Influence of Material Parameters on the Contact Pressure Characteristics of a Multi-Disc Clutch
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Thermodynamic Model
2.1. Contact Pressure Model
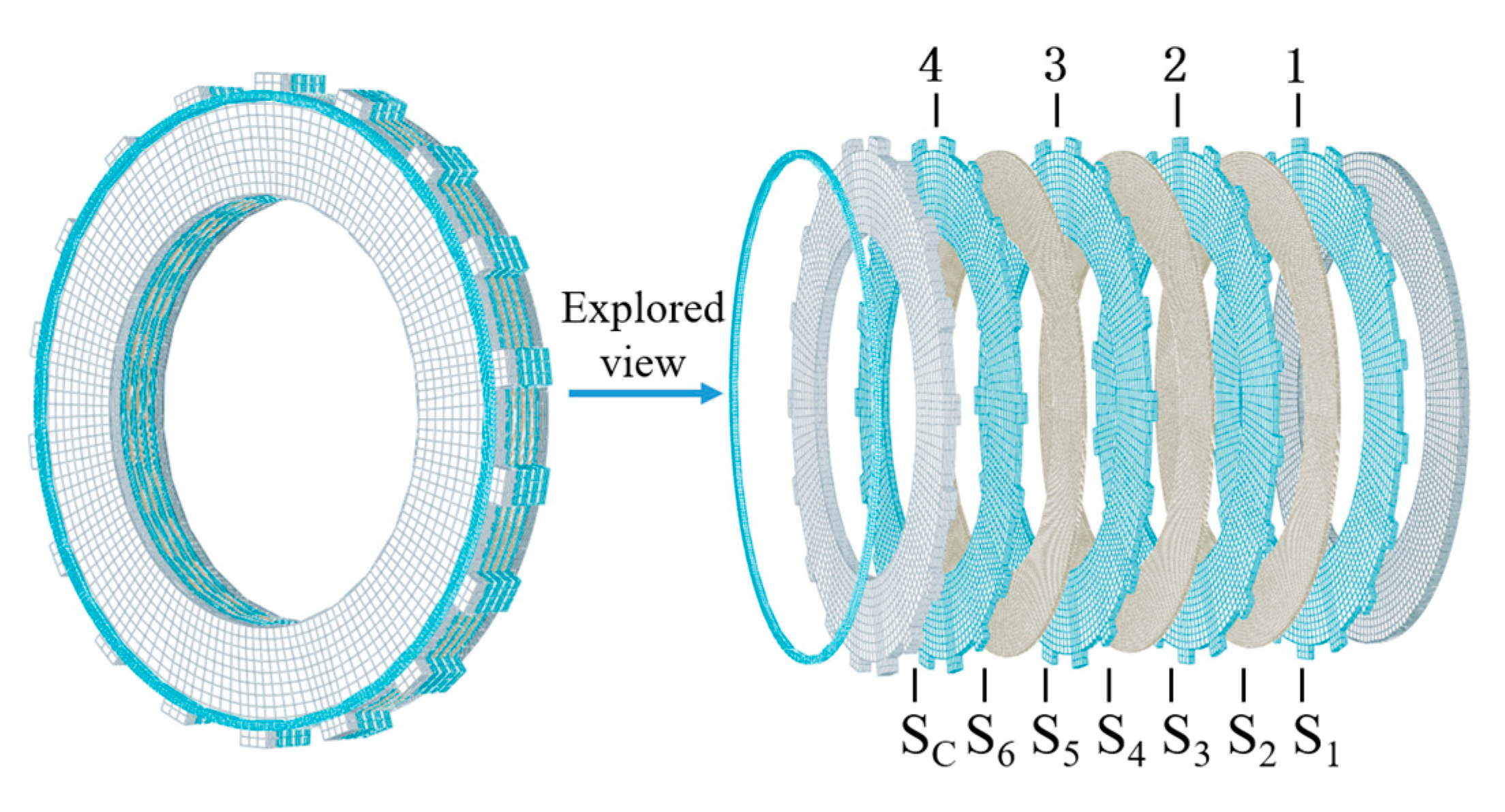
2.2. Thermodynamic Numerical Model
3. Distribution of the Initial Contact Pressure
4. Effect of Material Parameters on the Contact Pressure
4.1. Elastic Modulus
4.2. Poisson’s Ratio
5. Optimization of Material Parameters
6. Experimental Verification
6.1. Test Rig
6.2. Test Results and Discussion
7. Temperature Field Comparison
8. Conclusions
- Increasing the EM and PR of the backplate and reducing the PR of the steel discs can dramatically reduce the difference in clutch pressure distribution.
