Utilization of High Iron Content Sludge and Ash as Partial Substitutes for Portland Cement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mixture Design
2.3. Sample Preparation and Characterizations
2.3.1. Compressive Strength Study on Mortars
2.3.2. Setting Time Test
2.3.3. XRD, TG/DTG, and SEM
2.3.4. Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP)
3. Results and Discussion
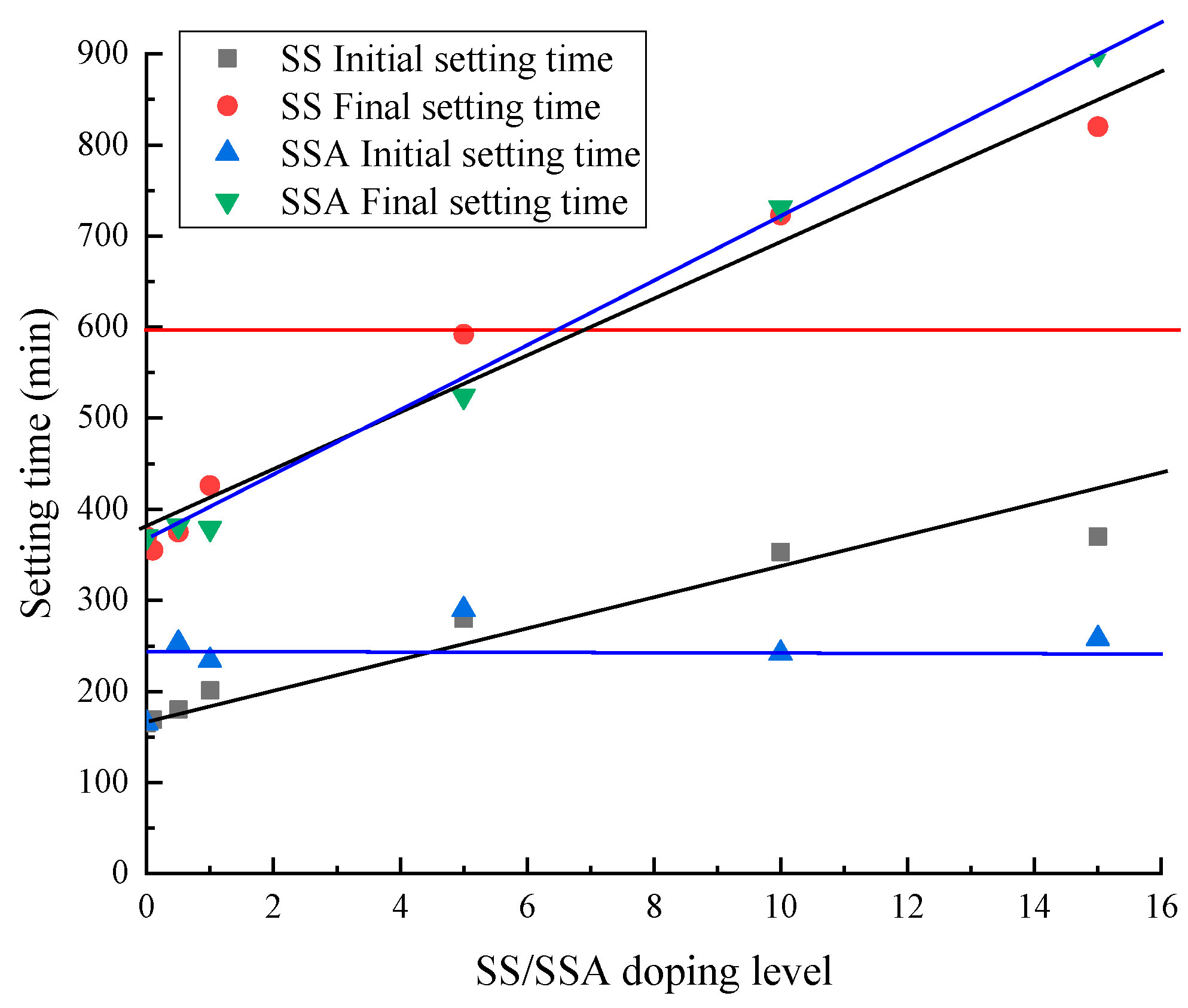
3.1. Setting Times
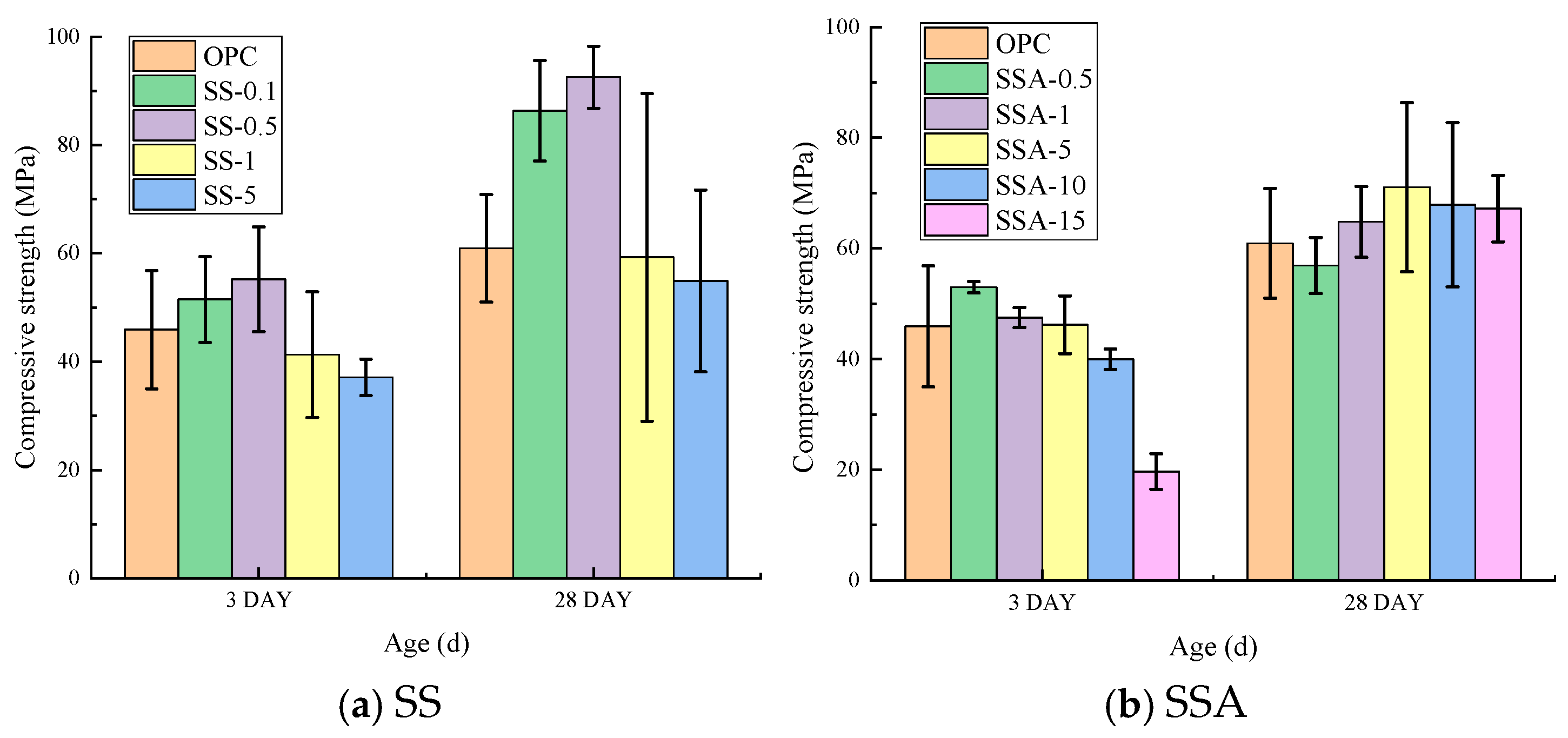
