Effect of Types of Microparticles on Vibration Reducibility of Cementitious Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Test Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mixture Proportion and Specimen Details
2.3. Test Methods
2.3.1. Compressive Strength and Flexural Strength Tests
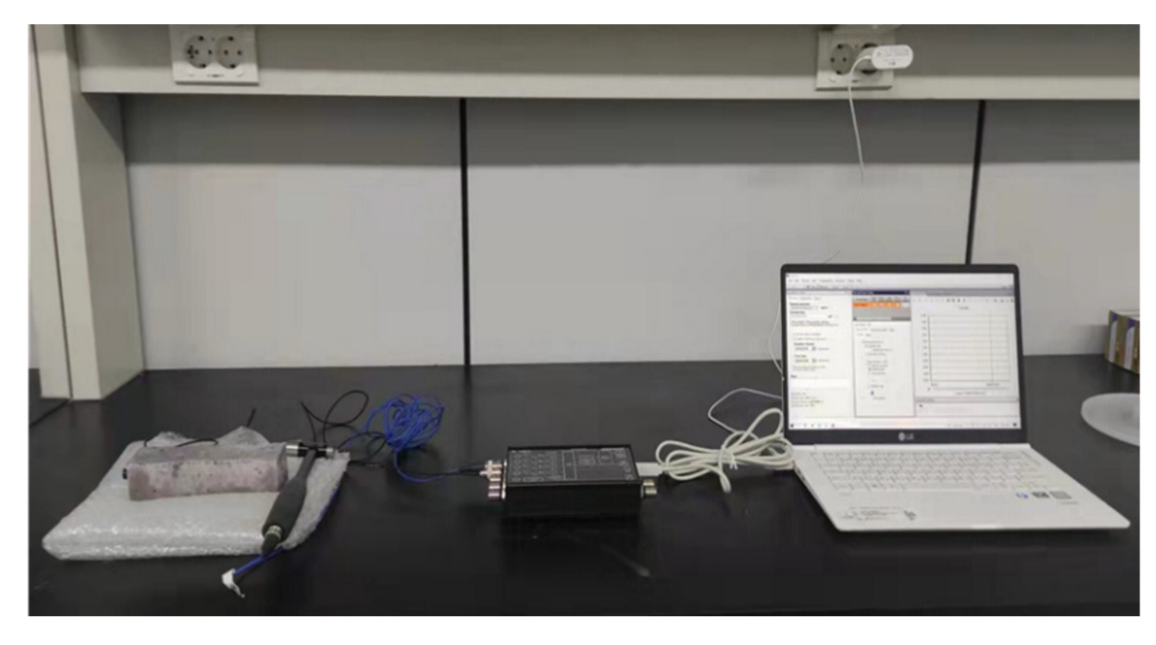
2.3.2. Damping Ratio Test
2.3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis for HGM and CS Specimens
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Damping Ratio
3.2. Compressive Strength
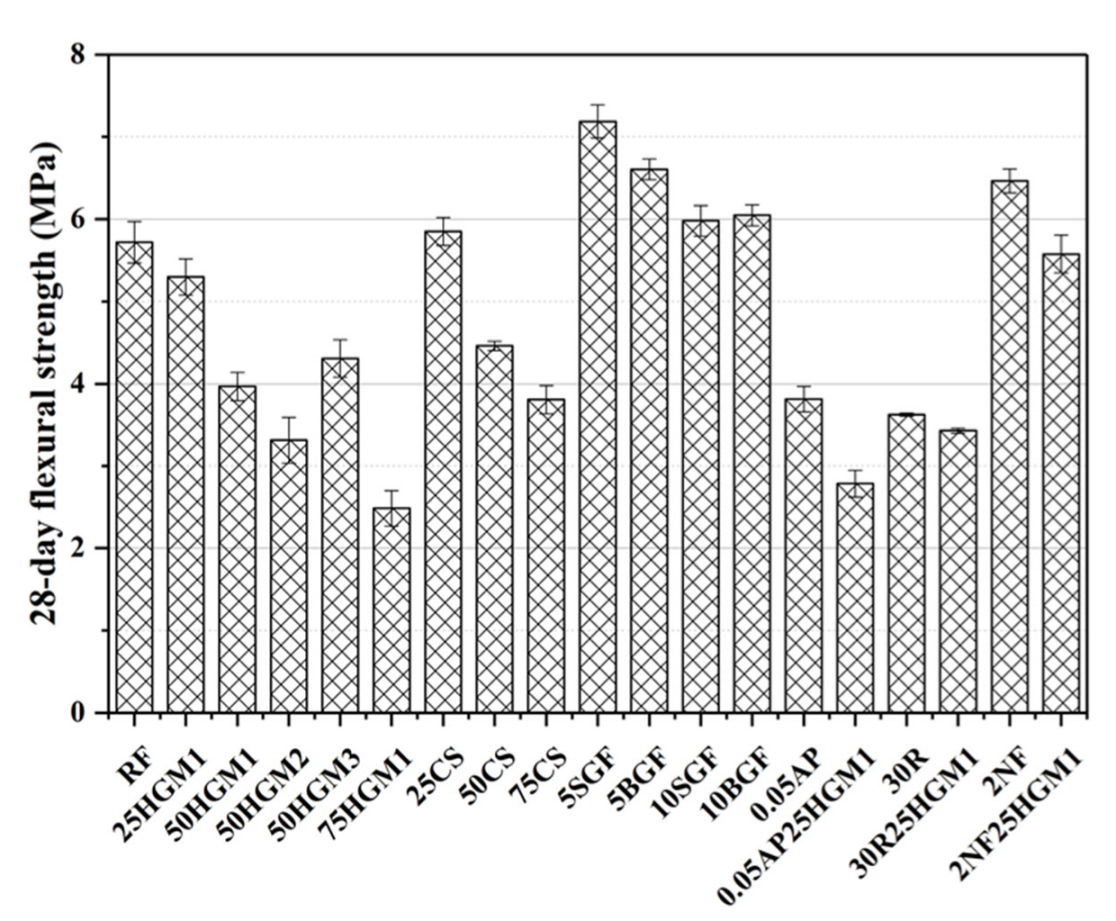
3.3. Flexural Strength
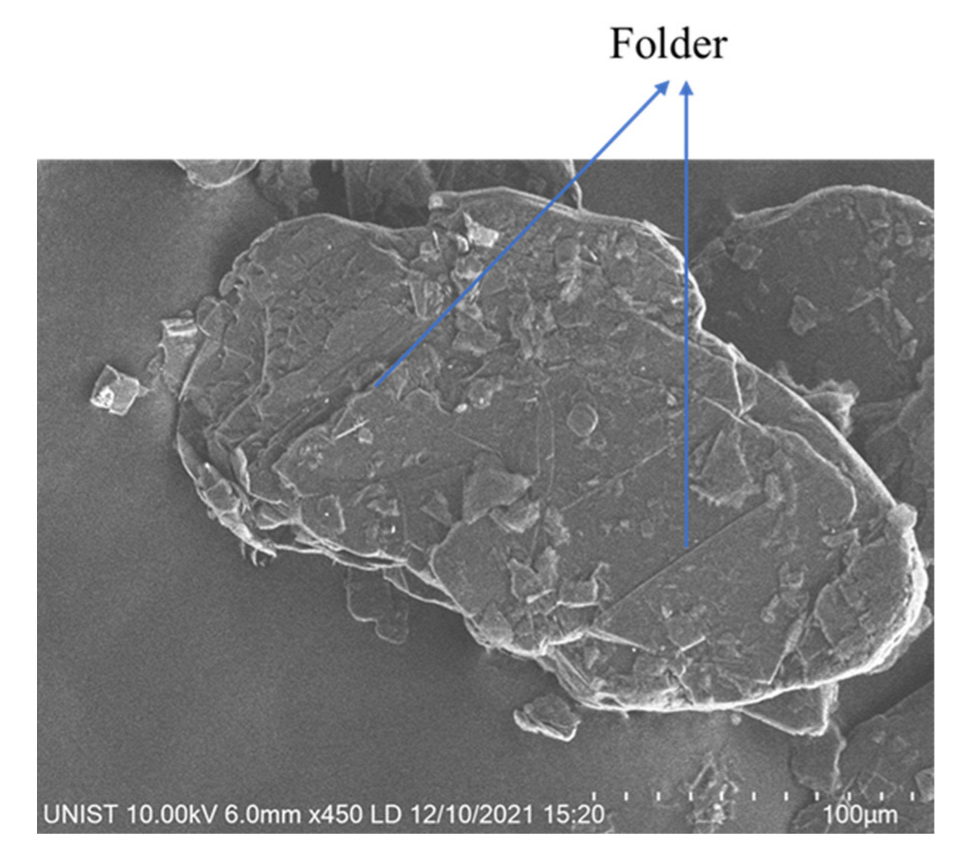
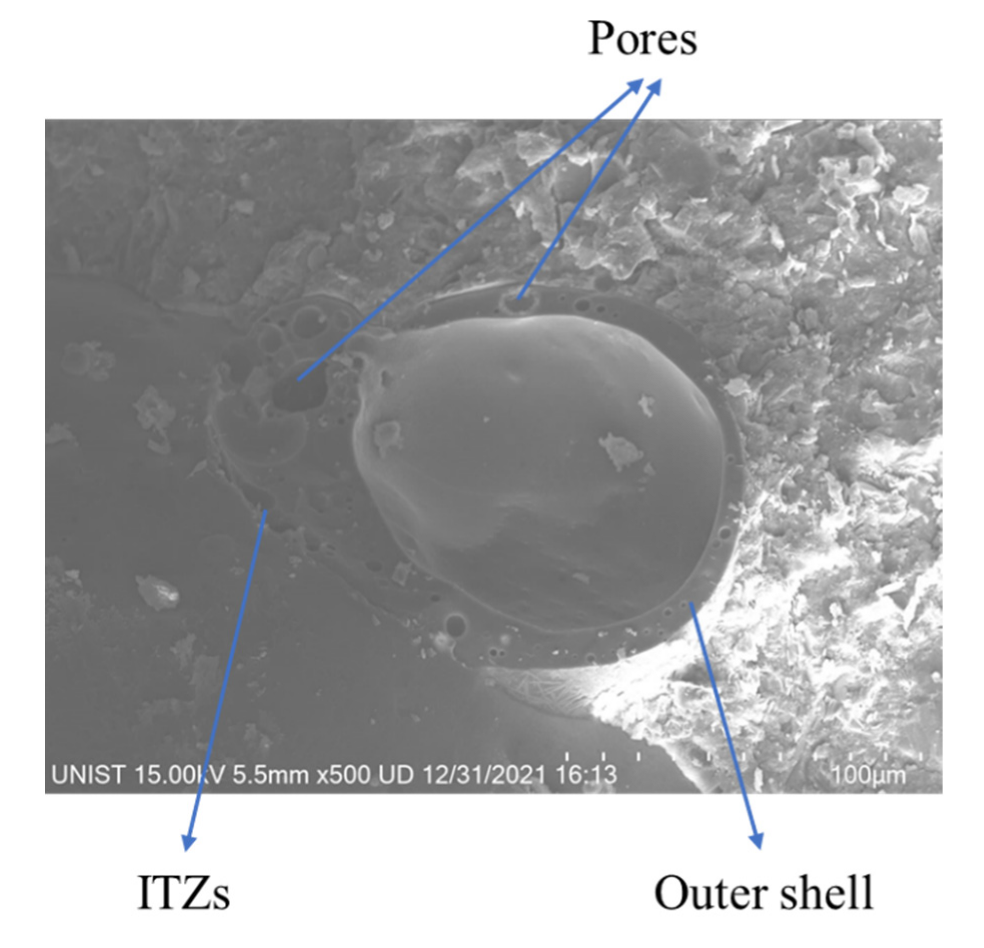
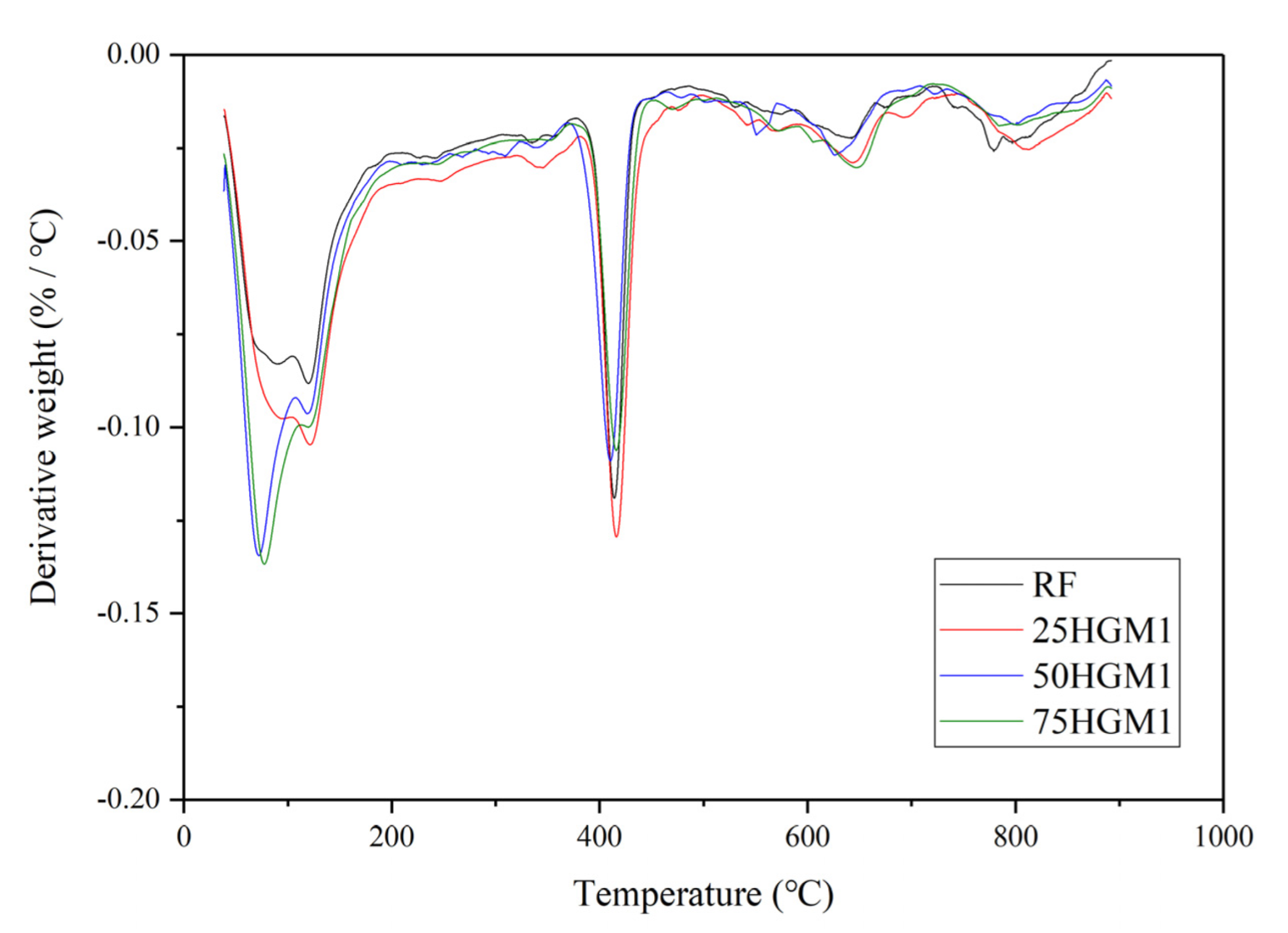
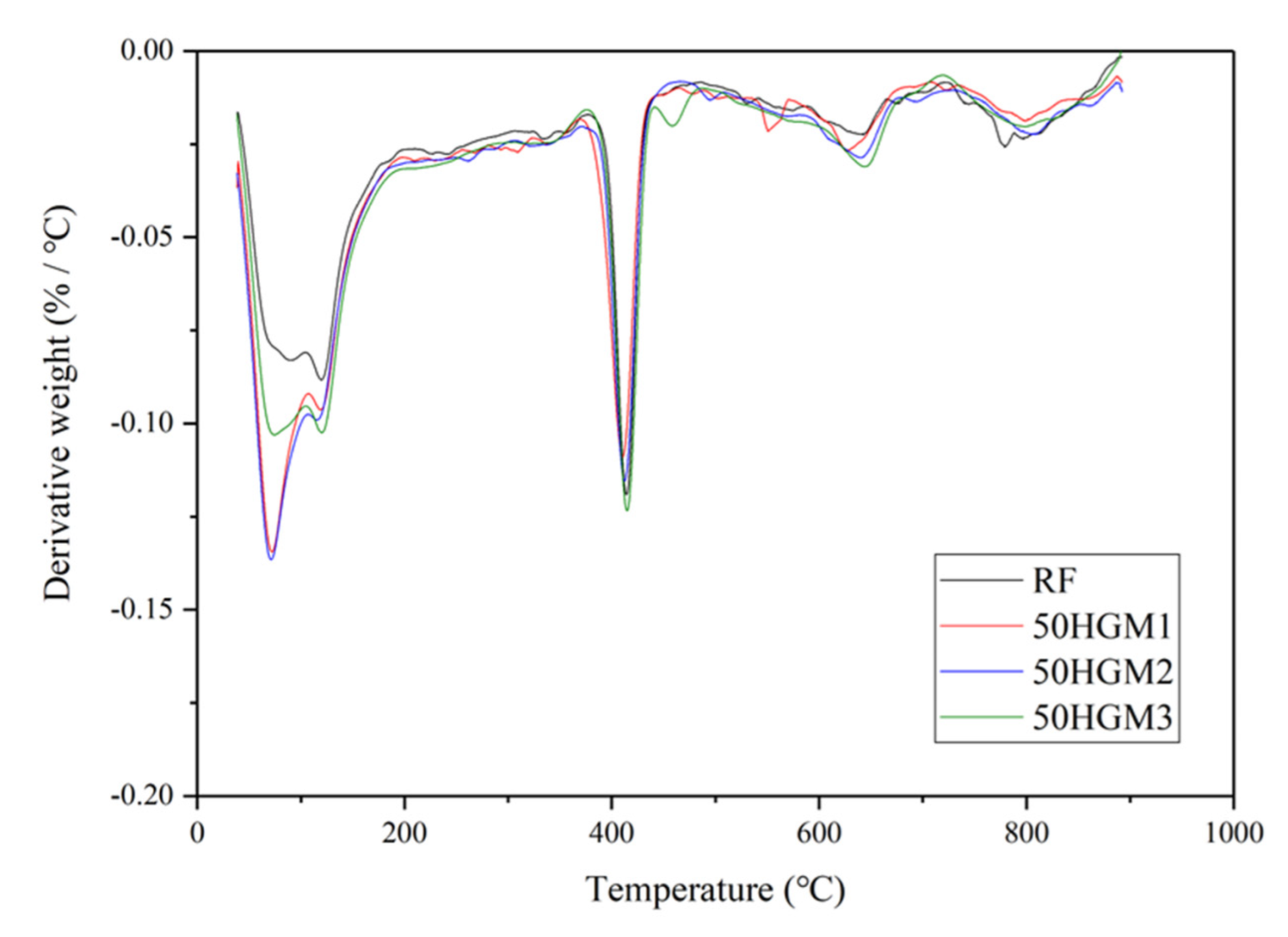
3.4. TGA Results of HGM and CS Specimens
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, Y.; Qi, H.; Liu, S.; Nian, V.; Zhang, Z. Study of Noise and Vibration Impacts to Buildings Due to Urban Rail Transit and Mitigation Measures. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzeb, J.; Chudzikiewicz, A. Evaluation of the vibration impacts in the transport infrastructure environment. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2015, 85, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, T.; Bian, X.C.; Xiao, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.B.; Li, Y. Experimental study on a geosynthetics isolator for the base vibration isolation of buildings neighboring metro transportation. Geotext. Geomembr. 2021, 49, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trollé, A.; Marquis-Favre, C.; Parizet, É. Perception and annoyance due to vibrations in dwellings generated from ground transportation: A review. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2015, 34, 413–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadeghi, J.; Vasheghani, M. Safety of buildings against train induced structure borne noise. Build. Environ. 2021, 197, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Remennikov, A.M. Current state of practice in railway track vibration isolation: An Australian overview. Aust. J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 14, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Shinozuka, M. Rubberized concrete: A green structural material with enhanced energy-dissipation capability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 42, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesit, R.; Kaewunruen, S. Vibration characteristics of micro-engineered crumb rubber concrete for railway sleeper applications. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2017, 15, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Sharon Huo, X.; Yuan, Y. Experimental investigation on dynamic properties of rubberized concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Liu, T.; Xiao, J.; Zou, D.; Yang, Q. The damping property of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, S.; Cherkawi, N.; Hamad, B. Studies on Hemp and Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2020, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Liu, H.; Yao, Z.; Tang, Z. Experimental study on the compressive strength, damping and interfacial transition zone properties of modified recycled aggregate concrete. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.; Pei, X.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. Mechanical and damping properties of recycled aggregate concrete modified with air-entraining agent and polypropylene fiber. Materials 2020, 13, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, L. Property Assessment of High-Performance Concrete Containing Three Types of Fibers. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2021, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, V.T.; Baeza, F.J.; Ivorra, S.; Zornoza, E.; Galao, Ó. Effect of steel and carbon fiber additions on the dynamic properties of concrete containing silica fume. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neithalath, N. Damage assessment in cellulose-cement composites using dynamic mechanical characteristics. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2006, 28, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.; Lu, S.; Yao, Y. Damping additives used in cement-matrix composites: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 164, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Ji, W.M.; Liu, Y.; Xing, F.; Liu, Y.K. Damping Property of a Cement-Based Material Containing Carbon Nanotube. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 371404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Song, B.; Qiao, K.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L. Effect of dimensions and agglomerations of carbon nanotubes on synchronous enhancement of mechanical and damping properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bas, H.K.; Jin, W.; Gupta, N.; Behera, R.K. In-situ micro-CT characterization of mechanical properties and failure mechanism of cementitious syntactic foams. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 90, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, F.B.; Montedo, O.R.K.; Grassi, R.L.; Antunes, E.G.P. Lightweight high-strength concrete with the use of waste cenosphere as fine aggregate. Rev. Mater. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Pae, J.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, H.; Moon, J. Development of high strength & lightweight cementitious composites using hollow glass microsphere in a low water-to-cement matrix. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 130, 104541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Wang, Q. Effects of graphite on electrically conductive cementitious composite properties: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3M. 3M Glass Bubbles Series; 3M: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Chaudhary, S. Use of fly ash for the development of sustainable construction materials. In New Materials in Civil Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 677–689. [Google Scholar]
- Solfiti, E.; Berto, F. Mechanical properties of flexible graphite: Review. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2020, 25, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, Q.; Guo, S. Laboratory performance evaluation of both flake graphite and exfoliated graphite nanoplatelet modified asphalt composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, B.; Yin, G. Analysis of stiffness and damping performance of the composite leaf spring. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Kim, H.; Koh, T.; Pyo, S. Microstructural characteristics of sound absorbable porous cement-based materials by incorporating natural fibers and aluminum powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 243, 118167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillinger, B.; Clark, D.; Suchicital, C.; Wicks, G. Crush strength analysis of hollow glass microspheres. Ceram. Eng. Sci. Proc. 2018, 38, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- 3M. Safety Data Sheet-Type K and S; 3M: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- 3M. Safety Data Sheet-iM30K; 3M: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2011; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, A.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z. Utilization of fly ash cenosphere as lightweight filler in cement-based composites—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C109/C109M-02; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005.
