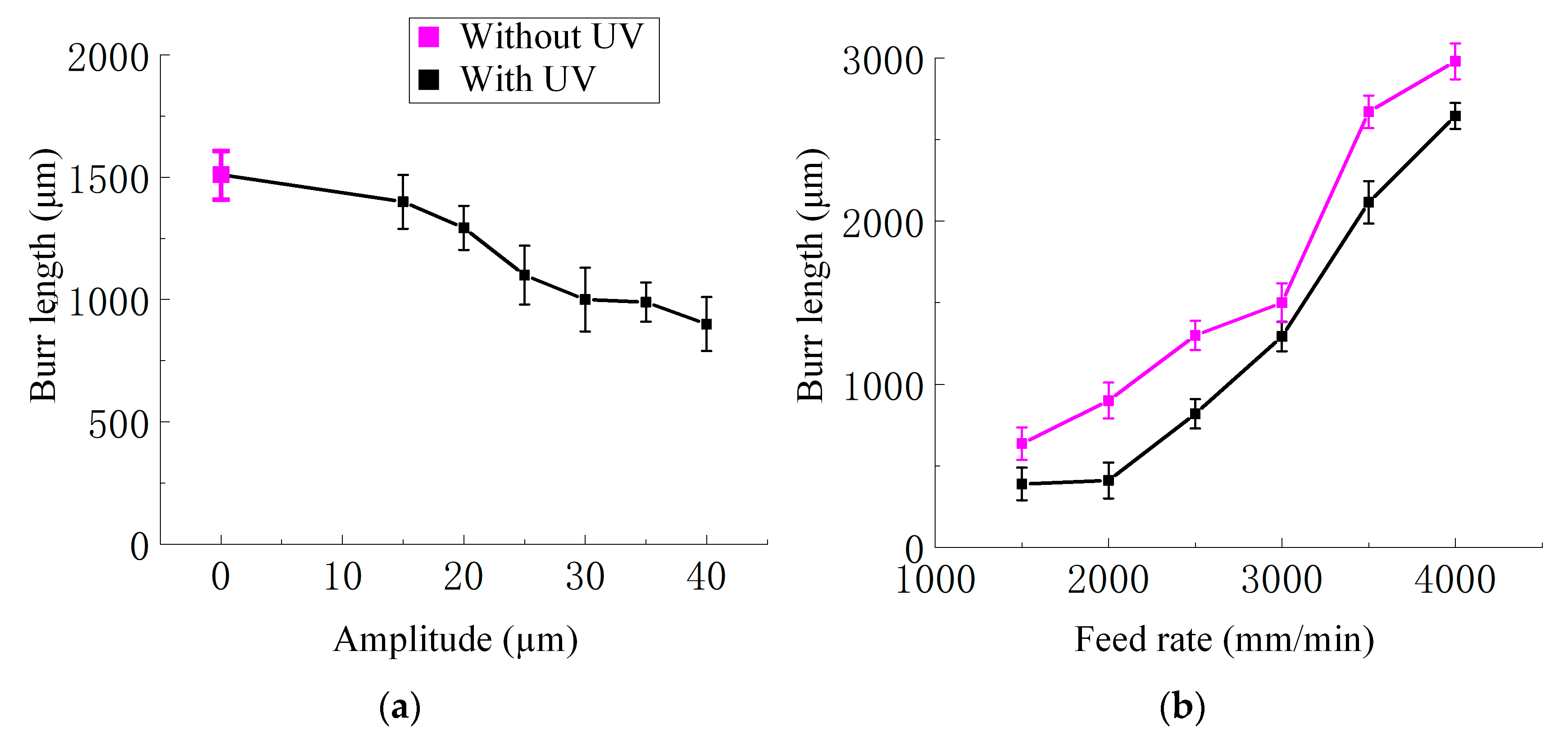
- At the microscopic scale, the prediction error for the burr length at normal direction in orthogonal experiments is 5.6%. As the ultrasonic amplitude increased, the maximum burr length was reduced by up to 36.7%. Conversely, higher feed rates led to more long burrs due to insufficient material separation. Ultrasonic vibration was shown to reduce burr length by limiting fiber pull-out and matrix tearing.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NHCs | Nomex honeycomb composites |
| DC | Disc cutter |
| UVA | Ultrasonic vibration-assisted |
| UV | Ultrasonic vibration |
References
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, K.; Zha, H.; Xu, J.; Song, G.; Cao, W.; Feng, P.; Feng, F. Enabling Thin-Edged Part Machining of Nomex Honeycomb Composites via Optimizing Variable Angle of Disc Cutters. Materials 2023, 16, 5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Feng, P.; Song, Z.; Zhu, S.; Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Yue, Q.; Jiang, E.; Ma, Y.; Song, G.; et al. Wear Mechanisms of Straight Blade Tool by Dual-Periodic Impact Platform. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 288, 110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Singhal, S. Rotary Ultrasonic Machining: A Review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 1795–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoe, T.; Aspinwall, D.; Wise, M. Review on Ultrasonic Machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1998, 38, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Zhang, J.; Feng, P.; Yu, D.; Wu, Z.; Ke, M. Processing Technologies for Nomex Honeycomb Composites (NHCs): A Critical Review. Compos. Struct. 2020, 250, 112545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Sun, J.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Kang, R.; Wang, Y. Cutting Force Reduction Mechanism in Ultrasonic Cutting of Aramid Honeycomb. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 273, 109317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Hu, W. A Study on Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Panel Structure. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, S.M.; Popham, E.; Miles, M.E. An Investigation of the Skin/Core Bond in Honeycomb Sandwich Structures Using Statistical Experimentation Techniques. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, G.G.; Vinquist, C.; Es-Said, O.S. Theoretical Design and Analysis of a Honeycomb Panel Sandwich Structure Loaded in Pure Bending. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2008, 15, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, B.; Feng, F.; Xu, J.; Song, G.; Liang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, F.; Feng, P. False Boss Connection for Precision Machining of Composites with Soft and Brittle Characteristics. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Wu, B.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Tang, J. Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Cutting of Nomex Honeycomb Core Materials. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 20, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Bao, Y.; Chen, K.; Dong, Z.; Kang, R.; Guo, D.; Sun, J. Prediction and Analysis of Grinding Burr of CFRP Circular Tube with a Rounded Corner Grinding Wheel. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 133, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Qin, Y.; Xing, W.; Kang, R.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y. Study on Cell Wall Deformation in Ultrasonic Cutting Aluminum Honeycomb by Straight-Blade Knife. Ultrasonics 2024, 144, 107444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhou, W.; Hui, D. On the Influence of Structural Defects for Honeycomb Structure. Compos. Part B 2018, 142, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Wang, M.; Kang, R.; Dong, Z. Equivalent Mechanical Model of Resin-Coated Aramid Paper of Nomex Honeycomb. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 240, 107935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Kang, R.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Dong, Z. A Form Error Evaluation Method of Honeycomb Core Surface. Measurement 2022, 201, 111667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Feng, P.; Gong, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Feng, F. Exploiting Damage for Inhibiting Damage: A Counterintuitive Reasoning out of in-Situ Orthogonal Cutting for Brittle Fiber Composite. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2025, 343, 118961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, T.; Zuo, C.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J. Investigating Damage Mechanisms of Honeycomb Cores Machined with PCD Circular Saw Blades. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 327, 118381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, E.; Yue, Q.; Xu, J.; Fan, C.; Song, G.; Yuan, X.; Ma, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, P.; Feng, P.; et al. A Wear Testing Method of Straight Blade Tools for Nomex Honeycomb Composites Machining. Wear 2024, 546–547, 205325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, K.; Zha, H.; Liu, J.; Yuan, X.; Cai, X.; Xu, C.; Ma, Y.; Feng, P.; Feng, F. Surface Integrity of Nomex Honeycomb Composites after Ultrasonic Vibration Machining by Using Disc Cutters. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 102, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yue, Q.; Zha, H.; Yuan, X.; Cai, X.; Xu, C.; Ma, Y.; Feng, P.; Feng, F. Wear Reduction by Toughness Enhancement of Disc Tool in Nomex Honeycomb Composites Machining. Tribol. Int. 2023, 185, 108475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Feng, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J. Modeling the Load Capacity of Frequency-Tracked Rotary Ultrasonic Machining System. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 246, 108136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, R.; Dong, Z.; Wang, X.; Huo, D.; Zhang, X. A Novel Method of Blade-Inclined Ultrasonic Cutting Nomex Honeycomb Core with Straight Blade. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2021, 143, 041012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, C.T.; Annaidh, A.N.; Gilchrist, M.D. On the Sharpness of Straight Edge Blades in Cutting Soft Solids: Part II—Analysis of Blade Geometry. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2010, 77, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. Research on Ultrasonic Cutting Mechanism of Nomex Honeycomb Composites Based on Fracture Mechanics. J. Mech. Eng. 2015, 51, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Feng, P.; Zha, H.; Feng, F. Building of Longitudinal Ultrasonic Assisted Turning System and Its Cutting Simulation Study on Bulk Metallic Glass. Materials 2020, 13, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, Z. Formation Mechanism of Tearing Defects in Machining Nomex Honeycomb Core. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 112, 3167–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Wu, B.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Feng, H. Ultrasonic Longitudinal-Torsional Vibration-Assisted Cutting of Nomex® Honeycomb-Core Composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 100, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, R.; Qin, Y.; Meng, Q.; Dong, Z. Effects of Inclination Angles of Disc Cutter on Machining Quality of Nomex Honeycomb Core in Ultrasonic Cutting. Front. Mech. Eng. 2021, 16, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrouk, T.; Nouari, M.; Salhi, J.