3.2. Compressive Strengths
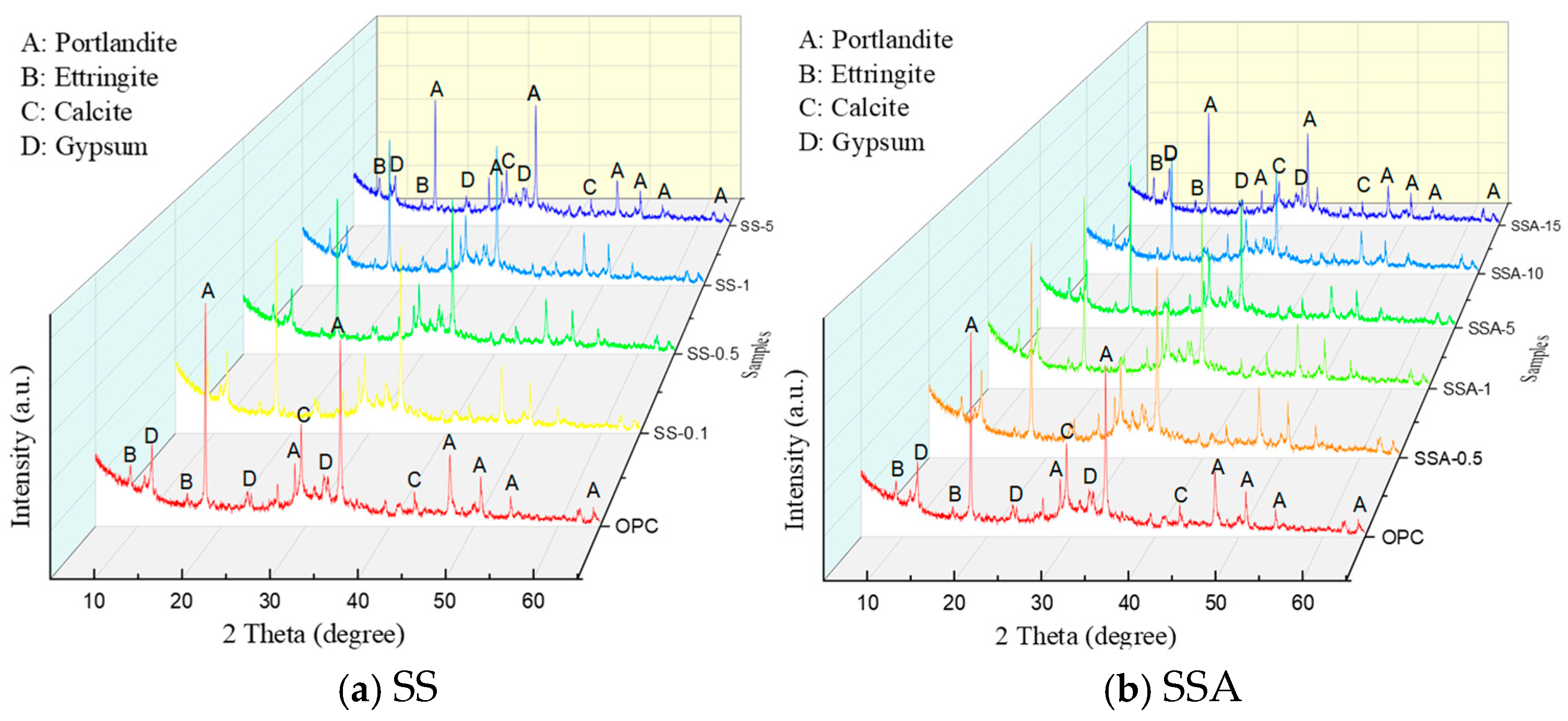
3.3. Hydration Products
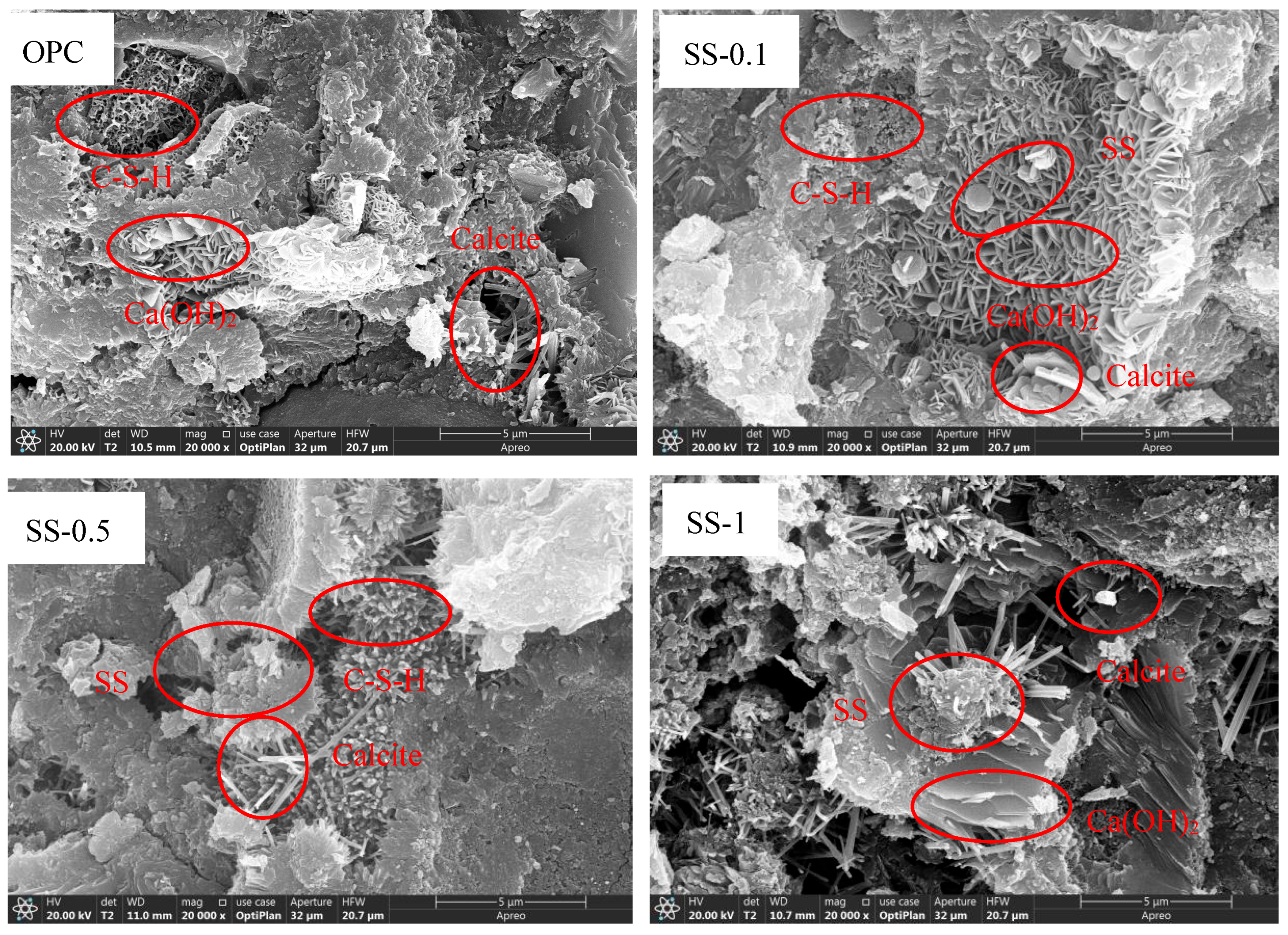
3.4. Microstructure
3.5. Environmental Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The mixing of SS and SSA will prolong the setting time of the cementitious material, and the setting time of the cementitious material meets the requirements of the national standard GB/175-2007 when the mixing amount does not exceed 5%.
- (2)
- The compressive strength of mortar doped with not more than 1% SS has some improvement, and the compressive strength of SS- and SSA-doped with not more than 5% is comparable to that of the control mortar. The long-term performance of SS- and SSA-doped cementitious materials is better than the short-term performance. At low dosage, it is more economical to directly mix SS.
- (3)
- The hydration products of mortars with different dosages of SS and SSA were the same at 28 days. XRD analysis showed that the crystalline phases and chemical composition contain portlandite, ettringite, calcite, and gypsum. TG-DTG analysis showed four exothermic peaks: C-S-H and AFt, AFm, Ca(OH)2, and CaCO3. SEM showed a denser microstructure for mortars doped with up to 1% SS. SS and SSA with high iron content are partly involved in hydration and partly used as filler materials in the pores in cement mortar, and the microstructure is denser when SS and SSA are doped up to 5%.