- ASTM C78/C78M-22; Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using Simple Beam with Third-Point Loading). ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C215-19; Standard Test Method for Fundamental Transverse, Longitudinal, and Torsional Resonant Frequencies of Concrete Specimens. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Choi, J.I.; Park, S.E.; Hwang, J.S.; Lee, B.Y. Damping property of prepacked concrete incorporating coarse aggregates coated with polyurethane. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 93, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, B.J.; Richardson, M.H. Método de Análisis Modal Experimental. 1999, pp. 1–12. Available online: http://papers.vibetech.com/Paper28-ExperimentalModalAnalysis.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Daugherty, J.W.; Lacey, D.E.; Korty, P. Problems in aerial application: I. Some biochemical effects of lindane and dieldrin on vertebrates. Rep. Civ. Aeromed. Res. Inst. USA 1962, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Moges, K.A.; Wu, S.; Pyo, S. Characteristics of hybrid alkaline cement composites with high cement content: Flash set and high compressive strength. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 1582–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, F.V.; Leite, D.N.F.; de Castro, J.A. Correlation between Voids Ratio and Characteristic Responses to Ultrasonic Pulses Through Sandy Soils. J. Mater. Sci. Res. 2020, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, A.D.; Hazelwood, R.A.; Popper, A.N.; Macey, P.C. Substrate vibrations and their potential effects upon fishes and invertebrates. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z. Effects of cenosphere on the mechanical properties of cement-based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 120527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, Z. Experimental study of the mechanical properties and microstructures of lightweight toughness cement-based composites. Materials 2019, 12, 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Hao, W.; Meng, X.; Zhang, P.; Sun, X.; Shen, Y. Influence of Graphite Powder on the Mechanical and Acoustic Emission Characteristics of Concrete. Buildings 2022, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Kachhavah, V.S.; Kar, K.K. Mechanical and thermal behaviours of graphite flake-reinforced acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene composites and their correlation with entanglement density, adhesion, reinforcement and: C factor. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50559–50571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamashausky, A.V. Surface enhanced flake graphite and its utility as a functional extender for molybdenum disulfide. NLGI Spokesm. 2006, 70, 8–16. [Google Scholar]








| Material | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | MgO | SO3 | P2O5 | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 19.38 | 4.48 | 64.48 | 3.46 | 0.29 | 2.82 | 3.31 | - | - |
| HGM | 80.59 | 0.15 | 13.54 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.80 | 4.47 |
| Cenosphere | 67.28 | 23.22 | 0.31 | 1.51 | 0.39 | 0.38 | - | 0.49 | 0.47 |
| Materials | Median Particle Size (μm) | Density (kg/m3) | Crushing Strength (MPa) | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HGM1 [31] | 55 | 150 | 2.1 | 3MTM |
| HGM2 [31] | 45 | 460 | 41 | 3MTM |
| HGM3 [32] | 16 | 600 | 193.1 | 3MTM |
| CS | 407 | 650 | 70–140 [33] | Seokyung Cmt |
| Rubber particle (RP) | 65 | 1450 | - | Hangil RMB |
| Aluminum powder (AP) | - | 2700 | - | KMB Co., Ltd. |
| Natural fiber (NF) * | - | 1797 | - | Soo Industry Co. |
| SGF | 81.5 | 2214 | - | Merck KGaA |
| BGF | 430 | 2260 | - | Merck KGaA |
| Mixture ID | Cement | Sand | HGM | RP | AP | NF | GF | CS | Water | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF * | 867.0 | 867.0 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 25HGM1 | 650.3 | 12.5 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 50HGM1 | 433.5 | 25 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 50HGM2 | 433.5 | 76.7 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 50HGM3 | 433.5 | 100.0 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 75HGM1 | 216.8 | 37.5 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 30R | 606.8 | 144.8 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 0.05AP | 867.0 | 0.434 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 2NF | 849.5 | 12.7 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 30R25HGM1 | 390.1 | 12.5 | 144.8 | 390.2 | ||||||
| 0.05AP25HGM1 | 650.9 | 12.5 | 0.434 | 390.2 | ||||||
| 2NF25HGM1 | 632.7 | 12.5 | 12.7 | 390.2 | ||||||
| 5SGF | 823.0 | 37.6 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 5BGF | 823.0 | 36.9 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 10SGF | 779.0 | 75.3 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 10BGF | 779.0 | 73.9 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 25CS | 650.3 | 54.3 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 50CS | 433.5 | 108.5 | 390.2 | |||||||
| 75CS | 216.8 | 162.6 | 390.2 | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.; Park, S.; Pyo, S. Effect of Types of Microparticles on Vibration Reducibility of Cementitious Composites. Materials 2022, 15, 4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144821
Wu S, Park S, Pyo S. Effect of Types of Microparticles on Vibration Reducibility of Cementitious Composites. Materials. 2022; 15(14):4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144821
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Siyu, Sungwoo Park, and Sukhoon Pyo. 2022. "Effect of Types of Microparticles on Vibration Reducibility of Cementitious Composites" Materials 15, no. 14: 4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144821
APA StyleWu, S., Park, S., & Pyo, S. (2022). Effect of Types of Microparticles on Vibration Reducibility of Cementitious Composites. Materials, 15(14), 4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144821