-E.; Benbouaza, A. Numerical Simulation of Rotary Ultrasonic Machining of the Nomex Honeycomb Composite Structure. Machines 2024, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrouk, T.; Salhi, J.-E.; Nouari, M.; Bouali, A. Enhancing the Machining Performance of Nomex Honeycomb Composites Using Rotary Ultrasonic Machining: A Finite Element Analysis Approach. Materials 2024, 17, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrouk, T.; Nouari, M.; Salhi, J.-E. Numerical Study on Rotary Ultrasonic Machining (RUM) Characteristics of Nomex Honeycomb Composites (NHCs) by UCSB Cutting Tool. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 132, 5351–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrouk, T.; Salhi, J.-E.; Nouari, M.; Barboucha, M. Modeling of Nomex Honeycomb Structure Milling Assisted by Longitudinal–Torsional Vibrations with a CZ10 Combined Tool: Optimization of Tool Wear and Surface Integrity. Appl. Mech. 2025, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Zhang, J.; Feng, P.; Yu, D.; Wu, Z. Experimental Study on Rotary Ultrasonic Machining (RUM) Characteristics of Nomex Honeycomb Composites (NHCs) by Circular Knife Cutting Tools. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Feng, P.; Jiang, E.; Feng, F. Meso-Scale Cracks Initiation of Nomex Honeycomb Composites in Orthogonal Cutting with a Straight Blade Cutter. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 233, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Nguyen, K.H.; Park, Y.B.; Kweon, J.H.; Choi, J.H. Testing and Modeling of NomexTM Honeycomb Sandwich Panels with Bolt Insert. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 56, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Kang, R.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X. Burr Removal from Measurement Data of Honeycomb Core Surface Based on Dimensionality Reduction and Regression Analysis. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2018, 29, 115010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Qin, Y.; Kang, R.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y. Robust Cell Wall Recognition of Laser Measured Honeycomb Cores Based on Corner Type Identification. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 136, 106321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, X.; Zhao, M. Micromechanical Modeling of Fiber-Reinforced Composites with Statistically Equivalent Random Fiber Distribution. Materials 2016, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsden, J.J. Review of New Experimental Techniques for Investigating Random Sequential Adsorption. J. Stat. Phys. 1993, 73, 853–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Kang, R.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Dong, Z. A Novel Ultrasonic Trepanning Method for Nomex Honeycomb Core. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, G.; Aglietti, G.S.; Richardson, G. Static and Fatigue Behaviour of Hexagonal Honeycomb Cores under In-Plane Shear Loads. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2012, 19, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, M.; Nouari, M.; Makich, H.; Moufki, A. 3D Numerical Modeling and Experimental Validation of Machining Nomex® Honeycomb Materials. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 115, 2853–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Analysis of Influence on Ultrasonic-Assisted Cutting Force of Nomex Honeycomb Core Material with Straight Knife. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 53, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, C. Study on the Cutting Damage Mechanism of Aramid Honeycomb Based on the Progressive Damage Model. Materials 2022, 15, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Ni, C.; Lin, B. Review of Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Machining in Advanced Materials. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2020, 156, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, C.; Rahman, M. Effect of Machining Parameters in Ultrasonic Vibration Cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Zhu, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z. Analytical Modeling of Tool-Workpiece Contact Rate and Experimental Study in Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Milling of Ti–6Al–4V. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 142–143, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zha, J.; Chen, Y. Cutting Force Prediction and Experiment Verification of Paper Honeycomb Materials by Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Machining. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | NH-1-1.83-29 |
| Density | 29 kg/m3 |
| Length | 1.83 mm |
| Size |
| Group | Ultrasonic Amplitude (μm) | Feed Rate (mm/min) | Spindle Speed (r/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 | 3000 | 3000 |
| 2 | 20 | 3000 | 3000 |
| 3 | 25 | 3000 | 3000 |
| 4 | 30 | 3000 | 3000 |
| 5 | 35 | 3000 | 3000 |
| 6 | 40 | 3000 | 3000 |
| 7 | 20 | 1500 | 3000 |
| 8 | 20 | 2000 | 3000 |
| 9 | 20 | 2500 | 3000 |
| 10 | 20 | 3000 | 3000 |
| 11 | 20 | 3500 | 3000 |
| 12 | 20 | 4000 | 3000 |
| 13 | 20 | 3000 | 1500 |
| 14 | 20 | 3000 | 2000 |
| 15 | 20 | 3000 | 2500 |
| 16 | 20 | 3000 | 3000 |
| 17 | 20 | 3000 | 3500 |
| 18 | 20 | 3000 | 4000 |
| 19 | 0 | 1500 | 3000 |
| 20 | 0 | 2000 | 3000 |
| 21 | 0 | 2500 | 3000 |
| 22 | 0 | 3000 | 3000 |
| 23 | 0 | 3500 | 3000 |
| 24 | 0 | 4000 | 3000 |
| 25 | 0 | 3000 | 1500 |
| 26 | 0 | 3000 | 2000 |
| 27 | 0 | 3000 | 2500 |
| 28 | 0 | 3000 | 3000 |
| 29 | 0 | 3000 | 3500 |
| 30 | 0 | 3000 | 4000 |
| Feed Rate (mm/min) | Amplitude (μm) | Experimental Value (mm2) | Predicted Value (mm2) | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3000 | 40 | 8.14 | 7.98 | 2.3% |
| 4000 | 20 | 7.64 | 8.39 | 9.8% |
| 4000 | 0 | 7.22 | 8.63 | 19.5% |
| Feed Rate (mm/min) | Amplitude (μm) | Experimental Value (μm) | Predicted Value (μm) | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3000 | 40 | 900.0 | 922.0 | 2.44% |
| 4000 | 20 | 2645.3 | 2344.0 | 11.39% |
| 4000 | 0 | 2980.2 | 2892.0 | 2.96% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Feng, F.; Cao, W.; Song, G.; Yuan, X.; Xu, J.; Yue, Q.; Pan, S.; Jiang, E.; Ma, Y.; et al. Multi-Scale Study on Ultrasonic Cutting of Nomex Honeycomb Composites of Disc Cutters. Materials 2025, 18, 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153476
Liang Y, Feng F, Cao W, Song G, Yuan X, Xu J, Yue Q, Pan S, Jiang E, Ma Y, et al. Multi-Scale Study on Ultrasonic Cutting of Nomex Honeycomb Composites of Disc Cutters. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153476
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yiying, Feng Feng, Wenjun Cao, Ge Song, Xinman Yuan, Jie Xu, Qizhong Yue, Si Pan, Enlai Jiang, Yuan Ma, and et al. 2025. "Multi-Scale Study on Ultrasonic Cutting of Nomex Honeycomb Composites of Disc Cutters" Materials 18, no. 15: 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153476
APA StyleLiang, Y., Feng, F., Cao, W., Song, G., Yuan, X., Xu, J., Yue, Q., Pan, S., Jiang, E., Ma, Y., & Feng, P. (2025). Multi-Scale Study on Ultrasonic Cutting of Nomex Honeycomb Composites of Disc Cutters. Materials, 18(15), 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153476