- (4)
- For mortar samples with different SS or SSA dosages, the dissolved concentrations of heavy metals were below the specified TCLP limits and GB 5085.3-2007 limits. The mortar samples with low dosages of SS and SSA were not harmful to the environment.
- (5)
- Sludge and sludge ash from the sewage treatment plant of Liaocheng Jiaming Industrial Park with high ferric oxide content, at dosages less than 5%, are feasible as auxiliary cementitious materials for cement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, H.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.; Sheng, J.; Wang, J. Investigations into Replacing Calcined Clay with Sewage Sludge Ash in Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3). Materials 2025, 18, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.; Long, G.; Zhou, J.L.; Ma, C. Valorization of sewage sludge in the fabrication of construction and building materials: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb Consulting, Huajing Industrial Research Institute. China Sludge Treatment Industry Research and in-Depth Analysis Report; Webb Consulting, Huajing Industrial Research Institute: Beijing, China, 2024. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Lin, D.F. Applications of sewage sludge ash and nano-SiO2 to manufacture tile as construction material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3312–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobelak, A.; Czerwińska, K.; Murtaś, A. General Considerations on Sludge Disposal, Industrial and Municipal Sludge; ButterworthHeinemann: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 135–153. [Google Scholar]
- Scrivener, K.L.; John, V.M.; Gartner, E.M. Ecoefficient cements: Potential, economically viable solutions for a low-CO2 cement-based materials industry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 114, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juala, R.; Ballim, Y.; Mulopo, J. Assessment of local sewage sludge ash as a supplementary cementitious material—Effects of incineration temperature and cooling rate of the ash. J. S. Afr. Inst. Civ. Eng. 2022, 64, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.C.; Show, K.Y.; Cheong, H.K. Municipal solid waste fly ash as a blended cement material. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2003, 15, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Blanc, D.; Gautier, M.; Mehu, J.; Gourdon, R. Environmental and technical assessments of the potential utilization of sewage sludge ashes (SSAs) as secondary raw materials in construction. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyr, M.; Coutand, M.; Clastres, P. Technological and environmental behavior of sewage sludge ash (SSA) in cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, P.; Carrión, M.P.; García-Alcocel, E.; Payá, J.; Monzó, J.; Borrachero, M.V. Mechanical and physical properties of cement blended with sewage sludge ash. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.C.; Lin, J.D.; Tsai, C.C.; Wang, K.S. Study on cement mortar and concrete made with sewage sludge ash. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 1689–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza, F.; Payá, J.; Galao, O.; Saval, J.; Garcés, P. Blending of industrial waste from different sources as partial substitution of Portland cement in pastes and mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naamane, S.; Rais, Z.; Taleb, M. The effectiveness of the incineration of sewage sludge on the evolution of physicochemical and mechanical properties of Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Lin, Y.; Ding, Z.; An, Q.; Sun, Z.; Fu, Y. Local Oscillator Port-Integrated Resonators for Sensitivity Enhancement of VHF Band Rydberg Atomic Heterodyne Receivers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Qian, S.; Hou, K. Time-dependent Behavior Characteristics of Power-law Cement Grouts Applied in Geotechnical Engineering. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 21, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Hou, K.P.; Guo, T.T. Study on the effects of different water-cement ratios on the flow pattern properties of cement grouts. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 71, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Siddique, R. Recent advances in understanding the role of supplementary cementitious materials in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, N.; Bai, X.; Xi, W.; He, D.; et al. Column penetration and diffusion mechanism of Bingham fluid considering displacement effect. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 196-1:2016; Methods of Testing Cement—Part 1: Determination of Strength. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
- ASTM C109; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars. Annual Book of ASTM Standards: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016.