- The material parameters of the friction linings and circlip have a slight influence on the clutch pressure and temperature distribution.
- Compared with the initial material conditions, the maximum pressure and temperature differences of the optimized material conditions were reduced by 74 kPa and 14.9 °C, about 27.2% and 10.3%, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, D.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S. Applying Low-Frequency Vibration for the Experimental Investigation of Clutch Hub Forming. Materials 2018, 11, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Ma, B.; Chen, M.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Li, M. Investigation on the failure mechanism and safety mechanical-thermal boundary of a multi-disc clutch. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 103, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ma, B.; Chen, M.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Investigation on the thermodynamic characteristics of the deformed separate plate in a multi-disc clutch. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 110, 104385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, J.; Huang, J.; Ouyang, H.; Xu, Z.; Yao, C. Effect of carbon fiber content on the friction and wear performance of paper-based friction materials. Tribol. Int. 2015, 87, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Gao, F.; Song, B. Effects of Fe on Friction and Wear Properties of Cu-Based Friction Aterial. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 194–196, 1830–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ma, B.; Chen, M.; Li, H.; Ma, C.; Liu, J. Comparison of the Friction and Wear Characteristics between Copper and Paper Based Friction Materials. Materials 2019, 12, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, E.; Ma, B.; Li, H. Study on the High Temperature Friction and Wear Behaviors of Cu-Based Friction Pairs in Wet Clutches by Pin-on-Disc Tests. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, e6373190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Ma, B.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Yu, L. Analysis of the thermal buckling of annular disks in clutches under the condition of radial temperature gradient. J. Therm. Stress. 2017, 40, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Yi, Y. Finite element analysis of thermal buckling in automotive clutch plates. J. Therm. Stress. 2016, 39, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Han, J.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Pan, L.; Shi, X. Analyzing the mechanisms of fatigue crack initiation and propagation in CRH EMU brake discs. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 34, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z. Thermal crack growth-based fatigue life prediction due to braking for a high-speed railway brake disc. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 87, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Han, J.; Yang, Z.; Pan, L. The effect of braking energy on the fatigue crack propagation in railway brake discs. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2014, 44, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, J.; Fei, J.; Cao, L.; Yao, C. Simulation and application of temperature field of carbon fabric wet clutch during engagement based on finite element analysis. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 71, 180–187. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, J.; Li, W.; Huang, J.; Cao, L.; Yao, C. Variation of the tribological properties of carbon fabric composites in their whole service life. Tribol. Int. 2016, 99, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Ma, B.; Chen, M.; Xue, J.; Zhao, P. Variation mechanism of the friction torque in a Cu-based wet clutch affected by operating parameters. Tribol. Int. 2020, 147, 106169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ru, H. Effect of Lubricating Phase on Microstructure and Properties of Cu–Fe Friction Materials. Materials 2019, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marklund, P.; Larsson, R.; Lundström, T.S. Permeability of Sinter Bronze Friction Material for Wet Clutches. Tribol. Trans. 2008, 51, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingesten, N.; Marklund, P.; Höglund, E. The influence of repeated high-energy engagements on the permeability of a paper-based wet clutch friction material. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2017, 231, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Luan, C.; Fan, S.; Deng, J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Comparison of braking behaviors between iron- and copper-based powder metallurgy brake pads that used for C/C–SiC disc. Tribol. Int. 2021, 154, 106686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Xiao, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C. Wear mechanism of Cu-based brake pad for high-speed train braking at speed of 380 km/h. Tribol. Int. 2020, 150, 106357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zou, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B. Effects of operating and material parameters on the thermal characteristics of a wet clutch. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2021, 13, 16878140211034100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S.F.; Pahlovy, S.A.; Ogawa, M. Simulation to Estimate the Output Torque Characteristics and Temperature Rise of a Transmission Wet Clutch during the Engagement Process; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.; Jang, S. Temperature Analysis of Wet Clutch Surfaces during Clutch Engagement Processes Based on Friction Pad Patterns. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2020, 21, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Ma, B.; Li, H. The Tribological Characteristics of Cu-Based Friction Pairs in a Wet Multidisk Clutch Under Nonuniform Contact. J. Tribol. 2017, 140, 011401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ma, B.; Li, H.; Li, M. The effect of circlip induced contact pressure on the temperature distribution in multi-disc clutches. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2018, 77, 132–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ma, B.; Ahmadian, M.; Li, H.; Vick, B. Pressure Distribution of a Multidisc Clutch Suffering Frictionally Induced Thermal Load. Tribol. Trans. 2016, 59, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoić, M.; Kranjčević, N.; Herold, Z.; Deur, J.; Ivanović, V. Modeling of dry dual-clutch axial dynamics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2018, 232, 220–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ma, B.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Li, M. Numerical and Experimental Studies of a Wet Multidisc Clutch on Temperature and Stress Fields Excited by the Concentrated Load. Tribol. Trans. 2019, 62, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindlin, R.D. Force at a Point in the Interior of a Semi-Infinite Solid. Physics 1936, 7, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, A.; Kchaou, M.; Elleuch, R.; Desplanques, Y. Thermal analysis of pad-on-disc contact under tribological solicitations: A coupled numerical–experimental approach to identify surface temperatures and flow partition coefficient. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 52, 1923–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Friction Components | Inner Diameter rin/mm | Outer Diameter rout/mm | Thickness H/mm | Poisson’s Ratio v | Elastic Modulus E/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piston | 85 | 125 | 6 | 0.29 | 210 |
| Steel disc | 85 | 125 | 3 | 0.29 | 210 |
| Friction lining | 85 | 125 | 0.6 | 0.27 | 2.2 |
| Friction core | 85 | 125 | 2 | 0.29 | 210 |
| Backplate | 85 | 125 | 6 | 0.29 | 210 |
| Circlip | 122 | 125 | 3 | 0.29 | 210 |
| PDI | k1 | k2 | k3 (k1 + k2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial group | 0.46 | 14.56 | 15.02 | |||
| Material parameters | EM | Backplate | 210 GPa | 0.45 | 12.45 | 12.9 |
| 260 GPa | 0.46 | 11.07 | 11.53 | |||
| PR | Backplate | 0.09 | −7.03 | 22.51 | 29.52 | |
| 0.19 | −3.04 | 18.59 | 21.63 | |||
| Steel discs | 0.09 | 2.04 | 11.63 | 13.67 | ||
| 0.19 | 1.61 | 13.15 | 14.76 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Feng, Y. Influence of Material Parameters on the Contact Pressure Characteristics of a Multi-Disc Clutch. Materials 2021, 14, 6391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216391
Liu Y, Chen M, Yu L, Wang L, Feng Y. Influence of Material Parameters on the Contact Pressure Characteristics of a Multi-Disc Clutch. Materials. 2021; 14(21):6391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216391
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yujian, Man Chen, Liang Yu, Liang Wang, and Yuqing Feng. 2021. "Influence of Material Parameters on the Contact Pressure Characteristics of a Multi-Disc Clutch" Materials 14, no. 21: 6391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216391
APA StyleLiu, Y., Chen, M., Yu, L., Wang, L., & Feng, Y. (2021). Influence of Material Parameters on the Contact Pressure Characteristics of a Multi-Disc Clutch. Materials, 14(21), 6391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216391