- ISO 9597:2008; EN Cement—Test methods—Determination of Setting Time and Soundness. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Pinarli, V.; Dhir, R.K.; Dyer, T.D.; Paine, K.A. Sustainable Waste Management—Studies on the Use of Sewage Sludge Ash in Construction Industry as Concrete Material, Sustainable Construction: Use of Incinerator Ash; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 2000; pp. 415–426. [Google Scholar]
- Monzo, J.; Paya, J.; Borrachero, M.V.; Girbes, I. Reuse of sewage sludge ashes (SSA) in cement mixtures: The effect of SSA on the workability of cement mortars. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 175-2007; Common Portland Cement. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB 5085.3-2007; Chinese Standard: Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes-Identification for Extraction Toxicity. PRC Environmental Protection Agency: Beijing, China, 2007.



| Material | Chemical Composition (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | SO3 | |
| Cement | 25.48 | 54.45 | 7.89 | 4.35 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.64 | 0.15 | 4.12 |
| SS | 14.67 | 3.23 | 4.05 | 58.31 | 1.17 | 1.71 | 0.97 | 9.04 | 3.1 |
| SSA | 16.06 | 3.61 | 4.98 | 54.83 | 1.23 | 1.41 | 1.08 | 11.97 | 2.23 |
| System | w/b | Cement | SS | SSA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportions | Calcination Temperature | ||||
| OPC | 0.4 | 100 | 0 | / | / |
| SS-0.1 | 0.4 | 99.9 | 0.1 | ||
| SS-0.5 | 0.4 | 99.5 | 0.5 | ||
| SS-1 | 0.4 | 99 | 1 | / | / |
| SS-5 | 0.4 | 95 | 5 | / | / |
| SSA-0.5 | 0.4 | 99.5 | / | 0.5 | 800 |
| SSA-1 | 0.4 | 99 | / | 1 | 800 |
| SSA-5 | 0.4 | 95 | / | 5 | 800 |
| SSA-10 | 0.4 | 90 | / | 10 | 800 |
| SSA-15 | 0.4 | 85 | / | 15 | 800 |
| Application | Metal(loid) (mg/L) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | Cd | Cr | Cu | Pb | Zn | Ba | Ni | |
| SS-0.1 | ND | ND | 0.0010 | 0.0062 | 0.0053 | 0.0020 | 2.7913 | 0.0027 |
| SS-0.5 | ND | ND | 0.0037 | 0.0318 | 0.0053 | 0.0031 | 3.0953 | 0.0106 |
| SS-1 | ND | ND | 0.0014 | 0.0733 | 0.0056 | 0.0033 | 2.9892 | 0.0260 |
| SS-5 | ND | ND | 0.0038 | 0.1007 | 0.0062 | 0.0056 | 2.2478 | 0.0582 |
| SSA-0.5 | 0.0001 | ND | 0.0044 | 0.0015 | 0.0032 | 0.0031 | 2.9940 | 0.0008 |
| SSA-1 | ND | ND | 0.0034 | 0.0014 | 0.0036 | 0.0028 | 3.0494 | 0.0008 |
| SSA-5 | ND | ND | 0.0148 | 0.0012 | 0.0035 | 0.0043 | 2.8374 | 0.0008 |
| SSA-10 | ND | ND | 0.0139 | 0.0029 | 0.0032 | 0.0049 | 2.6573 | 0.0010 |
| SSA-15 | ND | ND | 0.0077 | 0.0012 | 0.0040 | 0.0033 | 2.4074 | 0.0008 |
| TCLP a regulatory limit | 5 | 1 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 25 | 100 | 25 |
| GB 5085.3-2007 b limit | 5 | 1 | 15 | 100 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Meng, Z.; Sheng, J. Utilization of High Iron Content Sludge and Ash as Partial Substitutes for Portland Cement. Materials 2025, 18, 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102309
Gu H, Zhang Z, Li W, Meng Z, Sheng J. Utilization of High Iron Content Sludge and Ash as Partial Substitutes for Portland Cement. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102309
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Hui, Zhenyong Zhang, Wen Li, Zhaobo Meng, and Jianxiong Sheng. 2025. "Utilization of High Iron Content Sludge and Ash as Partial Substitutes for Portland Cement" Materials 18, no. 10: 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102309
APA StyleGu, H., Zhang, Z., Li, W., Meng, Z., & Sheng, J. (2025). Utilization of High Iron Content Sludge and Ash as Partial Substitutes for Portland Cement. Materials, 18(10), 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102309





